A Fast Power Allocation Algorithm in a Collocated MIMO Radar under Low Interception Backgrounds
-
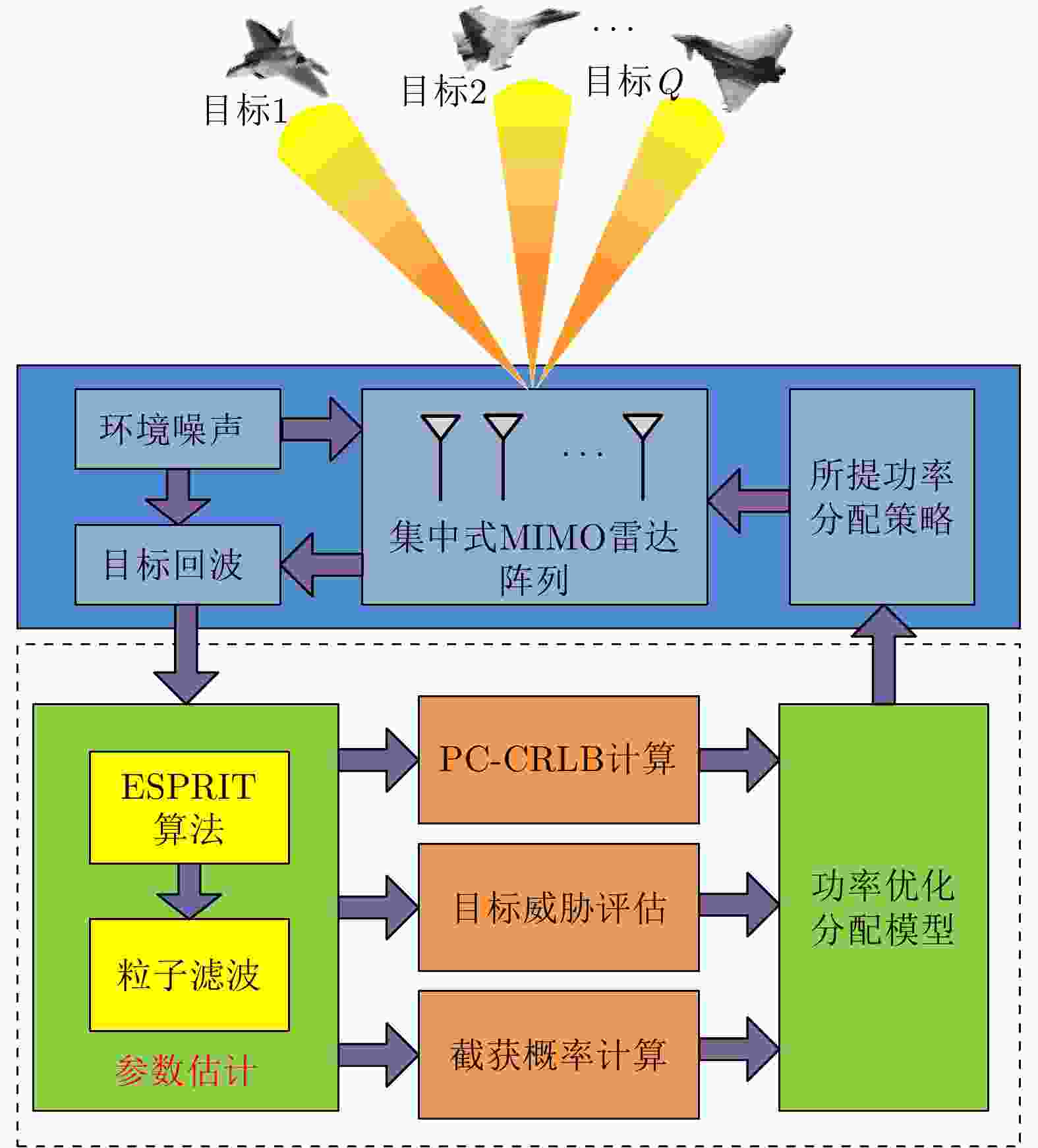
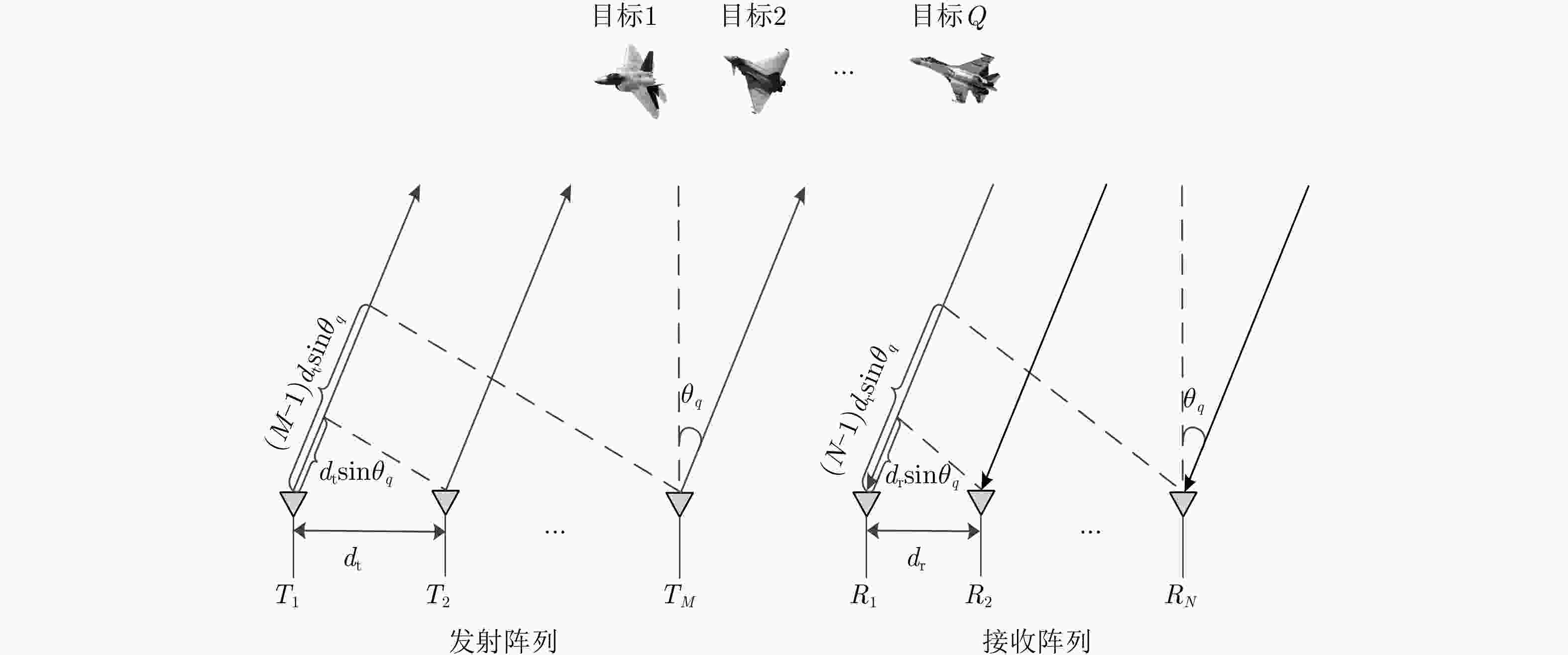
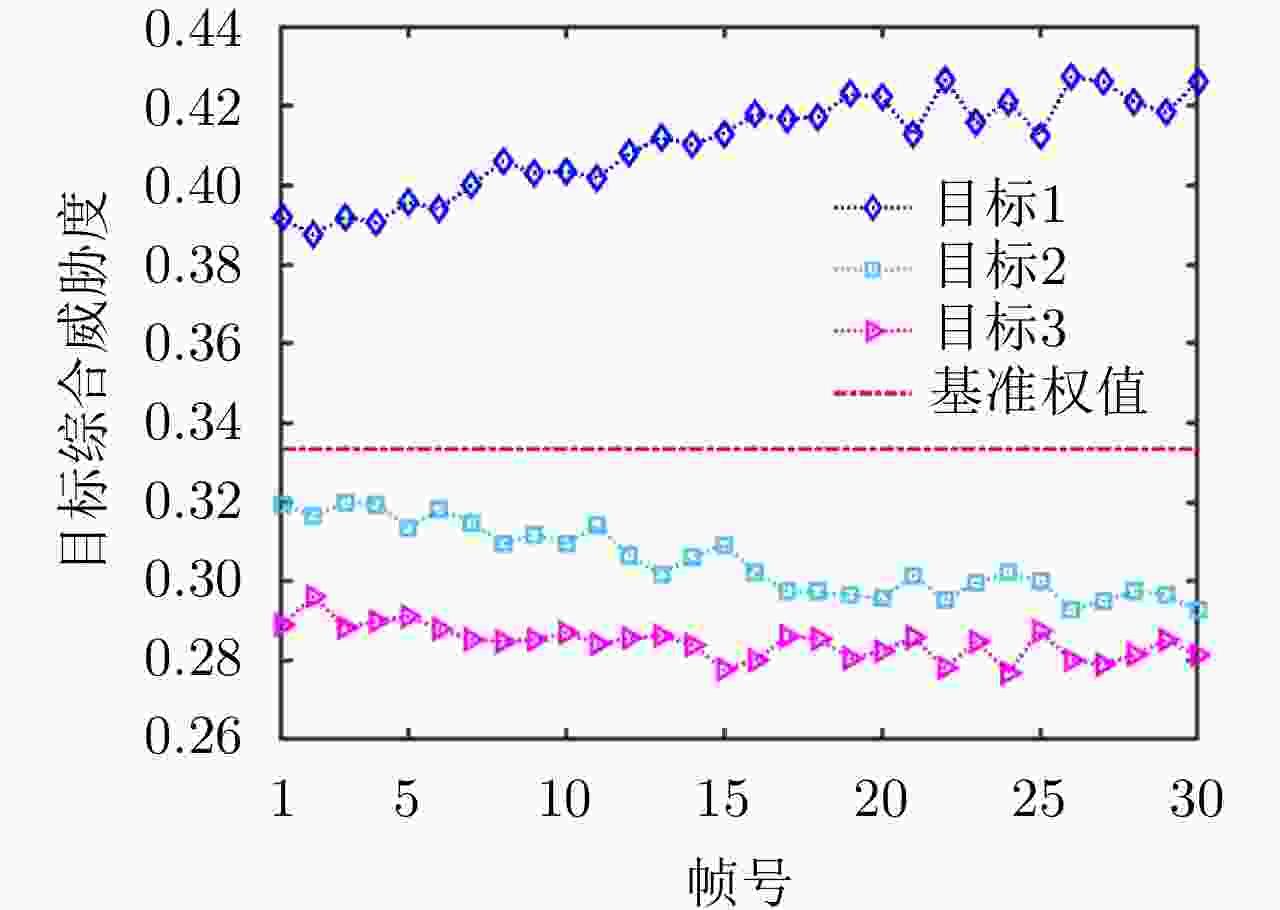
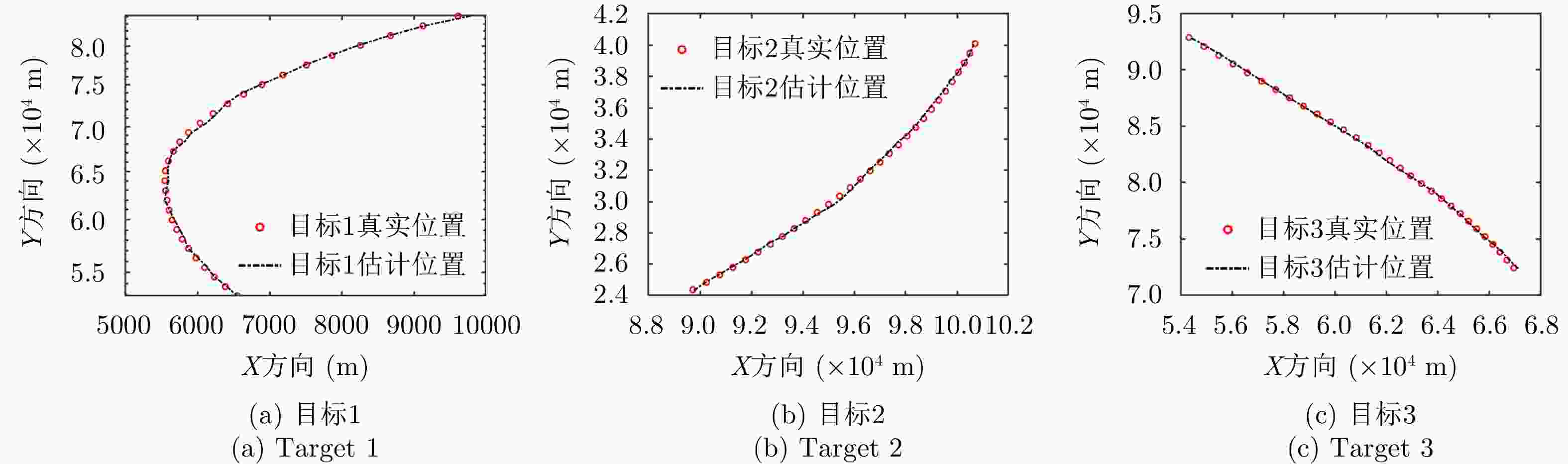
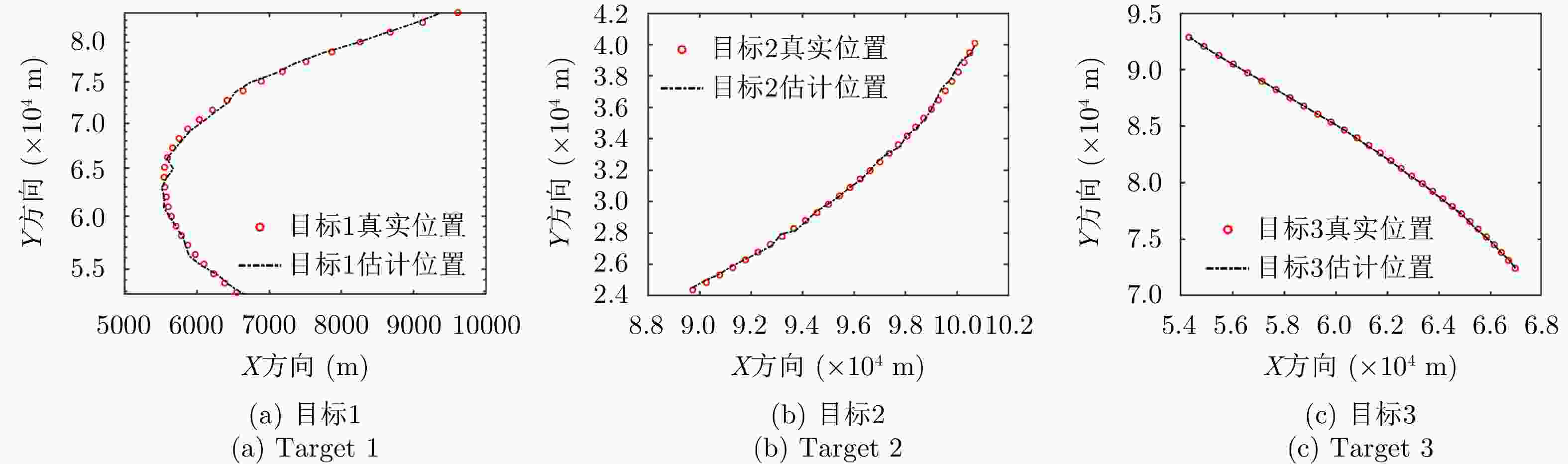
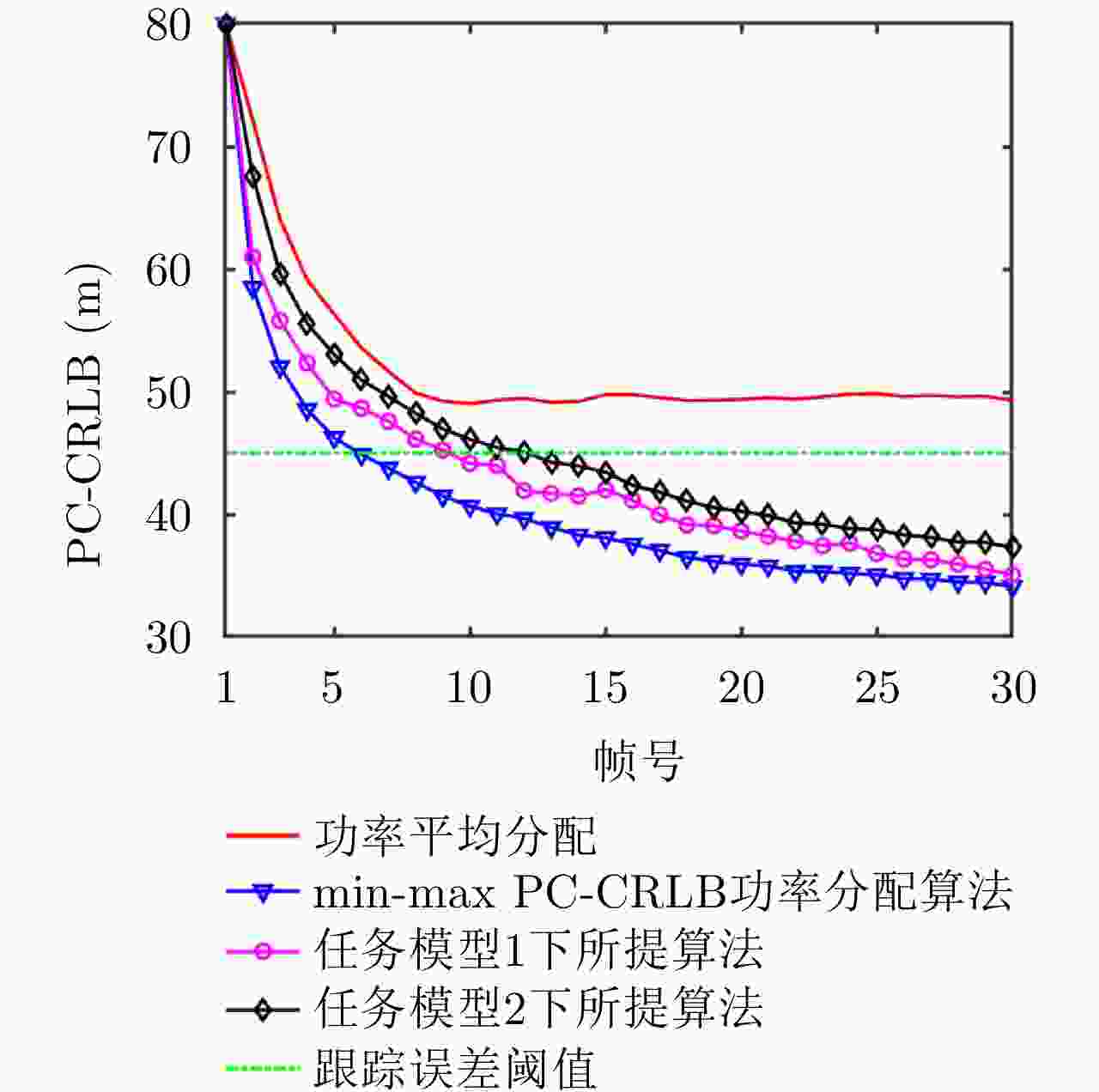
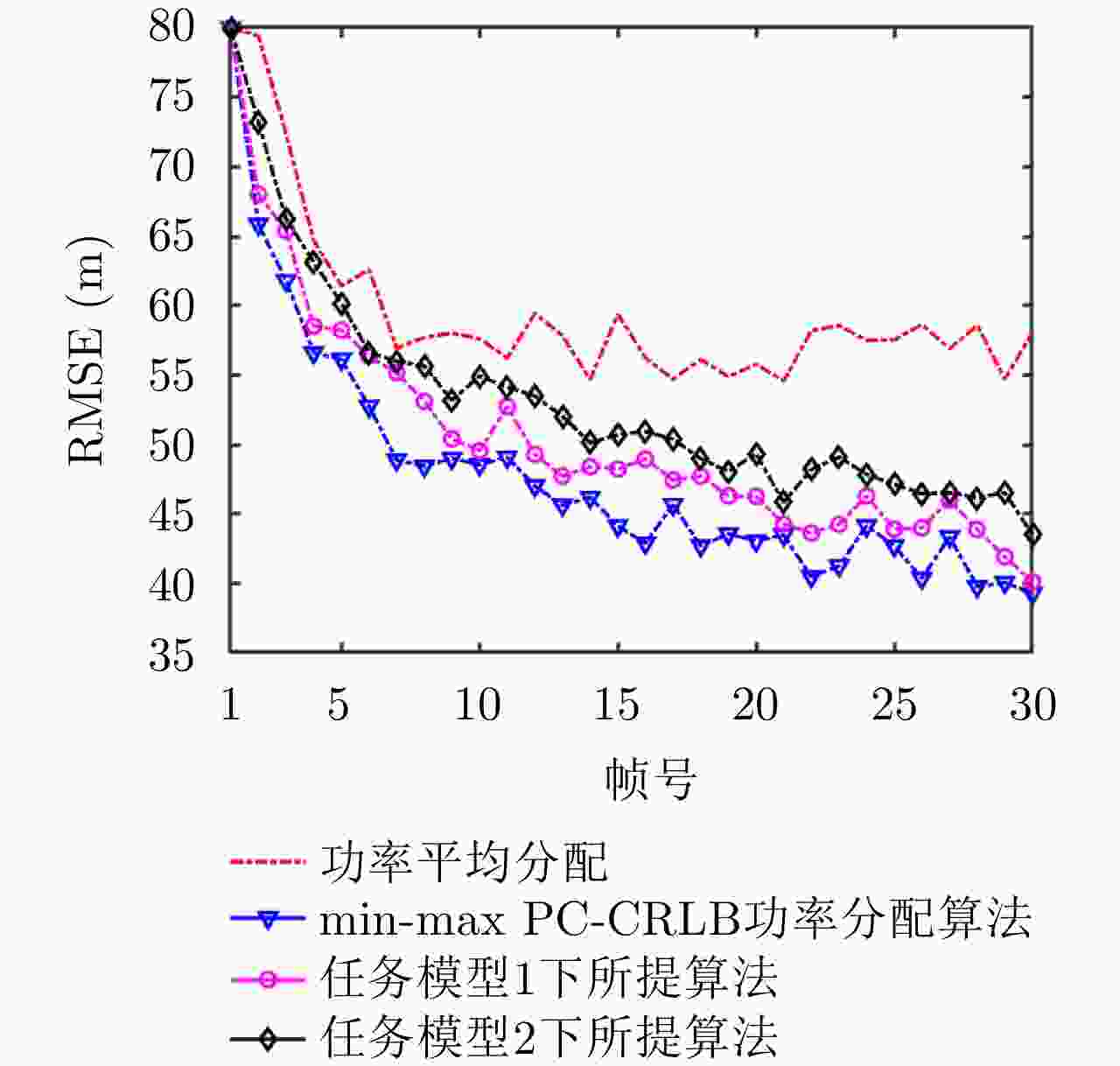
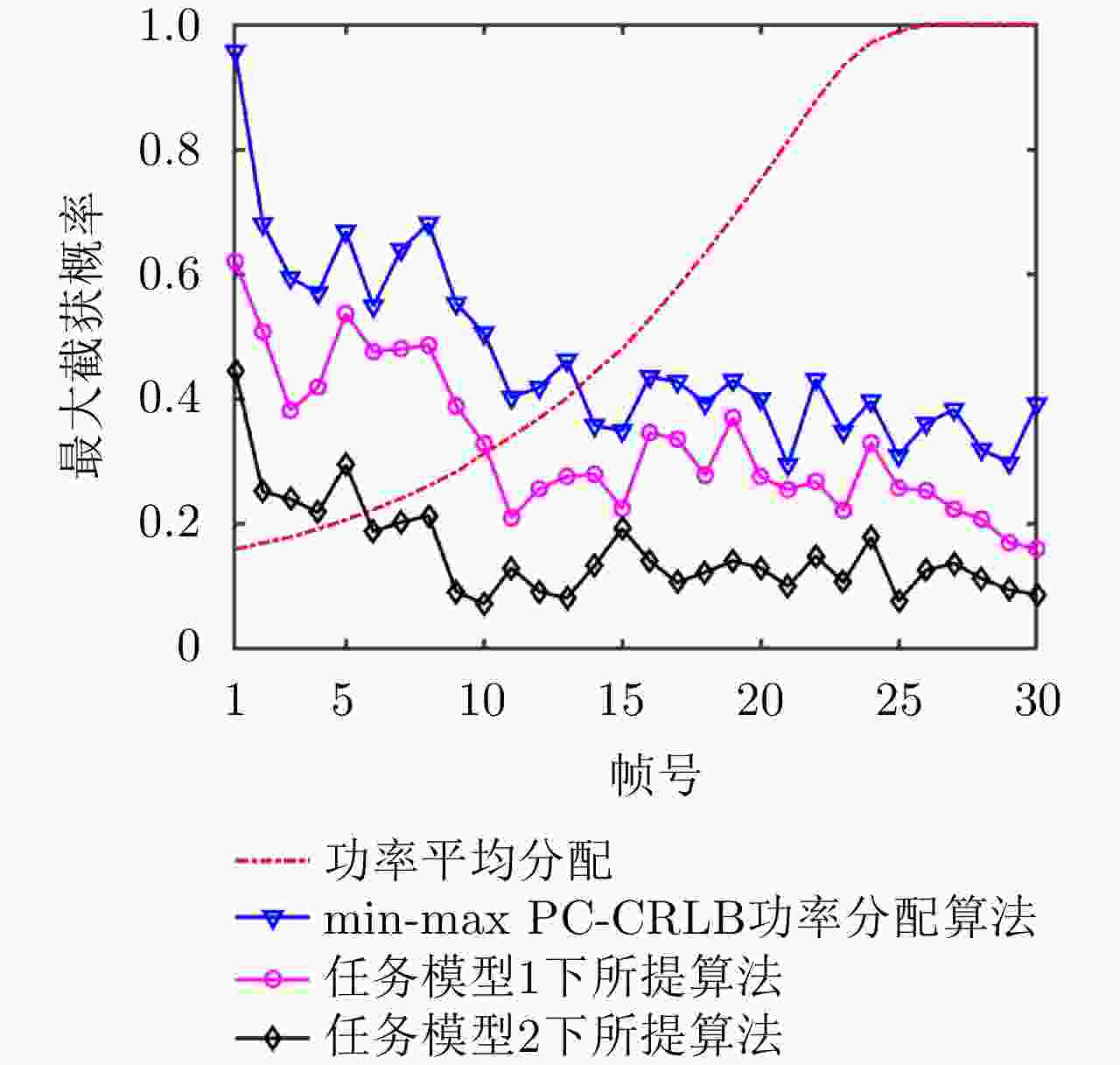
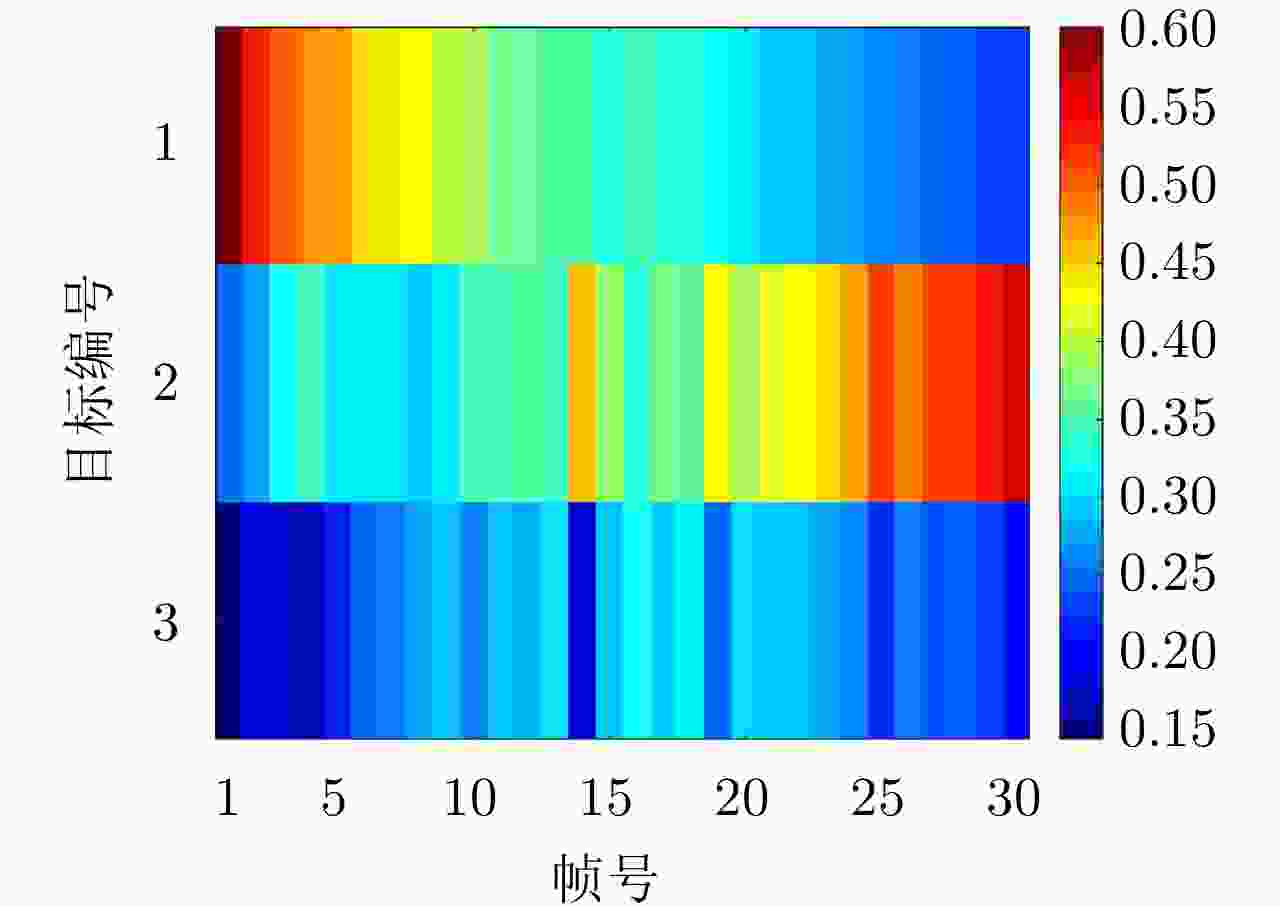
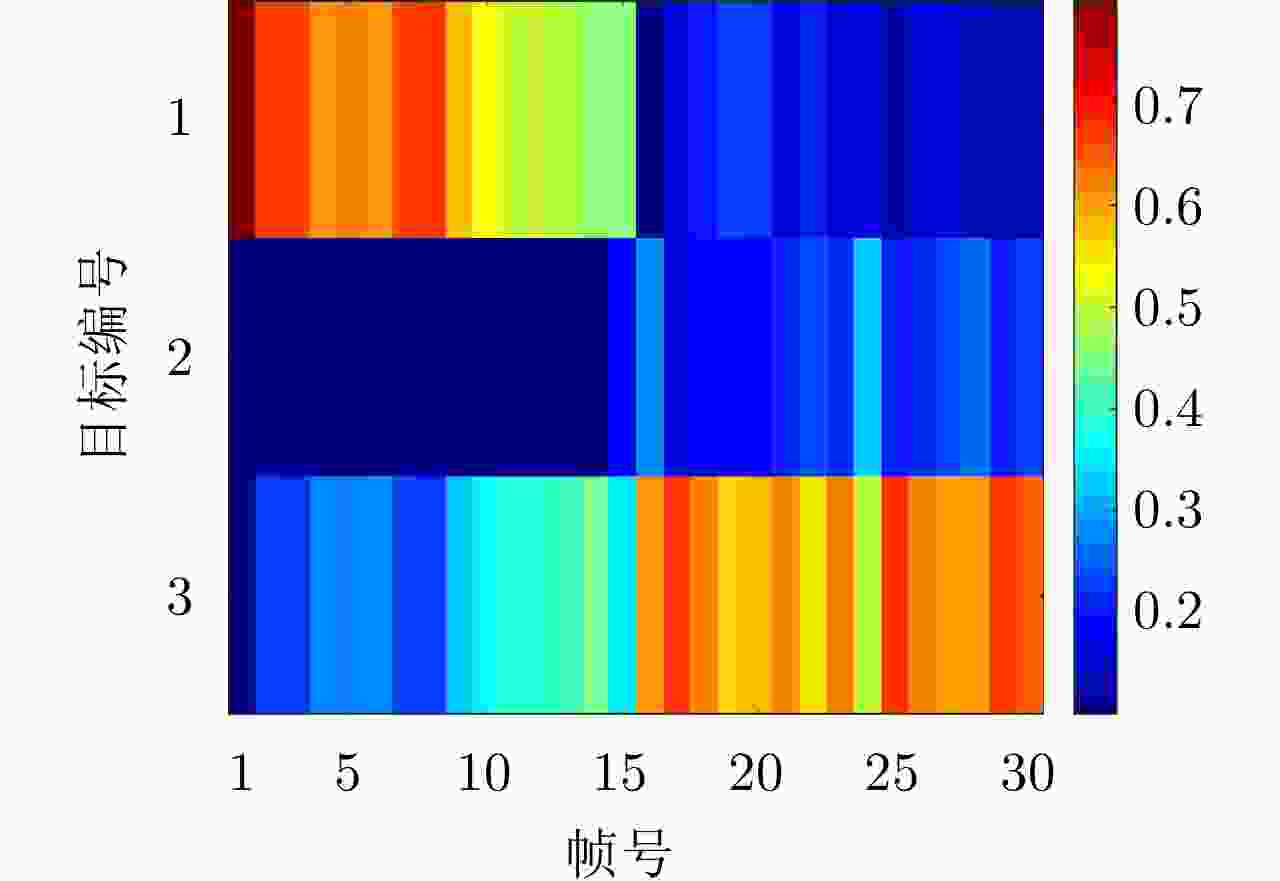
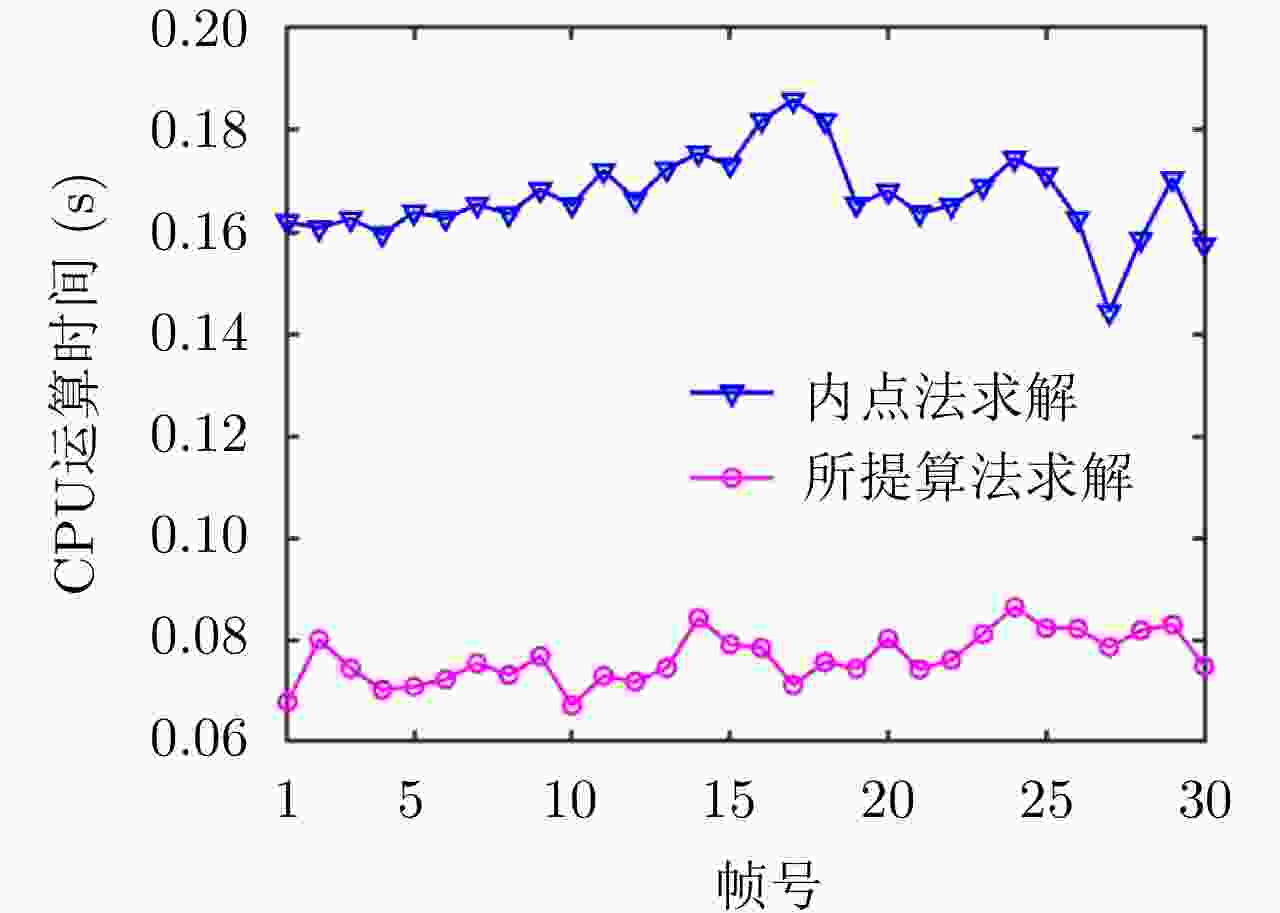
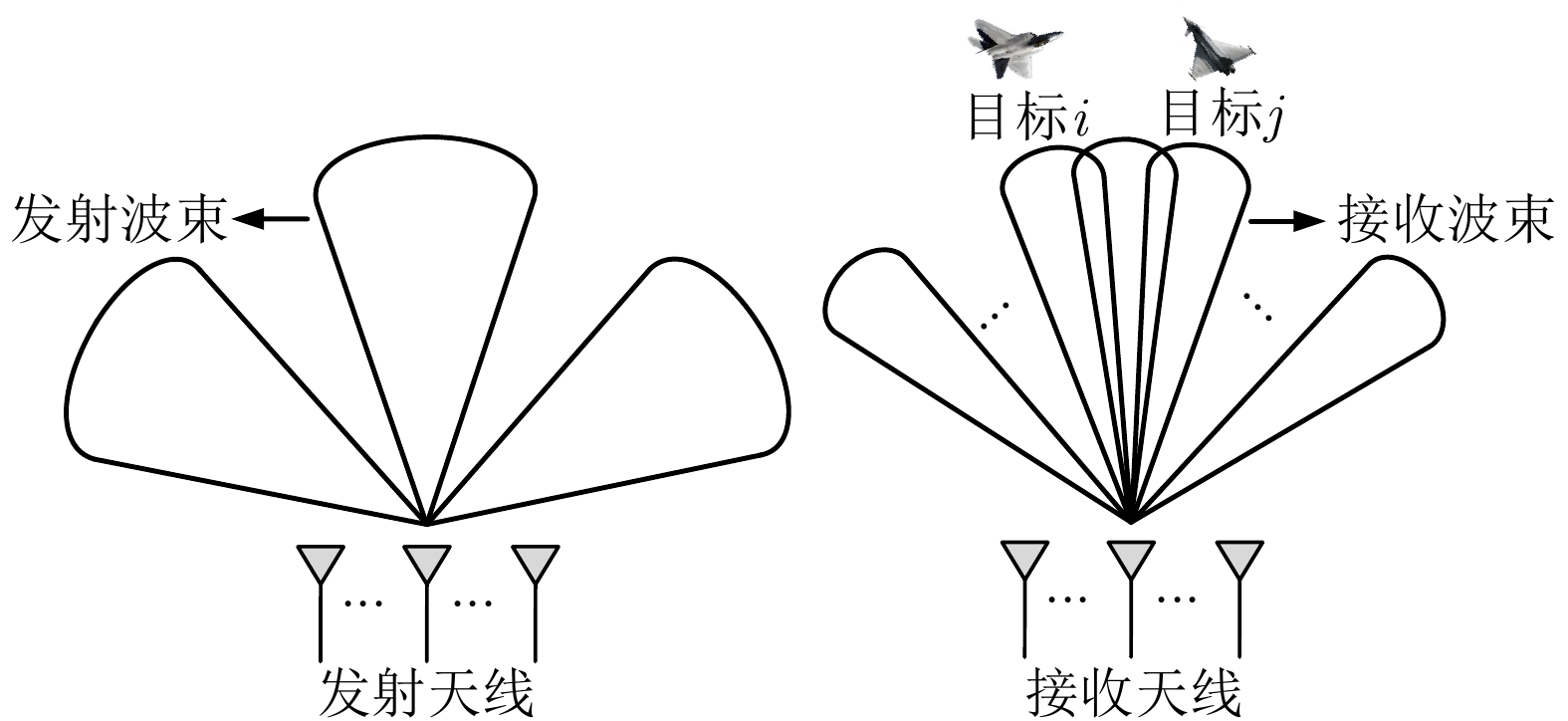
摘要: 针对集中式MIMO雷达同时跟踪多批机动目标场景,该文提出一种低截获背景下的快速功率分配算法。首先,将目标机动过程建模为自适应当前统计(ACS)模型,并采用粒子滤波对各目标状态进行估计。其次,对条件克拉默-拉奥下界(PC-CRLB)进行推导,并基于目标运动特性和电磁特性构建目标综合威胁度评估模型。随后,将目标跟踪误差评估指数和雷达未被截获概率的加权和作为优化目标,建立了关于发射功率的优化模型,利用目标函数单调递减性质,提出了一种基于序列松弛的求解算法进行模型求解。最后,通过仿真验证所提算法的有效性和时效性。结果表明,所提算法能够有效提高目标跟踪精度和雷达系统低截获性能,相比采用内点法求解运算速度提高近50%。
-
关键词:
- 集中式MIMO雷达 /
- 功率分配 /
- 机动跟踪 /
- 低截获性能 /
- 条件克拉默-拉奥下界(PC-CRLB)
Abstract: This study proposes a fast power allocation algorithm under a low interception background for a collocated MIMO radar that simultaneously tracks multiple maneuvering targets. First, the target maneuver process is modeled as an Adaptive Current Statistical (ACS) model, and a particle filter is used to estimate the state of each target. Second, the Predicted Conditional Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (PC-CRLB) is derived, and the target comprehensive threat assessment model is constructed based on the target motion and electromagnetic characteristics. Subsequently, an optimization model with respect to transmitting power is established by developing the weighted sum of the target tracking error evaluation index and the unintercepted probability of radar as the optimization objective. Thereafter, to solve the model using the monotonically decreasing property of the objective function, a solving algorithm based on sequence relaxation is proposed. Finally, a simulation is conducted to verify the effectiveness and timeliness of the proposed algorithm. The results indicate that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the target tracking accuracy and low interception performance of the radar system. Further, its run speed is increased by nearly 50% compared with that of the interior point method. -
表 1 功率快速求解算法
Table 1. Fast power solving algorithm
步骤1 应用式(30)计算$ {D_k} $; 步骤2 定义${{\boldsymbol{Q}}_0}$为集合${\boldsymbol{Q}} = \{ 1,2,\cdots,Q\}$中所有满足不等式
${D_k} > {{\rm{fun}}_q}(\arg \min ({\bf{1} }_Q^{\text{T} }{ {\boldsymbol{P} }_k}))$元素的集合。若${{\boldsymbol{Q}}_0} \ne \varnothing$,则进入
步骤3;否则,令${P_{k,q,{\text{opt} } } } = {\bar P_{\min } }$, ${ {\boldsymbol{Q} }_0} = { {\boldsymbol{Q} }_0} \cup \{ q\}$,
${\boldsymbol{Q}} = {\boldsymbol{Q}}\backslash \{ q\}$,并返回步骤1;步骤3 令对目标q进行功率分配结果的最优解为
${P_{k,q,{\text{opt} } } } = {\rm{fun}}_q^{ - 1}({D_k})$;步骤4 令最优解对应函数值为$ {D_{k,{\text{opt}}}} = {D_k} $。 表 2 仿真参数设置
Table 2. Simulation parameter setting
参数 取值 参数 取值 $ {p_{{\text{fa}}}} $ 10–8 $ {G_{\text{t}}} $ 30 dB $ {G_{\text{I}}} $ 6 dB $ {G_{{\text{IP}}}} $ 3 dB $ {\beta _{k,q}} $ 1 MHz $ {T_{k,q}} $ 1 ms $ \lambda $ 0.3 m $ \eta $ 45 m ${T_{\rm{s}}}$ 1 s $ {P_{{\text{total}}}} $ 5 kW $ {\bar P_{{\text{max}}}} $ 4 kW $ {\bar P_{\min }} $ 0.5 kW 表 3 初始时刻目标运动参数
Table 3. Initial target motion parameters
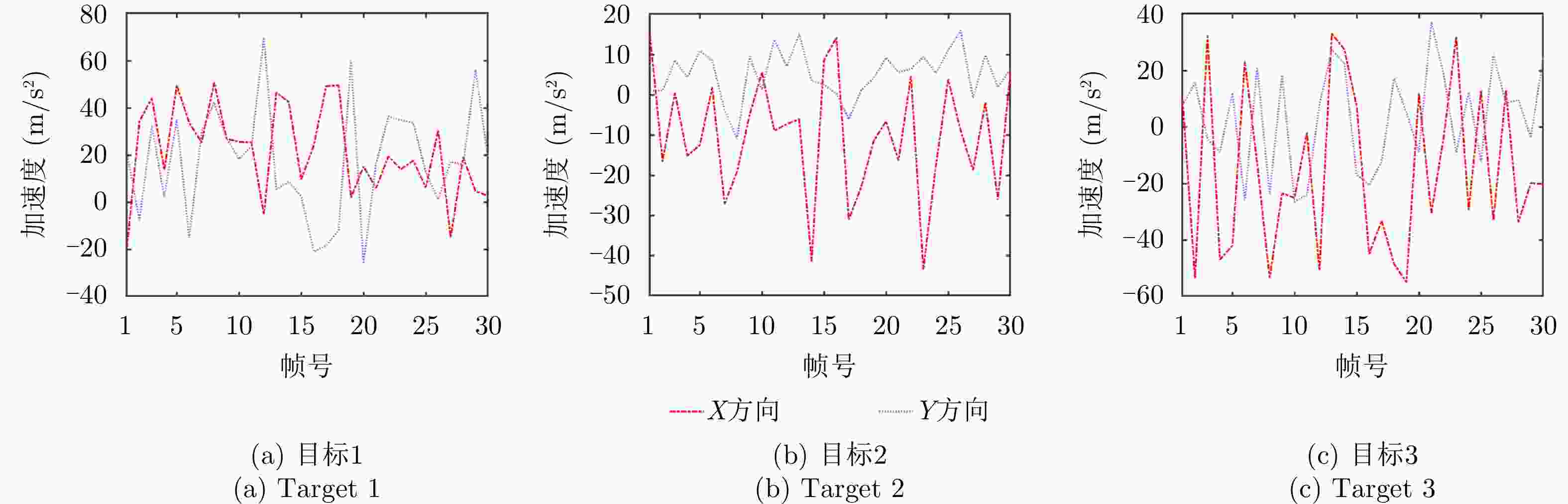
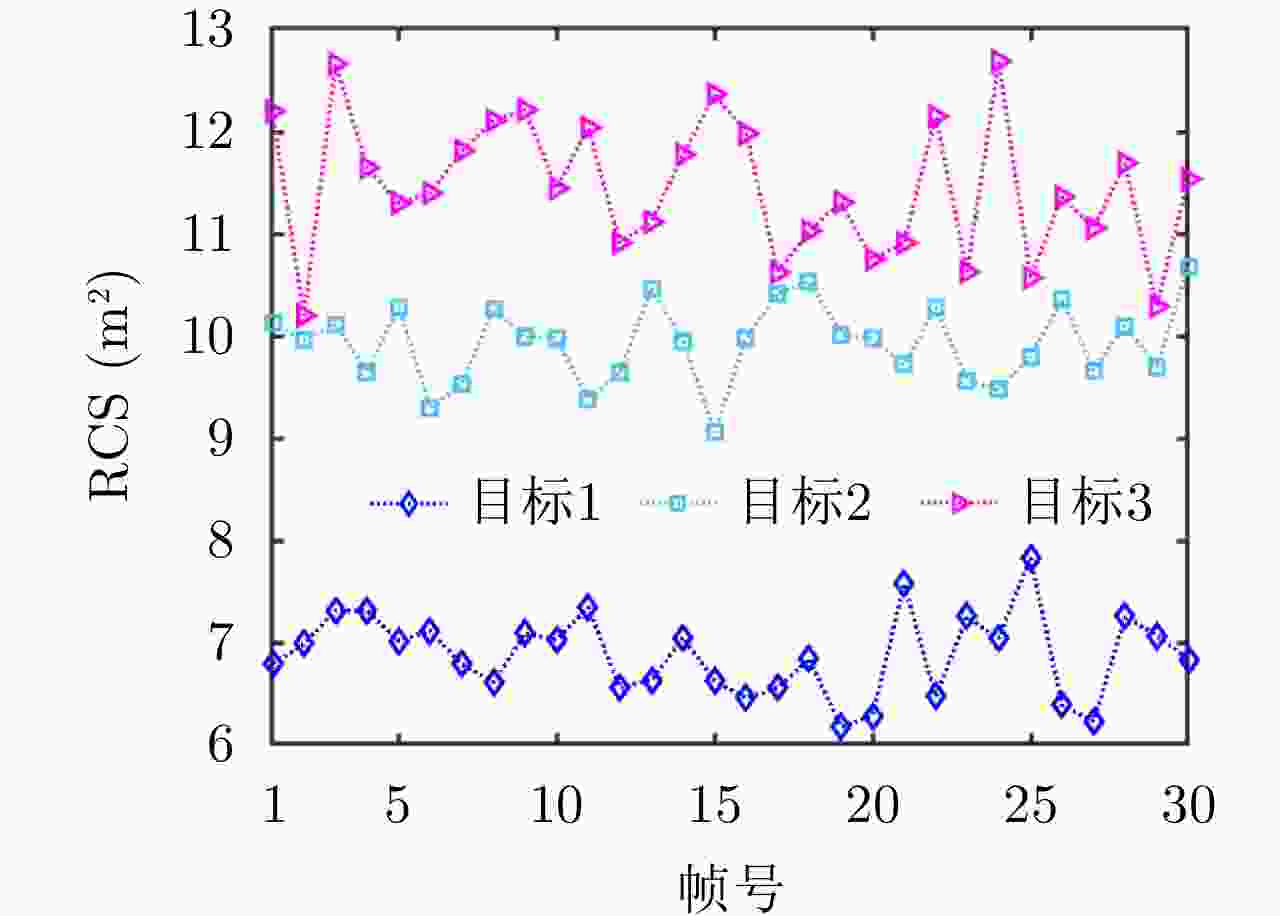
目标编号 位置(km) 速度(m/s) 加速度(m/s2) 最大加速度(m/s2) 1 (9.6, 84.1) (–494.2, –1346.1) (–19.4, 20.7) 80 2 (89.7, 24.4) (533.2, 468.5) (14.6, 0.9) 50 3 (66.9, 72.4) (–257.1, 695.1) (9.6, 7.7) 60 -
[1] 何子述, 程子扬, 李军, 等. 集中式MIMO雷达研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128HE Zishu, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. A survey of collocated MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128 [2] 范文, 蔚保国, 陈镜, 等. 基于波形优化和天线位置选择的MIMO雷达波束扫描算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 530–542. doi: 10.12000/JR22135FAN Wen, YU Baoguo, CHEN Jing, et al. Joint waveform optimization and antenna position selection for MIMO radar beam scanning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 530–542. doi: 10.12000/JR22135 [3] 严俊坤, 陈林, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于机会约束的MIMO雷达多波束稳健功率分配算法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(6): 1230–1235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.007YAN Junkun, CHEN Lin, LIU Hongwei, et al. Chance constrained based robust multibeam power allocation algorithm for MIMO radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(6): 1230–1235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.007 [4] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812 [5] 韩金旺, 张子敬, 刘军, 等. 基于贝叶斯的高斯杂波背景下MIMO雷达自适应检测算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 501–509. doi: 10.12000/JR18090HAN Jinwang, ZHANG Zijing, LIU Jun, et al. Adaptive Bayesian detection for MIMO radar in Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 501–509. doi: 10.12000/JR18090 [6] HAYKIN S, ZIA A, XUE Yanbo, et al. Control theoretic approach to tracking radar: First step towards cognition[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2011, 21(5): 576–585. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2011.01.004 [7] YAN Junkun, JIAO Hao, PU Wenqiang, et al. Radar sensor network resource allocation for fused target tracking: A brief review[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 86/87: 104–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.06.009 [8] YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, JIU Bo, et al. Simultaneous multibeam resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3110–3122. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2417504 [9] ZHANG Haowei, ZONG Binfeng, and XIE Junwei. Power and bandwidth allocation for multi-target tracking in collocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9795–9806. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3002899 [10] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Joint node selection and power allocation strategy for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2777394 [11] LI Zhengjie, XIE Junwei, ZHANG Haowei, et al. Joint beam selection and resource allocation for cognitive multiple targets tracking in MIMO radar with collocated antennas[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(12): 2000–2009. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2020.0332 [12] YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, and BAO Zheng. Power allocation scheme for target tracking in clutter with multiple radar system[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 144: 453–458. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.11.006 [13] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, XIE Junwei, et al. Joint subarray selection and power allocation for cognitive target tracking in large-scale MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 2569–2580. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2960401 [14] YI Wei, YUAN Ye, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Resource scheduling for distributed multi-target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1602–1617. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2976587 [15] YAN Junkun, ZHANG Peng, DAI Jinhui, et al. Target capacity based simultaneous multibeam power allocation scheme for multiple target tracking application[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 178: 107794. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107794 [16] LI Zhengjie, XIE Junwei, ZHANG Haowei, et al. Joint beam selection and power allocation in cognitive collocated MIMO radar for potential guidance application under oppressive jamming[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 127: 103579. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103579 [17] 时晨光, 丁琳涛, 汪飞, 等. 面向射频隐身的组网雷达多目标跟踪下射频辐射资源优化分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 539–546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200636SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Radio frequency stealth-based optimal radio frequency resource allocation algorithm for multiple-target tracking in radar network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 539–546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200636 [18] LU Xiujuan, XU Zhenchang, REN Haiwei, et al. LPI-based resource allocation strategy for target tracking in the moving airborne radar network[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. [19] YUAN Ye, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust power allocation for resource-aware multi-target tracking with colocated MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 443–458. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047519 [20] LI Xi, CHENG Ting, SU Yang, et al. Joint time-space resource allocation and waveform selection for the collocated MIMO radar in multiple targets tracking[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: 107650. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107650 [21] HAN Qinghua, PAN Minghai, LONG Weijun, et al. Joint adaptive sampling interval and power allocation for maneuvering target tracking in a multiple opportunistic array radar system[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(4): 981. doi: 10.3390/s20040981 [22] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Joint target assignment and resource optimization framework for multitarget tracking in phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 4379–4390. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3025867 [23] SHI Chenguang, WANG Yijie, SALOUS S, et al. Joint transmit resource management and waveform selection strategy for target tracking in distributed phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2762–2778. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3138869 [24] 张浩为, 谢军伟, 葛佳昂, 等. 自适应CS模型的强跟踪平方根容积卡尔曼滤波算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(6): 1186–1194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.06.03ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, et al. Strong tracking square-root cubature Kalman filter over adaptive current statistical model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1186–1194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.06.03 [25] ZHOU Hongren and KUMAR K S P. A ‘current’ statistical model and adaptive algorithm for estimating maneuvering targets[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1984, 7(5): 596–602. doi: 10.2514/3.19900 [26] KHALOOZADEH H and KARSAZ A. Modified input estimation technique for tracking manoeuvring targets[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2009, 3(1): 30–41. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20080028 [27] YANG Yongjian, FAN X, WANG Shengda, et al. A new parameters adaptively adjusting method of current statistical model[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 2015: 1738–1742. [28] ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, et al. Adaptive strong tracking square-root cubature Kalman filter for maneuvering aircraft tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 10052–10061. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2808170 [29] 梁浩, 崔琛, 代林, 等. 基于ESPRIT算法的L型阵列MIMO雷达降维DOA估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(8): 1828–1835. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141295LIANG Hao, CUI Chen, DAI Lin, et al. Reduced-dimensional DOA estimation based on ESPRIT algorithm in MIMO radar with L-shaped array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(8): 1828–1835. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141295 [30] BELL K L, BAKER C J, SMITH G E, et al. Cognitive radar framework for target detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1427–1439. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2465304 [31] ZHENG Yujiao, OZDEMIR O, NIU Ruixin, et al. New conditional posterior Cramér-Rao lower bounds for nonlinear sequential Bayesian estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(10): 5549–5556. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2205686 [32] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, ZONG Binfeng, et al. An efficient power allocation strategy for maneuvering target tracking in cognitive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1591–1602. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047227 [33] 王祥丽, 易伟, 孔令讲. 基于多目标跟踪的相控阵雷达波束和驻留时间联合分配方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 602–610. doi: 10.12000/JR17045WANG Xiangli, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint beam selection and dwell time allocation for multi-target tracking in phased array radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 602–610. doi: 10.12000/JR17045 [34] 史小斌, 顾红, 苏卫民, 等. 地面侦察雷达目标威胁度评估方法研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(6): 1128–1135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.06.024SHI Xiaobin, GU Hong, SU Weimin, et al. Study of target threat assessment for ground surveillance radar[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(6): 1128–1135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.06.024 [35] 刘秀祥, 雷振亚, 谢拥军, 等. 空中隐身目标威胁等级的仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(7): 46–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.07.013LIU Xiuxiang, LEI Zhenya, XIE Yongjun, et al. Simulation research of air stealth targets threat grade[J]. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(7): 46–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.07.013 [36] 蒋春启, 郑娜娥, 左宗, 等. 突出重点目标跟踪的分布式MIMO雷达阵元选取[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(10): 2860–2868. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.20JIANG Chunqi, ZHENG Na’e, ZUO Zong, et al. Antenna selection of distributed MIMO radar on target tracking with key target highlighted[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(10): 2860–2868. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.20 [37] ZHANG Weiwei, SHI Chenguang, SALOUS S, et al. Convex optimization-based power allocation strategies for target localization in distributed hybrid non-coherent active-passive radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 2476–2488. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3173756 [38] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 67–78. [39] GOLUB G H and VAN LOAN C F. Matrix Computations[M]. 3rd ed. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996: 509–520. [40] LUSS H and SMITH D R. Resource allocation among competing activities: A lexicographic minimax approach[J]. Operations Research Letters, 1986, 5(5): 227–231. doi: 10.1016/0167-6377(86)90012-X [41] BAZARAA M S and SHETTY C M. Nonlinear Programming: Theory and Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley, 1979: 538–557. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: