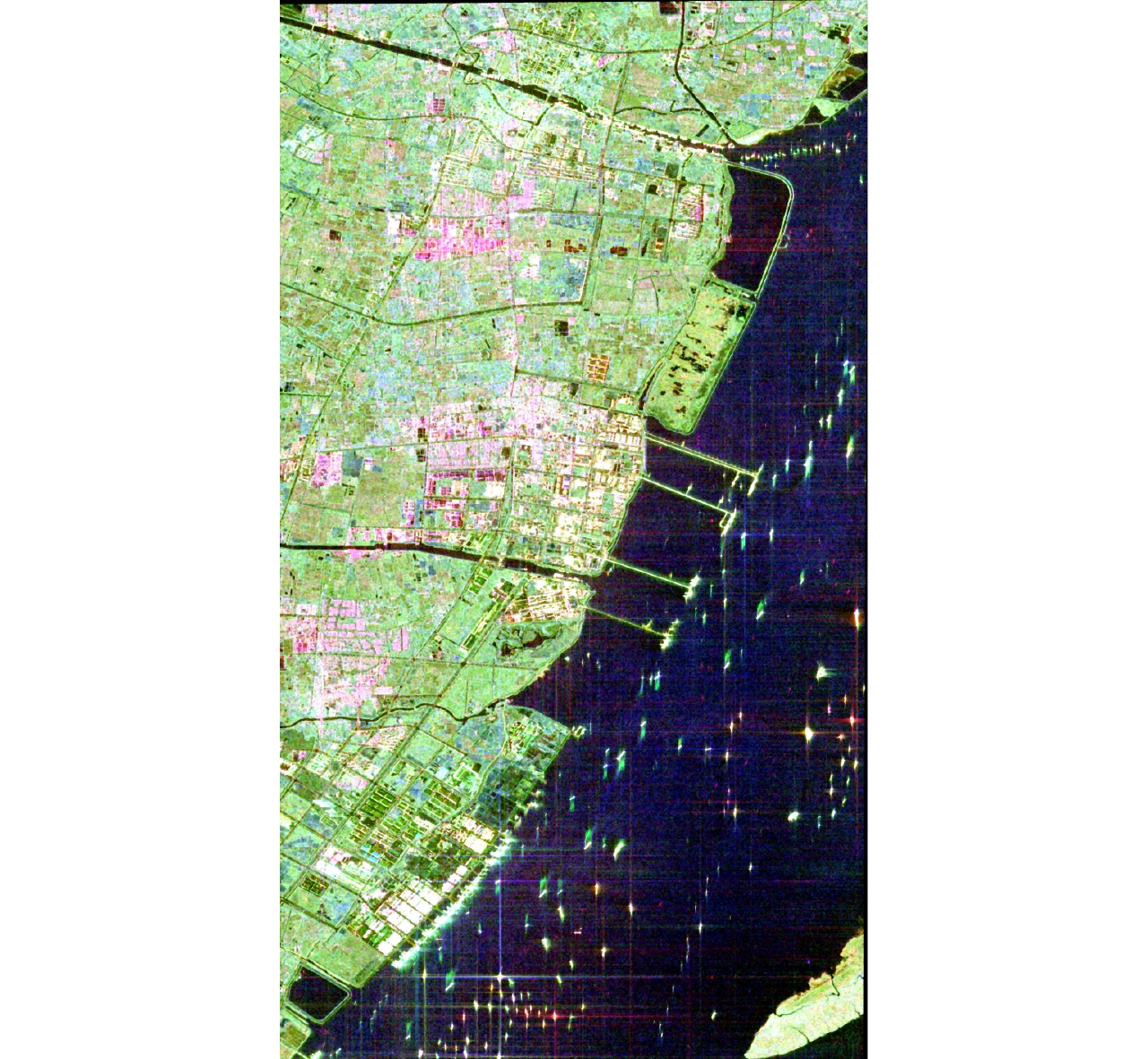
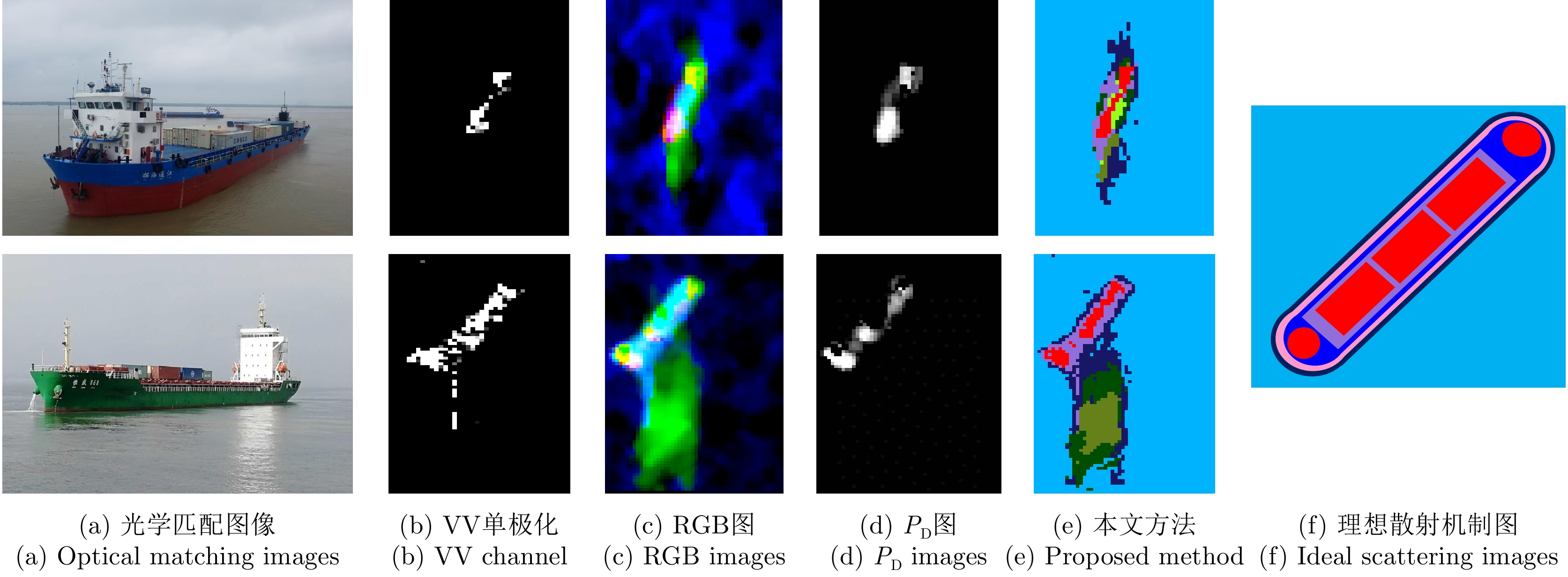
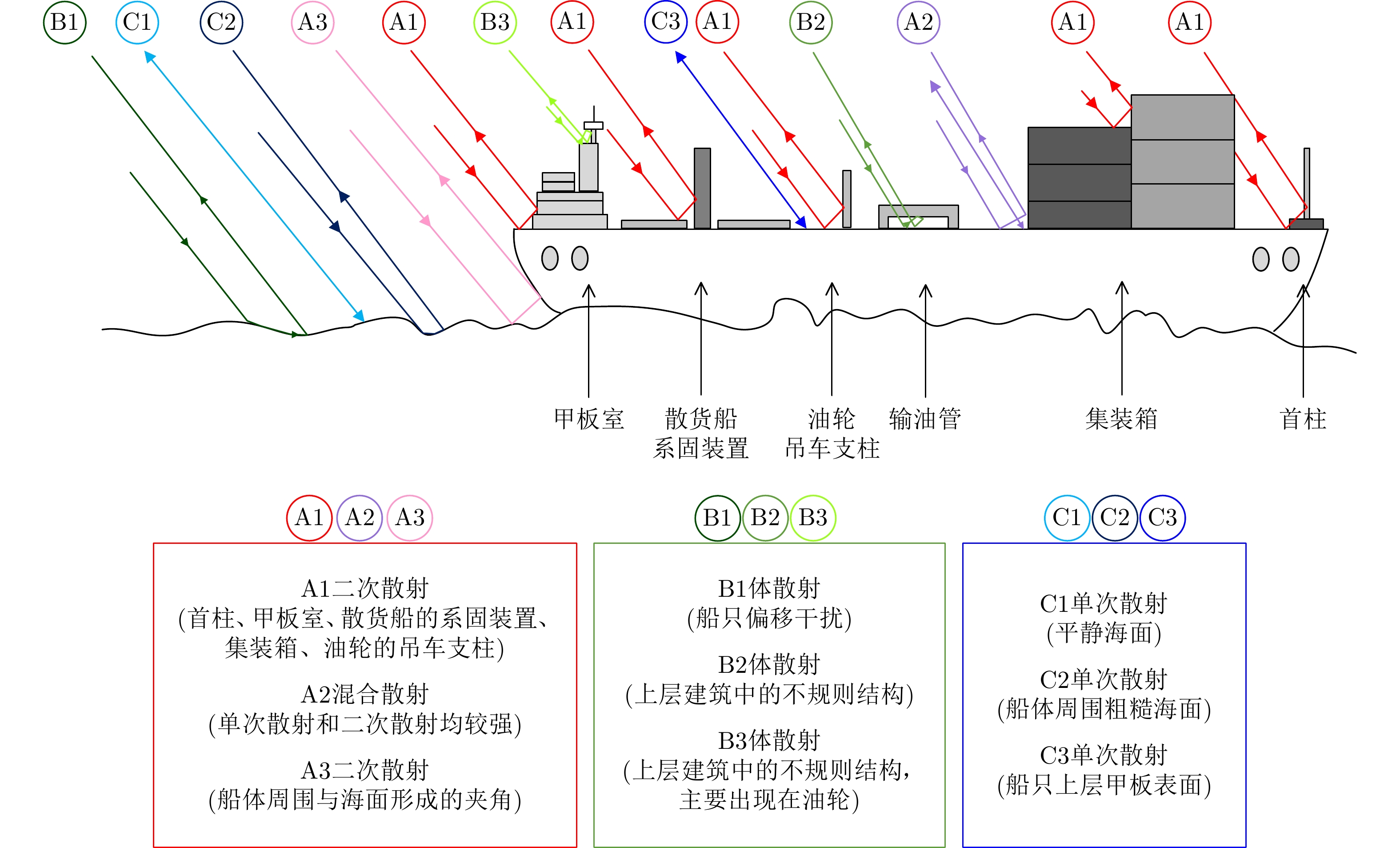
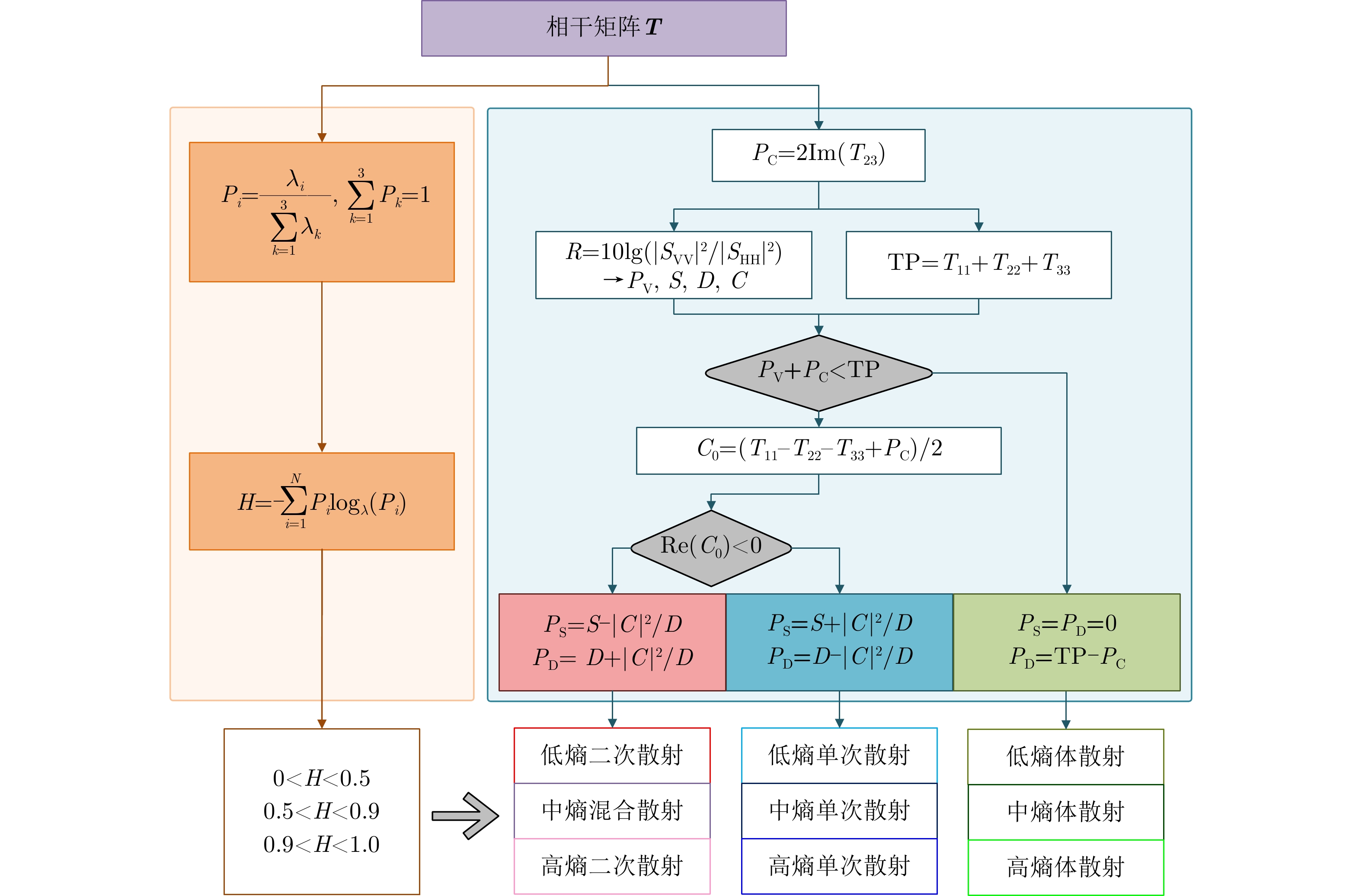
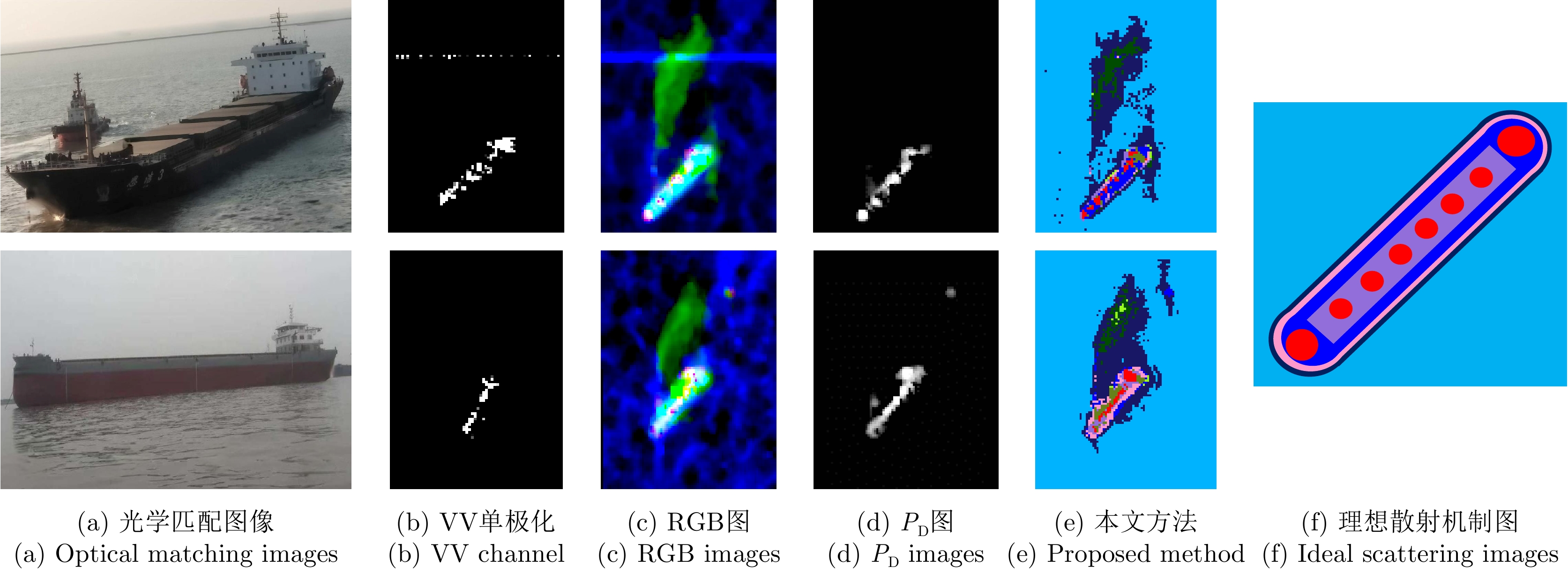
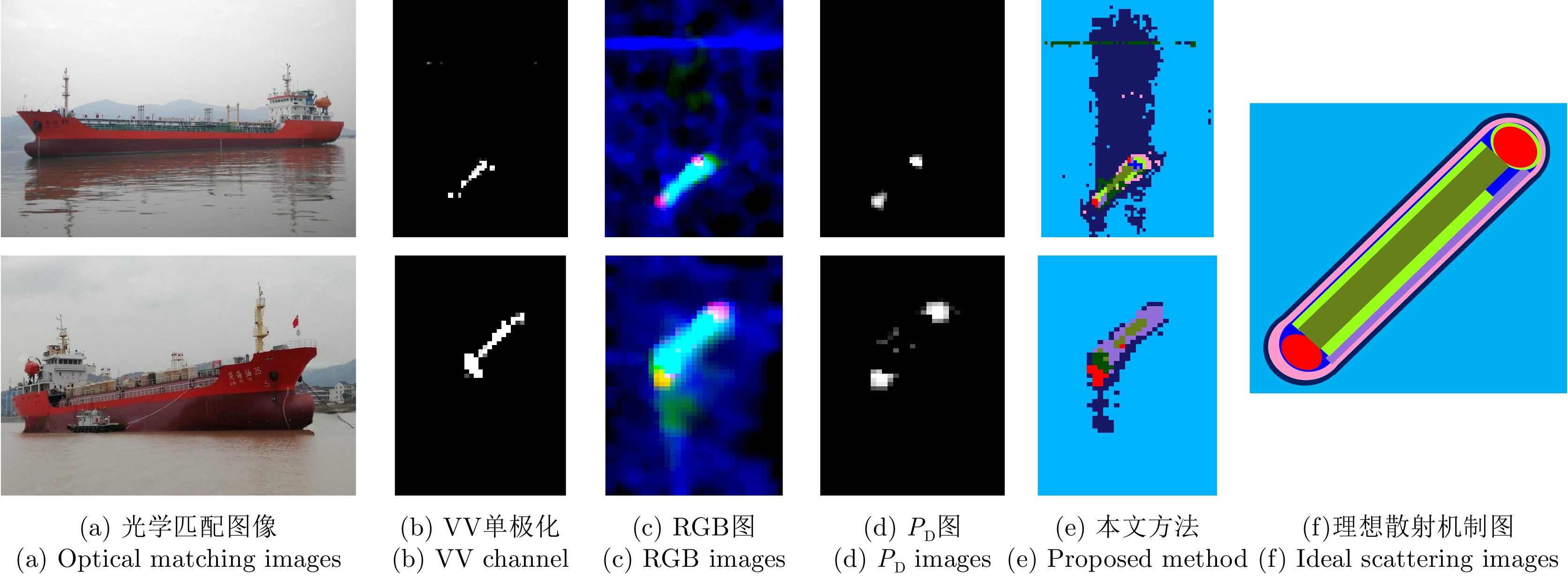
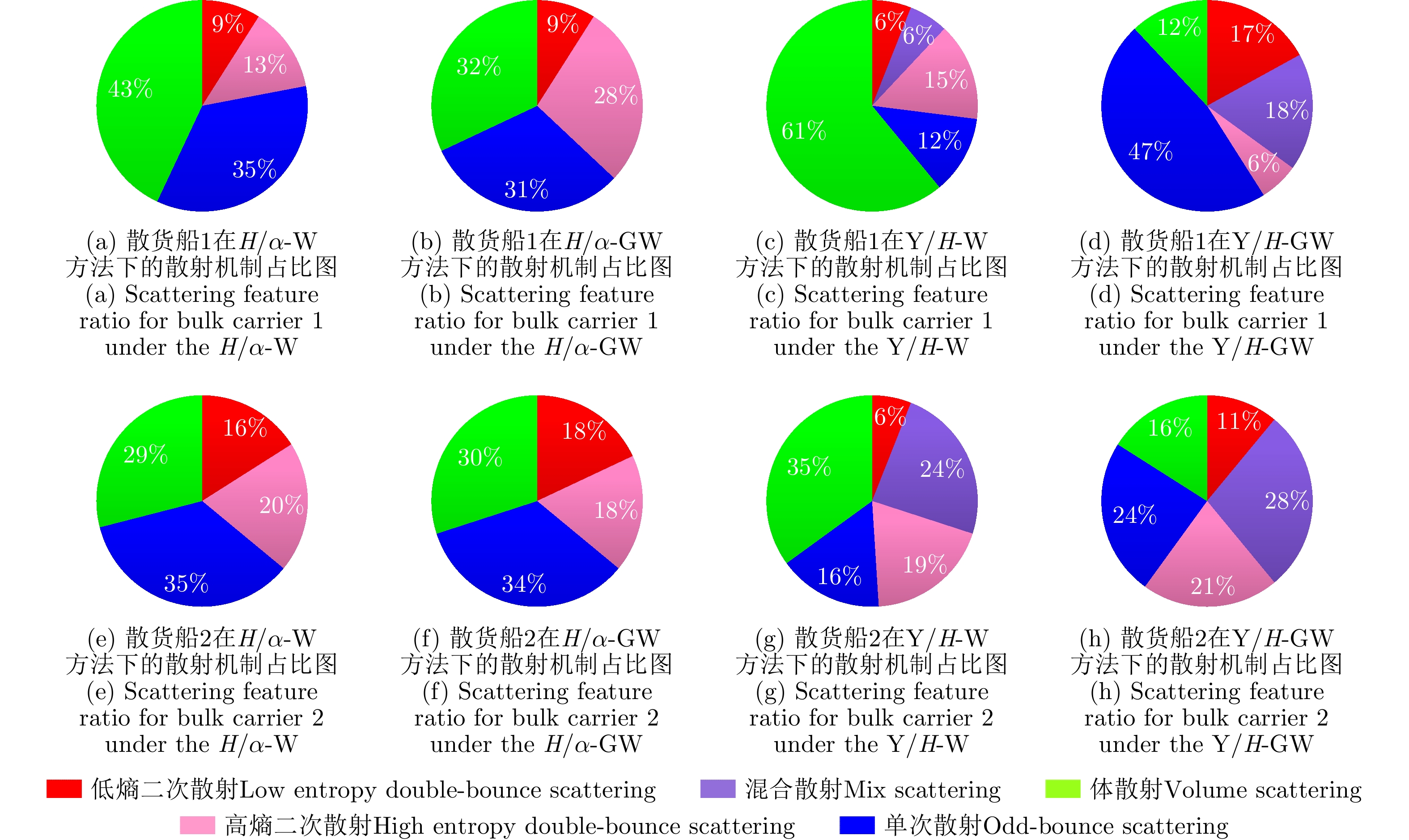
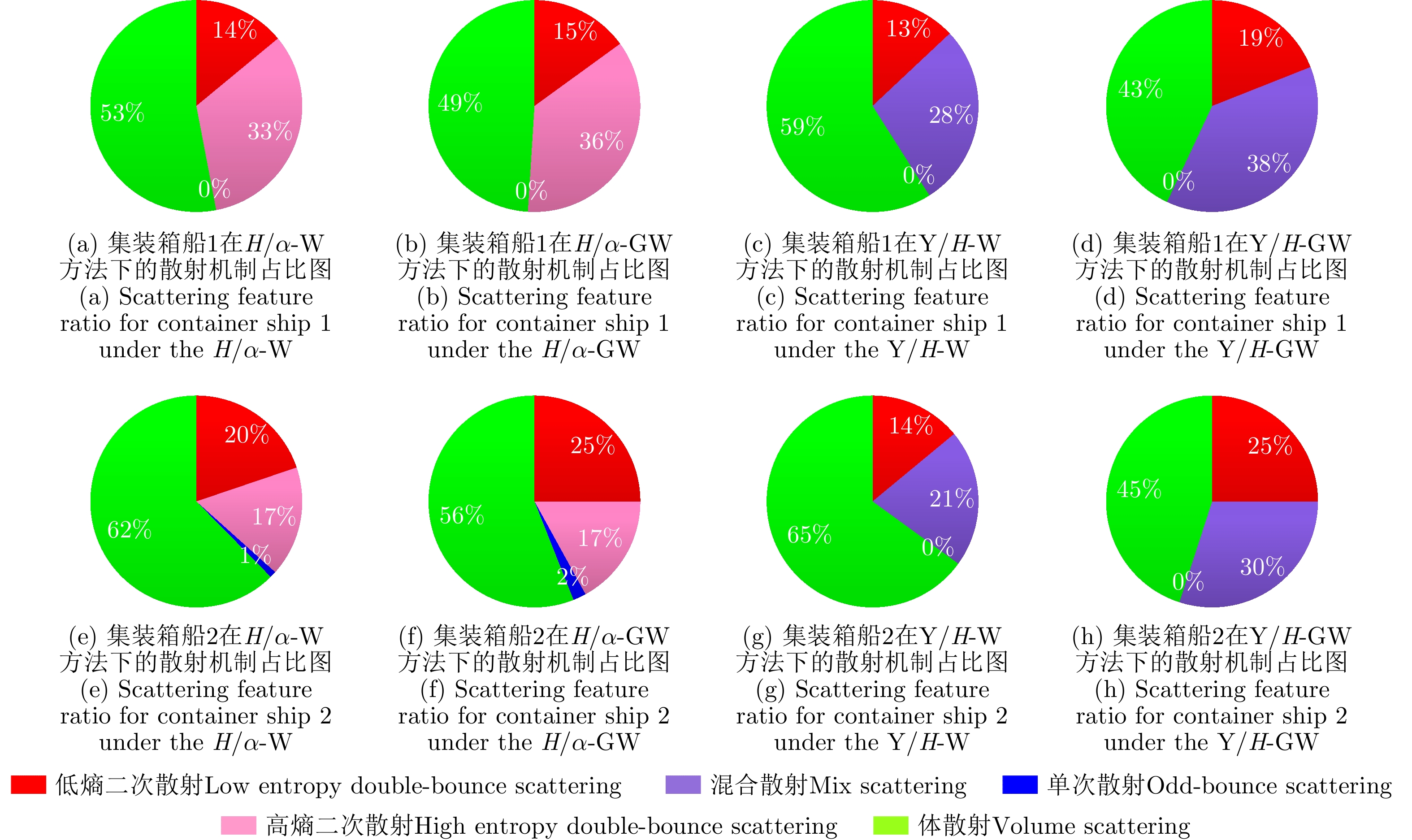
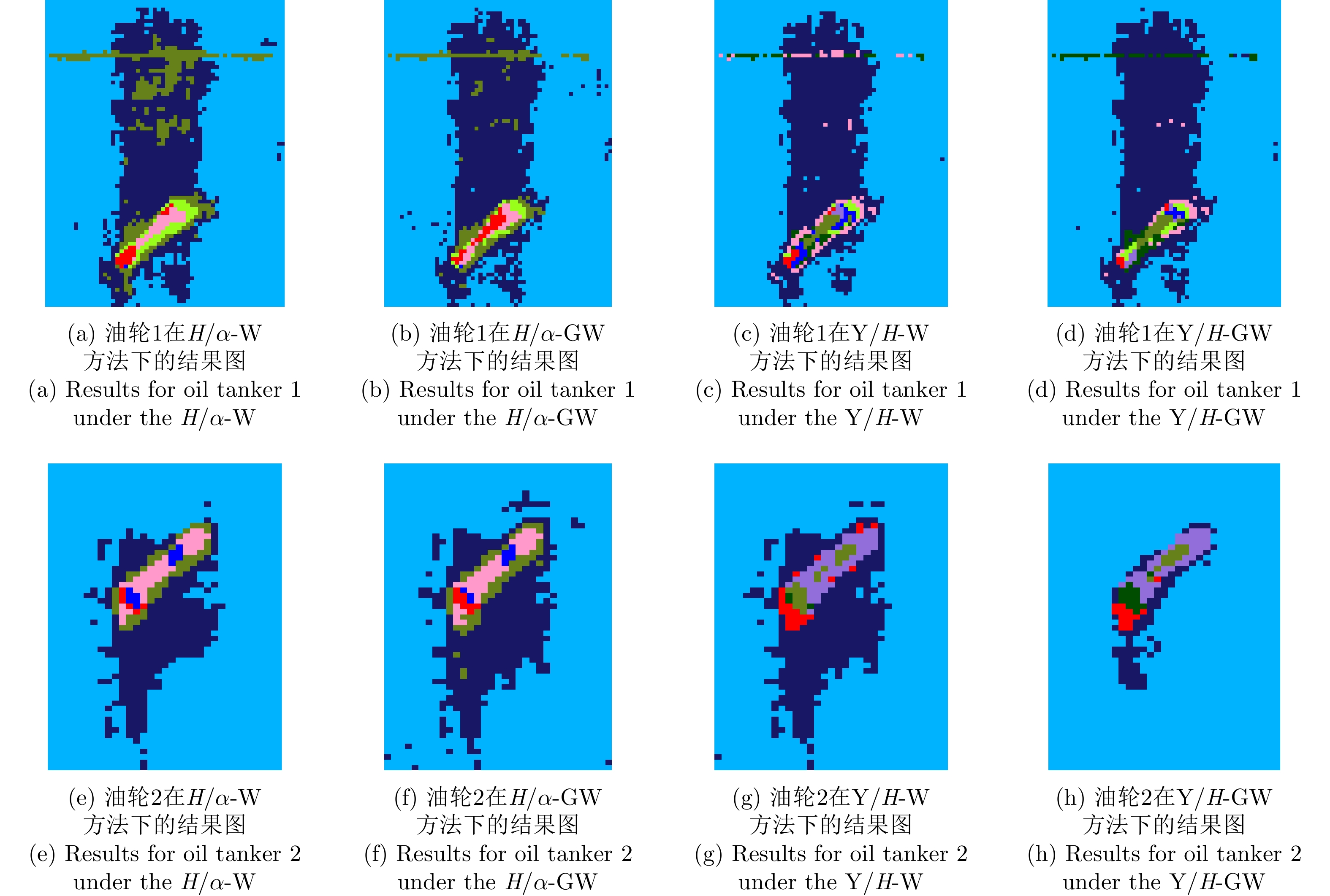
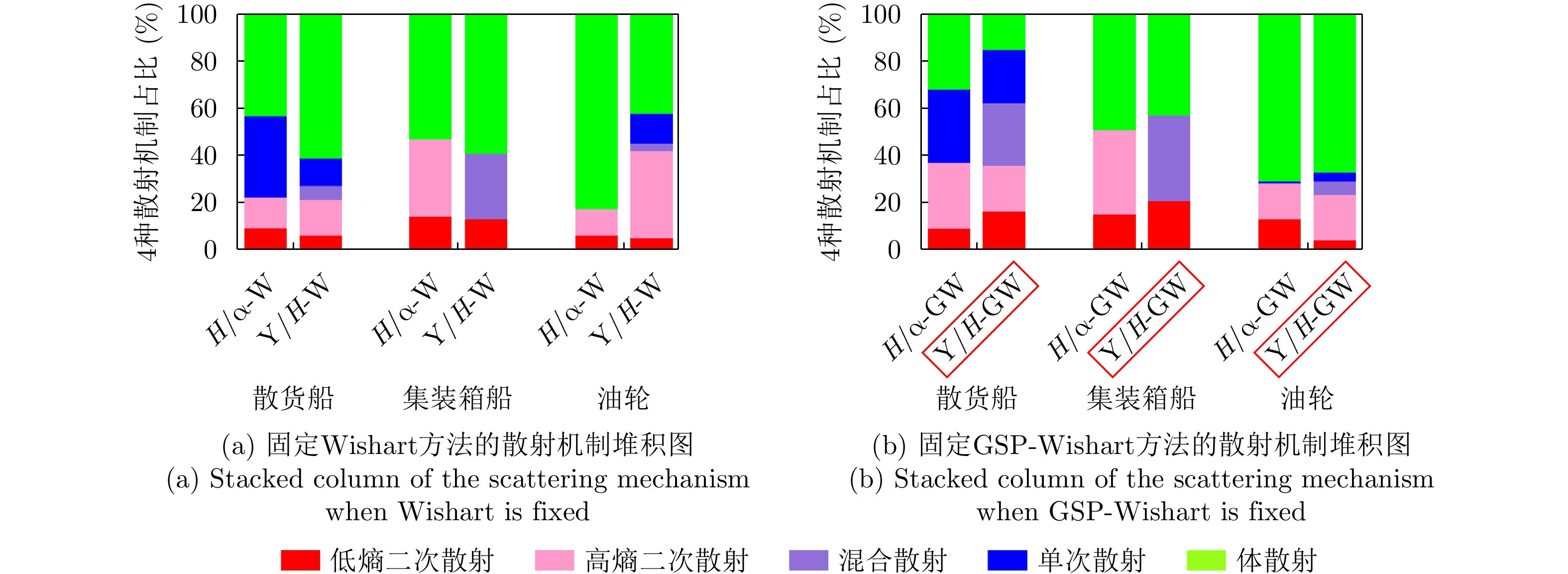
| [1] |
张杰, 张晰, 范陈清, 等. 极化SAR在海洋探测中的应用与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124. ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Xi, FAN Chenqing, et al. Discussion on application of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in marine surveillance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124. |
| [2] |
代大海, 廖斌, 肖顺平, 等. 雷达极化信息获取与处理的研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 143–155. doi: 10.12000/JR15103. DAI Dahai, LIAO Bin, XIAO Shunping, et al. Advancements on radar polarization information acquisition and processing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 143–155. doi: 10.12000/JR15103. |
| [3] |
赵春雷, 王亚梁, 阳云龙, 等. 雷达极化信息获取及极化信号处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092. ZHAO Chunlei, WANG Yaliang, YANG Yunlong, et al. Review of radar polarization information acquisition and polarimetric signal processing techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092. |
| [4] |
SATO A, YAMAGUCHI Y, SINGH G, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with extended volume scattering model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(2): 166–170. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2162935. |
| [5] |
CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. General polarimetric model-based decomposition for coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1843–1855. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2255615. |
| [6] |
XI Yuyang, LANG Haitao, TAO Yunhong, et al. Four-component model-based decomposition for ship targets using PolSAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 621. doi: 10.3390/rs9060621. |
| [7] |
SINGH G and YAMAGUCHI Y. Model-based six-component scattering matrix power decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5687–5704. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2824322. |
| [8] |
SINGH G, MALIK R, MOHANTY S, et al. Seven-component scattering power decomposition of POLSAR coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8371–8382. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2920762. |
| [9] |
PAN Xueli, WU Zhenhua, YANG Lixia, et al. Ship detection method based on scattering contribution for PolSAR image[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4503205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3138796. |
| [10] |
全斯农, 范晖, 代大海, 等. 一种基于精细极化目标分解的舰船箔条云识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 61–73. doi: 10.12000/JR20123. QUAN Sinong, FAN Hui, DAI Dahai, et al. Recognition of ships and chaff clouds based on sophisticated polarimetric target decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 61–73. doi: 10.12000/JR20123. |
| [11] |
LIU Dongsheng and HAN Ling. Integration of fine model-based decomposition and guard filter for ship detection in PolSAR images[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(13): 4295. doi: 10.3390/s21134295. |
| [12] |
QUAN Sinong, ZHANG Tao, WANG Wei, et al. Exploring fine polarimetric decomposition technique for built-up area monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5204719. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3257773. |
| [13] |
CUI Xingchao, SU Yi, and CHEN Siwei. A saliency detector for polarimetric SAR ship detection using similarity test[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(9): 3423–3433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2925833. |
| [14] |
LIN Huiping, WANG Hongmiao, WANG Jing, et al. A novel ship detection method via generalized polarization relative entropy for PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4001205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3019196. |
| [15] |
YIN Junjun, PENG Jiayao, YANG Jian, et al. Refined polarimetric SAR image classification based on localized competition[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(5): 499–508, 516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.05.005. |
| [16] |
XING Xiangwei, JI Kefeng, ZOU Huanxin, et al. Ship classification in TerraSAR-X images with feature space based sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1562–1566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2262073. |
| [17] |
张晰, 张杰, 纪永刚, 等. 基于结构特征的SAR船只类型识别能力分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(1): 146–152.
ZHANG Xi, ZHANG Jie, JI Yonggang, et al. The capability analysis of ship classification by structure feature using SAR images[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(1): 146–152.
|
| [18] |
LANG Haitao, ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Xi, et al. Ship classification in SAR image by joint feature and classifier selection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 212–216. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2506570. |
| [19] |
WANG Juan, HUANG Weigen, YANG Jingsong, et al. Polarization scattering characteristics of some ships using polarimetric SAR images[C]. SPIE 8179, SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XI, Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 265–271.
|
| [20] |
LUO M R, CUI G, and RIGG B. The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000[J]. Color Research & Application, 2001, 26(5): 340–350. doi: 10.1002/col.1049. |
| [21] |
CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935. |
| [22] |
YAMAGUCHI Y, MORIYAMA T, ISHIDO M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(8): 1699–1706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084. |
| [23] |
AN Wentao, ZHANG Weijie, YANG Jian, et al. On the similarity parameter between two targets for the case of multi-look polarimetric SAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2009, 18(3): 545–550. doi: 10.23919/CJE.2009.10138264. |
| [24] |
ZHANG Qingjun. System design and key technologies of the GF-3 satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049. |
| [25] |
周伟, 孙艳丽, 许成斌, 等. 一种多极化SAR舰船目标与方位向模糊鉴别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 84–92. doi: 10.12000/JR14147. ZHOU Wei, SUN Yanli, XU Chengbin, et al. A method for discrimination of ship target and azimuth ambiguity in multi-polarimetric SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 84–92. doi: 10.12000/JR14147. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: