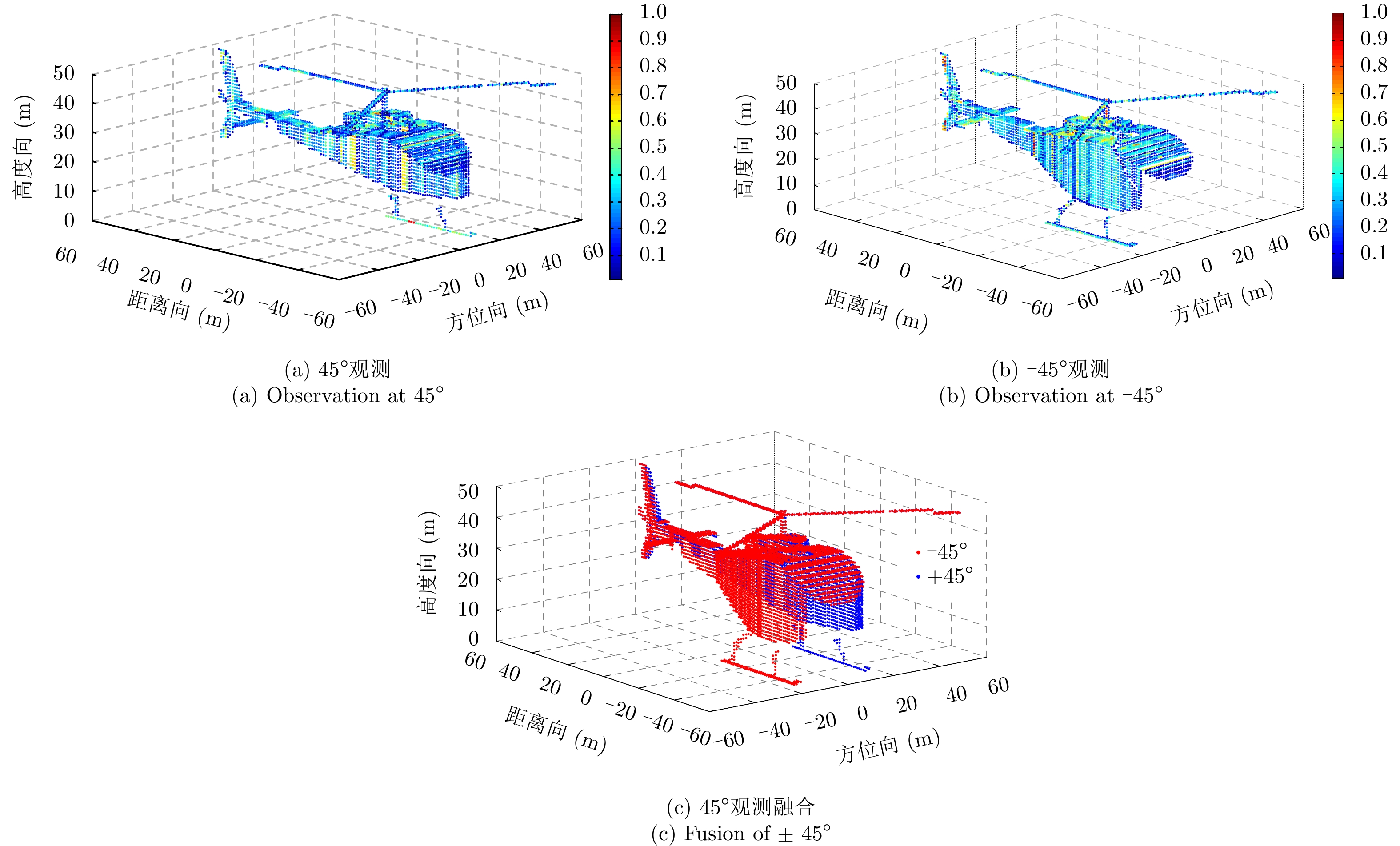
| [1] |
Li Chun-sheng, Wang Wei-jie, Wang Peng-bo, et al. Current situation and development trends of spaceborne SAR technology[J]. Journal of Electronics& Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 229–240. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT151116 |
| [2] |
Jung H S, Lu Z, Shepherd A, et al. Simulation of the SuperSAR multi-azimuth synthetic aperture radar imaging system for precise measurement of three-dimensional earth surface displacement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(11): 6196–6206. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2435776 |
| [3] |
Zhu X X and Bamler R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487 |
| [4] |
Zhu X X, Shahzad M, and Bamler R. From TomoSAR point clouds to objects: Façade reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of 2012 Tyrrhenian Workshop on Advances in Radar and Remote Sensing, Naples, Italy, 2012: 106–113.
|
| [5] |
Shahzad M, Zhu X X, and Bamler R. Façade structure reconstruction using spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 467–470. DOI: 10.1109/IGARRSS.2012.6351385. |
| [6] |
Wang Y Y and Zhu X X. Feature-based fusion of tomosar point clouds from multiview TerraSAR-X data stacks[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 85–88. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2013.6721098. |
| [7] |
Zhu X X and Shahzad M. Facade reconstruction using multiview spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3541–3552. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2273619 |
| [8] |
Fornaro G, Serafino F, and Soldovieri F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 |
| [9] |
孙希龙. SAR层析与差分层析成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012.
Sun Xi-long. Research on SAR tomography and differential SAR tomography imaging technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012.
|
| [10] |
Curlander J C and McDonough R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991.
|
| [11] |
Bara M, Scheiber R, Broquetas A, et al. Interferometric SAR signal analysis in the presence of squint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2164–2178. DOI: 10.1109/36.868875 |
| [12] |
Schmitt M. Reconstruction of urban surface models from multi-aspect and multi-baseline interferometric SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2014.
|
| [13] |
Zhou Yue-qin, Zheng Zhao-bao, Li De-ren, et al. Stereopair positioning algorithm for SAR images and its accuracy analysis model[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 2(4): 245–250. DOI: 10.11834/jrs.19980402 |
| [14] |
王青松, 黄海风, 董臻. 星载干涉合成孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.
Wang Qing-song, Huang Hai-feng, and Dong Zhen. Spaceborne Interferometric SAR[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012.
|
| [15] |
王金峰. SAR层析三维成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2010.
Wang Jin-feng. Study of three-dimentional synthetic aperture radar tomography imaging technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010.
|
| [16] |
Moreira A and Scheiber R. A new method for accurate co-registration of interferometric SAR images[C]. 1998 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing. Symposium Proceedings, Seattle, USA, 1998, 2: 1091–1093. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.1998.699682. |
| [17] |
Yee K. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving maxwell’s equations in isotropic media[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1966, 14(3): 302–307. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.1966.1138693 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

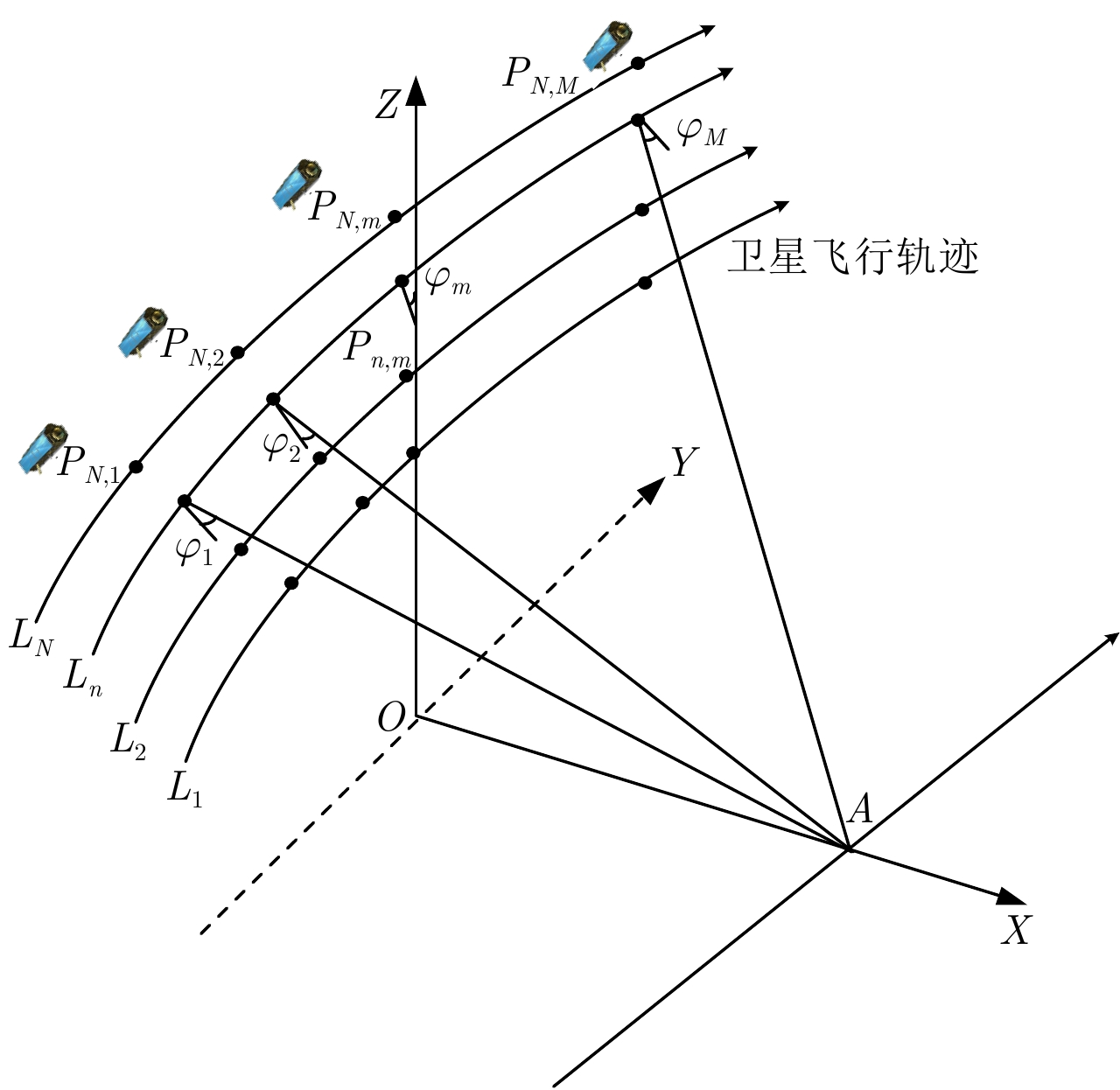



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: