Robust High Resolution Range Profile Recognition Method for Radar Targets in Noisy Environments
-
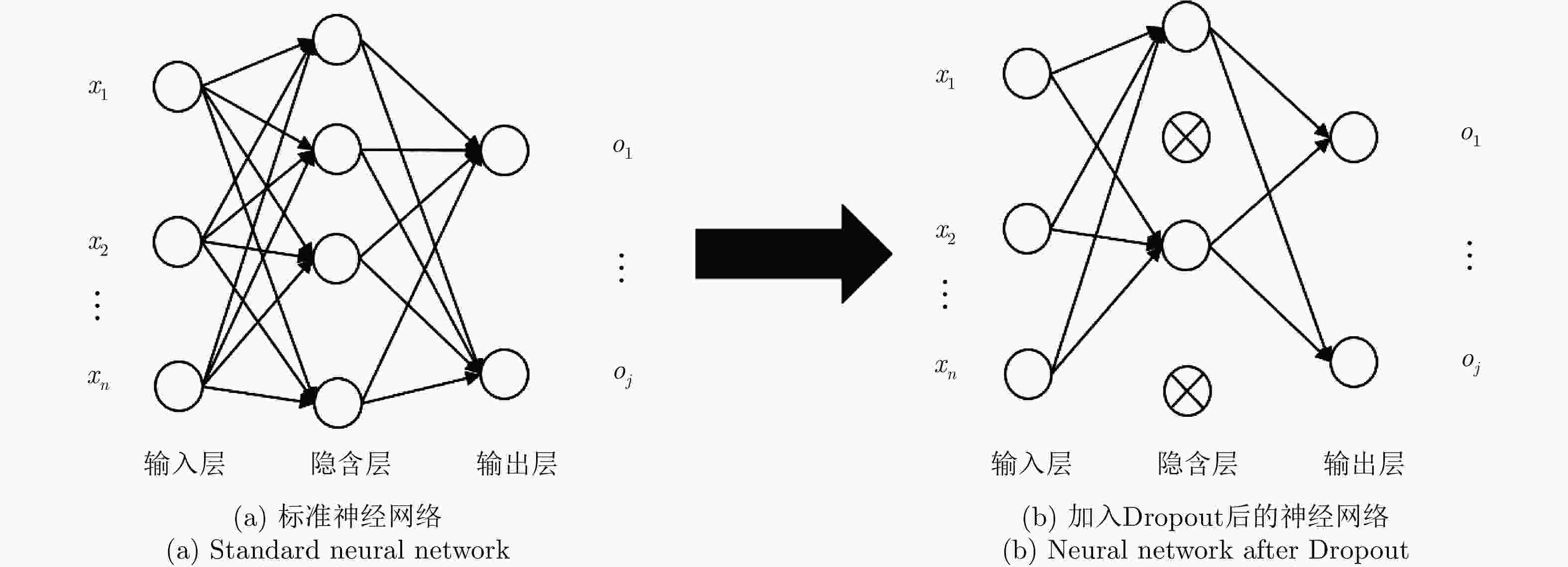
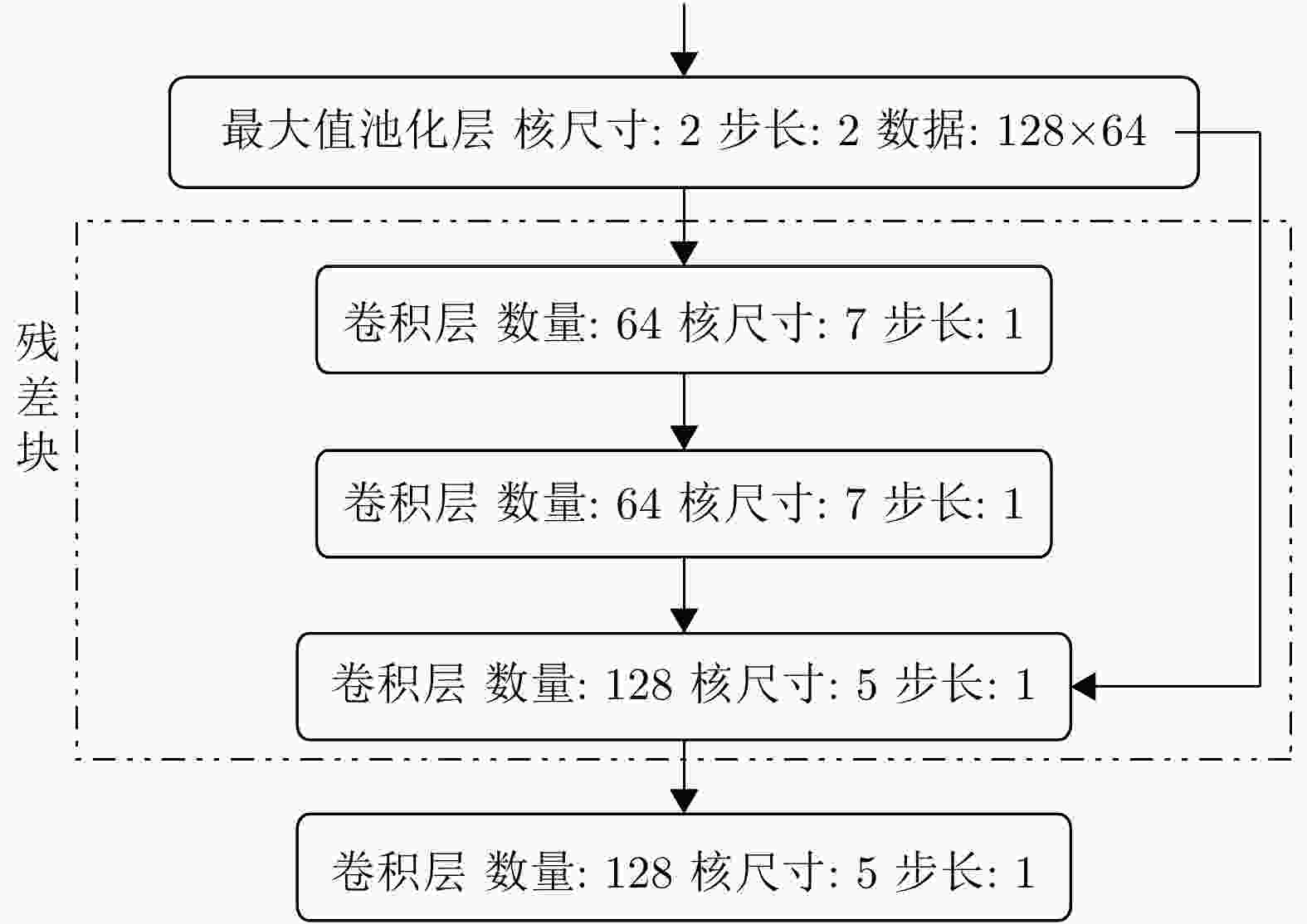
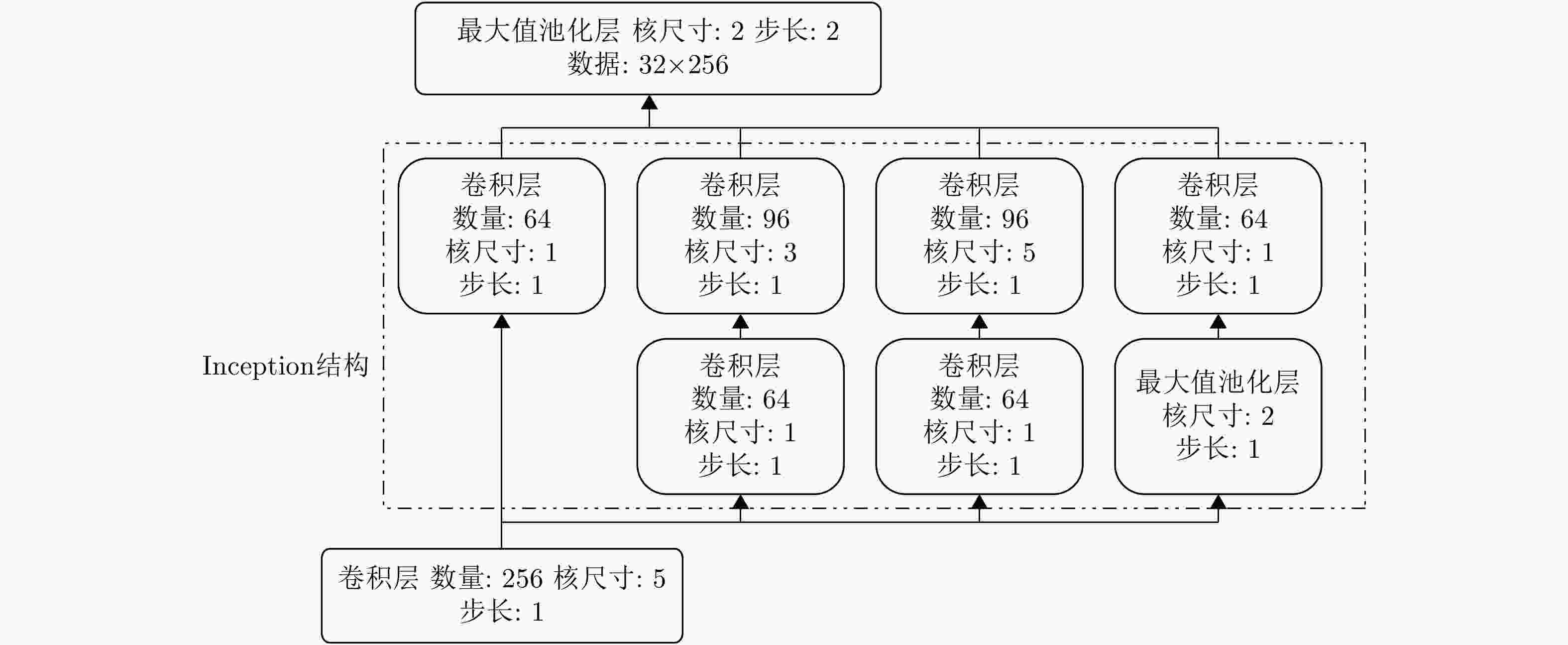
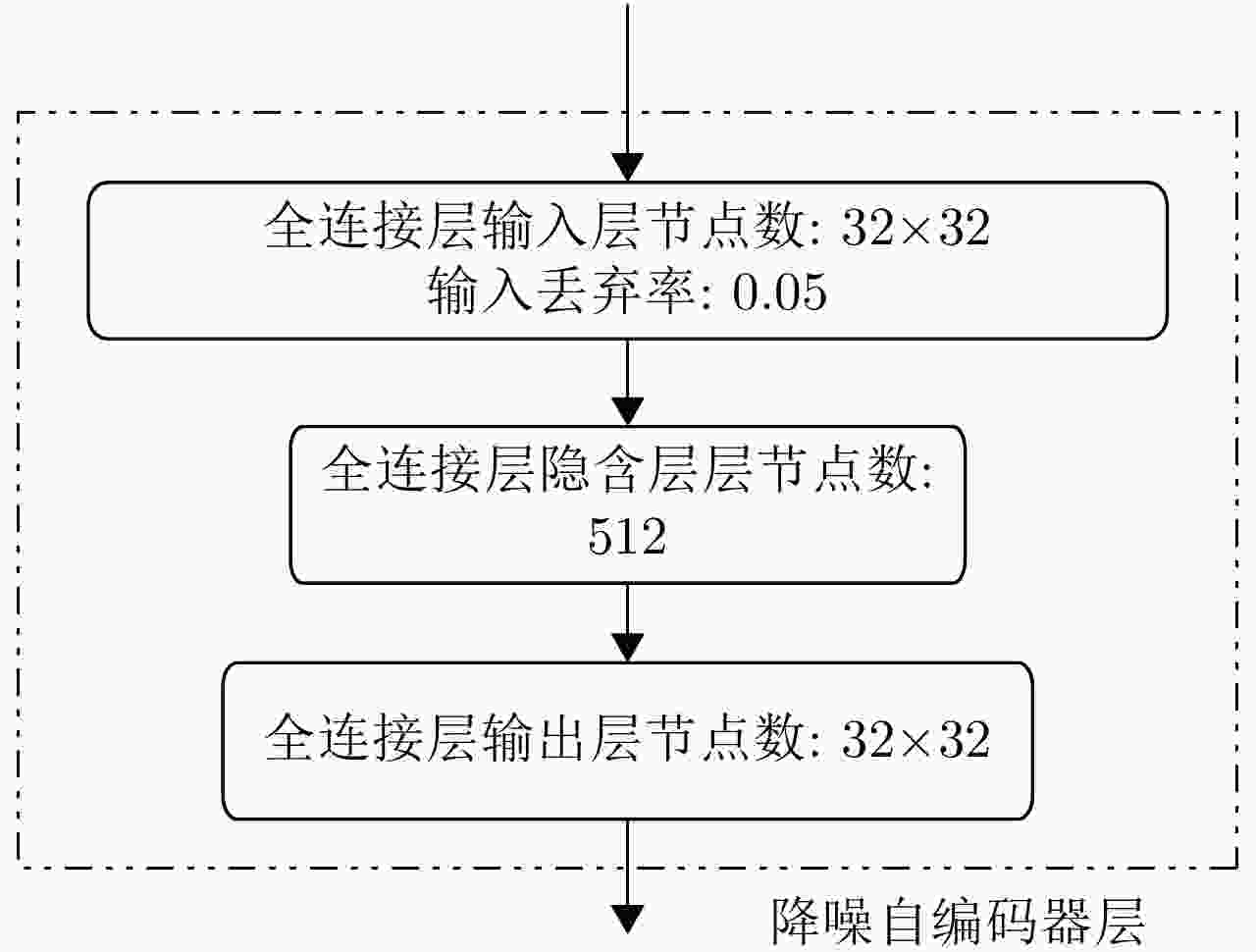
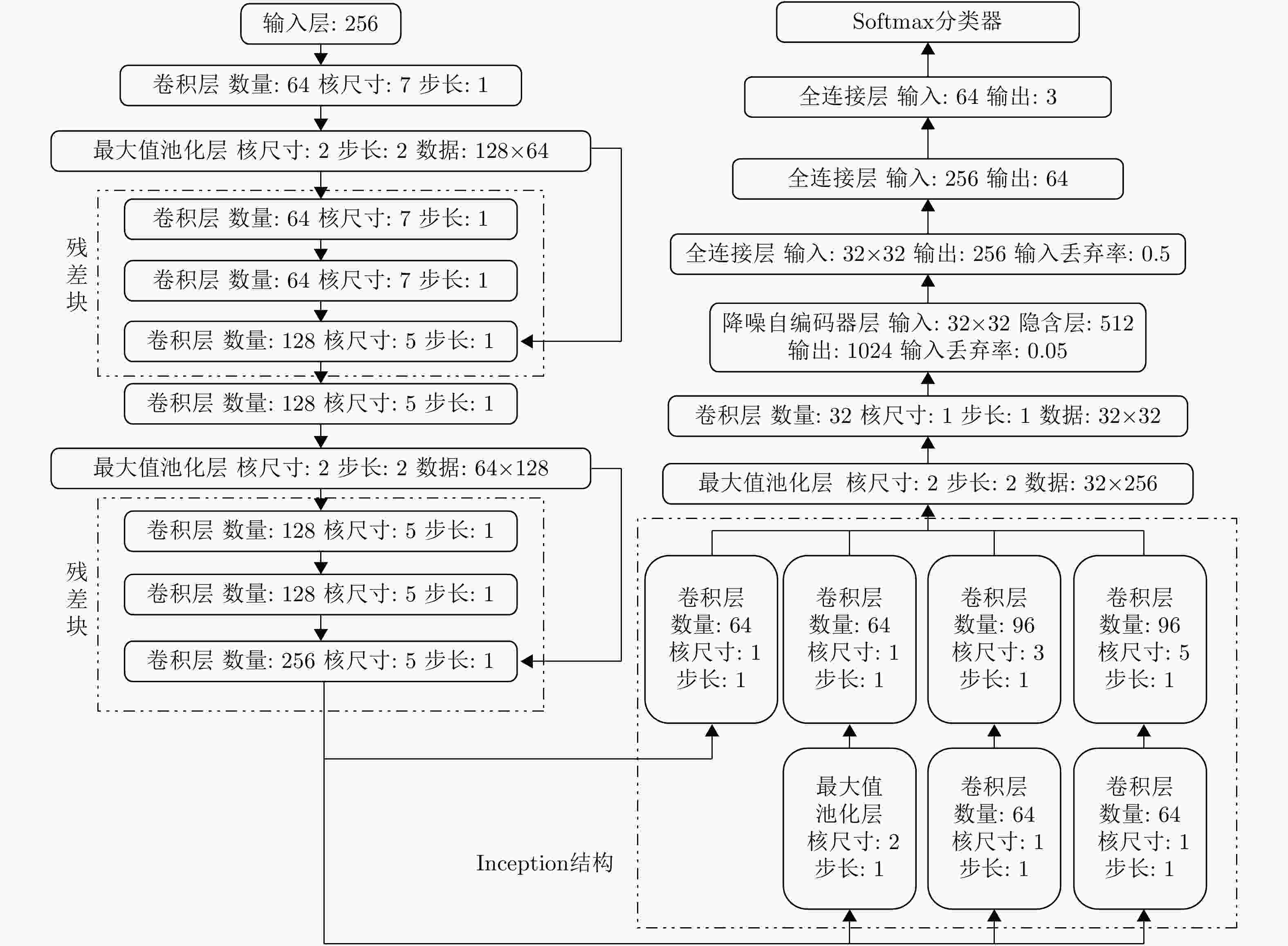
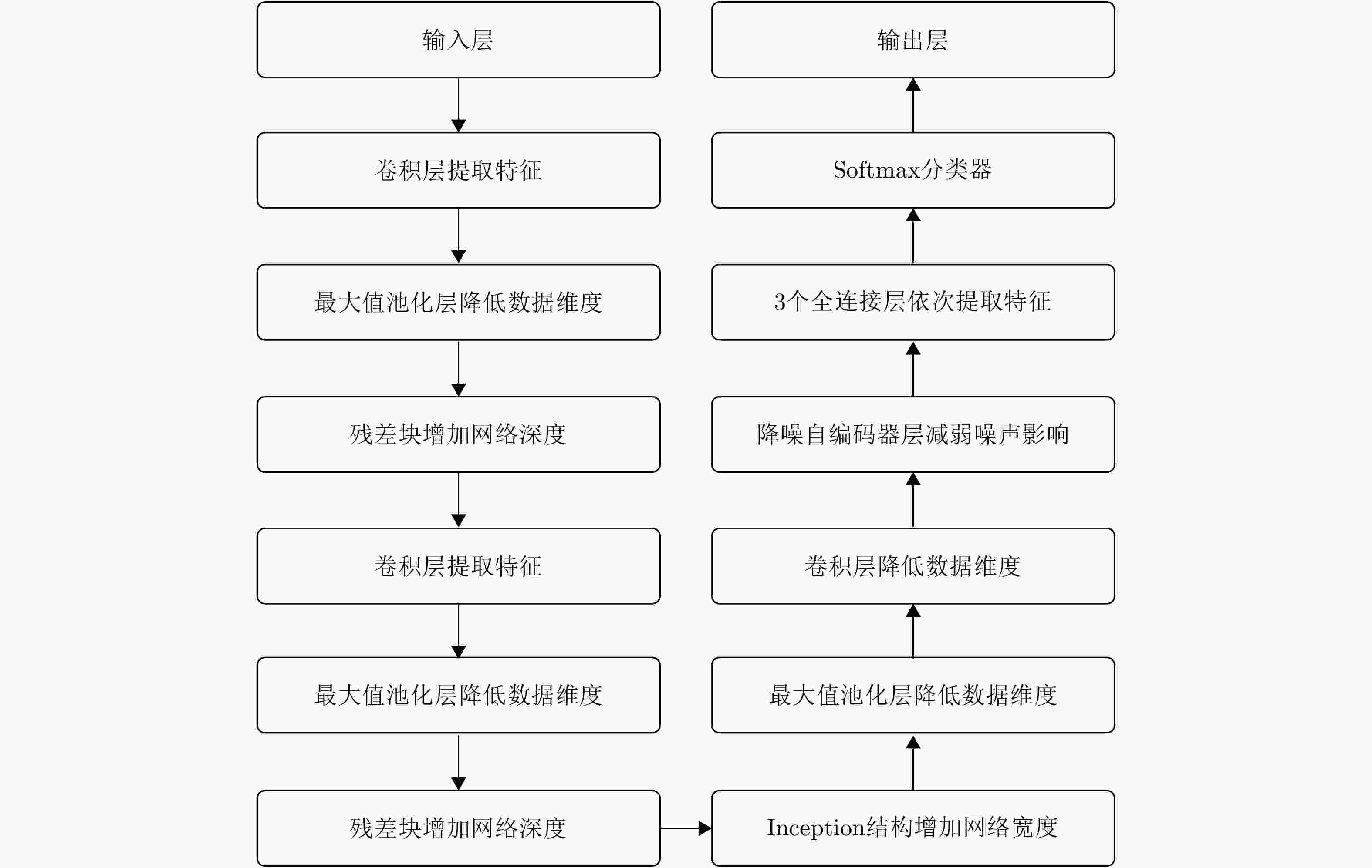
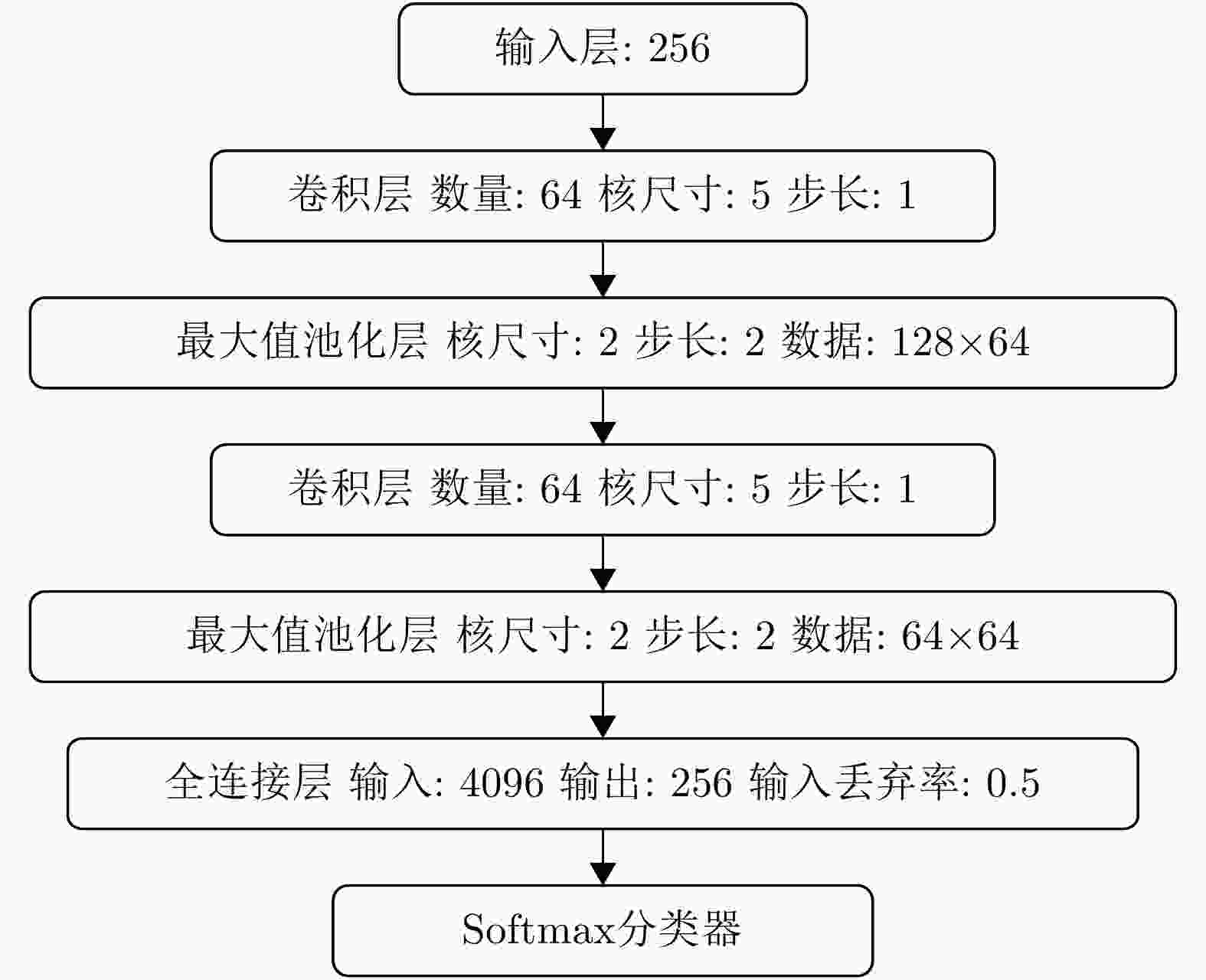
摘要: 随着深度学习技术被应用于雷达目标识别领域,其自动提取目标特征的特性大大提高了识别的准确率和鲁棒性,但噪声环境下的鲁棒性有待进一步研究。该文提出了一种在噪声环境下基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的雷达高分辨率距离像(HRRP)数据识别方法,通过增强训练集和使用残差块、inception结构和降噪自编码层增强网络结构,实现了在较宽信噪比范围下的较高识别率,其中在信噪比为0 dB的瑞利噪声条件下,识别率达到96.14%,并分析了网络结构和噪声类型对结果的影响。Abstract: With the application of deep learning technology in the radar target recognition field, the automatic extraction of the target feature greatly improves the accuracy and robustness of the recognition, but its robustness in noisy environments needs to be further investigated. This paper proposes a robust target recognition method for radar High Resolution Range Profile (HRRP) data based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). By enhancing training set and using the residual block, inception structure, and denoising sparse autoencoder layer to enhance the network structure, a higher recognition rate is achieved in a wider SNR range, under the condition of 0 dB Rayleigh noise, the recognition rate reaches 96.14%, and the influence of the network structure and noise type on results is analyzed.
-
表 1 飞机参数(m)
Table 1. Parameters of planes (m)
机型 机长 机高 机宽 安26 23.80 9.83 29.20 奖状 14.40 4.57 15.90 雅克42 36.38 9.83 34.88 表 2 训练集加入瑞利噪声结果
Table 2. Recognition results based on Rayleigh noise training set
信噪比(dB) –5 –3 0 3 5 10 15 20 测试集未加入噪声 图6改进CNN 平均识别率 91.14 93.98 96.14 97.37 97.71 98.58 99.24 99.53 99.81 安26识别率 88.83 92.97 96.47 97.80 98.50 98.93 99.13 99.40 99.90 奖状识别率 92.13 95.43 97.93 99.20 99.53 99.63 99.77 99.90 99.97 雅克42识别率 92.47 93.53 94.03 95.10 95.10 97.17 98.83 99.30 99.57 图6改进CNN
(训练集中未加噪声)平均识别率 51.51 57.89 63.41 65.14 65.72 66.40 66.58 66.68 99.81 安26识别率 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.03 99.47 奖状识别率 99.80 99.83 99.77 99.87 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 99.97 雅克42识别率 54.77 73.83 90.47 95.57 97.17 99.20 99.73 100.00 100.00 图9的CNN 平均识别率 85.30 90.43 94.90 96.66 97.30 98.19 98.36 98.44 99.63 安26识别率 72.13 79.27 86.53 90.57 92.10 94.73 95.20 95.47 99.97 奖状识别率 83.90 92.17 98.23 99.50 99.83 99.90 99.93 99.93 99.67 雅克42识别率 99.87 99.87 99.93 99.90 99.97 99.93 99.93 99.93 99.27 图9的CNN
(训练集中未加噪声)平均识别率 33.86 34.50 38.12 51.82 61.32 66.62 66.70 68.20 99.97 安26识别率 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.10 4.60 99.90 奖状识别率 1.57 3.50 14.37 55.47 83.97 99.87 100.00 100.00 100.00 雅克42识别率 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 表 3 训练集加入高斯白噪声结果
Table 3. Recognition results based on White Gaussian noise training set
信噪比(dB) –5 –3 0 3 5 10 15 20 测试集未加入噪声 图6改进CNN 平均识别率 85.99 91.61 96.04 98.07 99.00 99.68 99.88 99.94 99.94 安26识别率 86.63 90.20 94.00 96.30 98.07 99.30 99.70 99.83 99.87 奖状识别率 83.27 92.77 97.00 99.23 99.60 99.90 100.00 100.00 100.00 雅克42识别率 88.07 91.87 97.13 98.67 99.33 99.83 99.93 100.00 99.97 图6改进CNN
(训练集中未加噪声)平均识别率 55.93 58.89 63.91 69.10 70.94 75.49 82.73 93.01 99.90 安26识别率 12.00 13.47 15.17 20.37 21.33 29.63 49.43 79.40 99.83 奖状识别率 82.20 84.57 90.57 95.57 97.63 99.63 99.97 100.00 100.00 雅克42识别率 73.60 78.63 86.00 91.37 93.87 97.20 98.80 99.63 99.87 图9的CNN 平均识别率 80.61 87.23 93.74 96.59 97.59 98.87 99.08 99.21 99.19 安26识别率 71.37 78.50 86.77 91.73 93.90 96.87 97.63 97.80 97.73 奖状识别率 80.67 89.53 97.07 99.20 99.43 99.87 99.77 99.93 99.93 雅克42识别率 89.80 93.67 97.40 98.83 99.43 99.87 99.83 99.90 99.90 图9的CNN
(训练集中未加噪声)平均识别率 39.92 42.74 47.09 53.90 59.90 73.09 86.69 97.47 99.98 安26识别率 0.57 0.83 1.77 3.37 5.30 22.20 60.27 92.47 99.97 奖状识别率 21.73 28.90 40.33 58.83 74.63 97.10 99.83 99.97 100.0 雅克42识别率 97.47 98.50 99.17 99.50 99.77 99.97 99.97 99.97 99.97 表 4 不同噪声类型识别结果
Table 4. Recognition results based on different noise types
信噪比(dB) –5 –3 0 3 5 10 15 20 测试集未加入噪声 方案1 平均识别率 76.73 82.21 88.31 92.12 93.41 96.23 97.97 99.06 99.79 安26识别率 76.47 80.53 83.90 85.90 86.30 90.90 94.53 97.40 99.57 奖状识别率 73.37 78.43 87.10 92.67 95.37 98.23 99.47 99.80 99.80 雅克42识别率 80.37 87.67 93.93 97.80 98.57 99.57 99.90 99.97 100.00 方案2 平均识别率 81.68 87.18 92.53 94.93 95.52 96.70 96.94 97.08 97.18 安26识别率 63.63 72.97 82.20 87.23 88.50 91.03 91.57 91.87 92.13 奖状识别率 81.60 88.77 95.50 97.77 98.30 99.27 99.50 99.60 99.63 雅克42识别率 99.80 99.80 99.90 99.80 99.77 99.80 99.77 99.77 99.77 表 5 删除结构加入噪声结果
Table 5. Recognition results based on deleted structure
信噪比(dB) –5 –3 0 3 5 10 15 20 测试集未加入噪声 图6改进CNN 平均识别率 79.98 86.83 93.11 96.18 97.11 98.59 98.72 98.99 99.03 安26识别率 73.50 82.03 89.60 94.33 94.97 97.10 97.30 97.70 97.80 奖状识别率 81.90 89.50 96.63 98.77 99.50 99.77 99.90 99.90 99.87 雅克42识别率 84.53 88.97 93.10 95.43 96.87 98.90 98.97 99.37 99.43 删除第1个残差块 平均识别率 79.59 84.82 90.76 93.66 94.36 95.68 95.88 96.09 96.04 安26识别率 68.97 74.70 80.67 84.67 85.97 88.23 88.63 89.00 89.07 奖状识别率 82.50 88.43 96.80 98.83 99.50 99.73 99.83 99.83 99.83 雅克42识别率 87.30 91.33 94.80 97.47 97.60 99.07 99.17 99.43 99.23 删除第2个残差块 平均识别率 79.06 85.53 91.51 94.44 95.41 96.78 96.88 97.11 97.12 安26识别率 65.93 73.77 92.80 88.03 89.63 92.30 92.63 92.90 93.07 奖状识别率 94.60 91.00 96.27 98.47 99.20 99.50 99.50 99.63 99.57 雅克42识别率 86.63 91.27 95.57 96.93 97.40 98.53 98.50 98.80 98.73 删除第1, 2个残差块 平均识别率 74.51 82.38 89.67 92.31 93.21 93.93 94.28 94.54 94.44 安26识别率 58.33 69.17 78.00 81.87 83.13 84.60 85.57 86.27 85.93 奖状识别率 68.50 80.40 92.97 96.60 97.93 98.33 98.53 98.57 98.57 雅克42识别率 96.70 97.57 98.03 98.47 98.57 98.87 98.73 98.80 98.83 删除inception模块 平均识别率 78.08 84.42 90.10 92.81 93.71 95.14 95.26 95.48 95.58 安26识别率 73.73 79.13 85.17 88.37 89.13 90.97 91.03 91.30 91.30 奖状识别率 82.67 88.97 95.53 97.53 98.43 99.20 99.23 99.27 99.27 雅克42识别率 80.83 85.17 89.60 92.53 93.57 95.27 95.50 95.87 96.17 删除降噪自编码器层 平均识别率 78.59 83.60 90.00 93.62 94.83 96.32 96.99 97.40 97.33 安26识别率 71.97 76.90 83.63 88.80 90.37 92.30 93.33 93.73 93.53 奖状识别率 77.73 83.07 91.20 94.67 96.33 97.70 98.63 99.07 99.17 雅克42识别率 86.07 90.83 95.17 97.40 97.80 98.97 99.00 99.40 99.30 -
[1] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040 [2] LUNDÉN J and KOIVUNEN V. Deep learning for HRRP-based target recognition in multistatic radar systems[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/radar.2016.7485271. [3] 盖晴晴, 韩玉兵, 南华, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的极化雷达目标识别[J]. 电波科学学报, 2018, 33(5): 575–582. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2017112101GAI Qingqing, HAN Yubing, NAN Hua, et al. Polarimetric radar target recognition based on depth convolution neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2018, 33(5): 575–582. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2017112101 [4] JITHESH V, SAGAYARAJ M J, and SRINIVASA K G. LSTM recurrent neural networks for high resolution range profile based radar target classification[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology, Ghaziabad, India, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ciact.2017.7977298. [5] 徐彬, 陈渤, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于注意循环神经网络模型的雷达高分辨率距离像目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 2988–2995. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161034XU Bin, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Attention-based recurrent neural network model for radar high-resolution range profile target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 2988–2995. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161034 [6] 徐彬, 陈渤, 刘家麒, 等. 采用双向LSTM模型的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(2): 29–34.XU Bin, CHEN Bo, LIU Jiaqi, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition by the bidirectional LSTM model[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(2): 29–34. [7] 刘家麒, 陈渤, 介茜. 基于注意力机制和双向GRU模型的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 589–597. doi: 10.12000/JR19014LIU Jiaqi, CHEN Bo, and JIE Xi. Radar high-resolution range profile target recognition based on attention mechanism and bidirectional gated recurrent[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 589–597. doi: 10.12000/JR19014 [8] 赵飞翔, 刘永祥, 霍凯. 基于栈式降噪稀疏自动编码器的雷达目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 149–156. doi: 10.12000/JR16151ZHAO Feixiang, LIU Yongxiang, and HUO Kai. Radar target recognition based on stacked denoising sparse autoencoder[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 149–156. doi: 10.12000/JR16151 [9] 张欢. 基于射频隐身的机载雷达系统软件实现及HRRP目标识别研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2016.ZHANG Huan. RF stealth based airborne radar system simulation and HRRP target recognition research[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016. [10] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A, 赵申剑, 黎彧君, 符天凡, 等译. 深度学习[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017: 199–226.GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A, ZHAO Shenjian, LI Yujun, FU Tianfan, et al. translation. Deep Learning[M]. Beijing: Posts and Telecommunications Press. [11] HINTON G E, SRIVASTAVA N, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors[J]. arXiv:1207.0580, 2012. [12] NIELSEN M A. Neural Networks and Deep Learning[M]. San Francisco, USA: Determination Press, 2015. [13] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [14] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [15] XING Chen, MA Li, and YANG Xiaoquan. Stacked denoise autoencoder based feature extraction and classification for hyperspectral images[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2016, 2016: 3632943. [16] DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, WANG Penghui, et al. Noise robust radar HRRP target recognition based on multitask factor analysis with small training data size[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3546–3559. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2012.2191965 [17] RICHARDS M A, 邢孟道, 王彤, 李真芳, 等译. 雷达信号处理基础[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017: 64–67.RICHARDS M A, XING Mengdao, WANG Tong, LI Zhenfang, et al. translation. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017: 64–67. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: