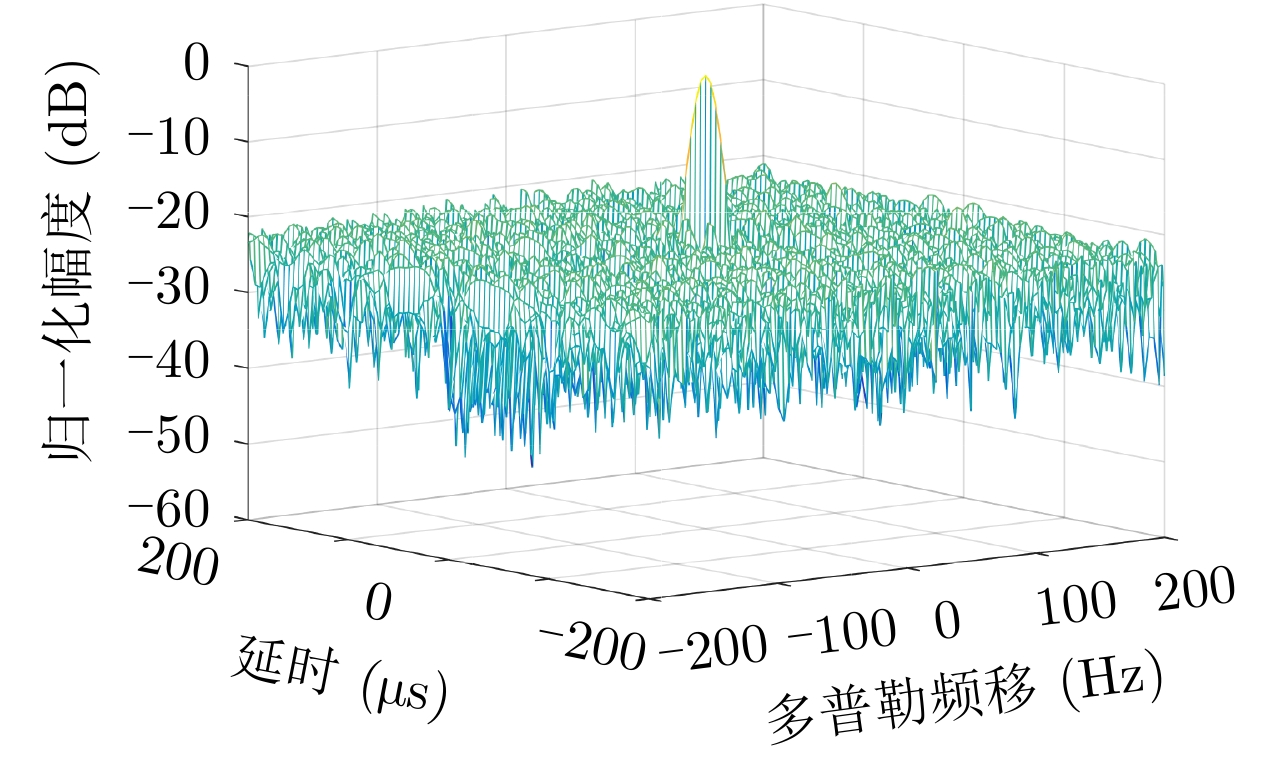
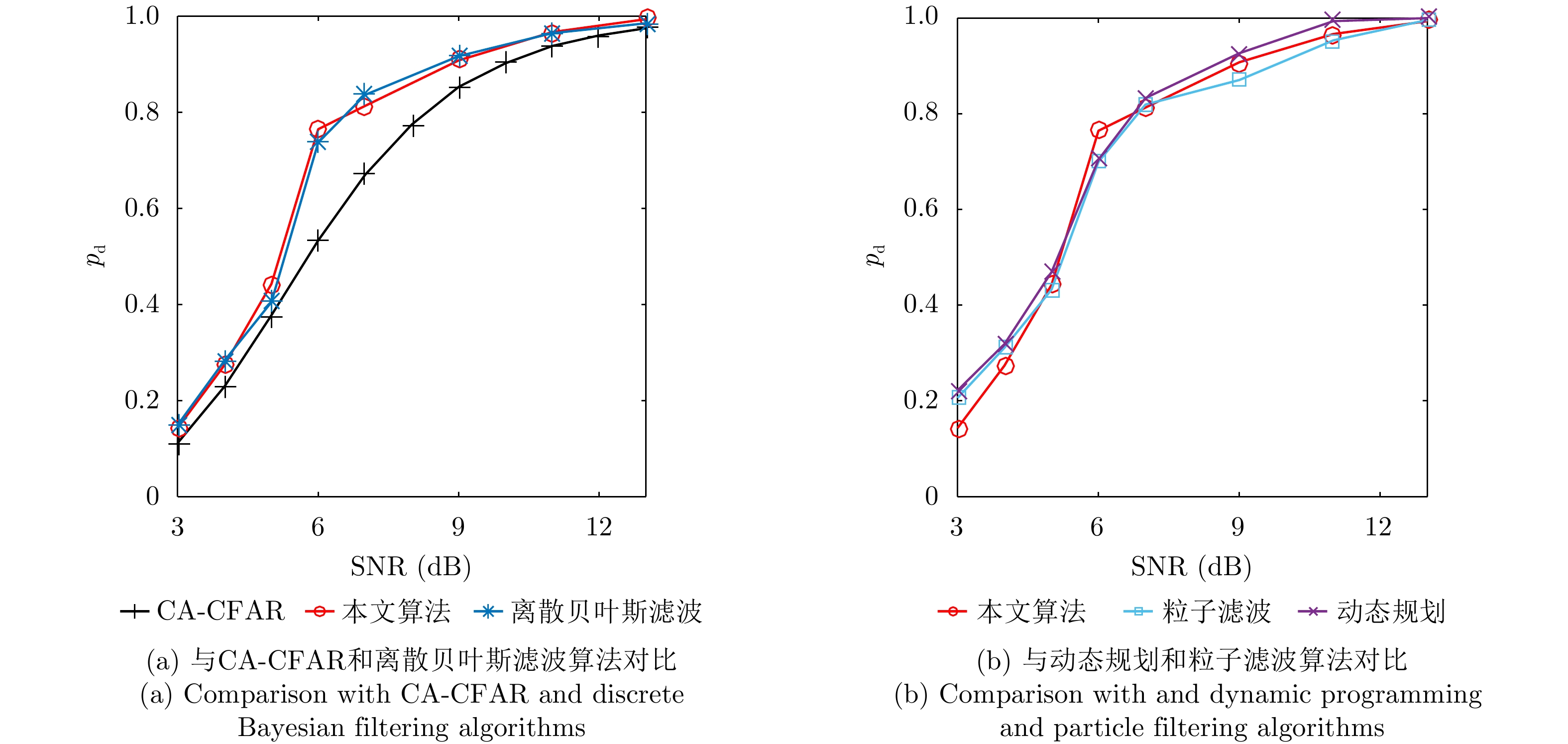
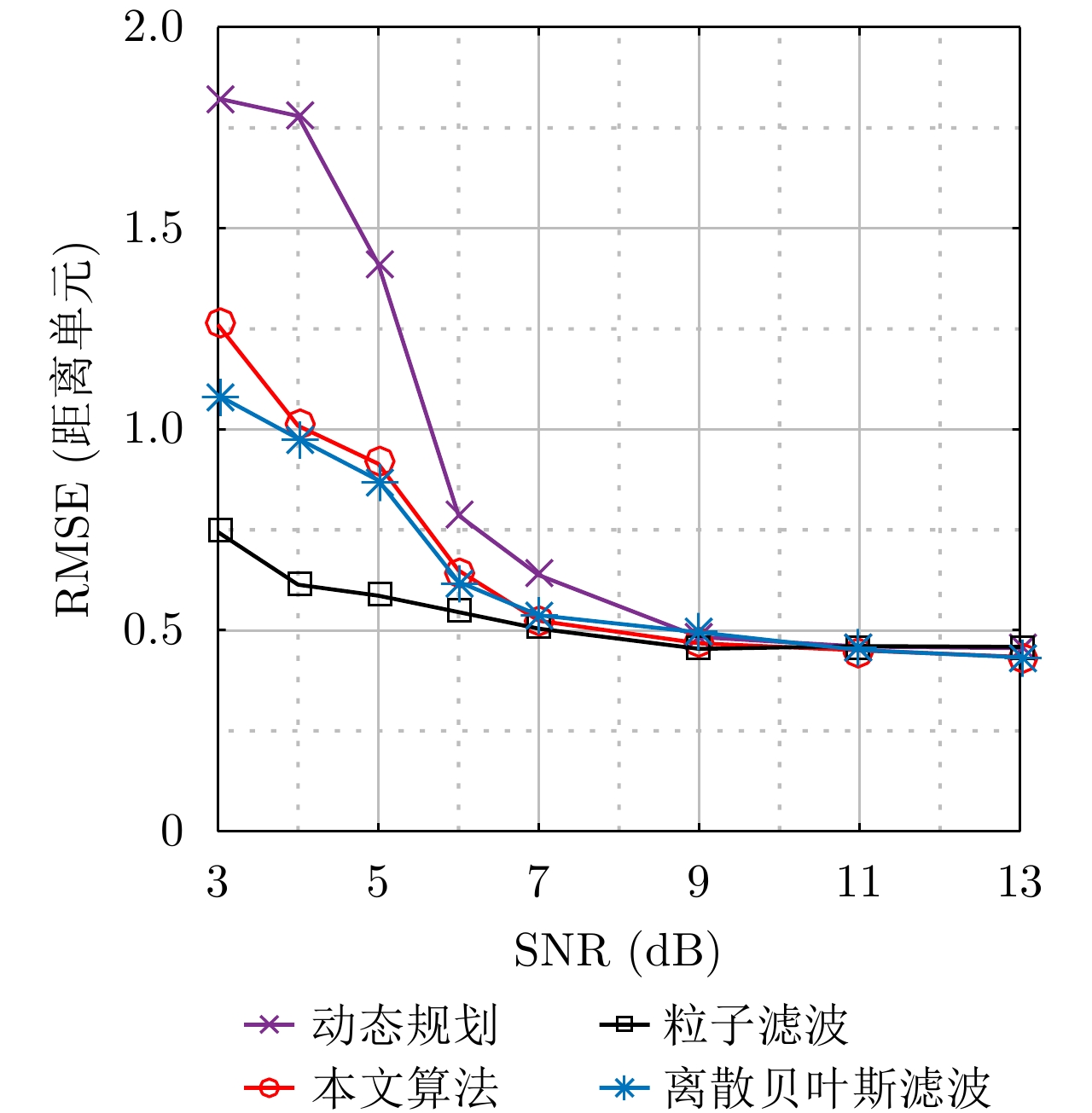
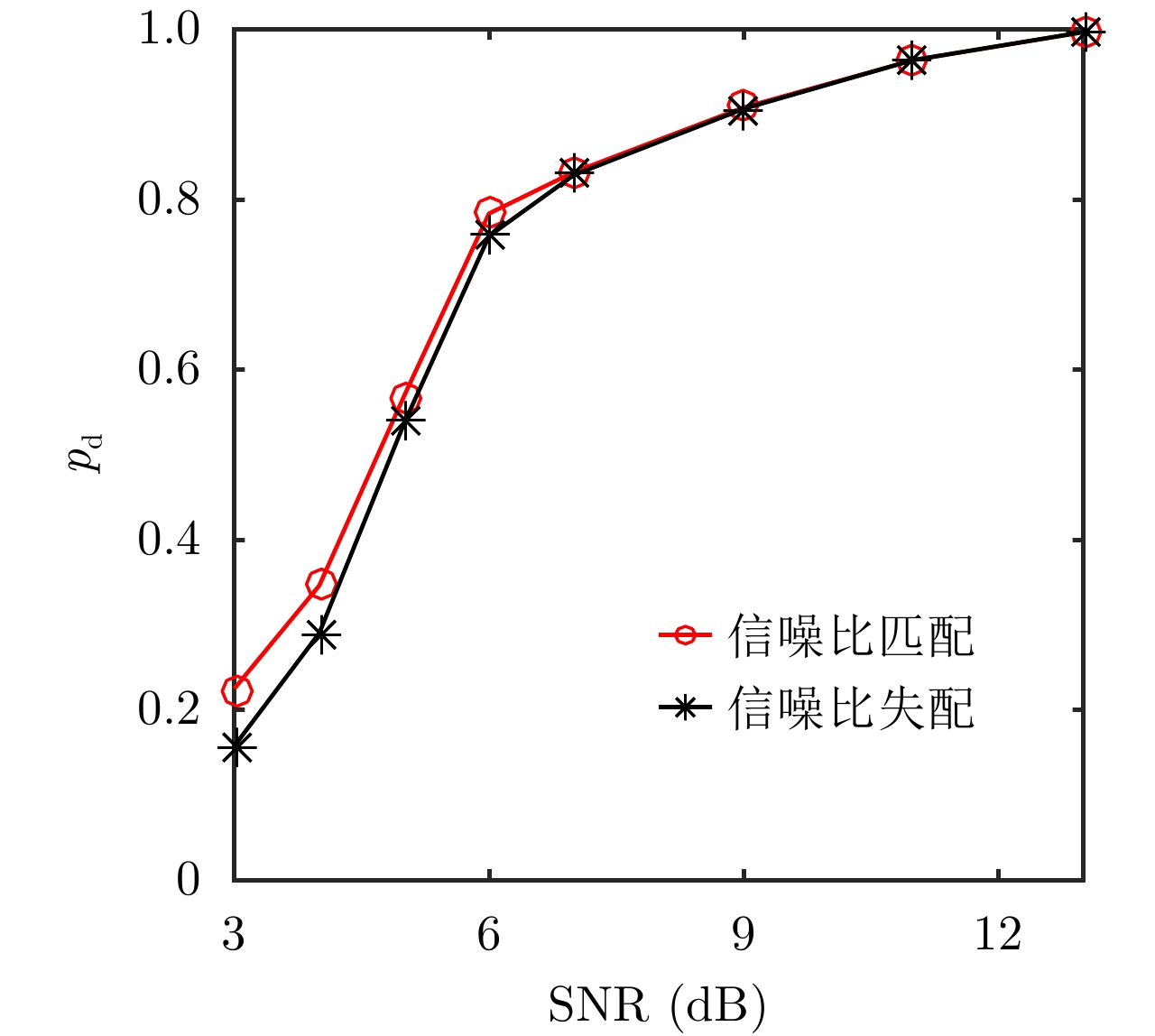
| [1] |
GRIFFITHS H D and BAKER C J. An Introduction to Passive Radar[M]. Boston, US: Artech House, 2017: 1–25.
|
| [2] |
WILLIS N J. Bistatic Radar[M]. Raleigh, US: SciTech Publishing, 2005: 15–57.
|
| [3] |
KULPA K and MALANOWSKI M. From Klein Heidelberg to modern multistatic passive radar[C]. The 2019 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 2019: 1–9. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8768176. |
| [4] |
何友, 关键, 孟祥伟, 等. 雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 36–40.
HE You, GUAN Jian, MENG Xiangwei, et al. Radar Target Detection and CFAR Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011: 36–40.
|
| [5] |
CARLSON B D, EVANS E D, and WILSON S L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. I. system concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(1): 102–108. doi: 10.1109/7.250410 |
| [6] |
BARNIV Y. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES–21(1): 144–156. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310548 |
| [7] |
YI Wei, JIANG Haichao, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Track-before-detect strategies for radar detection in G0-distributed clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(5): 2516–2533. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2702259 |
| [8] |
SALMOND D J and BIRCH H. A particle filter for track-before-detect[C]. 2001 American Control Conference, Arlington, USA, 2001: 3755–3760. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2001.946220. |
| [9] |
RUTTEN M G, GORDON N J, and MASKELL S. Recursive track-before-detect with target amplitude fluctuations[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(5): 345–352. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045041 |
| [10] |
RUTTEN M G, GORDON N J, and MASKELL S. Efficient particle-based track-before-detect in Rayleigh noise[C]. The 7th International Conference on Information Fusion, Stockholm, Sweden, 2004: 693–700.
|
| [11] |
JISHY K and LEHMANN F. A Bayesian track-before-detect procedure for passive radars[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013(1): 45. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-45 |
| [12] |
ROLLASON M and SALMOND D. Particle filter for track-before-detect of a target with unknown amplitude viewed against a structured scene[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(6): 603–609. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0483 |
| [13] |
STONE L D, CORWIN T L, and BARLOW C A. Bayesian Multiple Target Tracking[M]. Boston, US: Artech House, 2013: 65–77.
|
| [14] |
ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374 |
| [15] |
MAHAFZA B R. Introduction to Radar Analysis[M]. Boca Raton, US: CRC Press, 1998: 267–287.
|
| [16] |
DAVEY S J, RUTTEN M G, and CHEUNG B. A comparison of detection performance for several track-before-detect algorithms[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2007, 2008(1): 428036. doi: 10.1155/2008/428036 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: