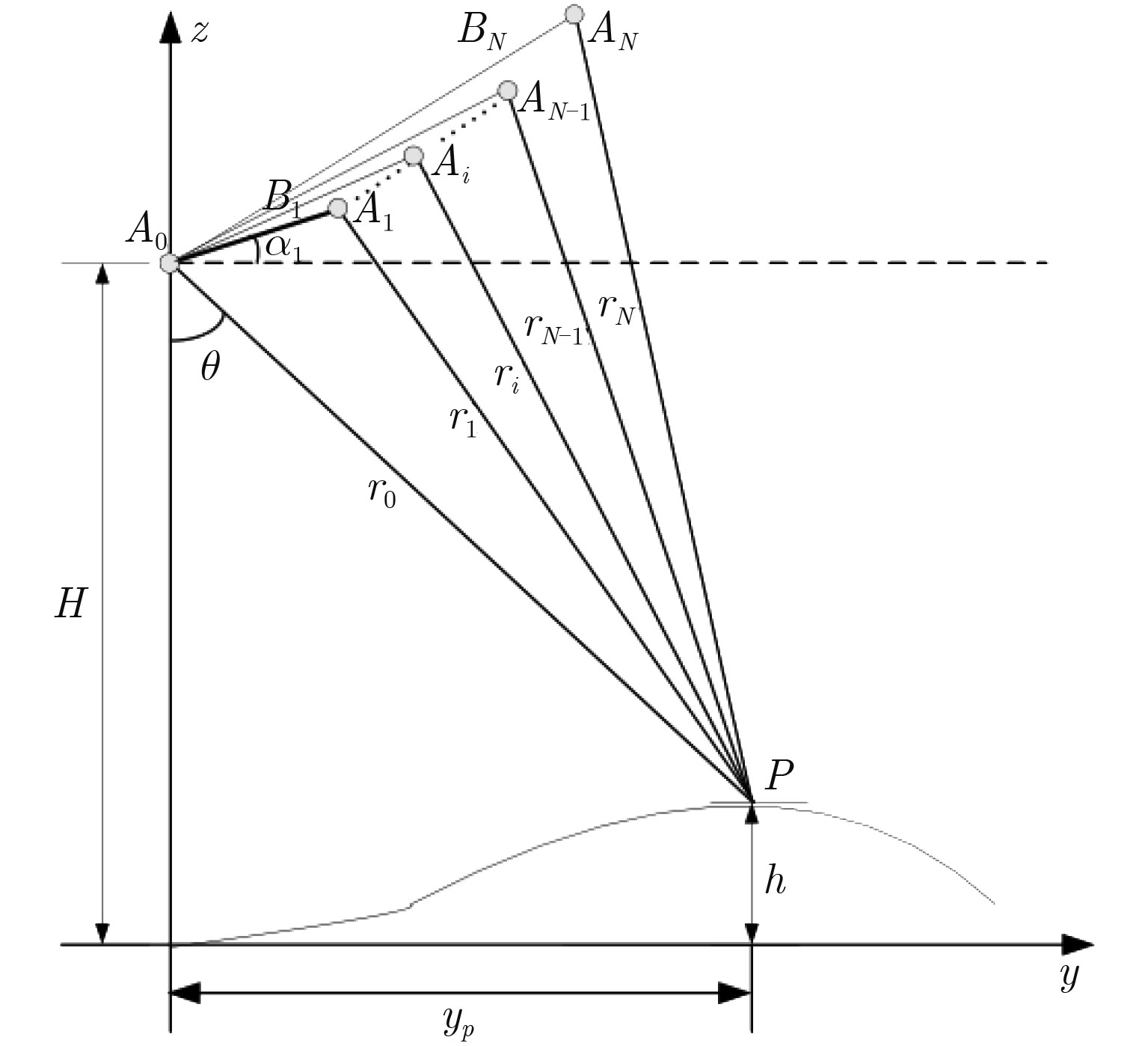
A Novel Cluster-Analysis Algorithm Based on MAP Framework for Multi-baseline InSAR Height Reconstruction
-
摘要:
多基线干涉SAR能有效减小由目标高度急剧变化和较大噪声干扰带来的不利影响,可以获取比单基线干涉SAR更精确的地表数字高程模型(DEM)。传统的基于最大似然估计(ML)的多基线高度重建算法在通道数目较少情况下重建结果不佳,基于最大后验估计(MAP)的多基线高度重建算法存在运行时间较长的问题,针对以上问题,该文提出了一种基于最大后验框架的聚类分析高度重建算法(CABMAP)。该算法首先利用了ML估计法得到粗略的DEM,以此为基础在每次迭代过程中利用聚类分析(CA)判断出邻域内的噪声像素,并通过计算后验概率完成重建,此外采用了一种改进措施提高精度。这样,既保留了ML估计法运行速度快的特征,又具有MAP估计法精度高的优点。经实验验证,该算法精度较好且运行效率较高。
Abstract:The multi-baseline InSAR can effectively reduce the adverse effect caused by the abrupt change of the target and the large noise disturbance and can obtain the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) that is more accurate than the single baseline InSAR. Traditional multi-baseline height reconstruction algorithm based on Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimation is poorly reconstructed in the case of fewer channels, and the height reconstruction algorithm based on Maximum A Posteriori estimation (MAP) has a long runtime defect; to solve this problem, this study proposes the cluster analysis based on maximum a posteriori algorithm. This algorithm uses the ML estimation to obtain a rough DEM. Based on this result, the noise pixels in the neighborhood in each iteration process are determined by cluster analysis. Finally, through the calculation of posterior probability to complete the reconstruction, an optimized method is adopted to improve the accuracy. Experiments reveal that the algorithm retains the speed of the ML method as well as the high precision of the MAP estimation, thus maintaining accuracy and high operating efficiency.
-
表 1 多基线干涉SAR系统仿真参数
Table 1. Multi-baseline InSAR system simulation parameters
参数 数值 景中心斜距(km) 500 平台高度(km) 433 视角(°) 30 基线角(°) 5 信号波长(cm) 3.1 信号带宽(MHz) 100 基线1长度(m) 199.794 基线2长度(m) 133.196 基线3长度(m) 79.918 信噪比(dB) 30 DEM网格间距(m) 1.5×1.5 表 2 算法性能对比(Isolation Peak仿真数据)
Table 2. Algorithm performance comparison (Simulation dataset: Isolation Peak)
算法模型 时间(s) 精度(归一化均方误差) 鲁棒性CRT 2.012318 1.2295 CA 0.868110 0.9139 CANOPUS 3.393945 0.8986 ML估计 4.198716 3.8801 ML估计后均值滤波 4.682451 2.0460 MAP估计 229.851504 0.0117 CABMAP 22.921332 0.0041 改进的CABMAP 24.109097 0.0028 表 3 信噪比和精度关系
Table 3. Relationship between SNR and accuracy
算法 信噪比(dB) 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 鲁棒性CRT 3.5594 3.1339 2.5860 2.0128 1.5663 1.2295 1.0121 CA 1.0152 0.9763 0.9495 0.9290 0.9133 0.9139 0.9025 CANOPUS 0.9311 0.9243 0.9177 0.9138 0.9019 0.8986 0.8919 ML估计 4.8221 4.6486 4.4204 4.1489 4.0443 3.8801 3.7875 ML估计后均值滤波 3.0314 2.7886 2.5026 2.2465 2.1602 2.0460 1.9831 MAP估计 1.2184 0.8829 0.4422 0.1285 0.0229 0.0117 0.0111 CABMAP 0.4145 0.2423 0.0768 0.0171 0.0064 0.0041 0.0030 改进的CABMAP 0.4075 0.2254 0.0574 0.0110 0.0045 0.0028 0.0021 表 4 不同聚类迭代次数下CABMAP算法精度
Table 4. The accuracy of CABMAP algorithm for different clustering iterations
聚类迭代次数N 精度(归一化均方误差) 0 0.2378 1 0.0081 2 0.0041 3 0.0168 4 0.0240 5 0.0299 表 5 不同阈值点数下CABMAP算法精度
Table 5. The accuracy of CABMAP algorithm for different threshold points
阈值点数 ${\rm{Hpt}}{{\rm{s}}_{{\rm{th}}}}$ 精度(归一化均方误差) 2 0.0158 3 0.0144 4 0.0107 5 0.0047 6 0.0041 7 0.0044 表 6 不同高程差下CABMAP算法精度
Table 6. The accuracy of CABMAP algorithm for different elevation difference
高程差 $\Delta h$ (m) 精度(归一化均方误差) 10 0.0042 20 0.0041 30 0.0043 40 0.0043 50 0.0043 60 0.0045 表 7 实测数据集参数
Table 7. Real dataset parameters
主图像获取时间
(年-月-日)副图像获取时间
(年-月-日)时间基线(d) 空间垂直基线(m) 2009-02-20 2009-02-09 11 151.5 2009-02-20 2009-01-29 11 86.6 表 8 算法运行时间
Table 8. Run time of the algorithms
算法 时间(s) 鲁棒性CRT 0.320831 CA 0.518862 CANOPUS 2.009810 ML估计 0.161702 ML估计后均值滤波 0.164832 MAP估计 11.617357 CABMAP 5.175075 改进的CABMAP 5.253087 -
[1] Bamler P and Hartl P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Inverse Problems, 1998, 14(4): R1–R54. DOI: 10.1088/0266-5611/14/4/001 [2] Rosen P A, Hensley S, Joughin I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. DOI: 10.1109/5.838084 [3] Richards M A. A beginner’s guide to interferometric SAR concepts and signal processing [AESS Tutorial IV][J].IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2007, 22(9): 5–29. DOI: 10.1109/MAES.2007.4350281 [4] Karout S. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Liverpool John Moores University, 2007. [5] 张妍, 冯大政, 曲小宁. 枝切法与曲面拟合结合的InSAR相位展开算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 39(5): 47–53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2012.05.009Zhang Yan, Feng Dazheng, and Qu Xiaoning. Hybrid phase unwrapping algorithm combining branch-cut and surface-fitting for InSAR[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science) , 2012, 39(5): 47–53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2012.05.009 [6] Krieger G, Hajnsek I, Papathanassiou K P, et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) missions employing formation flying[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(5): 816–843. DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2038948 [7] 庞蕾, 张继贤, 范洪冬. 多基线干涉SAR测量技术发展与趋势分析[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(9): 2152–2157Pang Lei, Zhang Jixian, and Fan Hongdong. Progress and tendency of multibaseline Synthetic Aperture Radar interferometry technique[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(9): 2152–2157 [8] 侯丽英, 林赟, 洪文. 干涉圆迹SAR的目标三维重建方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 538–547. DOI: 10.12000/JR16009Hou Liying, Lin Yun, and Hong Wen. Three-dimensional reconstruction method study based on interferometric circular SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 538–547. DOI: 10.12000/JR16009 [9] 师君, 张晓玲, 韦顺军, 等. 基于变分模型的阵列三维SAR最优DEM重建方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 20–28. DOI: 10.12000/JR14136Shi Jun, Zhang Xiao-ling, Wei Shun-jun, et al. An optimal DEM reconstruction method for linear array Synthetic Aperture Radar based on variational model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 20–28. DOI: 10.12000/JR14136 [10] 靳国旺, 张红敏, 徐青, 等. 多波段InSAR的CRT相位解缠方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 38(6): 97–102. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2011.06.015Jin Guowang, Zhang Hongmin, Xu Qing, et al. Phase unwrapping algorithm with CRT for multi-band InSAR[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science) , 2011, 38(6): 97–102. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2011.06.015 [11] Yuan Zhihui, Deng Yunkai, Li Fei, et al. Multichannel InSAR DEM reconstruction through improved closed-form robust Chinese remainder theorem[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1314–1318. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2238886 [12] Yu Hanwen, Li Zhenfang, and Bao Zheng. A cluster-analysis-based efficient multibaseline phase-unwrapping algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 478–487. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2055569 [13] Liu Huitao, Xing Mengdao, and Bao Zheng. A cluster-analysis-based noise-robust phase-unwrapping algorithm for multibaseline interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 494–504. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2324595 [14] Pascazio V and Schirinzi G. Estimation of terrain elevation by multifrequency interferometric wide band SAR data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2001, 8(1): 7–9. DOI: 10.1109/97.889635 [15] Pascazio V and Schirinzi G. Multifrequency InSAR height reconstruction through maximum likelihood estimation of local planes parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(12): 1478–1489. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2002.804274 [16] Ferraiuolo G, Pascazio V, and Schirinzi G. Maximum a posteriori estimation of height profiles in InSAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(2): 66–70. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2003.822882 [17] Li S Z. Modeling image analysis problems using markov random fields[J]. Handbook of Statistics, 2003, 21: 473–513. DOI: 10.1016/S0169-7161(03)21015-4 [18] Ferraioli G, Shabou A, Tupin F, et al. Multichannel phase unwrapping with graph cuts[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 562–566. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2021165 [19] Deledalle C A, Denis L, Ferraioli G, et al.. Combining patch-based estimation and total variation regularization for 3D InSAR reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 2015: 2485–2488. [20] Ferraiuolo G, Meglio F, Pascazio V, et al. DEM reconstruction accuracy in multichannel SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 191–201. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002644 [21] Saquib S S, Bouman C A, and Sauer K. ML parameter estimation for markov random fields with applications to bayesian tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1998, 7(7): 1029–1044. DOI: 10.1109/83.701163 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: