Joint Beam Selection and Dwell Time Allocation for Multi-target Tracking in Phased Array Radar System
-
摘要:
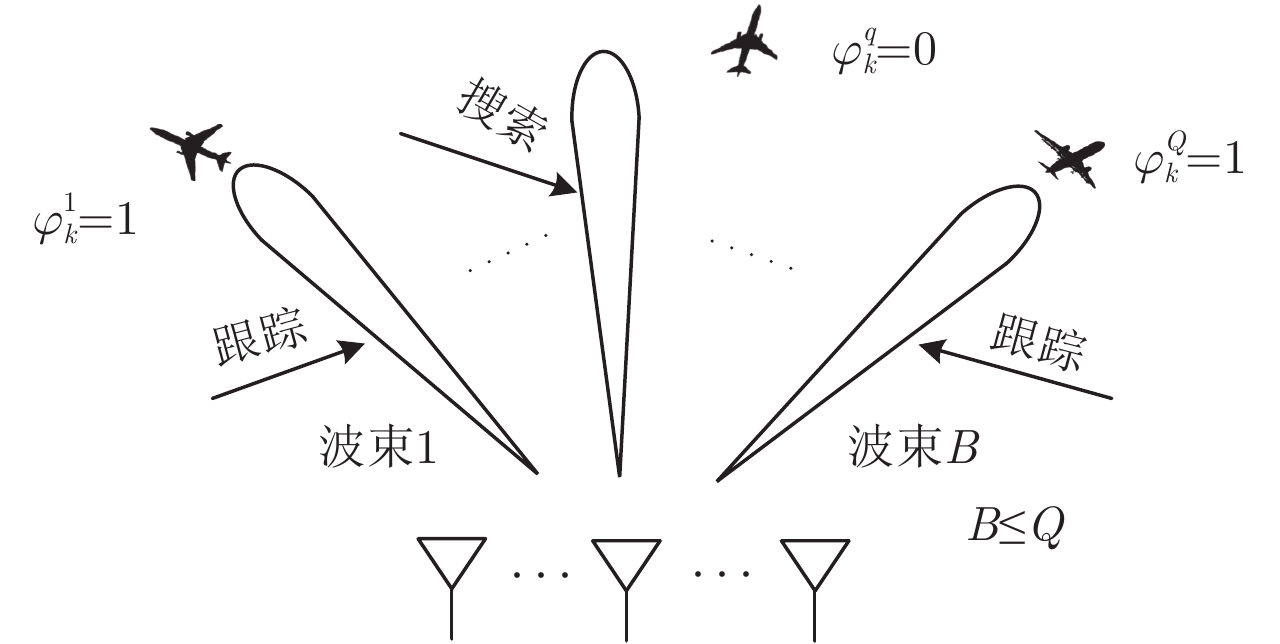
相控阵雷达能同时发射多个波束,其波束指向灵活,且能实现无惯性的快速扫描。为了使相控阵雷达用尽量少的系统资源去实现多个目标的同时跟踪,该文提出了一种基于多目标跟踪的波束和驻留时间联合分配方法。该方法通过建立和求解一个在各目标跟踪精度满足一定要求的前提下,最小化总波束驻留时间的非凸优化数学问题来实现资源的联合分配。贝叶斯克拉美罗界(BCRLB)为目标状态估计的误差提供了一个下界,该文推导了带有资源参数变量的BCRLB并将它作为跟踪性能的准则。随后针对上述非凸优化问题,该文提出一个先确立波束指向再分配驻留时间的两步分解算法。最后,根据资源分配结果,采用粒子滤波算法实现了多目标跟踪。仿真结果证明,和平均分配资源的固定操作方式相比,该文方法不仅能节约系统资源而且能保证坏目标的跟踪性能,体现了该文方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 贝叶斯克拉美罗界(BCRLB) /
- 优化问题 /
- 资源联合分配 /
- 多目标跟踪
Abstract:Phased array radar can simultaneously form multiple beams that can scan without inertia allowing for flexible pointing. In this paper, we propose a joint beam and dwell time allocation strategy for multi-target tracking in a phased array radar system to achieve multi-target tracking with less system resources. First, we formulate an optimization problem for minimizing the total dwell time on all targets while guaranteeing to meet a predetermined target-tracking accuracy requirement. The Bayesian Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (BCRLB) is introduced as the tracking performance metric since it provides a lower bound for the error of target state estimate. Second, after proving the optimization problem is nonconvex, we propose a two-step decomposition algorithm which is first to determine the beam pointing and then allocate the beam dwell time to solve it. Finally, we achieve multi-target tracking based on the resource allocation results. Simulation results show that our optimization strategy is effective in saving resources and is favorable for achieving a better tracking performance of worse targets as compared to an operating mode wherein uniform resource allocation occurs.
-
表 1 目标初始状态及距离雷达距离
Table 1. Initial target state and distance from each target to radar
目标标号 目标位置(km) 目标速度(km/s) 距离(km) 1 (–120, 20) (0, 0.6) 122 2 (–20, 100) (0.7, 0) 100 3 (110, 110) (0.3, –0.6) 150 -
[1] Izquierdo-Fuente A and Casar-Corredera J R. Optimal radar pulse scheduling using a neural network[C]. Proceedings of 1994 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, Florida, USA, 1994, 7: 4588–4591. [2] Kirubarajan T, Bar-Shalom Y, and Daeipour E. Adaptive beam pointing control of a phased array radar in the presence of ECM and false alarms using IMMPDAF[C]. Proceedings of the 1995 American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 1995, 4: 2616–2620. [3] Daeipour E, Bar-Shalom Y, and Li X. Adaptive beam pointing control of a phased array radar using an IMM estimator[C]. Proceedings of 1994 American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994, 2: 2093–2097. [4] 何友, 修建娟, 关欣, 等. 雷达数据处理及应用[M]. 第3版, 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013: 308–313.He You, Xiu Jian-juan, Guan Xin, et al.. Radar Data Processing with Applications[M]. Third edition, Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013: 308–313. [5] Zwaga J H and Driessen H. Tracking performance constrained MFR parameter control: Applying constraints on prediction accuracy[C]. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information Fusion, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, 2005: 1–6. [6] Narykov A S, Krasnov O A, and Yarovoy A. Algorithm for resource management of multiple phased array radars for target tracking[C]. Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 2013: 1258–1264. [7] Shi Chen-guang, Wang Fei, Zhou Jian-jiang, et al.. Resource management for target tracking in distributed radar network system[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Ningbo, China, 2015: 1–5. [8] Lu Jian-bin, Hu Wei-dong, and Yu Wen-xian. Adaptive beam scheduling algorithm for an agile beam radar in multi-target tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006: 1–4. [9] 鲁彦希, 何子述, 程子扬, 等. 多目标跟踪分布式MIMO雷达收发站联合选择优化算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 73–80. DOI: 10.12000/JR16106Lu Yanxi, He Zishu, Cheng Ziyang, et al. Joint selection of transmitters and receivers in distributed multi-input multi-output radar network for multiple targets tracking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 73–80. DOI: 10.12000/JR16106 [10] Yan Junkun, Liu Hongwei, Jiu Bo, et al. Simultaneous multibeam resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3110–3122. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2417504 [11] Yan Junkun, Liu Hongwei, Pu Wenqiang, et al. Joint beam selection and power allocation for multiple target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(24): 6417–6427. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2607147 [12] Richards M A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2005. [13] 丁鹭飞, 耿富录. 雷达原理[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2006: 291–299.Ding Lu-fei and Geng Fu-lu. Radar Principles[M]. Xi’an: Publishing House of Xidian University, 2006: 291–299. [14] Van Trees H L. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory, Part III: Radar-Sonar Signal Processing and Gaussian Signals in Noise[M]. New York: Wiley, 1971. [15] Van Trees H L. Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory[M]. New York: Wiley, 2002. [16] Tichavsky P, Muravchik C H, and Nehorai A. Posterior Cramér-Rao bounds for discrete-time nonlinear filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1998, 46(5): 1386–1396. DOI: 10.1109/78.668800 [17] Godrich H, Chiriac V M, Haimovich A M, et al.. Target tracking in MIMO radar systems: Techniques and performance analysis[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 2010: 1111–1116. [18] Zuo Long, Niu Rui-xin, and Varshney P K. Conditional posterior Cramér-Rao lower bounds for nonlinear sequential Bayesian estimation[J].IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(1): 1–14. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2080268 [19] Hernandez M L, Farina A, and Ristic B. PCRLB for tracking in cluttered environments: Measurement sequence conditioning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(2): 680–704. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1642582 [20] Boyd S and Vandenberghe L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [21] Grant M, Boyd S, and Ye Y. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming[Z]. 2008. [22] Gustafsson F. Particle filter theory and practice with positioning applications[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2010, 25(7): 53–82. DOI: 10.1109/MAES.2010.5546308 [23] Arulampalam M S, Maskell S, Gordon N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. DOI: 10.1109/78.978374 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: