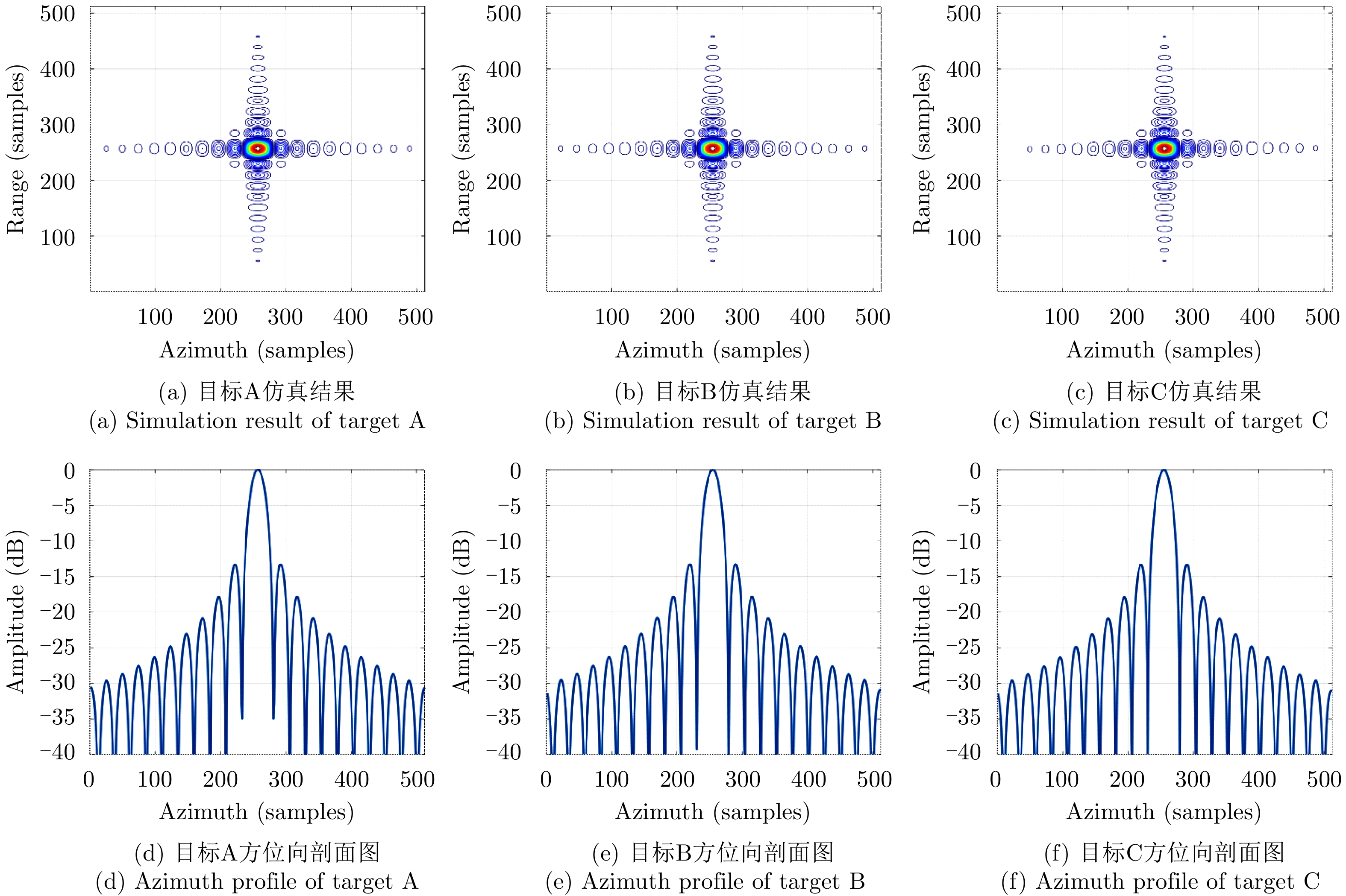
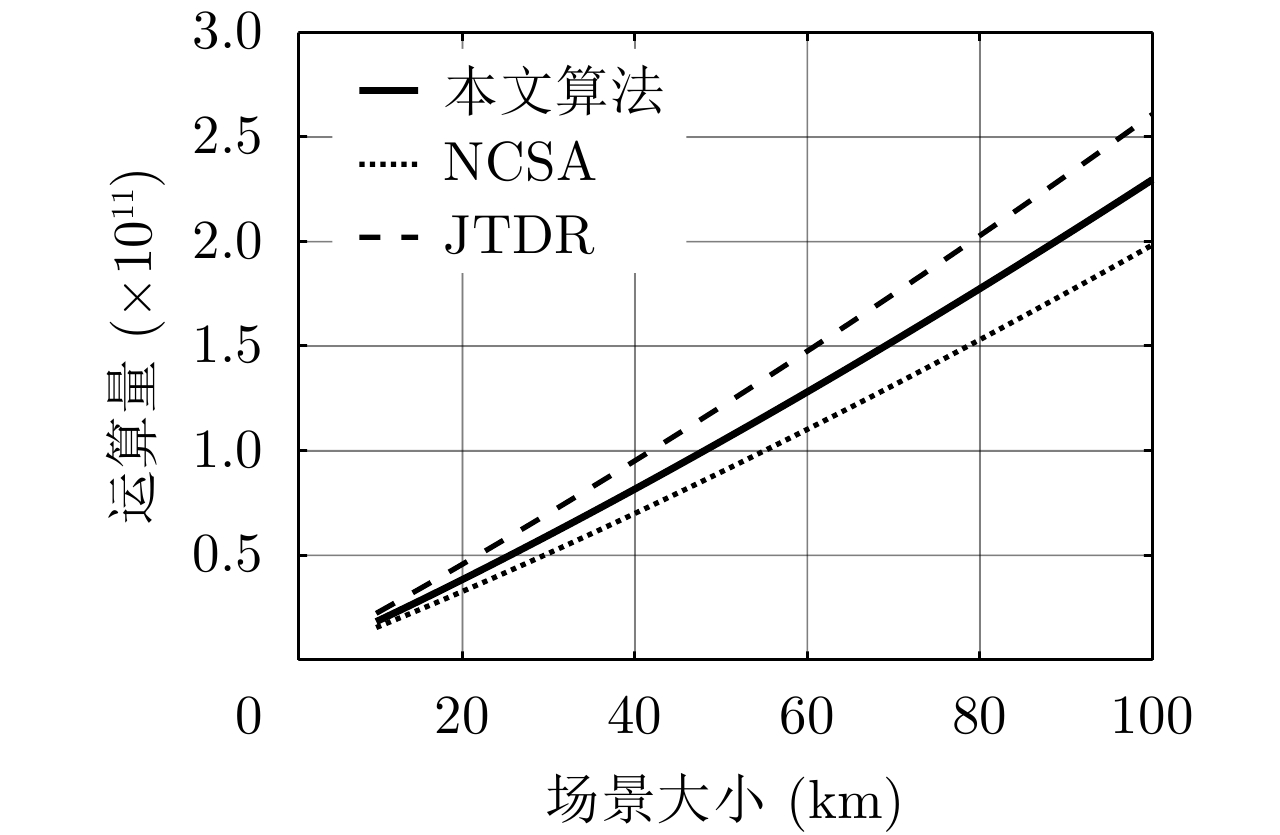
| [1] |
李春升, 于泽, 陈杰. 高分辨率星载SAR成像与图像质量提升方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 717–731. doi: 10.12000/JR19085LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, and CHEN Jie. Overview of techniques for improving high-resolution spaceborne SAR imaging and image quality[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 717–731. doi: 10.12000/JR19085 |
| [2] |
SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. A 2-D space-variant chirp scaling algorithm based on the RCM equalization and subband synthesis to process geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4868–4880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2285721 |
| [3] |
SUN Guangcai, JIANG Xiuwei, XING Mengdao, et al. Focus improvement of highly squinted data based on azimuth nonlinear scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2308–2322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2102040 |
| [4] |
HU Bin, JIANG Yicheng, ZHANG Shunsheng, et al. Generalized omega-k algorithm for geosynchronous SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(11): 2286–2290. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2470516 |
| [5] |
LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071 |
| [6] |
WONG F W and YEO T S. New applications of nonlinear chirp scaling in SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(5): 946–953. doi: 10.1109/36.921412 |
| [7] |
RANEY R K, RUNGE H, BAMLER R, et al. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(4): 786–799. doi: 10.1109/36.298008 |
| [8] |
SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, LIU Yan, et al. Extended NCS based on method of series reversion for imaging of highly squinted SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 446–450. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2084562 |
| [9] |
SHIN H S and LIM J T. Omega-K algorithm for spaceborne spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 343–347. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2168380 |
| [10] |
SHIN H S and LIM L T. Omega-k algorithm for airborne spatial invariant bistatic spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 238–250. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002954 |
| [11] |
ZHANG Tianyi, DING Zegang, TIAN Weiming, et al. A 2-D nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high squint GEO SAR imaging based on optimal azimuth polynomial compensation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(12): 5724–5735. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2765353 |
| [12] |
HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Medium-earth-orbit SAR focusing using range doppler algorithm with integrated two-step azimuth perturbation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 626–630. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2353674 |
| [13] |
LI Dong, LIN Huan, LIU Hongqing, et al. Focus improvement for high-resolution highly squinted SAR imaging based on 2-D spatial-variant linear and quadratic RCMs correction and azimuth-dependent Doppler equalization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(1): 168–183. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2569561 |
| [14] |
LI Dexin, WU Manqing, SUN Zaoyu, et al. Modeling and processing of two-dimensional spatial-variant geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 3999–4009. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2418814 |
| [15] |
WANG Bingnan and XIANG Maosheng. Three-dimensional resolution analysis for geosynchronous circular SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(3): 314–322. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20044 |
| [16] |
CHEN Jianlai, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A TSVD-NCS algorithm in Range-Doppler domain for geosynchronous synthetic aperture Radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1631–1635.
|
| [17] |
TANG Shiyang, LIN Chunhui, ZHOU Yu, et al. Processing of long integration time spaceborne SAR data with curved orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 888–904. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2756109 |
| [18] |
LI Zhuo, LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, et al. Back projection algorithm for high resolution GEO-SAR image formation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 336–339.
|
| [19] |
RAN Lei, LIU Zheng, LI Tao, et al. An adaptive fast factorized back-projection algorithm with integrated target detection technique for high-resolution and high-squint spotlight SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 171–183. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2771503 |
| [20] |
ZHANG Lei, LI Haolin, QIAO Zhijun, et al. A fast BP algorithm with wavenumber spectrum fusion for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(9): 1460–1464.
|
| [21] |
LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. A modified CSA based on joint Time-Doppler resampling for MEO SAR stripmap mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3573–3586. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2802545 |
| [22] |
HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Focusing of medium-earth-orbit SAR with advanced nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 500–508. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053211 |
| [23] |
LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. Highly squinted MEO SAR focusing based on extended Omega-K algorithm and modified joint time and Doppler resampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9188–9200. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2925385 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: