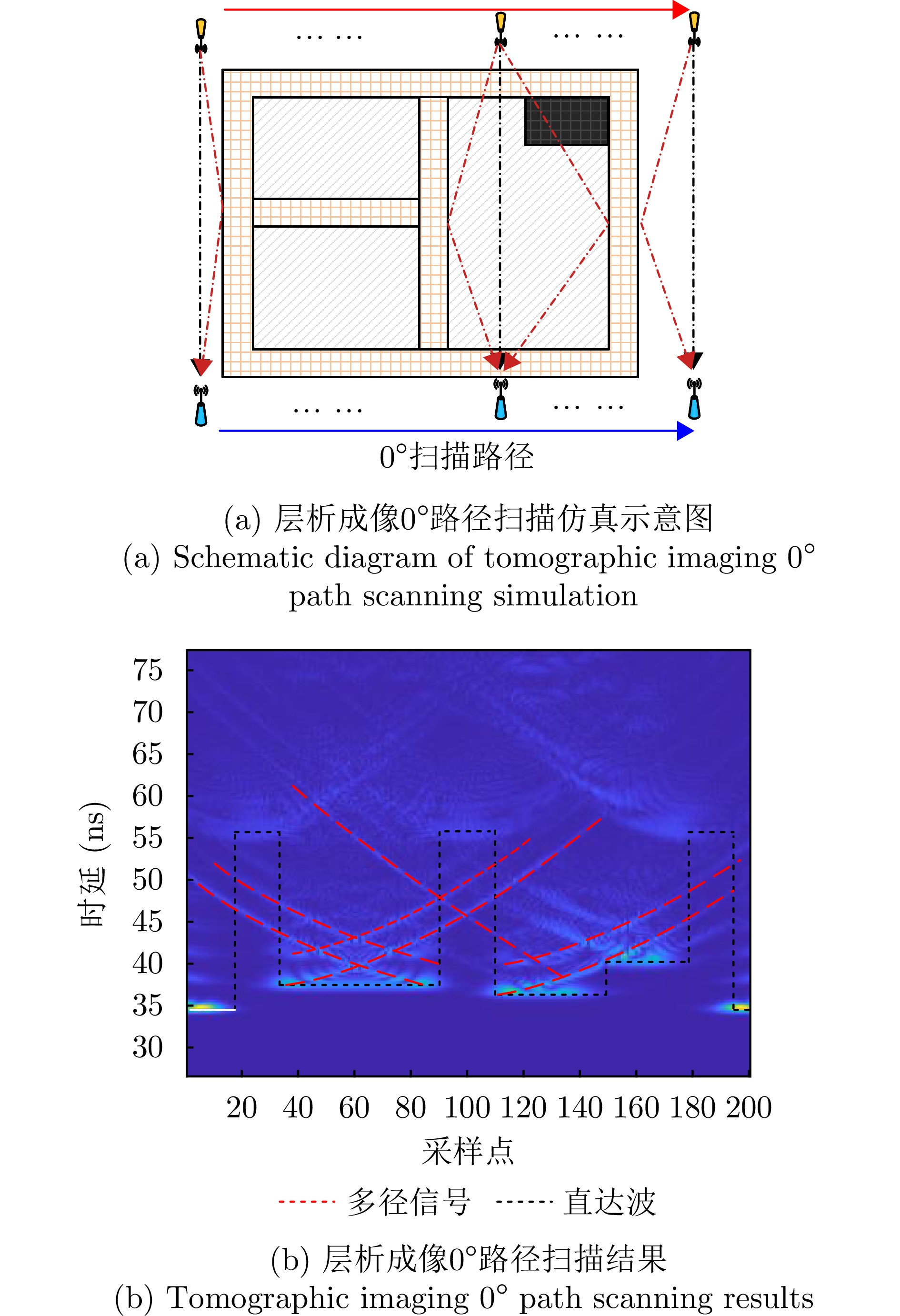
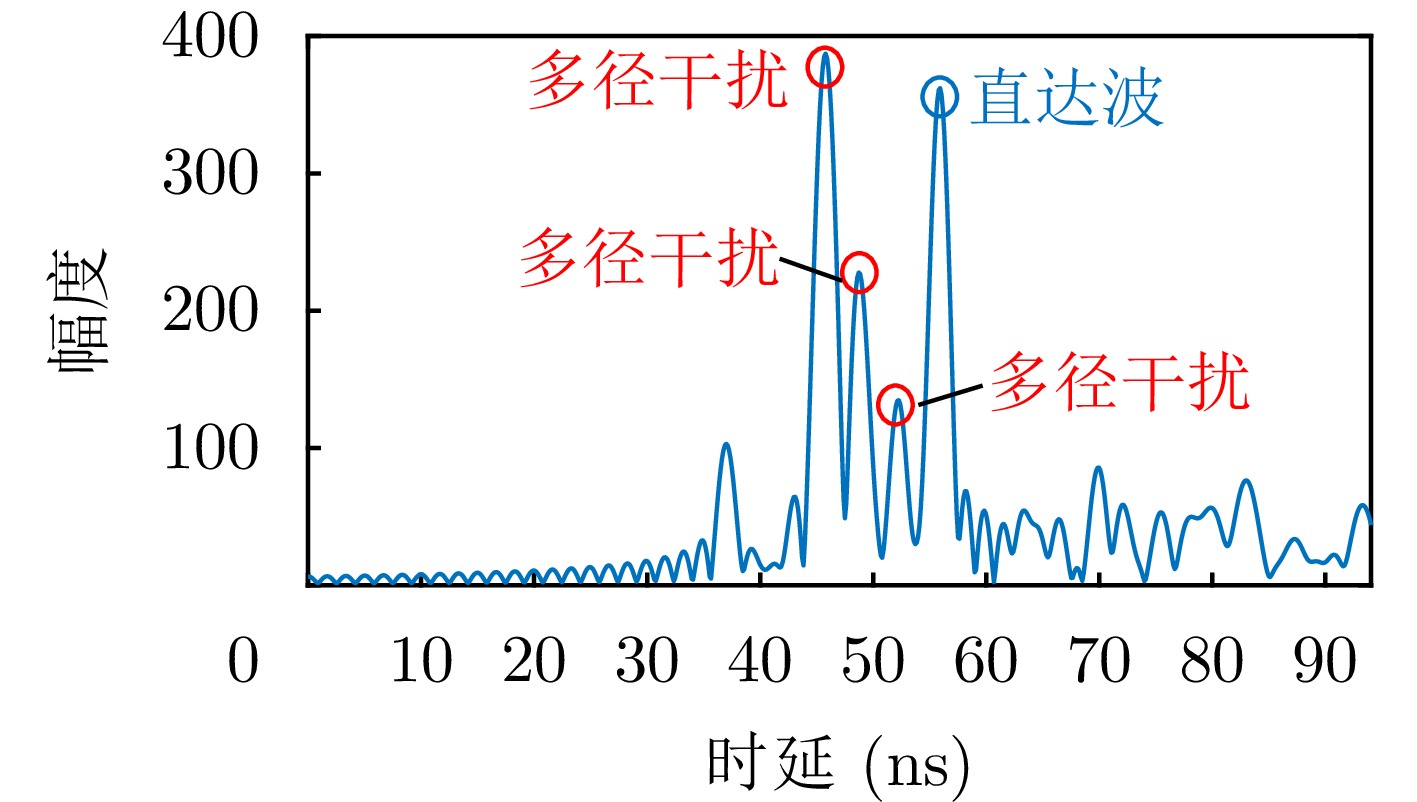
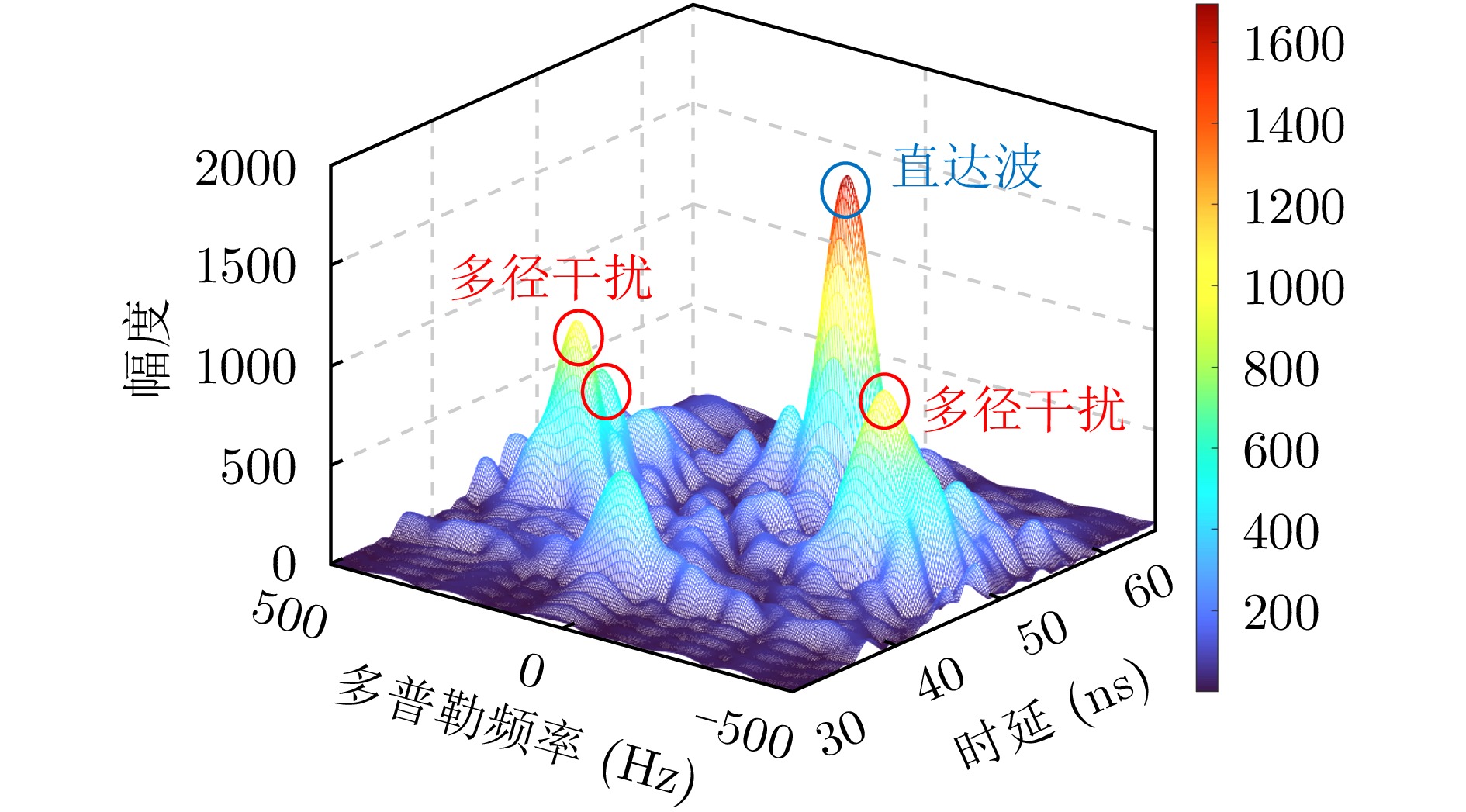
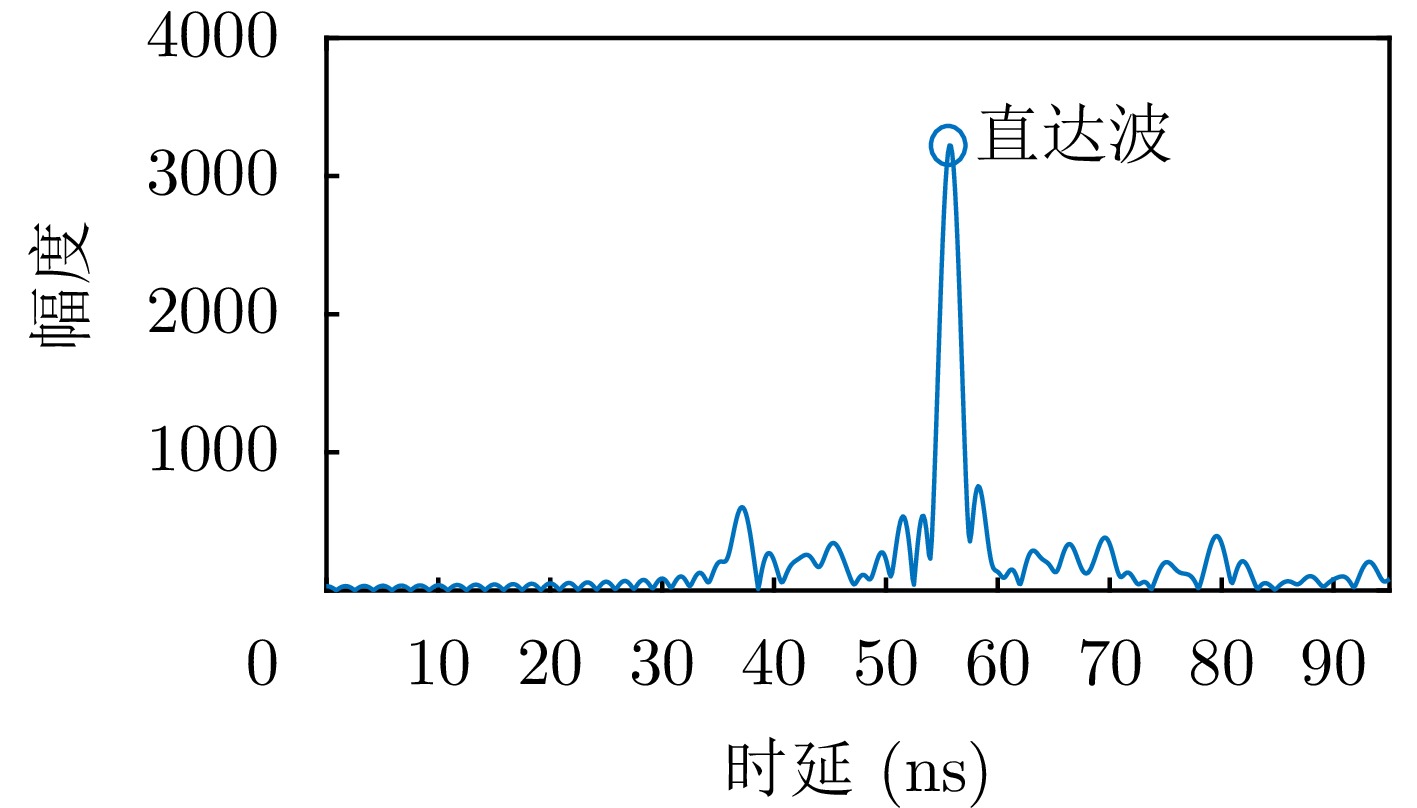
| [1] |
金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. |
| [2] |
AHMAD F and AMIN M G. Noncoherent approach to through-the-wall radar localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(4): 1405–1419. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.314581. |
| [3] |
崔国龙. 超宽带穿墙雷达合成孔径成像算法研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008: 6–16.
CUI Guolong. Research and implementation of synthetic aperture imaging algorithm for ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008: 6–16.
|
| [4] |
NKWARI P K M, SINHA S, and FERREIRA H C. Through-the-wall radar imaging: A review[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2018, 35(6): 631–639. doi: 10.1080/02564602.2017.1364146. |
| [5] |
GUO Shisheng, CUI Guolong, KONG Lingjiang, et al. An imaging dictionary based multipath suppression algorithm for through-wall radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 269–283. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756298. |
| [6] |
CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, LUO Haolan, et al. Non-line-of-sight multi-target localization algorithm for driver-assistance radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5332–5337. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3227971. |
| [7] |
CHEN Jiahui, LI Nian, GUO Shisheng, et al. Enhanced 3-D building layout tomographic imaging via tensor approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5105614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3391282. |
| [8] |
LI Nian, CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, et al. Building layout tomographic imaging based on MIMO-UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5108713. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3435831. |
| [9] |
NGUYEN L, RESSLER M, and SICHINA J. Sensing through the wall imaging using the Army Research Lab ultra-wideband synchronous impulse reconstruction (UWB SIRE) radar[C]. SPIE 6947, Radar Sensor Technology XII, Orlando, USA, 2008: 69470B. doi: 10.1117/12.776869. |
| [10] |
LE C, DOGARU T, NGUYEN L, et al. Ultrawideband (UWB) radar imaging of building interior: Measurements and predictions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2016653. |
| [11] |
JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Sparse imaging of building layouts in ultra-wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031. |
| [12] |
ZHANG Yang, CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, et al. Building layout tomographic reconstruction via commercial WiFi signals[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(20): 15500–15511. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3073912. |
| [13] |
MOSTOFI Y. Cooperative wireless-based obstacle/object mapping and see-through capabilities in robotic networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(5): 817–829. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.32. |
| [14] |
DEPATLA S, BUCKLAND L, and MOSTOFI Y. X-ray vision with only WiFi power measurements using Rytov wave models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(4): 1376–1387. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2397446. |
| [15] |
DEPATLA S, KARANAM C R, and MOSTOFI Y. Robotic through-wall imaging: Radio-frequency imaging possibilities with unmanned vehicles[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2017, 59(5): 47–60. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2017.2731302. |
| [16] |
KARANAM C R and MOSTOFI Y. 3D through-wall imaging with unmanned aerial vehicles using WiFi[C]. The 16th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Pittsburgh, USA, 2017: 131–142. doi: 10.1145/3055031.3055084. |
| [17] |
张扬. 建筑布局结构透视微波层析成像理论与方法[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022: 20–82.
ZHANG Yang. Theory and method of perspective microwave tomography of building layout structure[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 20–82.
|
| [18] |
GUO Qichang, LI Yanlei, LIANG Xingdong, et al. A novel CT-mode through-the-wall imaging method based on time delay estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(8): 1381–1385. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3000423. |
| [19] |
CHEN Jiahui, ZHANG Yang, LI Huquan, et al. Ultrawideband tomographic imaging in multipath-rich environment[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8016305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.30961830. |
| [20] |
YASWANTH K, BHATTACHARYA S, and KHANKHOJE U K. Algebraic reconstruction techniques for inverse imaging[C]. 2016 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Cairns, Australia, 2016: 756–759. doi: 10.1109/ICEAA.2016.7731509. |
| [21] |
ANDREU F, CASELLES V, DÍAZ J I, et al. Some qualitative properties for the total variation flow[J]. Journal of Functional Analysis, 2002, 188(2): 516–547. doi: 10.1006/jfan.2001.3829. |
| [22] |
LI Nian, ZHAN Yang, CHEN Jiahui, et al. Building layout tomographic imaging method with sparse scan angles[C]. The 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2022: 2128–2132. doi: 10.1109/ICCC56324.2022.10066042. |
| [23] |
GOLDSTEIN T and OSHER S. The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 323–343. doi: 10.1137/080725891. |
| [24] |
OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076. |
| [25] |
WARREN C, GIANNOPOULOS A, and GIANNAKIS I. GprMax: Open source software to simulate electromagnetic wave propagation for ground penetrating radar[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2016, 209: 163–170. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2016.08.020. |
| [26] |
HAMILTON B R, MA Xiaoli, BAXLEY R J, et al. Radio frequency tomography in mobile networks[C]. 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Ann Arbor, USA, 2012: 508–511. doi: 10.1109/SSP.2012.6319745. |
| [27] |
CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, CUI Guolong, et al. Building layout reconstruction with transmissive and reflective signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3199270. |
| [28] |
ZHAO Jifang, JIN Liangnian, and LIU Qinghua. Through-the-wall radar sparse imaging for building walls[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7403–7405. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0541. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: