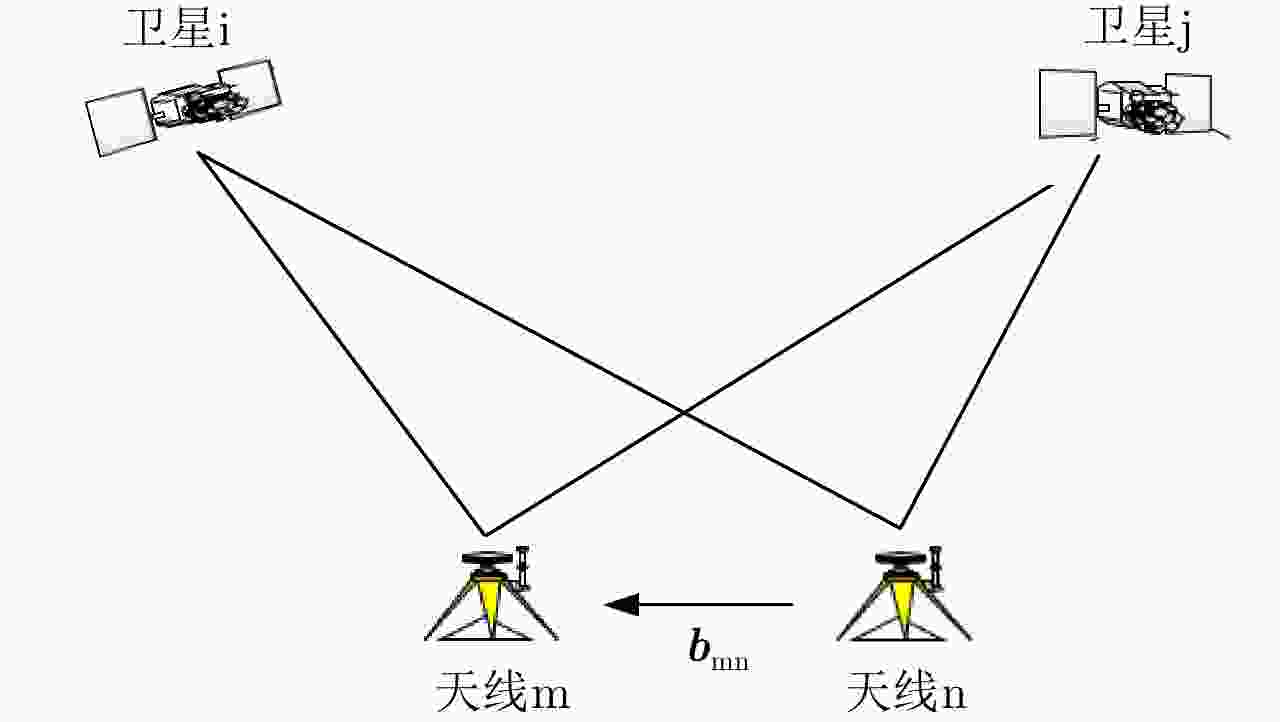
Multi-antenna Remote Differential Monitoring System Based on a Single GNSS-over-fiber Architecture
-
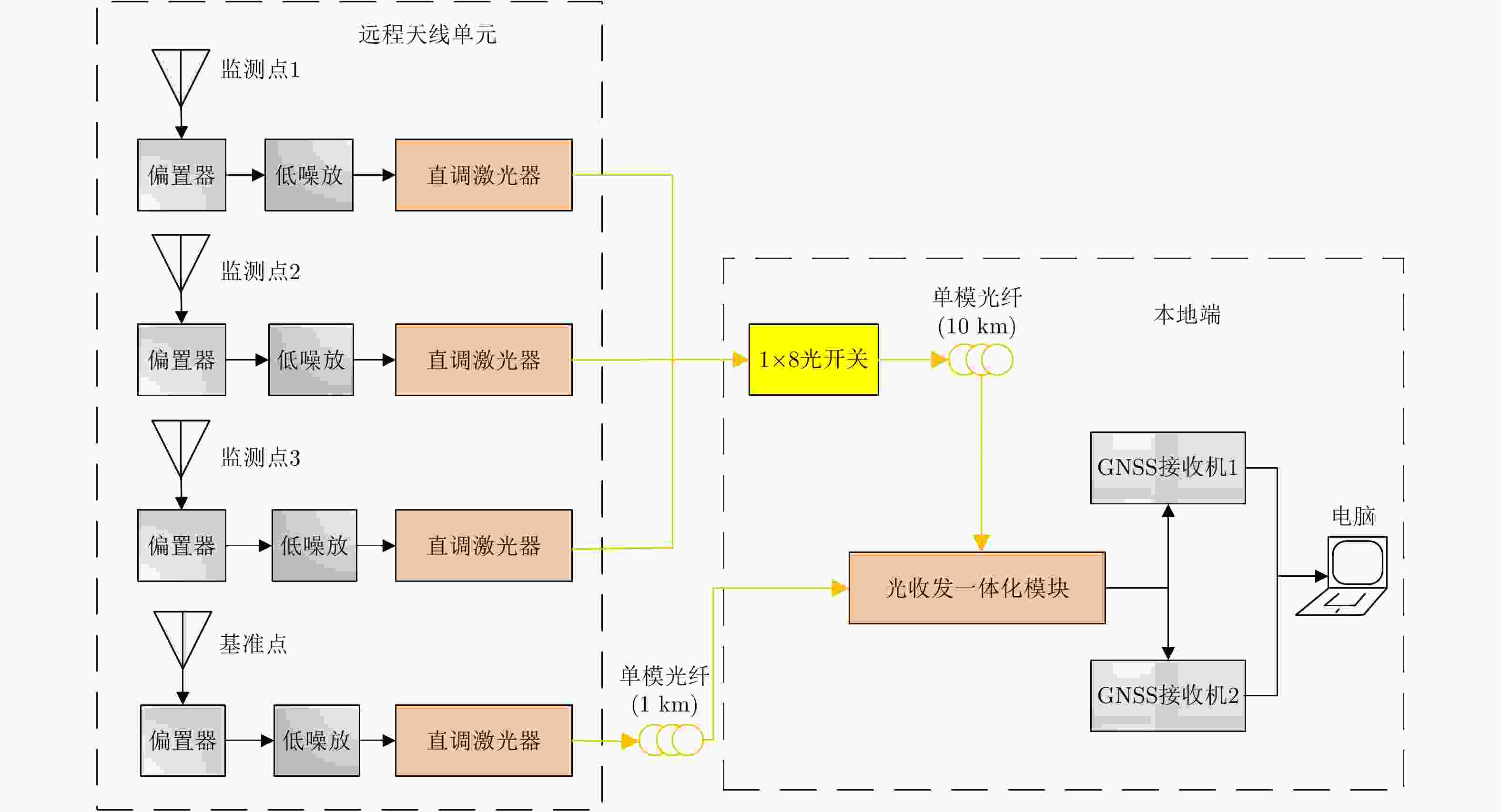
摘要: 该文设计了一种光载一机多天线远程全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)差分监测系统。该系统利用微波光子链路远程采集多个远端天线接收的GNSS信号,并传输回本地端;然后在本地端借助高速光开关,以时分模式依次建立各远端信号与参考基准信号的载波相位双差模型方程,处理后实时获得高定位精度。实验中布设了10 km微波光子链路,3个远程监测点在E, N, U方向定位精度都达到毫米量级、实时响应时间低于10 ms。与传统一机单天线方案相比,该光载一机多天线GNSS差分监测系统在不降低定位精度的前提下,显著提升了监测/覆盖范围、实时监测/响应时间,以及大规模监测的性价比。因此,该系统在大型土建工程、自然环境大规模监测具有重要应用价值。Abstract: In this study, we designed and demonstrated the performance of a multi-antenna remote differential monitoring system based on a single GNSS-over-fiber architecture. In this system, multiple GNSS signals are received by remote antennas through a microwave photonic link and are then transmitted to local end points. To enable fine positioning, we established a double differential model equation for use between the carrier phase of each remotely received signal and the reference GNSS signal, with the help of the time division mode using a high-speed optical switch. In our experiment, we established a 10 km microwave photonic link among three remote monitoring points. We estimate the resulting positioning accuracy to be within several millimeters and we obtained a response time of less than 10 ms. Compared with traditional single-antenna schemes, our designed system has significant advantages with respect to coverage area, real-time response time, and the performance cost of large-scale monitoring at no cost to the positioning accuracy. As such, this system will find important applications for the monitoring of large-scale civil engineering and natural environments.
-
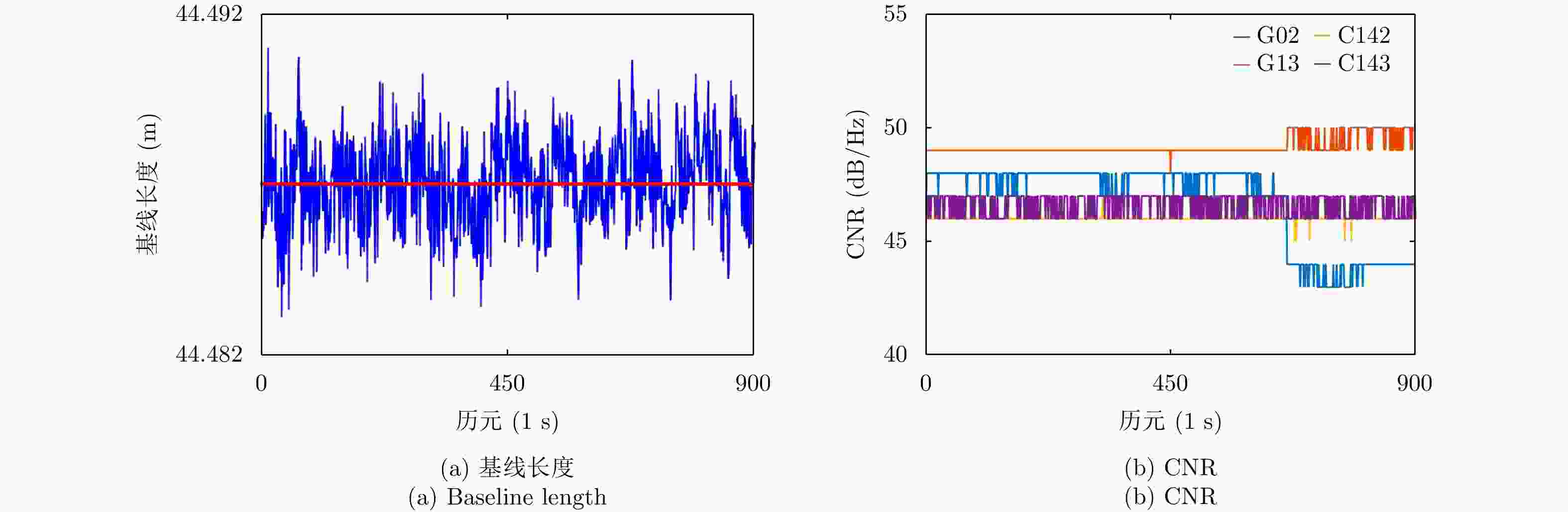
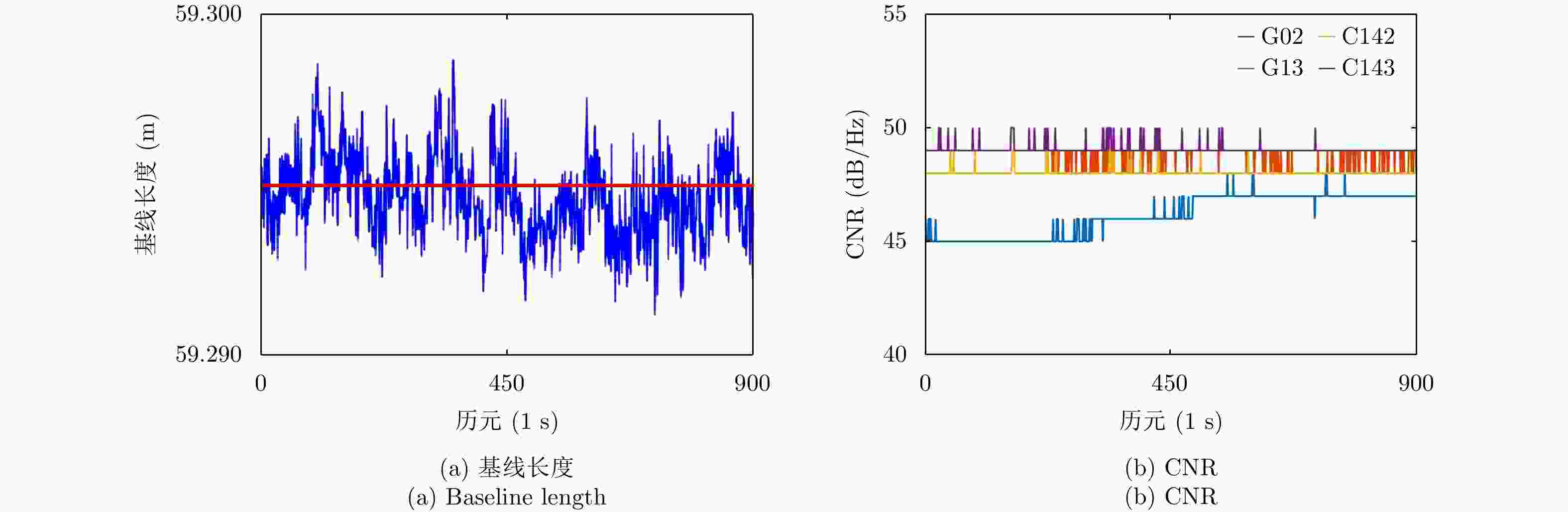
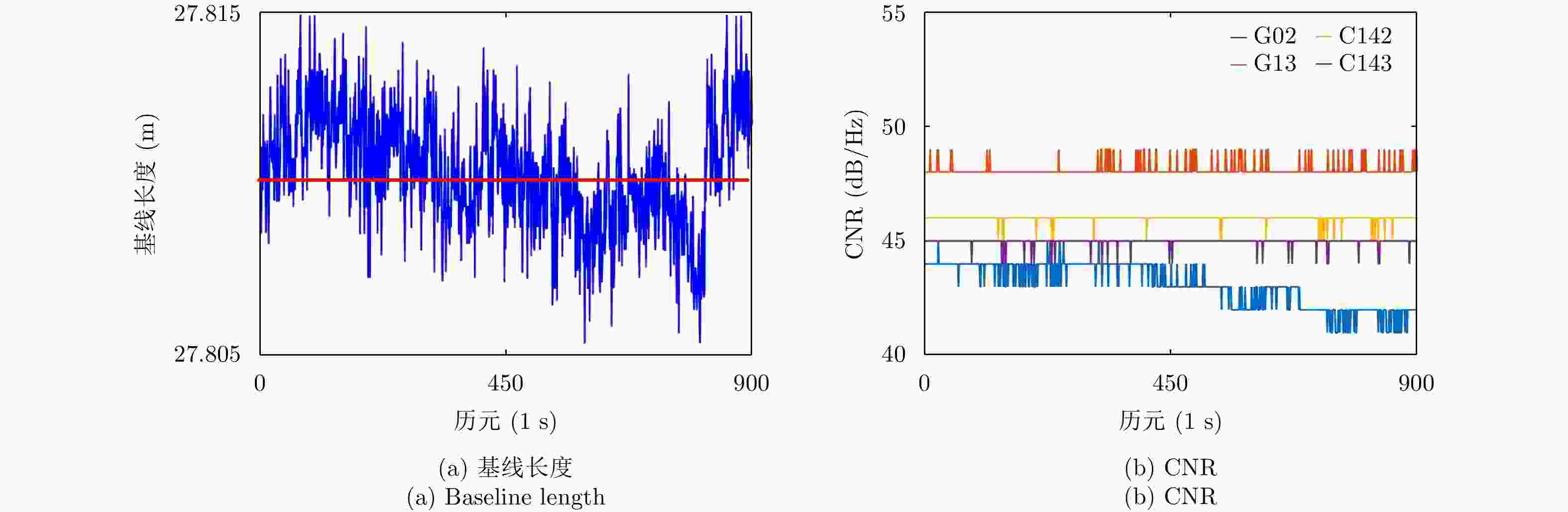
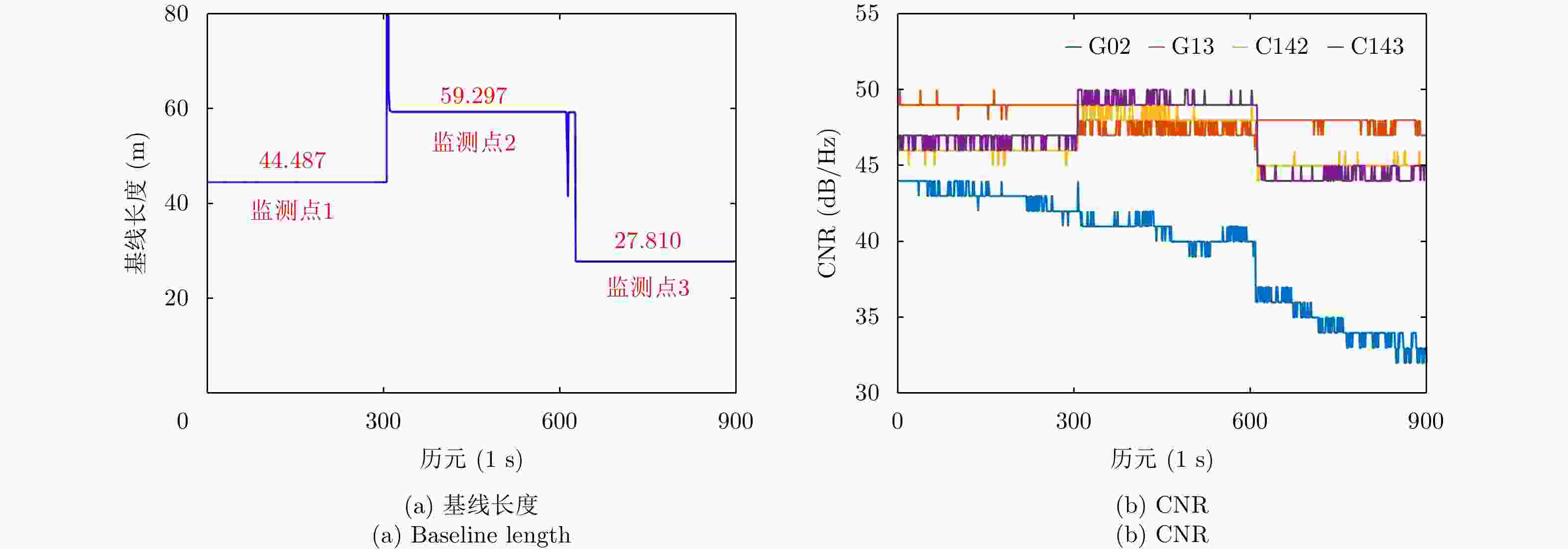
表 1 监测点1, 2, 3的E, N, U方向的平均值和标准差(Ⅰ:一机单天线GNSS系统. Ⅱ:光载一机多天线GNSS系统)
Table 1. Mean values and standard deviations in E, N and U directions of monitoring point 1, 2, 3 (Ⅰ: One-antenna GNSS system. Ⅱ: Multi-antenna GNSS system)
监测点 E方向 N方向 U方向 基线长度 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅱ 1 均值(m) 42.181 42.181 14.134 14.134 –0.003 –0.006 44.487 44.487 标准差(mm) 1.3 1.6 1.7 2.4 3.9 2.5 1.3 1.3 2 均值(m) 58.271 58.272 10.961 10.962 0.006 0.008 59.294 59.294 标准差(mm) 1.4 1.2 1.7 2.1 3.7 3.5 1.3 1.2 3 均值(m) 27.808 27.809 0.283 0.283 0.042 0.043 27.810 27.810 标准差(mm) 1.6 1.8 2.4 2.2 3.7 2.5 1.6 1.8 -
[1] 谢钢. 全球导航卫星系统原理: GPS、格洛纳斯和伽利略系统[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013.XIE Gang. Principles of GNSS: GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013. [2] 姚连璧, 姚平, 王人鹏, 等. 南浦大桥形变GPS动态监测试验及结果分析[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 36(12): 1633–1636, 1664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2008.12.007YAO Lianbi, YAO Ping, WANG Renpeng, et al. GPS-based dynamic monitoring and analysis of Nanpu Bridge deformation[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science) , 2008, 36(12): 1633–1636, 1664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2008.12.007 [3] 刘根友, 薛怀平, 郝晓光, 等. 三峡库区秭归GPS滑坡监测网数据分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2009, 29(3): 70–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2009.03.013LIU Genyou, XUE Huaiping, HAO Xiaoguang, et al. Data analysis of GPS slide monitoring network in Zigui zone of Three Gorges reservoir area[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2009, 29(3): 70–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2009.03.013 [4] 姜卫平, 刘鸿飞, 刘万科, 等. 西龙池上水库GPS变形监测系统研究及实现[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2012, 37(8): 949–952.JIANG Weiping, LIU Hongfei, LIU Wanke, et al. CORS development for Xilongchi dam deformation monitoring[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(8): 949–952. [5] 彭伟, 徐俊臣, 杜玉杰, 等. 基于北斗系统的海洋环境监测数据传输系统设计[J]. 海洋技术, 2009, 28(3): 13–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2009.03.004PENG Wei, XU Junchen, DU Yujie, et al. Design of marine monitoring data transmitting system based on Beidou satellites system[J]. Ocean Technology, 2009, 28(3): 13–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2009.03.004 [6] 丁盼, 席瑞杰, 肖玉钢. 北斗卫星导航系统用于东北地区高精度变形监测性能分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2016(4): 33–37. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2016.0116DING Pan, XI Ruijie, and XIAO Yugang. Performance analysis of high-precision deformation monitoring using Beidou navigation satellite system in Northeast China Region[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2016(4): 33–37. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2016.0116 [7] 王利, 张勤, 范丽红, 等. 北斗/GPS融合静态相对定位用于高精度地面沉降监测的试验与结果分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(1): 119–125. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2015.01.017WANG Li, ZHANG Qin, FAN Lihong, et al. Experiment and results of high precision land subsidence monitoring using fused BDS/GPS data and static relative positioning[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(1): 119–125. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2015.01.017 [8] XI Ruijie, CHEN Qusen, MENG Xiaolin, et al. Analysis of bridge deformations using real-time BDS measurements[C]. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology (ICCSNT), Dalian, China, 2017: 532–536. doi: 10.1109/ICCSNT.2017.8343756. [9] XIONG Chunbao, LU Huali, and ZHU Jinsong. Operational modal analysis of bridge structures with data from GNSS/accelerometer measurements[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 436. doi: 10.3390/s17030436 [10] XI Ruijie, JIANG Weiping, MENG Xiaolin, et al. Bridge monitoring using BDS-RTK and GPS-RTK techniques[J]. Measurement, 2018, 12: 128–139. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.02.001 [11] CHEN Yongqi, DING Xiaoli, HUANG Dingfa, et al. A multi-antenna GPS system for local area deformation monitoring[J]. Earth, Planets & Space, 2000, 52(10): 873–876. doi: 10.1186/BF03352298 [12] 何秀凤, 贾东振, 刘志平. 基于GPS一机多天线方法的大型桥梁动态变形监测[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(1): 44–48. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2011.01.010HE Xiufeng, JIA Dongzhen, and LIU Zhiping. Application of GPS multi-antenna method to dynamic deformation monitoring of long-span bridges[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences) , 2011, 39(1): 44–48. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2011.01.010 [13] XIE Feng and LI Quanwen. Highway slope monitoring system based multi-antenna GPS network[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 261-263: 1151–1155. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.261-263.1151 [14] 刘彦杰, 付庆伟, 倪自强. GPS一机多天线滑坡监测系统的建立和应用[J]. 人民长江, 2013, 44(15): 52–53, 97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2013.15.014LIU Yanjie, FU Qingwei, and NI Ziqiang. Establishment and application of landslide monitoring system using GPS of single instrument with multi-antennas[J]. Yangtze River, 2013, 44(15): 52–53, 97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2013.15.014 [15] 赵西安, 樊鹏昊, 樊英姿. GNSS一机多天线远程监测系统的研发[J]. 测绘通报, 2015(11): 4–7, 101. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2015.0333ZHAO Xi’an, FAN Penghao, and FAN Yingzi. Developing the remote monitoring system based on GNSS multi-antenna[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2015(11): 4–7, 101. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2015.0333 [16] ZHANG Yamei, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Optical single sideband polarization modulation for radio-over-fiber system and microwave photonic signal processing[J]. Photonics Research, 2014, 2(4): B80–B85. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.2.000B80 [17] KARIM A M, STAFFORD S J, and BAKER R B. Global positioning system over fiber for buoyant cable antennas[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 2012, 30(4): 309–320. [18] OLIVEIRA J M B, PESSOA L M, SALGADO H M, et al. Experimental evaluation of a differential GPS-over-fiber system for aircraft attitude determination[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Avionics, Fiber-Optics and Photonics Technology Conference (AVFOP), San Diego, CA, USA, 2013: 75–76. doi: 10.1109/AVFOP.2013.6661586. [19] PESSOA L M, OLIVEIRA J M B, COELHO D, et al. Transmission of differential GPS signals over fiber for aircraft attitude determination[C]. IEEE Avionics, Fiber-Optics and Photonics Digest CD, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2012: 80–81. doi: 10.1109/AVFOP.2012.6344032. [20] 宋希希, 郭荣辉, 周永刚, 等. 光载GPS一机多天线系统的实验验证[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2014, 29(6): 957–963. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.06.013SONG Xixi, GUO Ronghui, and ZHOU Yonggang, et al. Experimental demonstration of GPS-over-fiber multi-antenna receiver system[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2014, 29(6): 957–963. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.06.013 [21] MACIAS-VALADEZ D, SANTERRE R, LAROCHELLE S, et al. Improving vertical GPS precision with a GPS-over-fiber architecture and real-time relative delay calibration[J]. GPS Solutions, 2012, 16(4): 449–462. doi: 10.1007/s10291-011-0244-6 [22] CLIVATI C, CAPPELLINI G, LIVI L F, et al. Measuring absolute frequencies beyond the GPS limit via long-haul optical frequency dissemination[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(11): 11865–11875. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.011865 [23] LI Hongnan, REN Liang, JIA Ziguang, et al. State-of-the-art in structural health monitoring of large and complex civil infrastructures[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2016, 6(1): 3–16. doi: 10.1007/s13349-015-0108-9 [24] SMALL E E, ROESLER C J, and LARSON K M. Vegetation response to the 2012—2014 california drought from GPS and optical measurements[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 630. doi: 10.3390/rs10040630 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: