Tomographic SAR 3D Imaging Method Based on Geometry and Polarization Joint Constraints
-
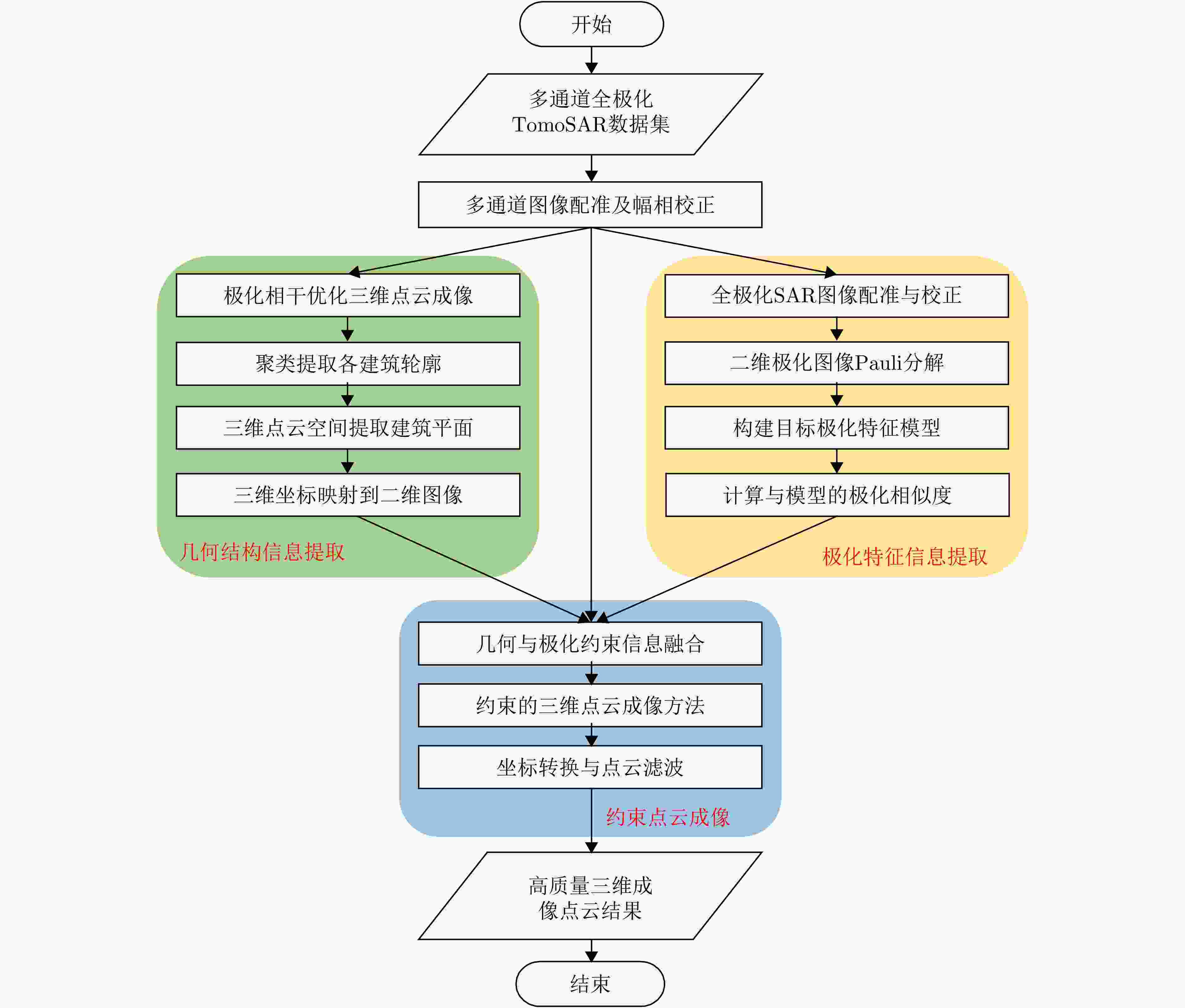
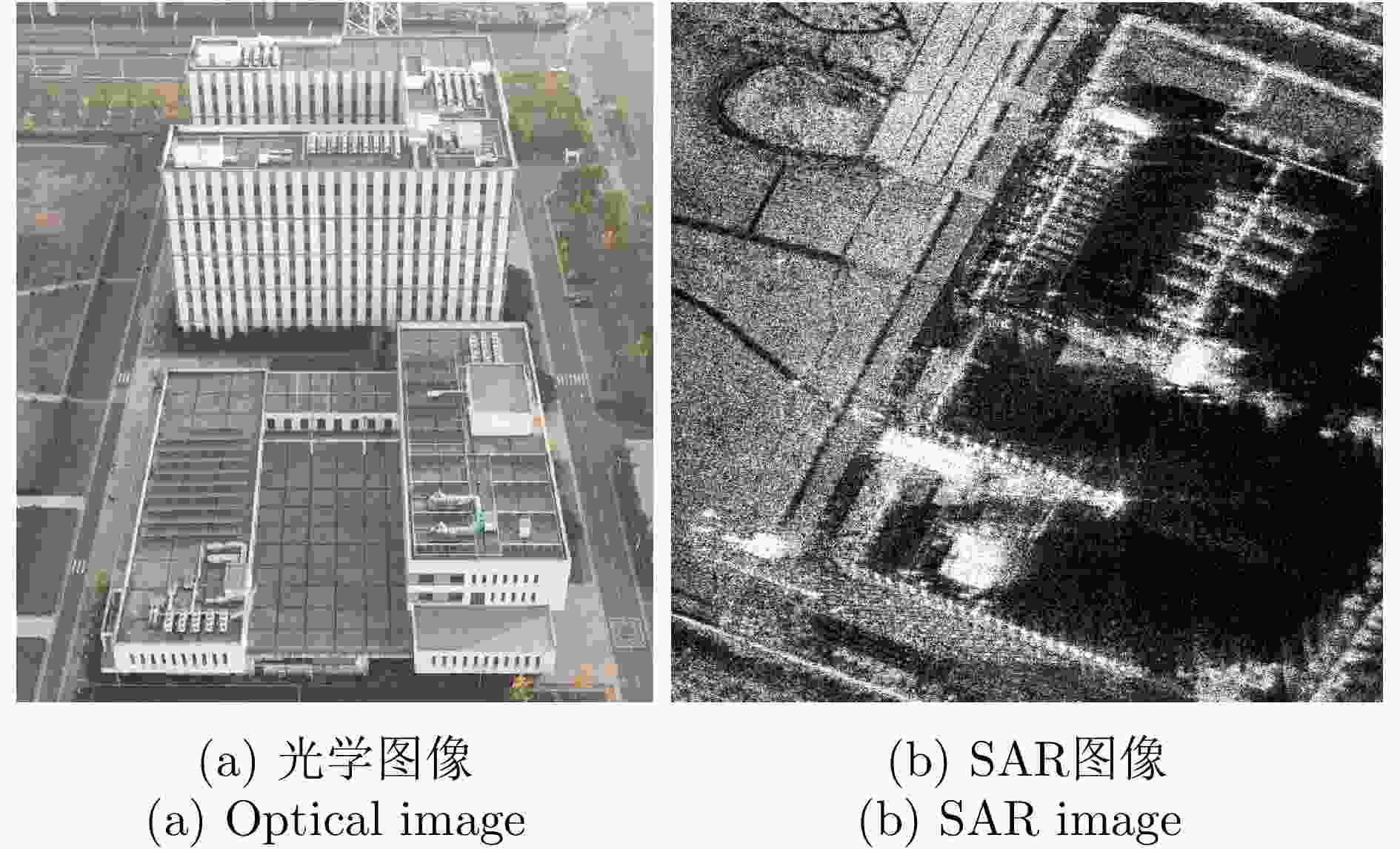
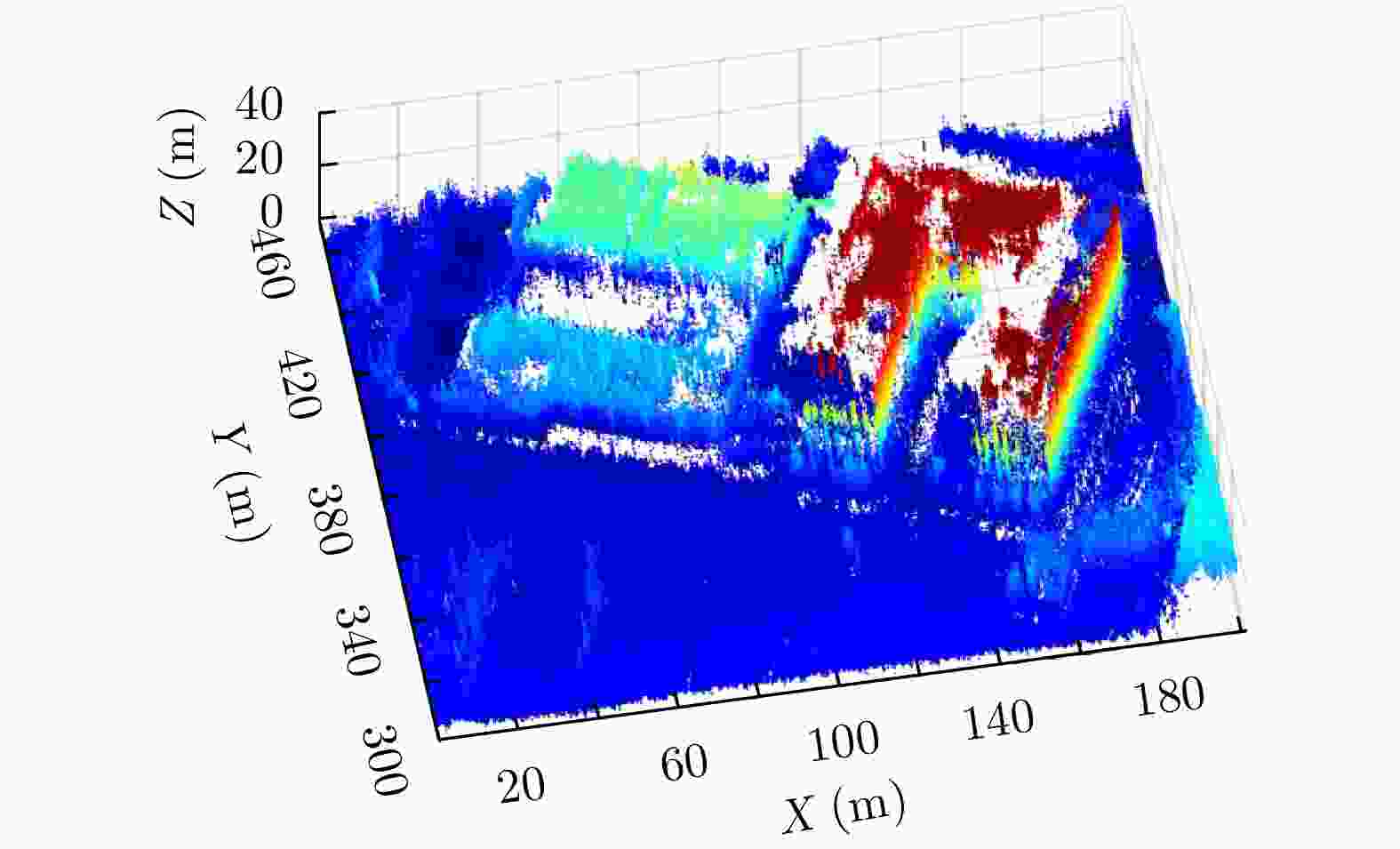
摘要: 层析合成孔径雷达(TomoSAR)是城市建筑物三维重建的重要技术。现有方法虽通过引入几何约束提升了成像质量,并在多极化条件下发展为极化层析SAR (PolTomoSAR),但仍面临复杂建筑结构下几何信息依赖性强、极化模型不完善等问题。为此,该文提出一种几何与极化联合约束的TomoSAR三维成像方法,融合建筑几何结构与Pauli极化相似度信息,结合极化相干最优处理及概率密度约束,显著提升点云成像质量。实验基于机载Ku波段4通道阵列苏州实测数据,结果表明所提方法在成像精度与完整性方面均优于现有方法,验证了其有效性与优越性。
-
关键词:
- 极化层析合成孔径雷达 /
- 几何约束 /
- 极化相似度 /
- 三维重建 /
- 点云
Abstract: Tomographic Synthetic Aperture Radar (TomoSAR) is a key technique for 3D reconstruction of urban buildings. Although existing methods improve imaging quality by incorporating geometric constraints and have evolved into Polarimetric TomoSAR (PolTomoSAR) with multi-polarization capabilities, challenges remain in handling complex structures due to heavy reliance on geometric accuracy and limitations in polarization modeling. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel TomoSAR 3D imaging method based on joint geometric and polarimetric constraints. The approach integrates building geometry with Pauli scattering similarity and incorporates polarization coherence optimization and probability density-based constraints to significantly enhance point cloud quality. Experiments using airborne Ku-band multi-channel SAR data over Suzhou, China, demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed method in both accuracy and completeness of 3D reconstruction. -
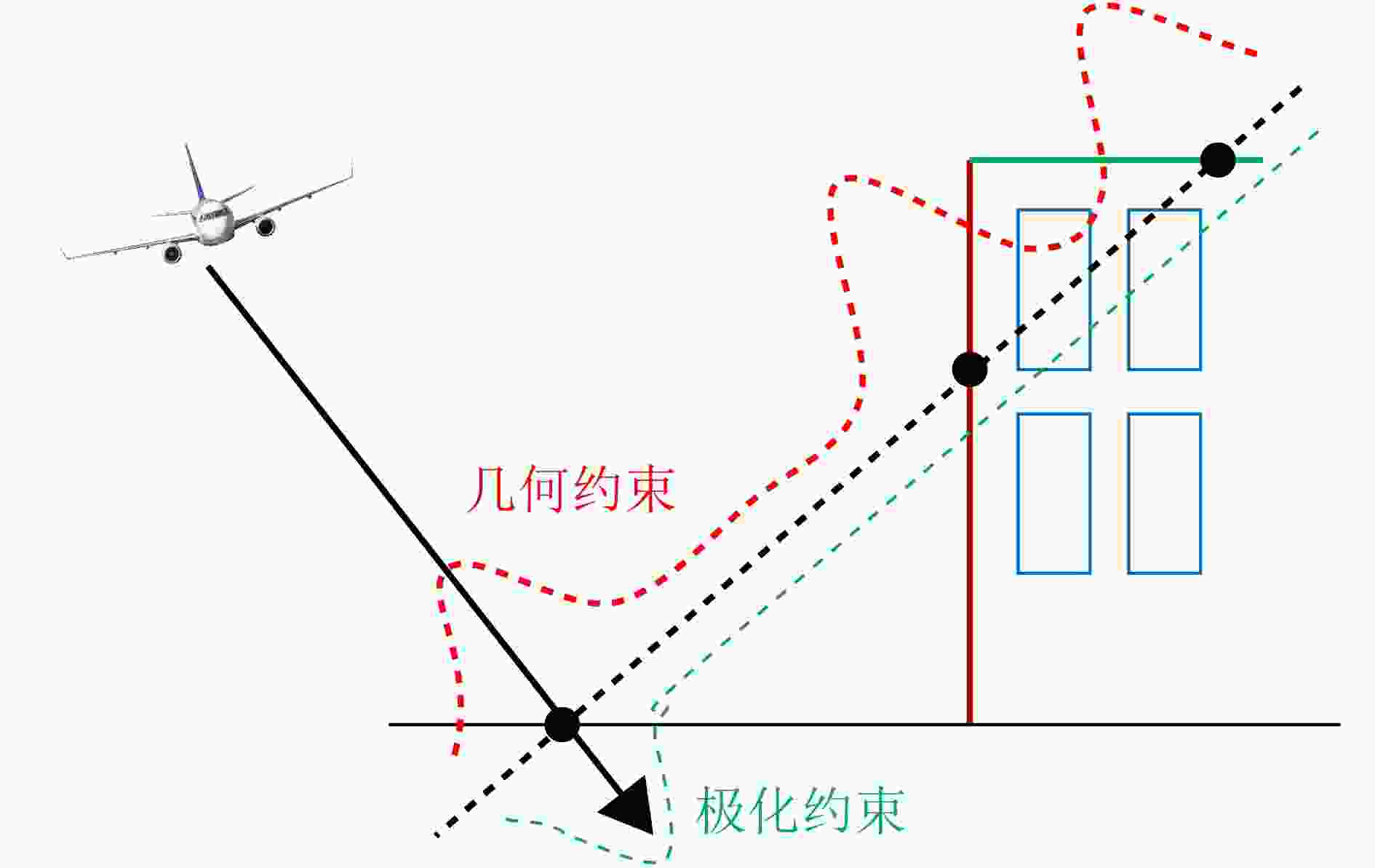
1 约束的压缩感知三维成像流程
1. Constrained CS 3D imaging process
初始化:残差$ {r}_{0}={\boldsymbol{y}} $,y为观测向量,索引集$ S= \varnothing $,稀疏度
$ K=n $,当前解$ {x}_{0}=0 $。步骤1:选择约束后与当前残差$ {r}_{k-1} $最相关的观测矩阵元素,
$ {j}_{k}=\arg {\max }_{j}|{\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{j}^{{\mathrm{T}}}{r}_{k-1}f\left(\theta \right)| $步骤2:将选中的索引$ {j}_{k} $添加到索引集S中,$ {S}_{k}={S}_{k-1}\cup\left\{{j}_{k}\right\} $ 步骤3:最小二乘法求解系数向量:
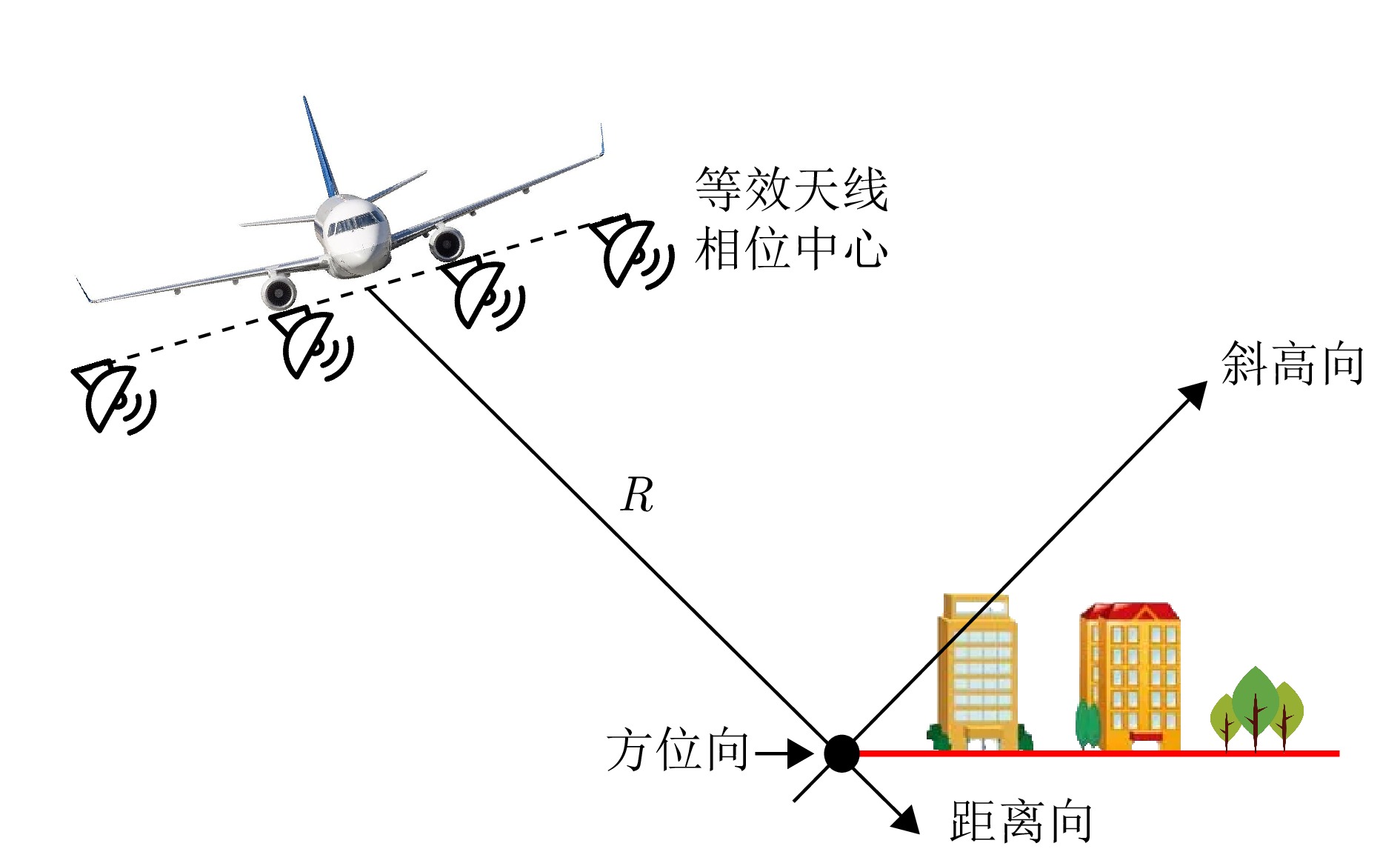
$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{k}=\arg {\min }_{{\boldsymbol{x}}}\|{\boldsymbol{y}}-{{\boldsymbol{A}}}_{s}{\boldsymbol{x}}{\|}_{2} $即$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{k}={\left({\boldsymbol{A}}_{s}^{{\mathrm{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{A}}}_{s}\right)}^{-1}{\boldsymbol{A}}_{s}^{{\mathrm{T}}}{\boldsymbol{y}} $ 步骤4:更新残差:$ {r}_{k}={\boldsymbol{y}}-{{\boldsymbol{A}}}_{s}{{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{k} $ 终止条件:(1) 当残差小于预设阈值:$ \|{r}_{j}{\|}_{2} \lt \epsilon $ (2) 达到设定的稀疏度:$ k=K $。 表 1 无人机载TomoSAR与飞行参数
Table 1. UAV TomoSAR and flight parameters
参数 指标 SAR类型 阵列 频段 Ku波段 飞行高度 400 m 带宽 1200 MHz 轨道/阵列数量 4 中心下视角 45° 平均基线间隔 17.8 cm 极化通道 HH, HV, VH, VV 表 2 点云质量定量评价参数与结果
Table 2. Point cloud quality quantitative evaluation parameters and results
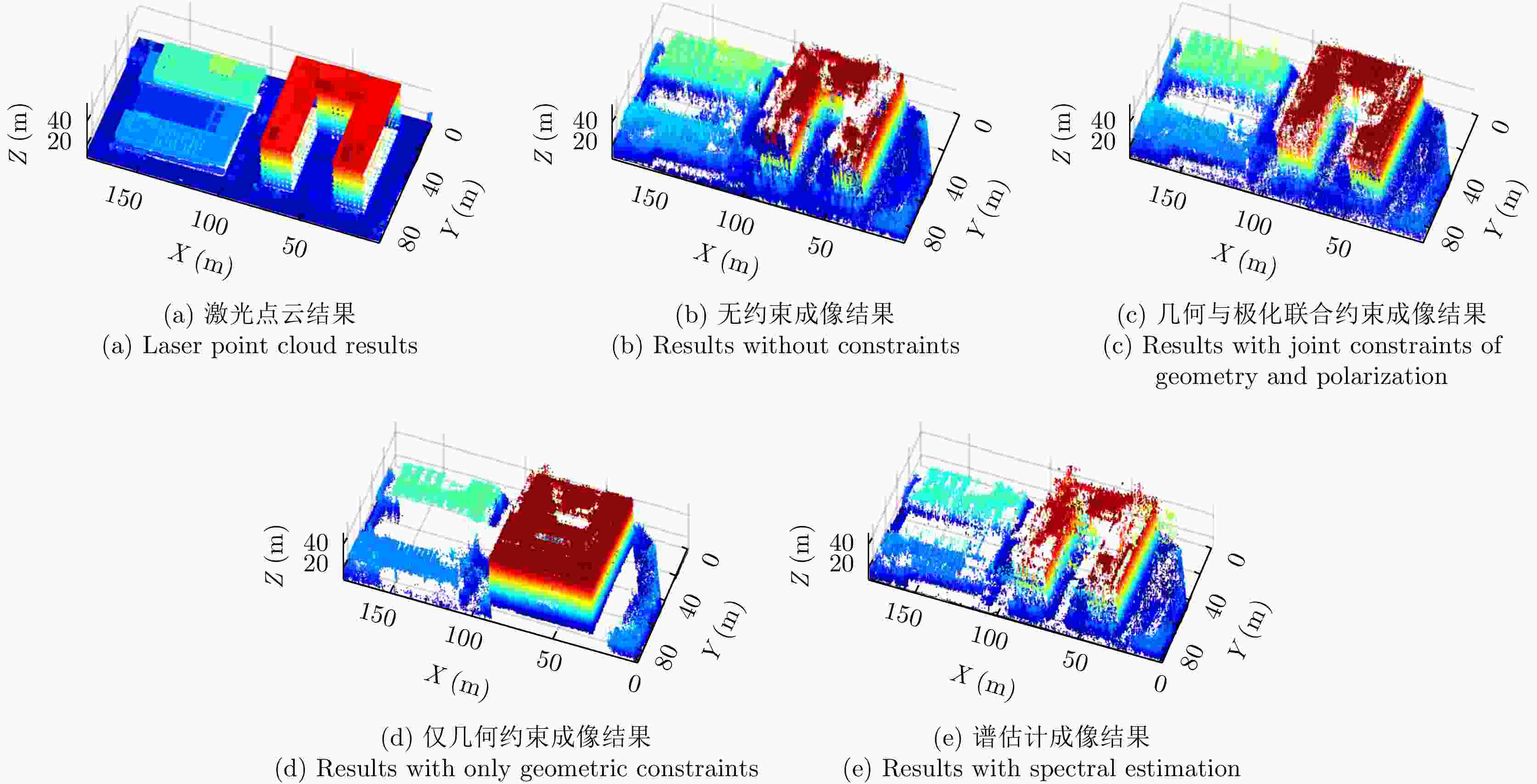
成像方法 RMSE 点云完整度 无约束三维点云 3.4827 1.2966 几何与极化联合约束三维点云 2.1240 0.8800 仅几何约束三维点云 2.9644 0.7155 谱估计三维点云 3.6703 1.6566 -
[1] BROWN W M. Synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1967, AES-3(2): 217–229. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1967.5408745. [2] WILEY C A. Synthetic aperture radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES-21(3): 440–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310578. [3] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013. [4] JIAO Zekun, QIU Xiaolan, DONG Shuhang, et al. Preliminary exploration of geometrical regularized SAR tomography[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 201: 174–192. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.05.019. [5] 李晓婉, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 基于几何约束移动最小二乘的TomoSAR山区点云高精度三维重建方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 363–375. doi: 10.12000/JR22049.LI Xiaowan, LIANG Xingdong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. A geometry constrained moving least squares-based high-precision 3D reconstruction method of mountains from TomoSAR point clouds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 363–375. doi: 10.12000/JR22049. [6] HAN Dong, ZHOU Liangjiang, JIAO Zekun, et al. Efficient 3D image reconstruction of airborne TomoSAR based on back projection and improved adaptive ISTA[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 47399–47410. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3066984. [7] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. [8] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027.QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027. [9] QIU Xiaolan, LUO Yitong, CHENG Yao, et al. SAR microwave vision 3D imaging dataset 3.0[EB/OL]. Journal of Radars, 2024. https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?newsColumnId=2f2748db-10ef-4ad0-bcc4-f087ce59b6f8&pageType=en. [10] 仇晓兰, 罗一通, 宋舒洁, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR实验系统及其全极化数据处理方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(5): 941–954. doi: 10.12000/JR24137.QIU Xiaolan, LUO Yitong, SONG Shujie, et al. Microwave vision three-dimensional SAR experimental system and full-polarimetric data processing method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(5): 941–954. doi: 10.12000/JR24137. [11] DONG Shuhang, JIAO Zekun, ZHOU Liangjiang, et al. Enhanced 3D reconstruction method for polarimetric coherent optimal-based tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 5494–5508. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3517843. [12] YANG Jian, PENG Yingning, and LIN Shiming. Similarity between two scattering matrices[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(3): 193–194. doi: 10.1049/el:20010104. [13] 张锐, 洪峻, 明峰. 基于极化相似度的全极化SAR自动目标识别算法[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2010, 29(5): 24–27, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2010.05.005.ZHANG Rui, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. Full polarimetry SAR ATR algorithm based on polarimetry similarity[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2010, 29(5): 24–27, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2010.05.005. [14] 徐牧, 王雪松, 肖顺平. 基于改善极化相似性的极化SAR目标增强新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(5): 1047–1051. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00754.XU Mu, WANG Xuesong, and XIAO Shunping. Target enhancement in POL-SAR imagery based on the improvement of polarization characteristics similarity[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(5): 1047–1051. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00754. [15] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582. [16] BARANIUK R G. Compressive sensing [lecture notes][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4): 118–121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571. [17] DONG Shuhang, JIAO Zekun, ZHOU Liangjiang, et al. A novel filtering method of 3D reconstruction point cloud from tomographic SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(12): 3076. doi: 10.3390/rs15123076. [18] WANG Chunyi, YAN Qiancheng, QIU Xiaolan, et al. A geometric semantic enhanced TomoSAR reconstruction algorithm in an urban area: Analysis and application[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2025, 5: 0583. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0583. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: