LASAR High-resolution 3D Imaging Algorithm Based on Sparse Bayesian Regularization
-
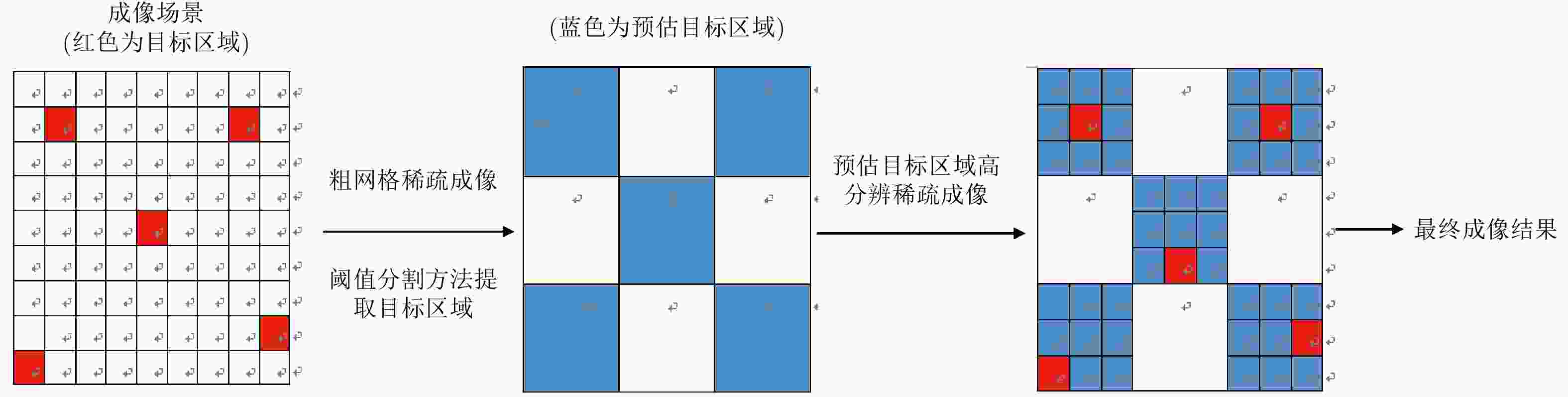
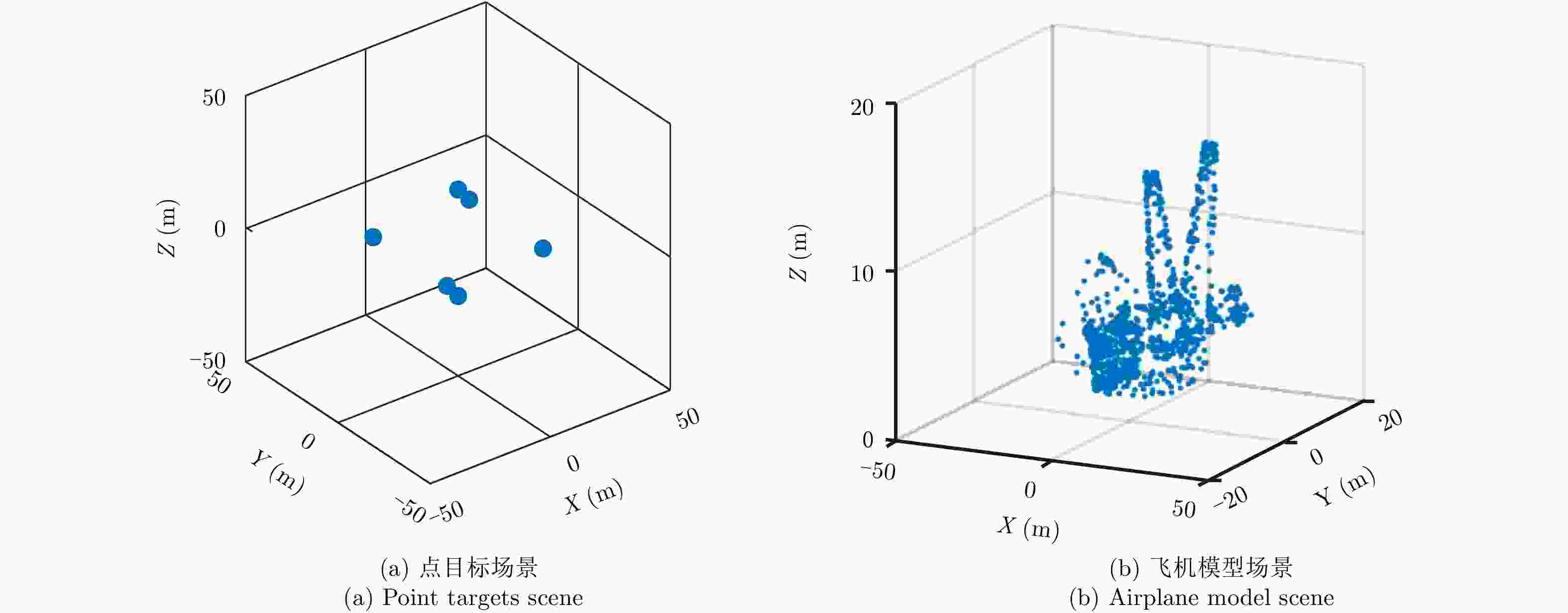
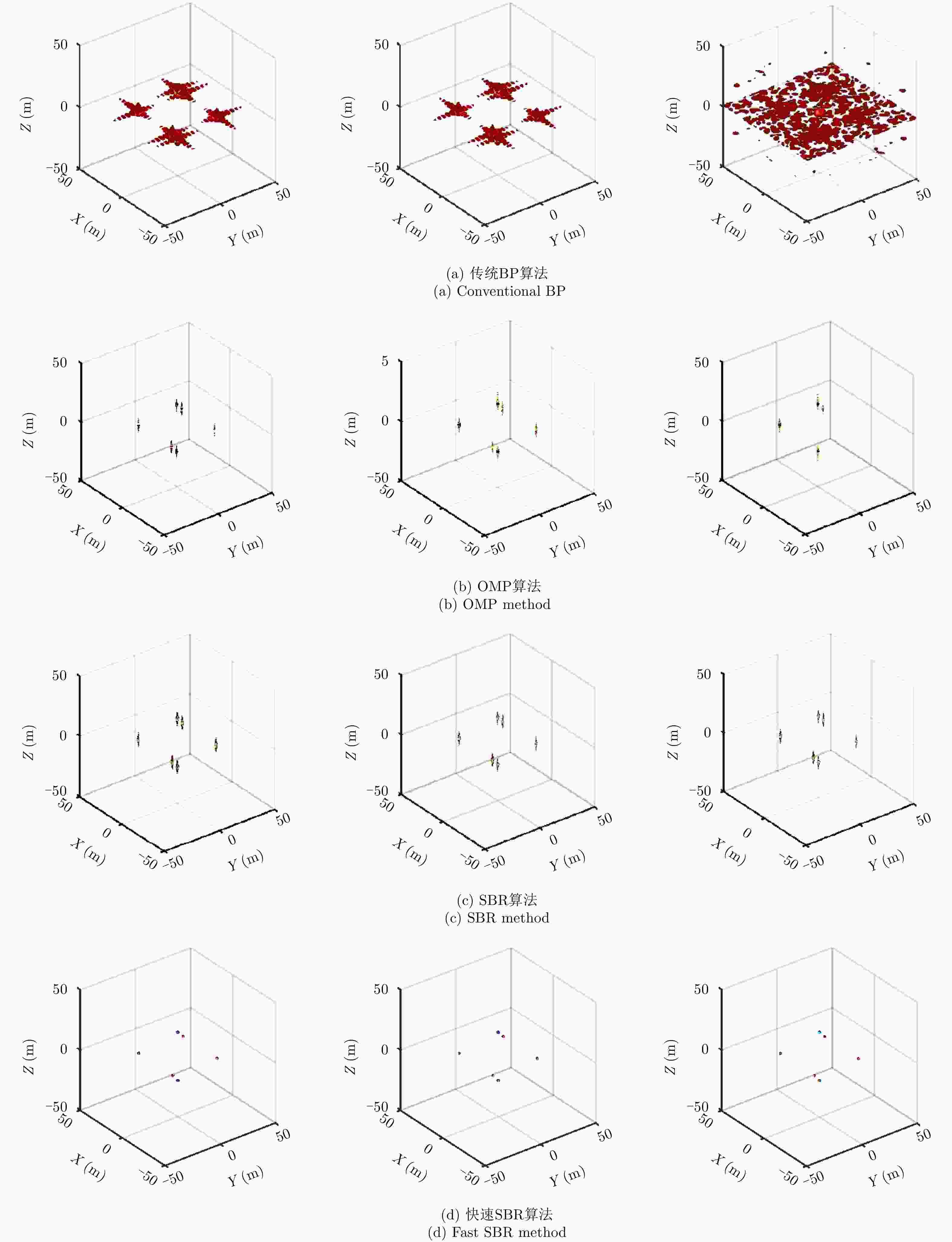
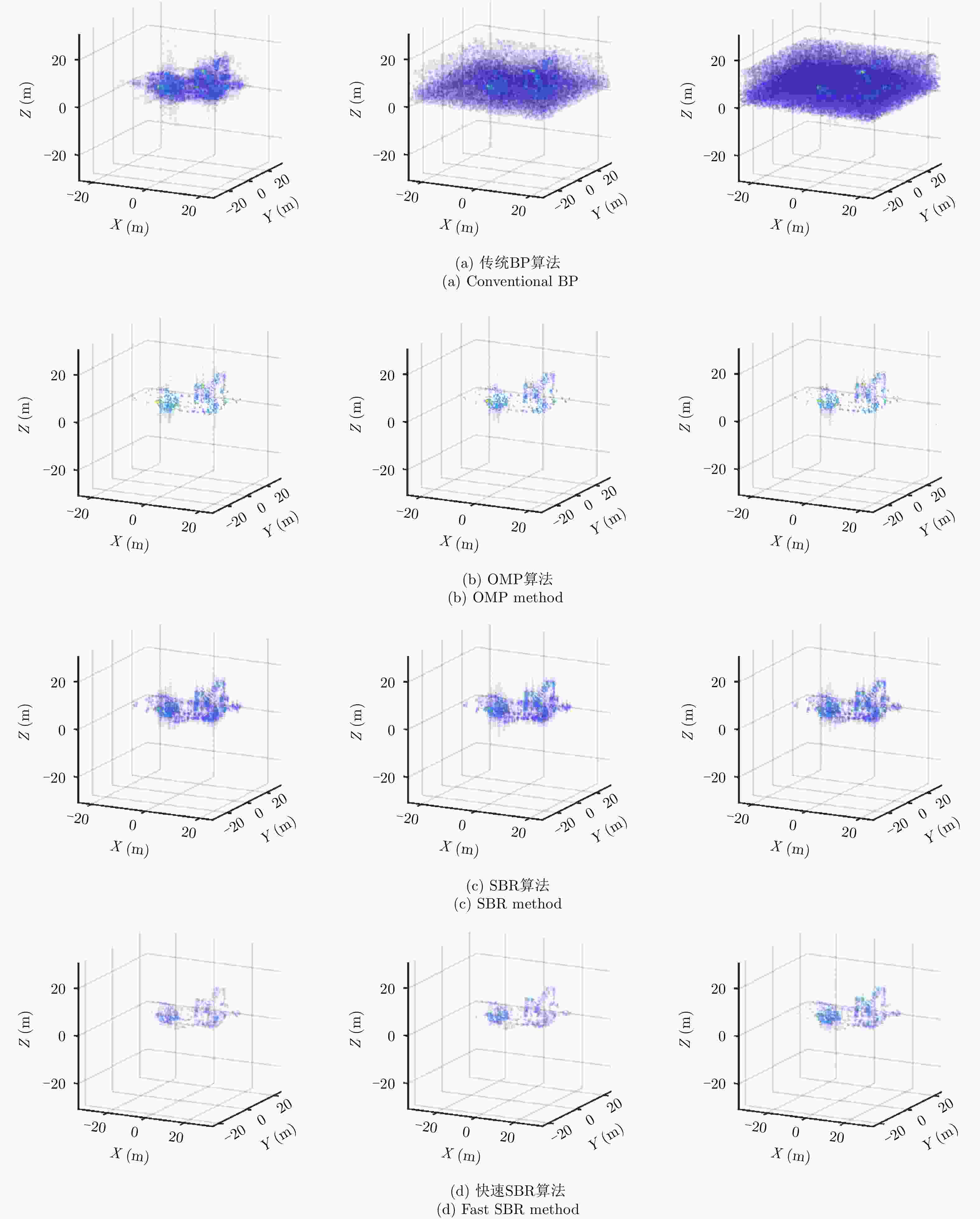
摘要: 阵列合成孔径雷达(Linear Array Synthetic Aperture Radar, LASAR) 3维成像技术是一种具有重要潜在应用价值的雷达成像新体制,但受线阵天线及平台尺寸限制,传统匹配滤波成像算法难以实现LASAR高分辨3维成像。该文利用LASAR回波信号及观测目标的先验分布特性,提出了一种基于快速稀疏贝叶斯正则化重构的LASAR高分辨3维成像算法。该算法先结合贝叶斯估计准则及最大似然估计原理,构造LASAR目标重构的稀疏贝叶斯最小化代价函数;再利用迭代正则化方法求解联合范数最优化问题实现LASAR稀疏目标高分辨3维成像。另外,针对稀疏贝叶斯正则化成像运算量大的问题,结合位置预测快速成像思路,利用阈值分割算法对稀疏粗成像进行强目标提取,进而提升算法运算效率。仿真数据和实测数据验证了该文算法的有效性。Abstract: Linear Array Synthetic Aperture Radar (LASAR) is a novel and promising radar imaging technique. It is difficult to achieve high-resolution LASAR three-dimensional (3D) imaging using the traditional imaging methods based on match filter, because of limitations by the sizes of the linear array antenna and the platform. In this paper, by exploiting the prior distribution of the LASAR echoes and the observed scene, an LASAR high-resolution 3D algorithm based on sparse Bayesian regularization is proposed. The algorithm first combines the Bayesian principle and maximum likelihood estimation theory, and then a sparse Bayesian minimum cost function is constructed for LASAR target recovery. Second, using an iterative regularization reconstruction method, high-resolution imaging of LASAR sparse targets is achieved by solving a joint-norms optimization problem. In addition, for the problem of a large amount of sparse Bayesian regularization imaging, combined with the position prediction fast imaging idea, the threshold segmentation algorithm is used to extract the strong target of sparse coarse imaging, and then the algorithm operation efficiency is improved. Simulation and experiment results are presented to confirm the effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
表 1 SBR算法
Table 1. SBR algorithm
算法:SBR算法 输入:测量信号 ${{{y}}_S}$,测量矩阵 ${{Θ}}$,迭代误差门限 $\gamma $
输出:稀疏散射系数 $\hat {{α}}$
初始化:估计值 ${\hat {{α}}^{\left( 0 \right)}} = {{{Θ}}^{\rm H}}{{{y}}_S}$, ${\hat \beta ^{\left( 0 \right)}} = {{\left\| {{{{y}}_S} - {{Θ}}{{\hat {{α}}}^{\left( 0 \right)}}} \right\|_2^2}\Bigr/N}$,
${{\hat \varepsilon } ^{\left( 0 \right)}} = {{\left\| {{{\hat {{α}}}^{\left( 0 \right)}}} \right\|_2^2}\Bigr/M}$,迭代次数 $n = 0$
循环开始
(1) 估计散射系数向量 ${\hat {{α}}^{(n)}}$:
${\hat {{α}}^{\left( n \right)}} = {\left( {{{{{Θ}}}^{\rm H}}{{{Θ}}} + {\beta ^{\left( {n - 1} \right)}}\Bigr/{\varepsilon ^{\left( {n - 1} \right)}}} \right)^{ - 1}}{{{{Θ}}}^{\rm H}}{{{y}}_S}$
(2) 估计噪声方差 ${\hat\beta ^{\left( n \right)}}$:
${\hat\beta ^{\left( n \right)}} = {{\left\| {{{{y}}_S} - {{Θ}}{{\hat {{α}}}^{(n)}}} \right\|_2^2}\Bigr/N}$
(3) 估计参数 ${\hat\varepsilon ^{\left( n \right)}}$:
${\hat\varepsilon ^{\left( n \right)}} = {{\left\| {{{\hat {{α}}}^{\left( n \right)}}} \right\|_2^2}\Bigr/M}$
(4) 迭代判定:若 ${{\left\| {{{{α}}^{\left( n \right)}} - {{{α}}^{\left( {n - 1} \right)}}} \right\|_2^{}}\Bigr/{\left\| {{{{α}}^{\left( n \right)}}} \right\|_2^{}}} \ge \gamma $且 $n < {I_{\rm iter}}$,则
$n \leftarrow n + 1$,执行(1)—(4);否则,结束循环。
循环结束
结果: $\hat {{α}} \leftarrow {{{α}}^{\left( n \right)}}$ -
[1] Liao K F, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Plane-wave synthesis and RCS extraction via 3-D linear array SAR[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 994–997. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2389264 [2] Han K Y, Wang Y P, Tan W X, et al. Efficient Pseudopolar format algorithm for down-looking linear-array SAR 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 572–576. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351792 [3] Zhuge X and Yarovoy A G. A sparse aperture MIMO-SAR-based UWB imaging system for concealed weapon detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 509–518. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053038 [4] Wei S J, Zhang X L, Shi J, et al. Sparse array microwave 3-D imaging: Compressed sensing recovery and experimental study[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 135: 161–181. DOI: 10.2528/PIER12082305 [5] 彭文杰. 基于压缩感知的阵列SAR三维成像方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.Peng Wen-jie. Array SAR3D imaging method based on compressed sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013. [6] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [7] Candès E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9/10): 589–592. DOI: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 [8] Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Linear array SAR Imaging via compressed sensing[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2011, 117: 299–319. DOI: 10.2528/PIER11033105 [9] Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Compressed sensing linear array SAR 3-D imaging via sparse locations prediction[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1887–1890. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946825. [10] Zhang S Q, Zhu Y T, Dong G G, et al. Truncated SVD-based compressive sensing for downward-looking three-dimensional SAR imaging with uniform/nonuniform linear array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1853–1857. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2431254 [11] Tan X, Fang Y, Feng X Y, et al.. Sparse linear array three-dimensional imaging approach based on compressed sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Beijing, China, 2016: 296–299. DOI: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2016.7888271. [12] Bao Q, Peng X M, Wang Z R, et al. DLSLA 3-D SAR imaging based on reweighted gridless sparse recovery method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 841–845. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2550057 [13] Zhang S Q, Dong G G, and Kuang G Y. Superresolution downward-looking linear array three-dimensional SAR imaging based on two-dimensional compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2184–2196. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2549548 [14] Peng X M, Tan W X, Hong W, et al. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR image reconstruction by combination of polar formatting and L1 regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 213–226. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2453202 [15] Su W G, Wang H Q, Deng B, et al.. Sparse Bayesian SAR imaging of moving target via the EXCOV method[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, Gold Coast, Australia, 2014: 448–451. DOI: 10.1109/SSP.2014.6884672. [16] Zou Y Q, Gao X Z, and Li X. Block sparse Bayesian learning based strip map SAR imaging method[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Davos, Switzerland, 2016: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/EuCAP.2016.7481637. [17] 康乐, 张群, 李涛泳, 等. 基于贝叶斯学习的下视三维合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. DOI: 10.3788/aos201737.0611003Kang Le, Zhang Qun, Li Tao-yong, et al. Imaging method of downward-looking three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar based on Bayesian learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. DOI: 10.3788/aos201737.0611003 [18] 韦顺军, 田博坤, 张晓玲, 等. 基于半正定规划的压缩感知线阵三维SAR自聚焦成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 664–675. DOI: 10.12000/JR17103Wei Shun-jun, Tian Bo-kun, Zhang Xiao-ling, et al. Compressed sensing linear array sar autofocusing imaging via semi-definite programming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 664–675. DOI: 10.12000/JR17103 [19] Yang J G, Thompson J, Huang X T, et al. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 983–994. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2204891 [20] Xu J, Pi Y, and Cao Z. Bayesian compressive sensing in synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2012, 6(1): 2–8. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2010.0375 [21] Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B(Methodological) , 1996, 58(1): 267–288. DOI: 10.1111/rssb.1996.58.issue-1 [22] Chartrand R and Yin W T. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, USA, 2008: 3869–3872. DOI: 10.1109/ICASSP.2008.4518498. [23] Ulander L M H, Hellsten H, and Stenstrom G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
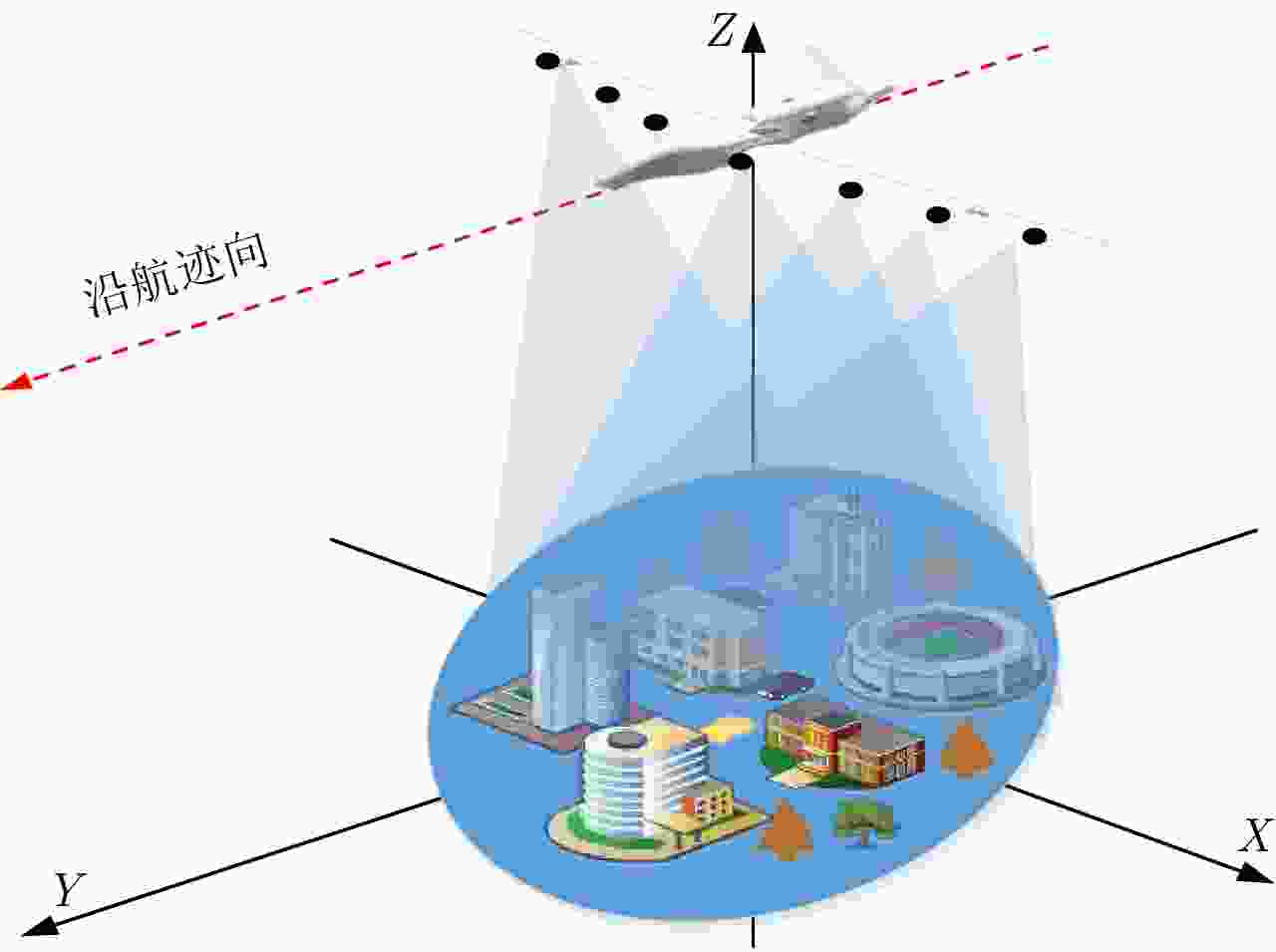
 下载:
下载: