Credible Inference of Near-field Sparse Array Synthesis for Three-dimensional Millimeter-wave Imagery(in English)
-
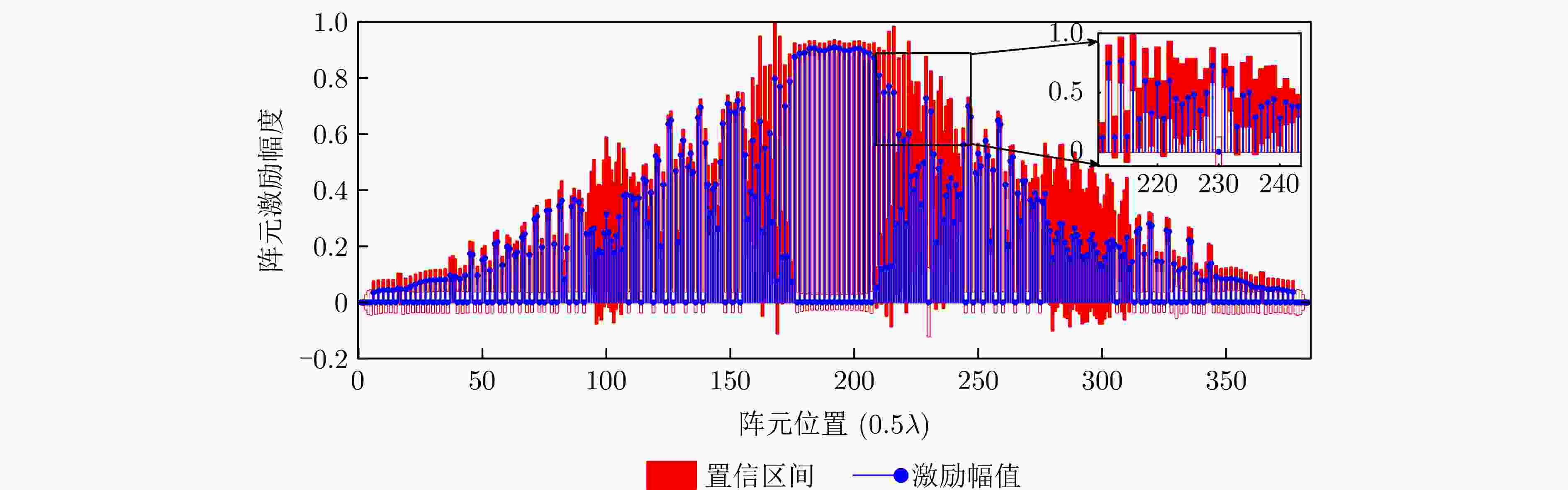
摘要: 考虑到主动式电扫描毫米波成像系统在实际应用中成像场景要求大,分辨率要求高,但毫米波的波长短,继而造成满足奈奎斯特采样定理的均匀阵列规模及馈电网络复杂度过高,面临着成像精度、成像速度和系统成本之间的矛盾。针对以上问题,该文提出了可信推断近场稀疏综合阵列算法(CBI-SAS),在全贝叶斯学习框架下,该算法基于贝叶斯推断对复激励权值进行稀疏优化,得到复激励权值的完全统计后验概率密度函数,从而利用其高阶统计信息得到复激励权值的最优值及其置信区间和置信度。在贝叶斯推断中,为了实现较少数量的阵元合成期望波束方向图,可通过对复值激励权值引入重尾的拉普拉斯稀疏先验。然而,由于先验概率模型与参考方向图数据模型非共轭,因此需对先验模型进行分层贝叶斯建模,从而保证得到的复激励权值完全后验分布具有闭合解析解。为了避免求解完全后验分布的高维积分,采用变分贝叶斯期望最大化方法计算复激励权值后验概率密度函数,实现复激励权值的可信推断。仿真模拟实验结果显示,相较于传统稀疏阵列合成方法,所提方法阵元稀疏度更低、归一化均方误差更小、匹配方向图精度更好。此外,基于设计的稀疏阵列采集近场一维电扫和二维平面全电扫实测回波数据后,利用改进三维时域算法进行三维重建,验证了所提CBI-SAS算法在保证成像结果的同时降低了系统复杂性的优势。Abstract: Due to the short wavelength of millimeter-wave, active electrical scanning millimeter-wave imaging system requires large imaging scenarios and high resolutions in practical applications. These requirements lead to a large uniform array size and high complexity of the feed network that satisfies the Nyquist sampling theorem. Accordingly, the system faces contradictions among imaging accuracy, imaging speed, and system cost. To this end, a novel, Credible Bayesian Inference of near-field Sparse Array Synthesis (CBI-SAS) algorithm is proposed under the framework of sparse Bayesian learning. The algorithm optimizes the complex-valued excitation weights based on Bayesian inference in a sparse manner. Therefore, it obtains the full statistical posterior Probability Density Function (PDF) of these weights. This enables the algorithm to utilize higher-order statistical information to obtain the optimal values, confidence intervals, and confidence levels of the excitation weights. In Bayesian inference, to achieve a small number of array elements to synthesize the desired beam orientation pattern, a heavy-tailed Laplace sparse prior is introduced to the excitation weights. However, considering that the prior probability model is not conjugated with the reference pattern data probability, the prior model is encoded in a hierarchical Bayesian manner so that the full posterior distribution can be represented in closed-form solutions. To avoid the high-dimensional integral in the full posterior distribution, a variational Bayesian expectation maximization method is employed to calculate the posterior PDF of the excitation weights, enabling reliable Bayesian inference. Simulation results show that compared with conventional sparse array synthesis algorithms, the proposed algorithm achieves lower element sparsity, a smaller normalized mean square error, and higher accuracy for matching the desired directional pattern. In addition, based on the measured raw data from near-field 1D electrical scanning and 2D plane electrical scanning, an improved 3D time domain algorithm is applied for 3D image reconstruction. Results verify that the proposed CBI-SAS algorithm can guarantee imaging results and reduce the complexity of the system.
-
表 1 不同稀疏阵列合成算法下的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different sparse array synthesis algorithms
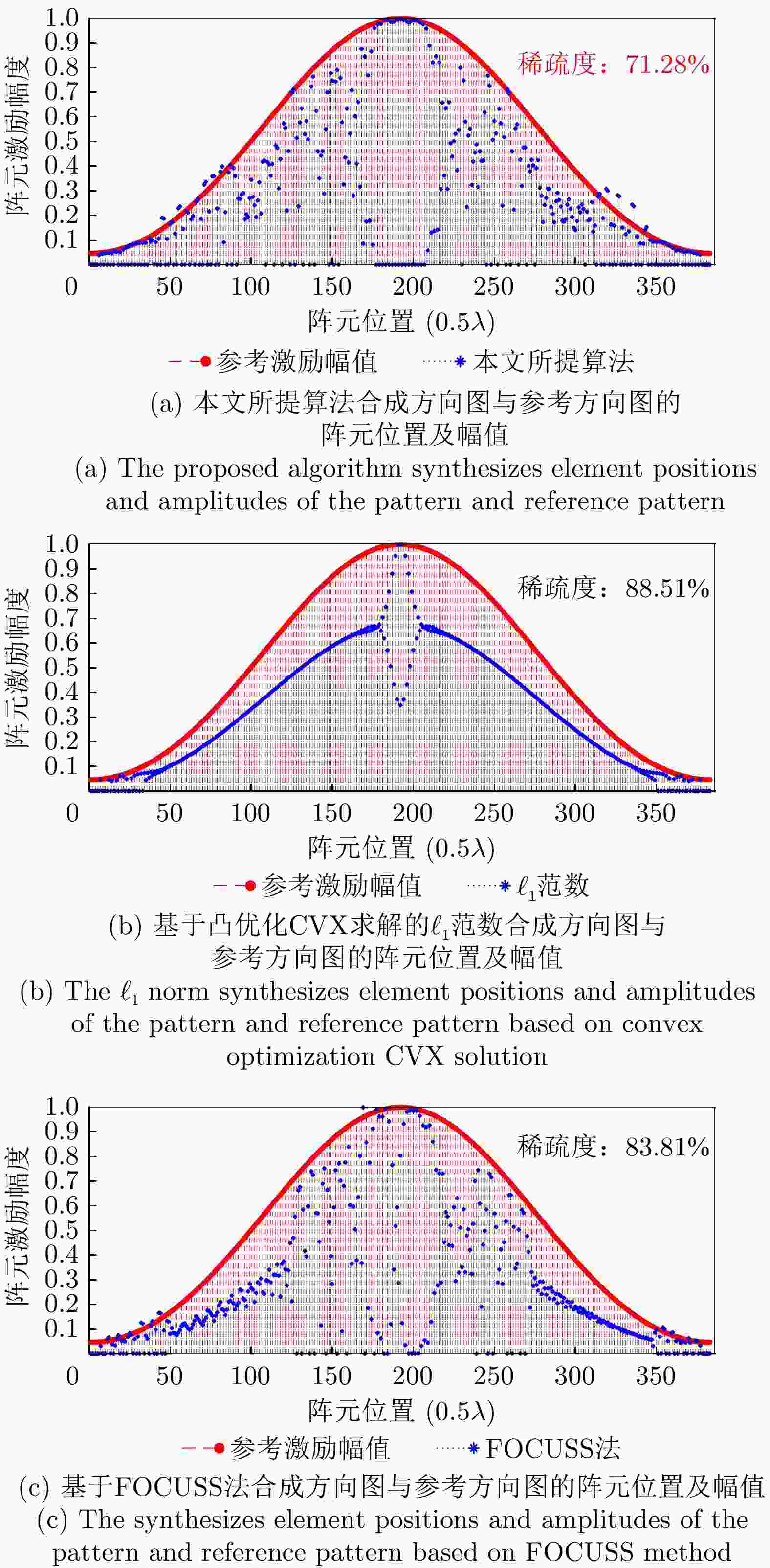
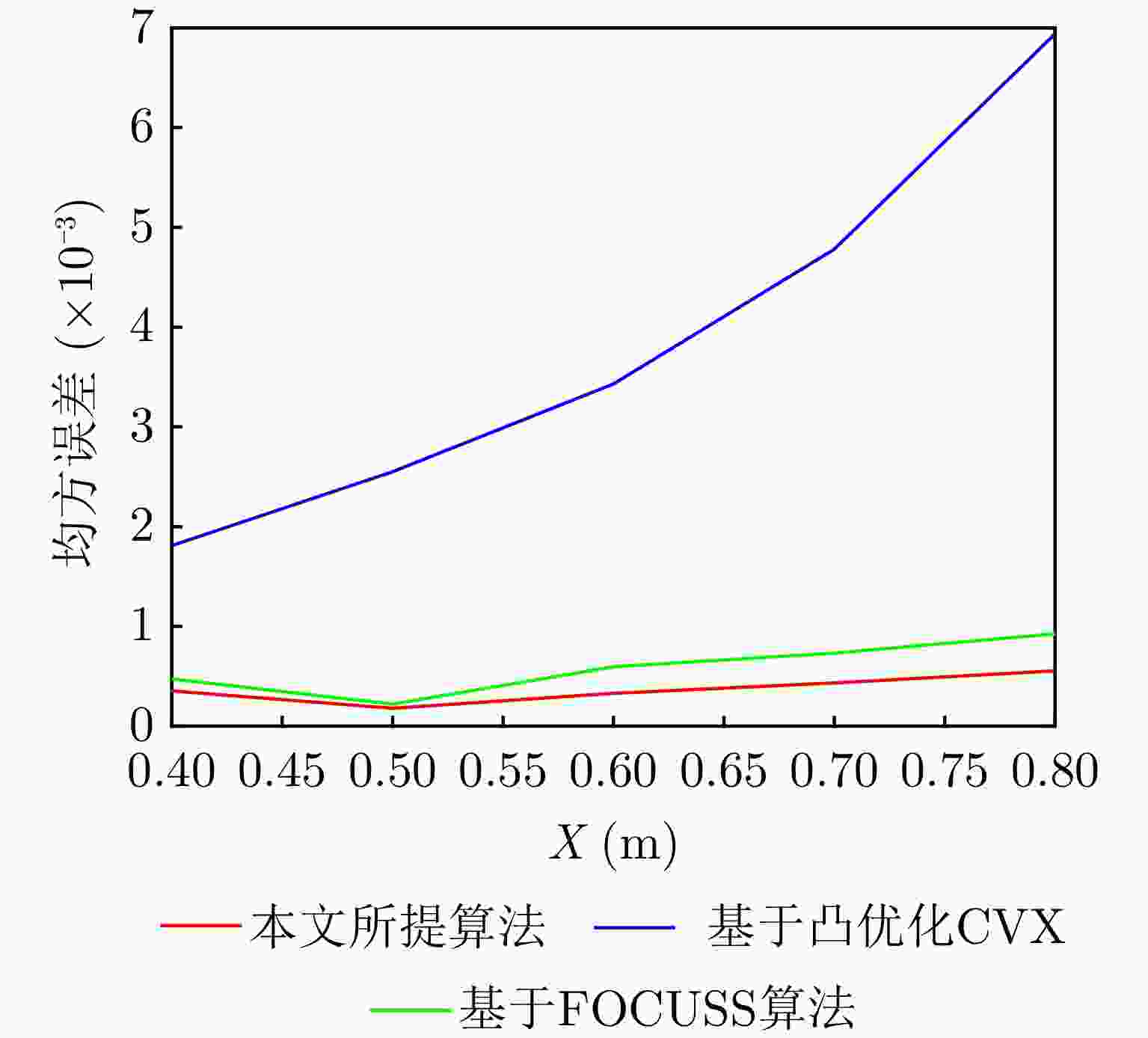
方法 峰值旁瓣电平(dB) 阵元个数 稀疏度(%) 均方误差 本文所提方法 –15.81 273 71.28 1.89×10–4 ${\ell _1}$范数 –15.76 339 88.51 3.50×10–3 FOCUSS法 –15.68 321 83.81 3.08×10–4 表 2 毫米波电扫描圆周成像系统相关参数
Table 2. Parameters of milli-meter wave electrical scanning circumferential imaging system
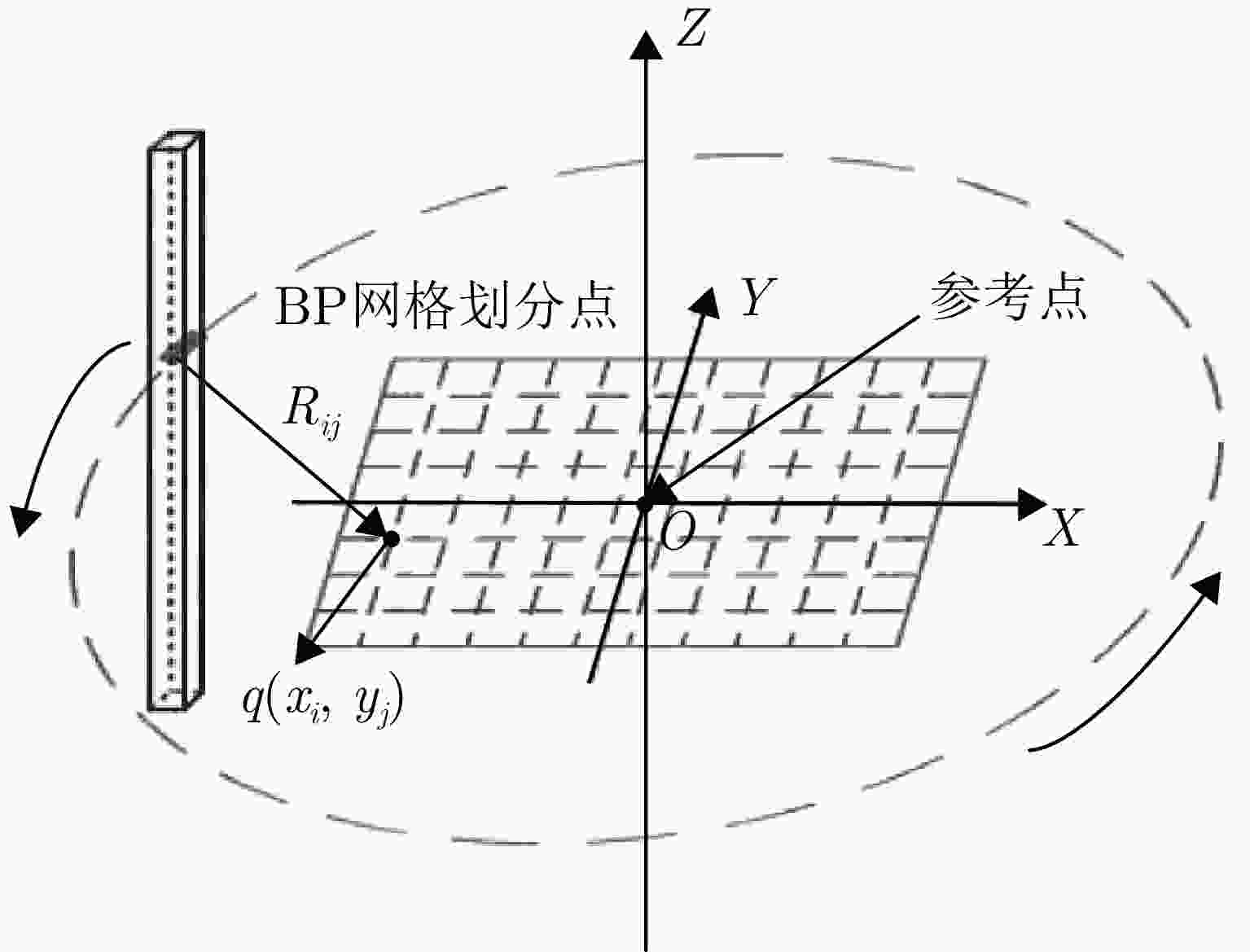
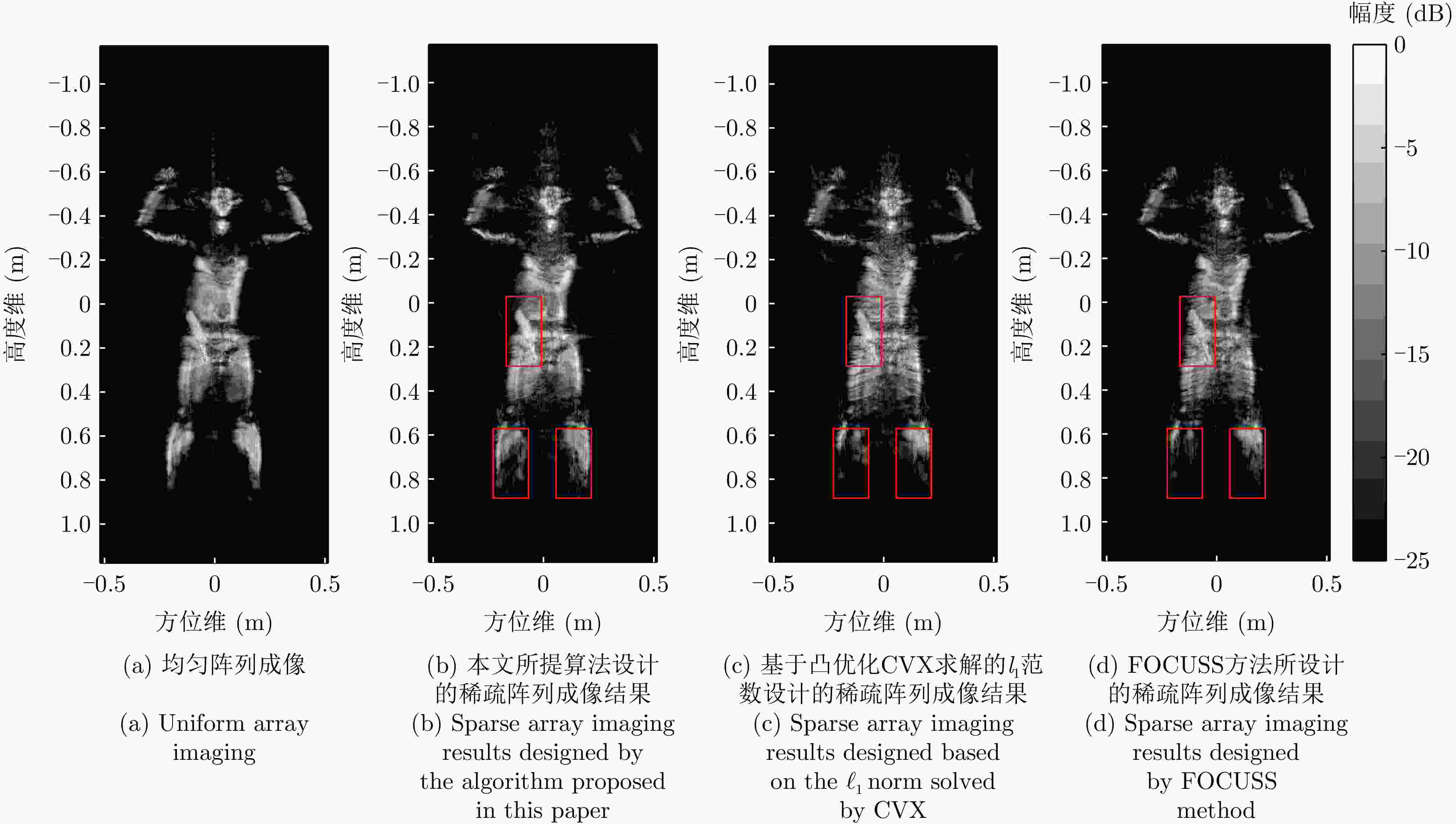
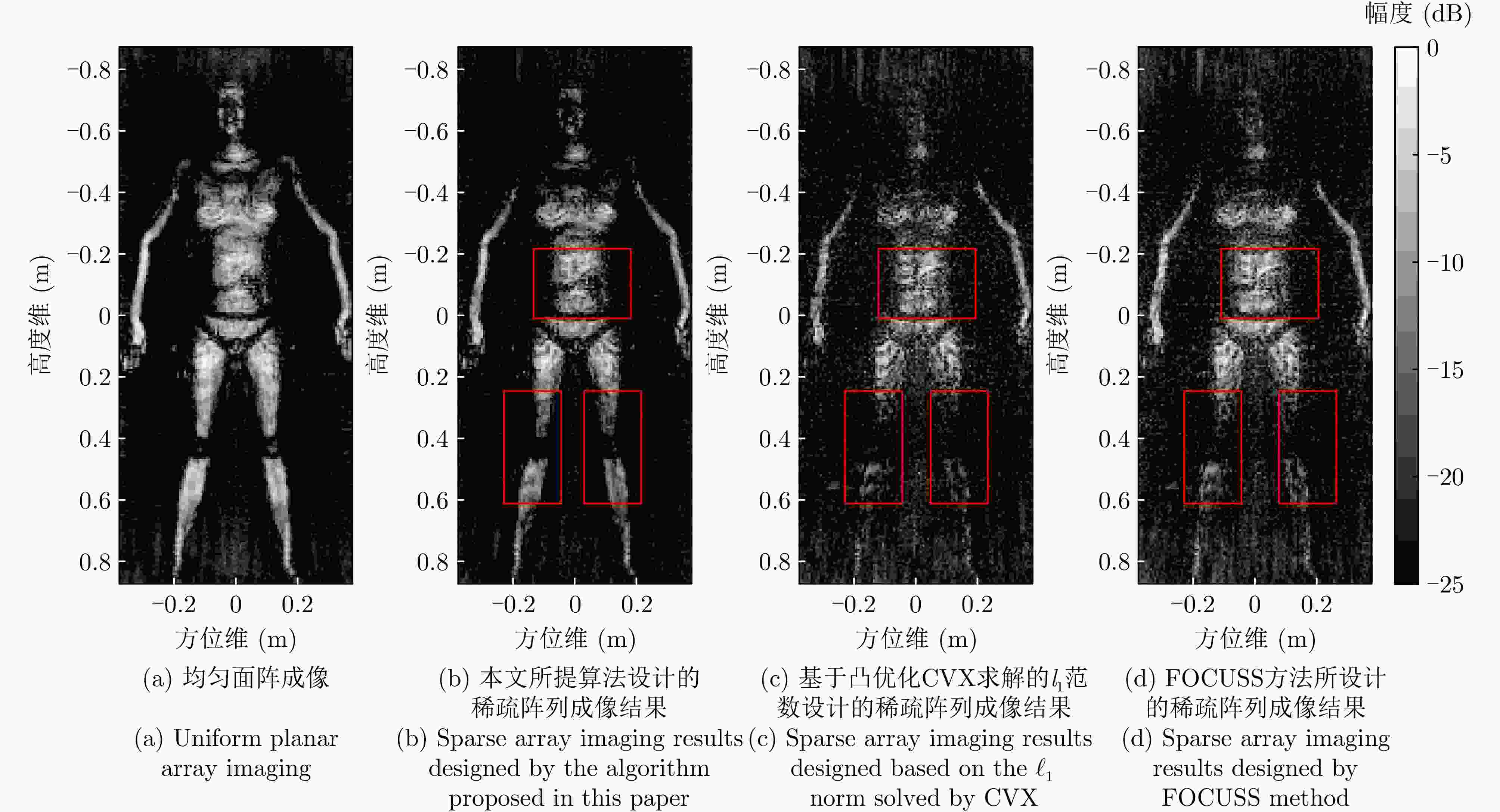
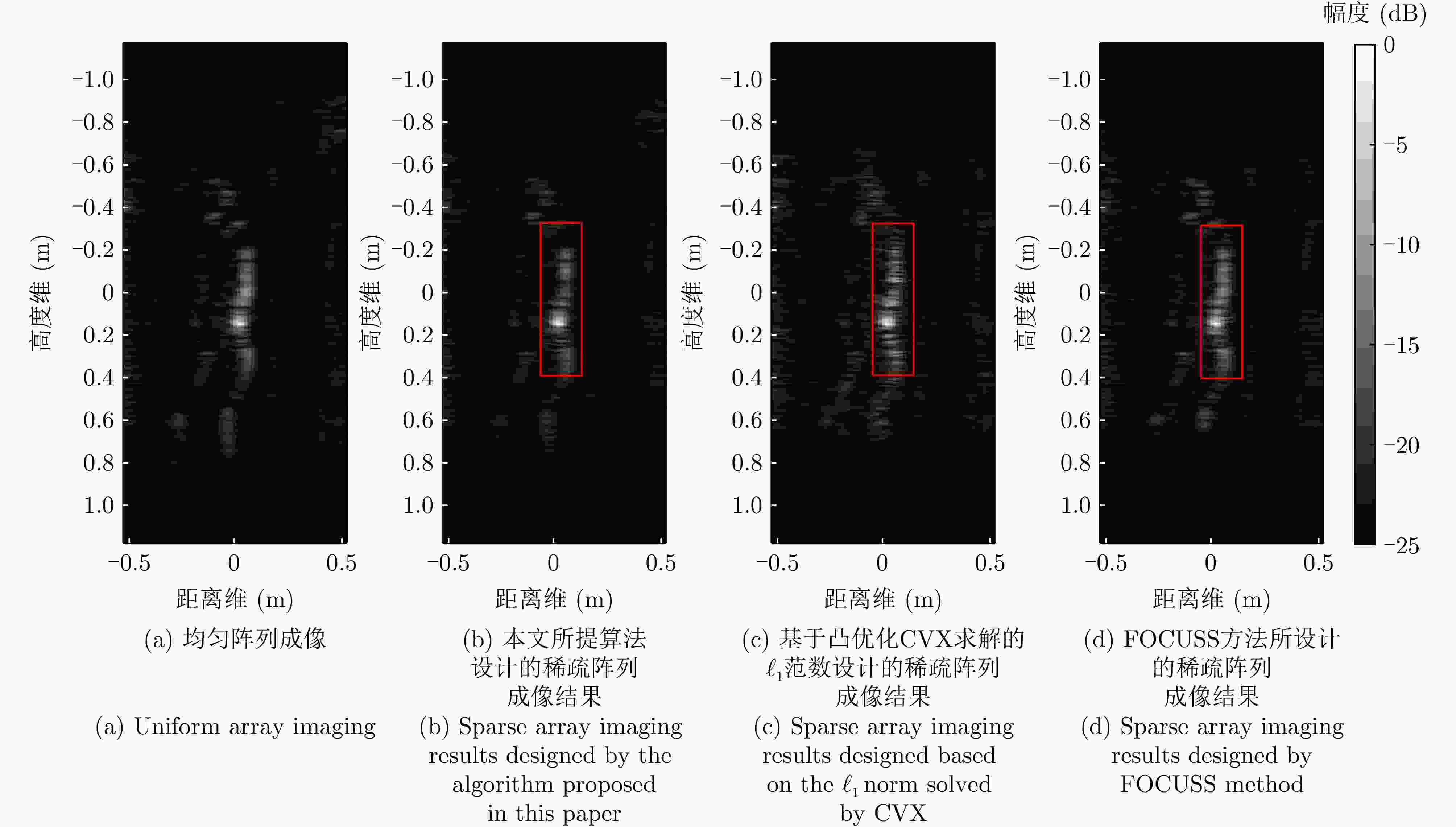
参数 数值 系统工作带宽 6.5 GHz 工作频率 27 GHz 目标距离 0.4~0.8 m 方位/俯仰角 55°/55° 采样点数 64 阵元间距 0.0052 m旋转次数 314 单次旋转角度 0.2867 °旋转半径 0.628 m 表 3 不同稀疏阵列综合方法成像结果边缘点的剖面图定量分析
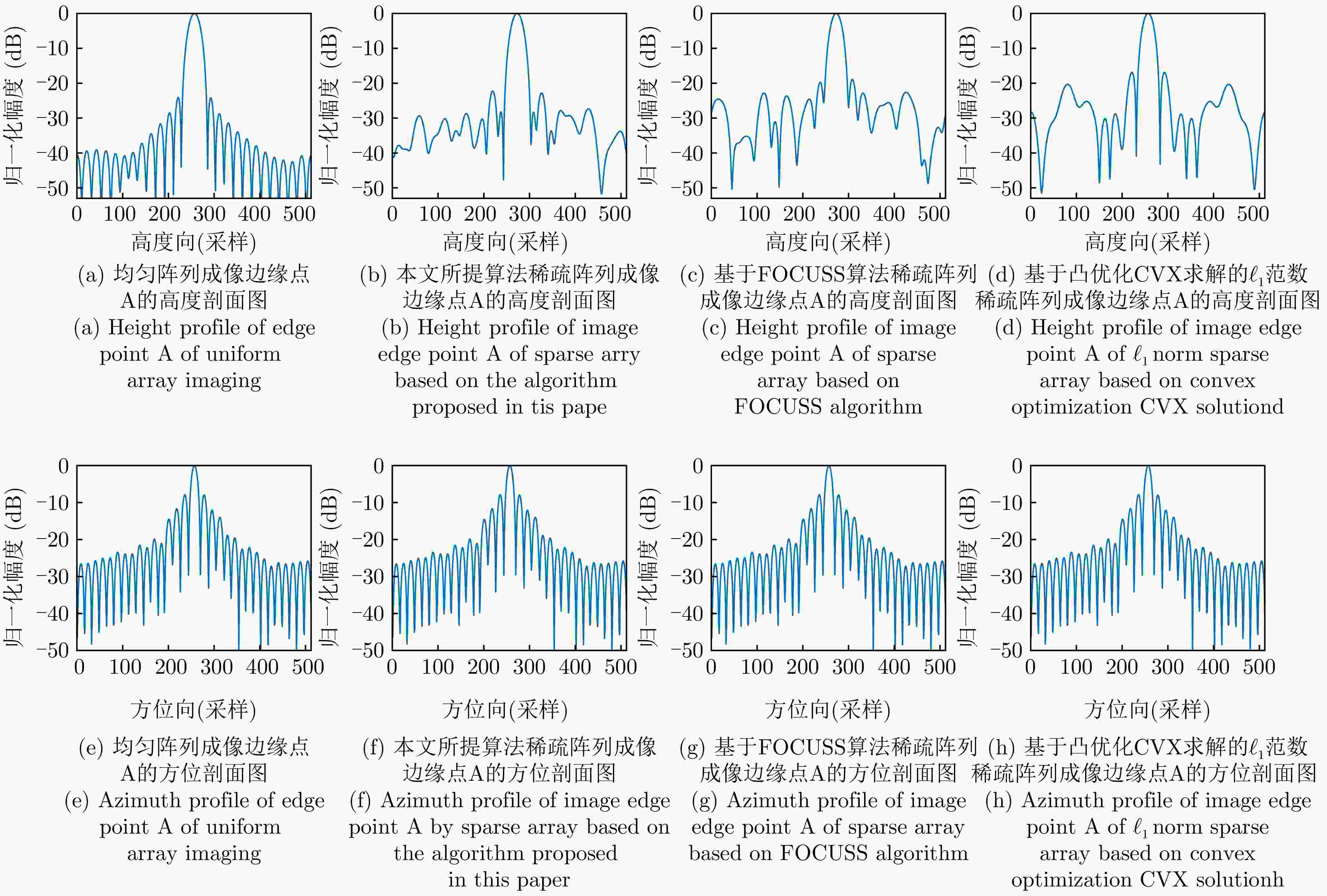
Table 3. Quantitative analysis of profile of edge points of imaging results by different sparse array synthesis methods
边缘点的成像结果 高度向峰值旁瓣比(dB) 3 dB宽度时高度
向分辨率(mm)方位向峰值旁瓣比(dB) 3 dB宽度时方位
向分辨率(mm)均匀阵列成像 –24.69 7.76 –8.01 4.2 本文所提算法稀疏阵列成像 –22.15 7.76 –8.01 4.2 基于FOCUSS算法稀疏阵列成像 –20.18 7.79 –8.01 4.2 基于凸优化CVX求解的${\ell _1}$范数稀疏阵列成像 –17.98 7.82 –8.01 4.2 表 1 Performance comparison of different sparse array synthesis algorithms
Method Peak sidelobe level (dB) Number of array elements Sparsity (%) Mean squared error The method proposed in this article –15.81 273 71.28 1.89×10 –4 ${\ell _1}$ norm –15.76 339 88.51 3.50×10 –3 FOCUS method –15.68 321 83.81 3.08×10 –4 表 2 Parameters of millimeter-wave electrical scanning circumferential imaging system
Parameter Numerical value System operating bandwidth 6.5 GHz Operating frequency 27 GHz Target distance 0.4~0.8 m Azimuth/elevation angle 55°/55° Sampling points 64 Element spacing 0.0052 mRotation times 314 Single rotation angle 0.2867 °Rotation radius 0.628 m 表 3 Quantitative analysis of profile of edge points of imaging results by different sparse array synthesis methods
Imaging results of edge points Height to peak sidelobe ratio (dB) Height resolution
(3 dB width) (mm)Azimuthal peak sidelobe ratio (dB) Azimuth Resolution
(3 dB width) (mm)Uniform array imaging –24.69 7.76 –8.01 4.2 The algorithm proposed in this article for sparse array imaging –22.15 7.76 –8.01 4.2 Sparse array imaging based on FOCUS algorithm –20.18 7.79 –8.01 4.2 ${\ell _1}$Norm sparse array imaging based on convex optimization CVX solution –17.98 7.82 –8.01 4.2 -
[1] 马宇欣, 海宇, 李中余, 等. 稀疏轨迹毫米波雷达三维高分辨成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1000–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR23001.MA Yuxin, HAI Yu, LI Zhongyu, et al. 3D high-resolution imaging algorithm with sparse trajectory for millimeter-wave radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1000–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR23001. [2] MA Zhaohui, WANG Jingyang, JING Handan, et al. Millimeter wave security imaging based on single-channel MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2020, 39(6): 709–717. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2020.06.008. [3] 刘可, 朱泽政, 于军, 等. 基于互质阵列孔洞分析的稀疏阵列设计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 372–379. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201024.LIU Ke, ZHU Zezheng, YU Jun, et al. Sparse array design methods based on hole analysis of the coprime array[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 372–379. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201024. [4] KARIMKASHI S and KISHK A A. Focused microstrip array antenna using a Dolph-Chebyshev near-field design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 57(12): 3813–3820. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2033435. [5] 赵磊, 黄昆, 郝鑫, 等. 近场雷达成像非均匀稀疏阵设计[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2017, 15(5): 707–710. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201705.0707.ZHAO Lei, HUANG Kun, HAO Xin, et al. Non-uniform sparse array design in near field radar imaging[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2017, 15(5): 707–710. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201705.0707. [6] ZHAO Dongdong, LIU Xuesong, CHEN Wenyuan, et al. Optimized design for sparse cross arrays in both near-field and far-field[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44(3): 783–795. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2018.2837458. [7] LEMAITRE-AUGER P, ABIELMONA S, and CALOZ C. Generation of Bessel beams by two-dimensional antenna arrays using sub-sampled distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(4): 1838–1849. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2232263. [8] LI Pengfa, QU Shiwei, YANG Shiwen, et al. Focused array antenna based on subarrays[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 888–891. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2613887. [9] RUDOLPH D L and BAROTT W C. Reduction of near-field grating lobes in sparse linear phased arrays[C]. 2014 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Memphis, USA, 2014: 1155–1156. doi: 10.1109/APS.2014.6904904. [10] OLIVERI G and MASSA A. Bayesian compressive sampling for pattern synthesis with maximally sparse non-uniform linear arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2011, 59(2): 467–481. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2096400. [11] OLIVERI G, CARLIN M, and MASSA A. Complex-weight sparse linear array synthesis by Bayesian compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(5): 2309–2326. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2189742. [12] 杨磊, 陈英杰, 王腾腾, 等. 旅客人身时频调和型毫米波三维重建[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2023, 42(3): 327–338. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2023.03.006.YANG Lei, CHEN Yingjie, WANG Tengteng, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm for passengers based on time-frequency coordination[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2023, 42(3): 327–338. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2023.03.006. [13] 陈秀琴, 李跃华, 孔令雄. 毫米波近场成像及图像增强算法研究[J]. 微波学报, 2023, 39(S1): 324–327.CHEN Xiuqin, LI Yuehua, and KONG Lingxiong. Research on millimeter wave near field imaging and image enhancement algorithms[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2023, 39(S1): 324–327. [14] 谢朋飞, 张磊, 吴振华. 融合ω-K和BP算法的圆柱扫描毫米波三维成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 387–394. doi: 10.12000/JR17112.XIE Pengfei, ZHANG Lei, and WU Zhenhua. A three-dimensional imaging algorithm fusion with ω-K and BP algorithm for millimeter-wave cylindrical scanning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 387–394. doi: 10.12000/JR17112. [15] LIN Zhenwei, CHEN Yaowu, LIU Xuesong, et al. Optimized design for sparse arrays in 3-D imaging sonar systems based on perturbed Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(10): 5554–5565. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2971568. [16] 宋嘉奇, 陶海红. 一种稀布阵列天线的近场波束综合算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(6): 14–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.06.003.SONG Jiaqi and TAO Haihong. Near-field beam synthesis algorithm for sparse array antennas[J]. Journal of Xidian University: Natural Science, 2018, 45(6): 14–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.06.003. [17] HUANG Zixuan and CHENG Yujian. Near-field pattern synthesis for sparse focusing antenna arrays based on Bayesian compressive sensing and convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(10): 5249–5257. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2860044. [18] KIM S, DONG H J, YU J W, et al. Phased array calibration system with high accuracy and low complexity[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2023, 69: 759–770. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2023.02.026. [19] 祁峥东, 卢阳沂, 孔玥, 等. 基于多凸优化的稀疏线性阵列综合方法[J]. 雷达与对抗, 2019, 39(4): 21–24, 49. doi: 10.19341/j.cnki.issn.1009-0401.2019.04.006.QI Zhengdong, LU Yangyi, KONG Yue, et al. Synthesis of sparse linear arrays based on multi-convex optimization[J]. Radar & ECM, 2019, 39(4): 21–24, 49. doi: 10.19341/j.cnki.issn.1009-0401.2019.04.006. [20] BABACAN S D, MOLINA R, and KATSAGGELOS A K. Bayesian compressive sensing using Laplace priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(1): 53–63. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2032894. [21] LIU Ying, ZHANG Zongyu, ZHOU Chengwei, et al. Robust variational Bayesian inference for direction-of-arrival estimation with sparse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(8): 8591–8602. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3173418. [22] ZHAO Xiaowen, YANG Qingshan, and ZHANG Yunhua. A hybrid method for the optimal synthesis of 3-D patterns of sparse concentric ring arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(2): 515–524. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2504377. [23] 李浩林, 陈露露, 张磊, 等. 快速分解后向投影SAR成像的自聚焦算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 938–945. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00011.LI Haolin, CHEN Lulu, ZHANG Lei, et al. Study of autofocus method for SAR imagery created by fast factorized backprojection[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 938–945. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00011. [24] MA Chengzheng, YEO T S, LIU Zhoufeng, et al. Target imaging based on ℓ1ℓ0 norms homotopy sparse signal recovery and distributed MIMO antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(4): 3399–3414. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140939. [25] 杨鹏, 闫飞, 张胜辉, 等. 基于FOCUSS算法的稀疏阵列综合[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2014, 43(2): 203–206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2014.02.008.YANG Peng, YAN Fei, ZHANG Shenghui, et al. Sparse array synthesis based on FOCUSS algorithm[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2014, 43(2): 203–206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2014.02.008. [26] 邢孟道, 马鹏辉, 楼屹杉, 等. 合成孔径雷达快速后向投影算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(1): 1–22. doi: 10.12000/JR23183.XING Mengdao, MA Penghui, LOU Yishan, et al. Review of fast back projection algorithmsin synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 1–22. doi: 10.12000/JR23183. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: