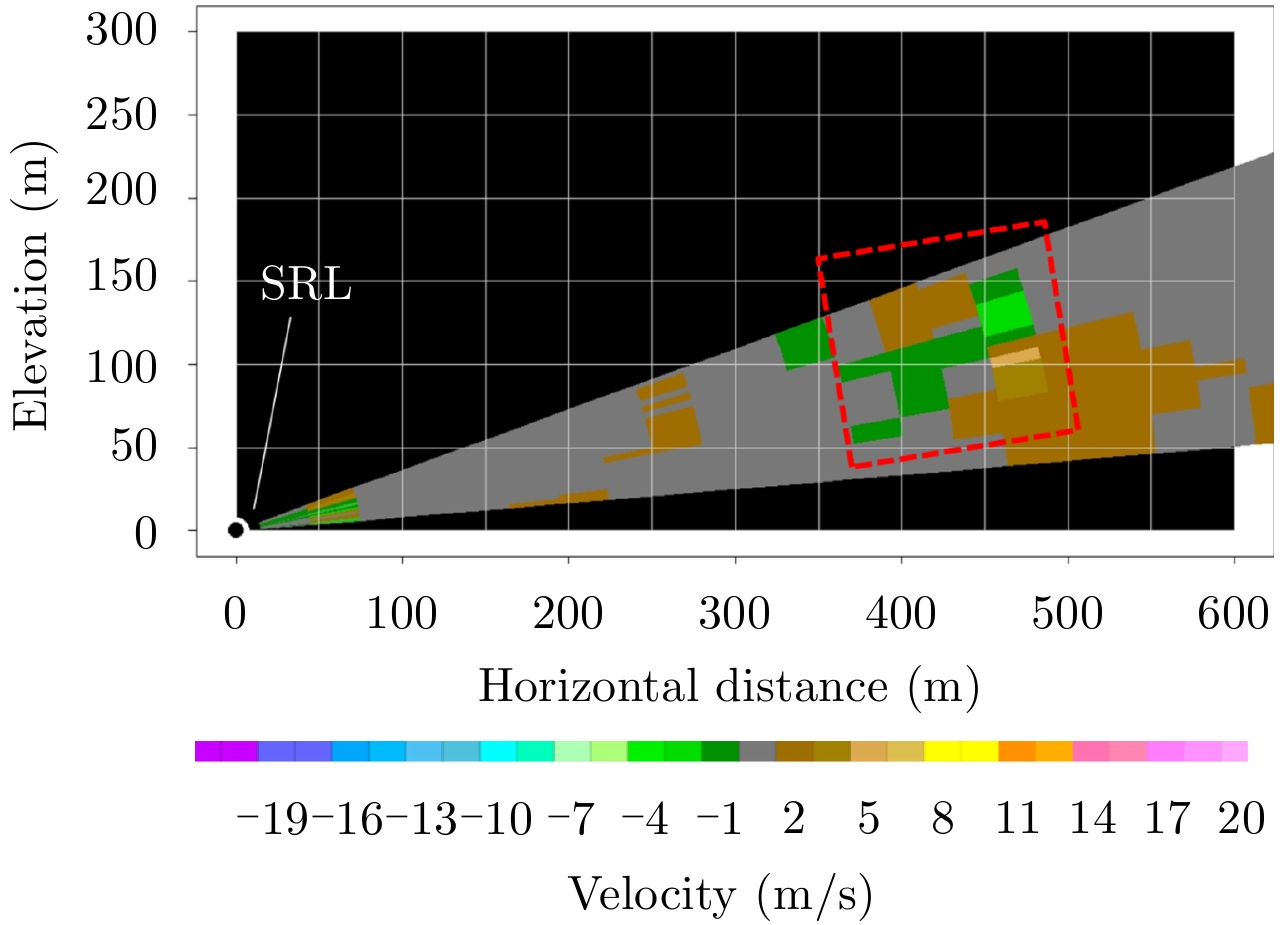
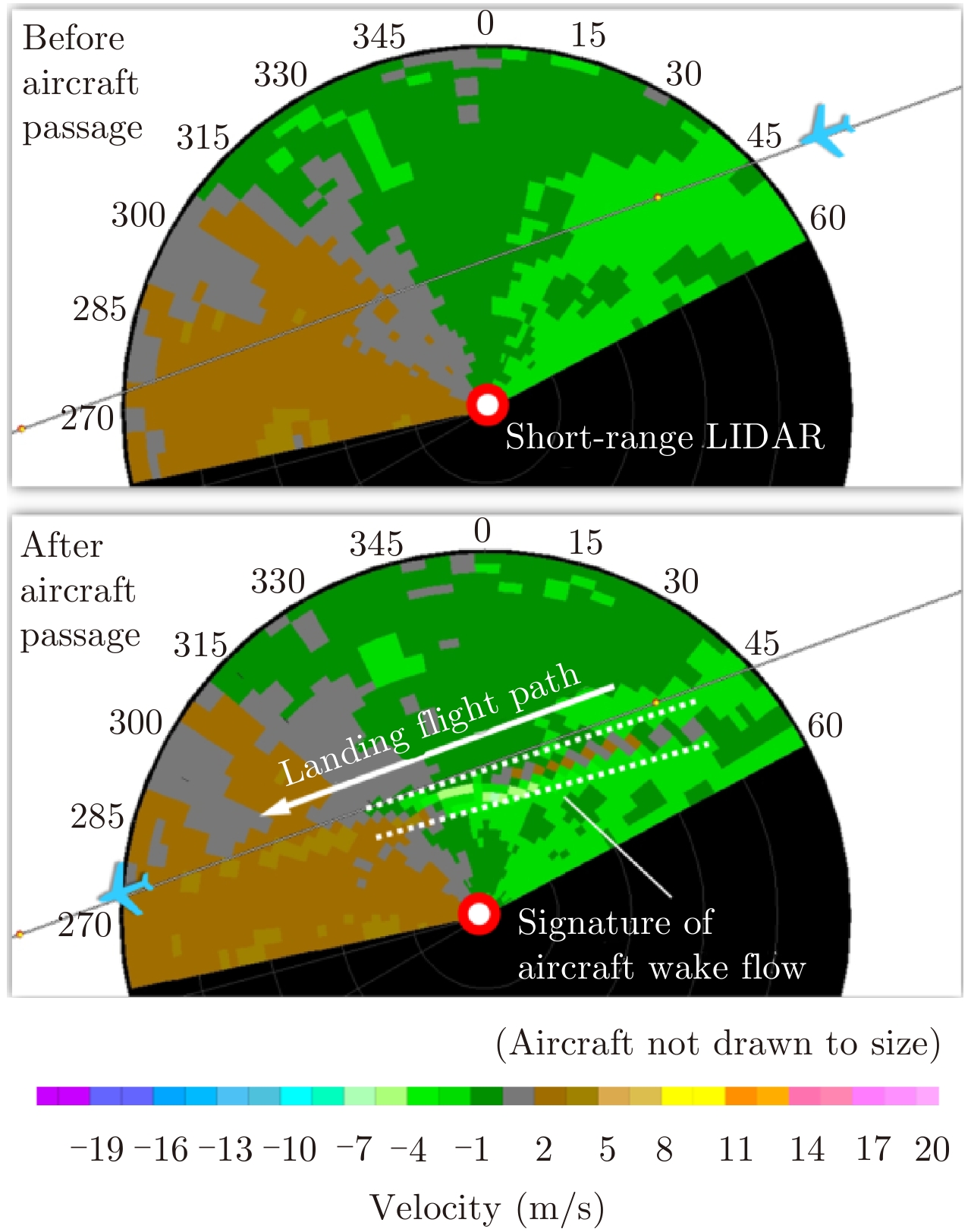
| [1] |
Hallock J N. Aircraft wake vortices: An assessment of the current situation[R]. U.S. Department of Transportation Report. DOT-FAA-RD-90-29. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Transportation, 1991: 59.
|
| [2] |
Rubin W L. Radar-acoustic detection of aircraft wake vortices[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2000, 17(8): 1058–1065. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0426(2000)017<1058:RADOAW>2.0.CO;2
|
| [3] |
Holzäpfel F, Gerz T, Köpp F, et al. Strategies for circulation evaluation of aircraft wake vortices measured by Lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2003, 20(8): 1183–1195. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<1183:SFCEOA>2.0.CO;2
|
| [4] |
Liu Zhong-xun, Jeannin N, Vincent F, et al. Modeling the radar signature of raindrops in aircraft wake vortices[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2013, 30(3): 470–484. DOI: 10.1175/JTECH-D-11-00220.1 |
| [5] |
Holzäpfel F and Robins R E. Probabilistic two-phase aircraft wake vortex model: Application and assessment[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2004, 41(5): 1117–1126. DOI: 10.2514/1.2280 |
| [6] |
Holzäpfel F, Kladetzke J, Amelsberg S, et al. Aircraft wake vortex scenarios simulation package for takeoff and departure[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2009, 46(2): 713–717. DOI: 10.2514/1.39346 |
| [7] |
ICAO. Procedures for air navigation services—air traffic management (Doc 4444)[Z]. 2016, 5: 1–36 (Technical document of the International Civil Aviation Organisation).
|
| [8] |
EUROCONTROL. European wake vortex mitigation benefits study (EuroBen)[Z]. High Level Benefits Analysis & Systemic Analysis, 2005 (Technical report of EUROCONTROL).
|
| [9] |
Tittsworth J A, Lang S R, Johnson E J, et al.. Federal aviation administration wake turbulence program-recent highlights[C]. 57th Air Traffic Control Association (ATCA) Annual Conference & Exposition, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012.
|
| [10] |
Federal Aviation Administration. Wake turbulence recategorization[Z]. Order JO 7110.659C, 2016 (Administrative order form FAA of USA).
|
| [11] |
Treve V and Rooseleer F. RECAT-EU proposal, validation and consultation[R]. WakeNet-EU, EUROCONTROL Experimental Centre, Bretigny, France, 2014.
|
| [12] |
Morris C, Peters J and Choroba P. Validation of the time based separation concept at London Heathrow Airport[C]. Tenth USA/Europe Air Traffic Management Research and Development Seminar, 2013.
|
| [13] |
French Civil Aviation Authority. Implementation of the RECAT-EU wake turbulence separation scheme at Paris Charles de Gaulle, Paris-le Bourget and Pontoise-Cormeilles-en-Vexin airports from March 22nd 2016[R]. AIC France A 03/16. 2016.
|
| [14] |
Federal Aviation Administration. Re-categorization (RECAT) of FAA wake turbulence separation categories at specific airports[R]. SAFO 12007. Washington, DC: SAFO, 2013.
|
| [15] |
Airport Authority Hong Kong. Hong Kong international airport fact sheet[EB/OL]. http://www.hongkongairport.com/eng/media/facts-figures/facts-sheets.html, 2016.
|
| [16] |
Airport Authority Hong Kong. Finalized civil international air traffic statistics at HKIA, Year 2016[EB/OL]. http://www.hongkongairport.com/eng/pdf/business/statistics/2016e.pdf, 2016.
|
| [17] |
Shun C M and Chan P W. Applications of an infrared Doppler Lidar in detection of wind shear[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2008, 25(5): 637–655. DOI: 10.1175/2007JTECHA1057.1 |
| [18] |
Hon K K, Chan P W, Chiu Y Y, et al.. Application of short-range LIDAR in early alerting for low-level windshear and turbulence at Hong Kong International Airport[J]. Advances in Meteorology, 2014, 2014: Article ID 162748.
|
| [19] |
Hon K K. First wake vortex measurements at the Hong Kong International Airport[EB/OL]. News bulletin for the aviation community, Hong Kong Observatory. http://www.hko.gov.hk/aviat/outreach/32nd/wakevortex.htm, 2015, January.
|
| [20] |
Smalikho I N, Banakh V A, Holzäpfel F, et al. Method of radial velocities for the estimation of aircraft wake vortex parameters from data measured by coherent Doppler Lidar[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(19): A1194–A1207. DOI: 10.1364/OE.23.0A1194 |
| [21] |
Loaec S, Thobois L, Cariou J P, et al.. Monitoring wake vortices with a scanning Doppler LIDAR[C]. Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Tropospheric Profiling, 2012.
|
| [22] |
Smalikho I, Köpp F, and Rahm S. Measurement of atmospheric turbulence by 2-μm Doppler Lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2005, 22(11): 1733–1747. DOI: 10.1175/JTECH1815.1 |
| [23] |
Chan P W and Hon K K. Performance of super high resolution numerical weather prediction model in forecasting terrain-disrupted airflow at the Hong Kong International Airport: Case studies[J]. Meteorological Applications, 2016, 23(1): 101–114. DOI: 10.1002/met.2016.23.issue-1 |
| [24] |
Hon K K and Chan P W. Sub-kilometer simulation of terrain-disrupted airflow at the Hong Kong International Airport-aviation applications and inter-comparison with LIDAR observations[C]. 16th Conference on Mountain Meteorology, 2014.
|
| [25] |
Wassaf H S, Tabrizi A, Wang F Y, et al.. Atmospheric turbulence effects on near-ground wake vortex demise[C]. 13th Conference on Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology, 2008.
|
| [26] |
Chan P W. Generation of an eddy dissipation rate map at the Hong Kong International airport based on Doppler Lidar data[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2011, 28(1): 37–49. DOI: 10.1175/2010JTECHA1458.1 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: