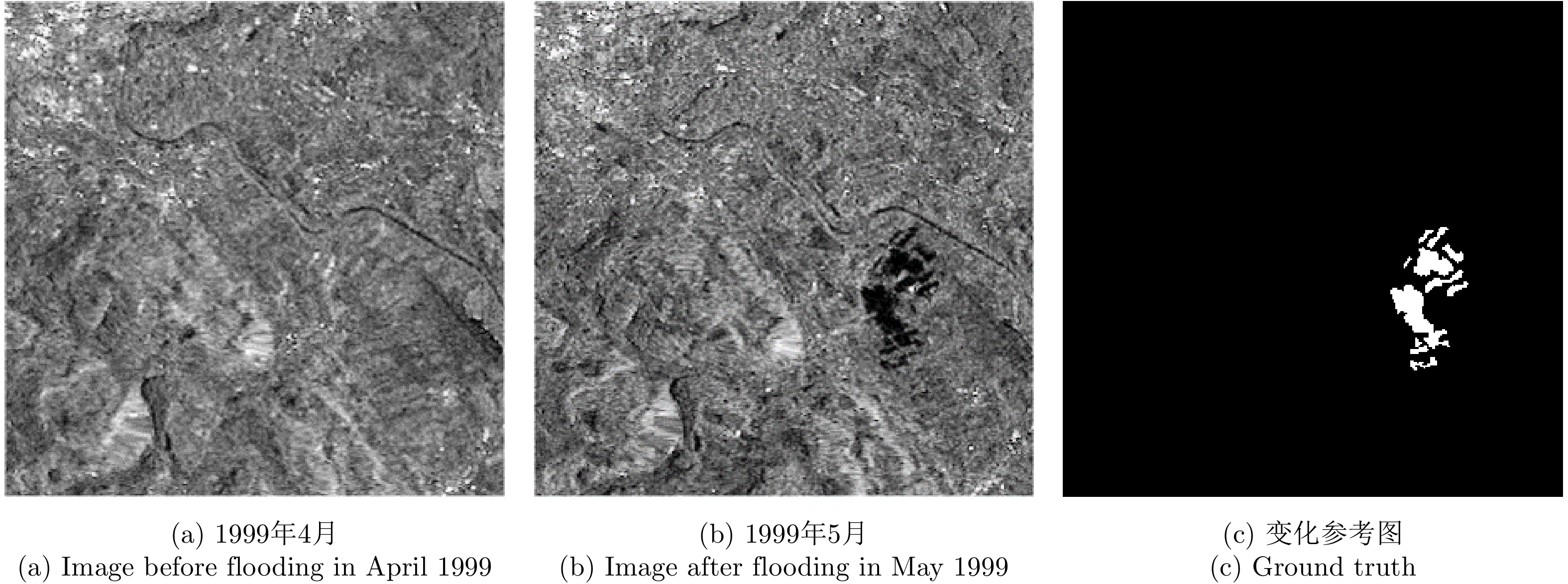
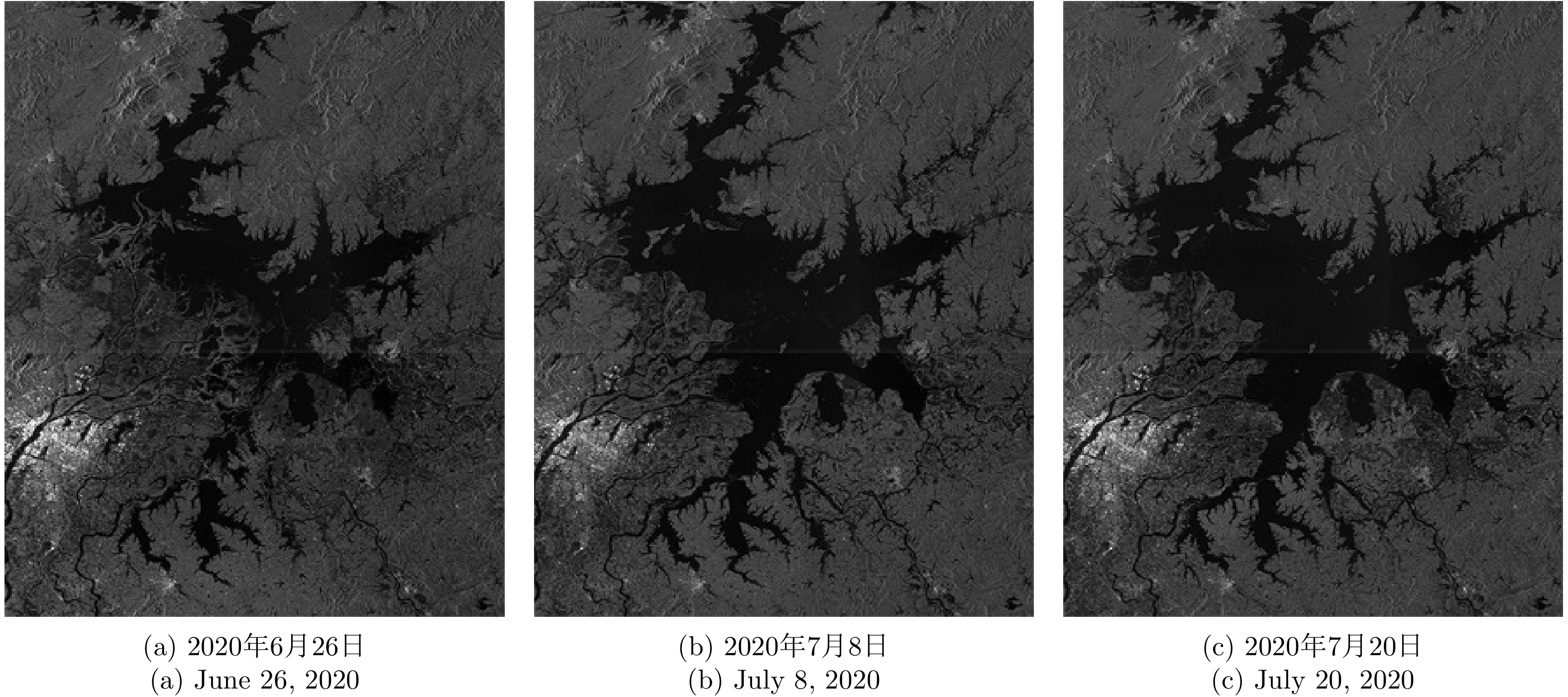
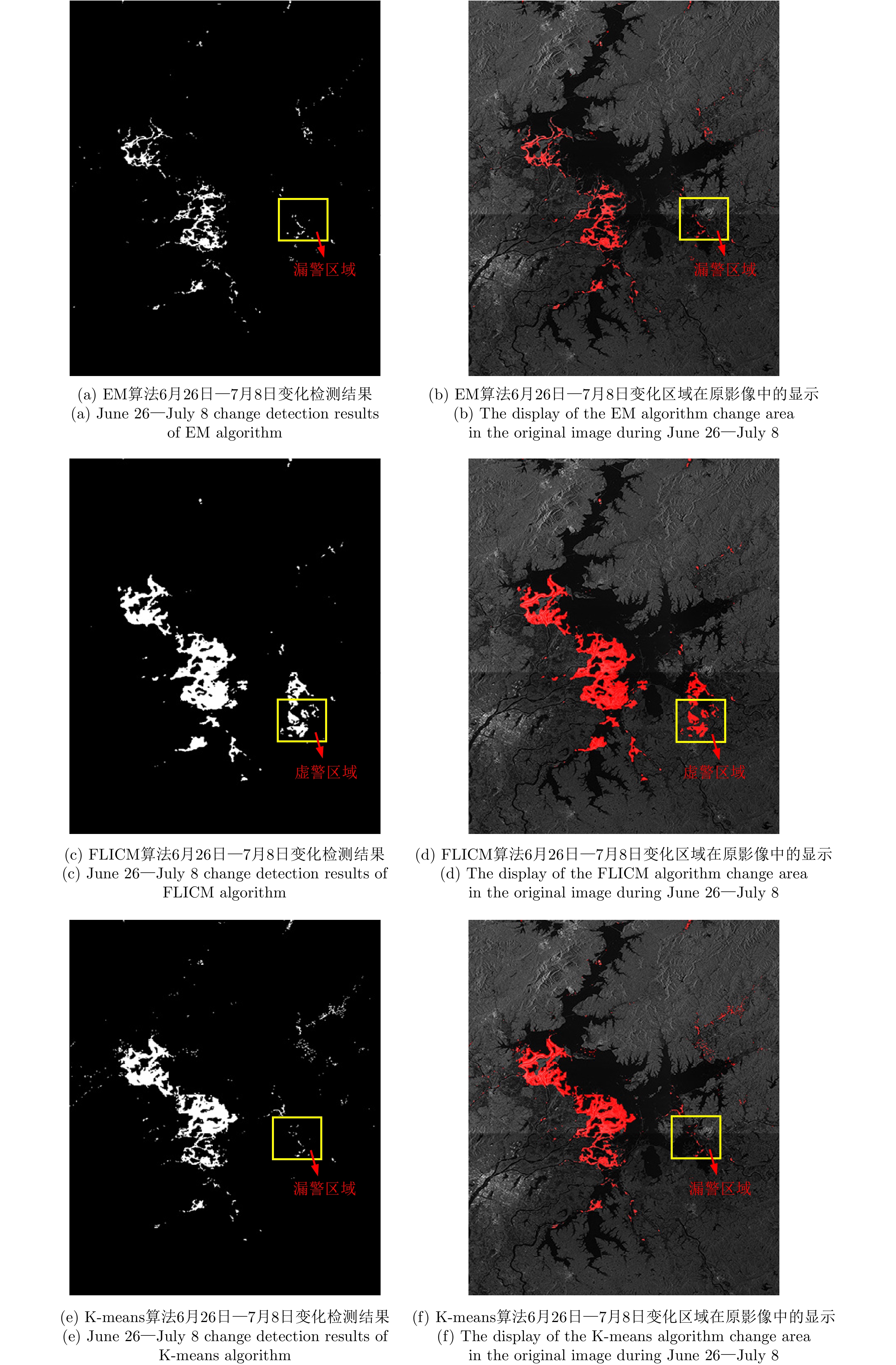
| [1] |
KRISHNA VANAMA V S and RAO Y S. Change detection based flood mapping of 2015 flood event of Chennai city using Sentinel-1 SAR images[C]. IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 9729–9732. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8899282. |
| [2] |
HOU Biao, WEI Qian, ZHENG Yaoguo, et al. Unsupervised change detection in SAR image based on gauss-log ratio image fusion and compressed projection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(8): 3297–3317. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2328344 |
| [3] |
ZHOU Licun, CAO Guo, LI Yupeng, et al. Change detection based on conditional random field with region connection constraints in high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3478–3488. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2514610 |
| [4] |
JIA Lu, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. SAR image change detection based on correlation kernel and multistage extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 5993–6006. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2578438 |
| [5] |
NAJAFI A, HASANLOU M, and AKBARI V. Land cover changes detection in polarimetric SAR data using algebra, similarity and distance based methods[J]. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017, XLII-4/W4: 195–200. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-4-W4-195-2017 |
| [6] |
GONG Maoguo, CAO Yu, and WU Qiaodi. A neighborhood-based ratio approach for change detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(2): 307–311. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2167211 |
| [7] |
ZHENG Yaoguo, ZHANG Xiangrong, HOU Biao, et al. Using combined difference image and k-means clustering for SAR image change detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(3): 691–695. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2275738 |
| [8] |
INGLADA J and MERCIER G. A new statistical similarity measure for change detection in multitemporal SAR images and its extension to multiscale change analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(5): 1432–1445. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.893568 |
| [9] |
JIA Meng, HUO Lina, and ZHANG Runzhao. An unsupervised change detection based on automatic relationship analysis[C]. The 2019 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Xi’an, China, 2019. doi: 10.1109/ICIEA.2019.8833683. |
| [10] |
WAN Ling, XIANG Yuming, and YOU Hongjian. A cooperative multitemporal segmentation method for SAR and optical images change detection[C]. IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1613–1616. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898866. |
| [11] |
MA Jingjing, GONG Maoguo, and ZHOU Zhiqiang. Wavelet fusion on ratio images for change detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(6): 1122–1126. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2191387 |
| [12] |
AMISSE C, JIJON-PALMA M E, and CENTENO J A S. Mapping extension and magnitude of changes induced by cyclone Idai with multi-temporal Landsat and SAR images[C]. 2020 IEEE Latin American GRSS & ISPRS Remote Sensing Conference (LAGIRS), Santiago, Chile, 2020: 574–578. doi: 10.1109/LAGIRS48042.2020.9165657. |
| [13] |
黄平平, 任慧芳, 谭维贤, 等. 基于地基雷达图像的无监督变化检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 514–524. doi: 10.12000/JR20004HUANG Pingping, REN Huifang, TAN Weixian, et al. Unsupervised change detection using ground-based radar image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 514–524. doi: 10.12000/JR20004 |
| [14] |
DING Yi, LIU Ming, LI Suju, et al. Mountainous landslide recognition based on gaofen-3 polarimetric SAR imagery[C]. IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 9634–9637. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8900478. |
| [15] |
GONG Maoguo, ZHOU Zhiqiang, and MA Jingjing. Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on image fusion and fuzzy clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 2141–2151. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2170702 |
| [16] |
HEIDARPOUR SHAHREZAEI I and KIM H C. Fractal analysis and texture classification of high-frequency multiplicative noise in SAR Sea-Ice images based on a transform-domain image decomposition method[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 40198–40223. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2976815 |
| [17] |
CELIK T and MA Kaikuang. Multitemporal image change detection using undecimated discrete wavelet transform and active contours[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 706–716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2066979 |
| [18] |
LI Dan, WU Baosheng, CHEN Bowei, et al. Review of water body information extraction based on satellite remote sensing[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2020, 60(2): 147–161. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2019.22.038 |
| [19] |
SUMAIYA M N and SHANTHA SELVA KUMARI R. Logarithmic mean-based thresholding for SAR image change detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1726–1728. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2606119 |
| [20] |
ZHANG Xiaohua, CHEN Jiawei, and MENG Hongyun. A novel SAR image change detection based on Graph-Cut and generalized gaussian model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(1): 14–18. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2189867 |
| [21] |
LI Mengke, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. SAR image change detection using PCANet guided by saliency detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 402–406. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2876616 |
| [22] |
LI Yangyang, PENG Cheng, CHEN Yanqiao, et al. A deep learning method for change detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5751–5763. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2901945 |
| [23] |
王志豪, 李刚, 蒋骁. 基于光学和SAR遥感图像融合的洪灾区域检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR19095WANG Zhihao, LI Gang, and JIANG Xiao. Flooded area detection method based on fusion of optical and SAR remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR19095 |
| [24] |
CUI Shiyong and LUO Chengfeng. Feature-based non-parametric estimation of kullback-leibler divergence for SAR image change detection[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(11): 1102–1111. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1212418 |
| [25] |
冷英, 李宁. 一种改进的变化检测方法及其在洪水监测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139LENG Ying and LI Ning. Improved change detection method for flood monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139 |
| [26] |
GIERULL C H. On the statistics of coherence estimators for textured clutter plus noise[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(5): 679–683. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2671747 |
| [27] |
KIM J and FESSLER J A. Intensity-based image registration using robust correlation coefficients[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2004, 23(11): 1430–1444. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.835313 |
| [28] |
PU Yunchen, XU Qiongcheng, and WANG Wei. Image change detection based on cross-correlation coefficient by using genetic algorithm[C]. 2012 the 1st International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 2012. doi: 10.1109/Agro-Geoinformatics.2012.6311693. |
| [29] |
BRUZZONE L and FERNANDEZ PRIETO D. An MRF approach to unsupervised change detection[C]. 1999 International Conference on Image Processing, Kobe, Japan, 1999: 143–147. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.1999.821583. |
| [30] |
WANG Guiting, FAN Yuanzhang, and JIAO Licheng. A new change detection method based on non-parametric density estimation and markov random fields[C]. The SPIE 7497, MIPPR 2009: Medical Imaging, Parallel Processing of Images, and Optimization Techniques, Yichang, China, 2009. doi: 10.1117/12.833052. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

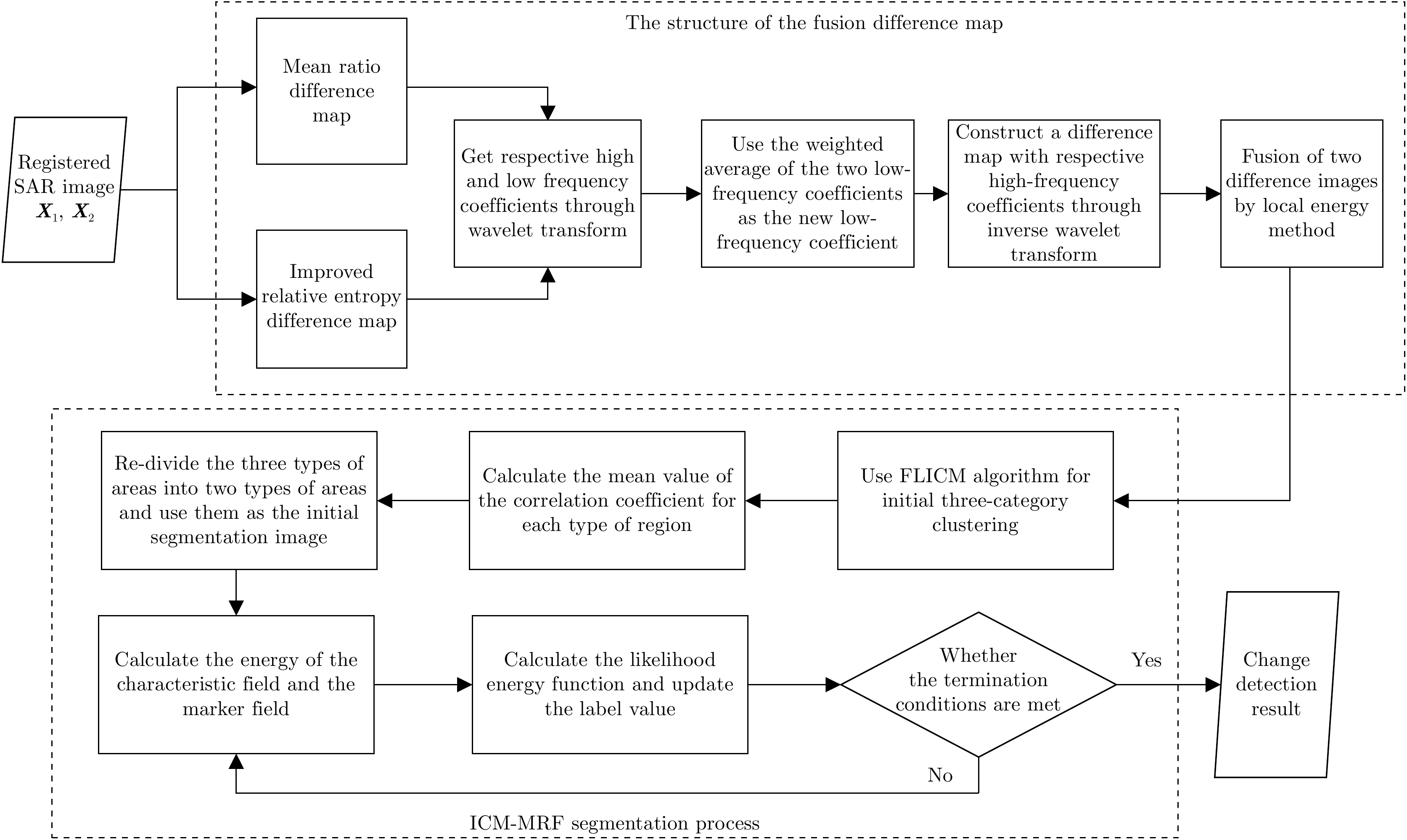



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: