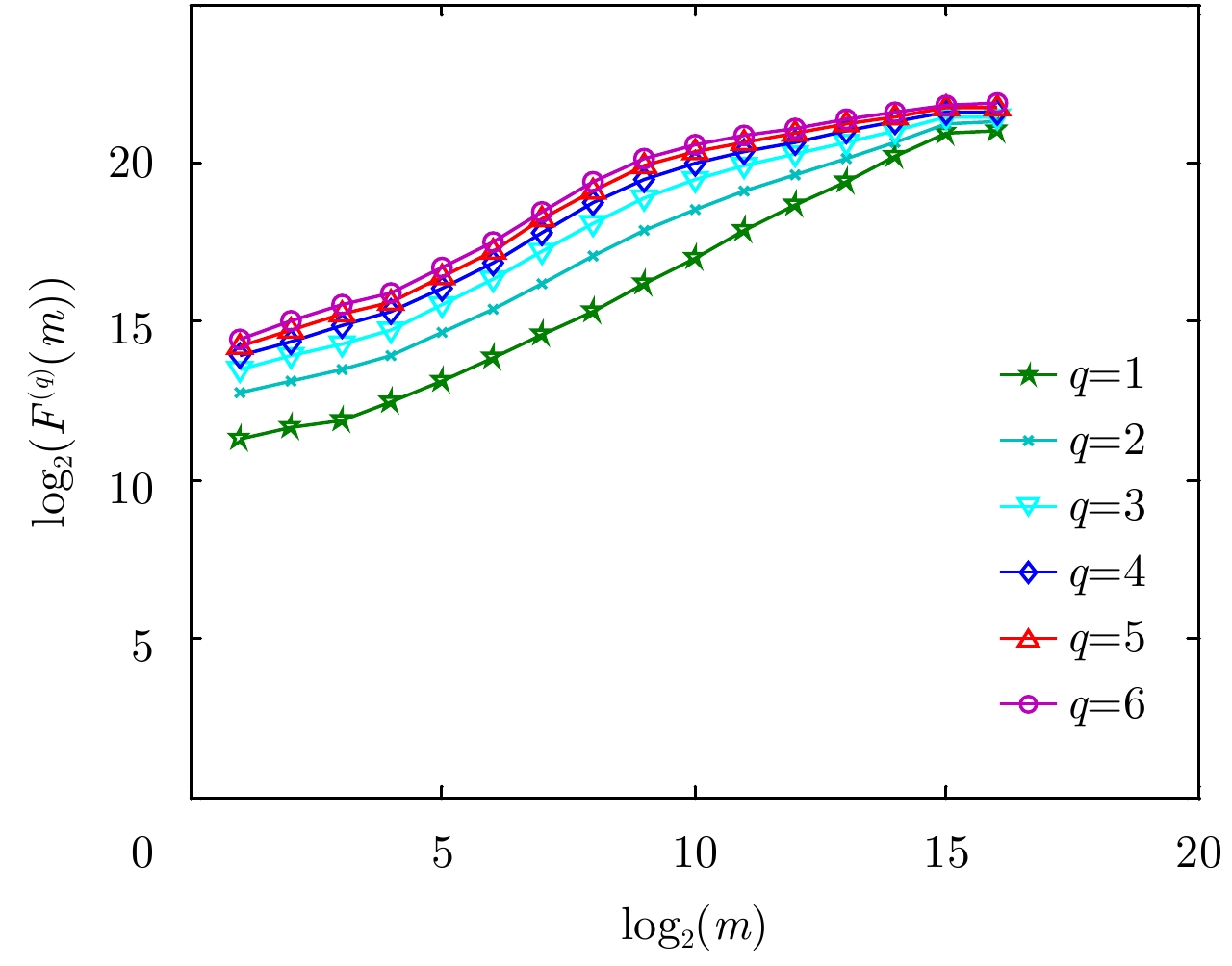
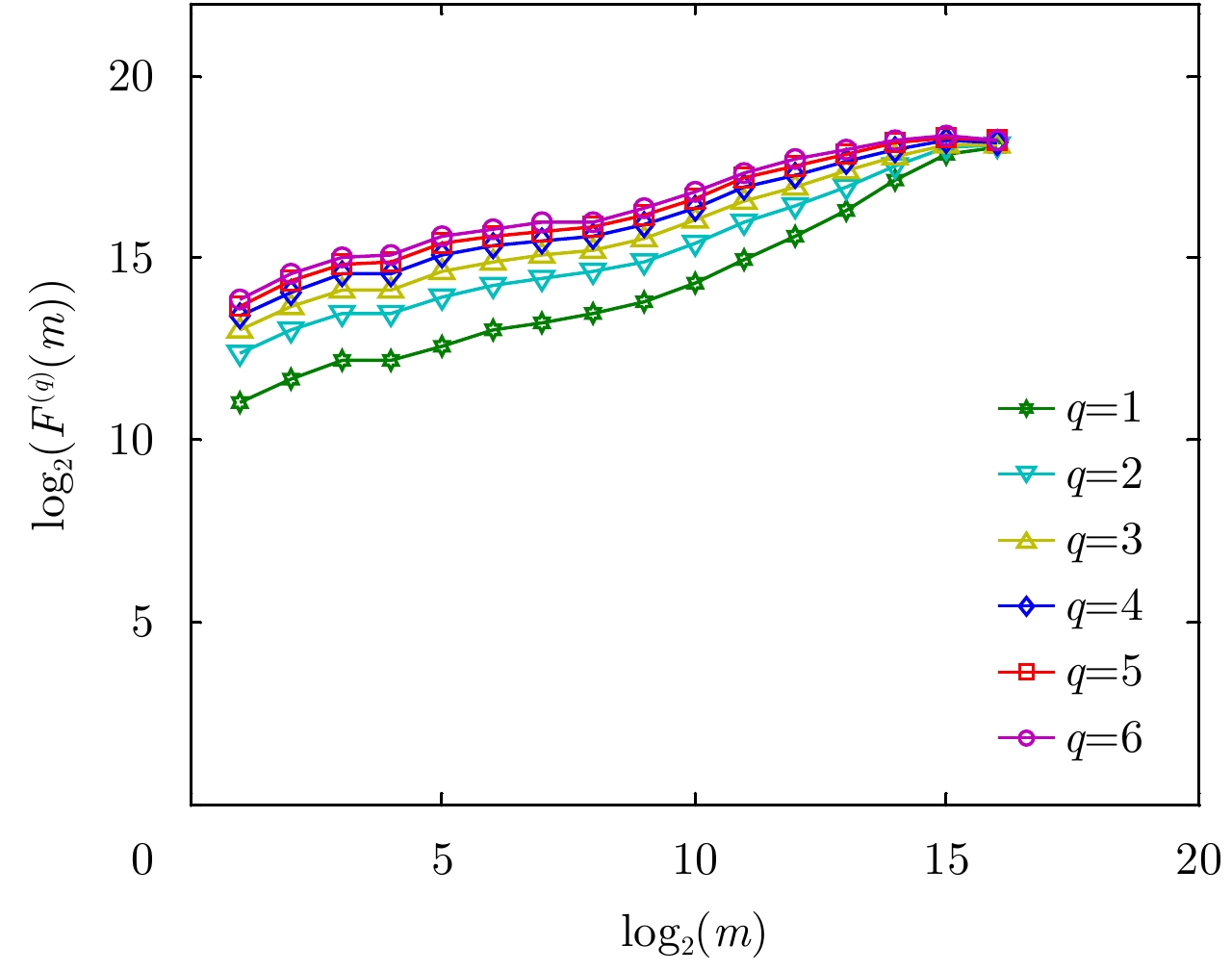
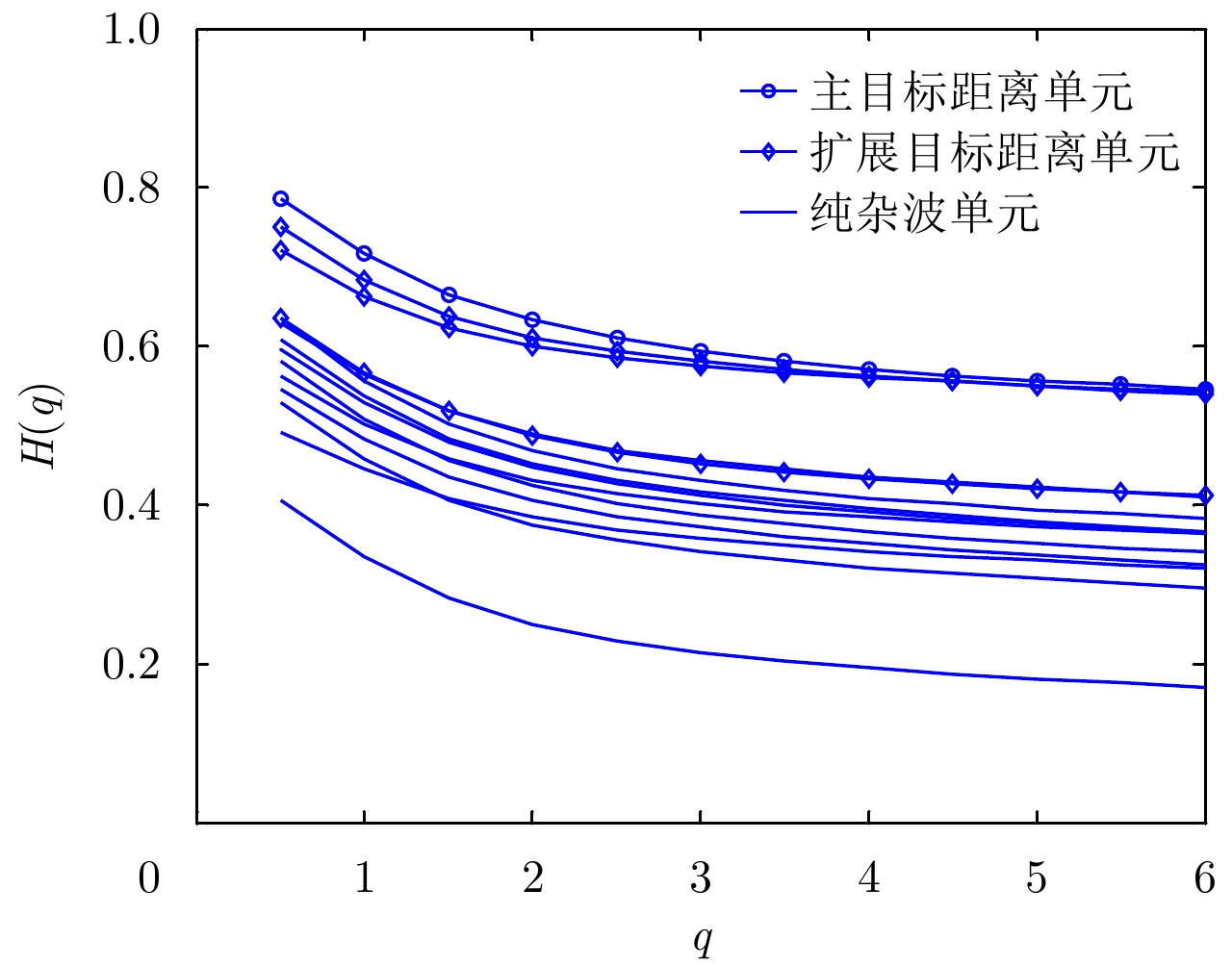
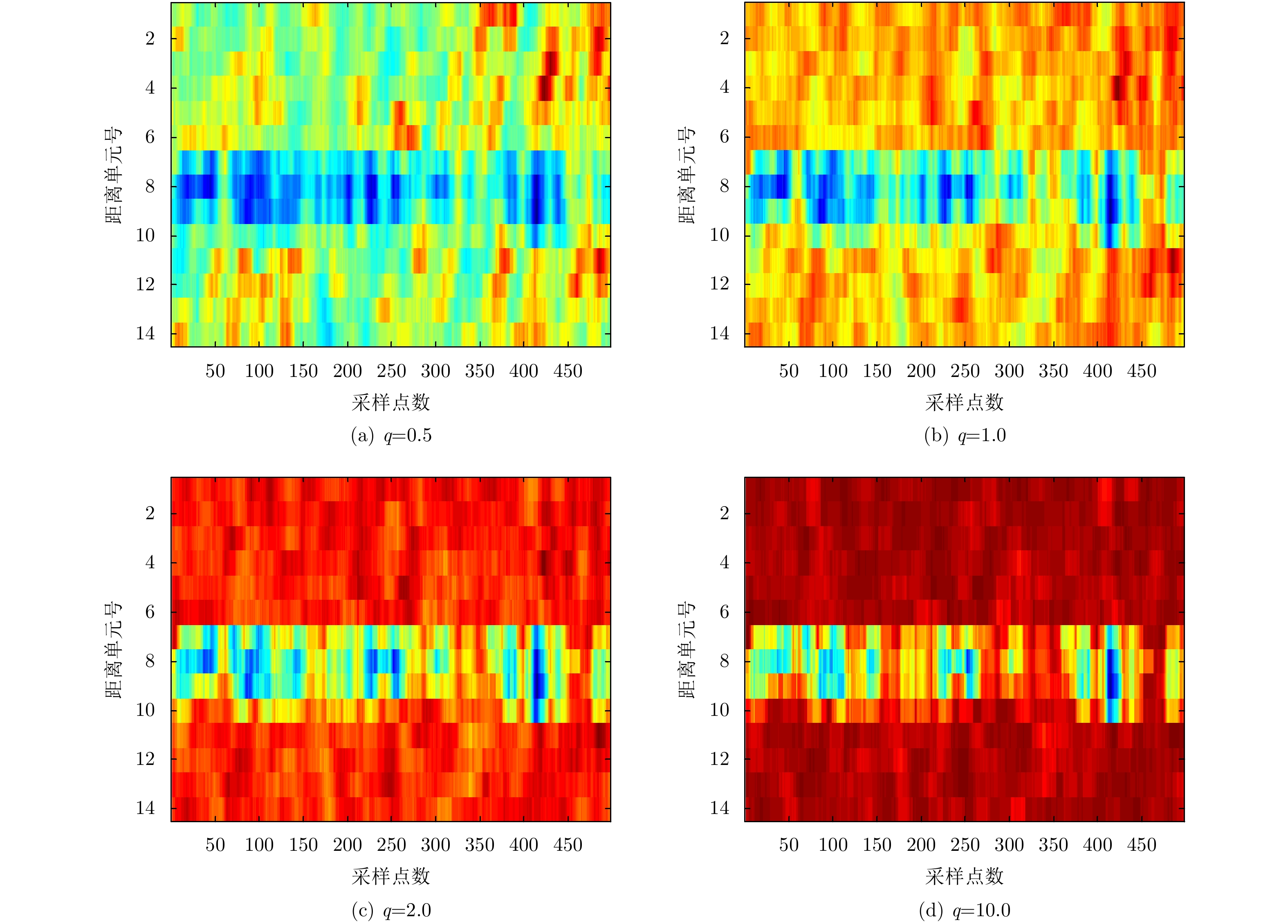
| [1] |
FARINA A and STUDER F A. A review of CFAR detection techniques in radar systems[J]. Microware Journal, 1986, 29(5): 115, 116, 118.
|
| [2] |
丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069DING Hao, DONG Yunlong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069 |
| [3] |
HAYKIN S, CURRIE B W, and KESLER S B. Maximum-entropy spectral analysis of radar clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1982, 70(9): 953–962. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1982.12426 |
| [4] |
LIU Jin, WANG Xue, and LIU Hongwei. Small target detection in sea clutter background based on Doppler spectrum characteristics[J]. Modern Radar, 2008, 30(11): 63–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2008.11.016 |
| [5] |
SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 |
| [6] |
DUK V, ROSENBERG L, and NG B W H. Target detection in sea-clutter using stationary wavelet transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1136–1146. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2667558 |
| [7] |
HAYKIN S, BAKKER R, and CURRIE B W. Uncovering nonlinear dynamics-the case study of sea clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2002, 90(5): 860–881. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2002.1015011 |
| [8] |
LO T, LEUNG H, LITVA J, et al. Fractal characterisation of sea-scattered signals and detection of sea-surface targets[J]. IEE Proceedings F - Radar and Signal Processing, 1993, 140(4): 243–250. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0034 |
| [9] |
SUN Kang, JIN Gang, and ZHU Xiaohua. Small target detection within sea clutter based on the fluctuation analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(4): 882–887. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00927 |
| [10] |
GAN D and SHOUHONG Z. Detection of sea-surface radar targets based on multifractal analysis[J]. Electronics Letters, 2000, 36(13): 1144–1145. doi: 10.1049/el:20000800 |
| [11] |
LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in frequency domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(3): 424–431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.002 |
| [12] |
LIU Ningbo, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Fractal analysis of real sea clutter in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 929–935. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.11.1146.2011.00856 |
| [13] |
LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, WANG Guoqing, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in FRFT domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(9): 1847–1853. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.029 |
| [14] |
CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Ningbo, SONG Jie, et al. Fractal feature discriminant of sea clutter in FRFT domain and moving target detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486 |
| [15] |
LUO Feng, ZHANG Danting, and ZHANG Bo. The fractal properties of sea clutter and their applications in maritime target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1295–1299. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2237750 |
| [16] |
FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. Weak target detection in sea clutter background using local-multifractal spectrum with adaptive window length[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(7): 835–842. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0286 |
| [17] |
FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. Fractal properties of autoregressive spectrum and its application on weak target detection in sea clutter background[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 1070–1077. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0473 |
| [18] |
TSALLIS C, PLASTINO A R, and ZHENG W M. Power-law sensitivity to initial conditions—New entropic representation[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 1997, 8(6): 885–891. doi: 10.1016/S0960-0779(96)00167-1 |
| [19] |
TSALLIS C and BRIGATTI E. Nonextensive statistical mechanics: A brief introduction[J]. Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 2004, 16(3): 223–235. doi: 10.1007/s00161-004-0174-4 |
| [20] |
FURUICHI S. On uniqueness theorems for Tsallis entropy and Tsallis relative entropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(10): 3638–3645. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.855606 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
BUNTE C and LAPIDOTH A. Maximum Rényi entropy rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(3): 1193–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2521364 |
| [23] |
范一飞, 罗丰, 李明, 等. 海杂波AR谱多重分形特性及微弱目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150581FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. The multifractal properties of AR spectrum and weak target detection in sea clutter background[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150581 |
| [24] |
STEIN D W J. Detection of random signals in Gaussian mixture noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1995, 41(6): 1788–1801. doi: 10.1109/18.476307 |
| [25] |
SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection by one-class classifier in time-frequency feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6395–6411. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838260 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: