Adaptive Angle-Doppler Compensation Method for Airborne Bistatic Radar Based on PAST
-
摘要:
自适应角度-多普勒补偿算法根据样本数据本身来自适应地估计补偿参数,从而避免惯导系统误差造成的补偿性能下降问题,但该算法必须对杂波协方差矩阵进行估计和特征分解,运算量巨大。针对这一问题,该文研究了基于近似投影子空间跟踪(PAST)处理的自适应角度-多普勒补偿算法,该方法先采用循环迭代处理快速估计出各距离单元主特征向量谱中心的位置参数,避免了矩阵特征分解带来的运算负担,然后通过补偿使得各单元的谱中心重合。仿真结果表明,该方法能有效解决机载双基雷达杂波非均匀问题,其性能与基于特征分解算法相当,但运算量显著降低,便于工程实现。
-
关键词:
- 机载双基雷达 /
- 近似投影子空间跟踪 /
- 自适应角度多普勒补偿 /
- 空时自适应处理
Abstract:The adaptive angle-Doppler compensation method adaptively extracts requisite information based on the data itself, thereby avoiding the problem of performance degradation due to inertial system error. However, this method requires the estimation and eigen decomposition of a sample covariance matrix, which has high computational complexity and limits its real-time application. In this paper, we investigate an adaptive angle-Doppler compensation method based on Projection Approximation Subspace Tracking (PAST). This method uses cyclic iterative processing to quickly estimate the positions of the spectral center of the maximum eigenvector in each range cell, thereby avoiding the computational burden of matrix estimation and eigen decompositon. Then, the spectral centers of all range cells are overlapped by two-dimensional compensation. Our simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively reduce the nonhomogeneity of airborne bistatic radar, with a performance is similar to that of eigen-decomposition algorithms, but with a reduced computational load and easy implementation.
-
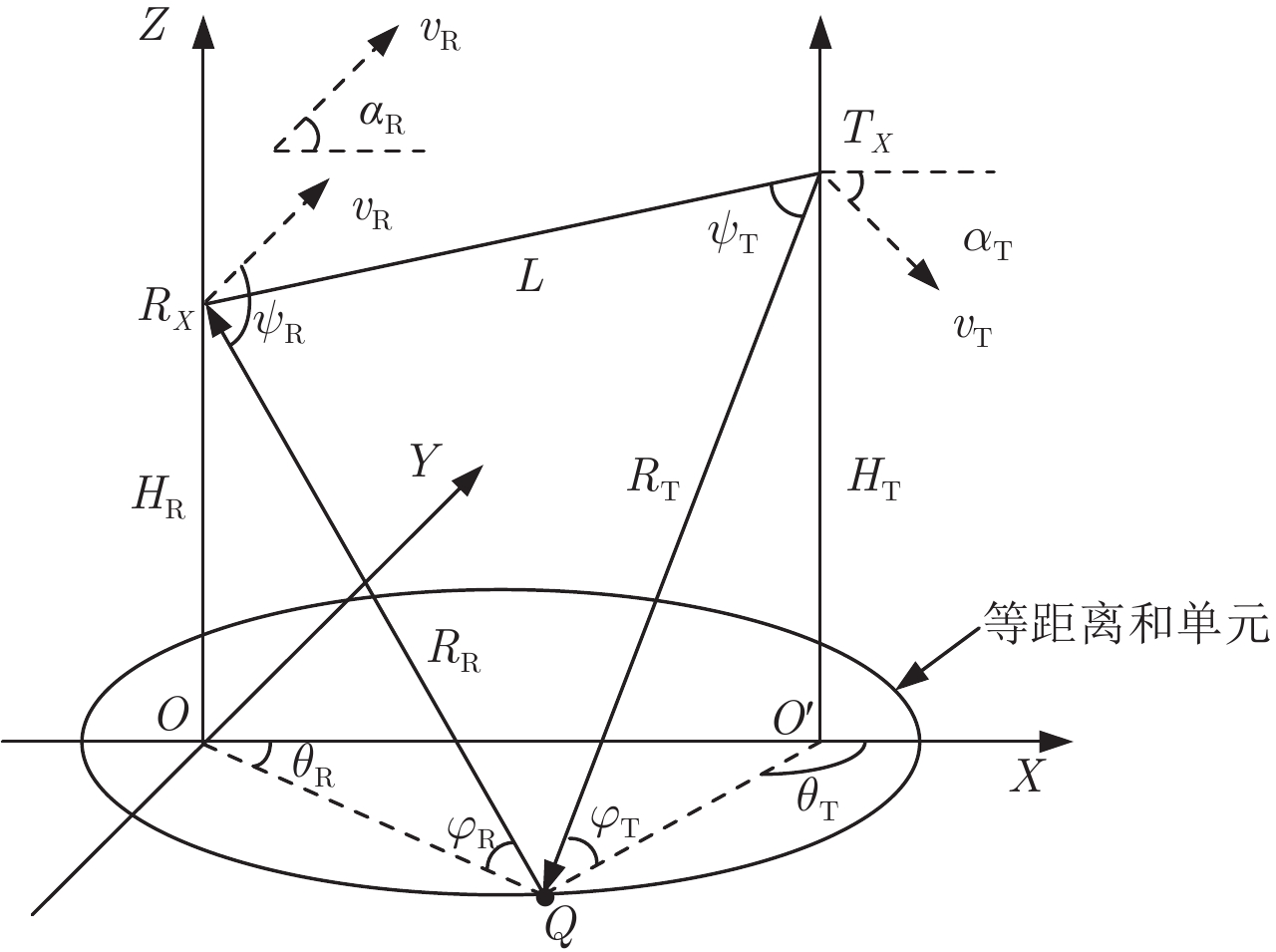
表 1 雷达仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters for radar
参数名称 参数数值 接收阵元数 N=10 相干处理脉冲数 K=10 脉冲重复频率(Hz) fr=2234 基线距离(km) L=100 双基距离和(km) Rs=153 发射平台高度(km) HT=8 接收平台高度(km) HR=6 发射机速度(m/s) vT=140 接收机速度(m/s) vR=140 雷达工作波长(m) λ=0.23 阵元间距 d=λ/2 单元输入杂噪比(dB) CNR=50 -
[1] 张良, 徐艳国. 机载预警雷达技术发展展望[J]. 现代雷达, 2015, 37(1): 1–7Zhang Liang and Xu Yan-guo. Prospect for technology of airborne early warning radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2015, 37(1): 1–7 [2] 张永顺, 冯为可, 赵杰, 等. 时变加权的机载双基雷达降维空时自适应处理[J]. 电波科学学报, 2015, 30(1): 194–200. DOI: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014040701Zhang Yong-shun, Feng Wei-ke, Zhao Jie, et al. A dimension-reduced STAP method for airborne bistatic radar based on time-varying weighting techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2015, 30(1): 194–200. DOI: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014040701 [3] Greve S, Ries P, Lapierre F, et al. Framework and taxonomy for radar space-time adaptive processing (STAP) methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 1084–1099. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383596 [4] 阳召成, 黎湘, 王宏强. 基于空时功率谱稀疏性的空时自适应处理技术研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2014, 42(6): 1194–1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.06.024Yang Zhao-cheng, Li Xiang, and Wang Hong-qiang. An overview of space-time adaptive processing technology based on sparsity of space time power spectrum[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(6): 1194–1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.06.024 [5] Borsari G K. Mitigating effects on STAP processing caused by an inclined array[C]. Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE National Radar Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 1998: 135–140. [6] 冯坤菊, 王春阳, 段垣丽, 等. 机载双基地STAP的OP-DW预处理算法及其性能研究[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(3): 700–704Feng Kun-ju, Wang Chun-yang, Duan Yuan-li, et al. Research on the OP-DW algorithm of bistatic radar and its performance[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(3): 700–704 [7] Himed B, Zhang Y, and Hajjari A. STAP with angle-Doppler compensation for bistatic airborne radars[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE National Radar Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2002: 311–317. [8] Himed B. Effects of bistatic clutter dispersion on STAP systems[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(1): 28–32. DOI: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030100 [9] Fallah A and Bakhshi H. Extension of adaptive angle-Doppler compensation (AADC) in STAP to increase homogeneity of data in airborne bistatic radar[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 6th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 2012: 367–372. [10] Melvin M L and Davis M E. Adaptive cancellation method for geometry-induced nonstationary bistatic clutter environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(2): 651–672. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4285360 [11] 王杰, 沈明威, 吴迪, 等. 基于主瓣杂波高效配准的机载非正侧视阵雷达STAP算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 235–240. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13122Wang Jie, Shen Ming-wei, Wu Di, et al. An efficient STAP algorithm for nonsidelooking airborne radar based on mainlobe clutter compensation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 235–240. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13122 [12] 马泽强, 王希勤, 刘一民, 等. 基于稀疏恢复的空时二维自适应处理技术研究现状[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 217–228. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14002Ma Ze-qiang, Wang Xi-qin, Liu Yi-min, et al. An overview on sparse recovery-based STAP[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 217–228. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14002 [13] Yang Bin. Projection approximation subspace tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(1): 95–107. DOI: 10.1109/78.365290 [14] Belkacemi H and Marcos S. Fast iterative subspace algorithms for airborne STAP radar[J]. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 2006, 2006: 037296. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: