A Land Bridge Extraction Method Based on Polarized Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar Images
-
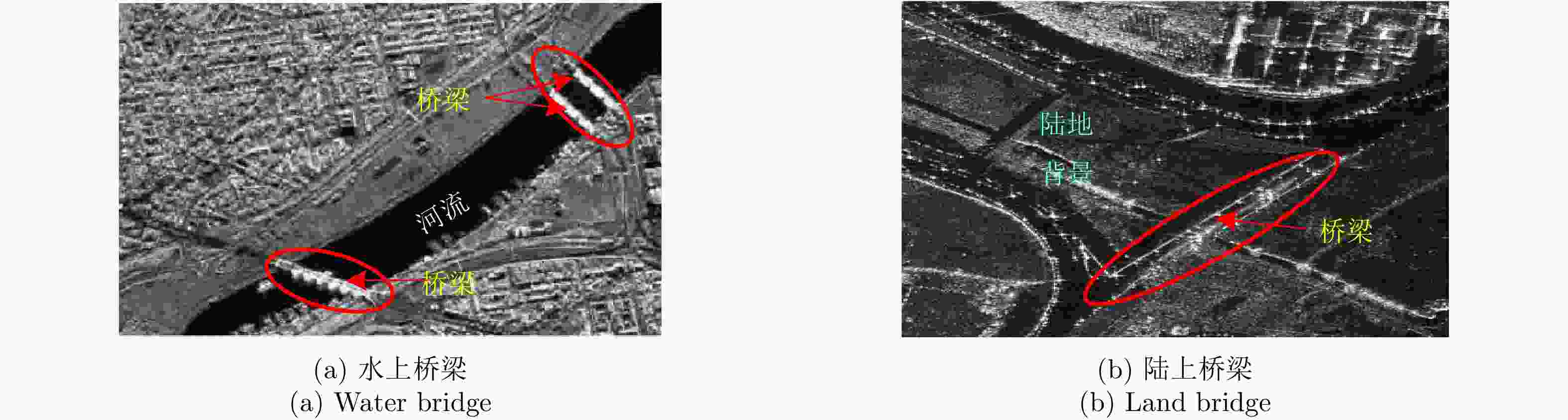
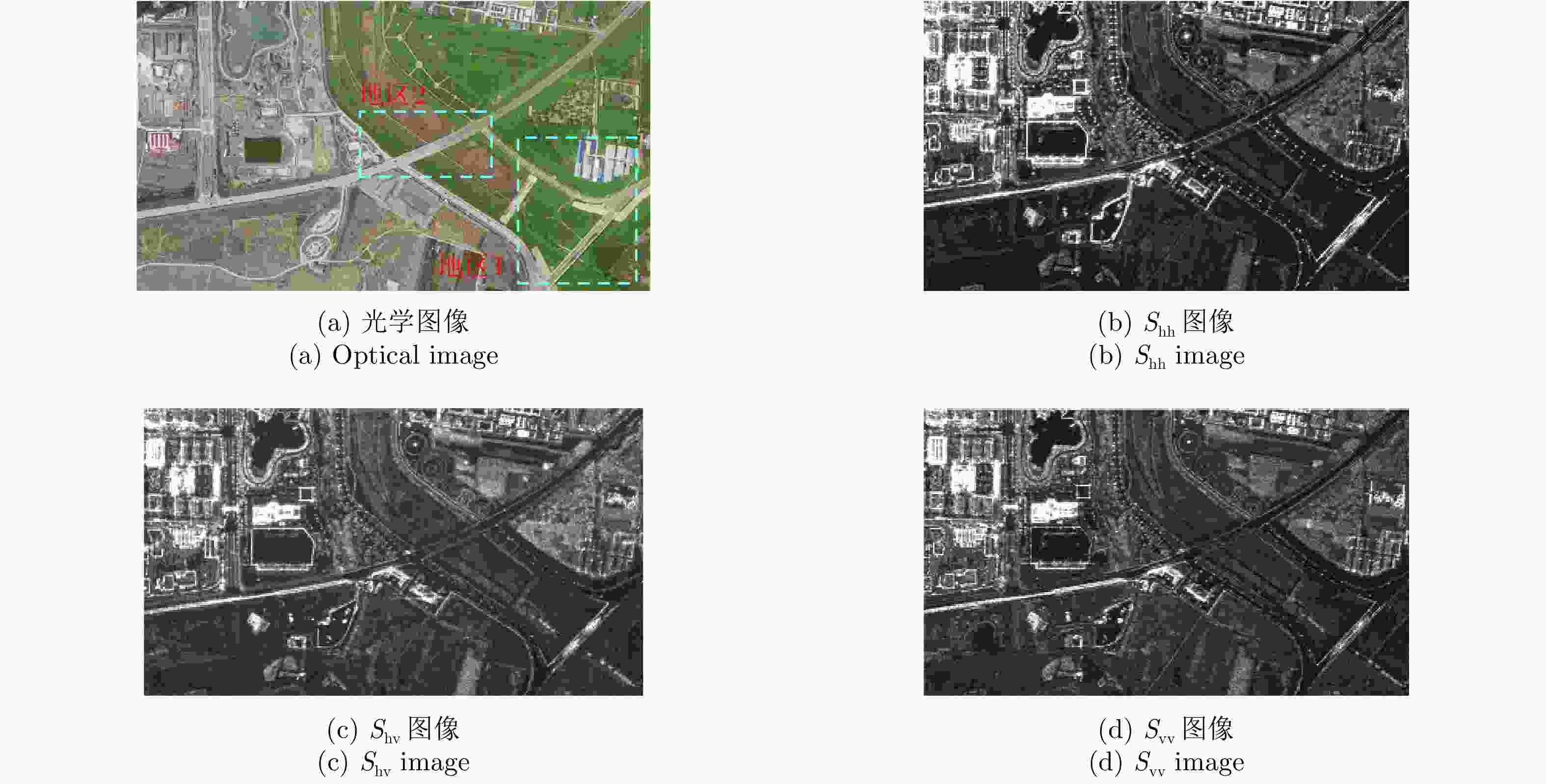
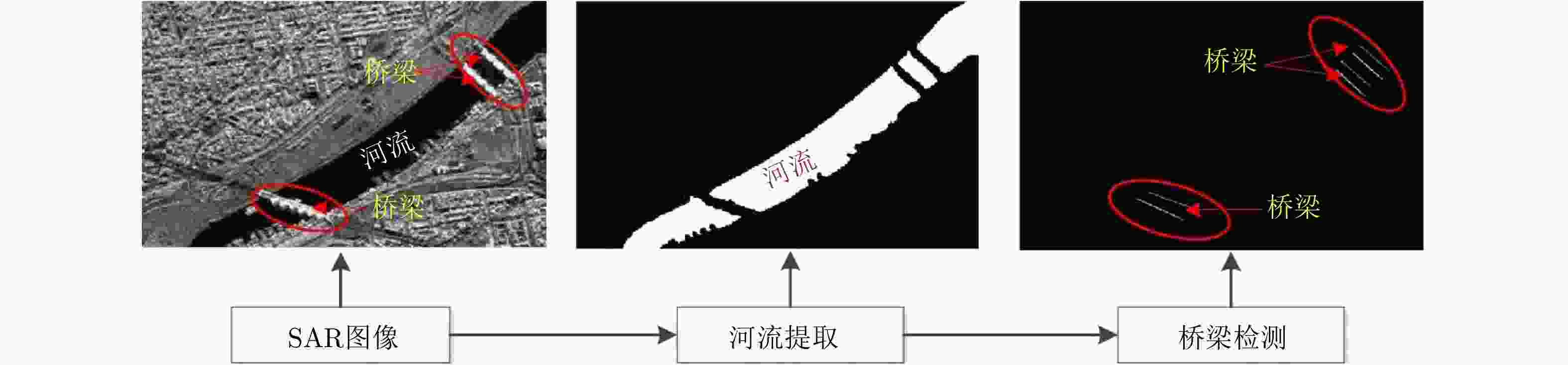
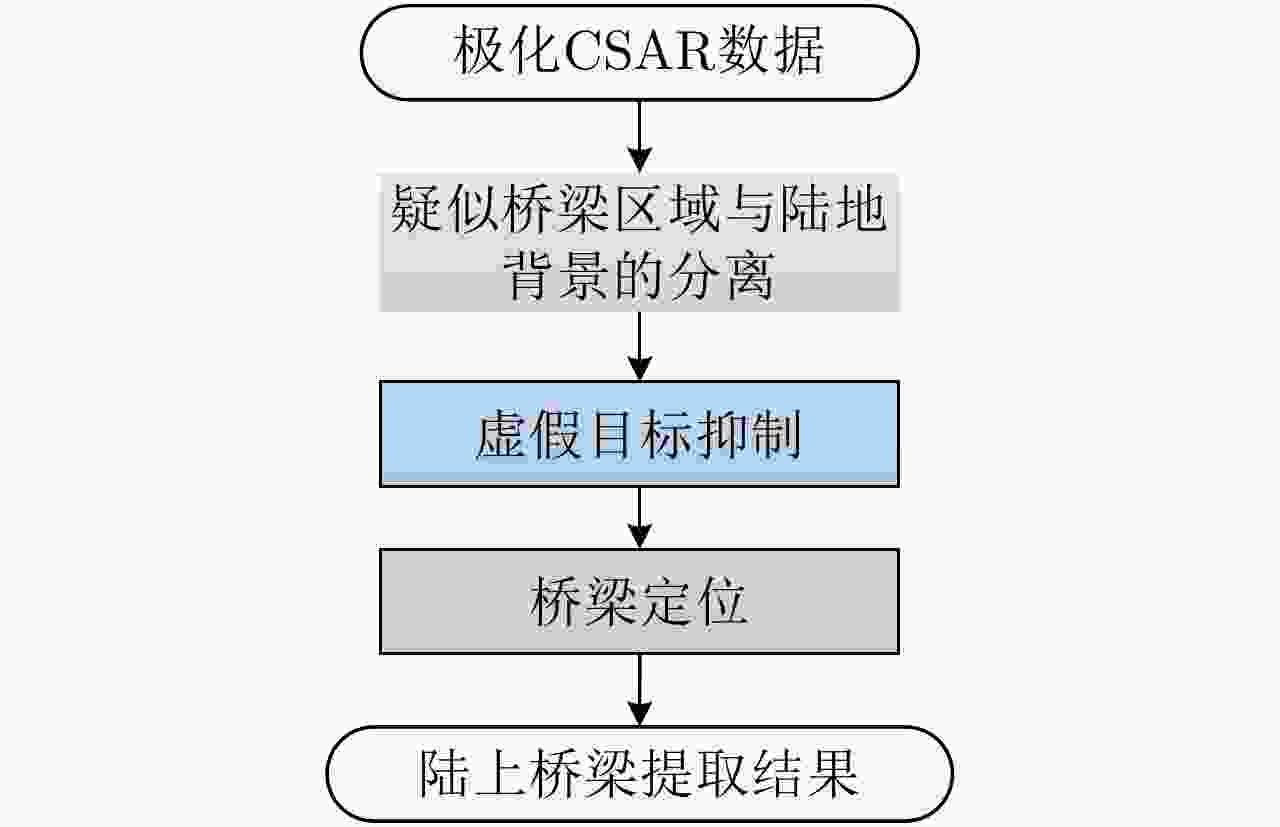
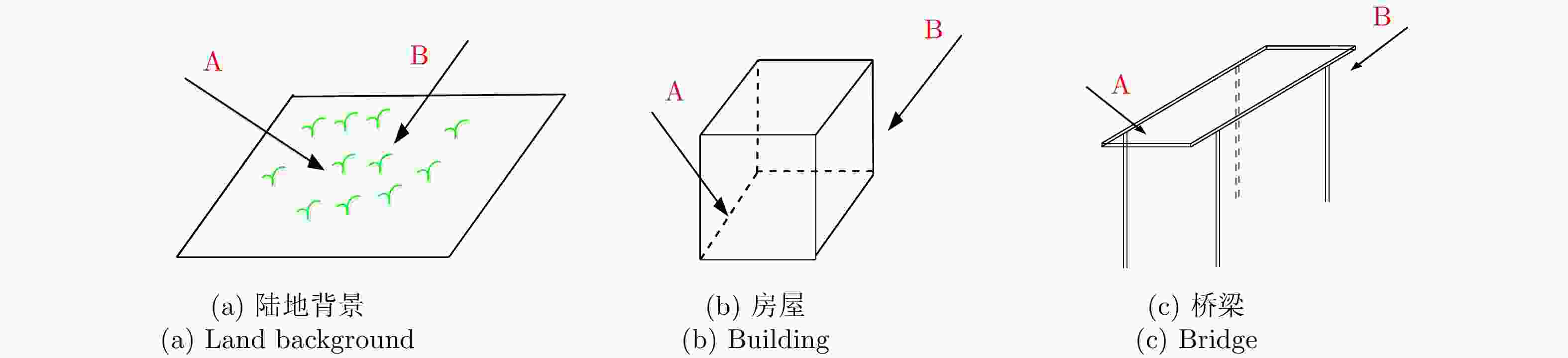
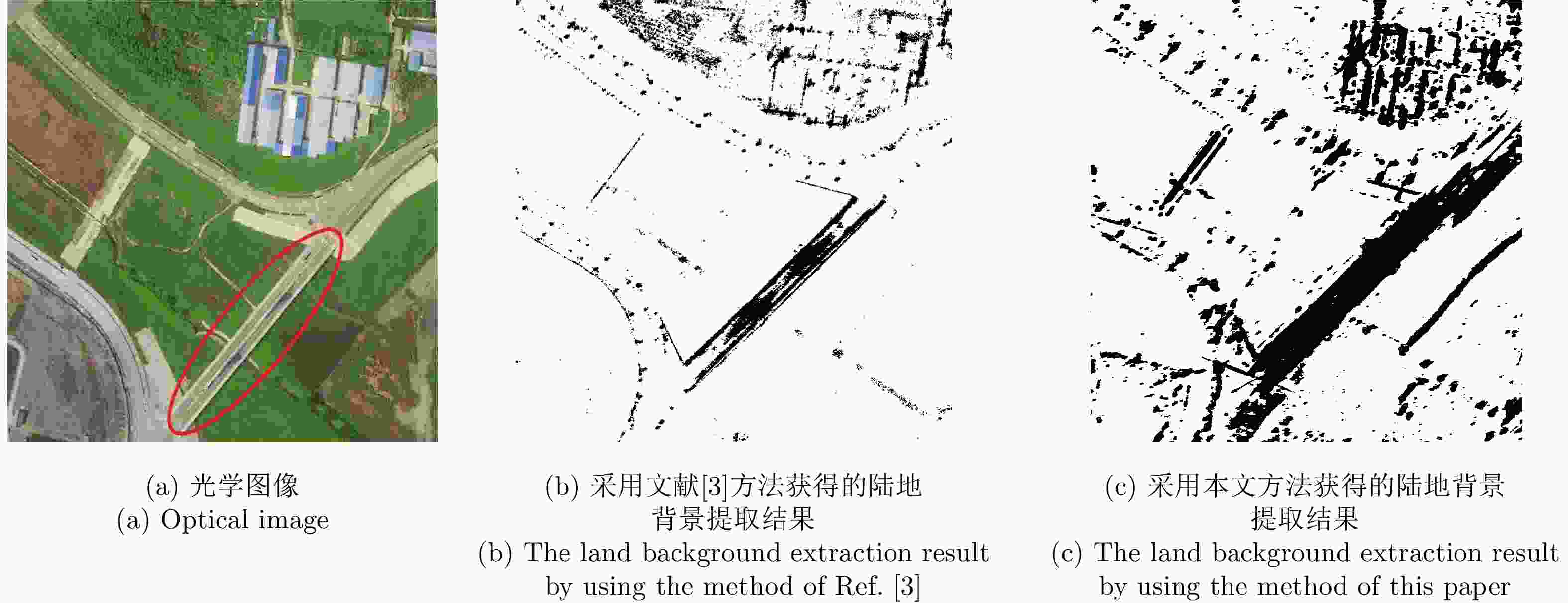
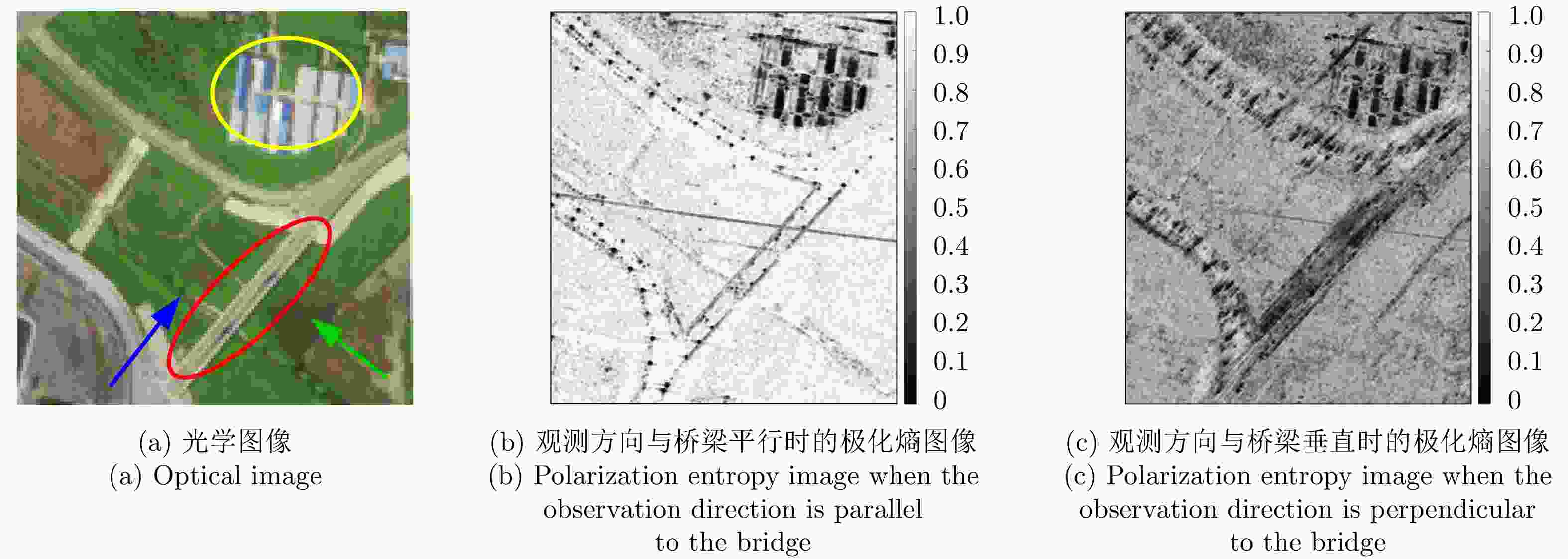
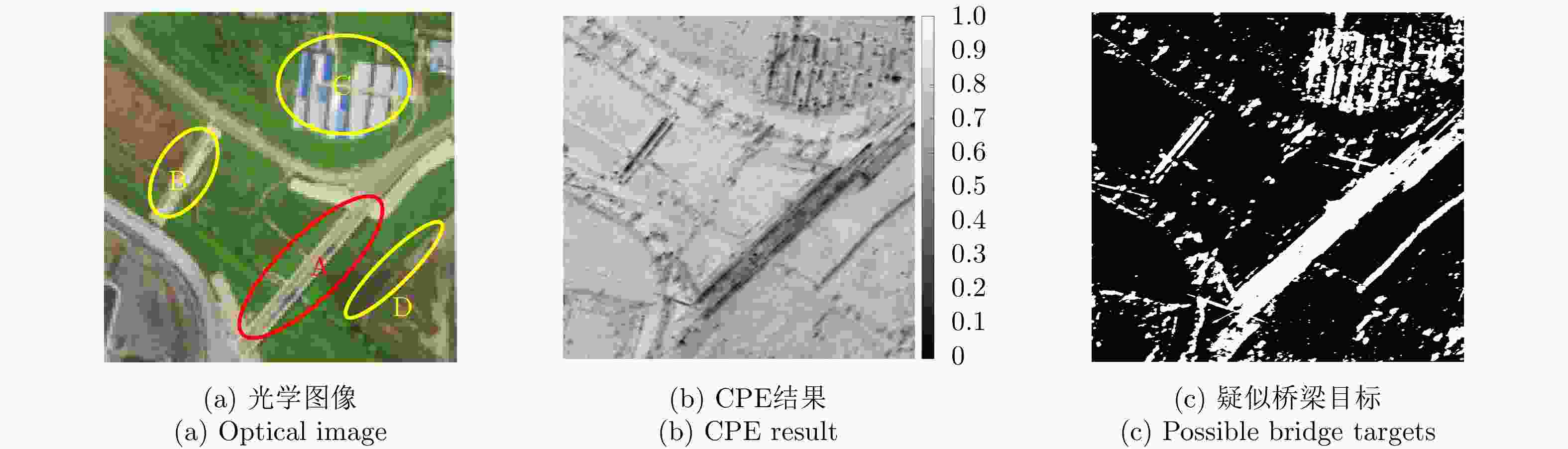
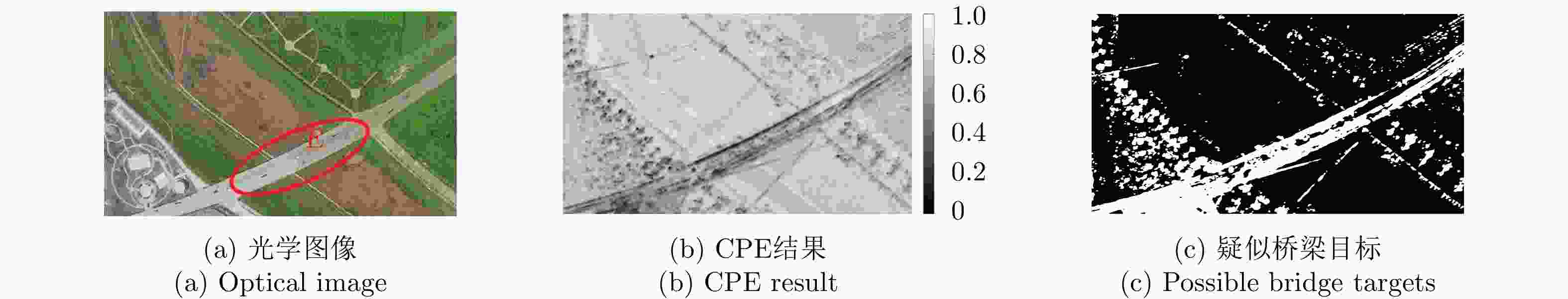
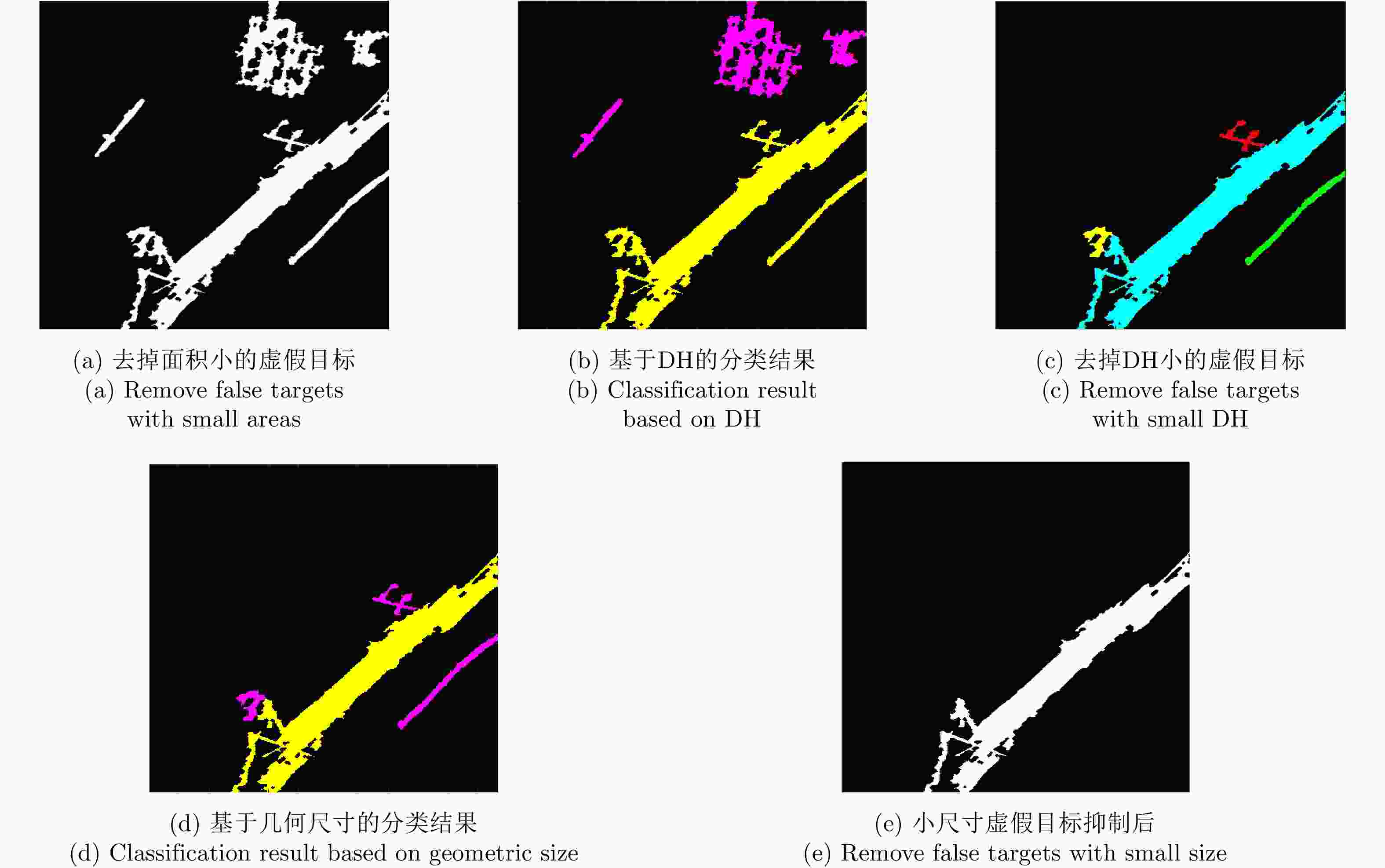
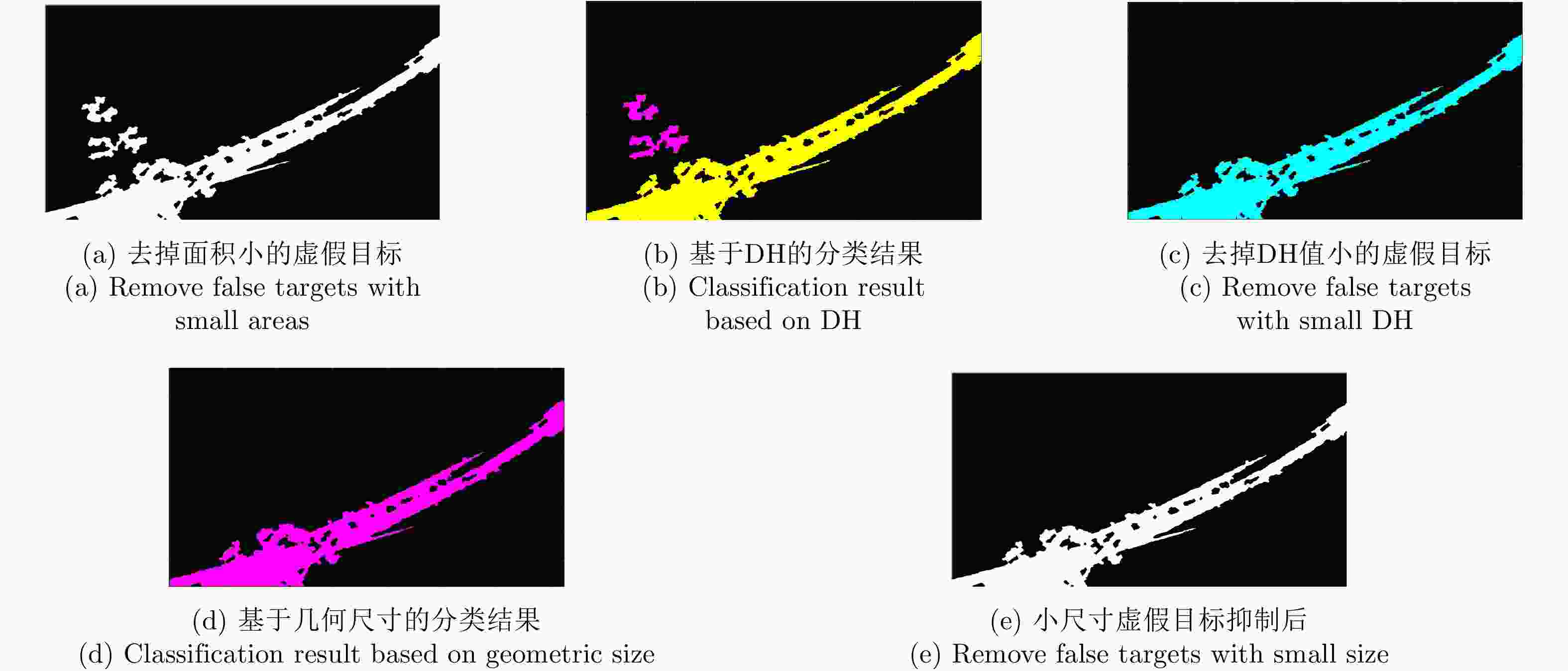
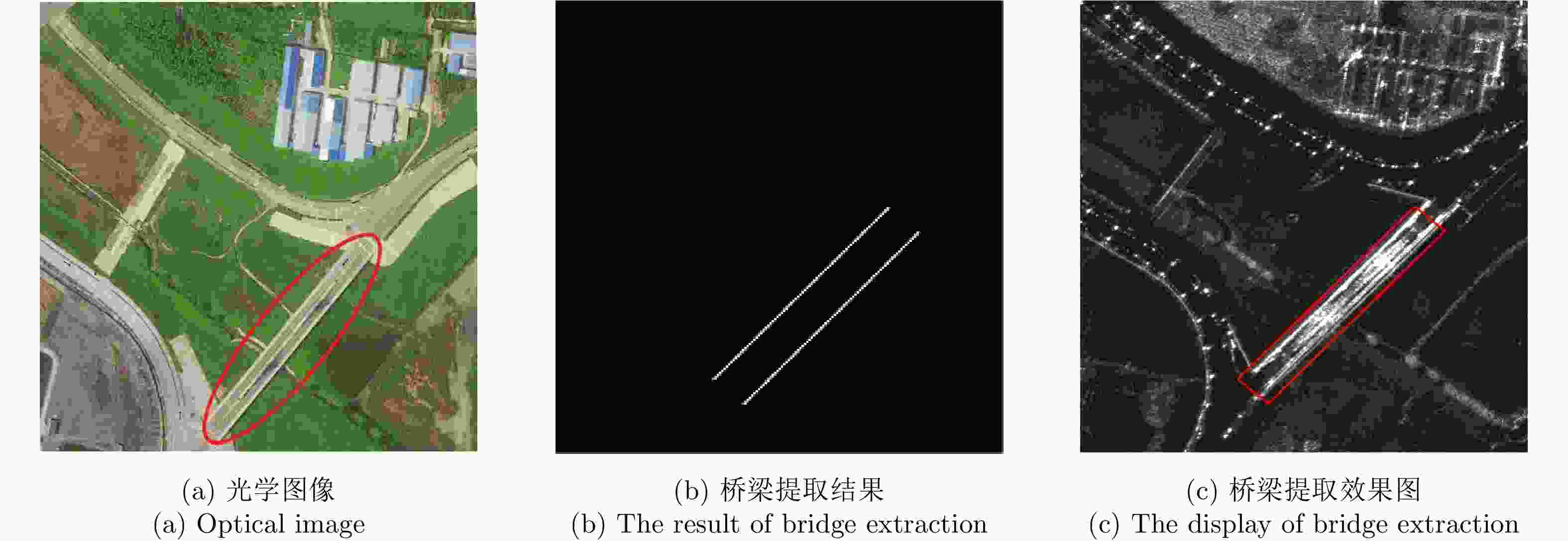
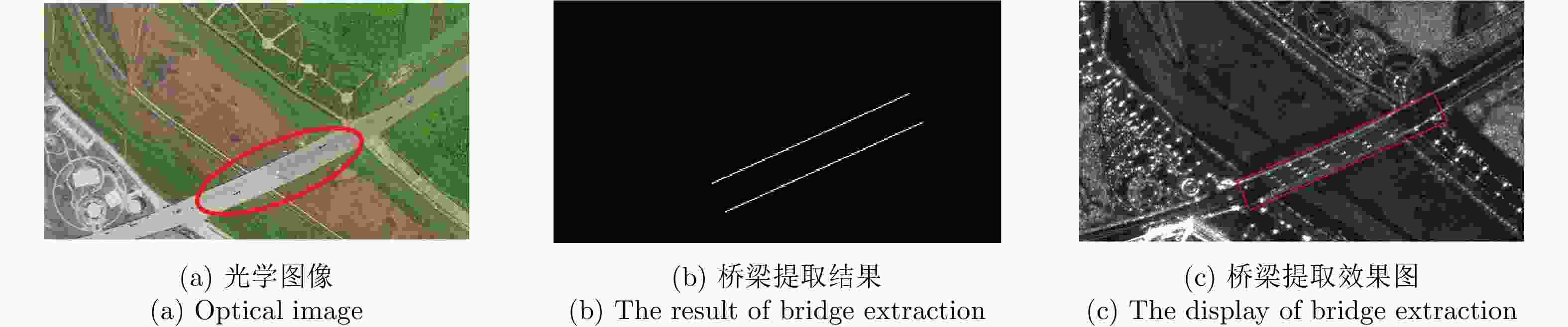
摘要: 桥梁作为重要的人造目标,一直都是合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像解译的重要对象之一。目前针对桥梁检测问题已开展了较多研究,核心思想是:首先提取出河流水体,然后再根据河流与桥梁的位置关系检测桥梁。然而,已有的桥梁检测方法依赖于河流提取,很难实现陆上桥梁检测。因为陆上桥梁下方的背景不再是河流,而是陆地,其散射特性、形状分布与河流不同,不能采用传统的水体提取方法来检测陆地背景,进而无法利用桥梁的位置先验知识定位桥梁。针对该问题,该文提出了一种基于极化圆周SAR(CSAR)图像的陆上桥梁检测方法。首先,利用观测场景的圆周极化熵(CPE)实现疑似桥梁目标与陆地背景的分离(该实验中桥梁的CPE均值为0.4018,陆地背景的CPE均值为0.7819,两者具有明差别);然后,根据地物目标的极化熵方差特征和桥梁尺寸特性,抑制虚假目标;最后,根据桥梁的几何特征实现陆上桥梁的准确提取。该文所提方法解决了传统桥梁检测方法需要基于河流提取结果才能实现桥梁检测的问题。机载L波段极化CSAR实测数据处理结果证明了所提方法的正确性、有效性和实用性。Abstract: As important man-made targets, bridges have been a major focus of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image interpretation, and many researchers have developed methods for bridge detection. The core frameworks of these methods are analogical, a river is first extracted, and a water bridge is detected based on the positional relationship between the river and bridge. However, existing bridge detection methods relying on river extraction; cannot be utilized detect land bridges. This is because the background environment under a bridge is land, not river, which has different scattering characteristics and shape layouts. As such, the traditional method for extracting rivers is not suitable for extracting land background, and it is impossible to locate a bridge based on prior knowledge of its location of. To resolve this problem, in this study, we propose a land bridge detection method based on polarized Circular SAR (CSAR) images. In our proposed method, the Circular Polarization Entropy (CPE) of an observed scene is introduced to separate possible bridge targets from a land background (In our experiment, the average CPE of the bridge is 0.4018, and that of the land background is 0.7819; thus there is a clear difference between the bridge and background). False targets are removed based on the difference in the polarization entropy variance features of the bridges and other ground objects; and the size characteristics of the bridges. Finally, accurate extractions of land bridges are obtained based on the geometric characteristics of the bridges. Experimental results based on real airborne L-band polarized CSAR data verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis and effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
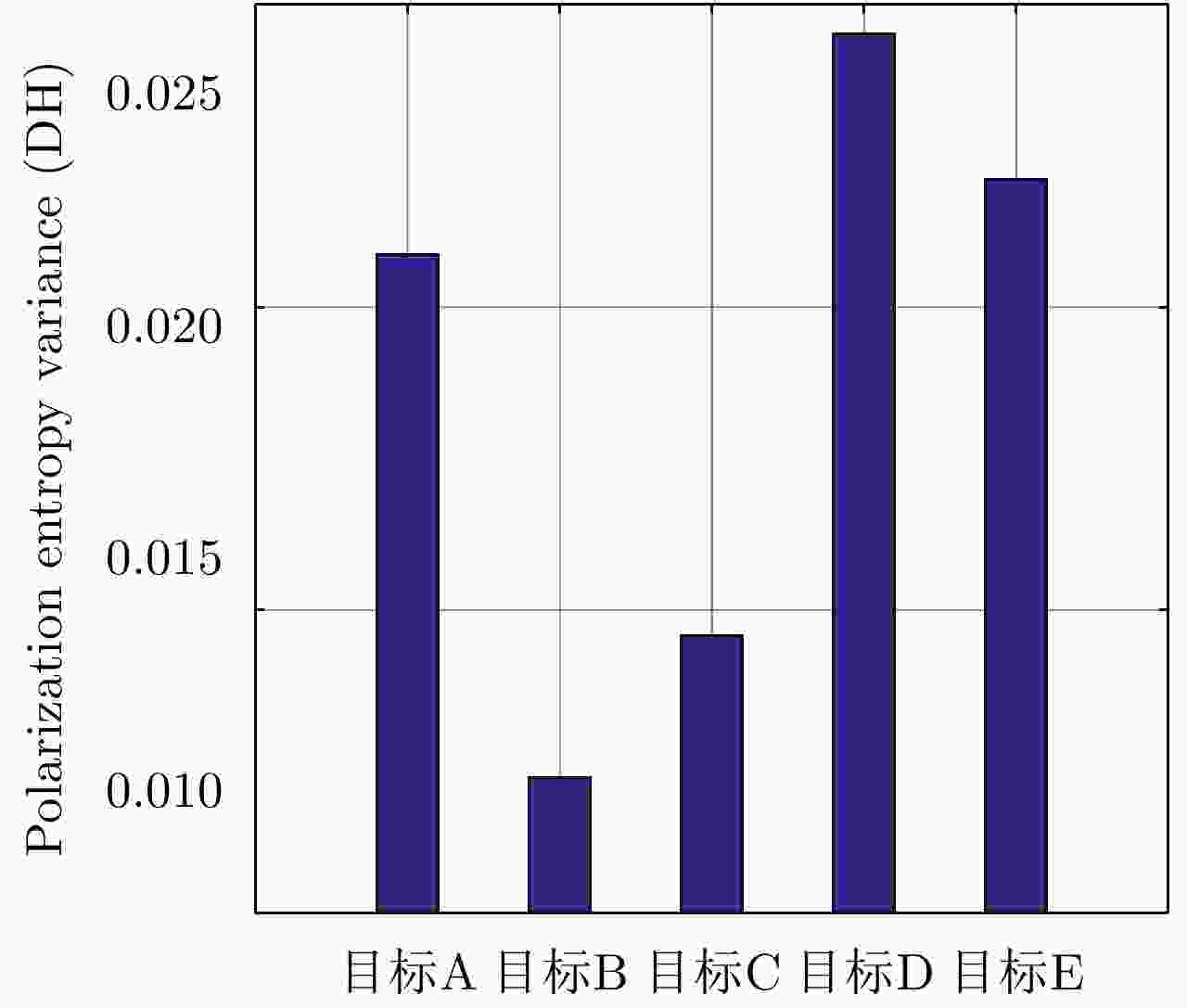
图 13 不同疑似桥梁目标(如图11(a)所示)的DH值
Figure 13. The DH values of different possible bridge targets (As shown in Fig. 11(a))
表 1 疑似桥梁区域与陆地背景的分离阈值
Table 1. The separation threshold between possible bridge region and land background
区域 分离阈值 地区1 0.6118 地区2 0.6549 表 2 桥梁和陆地背景的CPE均值
Table 2. The CPE mean value of land bridge and its background
目标 CPE均值 桥梁 0.4018 陆地背景 0.7819 表 3 桥梁边缘所在直线参数
Table 3. Straight line parameters at the edge of the bridges
区域 桥梁边缘直线斜率 (°) 桥梁边缘直线截距 (pixels) 地区1 47.5 –237 47.5 –387 地区2 24.8 –48 24.8 –155 -
[1] HAN Yu, ZHENG Hong, CAO Qiong, et al. An effective method for bridge detection from satellite imagery[C]. The 2007 2nd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Harbin, China, 2007: 2753–2757. [2] LUO J, MING D, LIU W, et al. Extraction of bridges over water from IKONOS panchromatic data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2007, 28(16): 3633–3648. doi: 10.1080/01431160601024226 [3] 赵冠雄, 沈汀. 高分辨率SAR图像桥梁自动提取算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2014, 35(8): 2793–2797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2014.08.034ZHAO Guanxiong and SHEN Ting. Automatic bridge extraction algorithm from high-resolution SAR image[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2014, 35(8): 2793–2797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2014.08.034 [4] ZHANG Xiongmei, SONG Jianshe, YI Zhaoxiang, et al. Extraction and recognition of bridges over water in high resolution SAR image[C]. 2011 MSEC International Conference on Multimedia, Software Engineering and Computing, Wuhan, China, 2011: 19–24. [5] 刘春, 杨健, 徐丰, 等. 基于水域跟踪的极化SAR图像桥梁检测[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 57(12): 1303–1309. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2017.25.057LIU Chun, YANG Jian, XU Feng, et al. Bridge detection in polarimetric SAR images based on water area tracing[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2017, 57(12): 1303–1309. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2017.25.057 [6] 张永梅, 孙静, 叶晨. 基于互补特征的桥梁识别方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2014, 31(3): 151–155, 158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2014.03.040ZHANG Yongmei, SUN Jing, and YE Chen. A bridge recognition method based on complementary features[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2014, 31(3): 151–155, 158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2014.03.040 [7] 熊伟, 钟娟娟, 曹兰英. 一种高分辨率SAR图像水上桥梁目标识别新方法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2014, 39(4): 133–136, 140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2014.04.033XIONG Wei, ZHONG Juanjuan, and CAO Lanying. A novel algorithm for bridge recognition over water in high resolution SAR image[J]. Fire Control &Command Control, 2014, 39(4): 133–136, 140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2014.04.033 [8] 安道祥, 陈乐平, 冯东, 等. 机载圆周SAR成像技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 221–242. doi: 10.12000/JR20026AN Daoxiang, CHEN Leping, FENG Dong, et al. Study of the airborne circular synthetic aperture radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 221–242. doi: 10.12000/JR20026 [9] 王建峰, 林赟, 郭胜龙, 等. 圆迹SAR的建筑物全方位优化成像方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 698–707. doi: 10.12000/JR15069WANG Jianfeng, LIN Yun, GUO Shenglong, et al. Circular SAR optimization imaging method of buildings[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 698–707. doi: 10.12000/JR15069 [10] 洪文. 圆迹SAR成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046HONG Wen. Progress in circular SAR imaging technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046 [11] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. Resolution analysis of circular synthetic aperture radar noncoherent imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(1): 231–240. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2890932 [12] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 吴一戎. 全息合成孔径雷达的概念、体制和方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, and WU Yirong. Concept, system, and method of holographic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063 [13] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [14] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047WU Yirong. Concept of multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047 [15] LUO Yuxiao, AN Daoxiang, WANG Wu, et al. Improved ROEWA SAR image edge detector based on curvilinear structures extraction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 631–635. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2926428 [16] 李洋, 王官云, 王彦平, 等. 多角度极化SAR图像散射特征分解及SVM分类[J]. 电波科学学报, 2019, 34(6): 771–777. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019043002LI Yang, WANG Guanyun, WANG Yanping, et al. Scattering feature decomposition and SVM classification of multi-angle polarimetric SAR images[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2019, 34(6): 771–777. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019043002 [17] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. A 3D reconstruction strategy of vehicle outline based on single-pass single-polarization CSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(11): 5545–5554. [18] XUE Feiteng, LIN Yun, HONG Wen, et al. Analysis of azimuthal variations using multi-aperture polarimetric entropy with circular SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(1): 123. doi: 10.3390/rs10010123 [19] XUE Feiteng, LIN Yun, HONG Wen, et al. An improved h/α unsupervised classification method for circular PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34296–34306. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2838329 [20] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: