- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | JIN Yan, QIU Xiaolan, PAN Jie, et al. MPOLSAR-1.0: Multidimensional SAR multiband fully polarized fine classification dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 525–538. doi: 10.12000/JR24002 |
MPOLSAR-1.0: Multidimensional SAR Multiband Fully Polarized Fine Classification Dataset(in English)
DOI: 10.12000/JR24002
More Information-
Abstract
Fine terrain classification is one of the main applications of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). In the multiband fully polarized SAR operating mode, obtaining information on different frequency bands of the target and polarization response characteristics of a target is possible, which can improve target classification accuracy. However, the existing datasets at home and abroad only have low-resolution fully polarized classification data for individual bands, limited regions, and small samples. Thus, a multidimensional SAR dataset from Hainan is used to construct a multiband fully polarized fine classification dataset with ample sample size, diverse land cover categories, and high classification reliability. This dataset will promote the development of multiband fully polarized SAR classification applications, supported by the high-resolution aerial observation system application calibration and verification project. This paper provides an overview of the composition of the dataset, and describes the information and dataset production methods for the first batch of published data (MPOLSAR-1.0). Furthermore, this study presents the preliminary classification experimental results based on the polarization feature classification and classical machine learning classification methods, providing support for the sharing and application of the dataset. -

-
References
[1] 亓宁轩, 罗征宇, 李彬. 基于多波段全极化SAR影像的湿地分类[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2017, 40(1): 171–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2017.01.051.QI Ningxuan, LUO Zhengyu, and LI Bin. Multi-band polarization SAR wetlands classification[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2017, 40(1): 171–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2017.01.051.[2] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 吴一戎. 全息合成孔径雷达的概念、体制和方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, and WU Yirong. Concept, system, and method of holographic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 399–412. doi: 10.12000/JR20063.[3] YIN Junjun and YANG Jian. A modified level set approach for segmentation of multiband polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(11): 7222–7232. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2309725.[4] 廖静娟, 郭华东, 邵芸. 多波段多极化成像雷达图象识别森林类型效果分析[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2000, 5(1): 30–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2000.01.007.LIAO Jingjuan, GUO Huadong, and SHAO Yun. Effect of forest types discrimination using multifrequency and multipolarization imaging radar images[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2000, 5(1): 30–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2000.01.007.[5] 王之禹, 朱敏慧, 白有天. 基于最优状态的多波段全极化SAR数据ML分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(5): 507–511.WANG Zhiyu, ZHU Minhui, and BAI Youtian. Optimal state based ml classification method for multi-band and full-polarization SAR data[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2001, 23(5): 507–511.[6] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.[7] VILLANO M. SNR and noise variance estimation in polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 278–282. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2255860.[8] JIANG Sha, QIU Xiaolan, HAN Bing, et al. A quality assessment method based on common distributed targets for GF-3 polarimetric SAR data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 807. doi: 10.3390/s18030807.[9] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127.[10] 曹芳. 基于Cloude-Pottier分解的全极化SAR数据非监督分类的算法和实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(电子学研究所), 2007.CAO Fang. The unsupervised classification based on the Cloude-Pottier decomposition for fully polarimetric SAR data[D]. Bejing: Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Science, 2007.[11] 徐乔, 张霄, 余绍淮, 等. 综合多特征的极化SAR图像随机森林分类算法[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(4): 685–694. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20197475.XU Qiao, ZHANG Xiao, YU Shaohuai, et al. Multi-feature-based classification method using random forest and superpixels for polarimetric SAR images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(4): 685–694. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20197475. -
Proportional views

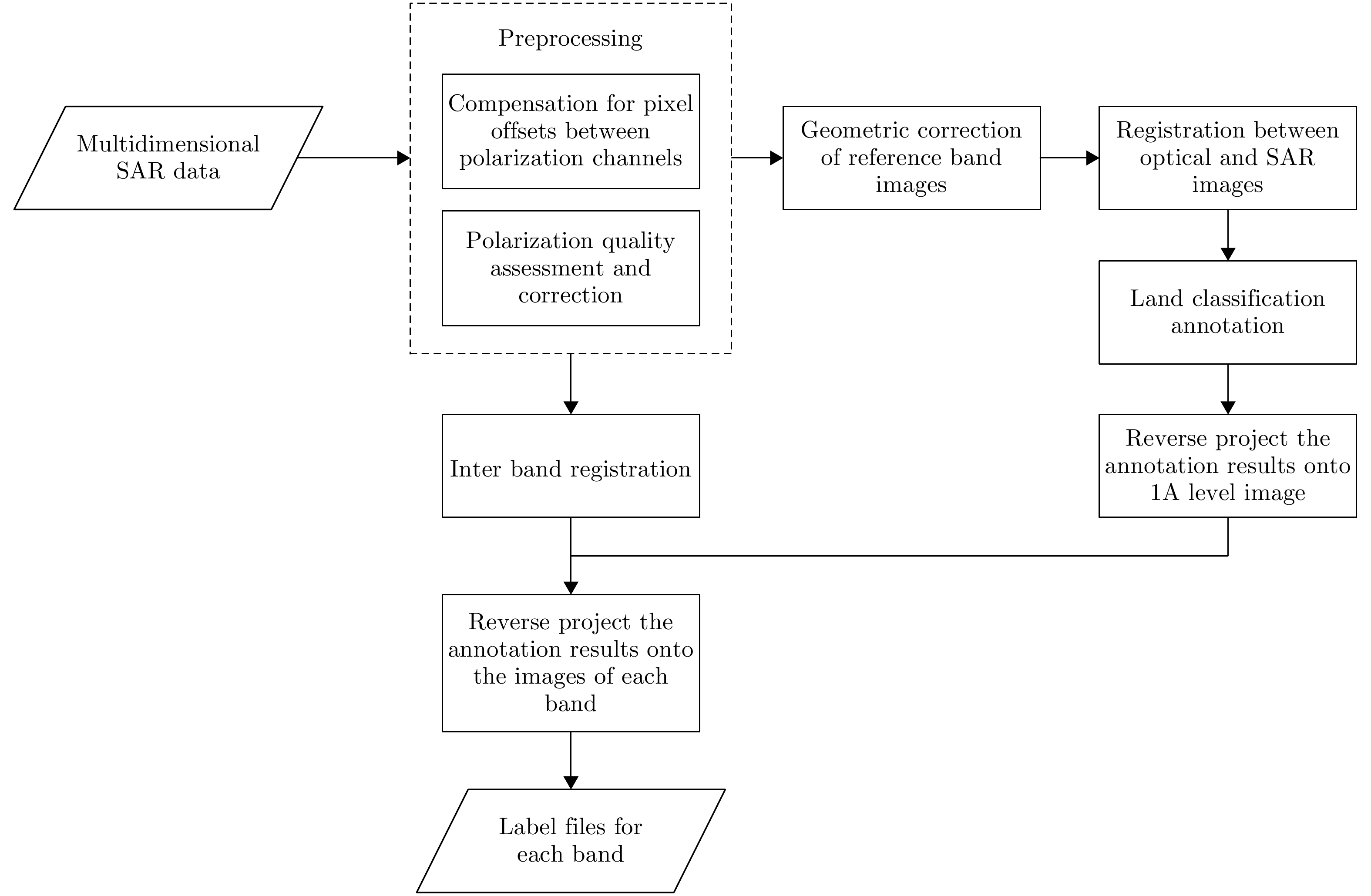
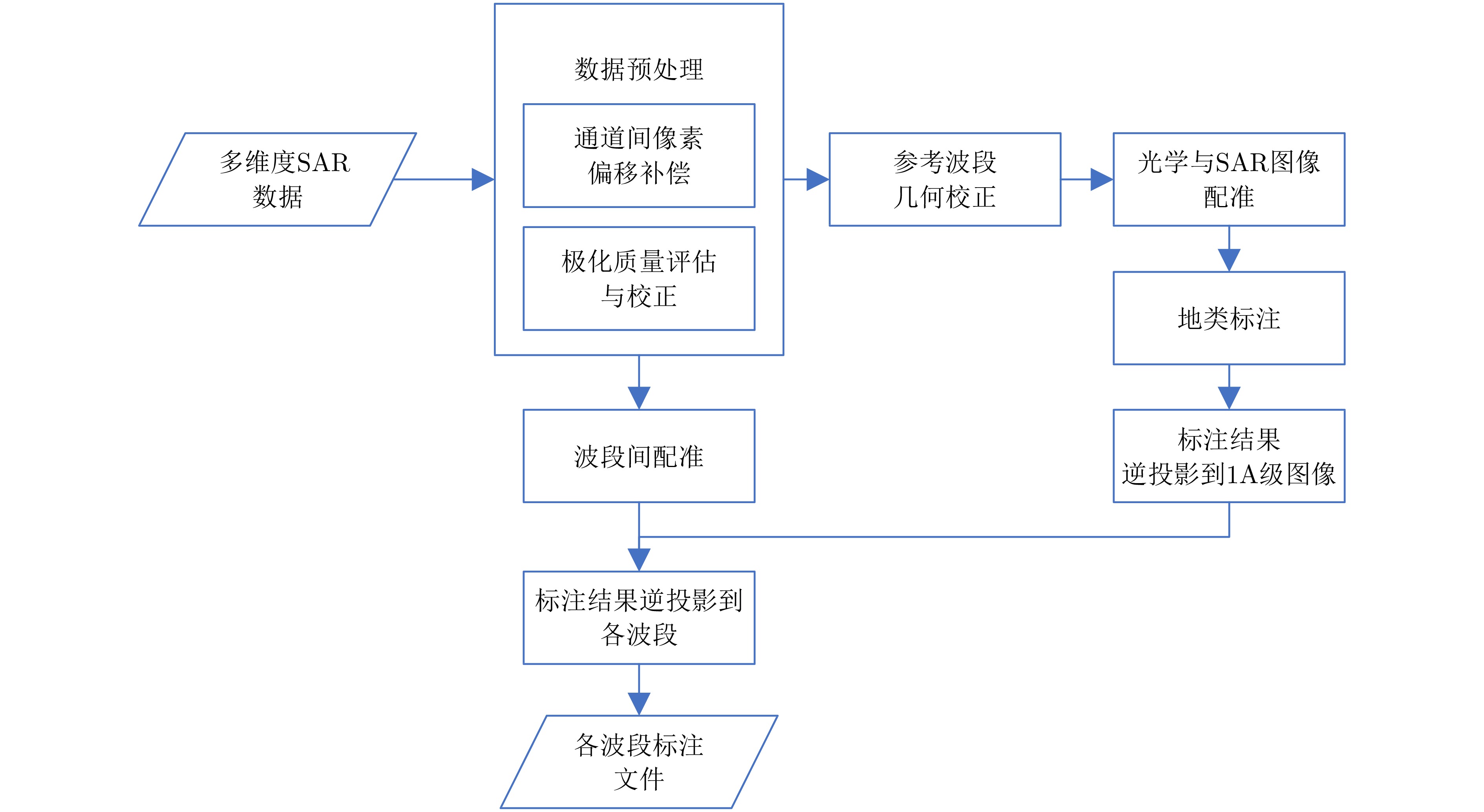
- Figure 1. Flowchart of MPOLSAR dataset construction
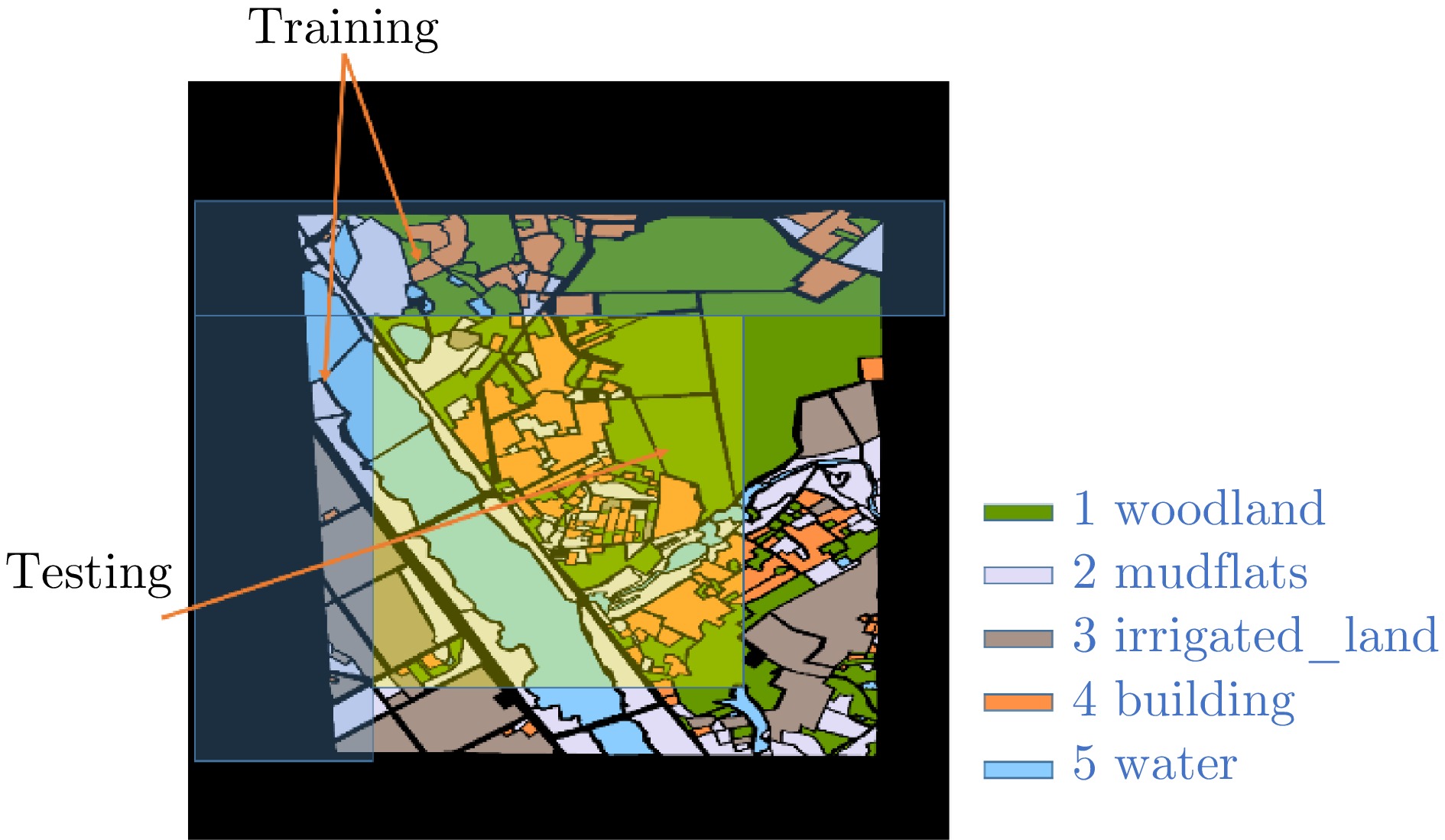
- Figure 2. Composition of MPOLSAR-1.0 (from left to right are HH, HV, VH, VV polarized SAR images and annotated images, respectively)
- Figure 3. Pixel migration detection between multidimensional SAR polarization channels
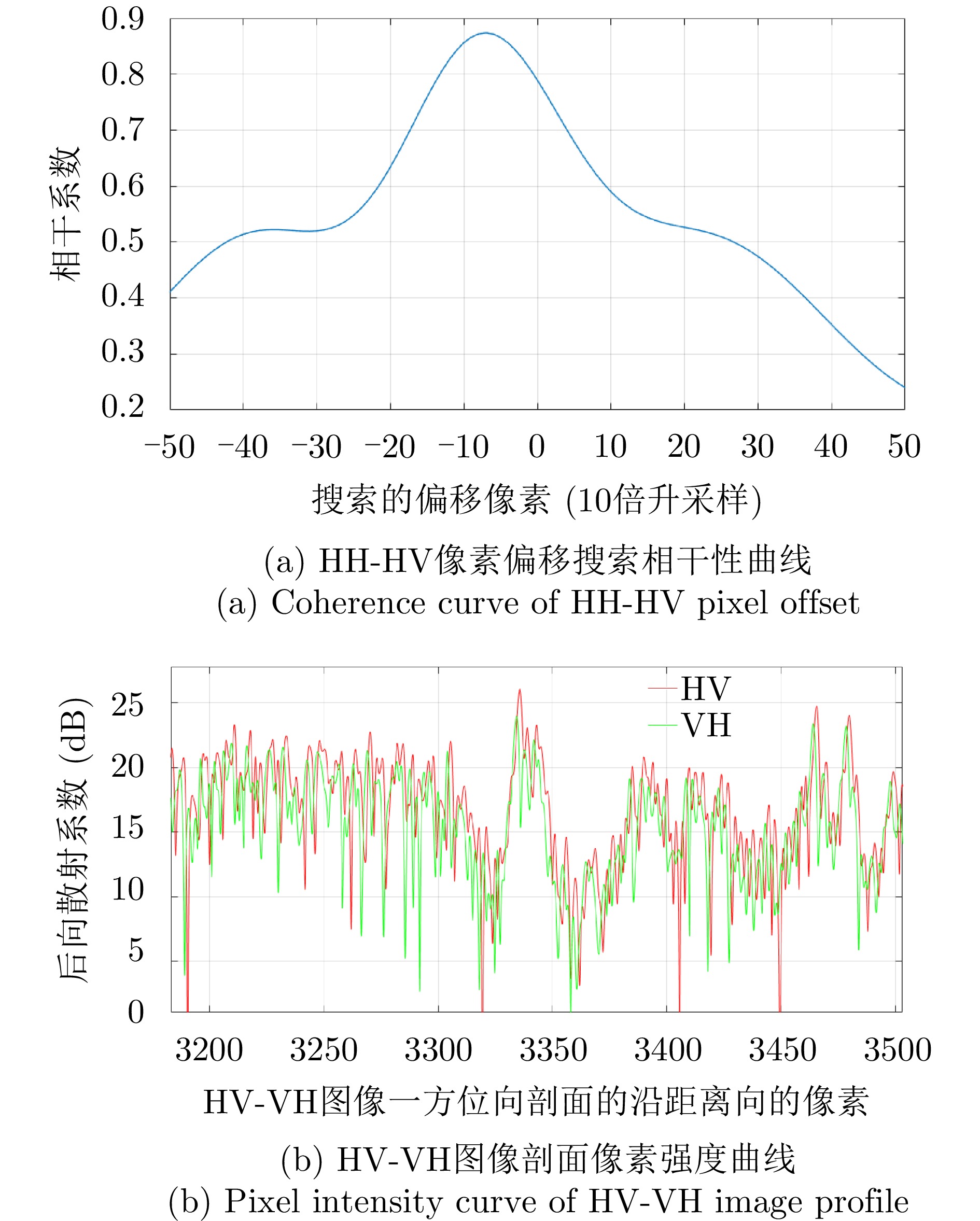
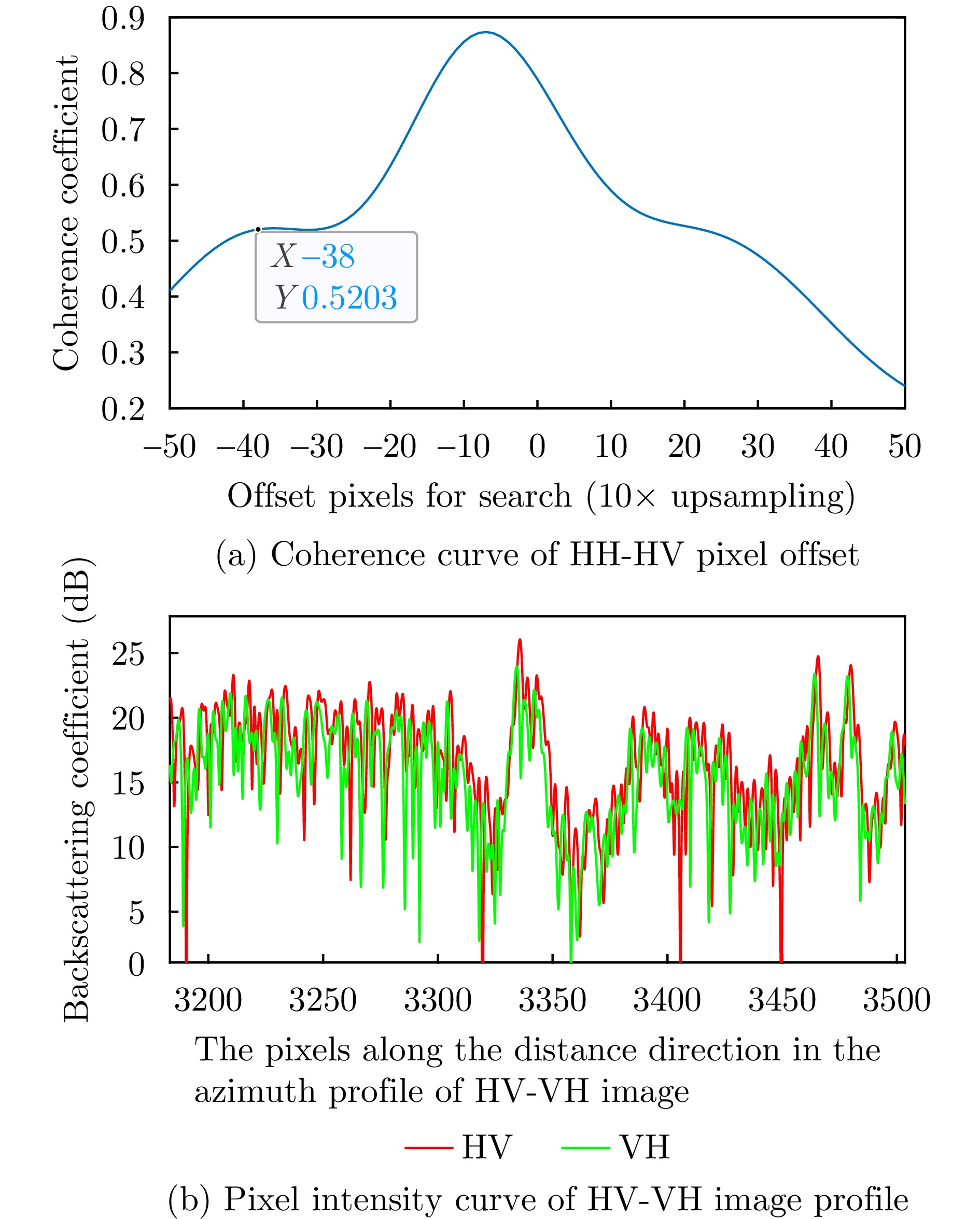
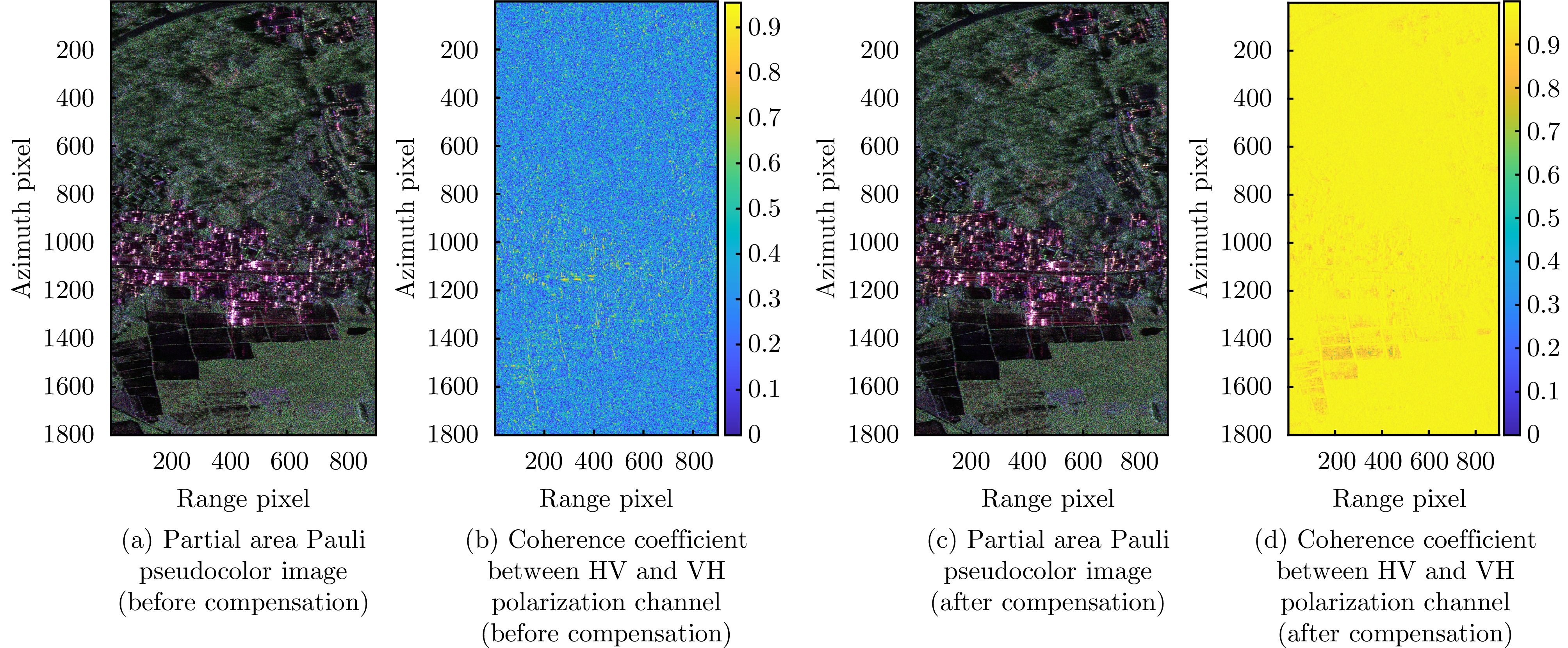
- Figure 4. Pixel offset compensation effect between HV, VH polarization channels in X band SAR
- Figure 5. The scenarios for SAR polarization distortion parameter estimation
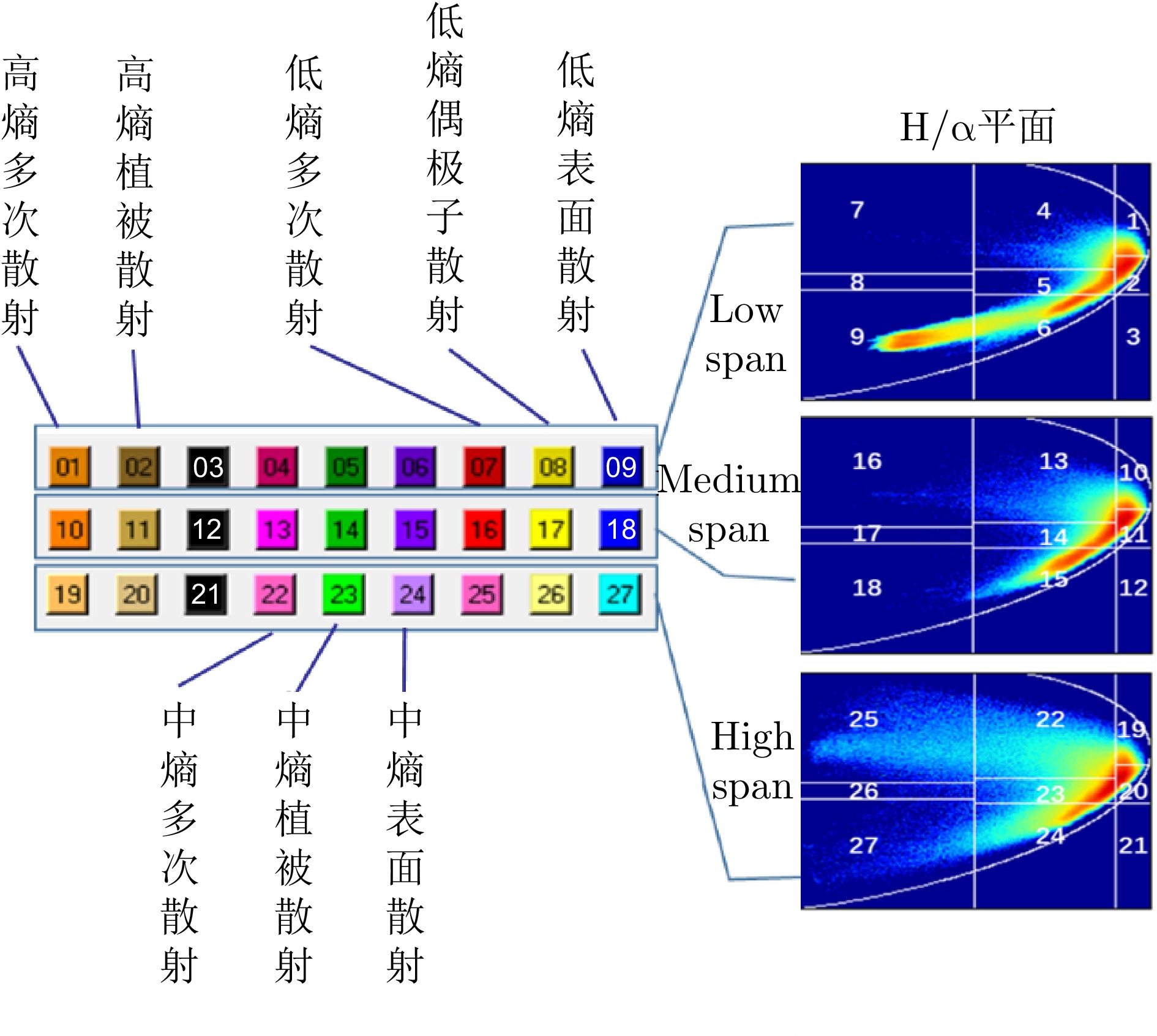
- Figure 6. Label categories and color schemes
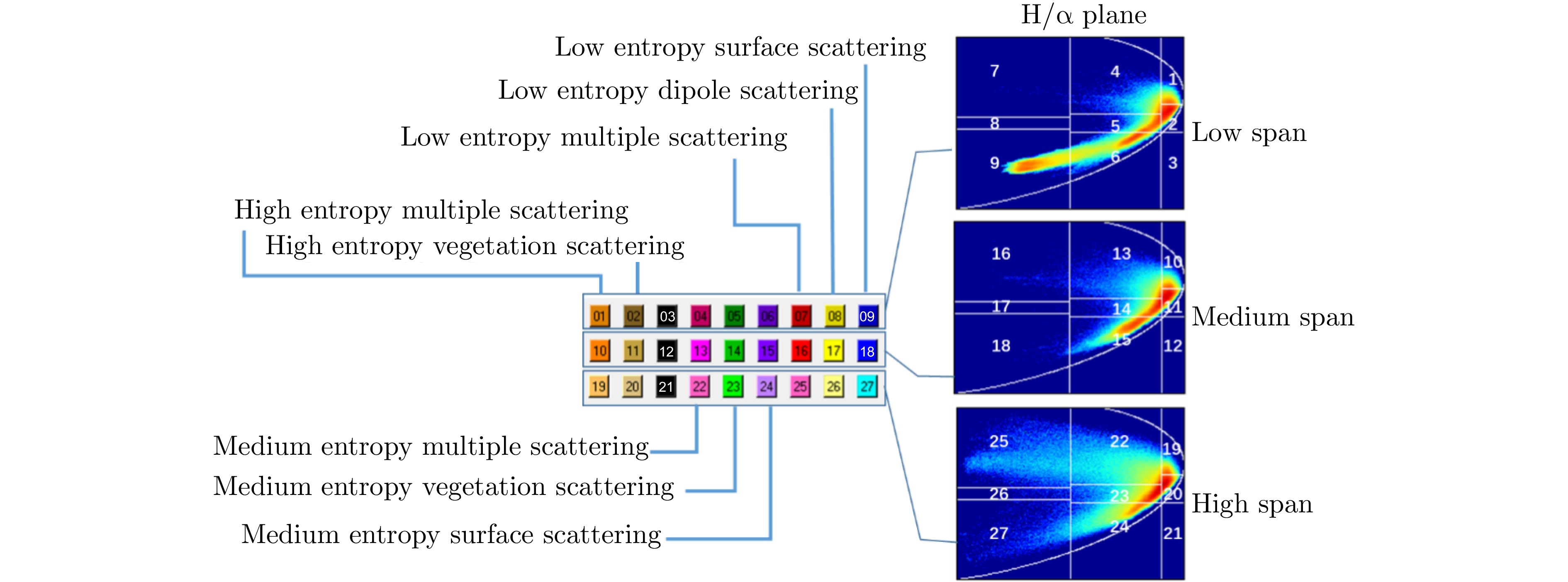
- Figure 7. H-alpha-span classification interval and color matching
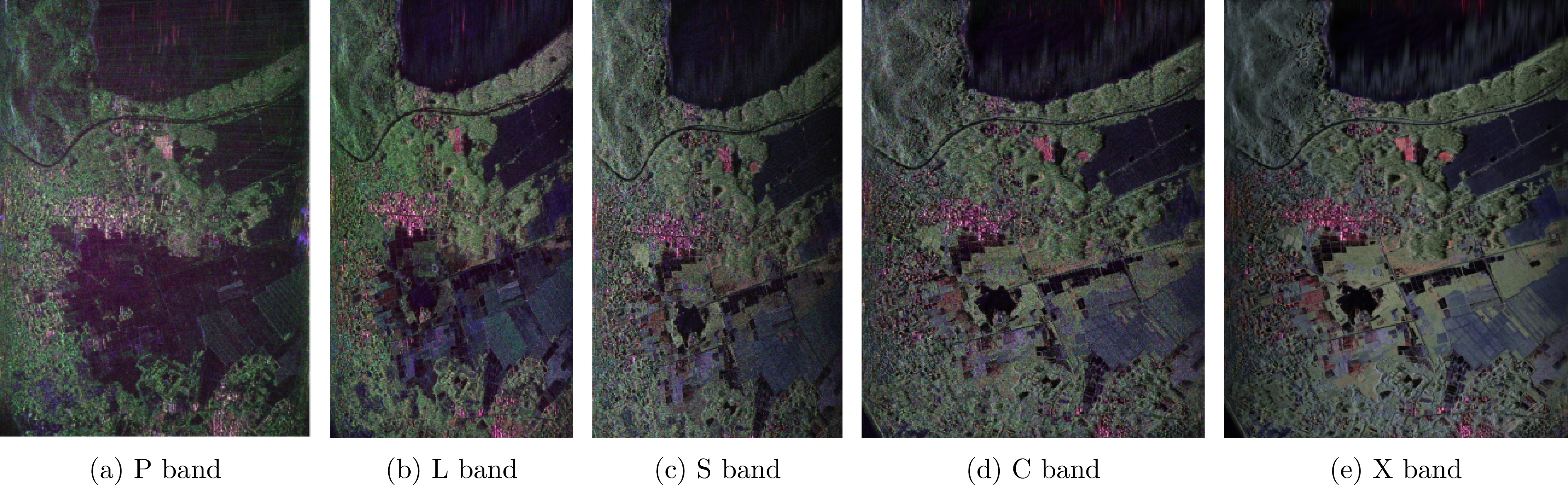
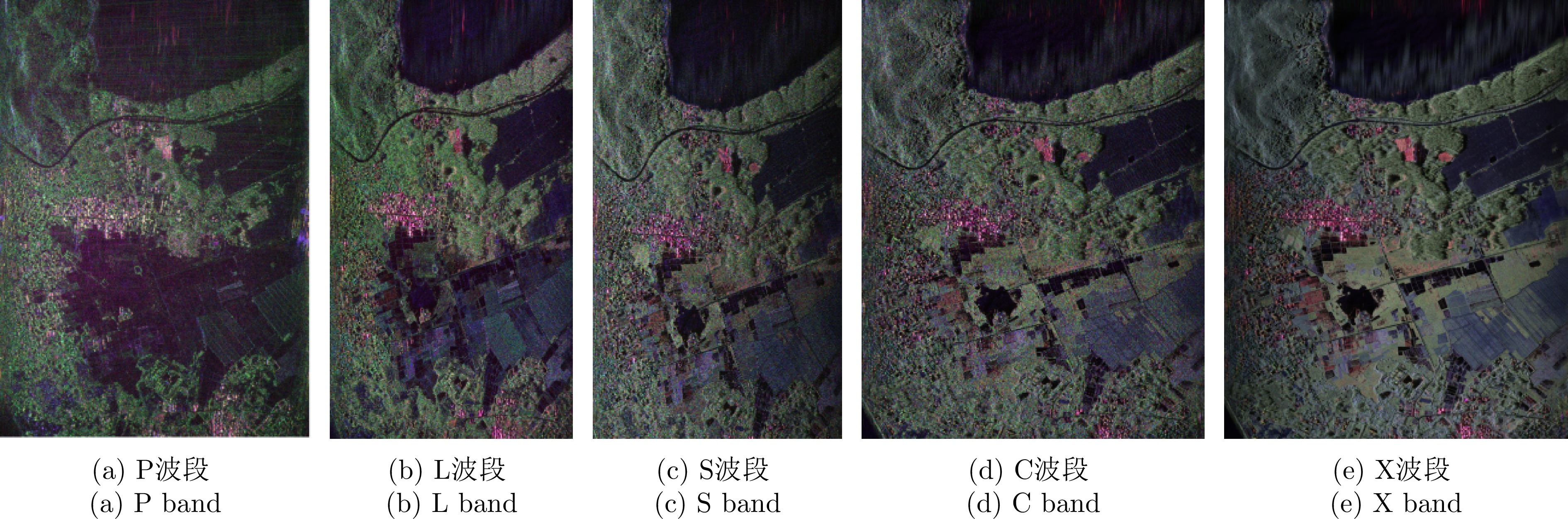
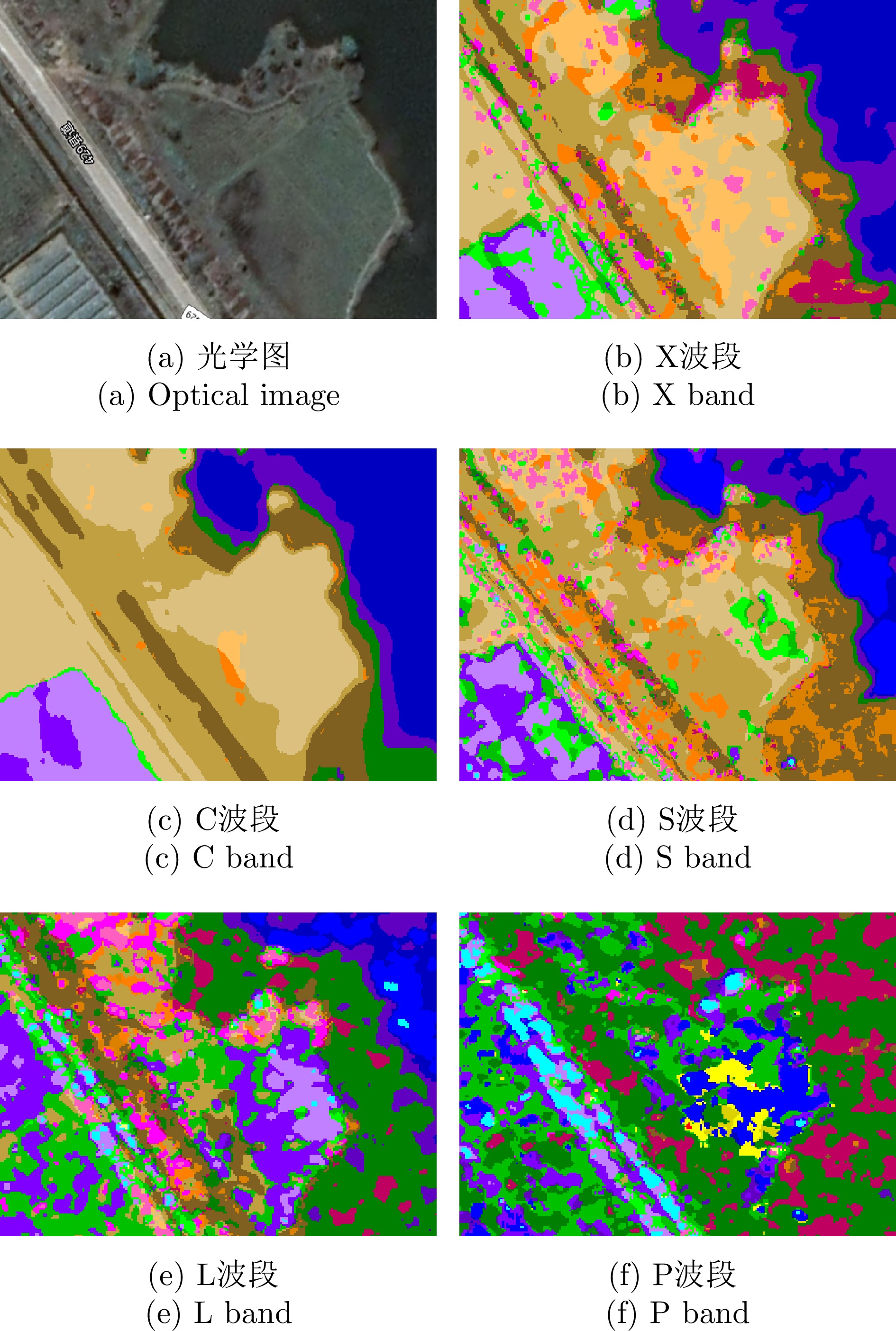
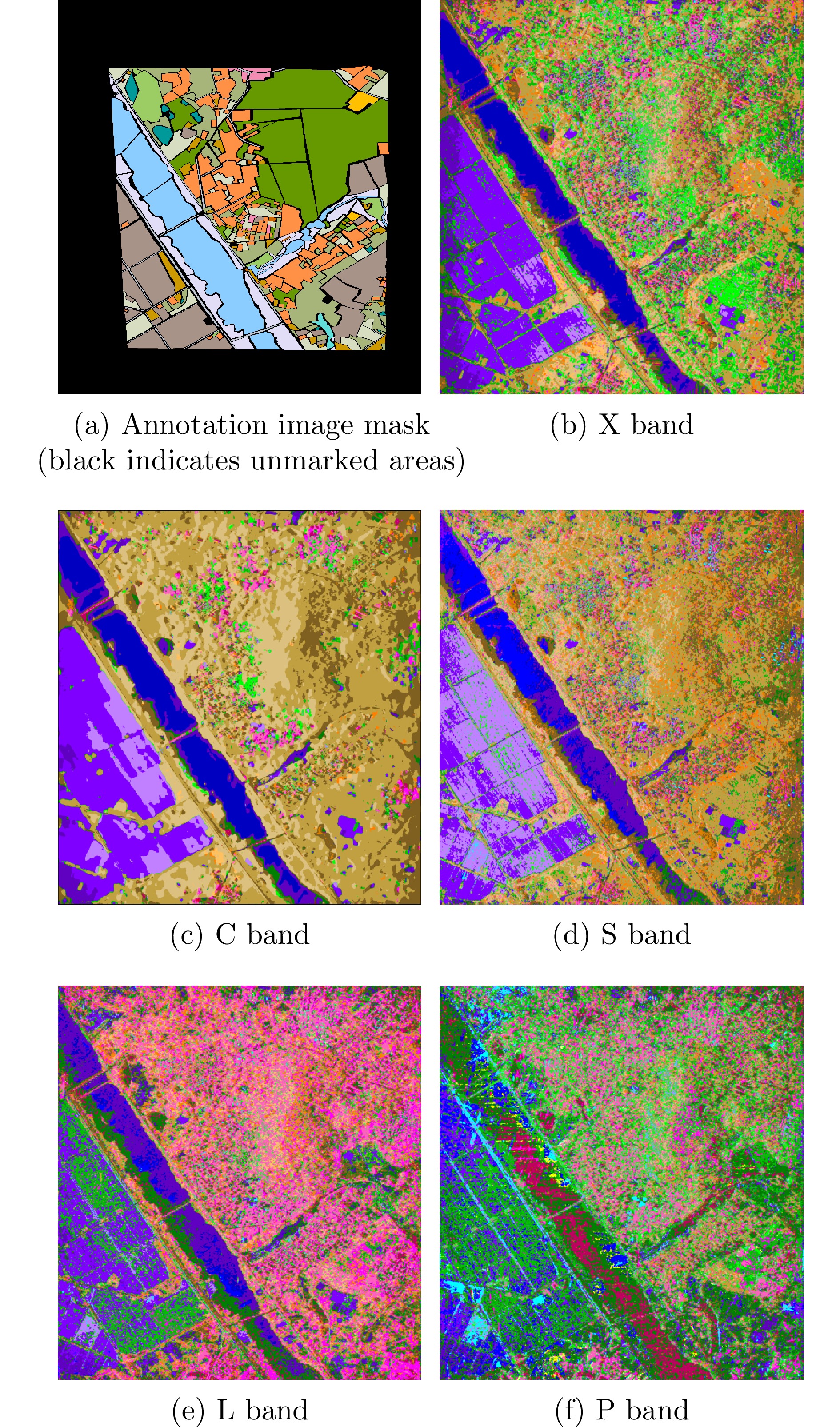
- Figure 8. Comparison of classification results for different bands
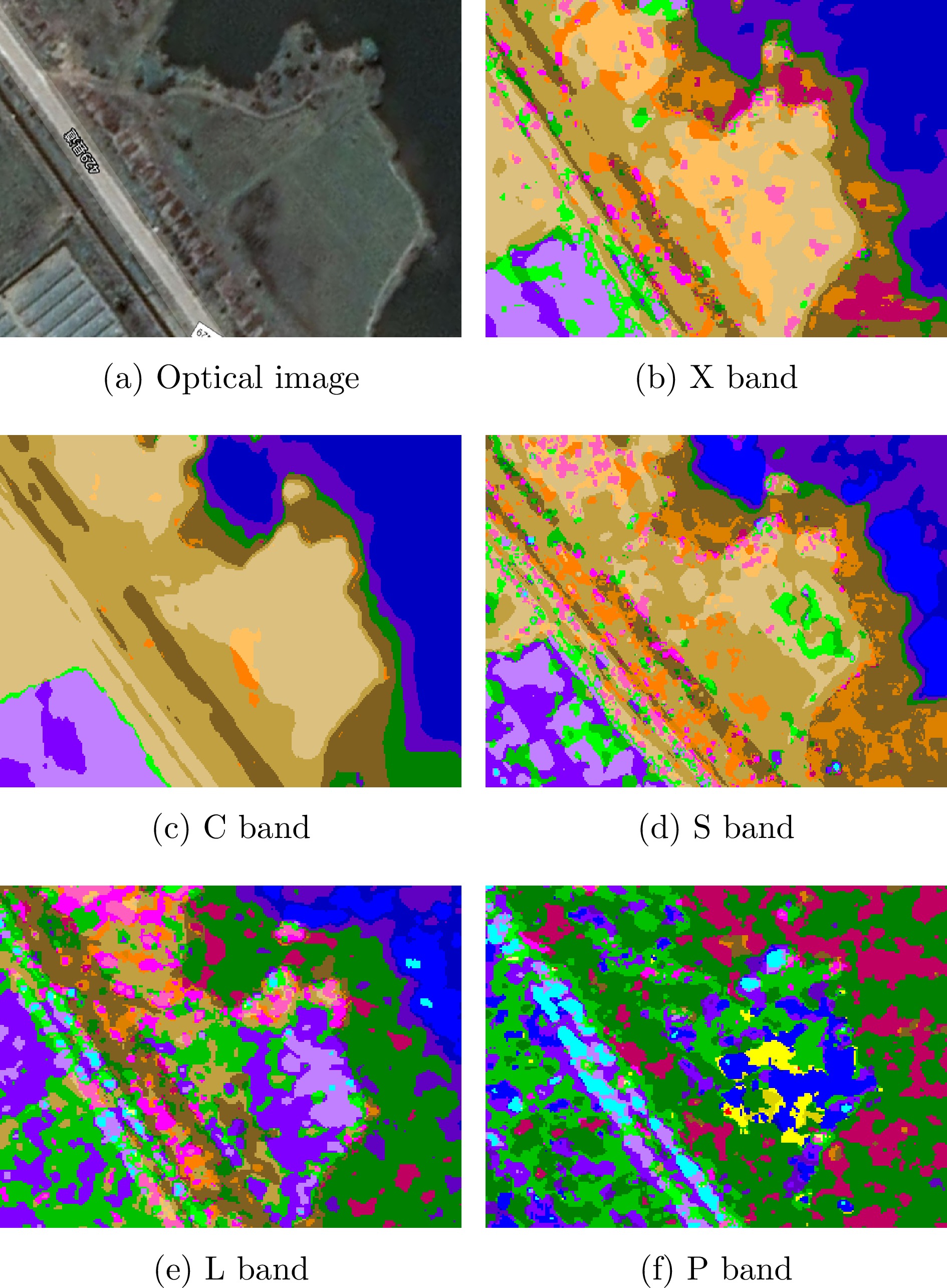
- Figure 9. Classification results of river area
- Figure 10. Classification results of inland madflats
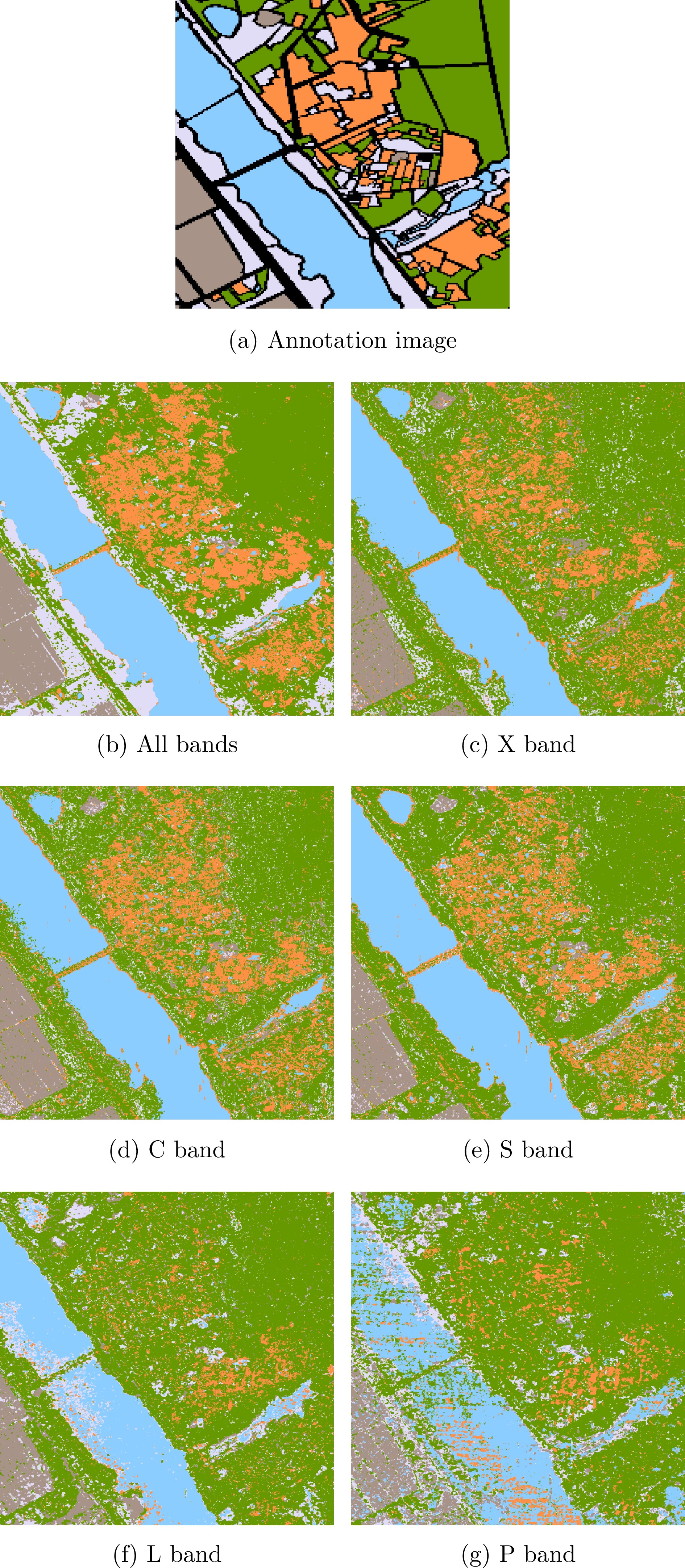
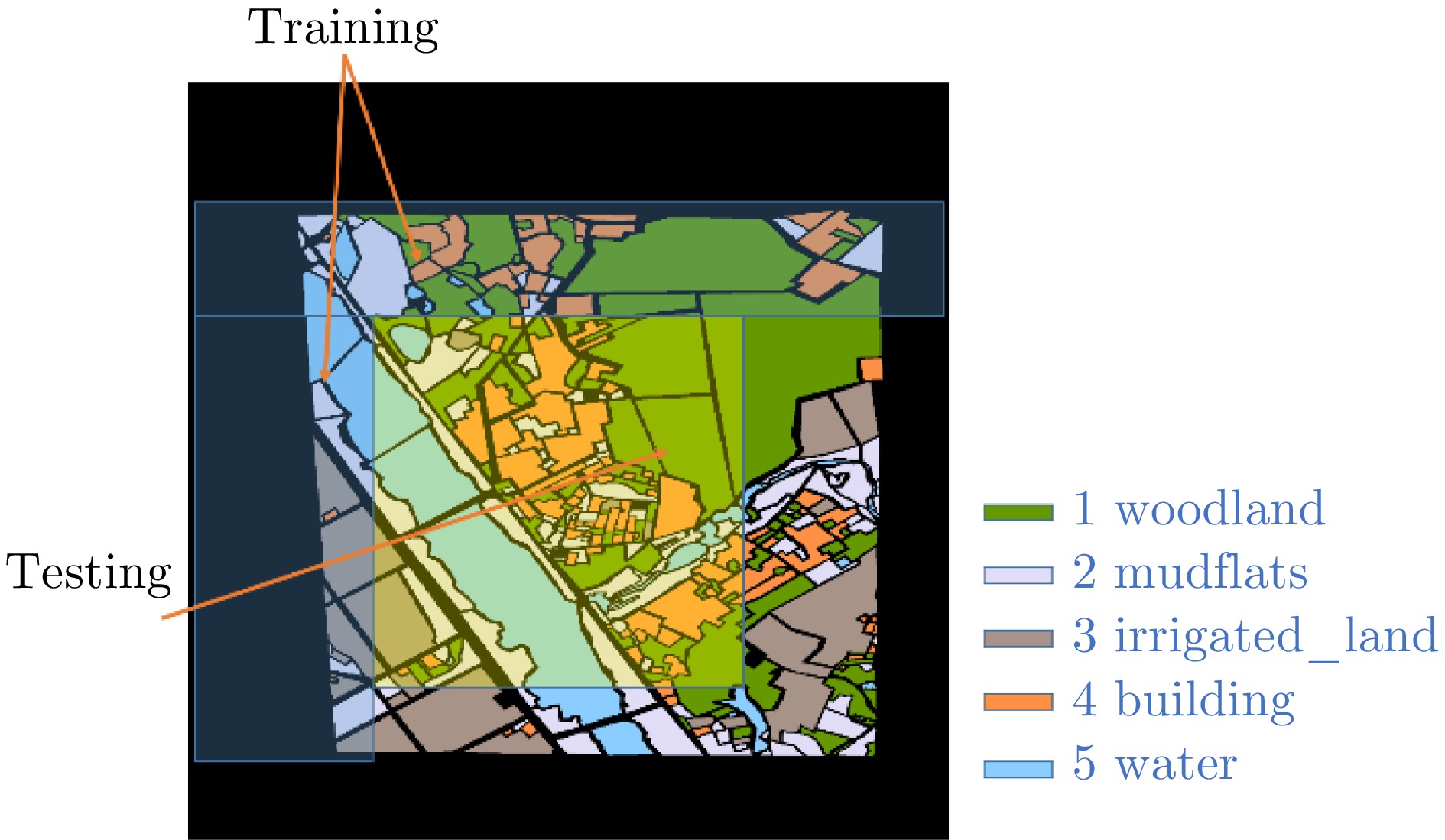
- Figure 11. Annotation diagram, schematic diagram of training and testing set partitioning
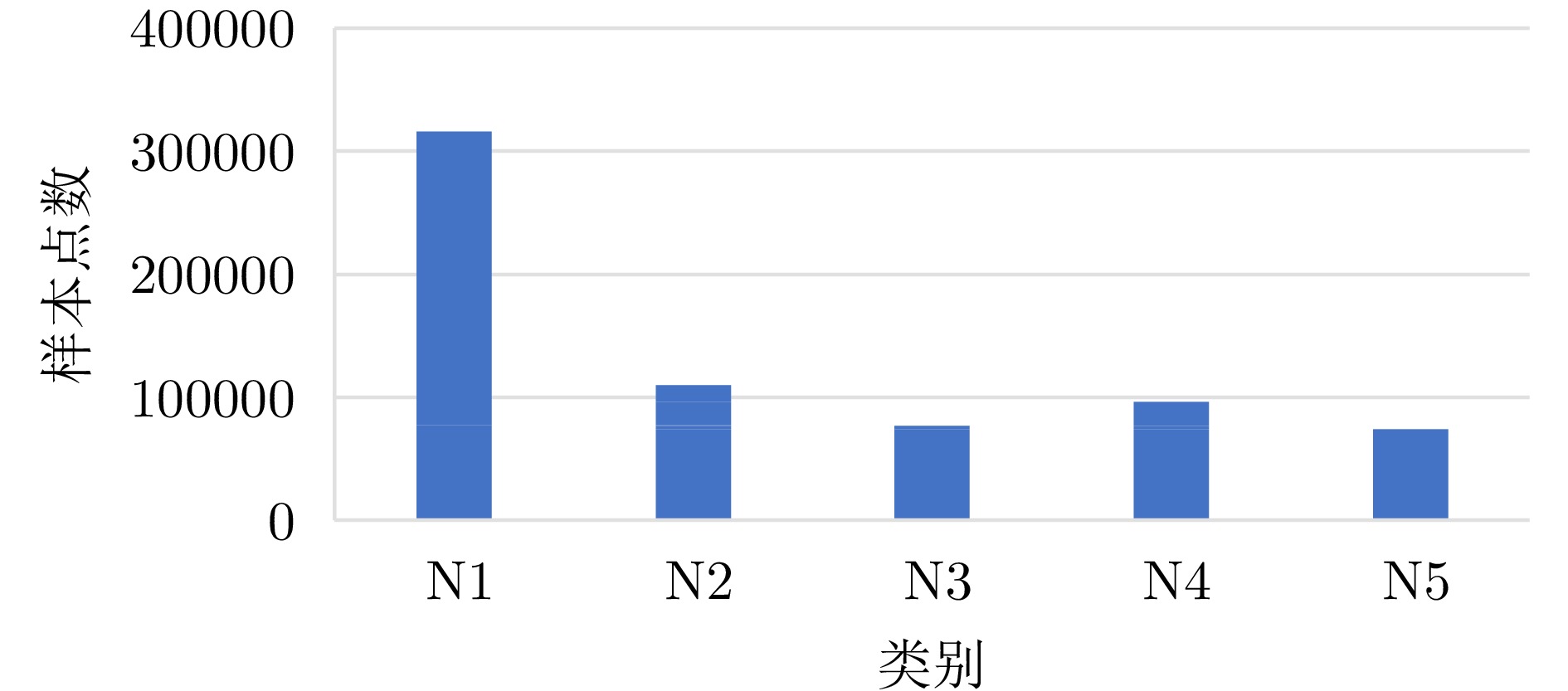
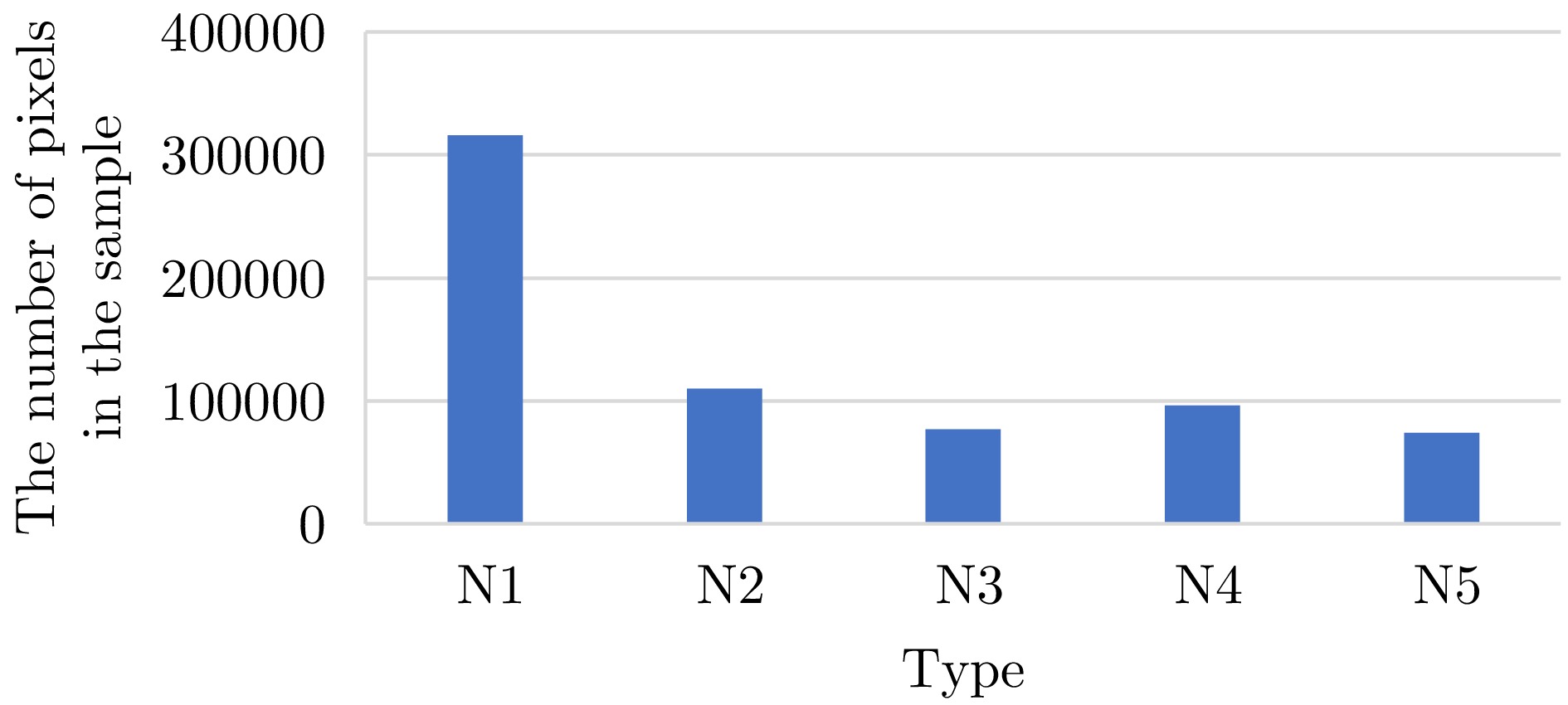
- Figure 12. Comparison chart of sample points for each category in the training set
- Figure 13. RF classification results
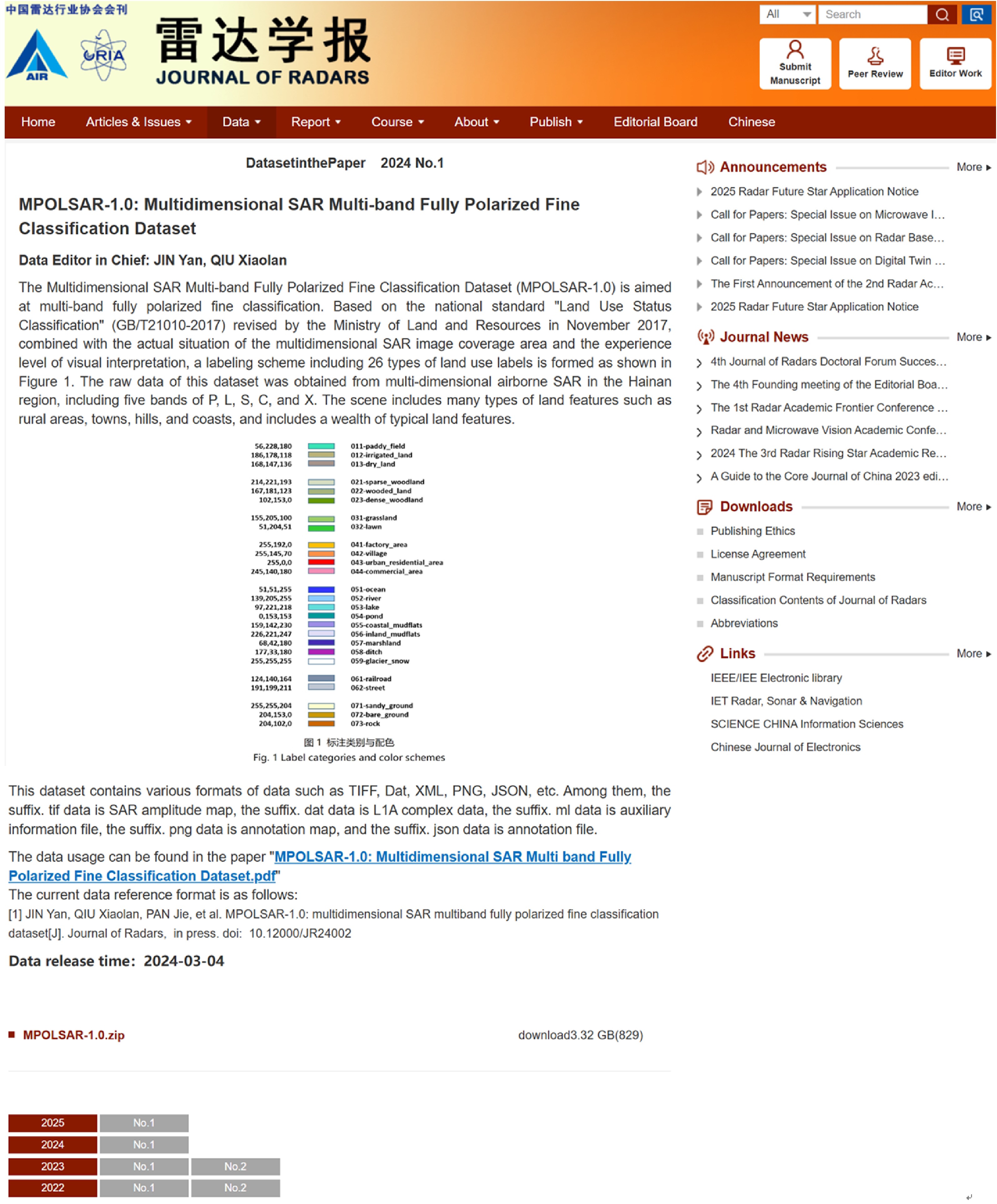
- Figure 1. Release webpage of multidimensional SAR multiband fully polarized fine classification dataset (MPOLSAR-1.0)
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
- Figure 6.
- Figure 7.
- Figure 8.
- Figure 9.
- Figure 10.
- Figure 11.
- Figure 12.
- Figure 13.
- Figure 1.


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: