A Fast Algorithm for Establishing 3-D Scattering Center Model for Ship Targets over Sea Surface Using the Shooting and Bouncing Ray Technique
-
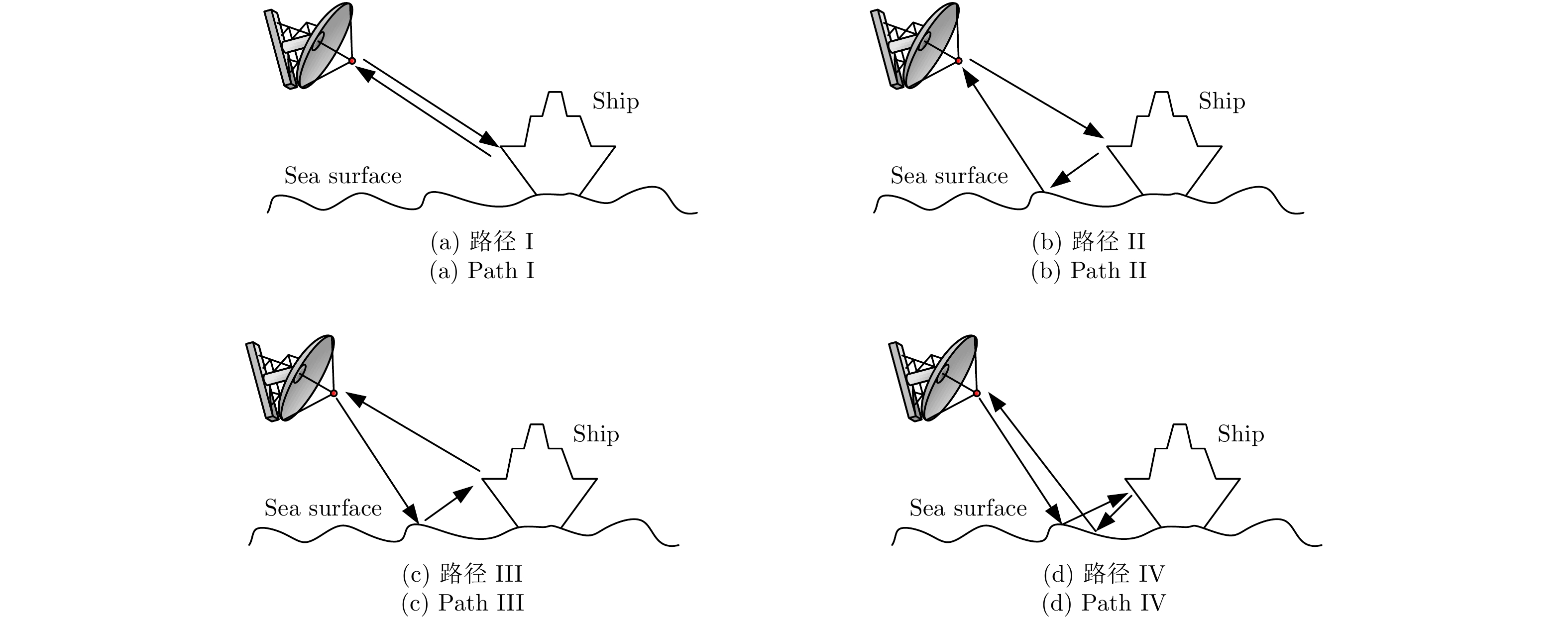
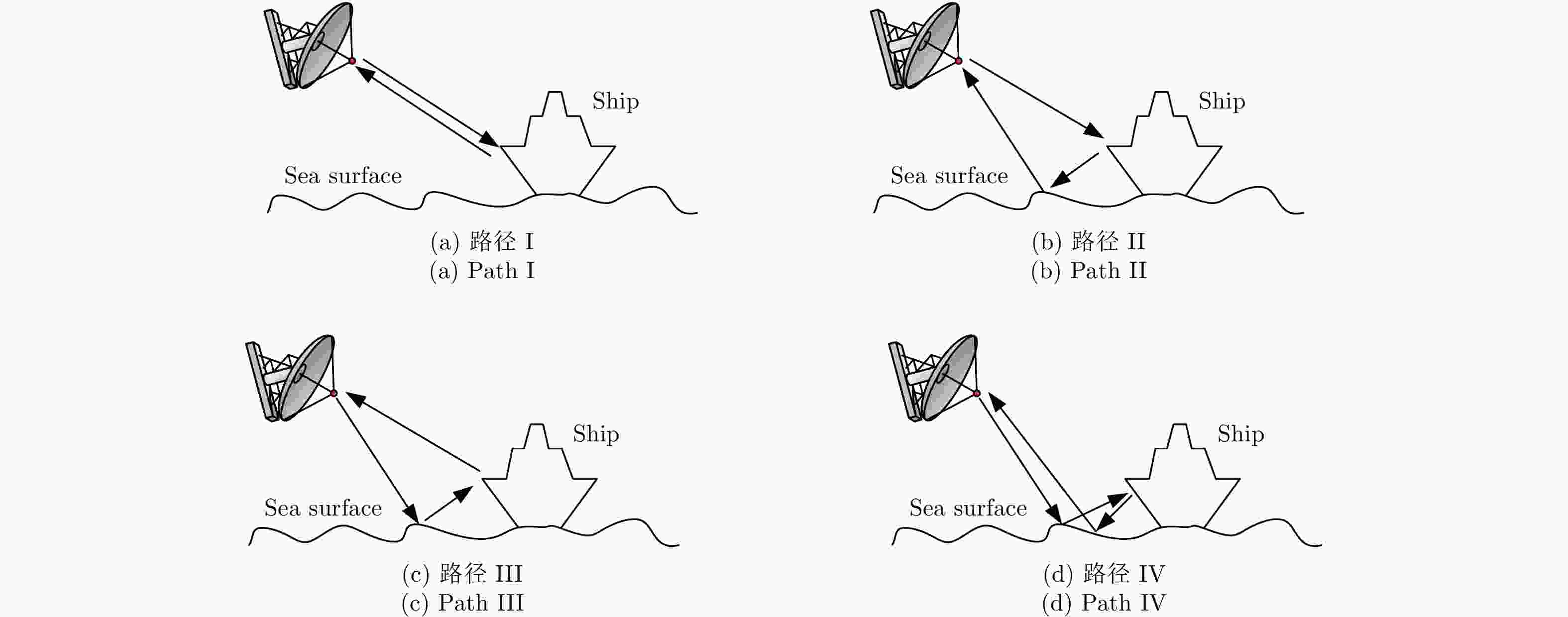
摘要: 海面舰船目标3维散射中心的快速建模对雷达目标信号快速仿真、特征提取与分类识别等应用具有重要意义。该文结合目标-海面耦合散射的“4路径”模型、随机海面散射修正Fresnel反射系数模型,以及基于射线管积分的快速3维成像等模型与方法,提出一种舰船-海面复合的快速3维成像方法,并通过CLEAN算法建立一种3维散射中心快速建模算法。该算法由于实现了单频、单视角条件下的目标3维成像,并且采用简化的海面模型避免了大量海面面元的构建,因而大大提高了3维散射中心建模的计算效率,从而满足实际工程应用的需求。典型海面舰船目标仿真实验结果表明,与传统基于FFT的3维成像算法相比,在典型计算条件下该算法的计算效率可提高4个数量级。不同海情下,3维散射中心重建的与直接仿真计算的1维距离像历程图和2维像的对比结果,也验证了算法的计算精度。Abstract: Fast construction of the 3-D scattering centers of ship targets on the sea surface is important for many radar applications, including the fast signature prediction, feature extraction, and automatic recognition of targets. Combining the " four-path” model for target-surface coupling scattering with modified Fresnel reflection coefficient model in the stochastic sea surface and ray tube integration method, we propose a 3-D image formation method for ship-surface compound targets. Using the CLEAN technique on 3-D image, we develop a fast algorithm for establishing 3-D scattering center model for ship targets on the sea surface. Because this algorithm realizes 3D imaging of targets at a single frequency and single aspect angle, and adopts simplified surface model to avoid the need to construct a large number of surface elements, the computational efficiency of the proposed alogrithm is greatly increased to meet the needs of practical engineering applications. Simulation experiments of a typical ship target show that the proposed algorithm can increase the speed by four orders of magnitude under typical conditions, as compared with the traditional FFT-based 3D imaging method. We validate the accuracy of this algorithm by comparing reconstructed 1-D range profiles and ISAR images obtain by the scattering center model with the ones that are directly simulated.
-
表 1 全方位(0°~360°)合成显示的3维散射中心模型及其重建的1维距离像历程图的重构度评估
Table 1. Display of synthesized 3D scattering center model at various azimuth (0°~360°) and comparison of sinograms calculated by direct simulation and rebuilt by the models
3维散射中心分布 仿真的1维距离像历程图 模型重建的1维距离像历程图 相似度(%) 


89.55 表 2 不同海情下3维散射中心模型及其重建的2维ISAR像重构度评估(方位90°)
Table 2. Display of 3D scattering center models and comparison of ISAR images calculated by direct simulation and rebuilt by the models under different sea conditions at azimuth 90°
海情等级 3维散射中心分布 仿真的2维像 模型重建的2维像 相似度(%) 0级 


89.66 1级 


82.89 2级 


81.75 3级 


81.76 表 3 不同入射方位下3维散射中心模型及其重建的2维ISAR像重构度评估(1级海情)
Table 3. Display of 3D scattering center models and comparison of ISAR images calculated by direct simulation and rebuilt by the models at different azimuth under level-1 sea condition
方位角(°) 3维散射中心分布 仿真的2维像 模型重建的2维像 相似度(%) 30 


79.11 60 


79.89 120 


86.25 150 


86.23 表 4 3维散射中心计算效率对比(以用于计算3维散射中心的3维成像分辨率取0.1 m×0.1 m×0.1 m为例)
Table 4. Comparison of computation time by traditional algorithm and proposed algorithm (take the resolution 0.1 m×0.1 m×0.1 m in 3D images as example)
方法 模块 计算条件 计算时间(min) 总计 效率提高比 传统算法 SBR:计算扫频扫角RCS幅相数据 采样点个数:频率600,方位600,俯仰600 360000 360008 72000倍 3D-FFT:计算3维像 点数:2048 5 CLEAN:提取3维散射中心 动态范围:50 dB 3 本文算法 3D-RIM:直接计算3维像 采样点个数:频率1,方位1,俯仰1 2 5 CLEAN:提取3维散射中心 动态范围:50 dB 3 注: RIM表示射线积分方法(Ray-tube Integration Method) -
[1] 黄培康, 殷红成, 许小剑. 雷达目标特性[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 230–237.HUANG Pei-kang, YIN Hong-cheng, and XU Xiao-jian. Radar Target Signature[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 230–237. [2] KELLER J B. Geometrical theory of diffraction[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1962, 52(2): 116–130. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.52.000116 [3] BHALLA R and LING H. A fast algorithm for signature prediction and image formation using the shooting and bouncing ray technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(7): 727–731. doi: 10.1109/8.391147 [4] TSENG N. A very efficient RCS data compression and reconstruction technique[D]. [Master dissertation], The Ohio State University, 1992. [5] CHANG L C. Removal of undesired scattering centers using a radar image technique[D]. [Master dissertation], The Ohio State University, 1993. [6] HURST M and MITTRA R. Scattering center analysis via Prony’s method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(8): 986–988. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1144210 [7] GARBER F D, CHAMBERLAIN N F, and SNORRASON O. Time-domain and frequency-domain feature selection for reliable radar target identification[C]. Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1988: 79–84. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1988.10934. [8] DUDGEON D E and LACOSS R T. An overview of automatic target recognition[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1993, 6(1): 3–10. [9] 陈勇, 董纯柱, 王超, 等. 基于HPP/PO的舰船与海面耦合散射快速算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(4): 589–592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.04.001CHEN Yong, DONG Chun-zhu, WANG Chao, et al. Fast algorithm based on HPP/PO for calculating coupling EM scattering from ship over sea surface[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(4): 589–592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.04.001 [10] 朱炜, 郭航. 现代舰船隐身技术的若干方法研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2014, 34(12): 22–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2014.12.006ZHU Wei and GUO Hang. Research on the methods of warship stealthy technology[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2014, 34(12): 22–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2014.12.006 [11] 王峰, 徐丰, 金亚秋. 利用序列ISAR图像获取空间目标3-D信息的方法[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2016, 31(5): 900–906. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2016.5.0900WANG Feng, XU Feng, and JIN Ya-qiu. 3-D information reconstruction of a space target from 2-D ISAR image sequence[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2016, 31(5): 900–906. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2016.5.0900 [12] ZHOU J X, SHI Z G, CHENG X, et al. Automatic target recognition of SAR images based on global scattering center model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3713–3729. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2162526 [13] BHALLA R, LING H, MOORE J, et al. 3D scattering center representation of complex targets using the shooting and bouncing ray technique: A review[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 1998, 40(5): 30–39. doi: 10.1109/74.735963 [14] ZHOU J X, SHI Z G, and FU Q. Three-dimensional scattering center extraction based on wide aperture data at a single eleva-tion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1638–1655. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346509 [15] POTTER L C, CHIANG D M, CARRIERE R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641 [16] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [17] JACKSON J A, RIGLING B D, and MOSES R L. Canonical scattering feature models for 3D and bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transac-tions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 525–541. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461639 [18] 王菁. 光学区雷达目标散射中心提取及其应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2010: 3–77. doi: 10.7666/d.d167227.WANG Jing. A study on radar optical region target scattering center extraction and its applications[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010: 3–77. doi: 10.7666/d.d167227. [19] 李飞, 纠博, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于稀疏表示的SAR图像属性散射中心参数估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 931–937. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00576LI Fei, JIU Bo, LIU Hong-wei, et al. Sparse representation based algorithm for estimation of attributed scattering center parameter on SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 931–937. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00576 [20] LI Z H, JIN K, XU B, et al. An improved attributed scattering model optimized by incremental sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(5): 2973–2987. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2509539 [21] 汪雄良, 冉承其, 王正明. 基于紧致字典的基追踪方法在SAR图像超分辨中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(6): 996–1001. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.06.005WANG Xiong-liang, RAN Cheng-qi, and WANG Zheng-ming. Super-resolution processing of SAR images by basis pursuit method based on compacted dictionary[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(6): 996–1001. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.06.005 [22] TSAO J and STEINBERG B D. Reduction of sidelobe and speckle artifacts in microwave imaging: The CLEAN technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1988, 36(4): 543–556. doi: 10.1109/8.1144 [23] KOETS M A and MOSES R L. Image domain feature extraction from synthetic aperture imagery[C]. Proceedings of 1999 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, USA, 1999: 2319–2322. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1999.758402. [24] KOETS M A and MOSES R L. Feature extraction using attributed scattering center models on SAR imagery[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 104–115. doi: 10.1117/12.357628. [25] BURKHOLDER R J, JANPUGDEE P, and COLAK D. Development of computational tools for predicting the radar scattering from targets on a rough sea surface[R]. Ohio State: Ohio State University ElectroScience Laboratory, 2001. [26] CUI K and XU X J. EM scattering calculation for complex targets over sea surface[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, 2005: 101–104. doi: 10.1109/APS.2005.1552186. [27] DONG C Z, WANG C, WEI X, et al. EM scattering from complex targets above a slightly rough surface[C]. Progress in Elec-tromagnetics Research Symposium 2007, Beijing, China, 2007: 1479–1482. [28] 董纯柱. 典型环境中复杂目标的电磁散射建模与应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国航天二院研究生院, 2007: 31–58, 61–62.DONG Chun-zhu. EM scattering modeling and application research of complex targets in the typical environment[D]. [Master dissertation], The Second Academy of China Aerospace, 2007: 31–58, 61–62. [29] JOHNSON J T. A study of the four-path model for scattering from an object above a half space[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2001, 30(2): 130–134. doi: 10.1002/mop.1242 [30] JOHNSON J T. A numerical study of scattering from an object above a rough surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(10): 1361–1367. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2002.802152 [31] MEISSNER T and WENTZ F J. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(9): 1836–1849. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.831888 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: