Radar Active Deception Jamming Recognition Method Based on the Time-varying Polarization-conversion Metasurface
-
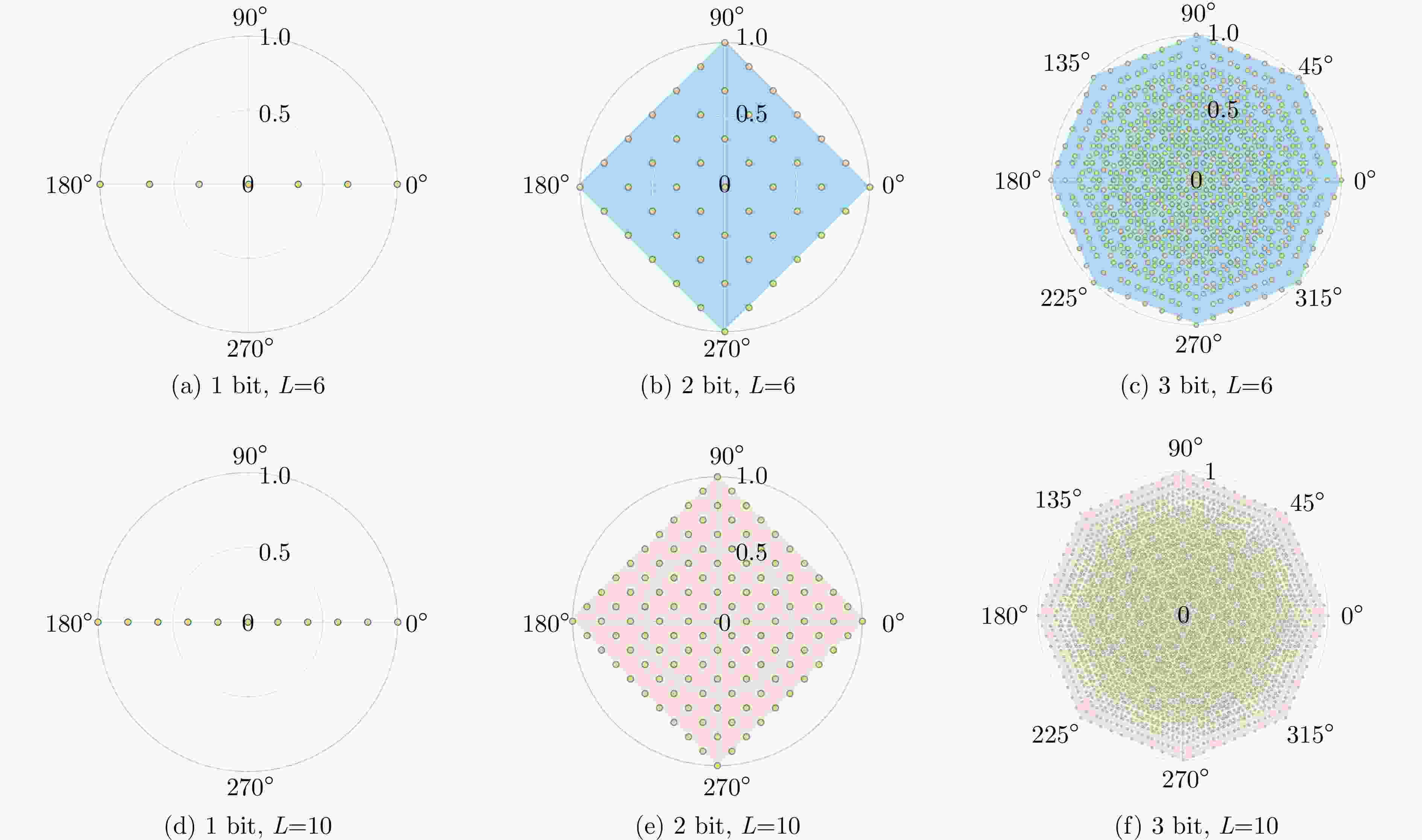
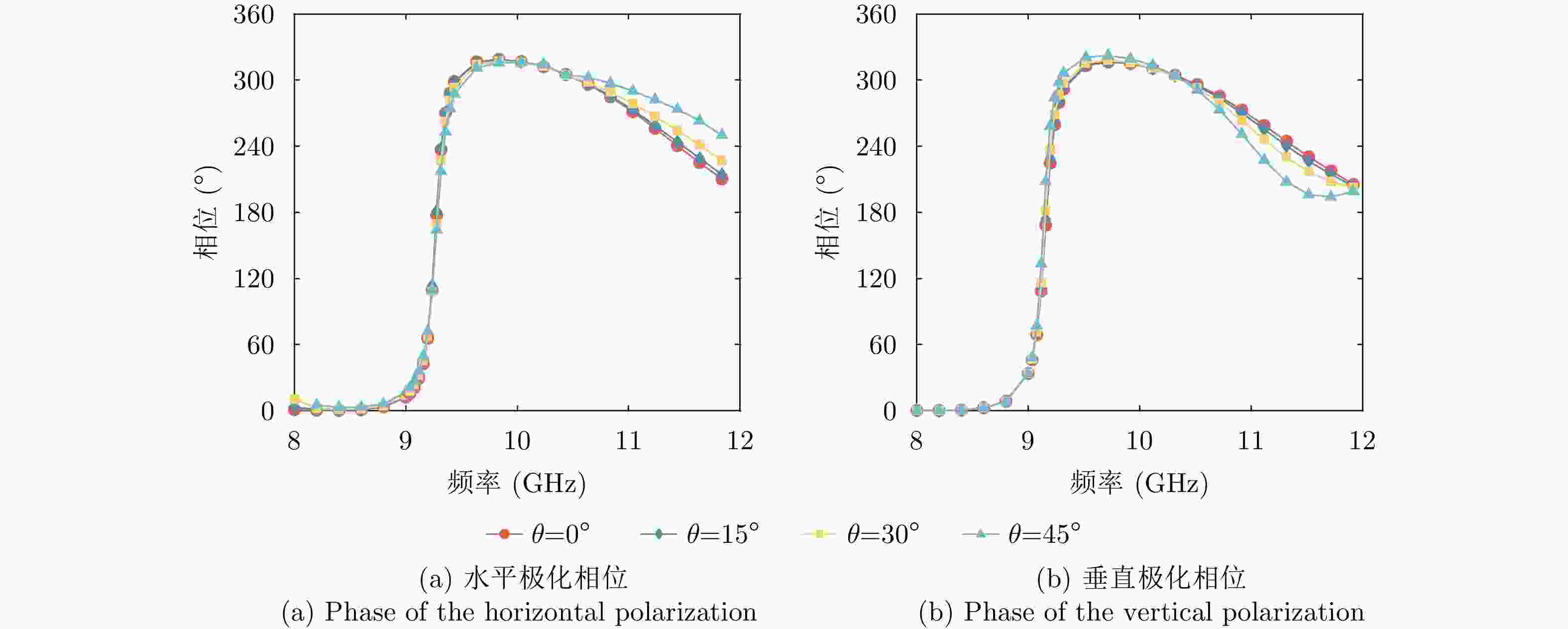
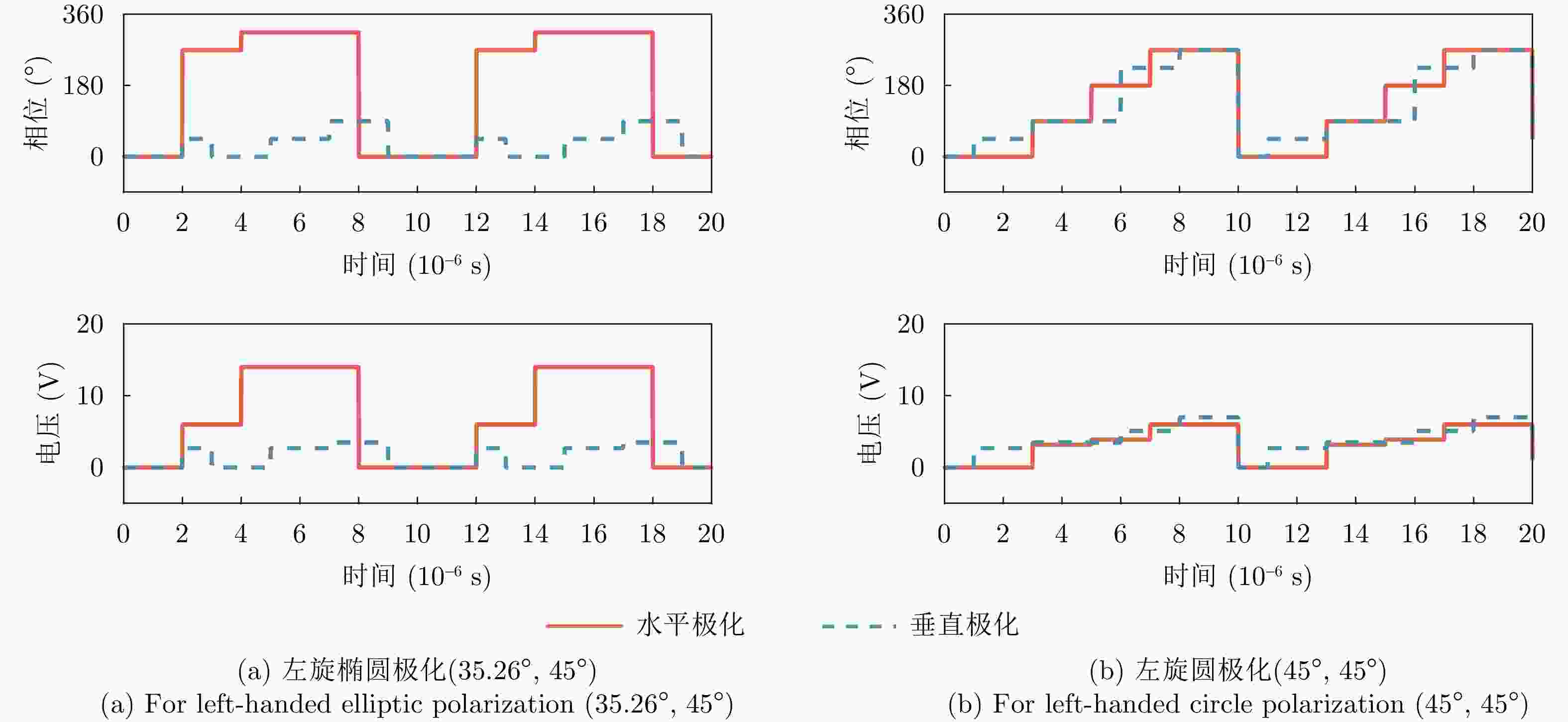
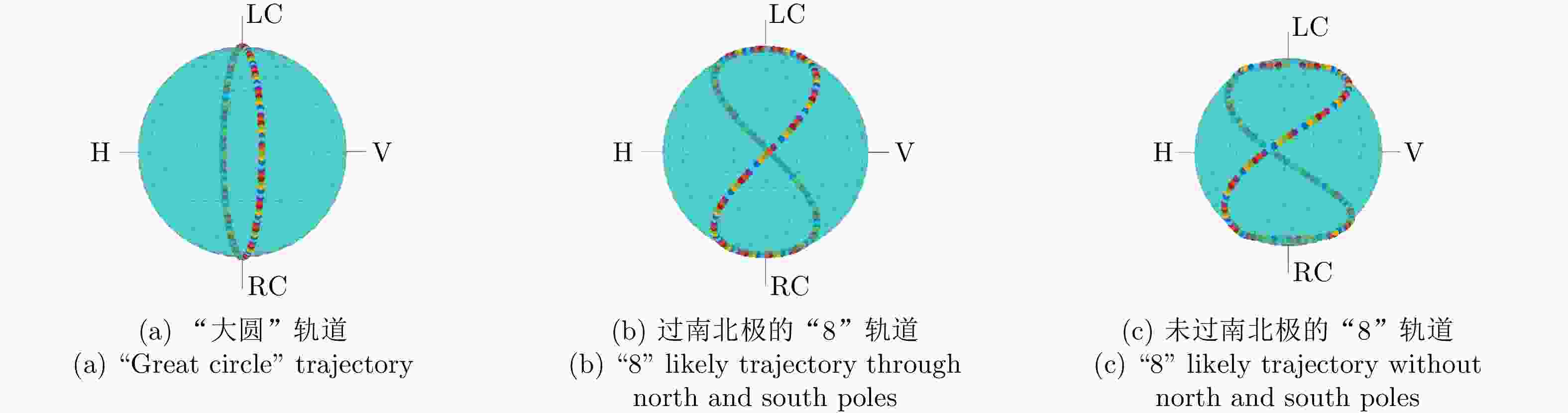
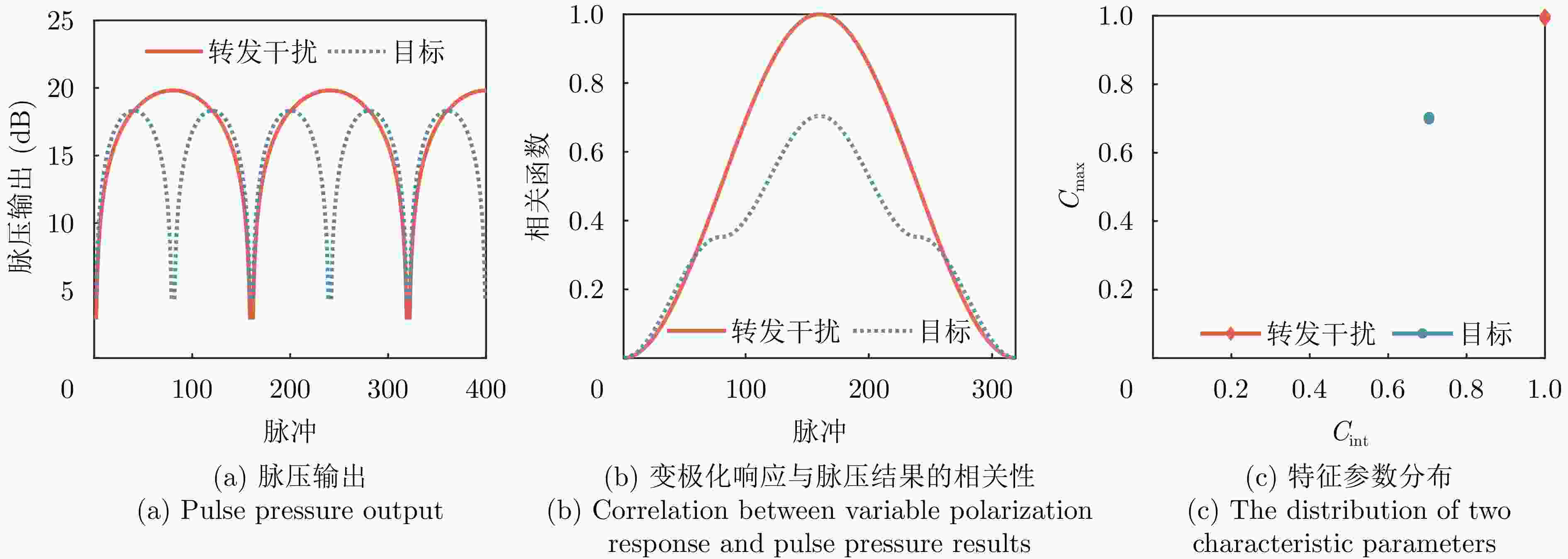
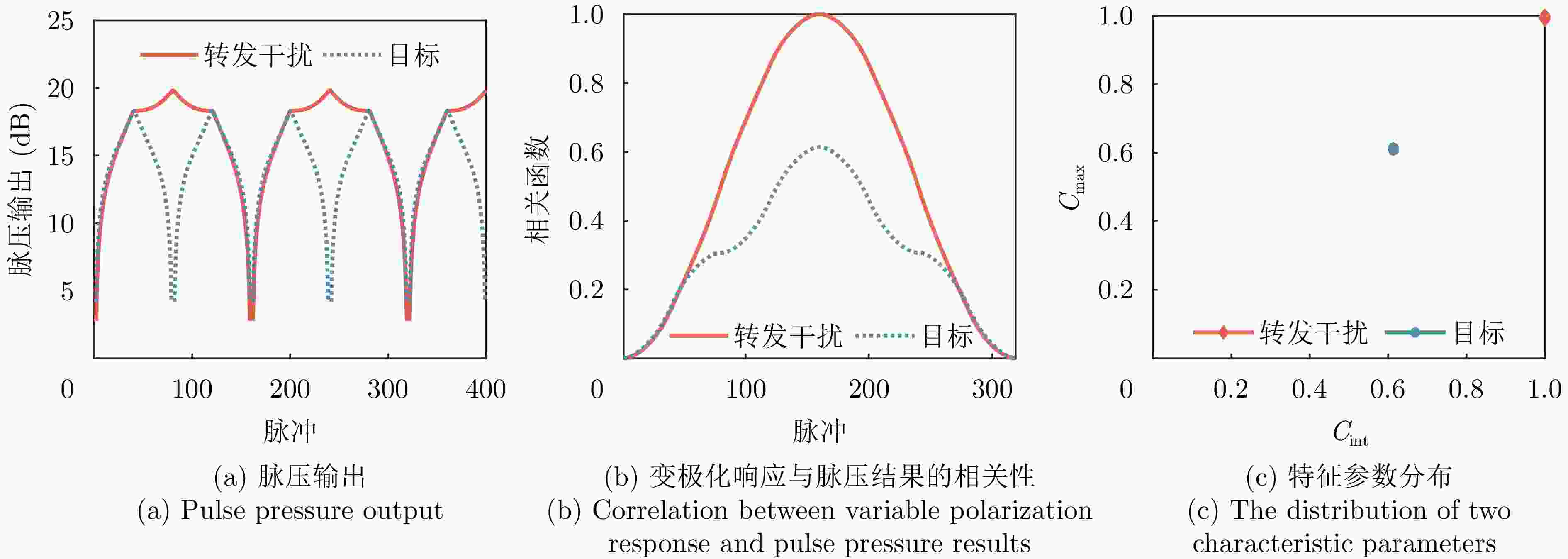
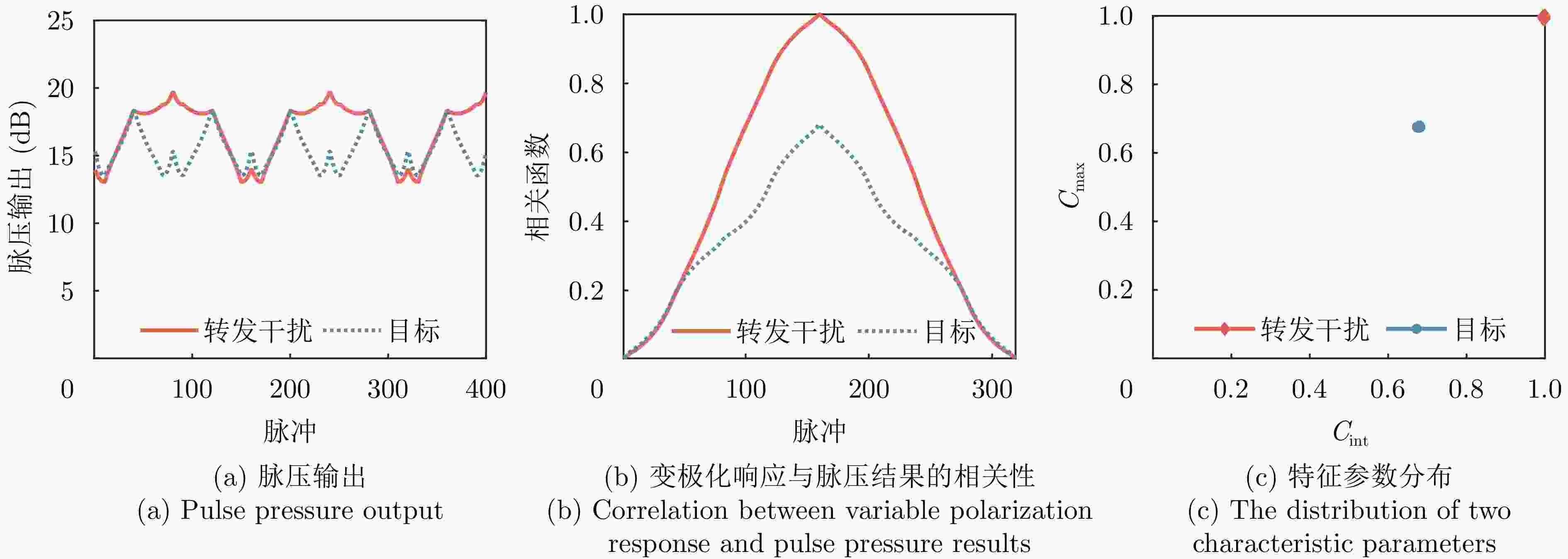
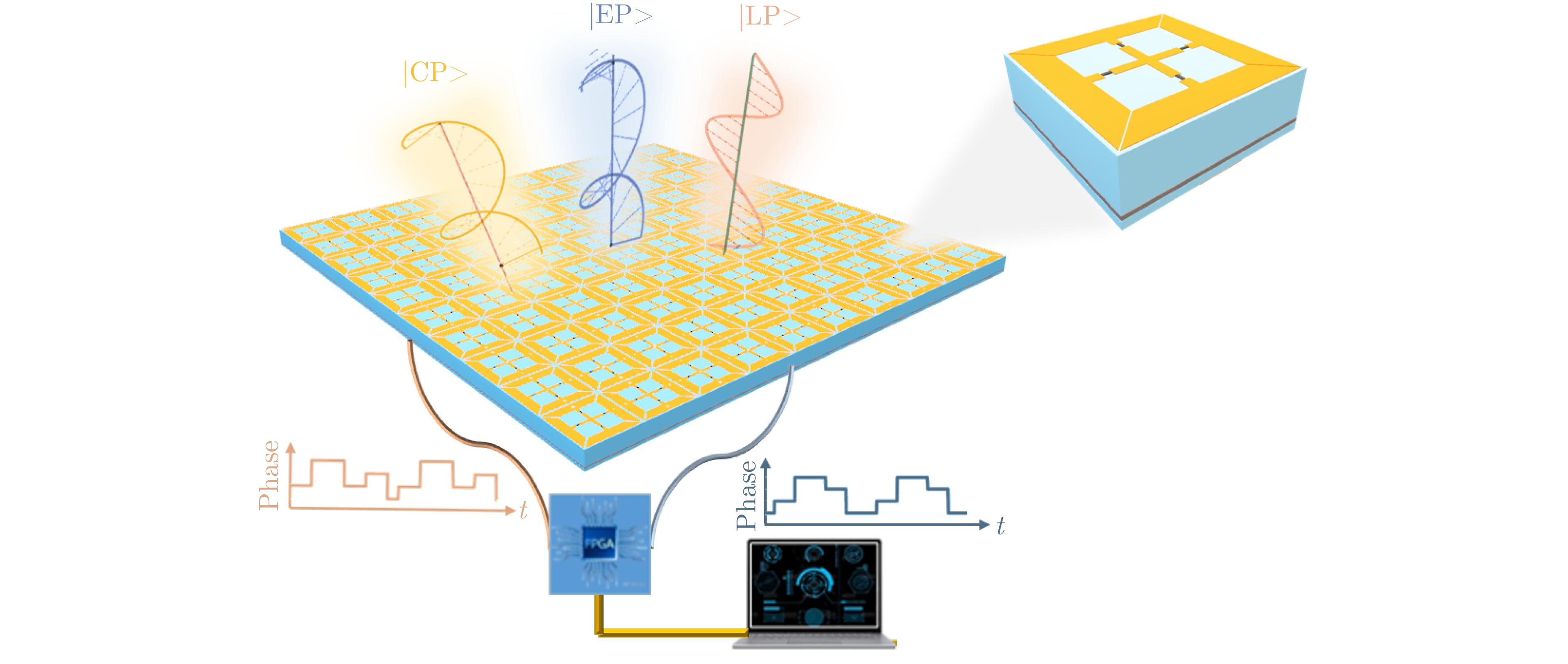
摘要: 聚焦雷达对抗中极化信息获取与利用的应用需求,该文研究了基于极化时变调控表面的有源欺骗干扰辨识方法。首先,设计了一套在9.6~10.1 GHz频带内支持3 bit相位量化的各向异性相位调制表面,通过优化相位调制编码序列,实现了极化态按需调控。然后,将极化调控表面加装在单极化雷达天线上,使天线发射和接收电磁波的极化态沿特定极化轨道变化,通过提取目标与有源欺骗干扰的极化域差异,实现两者辨识。仿真分析表明,在3种不同的极化轨道约束下,干扰与目标均具有显著的聚类效应,可获得稳定的干扰辨识效果。相较于依赖双极化或全极化雷达体制的干扰辨识方法,该文所提方法兼具低成本与高效性,在雷达抗干扰中具有很大的应用潜力。Abstract: In this study, aiming at fulfilling the requirement of polarization acquisition and utilization, a method for active deception jamming recognition based on the time-varying polarization-conversion metasurface is investigated. First, an anisotropic phase-modulated metasurface supporting 3-bit phase quantization in the 9.6~10.1 GHz frequency band is designed. By optimizing the periodical phase coding, the polarization state can be converted on demand. And then, loading the polarization-conversion metasurface on a single polarization radar antenna so that the polarization states of the antenna can change along a specific trajectory. By extracting the difference in the polarization domain between target and active deception jamming, the active deception jamming could be distinguished from the radar echo. The simulation results show that under the constraints of three different polarization trajectories, the active deception jamming and targets exhibit a significant clustering effect, and the identification effect is stable. Compared with jamming identification methods that rely on dual-polarization or full-polarization radar systems, the proposed method has both low cost and high efficiency, which has great application potential in radar anti-jamming.
-
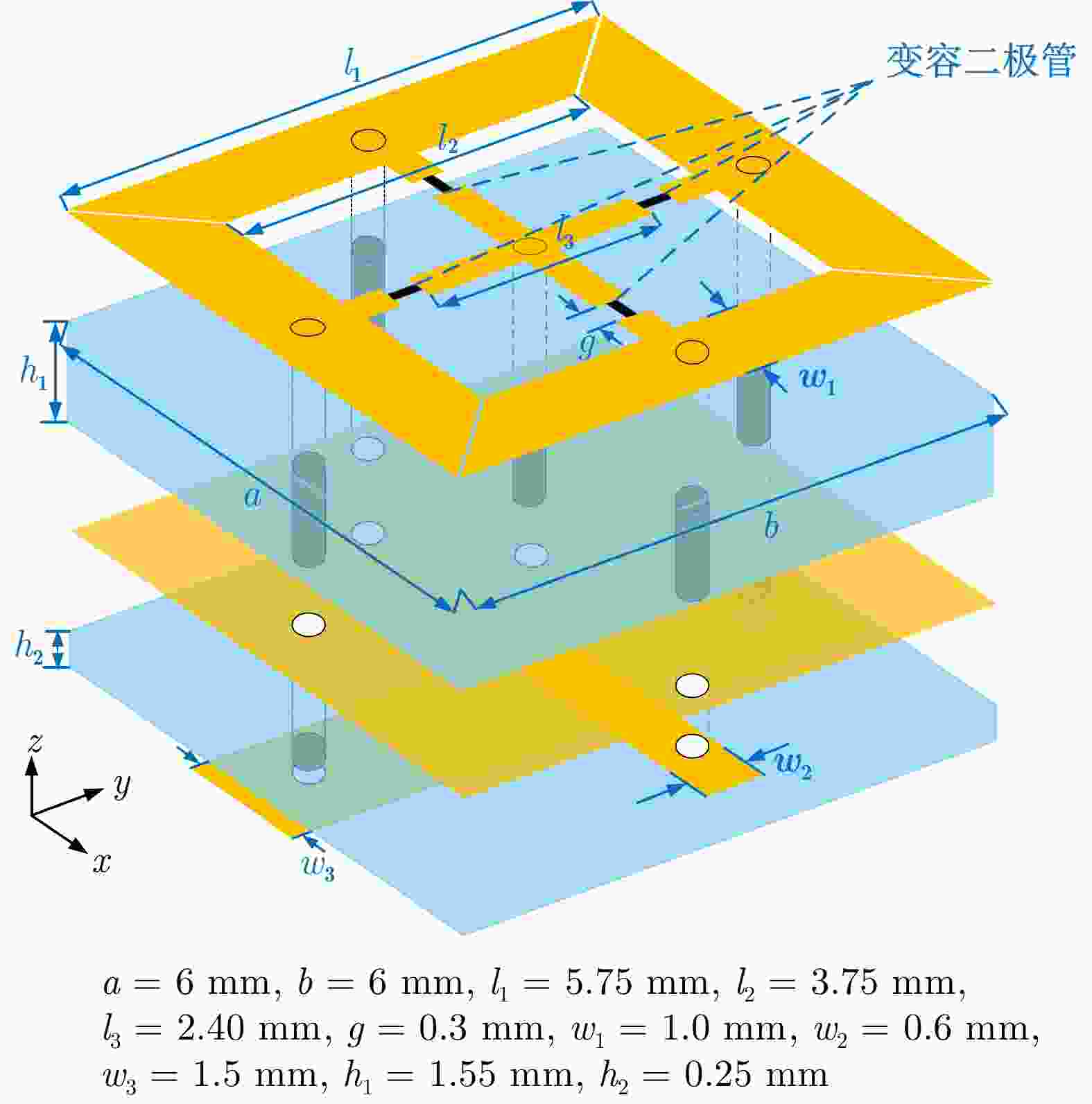
表 1 3 bit量化相位及偏置电压对应关系
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between 3 bit quantization phase and bias voltage
水平极化 垂直极化 VDC (V) $ \Delta \varphi $ (°) VDC (V) $ \Delta \varphi $ (°) 0 0 0 0 2.6 45 2.7 45 3.2 89 3.5 90 3.5 135 4.5 135 3.9 180 4.6 179 4.5 226 5.1 225 6.0 270 7.0 270 14.0 315 15.0 314 -
[1] ROOME S J. Digital radio frequency memory[J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1990, 2(4): 147. [2] 曹旭源. 基于DRFM的雷达干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2013: 5–19.CAO Xuyuan. Research on jamming against radar based on digital radio frequency memory[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2013: 5–19. [3] 高佳旭. 雷达信号有源干扰技术研究及实现[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021: 13–18.GAO Jiaxu. Research and realization of radar signal active jamming technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2021: 13–18. [4] 肖顺平, 徐振海, 代大海, 等. 雷达极化技术[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2022: 1–51.XIAO Shunping, XU Zhenhai, DAI Dahai, et al. Radar Polarization Techniques[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2022: 1–51. [5] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039.WANG Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039. [6] 施龙飞, 马佳智, 庞晨, 等. 极化雷达信号处理与抗干扰技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2019: 1–13.SHI Longfei, MA Jiazhi, PANG Chen, et al. Signal Processing and Anti-interference Techniques for Polarimetric Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2019: 1–13. [7] 马佳智, 施龙飞, 徐振海, 等. 单脉冲雷达多点源参数估计与抗干扰技术进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 125–139. doi: 10.12000/JR18093.MA Jiazhi, SHI Longfei, XU Zhenhai, et al. Overview of multi-source parameter estimation and jamming mitigation for monopulse radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 125–139. doi: 10.12000/JR18093. [8] 施龙飞, 任博, 马佳智, 等. 雷达极化抗干扰技术进展[J]. 现代雷达, 2016, 38(4): 1–7, 29. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.04.001.SHI Longfei, REN Bo, MA Jiazhi, et al. Recent developments of radar anti-interference techniques with polarimetry[J]. Modern Radar, 2016, 38(4): 1–7, 29. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.04.001. [9] 李永祯, 王雪松, 肖顺平, 等. 基于IPPV的真假目标极化鉴别算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2004, 26(9): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2004.09.011.LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. A new polarization discrimination algorithm for active decoy and radar target based on IPPV[J]. Modern Radar, 2004, 26(9): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2004.09.011. [10] 施龙飞, 王雪松, 肖顺平. 转发式假目标干扰的极化鉴别[J]. 中国科学 F辑: 信息科学, 2009, 39(4): 468–475.SHI Longfei, WANG Xuesong, and XIAO Shunping. Polarization discrimination between repeater false-target and radar target[J]. Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 2009, 39(4): 468–475. [11] ZONG Zhiwei, SHI Longfei, LI Yongzhen, et al. Detection-discrimination method for multiple repeater false targets based on radar polarization echoes[J]. Radioengineering, 2014, 23(1): 104–110. [12] 施龙飞, 帅鹏, 王雪松, 等. 极化调制假目标干扰的鉴别[J]. 信号处理, 2008, 24(6): 894–899. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.002.SHI Longfei, SHUAI Peng, WANG Xuesong, et al. Polarization discrimination between modulation polarization decoy and radar target[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 24(6): 894–899. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.002. [13] 王雪松. 宽带极化信息处理的研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 1999: 21–26, 127–179.WANG Xuesong. Study on wide-band polarization information processing[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 1999: 21–26, 127–179. [14] 蒋仁培, 苏丽萍. 雷达极化问题和铁氧体变极化技术[J]. 现代雷达, 2001, 23(1): 65–69, 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2001.01.014.JIANG Renpei and SU Liping. Problem of radar polarization and technique of ferrite variable polarization[J]. Modern Radar, 2001, 23(1): 65–69, 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2001.01.014. [15] 蒋仁培, 苏丽萍, 魏克珠. 广义铁氧体变极化理论[J]. 微波学报, 2000, 16(4): 336–342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2000.04.002.JIANG Renpei, SU Liping, and WEI Kezhu. Generalized theory of ferrite variable polarization[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2000, 16(4): 336–342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2000.04.002. [16] KARAMIRAD M, GHOBADI C, and NOURINIA J. Metasurfaces for wideband and efficient polarization rotation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(3): 1799–1804. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3012828. [17] WANG Yidan, SHI Hongyu, CHEN Juan, et al. Digital polarization programmable metasurface for continuous polarization angle rotation and radar applications[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2022, 9: 931868. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2022.931868. [18] TIAN Jianghao, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. A reconfigurable ultra-wideband polarization converter based on metasurface incorporated with PIN diodes[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(13): 135105. doi: 10.1063/1.5067383. [19] YANG Zhengyi, KOU Na, YU Shixing, et al. Reconfigurable multifunction polarization converter integrated with PIN diode[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2021, 31(6): 557–560. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2021.3064039. [20] YANG Heng, WANG Shicong, LI Peng, et al. A broadband multifunctional reconfigurable polarization conversion metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(7): 5759–5767. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3266498. [21] LI You, WANG Yi, and CAO Qunsheng. Design of a multifunctional reconfigurable metasurface for polarization and propagation manipulation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 129183–129191. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939200. [22] CERVENY M, FORD K L, and TENNANT A. Reflective switchable polarization rotator based on metasurface with PIN diodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(3): 1483–1492. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3026883. [23] LIN Baoqin, GUO Jianxin, LV Lintao, et al. Ultra-wideband and high-efficiency reflective polarization converter for both linear and circular polarized waves[J]. Applied Physics A, 2019, 125(2): 76. doi: 10.1007/s00339-018-2368-9. [24] HAO Jiaming, YUAN Yu, RAN Lixin, et al. Manipulating electromagnetic wave polarizations by anisotropic metamaterials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(6): 063908. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.063908. [25] WANG Shuai, DENG Zilan, WANG Yujie, et al. Arbitrary polarization conversion dichroism metasurfaces for all-in-one full Poincaré sphere polarizers[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2021, 10(1): 24. doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00468-y. [26] KE Junchen, DAI Junyan, CHEN Mingzheng, et al. Linear and nonlinear polarization syntheses and their programmable controls based on anisotropic time-domain digital coding metasurface[J]. Small Structures, 2021, 2(1): 2000060. doi: 10.1002/sstr.202000060. [27] HU Qi, CHEN Ke, ZHANG Na, et al. Arbitrary and dynamic Poincaré sphere polarization converter with a time-varying metasurface[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(4): 2101915. doi: 10.1002/adom.202101915. [28] ZHANG Xinge, YU Qian, JIANG Weixiang, et al. Polarization-controlled dual-programmable metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(11): 1903382. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903382. [29] 胡琪, 陈克, 郑依琳, 等. 时变极化编码表面及其在无线通信中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 304–312. doi: 10.12000/JR21042.HU Qi, CHEN Ke, ZHENG Yilin, et al. Time-varying polarization-converting programmable metasurface and its application in wireless communication system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 304–312. doi: 10.12000/JR21042. [30] DAI Junyan, ZHAO Jie, CHENG Qiang, et al. Independent control of harmonic amplitudes and phases via a time-domain digital coding metasurface[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2018, 7: 90. [31] 戴俊彦. 时域超表面理论研究与应用[D]. [博士论文], 东南大学, 2019: 41.DAI Junyan. Research and application of time-domain metasurface[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Southeast University, 2019: 41. [32] 程强, 崔铁军. 电磁超材料[M]. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 2022: 259–262.CHENG Qiang and CUI Tiejun. Metamaterials[M]. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 2022: 259–262. [33] SUN Guang, WANG Junjie, XING Shiqi, et al. A flexible conformal multifunctional time-modulated metasurface for radar characteristics manipulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023: 1–15. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3337646. [34] MACOM. MA46H120 varactor datasheet[EB/OL]. https://www.macom.com/products/product-detail/MA46H120. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: