Non-line-of-sight Target Relocation by Multipath Model in SAR 3D Urban Area Imaging
-
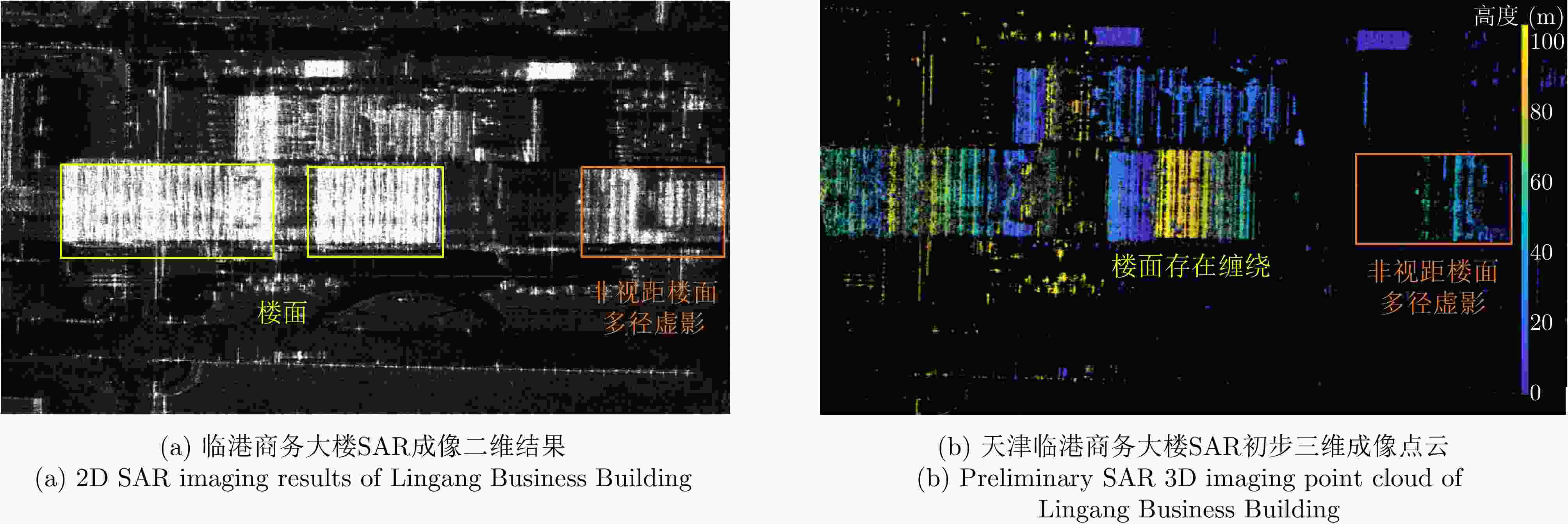
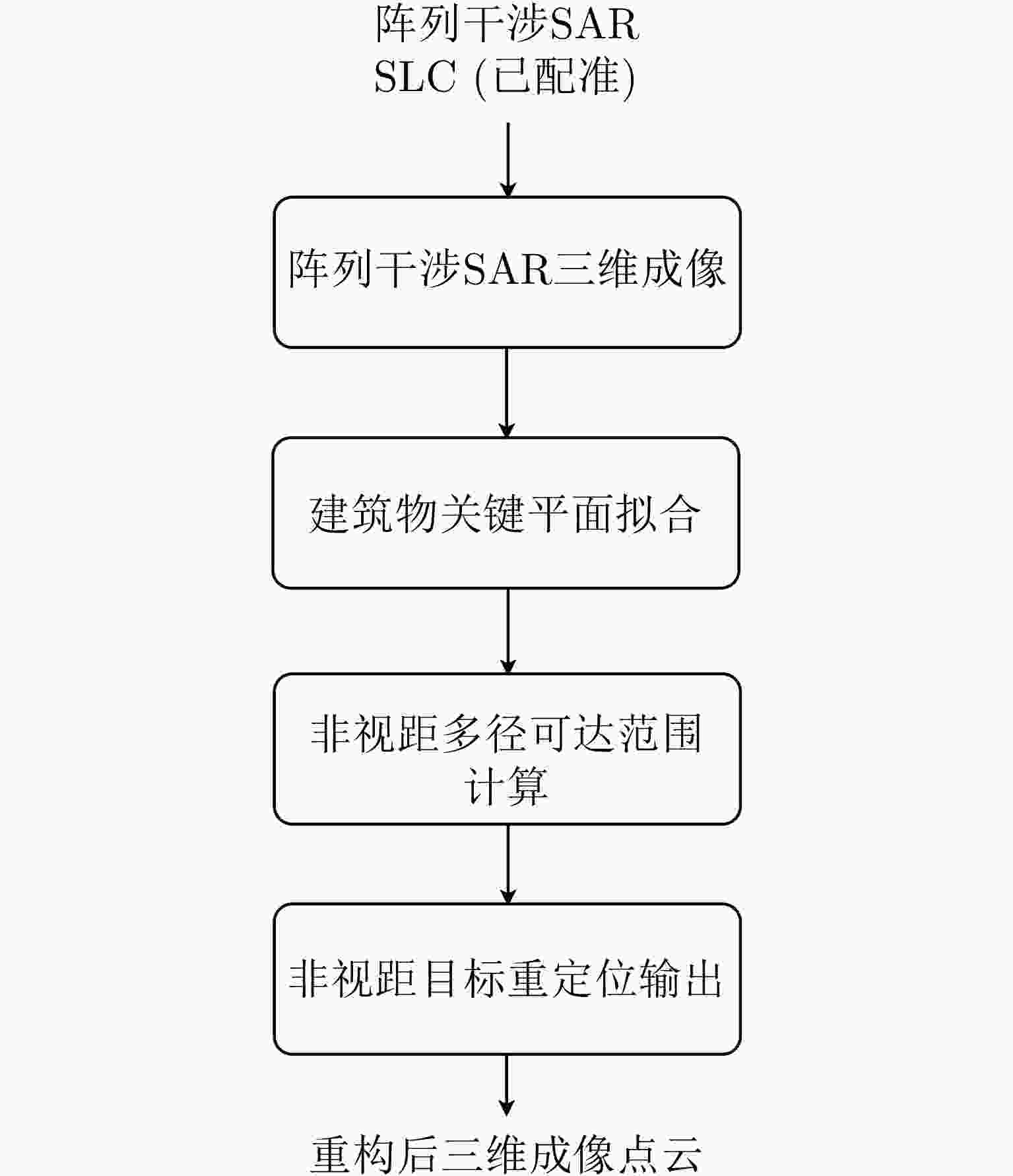
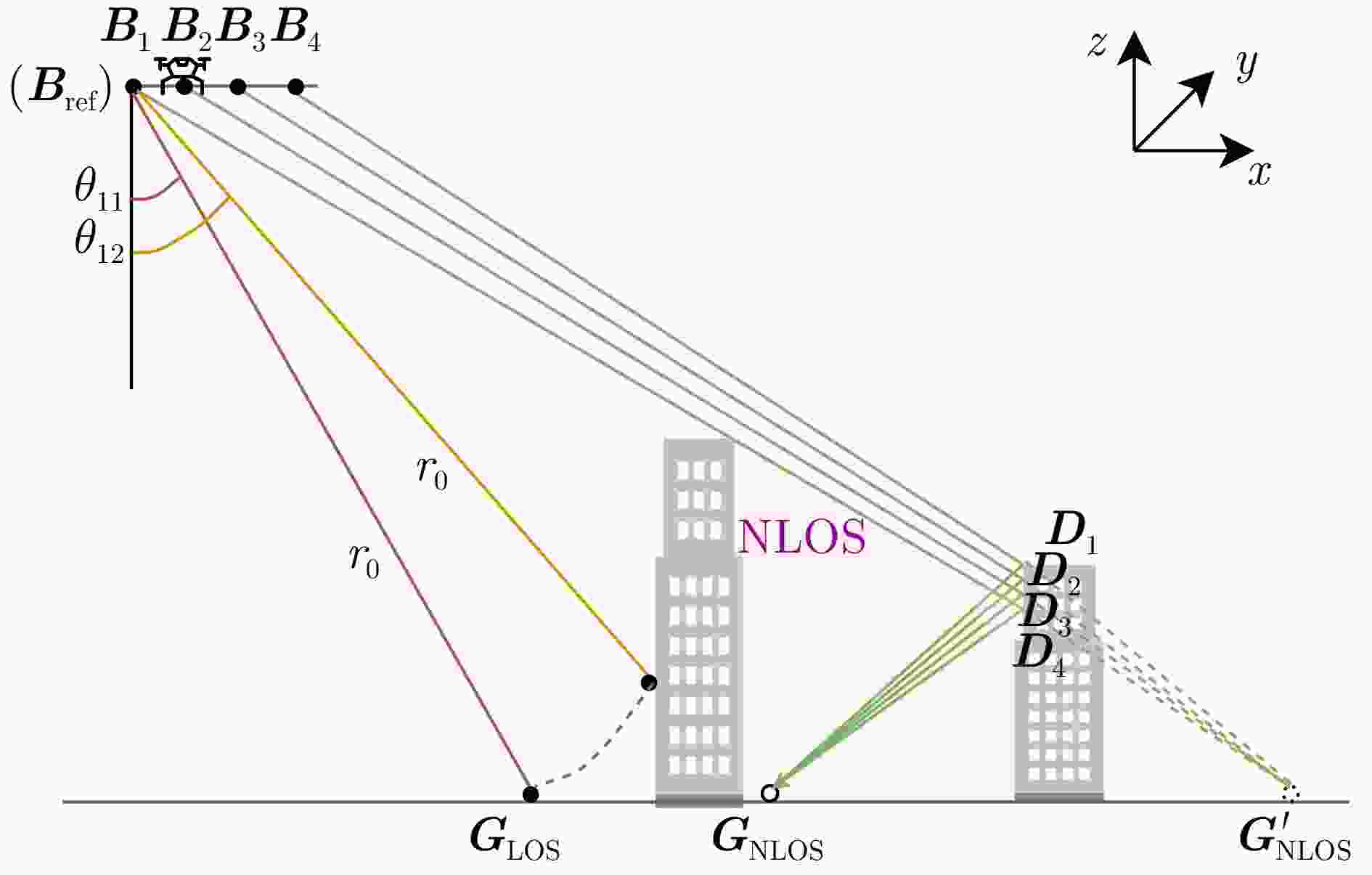
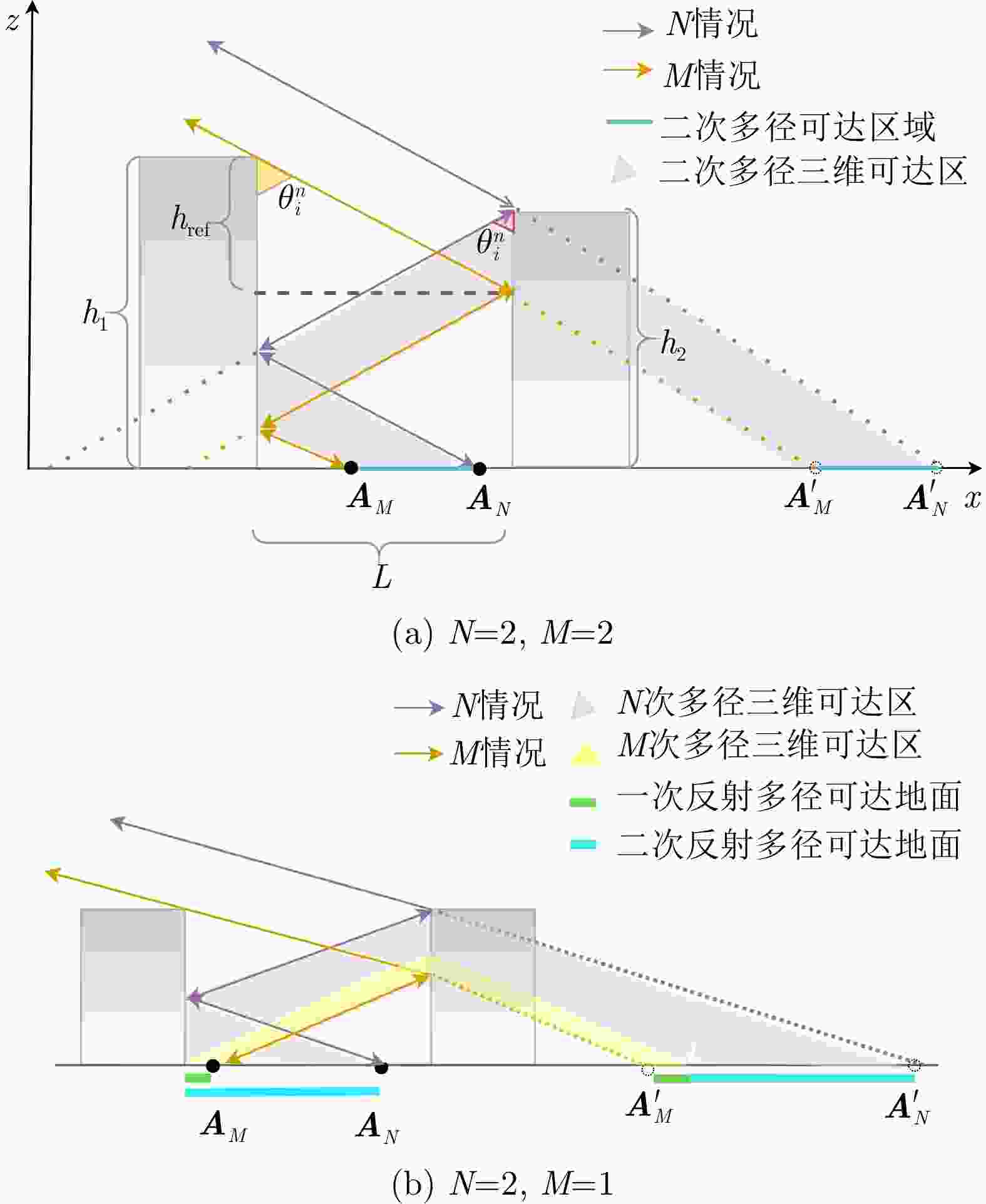
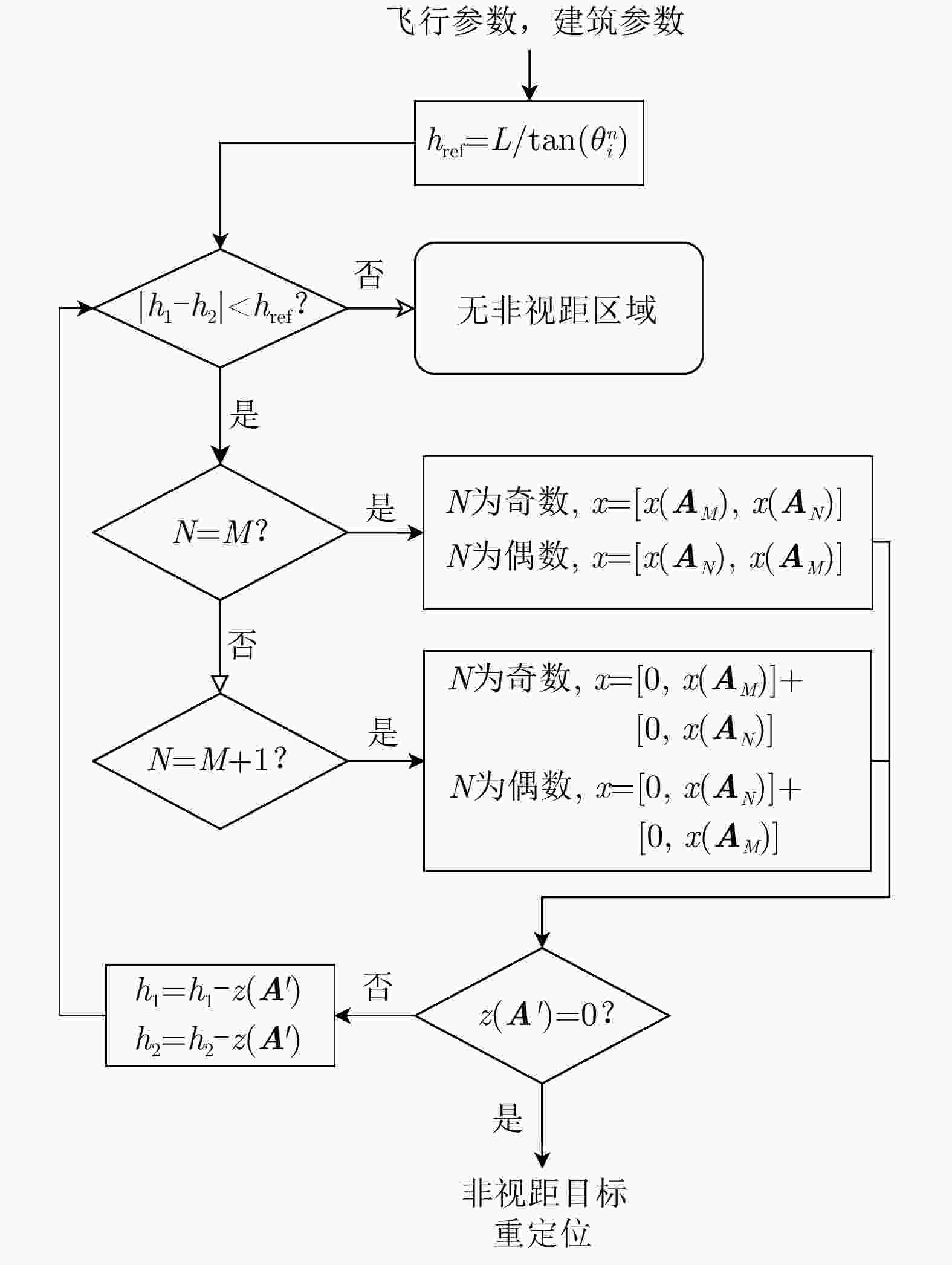
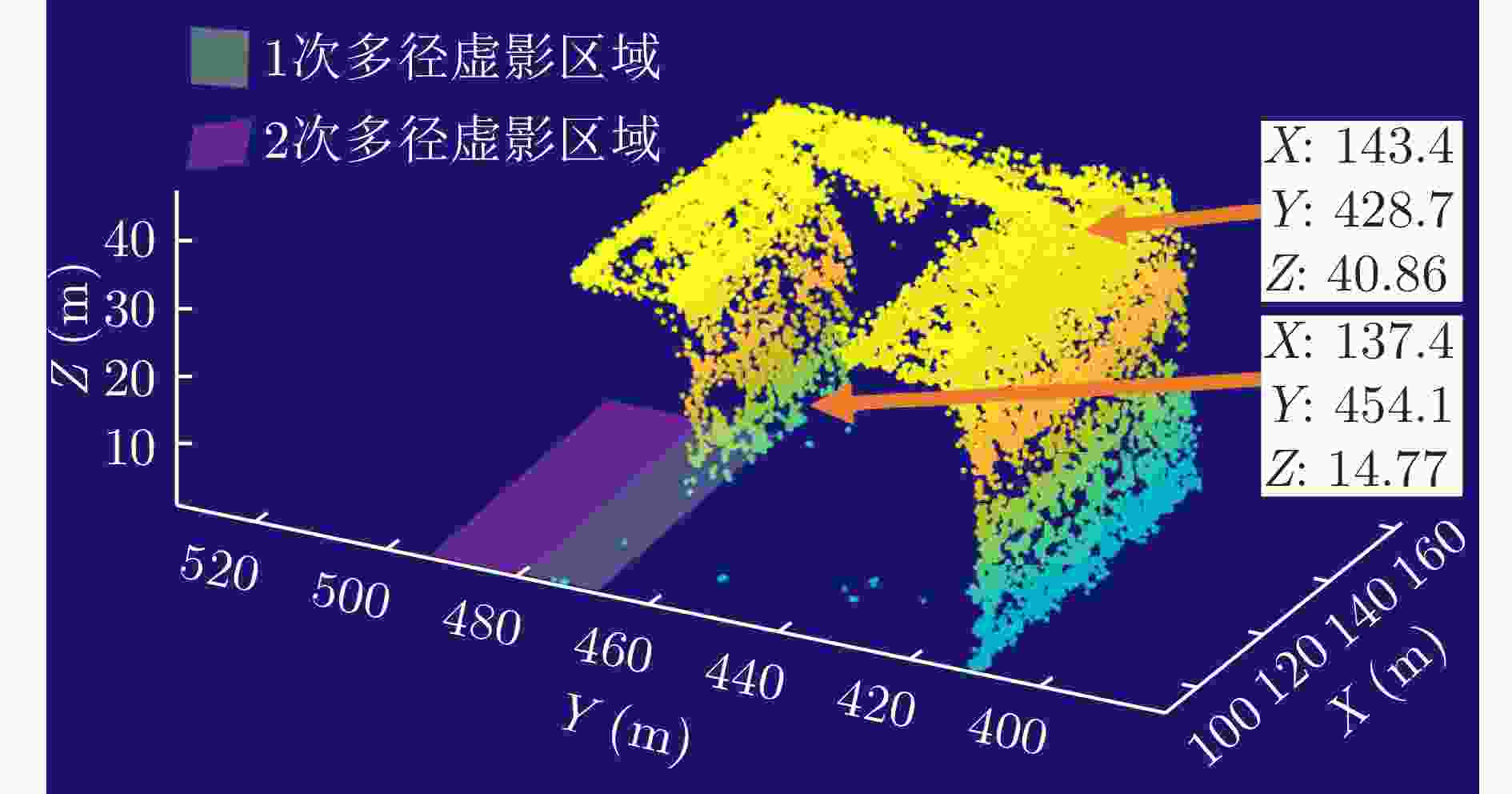
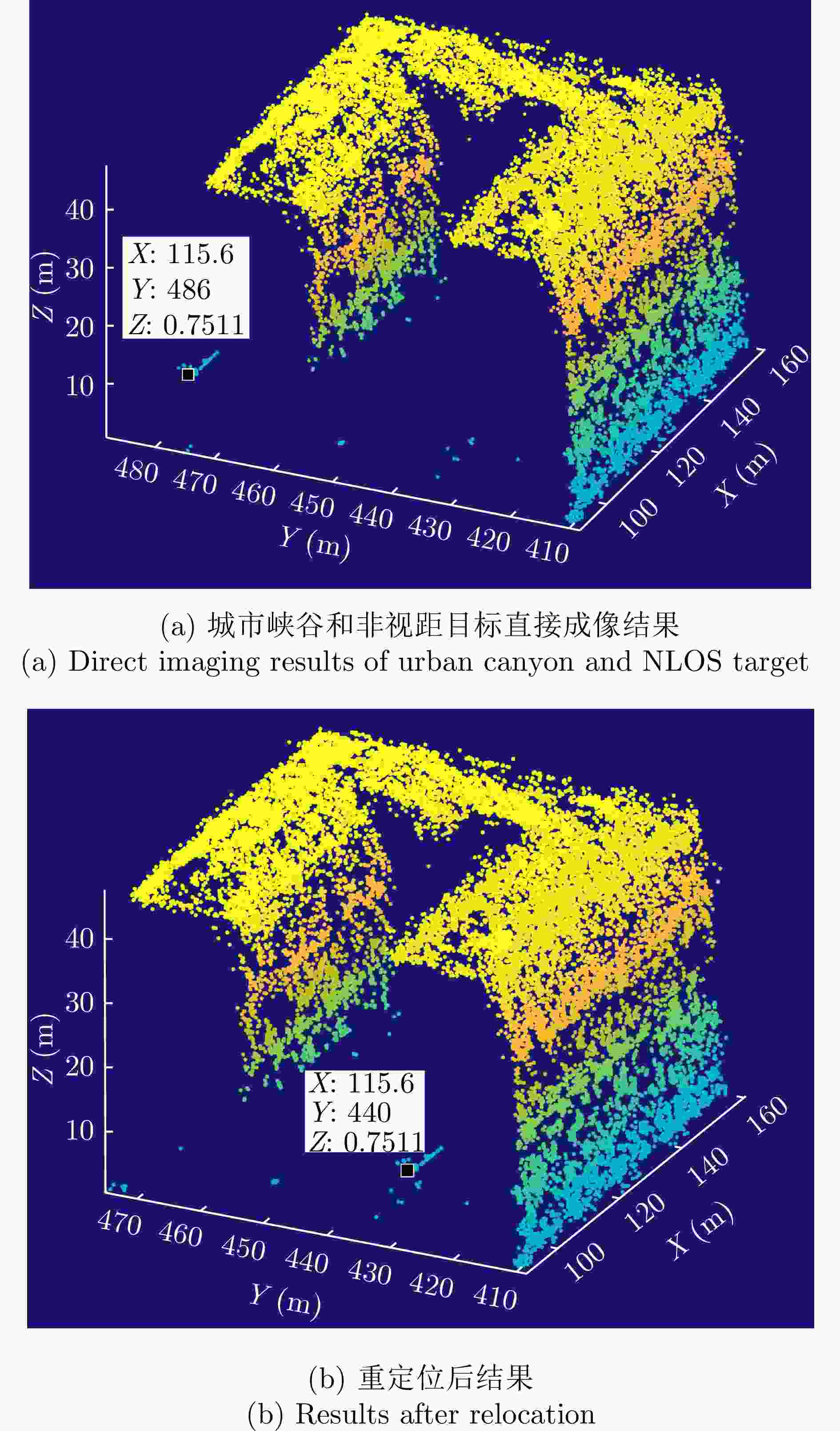
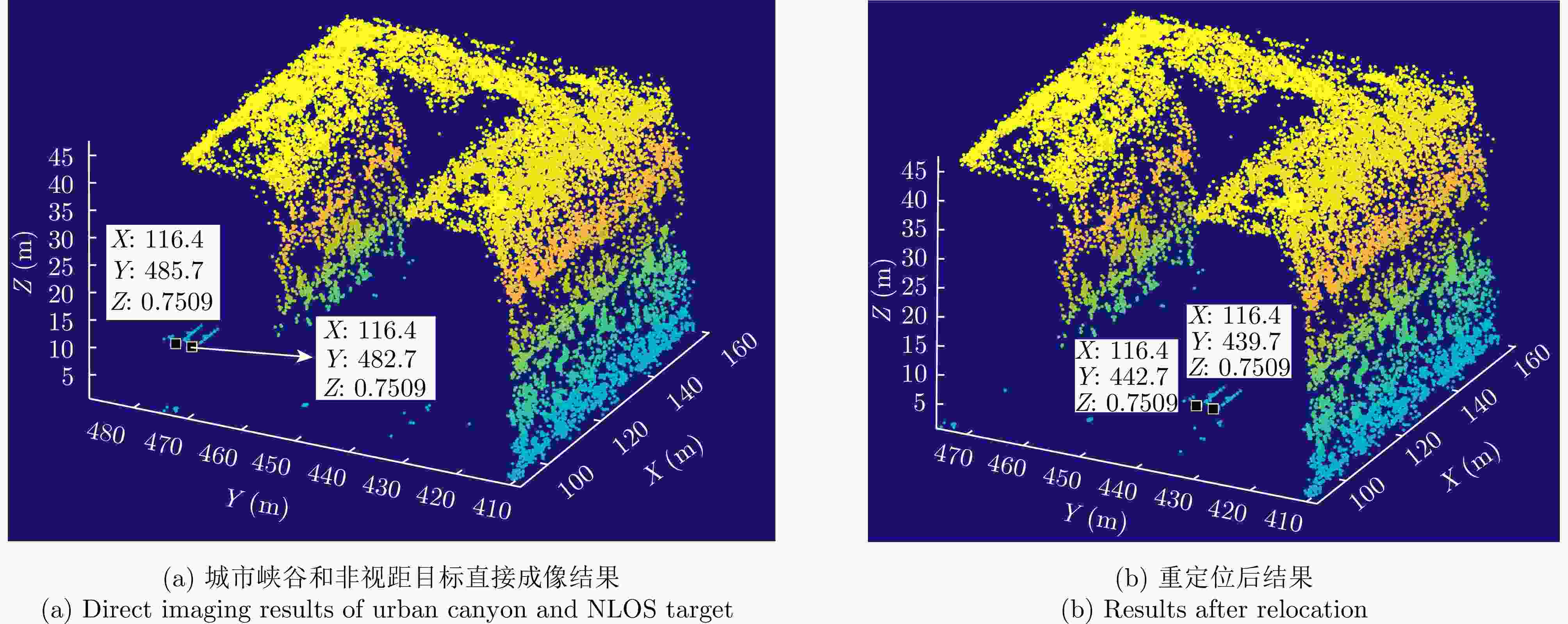
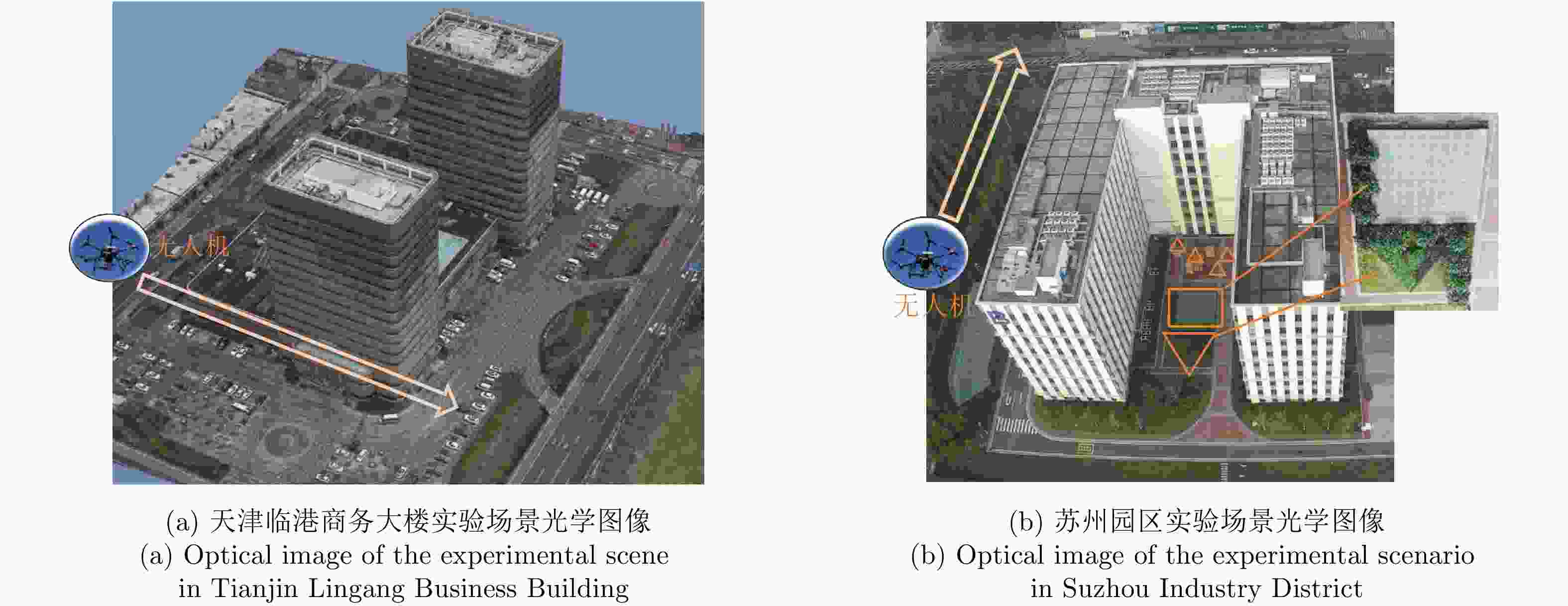
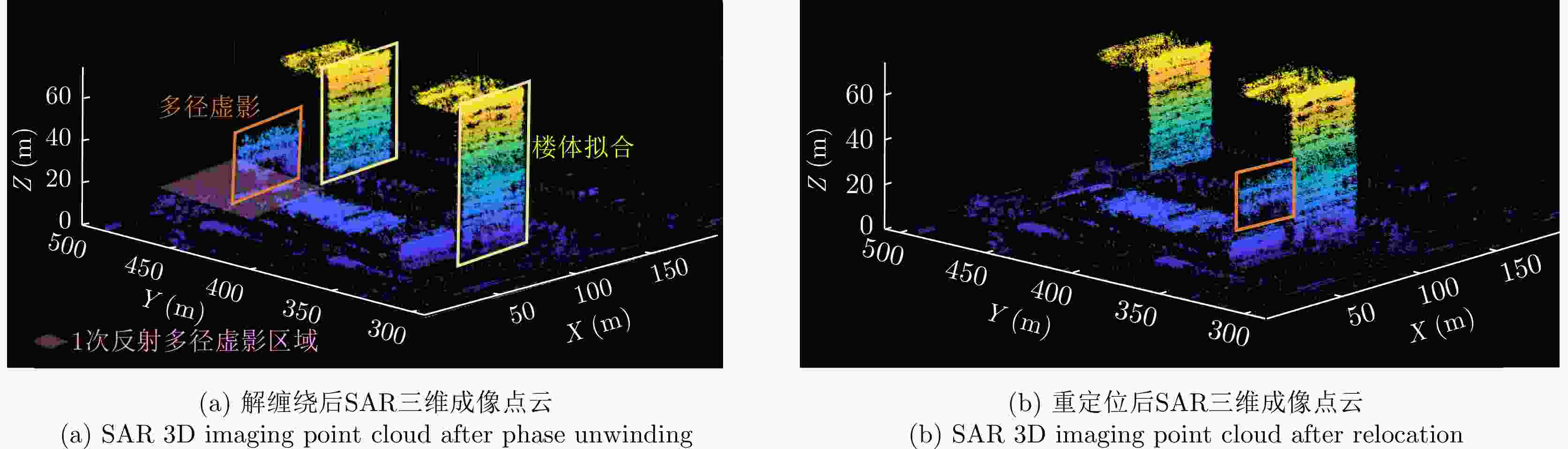
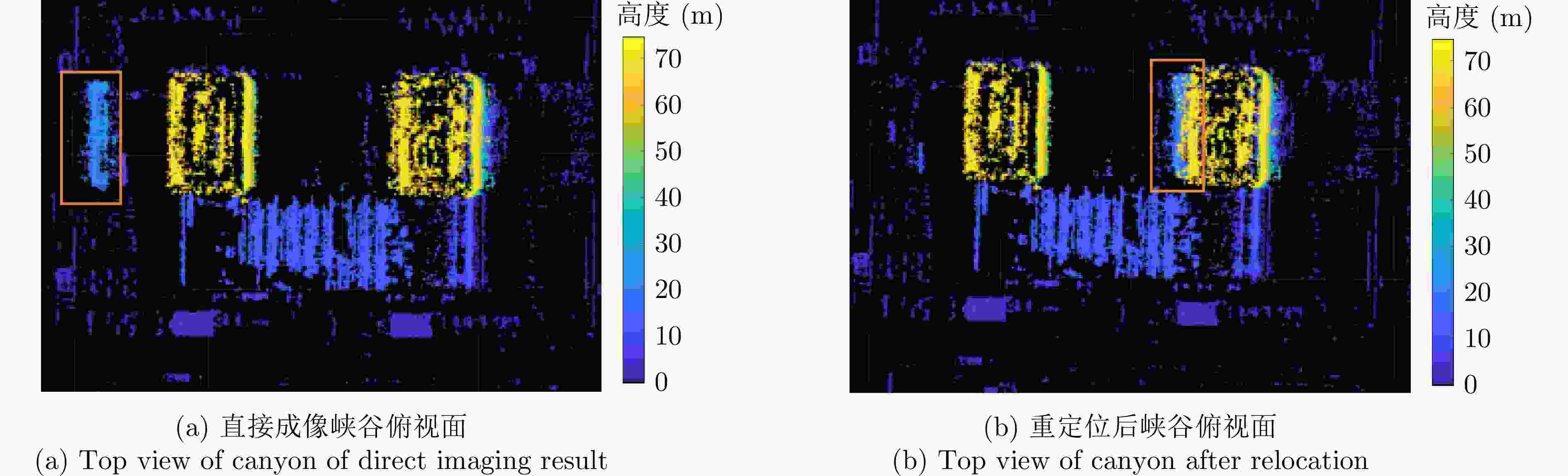
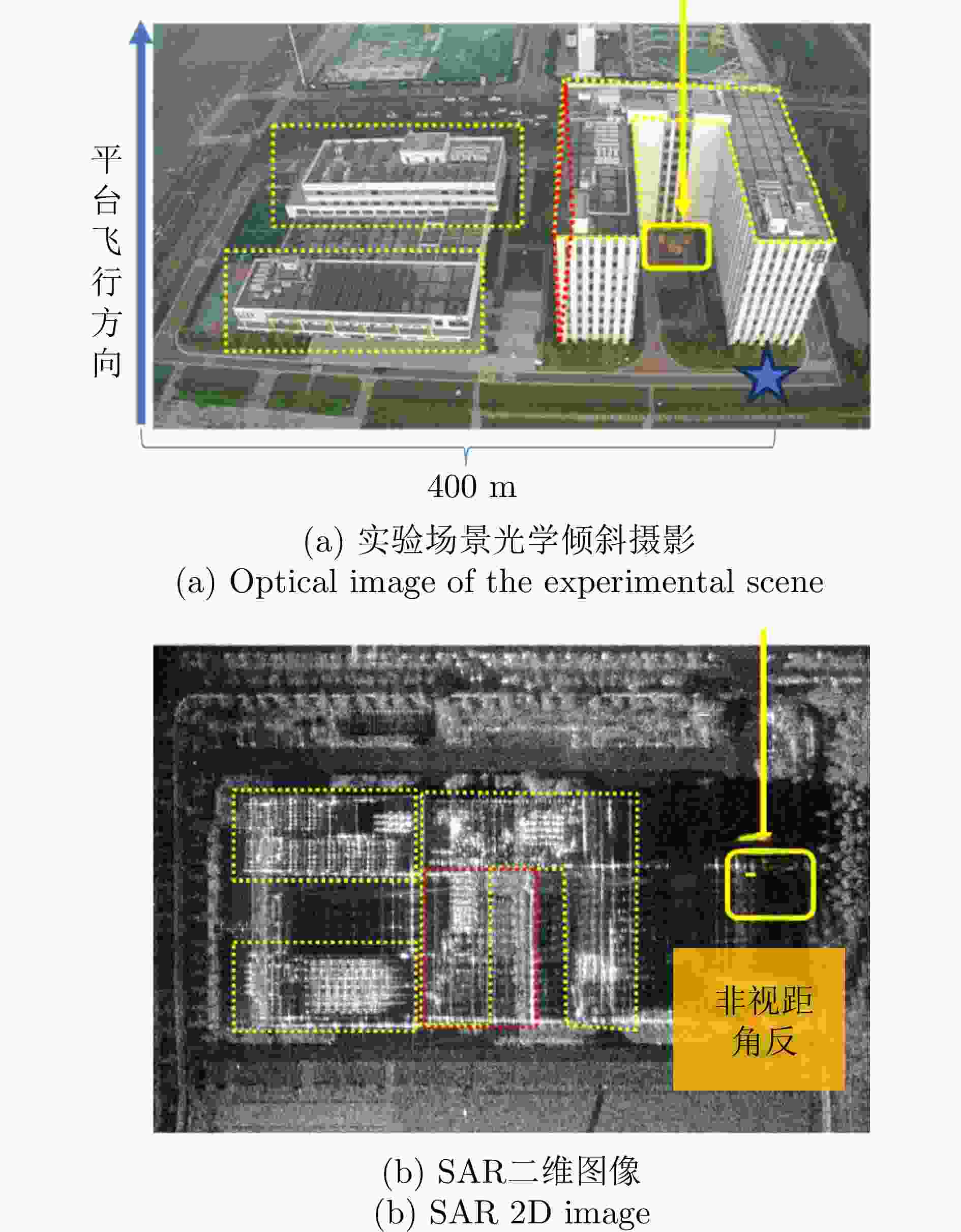
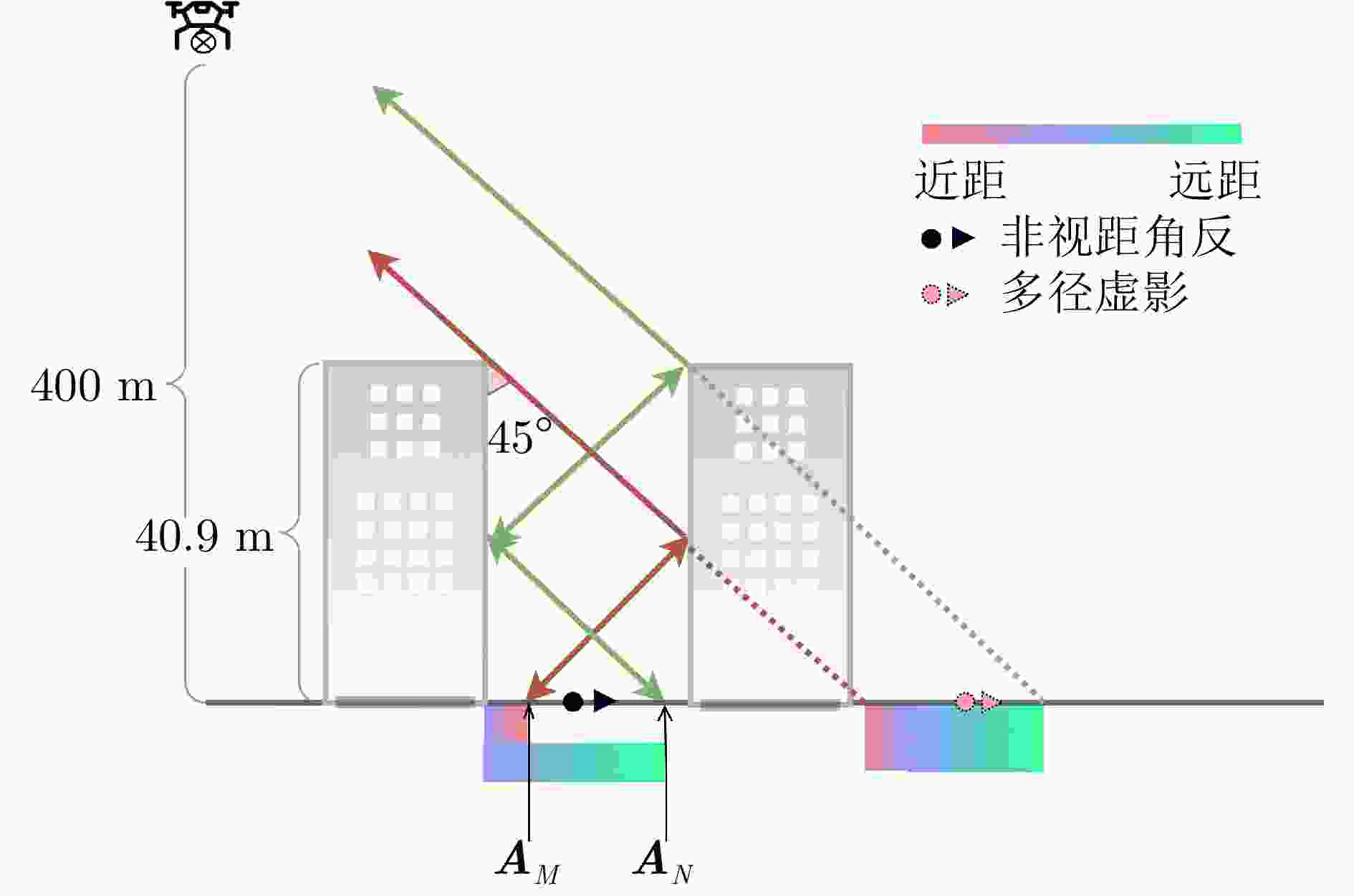
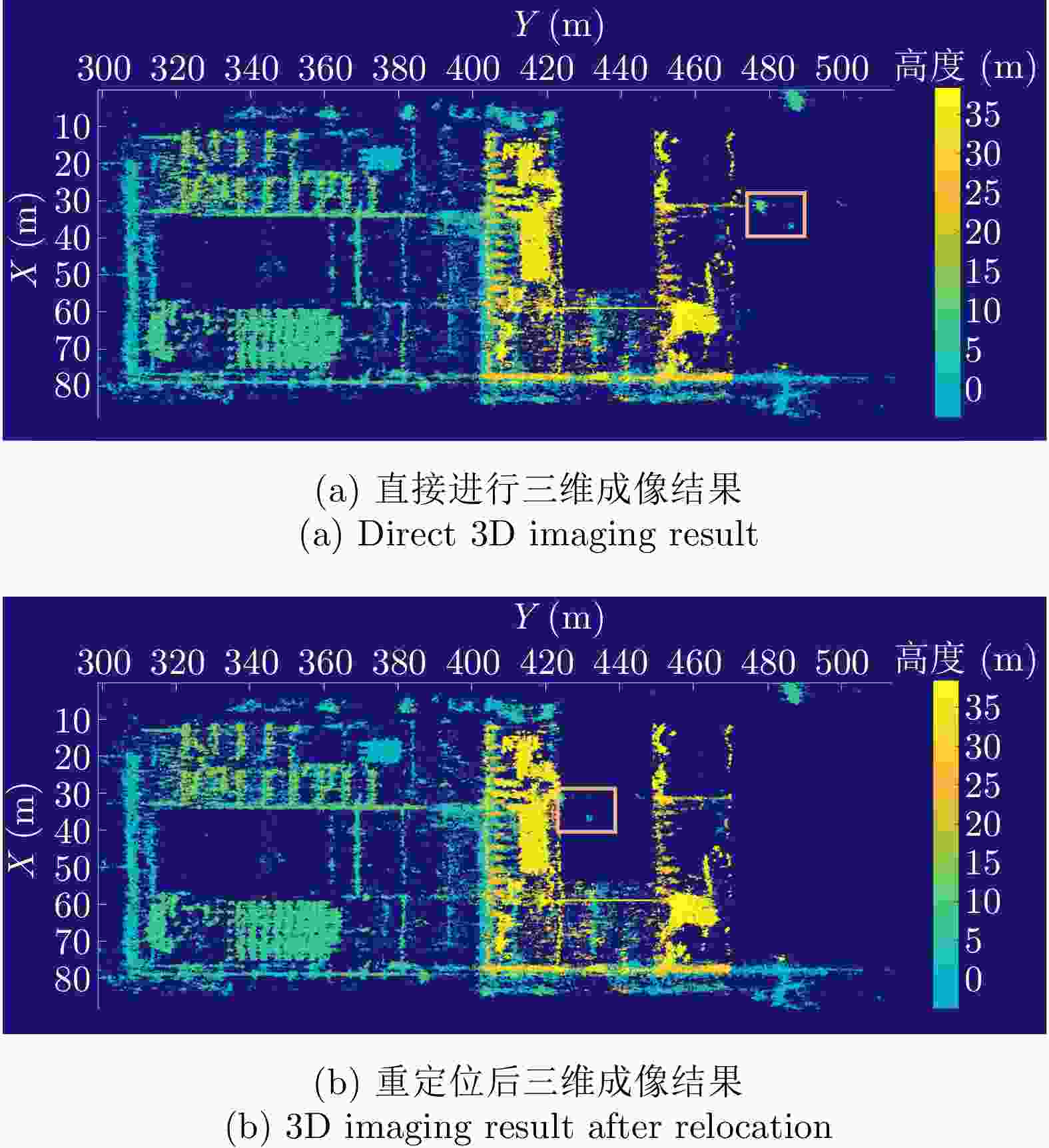
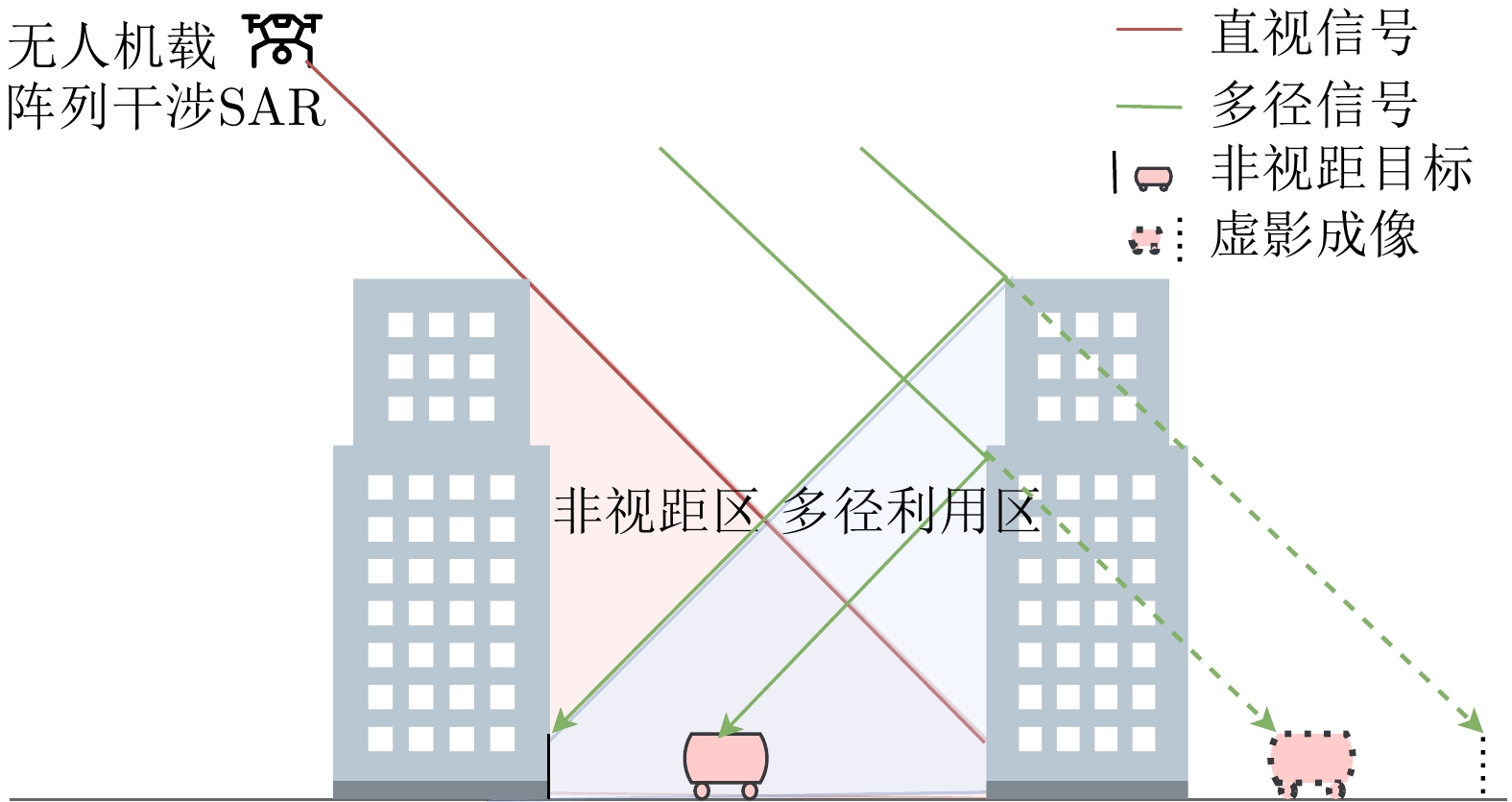
摘要: 随着合成孔径雷达(SAR)系统小型化技术、SAR三维成像技术的发展,当前已可利用无人机载小型化阵列干涉SAR实现城区三维成像,在城市测绘、复杂环境重建等领域具有重要应用前景。然而,SAR进行城市场景三维成像时,回波中存在多径信号,会导致成像结果解译困难,却也给非视距区域隐蔽目标的发现提供了重要手段。为此,该文针对低空无人机载阵列干涉SAR建筑区三维成像中的非视距目标进行了研究,建立了非视距目标在低空阵列干涉三维成像下的多径模型,给出了城市峡谷区域利用多径扩大可视范围的计算方法,并基于建筑平面拟合提出了非视距目标重定位方法。无人机载阵列干涉SAR的仿真和实际数据处理验证表明,所提出的方法可以对城市峡谷非视距目标进行有效的三维成像和重定位,重定位误差小于0.5 m,实现了对非视距区域信息的获取。Abstract: The advancement in the miniaturization technology of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems and SAR three-dimensional (3D) imaging has enabled the 3D imaging of urban areas through Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-borne array Interferometric SAR (array-InSAR), offering significant utility in urban cartography, complex environment reconstruction, and related domains. Despite the challenges posed by multipath signals in urban scene imaging, these signals serve as a crucial asset for imaging hidden targets in Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) areas. Hence, this paper studies NLOS targets in UAV-borne array-InSAR 3D imaging at low altitudes and establishes a multipath model for 3D imaging at low altitudes. Then, a calculation method is proposed for obtaining the multipath reachable range in urban canyon areas based on building plane fitting. Finally, a relocation method for NLOS targets is presented. The simulation and real data experiments of UAV-borne array-InSAR show that the proposed method can effectively obtain 3D images and relocate NLOS targets in urban canyon areas, with errors typically below 0.5 m, which realizes the acquisition of hidden NLOS region information.
-
Key words:
- Array-InSAR /
- 3D imaging /
- Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) /
- Multipath /
- UAV-borne SAR
-
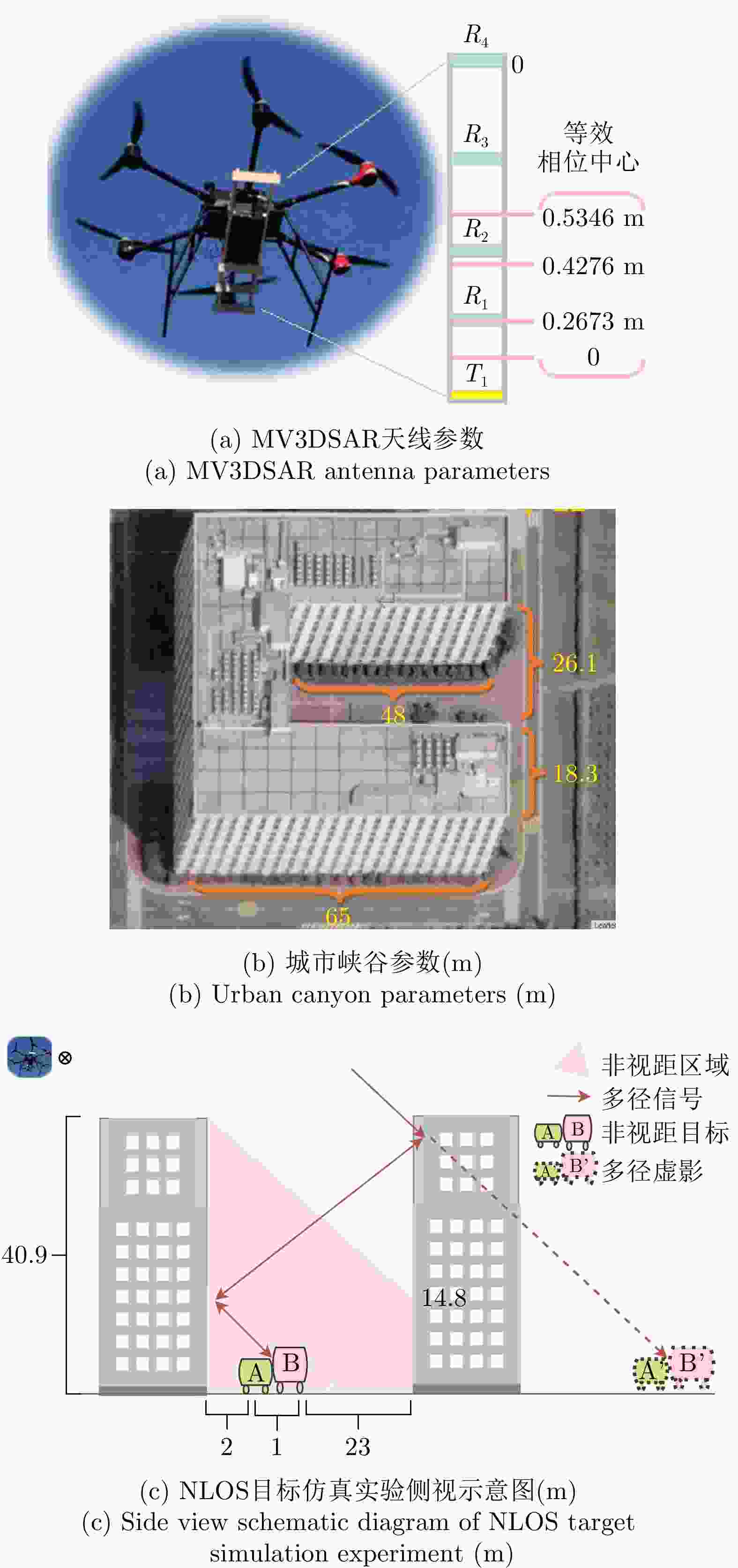
表 1 MV3DSAR实验参数(Ku波段)
Table 1. Parameters of the MV3DSAR experiment (Ku-band)
参数 指标 中心频率 15.2 GHz 信号形式 调频连续波(FMCW) 极化方式 全极化 信号带宽 1200 MHz天线尺寸(单通道) 0.05 m(俯仰)×0.32 m(方位) 分辨率 优于0.2 m×0.2 m 中心视角 45° 表 2 平面拟合和成像位置误差分析(m)
Table 2. Plane fitting and imaging position error analysis (m)
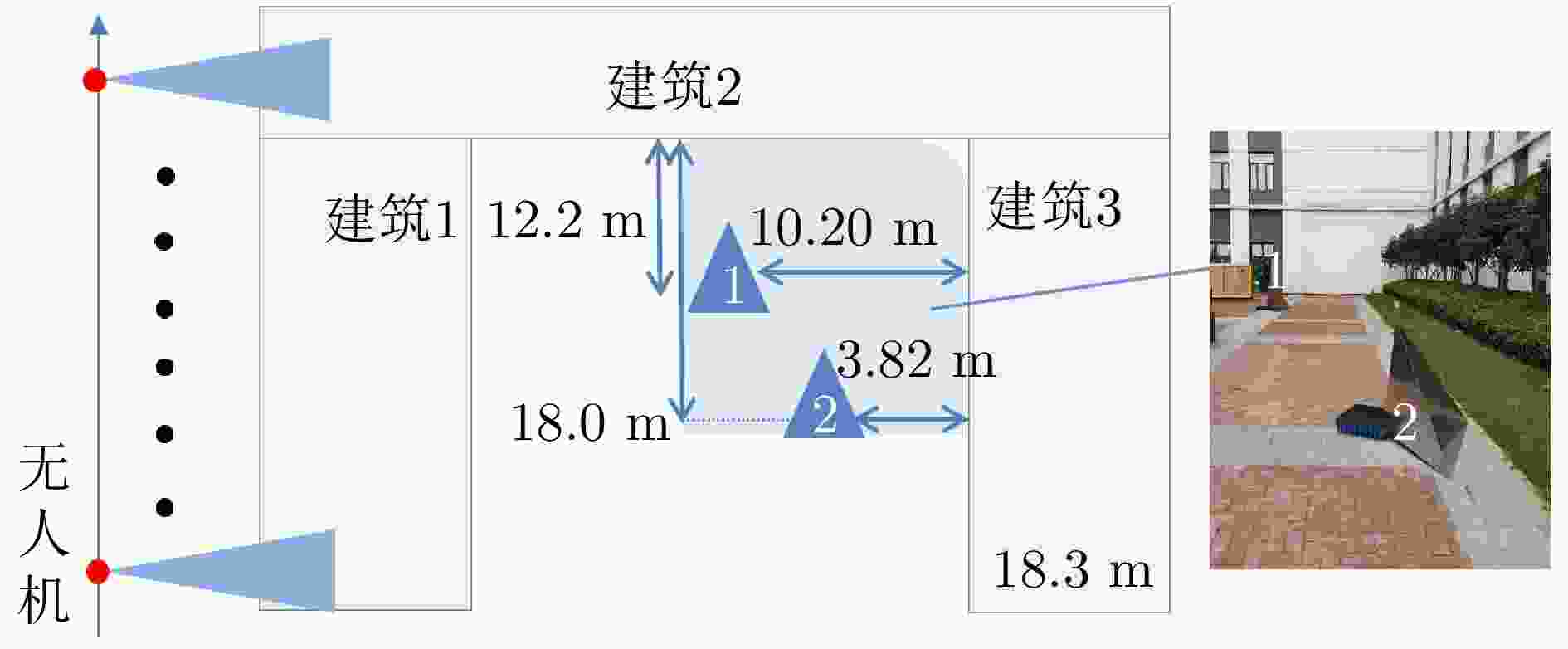
分析对象 ME RMSE 楼面拟合 5.87E–13 0.6982 峡谷长度拟合 0.3328 / 非视距角反1 0.43 0.4201 非视距角反2 0.41 -
[1] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. [2] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027.QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027. [3] 孔令讲, 郭世盛, 陈家辉, 等. 多径利用雷达目标探测技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(1): 23–45. doi: 10.12000/JR23134.KONG Lingjiang, GUO Shisheng, CHEN Jiahui, et al. Overview and prospects of multipath exploitation radar target detection technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 23–45. doi: 10.12000/JR23134. [4] LI Zhixing, JIANG Fan, WYMEERSCH H, et al. An iterative 5G positioning and synchronization algorithm in NLOS environments with multi-bounce paths[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(5): 804–808. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3244575. [5] PRICE R and GREEN P. A communication technique for multipath channels[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1958, 46(3): 555–570. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1958.286870. [6] SILVA C F, FERLIN S, ALAY O, et al. IoT traffic offloading with multiPath TCP[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(4): 51–57. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000915. [7] SAYEED A M and SIVANADYAN T. Wireless Communication and Sensing in Multipath Environments Using Multiantenna Transceivers[M]. HAYKIN S and LIU K J R. Handbook on Array Processing and Sensor Networks. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2010. doi: 10.1002/9780470487068.ch5. [8] SCHEINER N, KRAUS F, WEI Fangyin, et al. Seeing around street corners: Non-line-of-sight detection and tracking in-the-wild using doppler radar[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2065–2074. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00214. [9] SOUBIELLE J, FIJALKOW I, DUVAUT P, et al. GPS positioning in a multipath environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(1): 141–150. doi: 10.1109/78.972490. [10] HAN Ke, TANG Canyang, and DENG Zhongliang. A new method for multipath filtering in GPS static high-precision positioning[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 2704. doi: 10.3390/s19122704. [11] ZHANG Yueting, DING Chibiao, CHEN Hongzhen, et al. Special phenomena of the shadow region in the high resolution synthetic aperture radar image due to synthetic aperture[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2012, 33(10): 1052–1070. doi: 10.1007/s10762-012-9924-8. [12] AUER S, HINZ S, and BAMLER R. Ray-tracing simulation techniques for understanding high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1445–1456. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2029339. [13] SETLUR P, NEGISHI T, DEVROYE N, et al. Multipath exploitation in Non-LOS urban synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(1): 137–152. doi: 10.1109/jstsp.2013.2287185. [14] CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, CUI Guolong, et al. Building layout reconstruction with transmissive and reflective signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116612. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3199270. [15] CHEN Jiahui, ZHANG Yang, GUO Shisheng, et al. Joint estimation of NLOS building layout and targets via sparsity-driven approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114513. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3182429. [16] LI Nian, CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, et al. Building layout tomographic imaging with improved delay estimation algorithm[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2023, 22(5): 1079–1083. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2022.3232769. [17] ZHANG Fubo, LIANG Xingdong, CHENG Ruichang, et al. Building corner reflection in MIMO SAR tomography and compressive sensing-based corner reflection suppression[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(3): 446–450. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2019.2926301. [18] LINNEHAN R and SCHINDLER J. Multistatic scattering from moving targets in multipath environments[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2009.4977062. [19] LINNEHAN R, DEMING R and SCHINDLER J. Multipath analysis of dismount radar responses[C]. 2011 IEEE RadarCon, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 474–479. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960583. [20] NOUVEL J F, VAIZAN B, DU PLESSIS O R, et al. Ka band measurements over urban area, a study of NLOS back-scattering[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 3615–3618. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6350634. [21] NOUVEL J F, DUPUIS X, and LESTURGIE M. Non line of sight signal analysis: Investigation of interferometry modes over urban area[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059175. [22] COLIN-KOENIGUER E, SAR N, THIRION-LEFEVRE L, et al. Preliminary studies on the detection of a NLOS Target in a 2D urban canyon using PolInSAR data[C]. The 5th International Workshop on Science and Applications of SAR Polarimetry and Polarimetric Interferometry, Frascati, Italy, 2011. [23] MOKADEM A, THIRION-LEFEVRE L, COLIN-KOENIGUER E, et al. Determination ofmechanisms that can occur in NLOS urban canyon[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 99–102. [24] YAN Qiancheng, JIAO Zekun, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Comparison between different TomoSAR imaging models for airborne platform flying at low altitude[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(21): 5452. doi: 10.3390/rs14215452. [25] ZHU Xiaoxiang. Spectral estimation for synthetic aperture radar tomography[D]. [Master dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2008. [26] LI Hao, YIN Jie, JIN Shuang, et al. Synthetic aperture radar tomography in urban area based on compressive MUSIC[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2005: 012055. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2005/1/012055. [27] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1 -norm regularization—the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117. [28] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2010.2050487. [29] TORR P H S and ZISSERMAN A. MLESAC: A new robust estimator with application to estimating image geometry[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2000, 78(1): 138–156. doi: 10.1006/cviu.1999.0832. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: