-
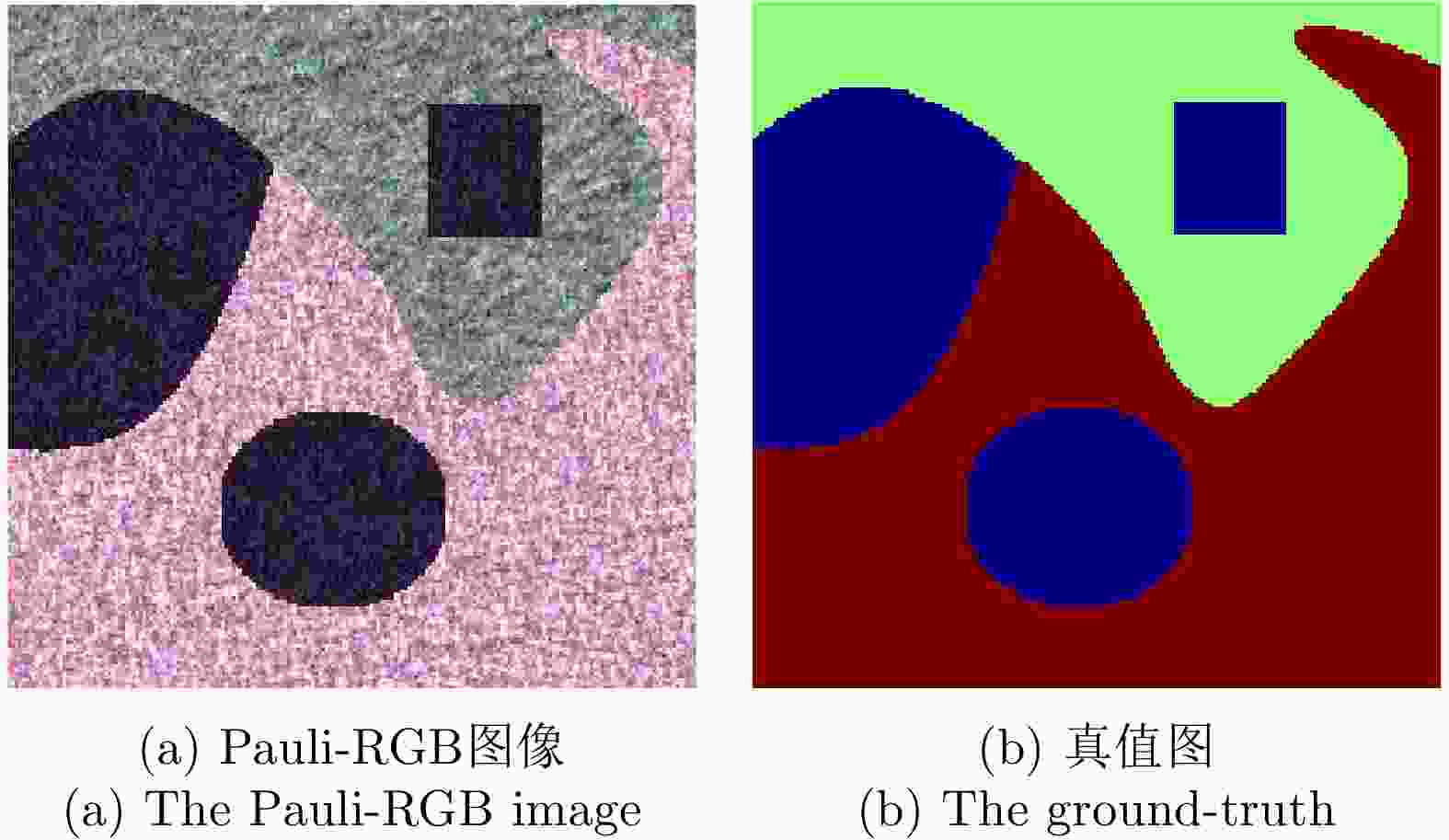
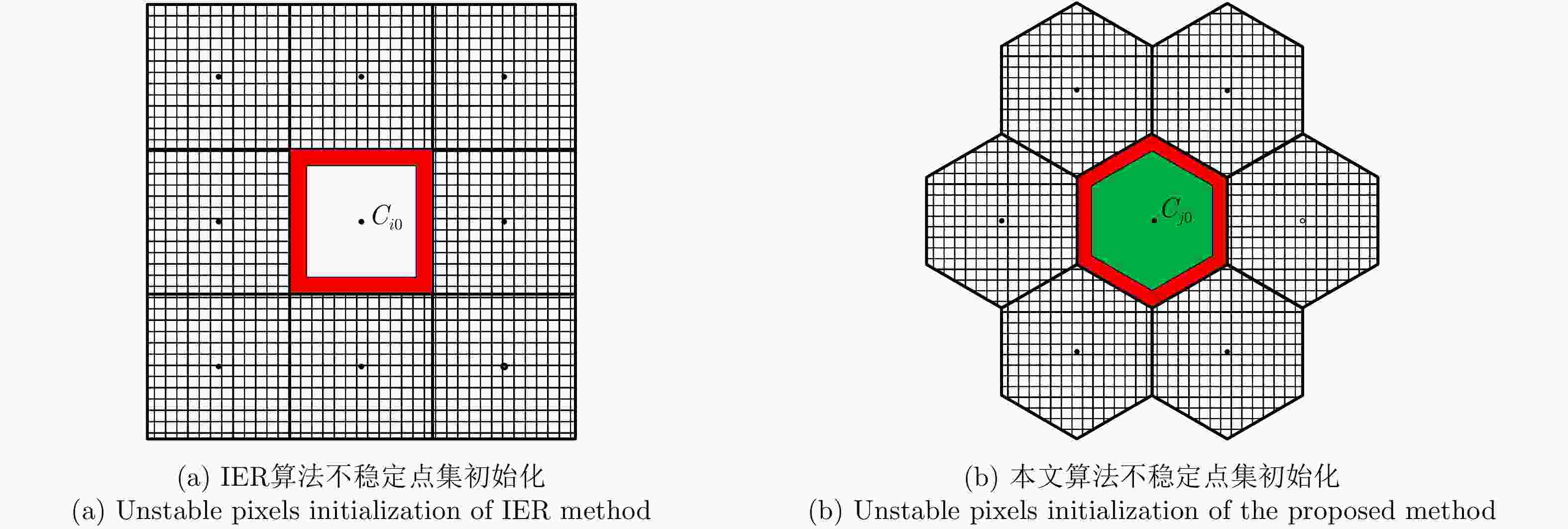
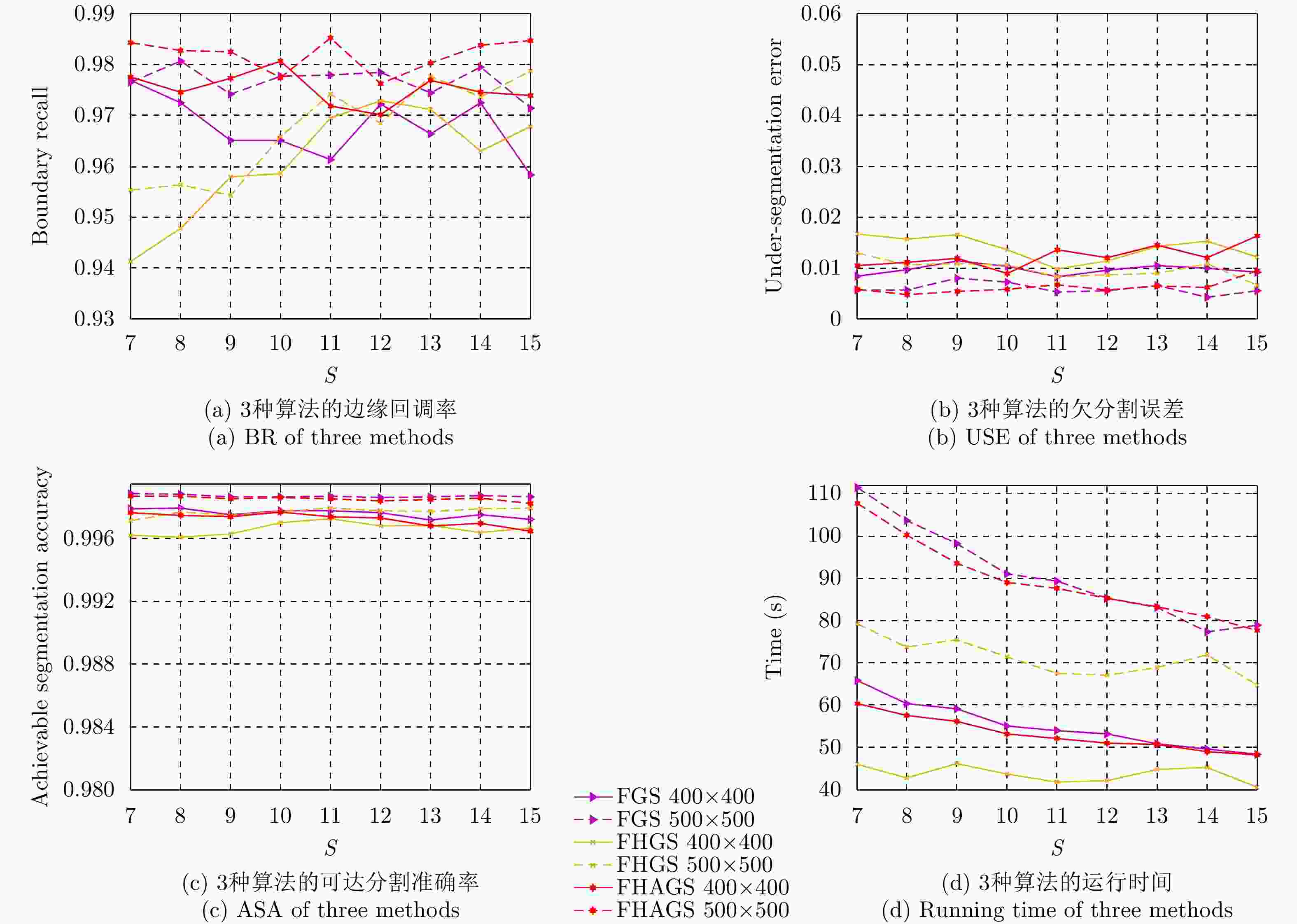
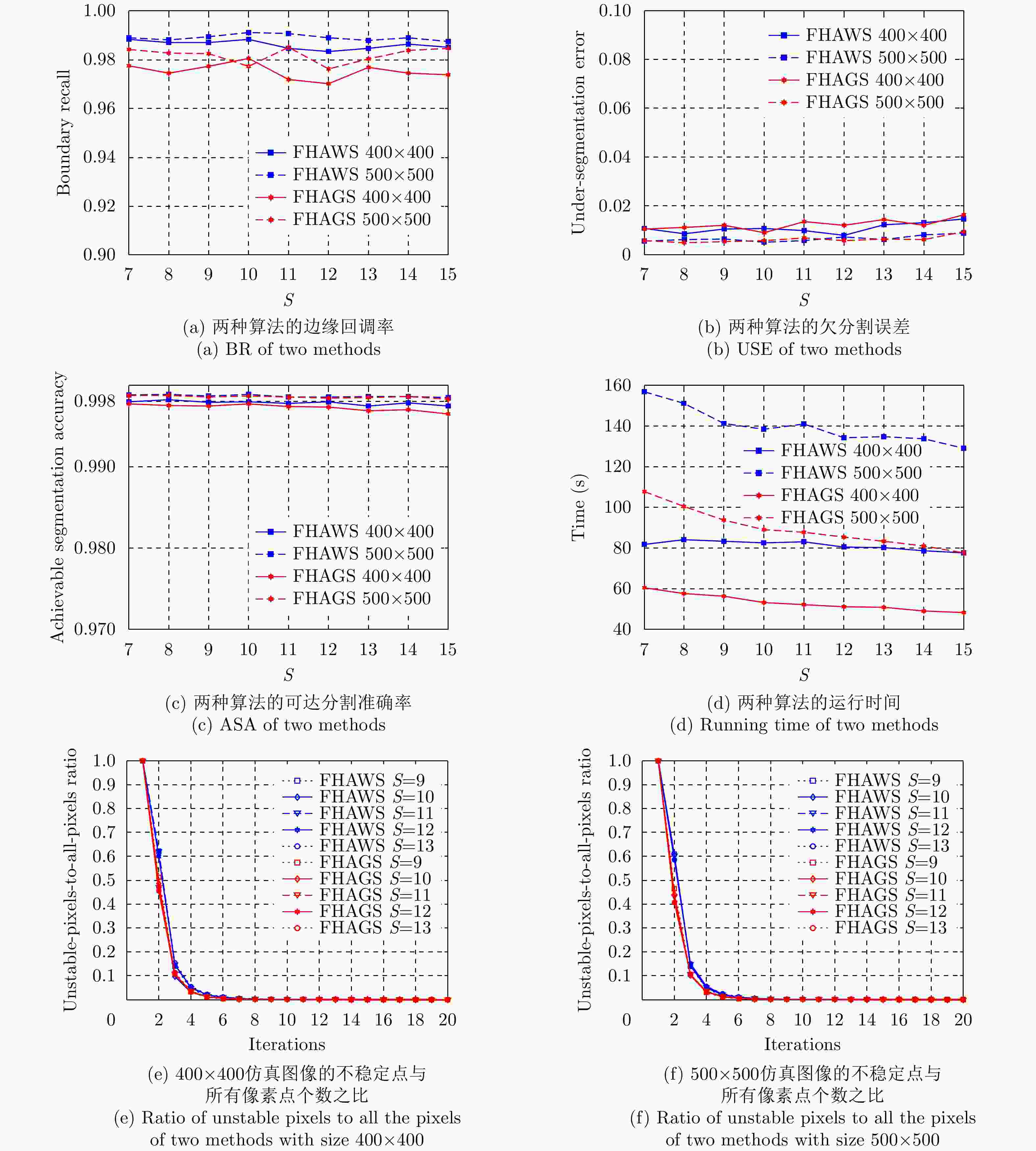
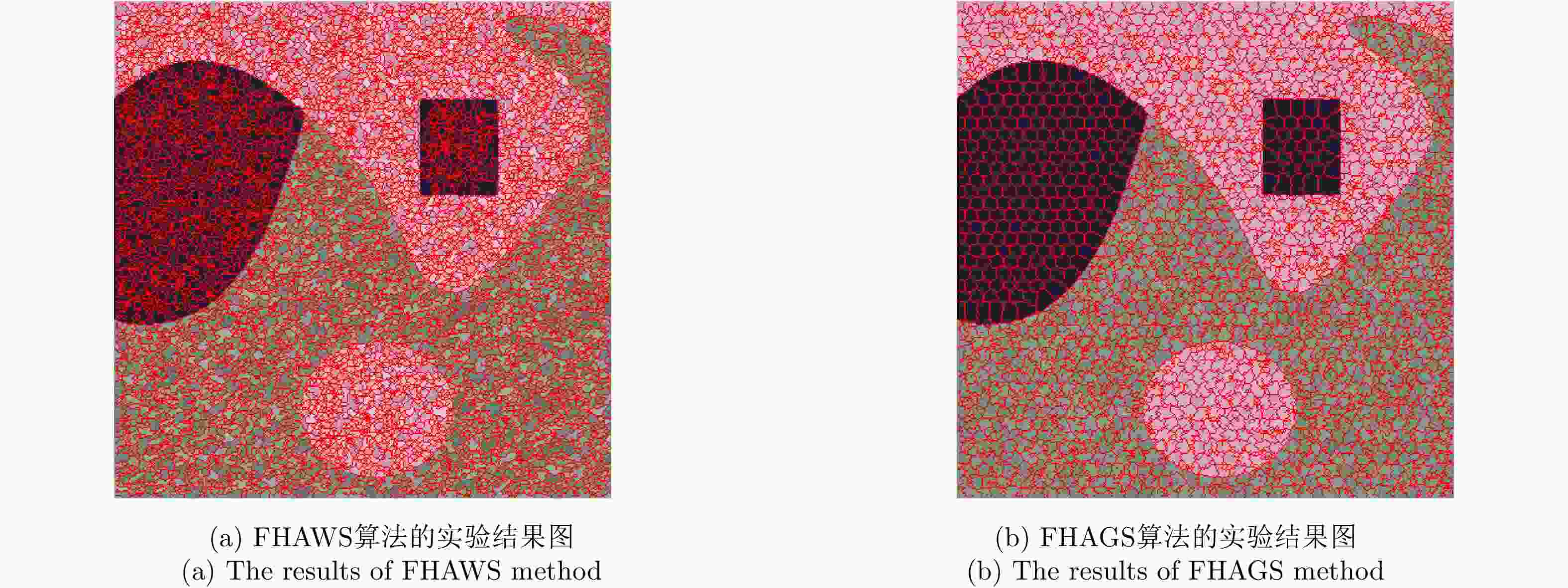
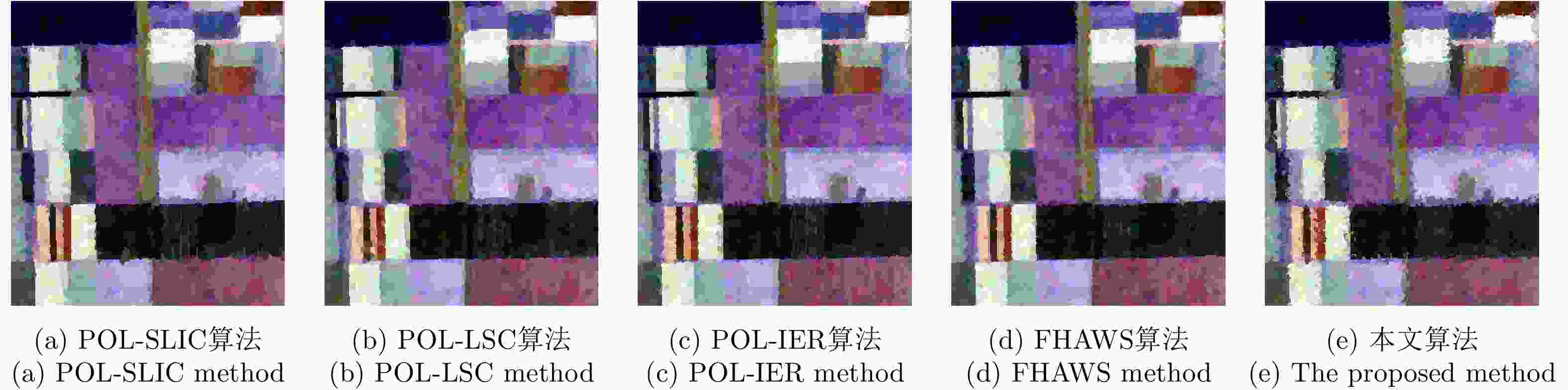
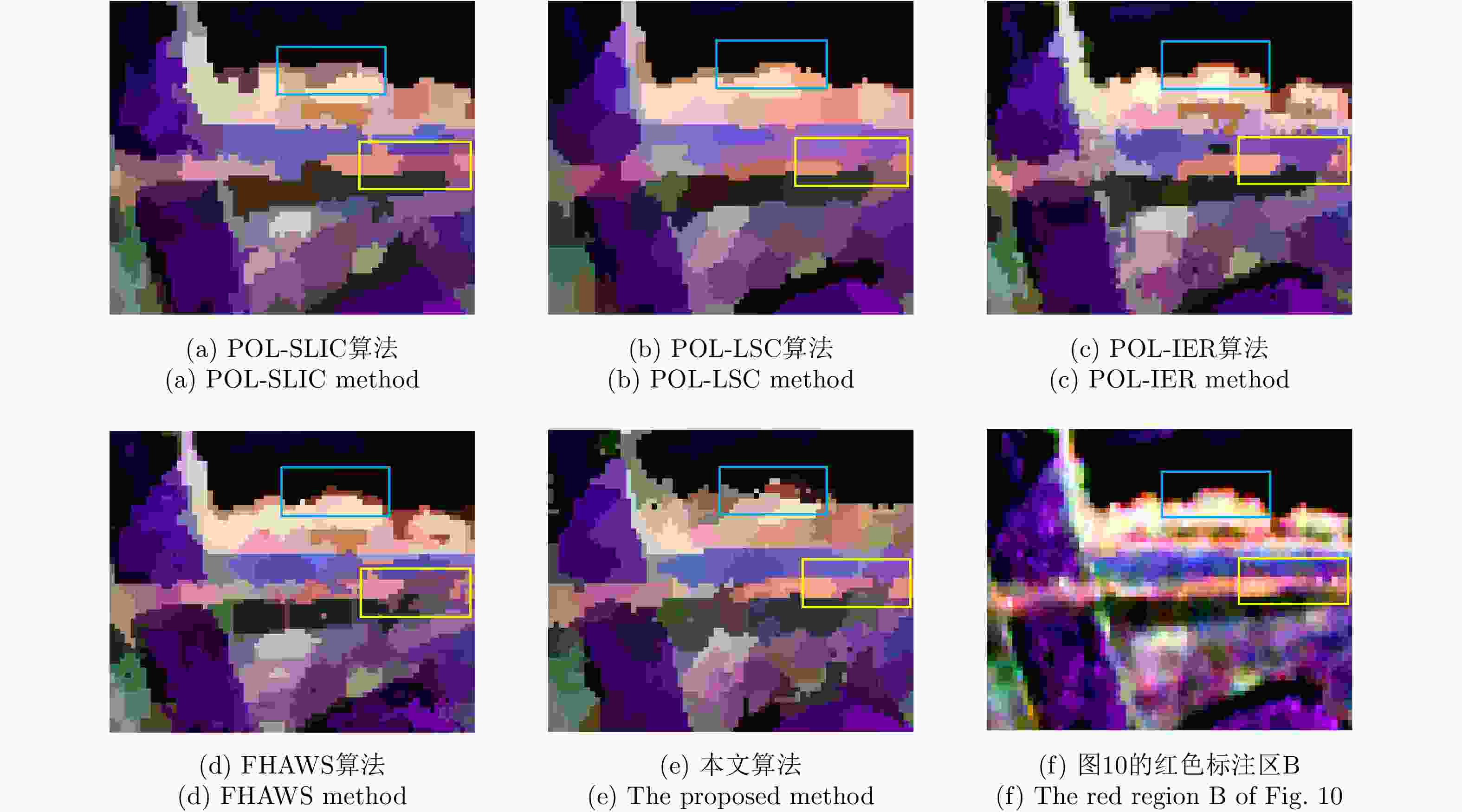
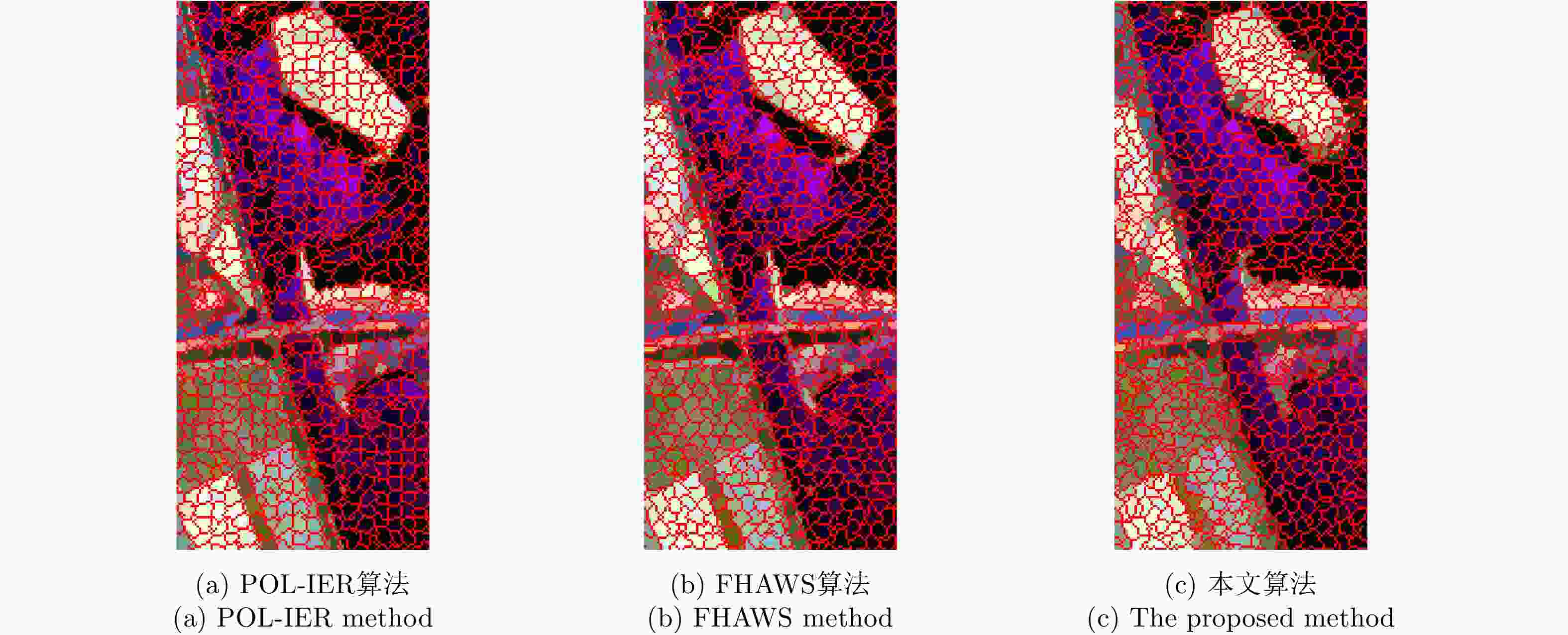
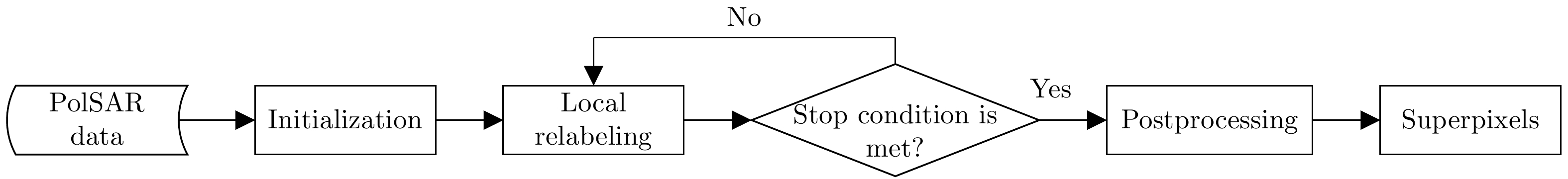
摘要: 针对传统的极化SAR(PolSAR)图像超像素分割算法中采用的距离度量对相似性表征能力不足的问题,该文提出了一种基于测地线距离的极化SAR图像快速超像素分割算法。首先,对图像进行正六边形初始化与不稳定点初始化;其次,利用实对称Kennaugh矩阵之间的测地线距离来度量当前不稳定点与其搜索范围内其他聚类中心点之间的相似度,以便更准确地为当前不稳定点分配标签,从而快速减少不稳定点的数量;最后,利用后处理步骤消除孤立像素点以生成最终的超像素。利用仿真极化SAR数据验证了初始化方法的有效性和测地线距离度量的高效性,并利用仿真和实测数据将该文算法与其他4种算法进行对比分析。实验结果表明,该文方法生成的超像素具有更规则的形状并且能够准确地贴合真实地物边缘,同时具有更高的运算效率。
-
关键词:
- 极化SAR图像 /
- 超像素分割 /
- Kennaugh矩阵 /
- 测地线距离 /
- 正六边形
Abstract: Considering the lack of similarity capabilities of the distance metric used in the traditional Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) image superpixel segmentation algorithm, a novel PolSAR image superpixel segmentation algorithm based on geodesic distance is proposed in this paper. First, the PolSAR image is initialized as a hexagonal distribution, and all pixels are initialized as unstable pixels. Thereafter, the geodesic distance between two real symmetric Kennaugh matrices is used to measure the similarity between the current unstable point and another cluster point in the search region to more accurately assign labels to unstable points, thereby effectively reducing the number of unstable points. Finally, the postprocessing procedure is used to remove small, isolated regions and generate the final superpixels. To verify the effectiveness of the initialization method and the high efficiency of the geodesic distance, extensive experiments are conducted using simulated PolSAR images. Moreover, the proposed algorithm is analyzed and compared with four other algorithms using simulated and real-world images. Experimental results show that the superpixels generated using the proposed method exhibit higher computational efficiency and a more regular shape that can more accurately fit the edges of real objects compared with those using the four other algorithms.-
Key words:
- PolSAR image /
- Superpixel segmentation /
- Kennaugh matrix /
- Geodesic distance /
- Hexagon
-
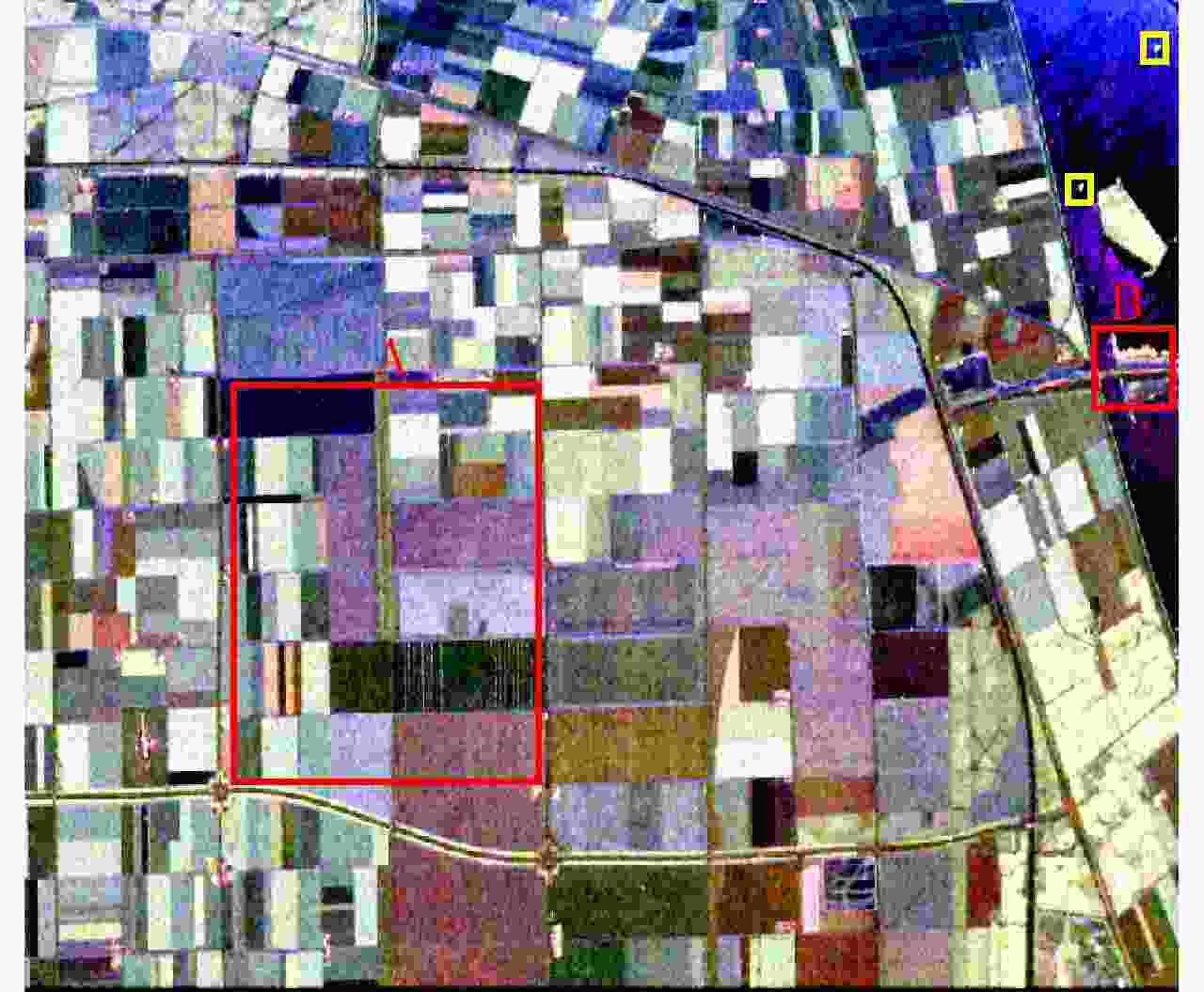
表 1 5种算法基于区域A的4种评价度量
Table 1. Four criteria of five methods for the region A of the real-world PolSAR image
算法 BR USE ASA 运行时间(s) POL-SLIC 0.6958 0.2558 0.9600 58 POL-LSC 0.5872 0.2276 0.9593 5 POL-IER 0.7762 0.2268 0.9602 32 FHAWS 0.7868 0.2097 0.9611 33 FHAGS 0.7321 0.2415 0.9596 26 表 2 针对实测极化SAR数据的5种超像素分割算法的运行时间
Table 2. Running Time(s) of five superpixel generation methods for the real-world PolSAR image
算法 运行时间(s) 分割后处理时间(s) 总时间(s) POL-SLIC 839 124 963 POL-LSC 371 – 371 POL-IER 641 65 706 FHAWS 618 66 684 FHAGS 523 64 587 -
[1] 邹焕新, 罗天成, 张月, 等. 基于组合条件随机场的极化SAR图像监督地物分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109ZOU Huanxin, LUO Tiancheng, ZHANG Yue, et al. Combined conditional random fields model for supervised PolSAR images classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109 [2] 邹焕新, 李美霖, 马倩, 等. 一种基于张量积扩散的非监督极化SAR图像地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057ZOU Huanxin, LI Meilin, MA Qian, et al. An unsupervised PolSAR image classification algorithm based on tensor product graph diffusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057 [3] STUTZ D, HERMANS A, and LEIBE B. Superpixels: An evaluation of the state-of-the-art[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 166: 1–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2017.03.007 [4] LI Meilin, ZOU Huanxin, MA Qian, et al. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR image based on tensor product graph diffusion[C]. The Fourth International Workshop on Pattern Recognition, Nanjing, China, 2019: 11198. [5] TIRANDAZ Z, AKBARIZADEH G, and KAABI H. PolSAR image segmentation based on feature extraction and data compression using weighted neighborhood filter bank and hidden Markov random field-expectation maximization[J]. Measurement, 2020, 153: 107432. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107432 [6] SONG Wanying, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Superpixel-based hybrid discriminative random field for fast PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 24547–24558. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899116 [7] LIN Huiping, BAO Junliang, YIN Junjun, et al. Superpixel segmentation with boundary constraints for polarimetric SAR images[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 6195–6198. [8] LANG Fengkai, YANG Jie, LI Deren, et al. Mean-shift-based speckle filtering of polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4440–4454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282036 [9] LANG Fengkai, YANG Jie, YAN Shiyong, et al. Superpixel segmentation of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images based on generalized mean shift[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1592. doi: 10.3390/rs10101592 [10] LIU Mingyu, TUZEL O, RAMALINGAM S, et al. Entropy rate superpixel segmentation[C]. CVPR 2011, Providence, USA, 2011: 2097–2104. [11] ZHANG Yuhang, HARTLEY R, MASHFORD J, et al. Superpixels via pseudo-Boolean optimization[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1387–1394. [12] LEVINSHTEIN A, STERE A, KUTULAKOS K N, et al. TurboPixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(12): 2290–2297. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.96 [13] NOCK R and NIELSEN F. Statistical region merging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(11): 1452–1458. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.110 [14] ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 [15] LI Zhengqin and CHEN Jiansheng. Superpixel segmentation using linear spectral clustering[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1356–1363. [16] ZHU Song, CAO Danhua, JIANG Shixiong, et al. Fast superpixel segmentation by iterative edge refinement[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(3): 230–232. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.3379 [17] FENG Jilan, CAO Zongjie, and PI Yiming. Polarimetric contextual classification of PolSAR images using sparse representation and superpixels[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(8): 7158–7181. doi: 10.3390/rs6087158 [18] XIANG Deliang, NI W, ZHANG H, et al. Superpixel segmentation for PolSAR images with local iterative clustering and heterogeneous statistical model[C]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2017: 499–506. [19] HOU Biao, YANG Chen, REN Bo, et al. Decomposition-feature-iterative-clustering-based superpixel segmentation for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(8): 1239–1243. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2833492 [20] 张月, 邹焕新, 邵宁远, 等. 一种用于极化SAR图像的快速超像素分割算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 564–573. doi: 10.12000/JR17018ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Fast superpixel segmentation algorithm for PolSAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 564–573. doi: 10.12000/JR17018 [21] RATHA D, DE S, CELIK T, et al. Change detection in polarimetric SAR images using a geodesic distance between scattering mechanisms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1066–1070. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2696158 [22] RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 [23] NAKAHARA M. Geometry, Topology and Physics[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2003. [24] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [25] YOU Biao, YANG Jian, YIN Junjun, et al. Decomposition of the Kennaugh matrix based on a new norm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(5): 1000–1004. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2284336 [26] QIN Fachao, GUO Jiming, and LANG Fengkai. Superpixel segmentation for polarimetric SAR imagery using local iterative clustering[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 13–17. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2322960 [27] VASILE G, TROUVÉ E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 [28] QIN Xianxiang, ZOU Huanxin, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Simulation of spatially correlated PolSAR images using inverse transform method[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2015, 9(1): 095082. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.9.095082 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: