Compressed Sensing Linear Array SAR Autofocusing Imaging via Semi-definite Programming
-
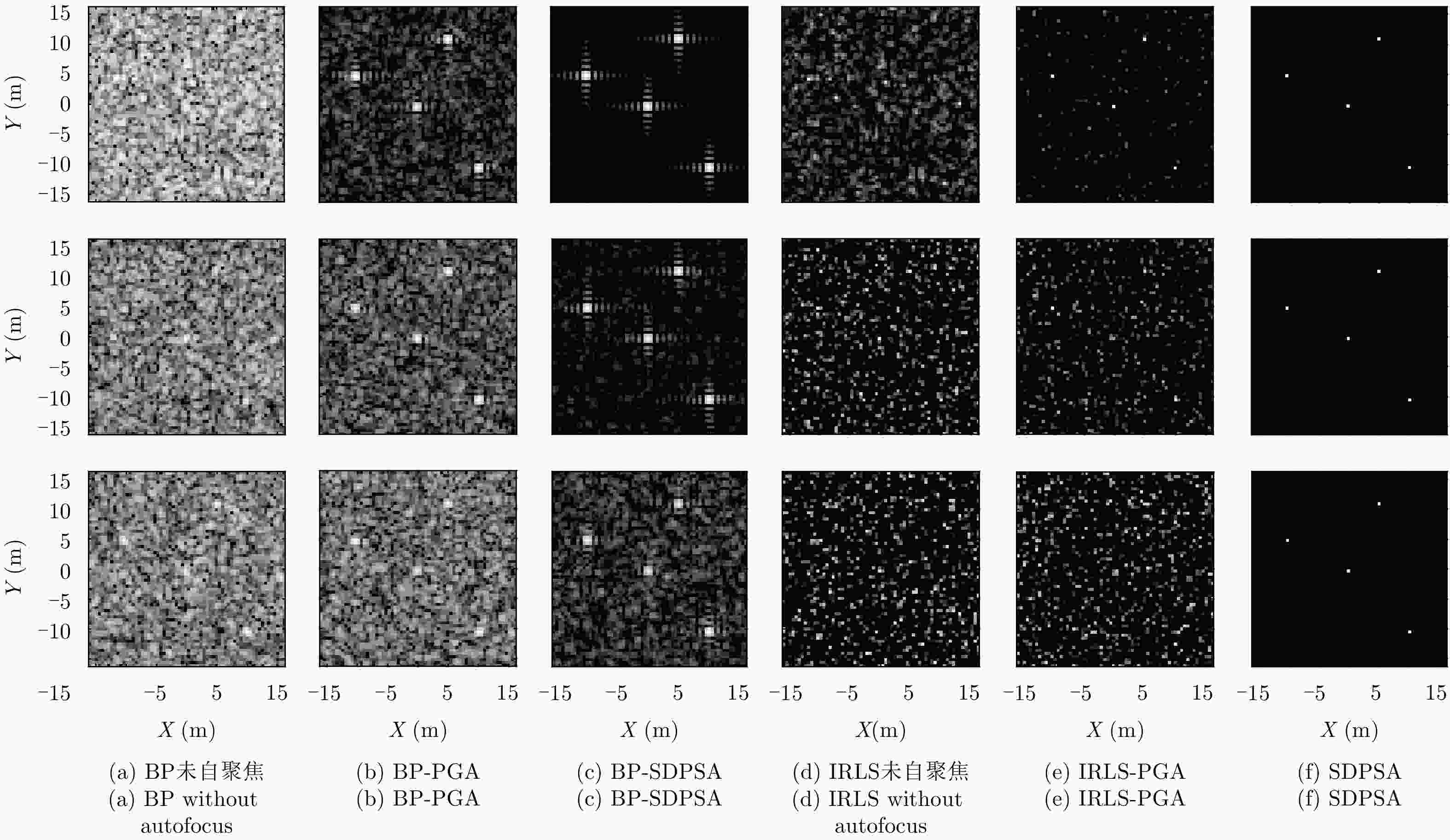
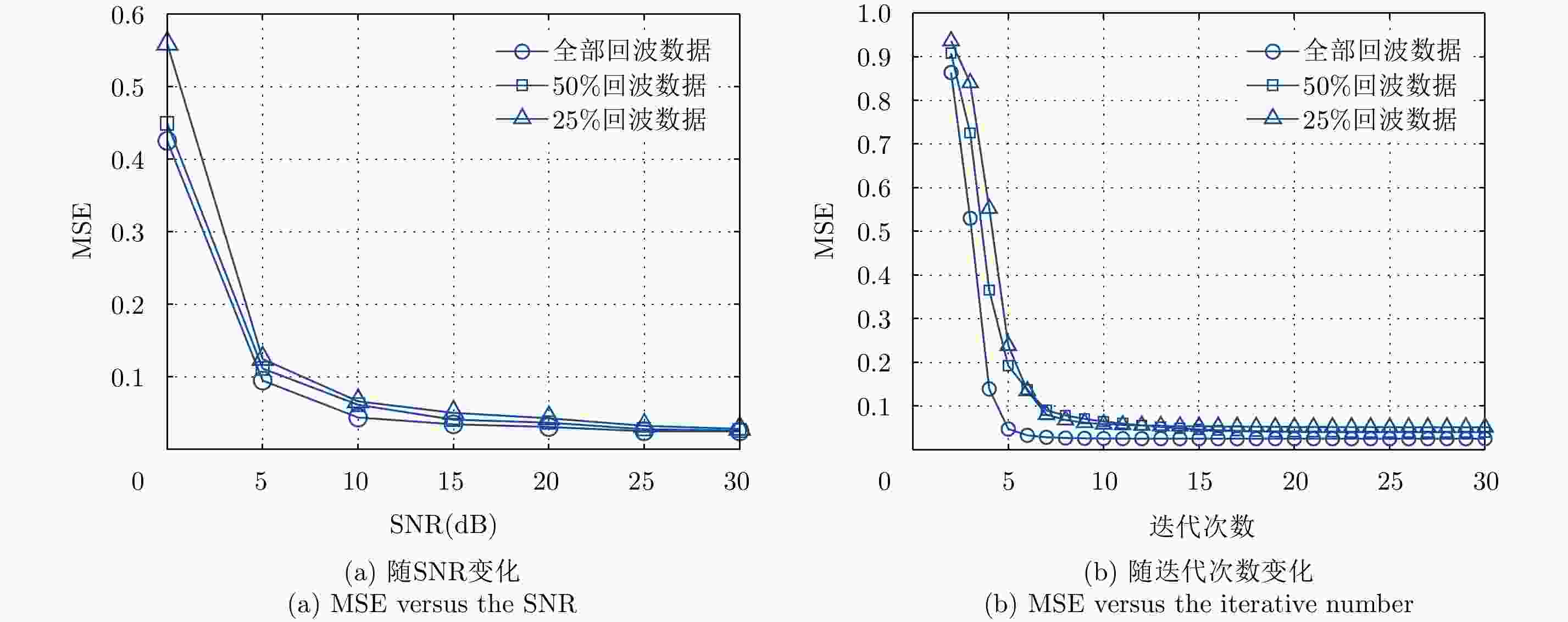
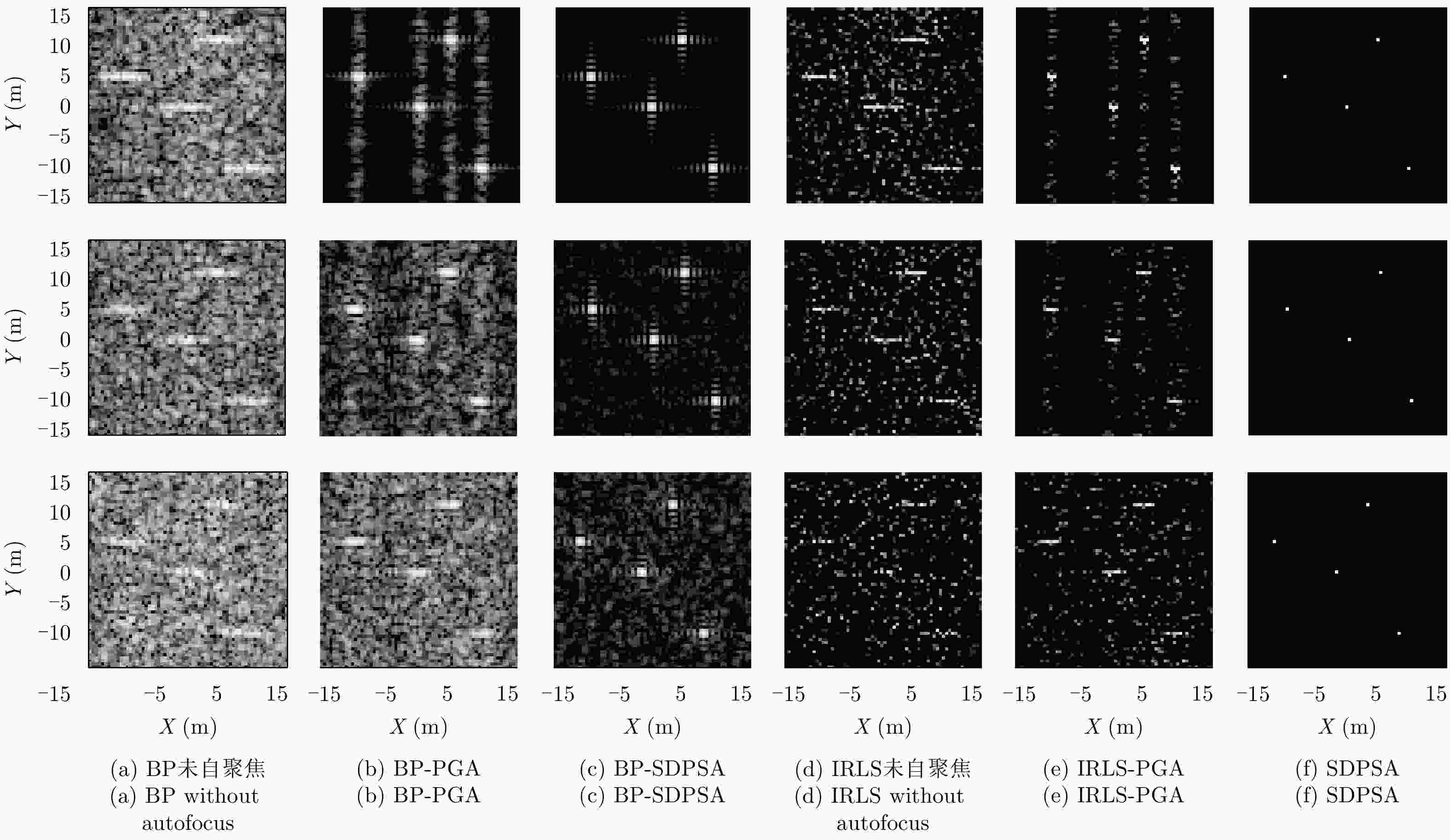
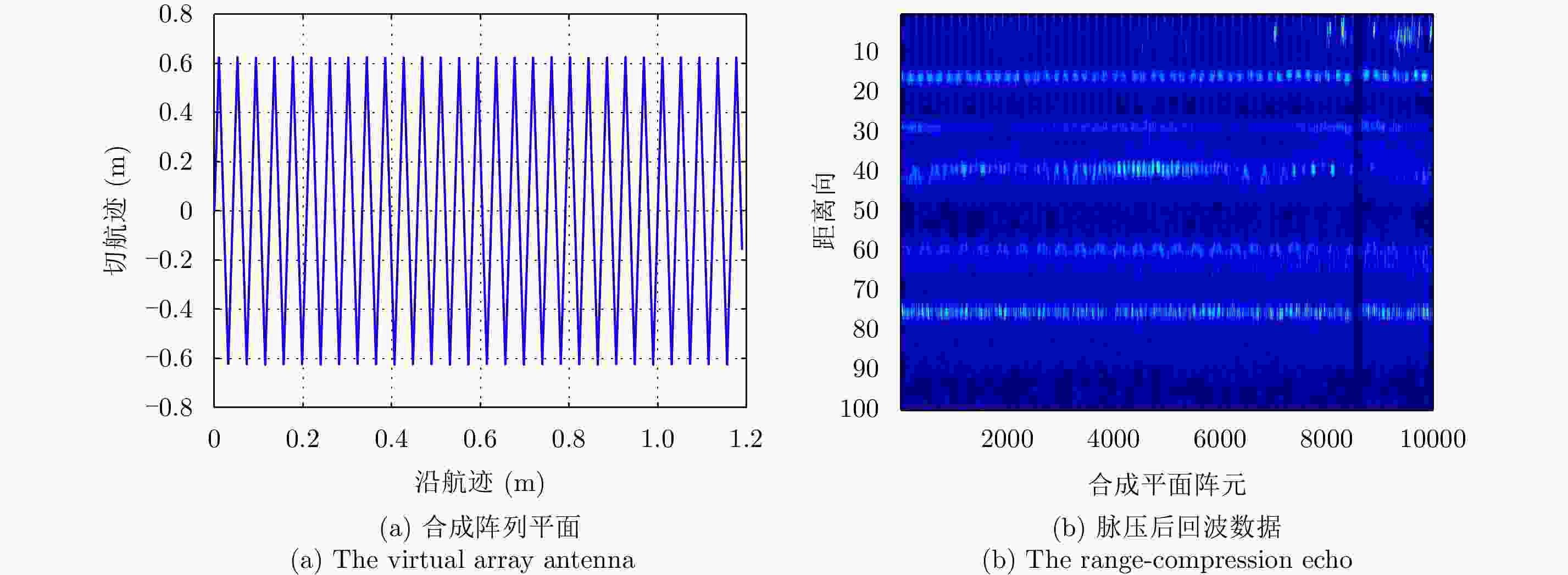
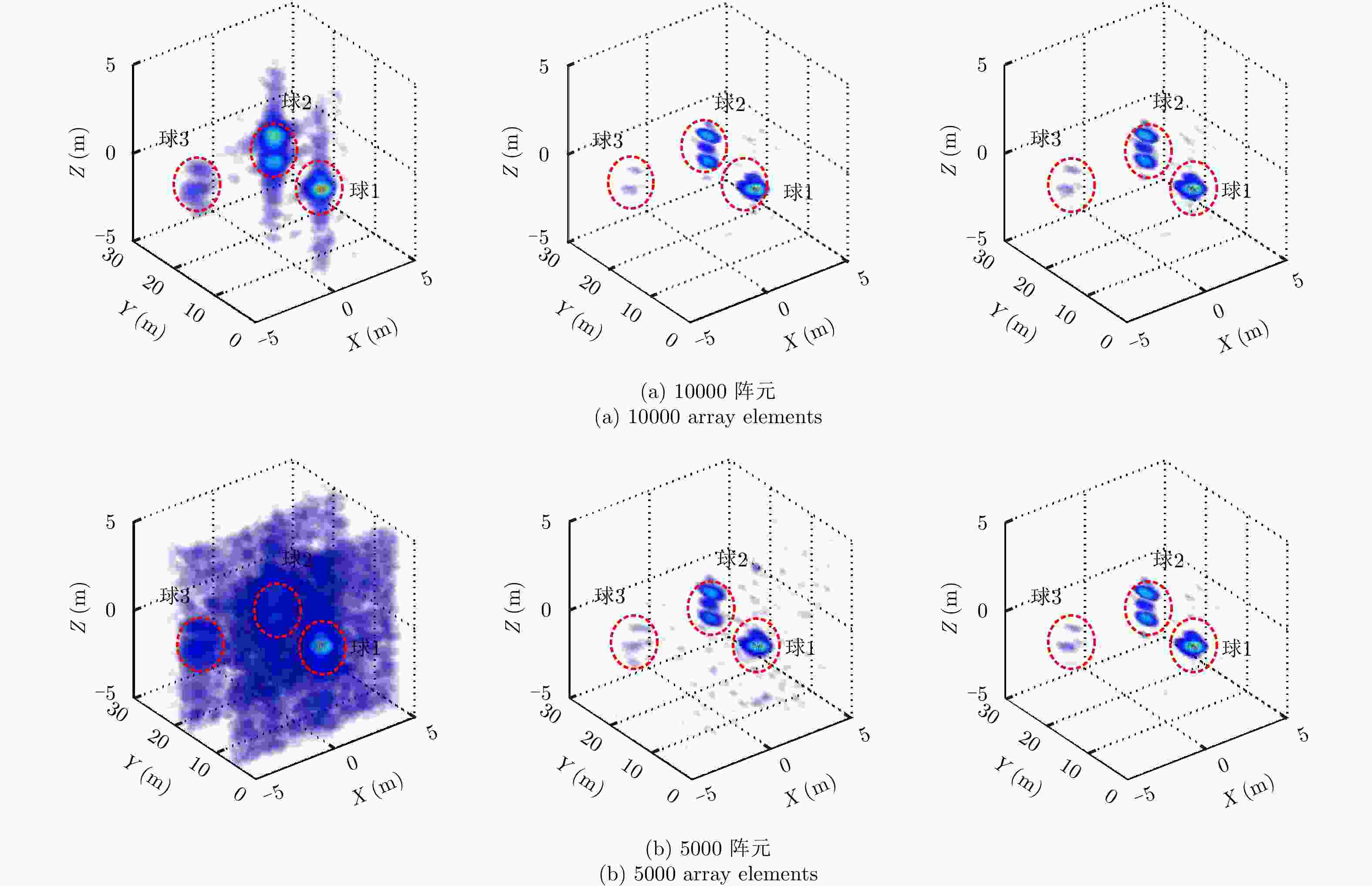
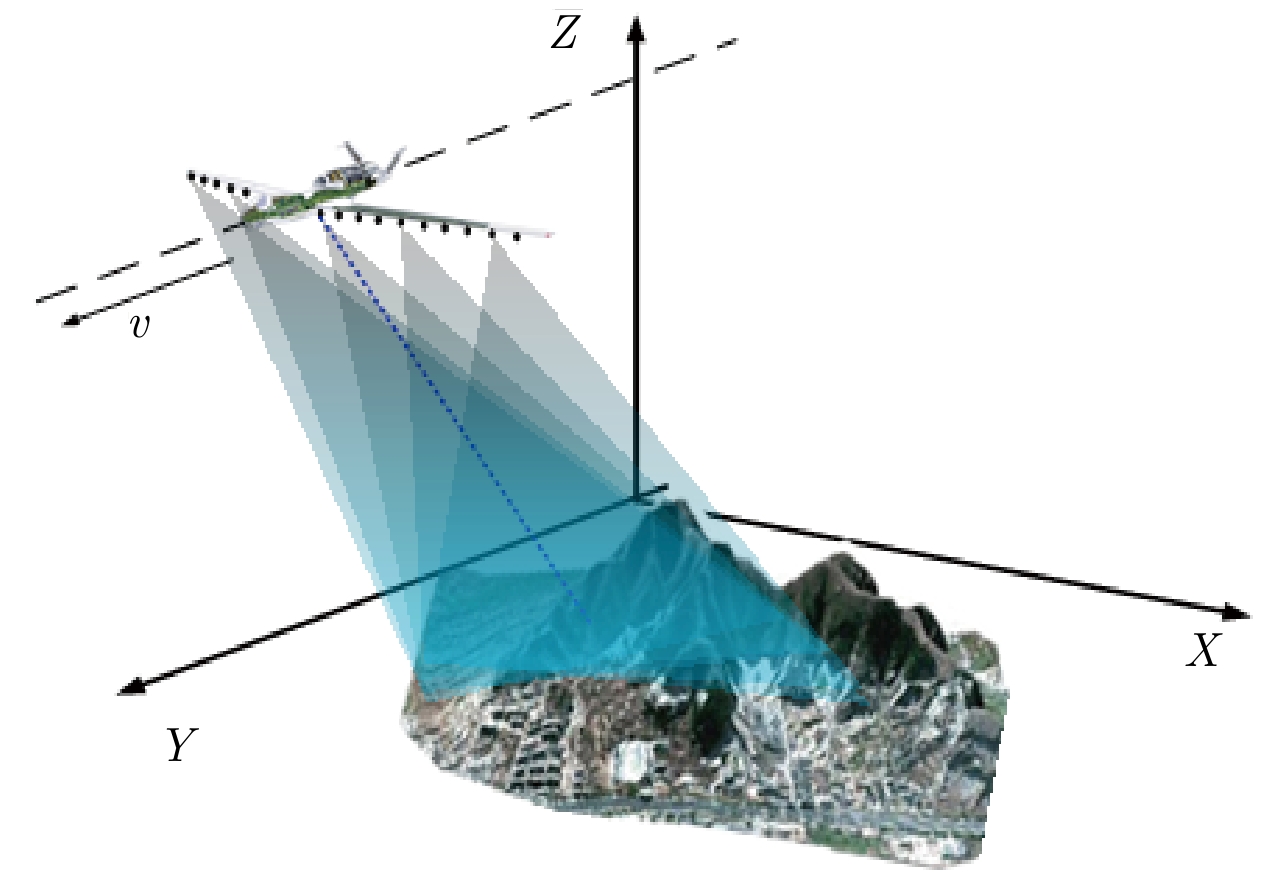
摘要: 线阵合成孔径雷达(Linear Array Synthetic Aperture Radar, LASAR)3维成像技术是一种具有重要潜在应用价值的新体制成像雷达,压缩感知稀疏重构是近几年实现LASAR高分辨3维成像的热点研究之一。但相对于传统2维SAR,受线阵稀疏分布及阵列-平台2维联动,压缩感知LASAR成像面临回波数据欠采样、多维度高阶相位误差等问题,传统SAR自聚焦算法难以适用于压缩感知LASAR 3维稀疏自聚焦成像。为克服欠采样条件下多维度高阶相位误差对LASAR成像的影响,该文提出了一种基于半正定规划的压缩感知LASAR自聚焦成像算法。首先,结合压缩感知成像理论、图像最大锐度及最小均方误差准则,构造欠采样条件下稀疏目标的相位误差估计模型;其次,利用松弛半正定规划方法估计相位误差;最后,利用迭代逼近方法提高相位误差估计精度,实现压缩感知LASAR高精度稀疏自聚焦成像。另外,通过主散射目标区域提取,仅采用主散射区域进行相位误差估计,进一步提高自聚焦算法运算效率。仿真数据和实测数据验证了该文算法的有效性。Abstract: Linear Array Synthetic Aperture Radar (LASAR) is a novel and promising radar imaging technique. In recent years, Compressed Sensing (CS) sparse recovery has been a research focus for high-resolution three-Dimensional (3-D) LASAR imaging. Compared with the traditional two-Dimensional (2-D) SAR imaging, LASAR suffers from many problems, including under-sampling data and multi-dimensional and higher-order phase errors due to its sparse Linear Array Antenna (LAA) and the joint 2-D motions of the platform and LAA. The conventional autofocusing methods of 2-D SAR may be not suitable for CS-based LASAR 3-D sparse autofocusing. To address the multi-dimensional and higher-order phase errors in LASAR 3-D imaging with respect to under-sampling data, in this paper, we propose a sparse autofocusing algorithm based on semi-definite programming for CS-based LASAR imaging. First, by combining CS-based imaging theory, image maximum sharpness, and the minimum square error principle, we construct a LASAR phase-error estimation model based on under-sampled data. Next, we use semi-definite programming relaxation to estimate the phase errors. Lastly, we employ an iterated approximation method to improve the precision of the phase-error estimation and achieve the final CS-based LASAR autofocusing. To further improve the efficiency of the algorithm, we select only the dominant scattering areas for LASAR phase-error estimation. We present our simulation and experimental results to confirm the effectiveness of out proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 SDPSA算法
Table 1. SDPSA algorithm
输入:代价函数 ${J_{\rm{1}}}\left( {{{{f}}},{{{φ}}} } \right)$和 ${J_{\rm{2}}}\left( {{{{f}}},{{{φ}}} } \right)$ 输出:估计值 $\left( {{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} ,{{\stackrel \frown{{φ}}} } } \right)$ 初始化:迭代次数 $i = 0$,相位误差 ${{{{φ}}} ^{\left( {\rm{0}} \right)}} = 0$,门限 ${{δ}} $,迭代总次数 $K$ 若 ${\left\| {{{{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} }^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}} - {{{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} }^{\left( i \right)}}} \right\|_2}\Bigr/{\left\| {{{{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} }^{\left( i \right)}}} \right\|_2} > {{δ}} $和 $i \le K$,循环开始 步骤1 构造稀疏目标重构的代价函数: ${J_{\rm{1}}}\left( {{{{f}}},{{{{{\stackrel \frown{φ}}} } }^{\left( i \right)}}} \right) = {{λ}} {\left\| {{{f}}} \right\|_1}{\rm{ + }} \left\| {{{{y}}} - {{{R}}}\left( {{{{{{\stackrel \frown{φ}}} } }^{\left( i \right)}}} \right){{{Af}}}} \right\|_2^{}$ 步骤2 利用IRLS算法进行稀疏目标重构: ${{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} ^{\left( {i{\rm{ + 1}}} \right)}} = \arg \mathop {\min }\limits_{f} {J_{\rm{1}}}\left( {{{{f}}},{{{{{\stackrel \frown{φ}}} } }^{\left( i \right)}}} \right)$ 步骤3 构造相位误差估计的代价函数: ${J_{\rm{2}}}\left( {{{{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} }^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}},{{{φ}}} } \right) \approx {{{γ} }^{\rm H}}{{{{Q}}}^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}}{{γ} }$ 步骤4 利用SDP方法求解最优问题: ${{{{\stackrel \frown{X}}}} _{\rm{opt}}} = \arg \mathop {\min }\limits_{X} {\rm tr}\left({{{{Q}}}^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}}{{{X}}}\right),\ {\rm s.t.} \ \ {{{X}}} \succeq 0,{{{{X}}}_{ii}} = {g_n},n = 1,2, ·\!·\!· ,N$ 步骤5 利用 ${{{{\stackrel \frown{X}}}} _{\rm {opt}}}$估计相位误差 ${{{{\stackrel \frown{φ}}} } ^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}}$; $i \leftarrow i + 1$ 循环结束 返回结果: ${{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} \leftarrow {{{{\stackrel \frown{f}}}} ^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}}$, $\stackrel \frown{{{{φ}}} } \leftarrow {\stackrel \frown{{{{φ}}} } ^{\left( {i + 1} \right)}}$ -
[1] Du L, Wang Y P, Hong W, et al. A three-dimensional range migration algorithm for downward-looking 3D-SAR with single-transmitting and multiple-receiving linear array antennas[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2010, 2010: 957916. DOI: 10.1155/2010/957916 [2] Liao K F, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Plane-wave synthesis and RCS extraction via 3-D linear array SAR[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 994–997. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2389264 [3] Han K Y, Wang Y P, Tan W X, et al. Efficient pseudopolar format algorithm for down-looking linear-array SAR 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 572–576. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351792 [4] Zhang S Q, Zhu Y T, and Kuang G Y. Imaging of downward-looking linear array three-dimensional SAR based on FFT-MUSIC[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 885–889. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2365611 [5] Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Linear array SAR imaging via compressed sensing[J]. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, 2011, 117: 299–319. DOI: 10.2528/PIER11033105 [6] Zhang S Q, Zhu Y T, Dong G G, et al. Truncated SVD-based compressive sensing for downward-looking three-dimensional SAR imaging with uniform/nonuniform linear array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1853–1857. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2431254 [7] Zhang S Q, Dong G G, Kuang G Y, et al. Superresolution downward-looking linear array three-dimensional SAR imaging based on two-dimensional compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2184–2196. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2549548 [8] Peng X M, Tan W X, Hong W, et al. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR image reconstruction by combination of polar formatting and L1 regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 213–226. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2453202 [9] Tian J H, Sun J P, Han X, et al.. Motion compensation for compressive sensing SAR imaging with autofocus[C]. Proceedings of the 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Beijing, China, 2011: 1564–1567. DOI: 10.1109/ICIEA.2011.5975839. [10] Cetin M, Stojanovic I, Onhon O, et al. Sparsity-driven synthetic aperture radar imaging: Reconstruction, autofocusing, moving targets, and compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 27–40. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312834 [11] Onhon N Ö and Cetin M. A sparsity-driven approach for joint SAR imaging and phase error correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 2075–2088. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2179056 [12] Zhe Z, Yao Z, Jiang C L, et al.. Autofocus of sparse microwave imaging radar based on phase recovery[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing (ICSPCC), Kunming, China, 2013: 1–5. DOI: 10.1109/ICSPCC.2013.6663989. [13] Chen Y C, Li G, Zhang Q, et al. Motion compensation for airborne SAR via parametric sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 551–562. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2611522 [14] Camlica S, Gurbuz A C, Arikan O, et al. Autofocused spotlight SAR image reconstruction of off-grid sparse scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(4): 1880–1892. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2675138 [15] Uḡur S and Arıkan O. SAR image reconstruction and autofocus by compressed sensing[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2012, 22(6): 923–932. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsp.2012.07.011 [16] Kelly S, Yaghoobi M, and Davies M. Sparsity-based autofocus for undersampled synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 972–986. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120502 [17] Uḡur S, Arıkan O, and Gürbüz A C. Off-grid sparse SAR image reconstruction by EMMP algorithm[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RADAR), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586034. [18] Wei S J and Zhang X L. Sparse autofocus recovery for under-sampled linear array SAR 3-D imaging[J]. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 140: 43–62. DOI: 10.2528/PIER13020614 [19] Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Sparse autofocus via Bayesian learning iterative maximum and applied for LASAR 3-D imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2014: 666–669. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875674. [20] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [21] Figueiredo M A T, Nowak R D, and Wright S J. Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: Application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(4): 586–597. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910281 [22] Ji S H, Xue Y, and Carin L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346–2356. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914345 [23] Grant M and Boyd S. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 1.21[R]. CVX Research, Inc., 2010. Available from: URL: http://cvxr.com/cvx. [24] Toh K C, Todd M J, and Tütüncü R H. SDPT3—A Matlab software package for semidefinite programming, version 1.3[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1/4): 545–581. DOI: 10.1080/10556789908805762 [25] Liu K H, Wiesel A, and Munson D C. Synthetic aperture radar autofocus via semidefinite relaxation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(6): 2317–2326. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2249084 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: