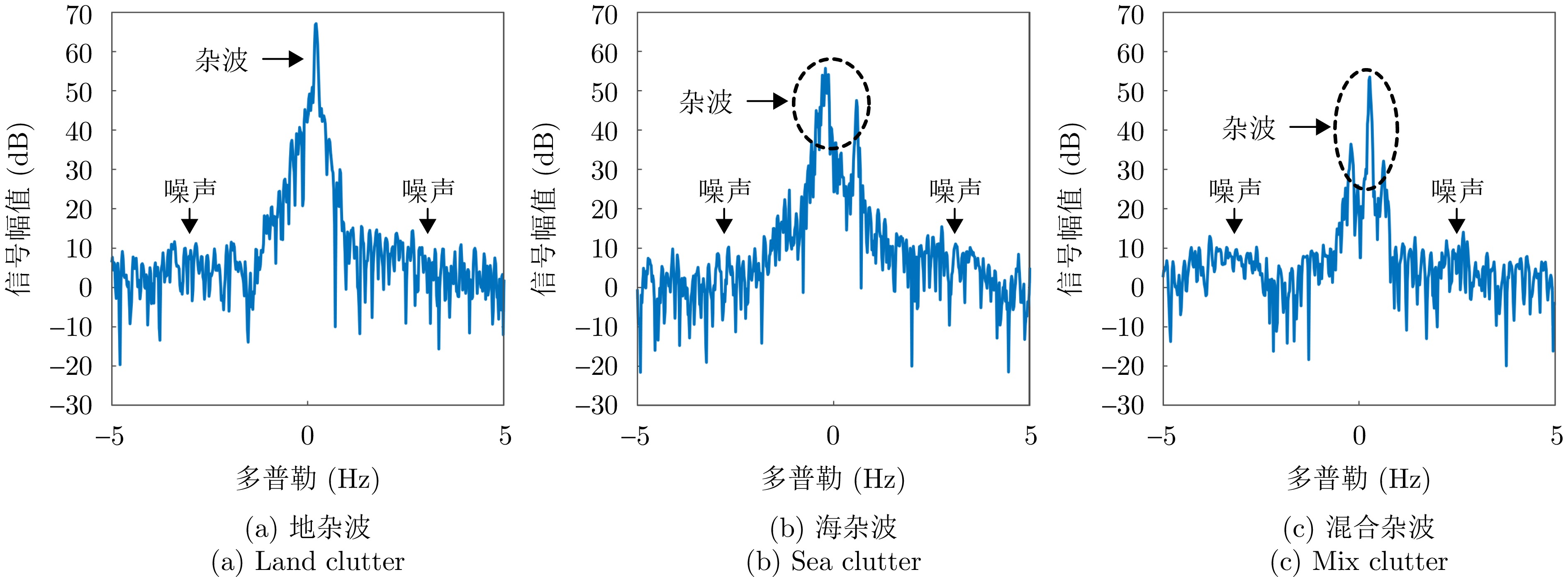
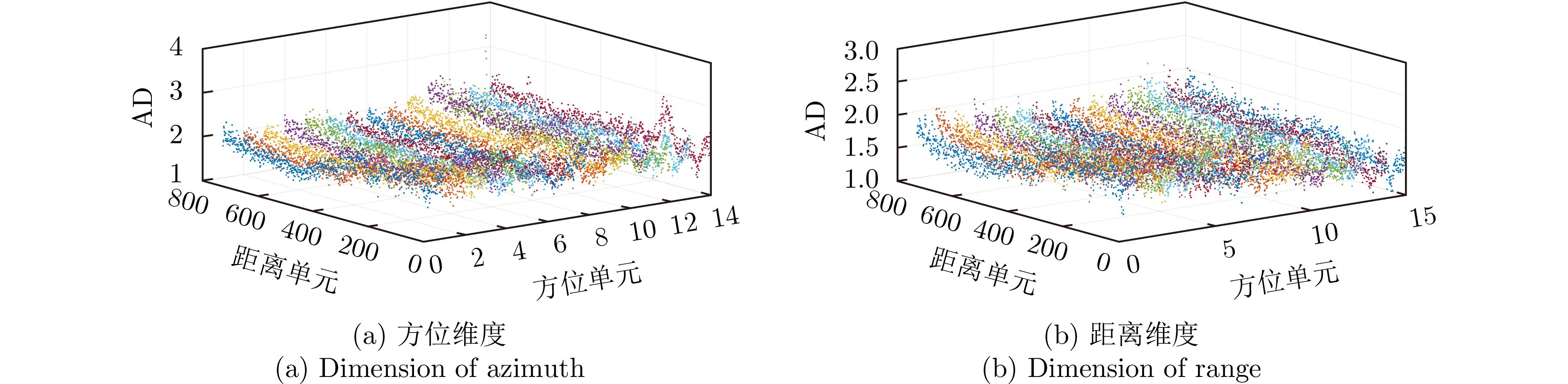
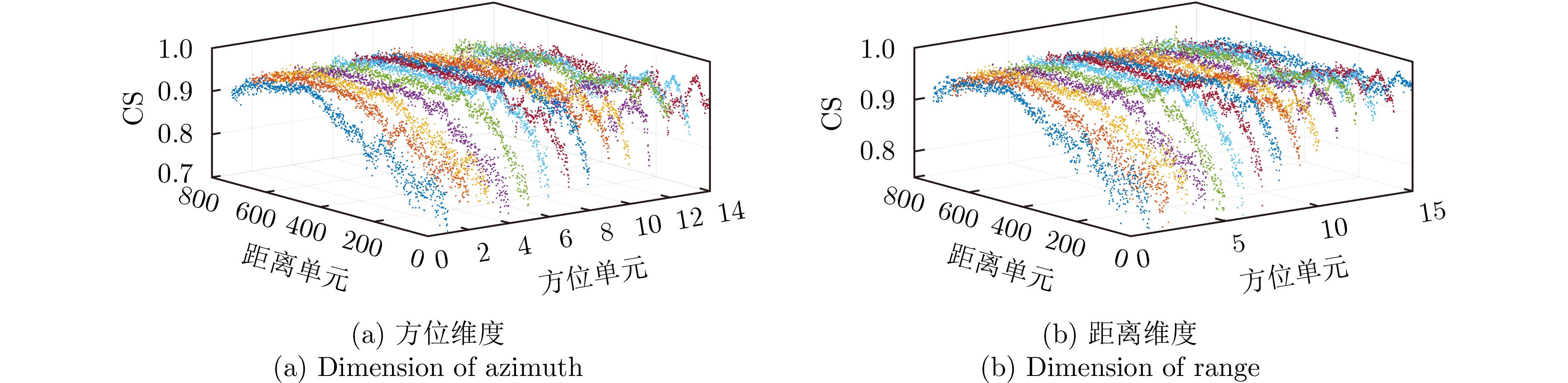
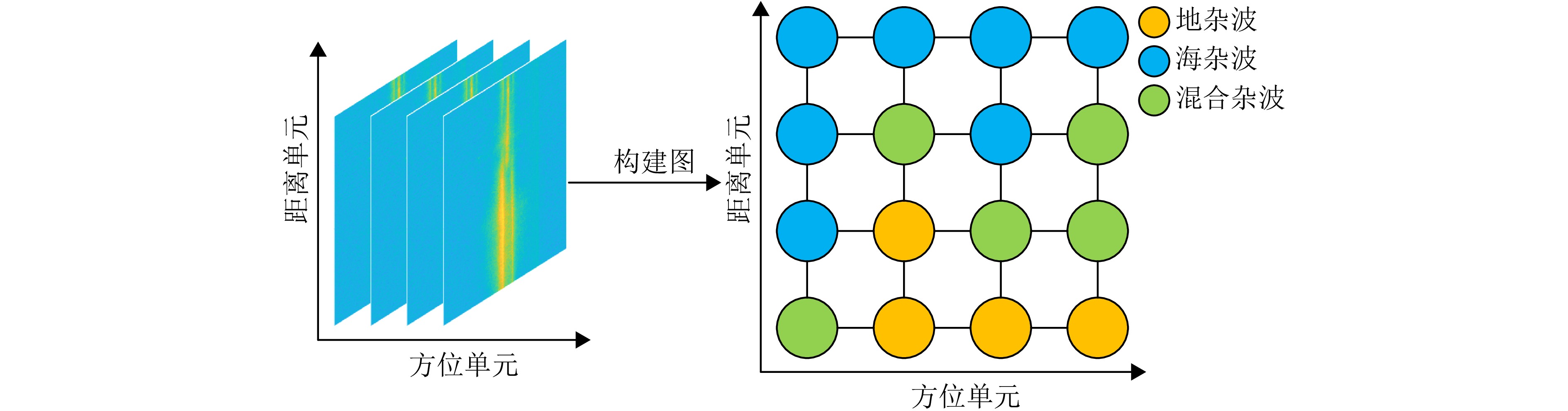
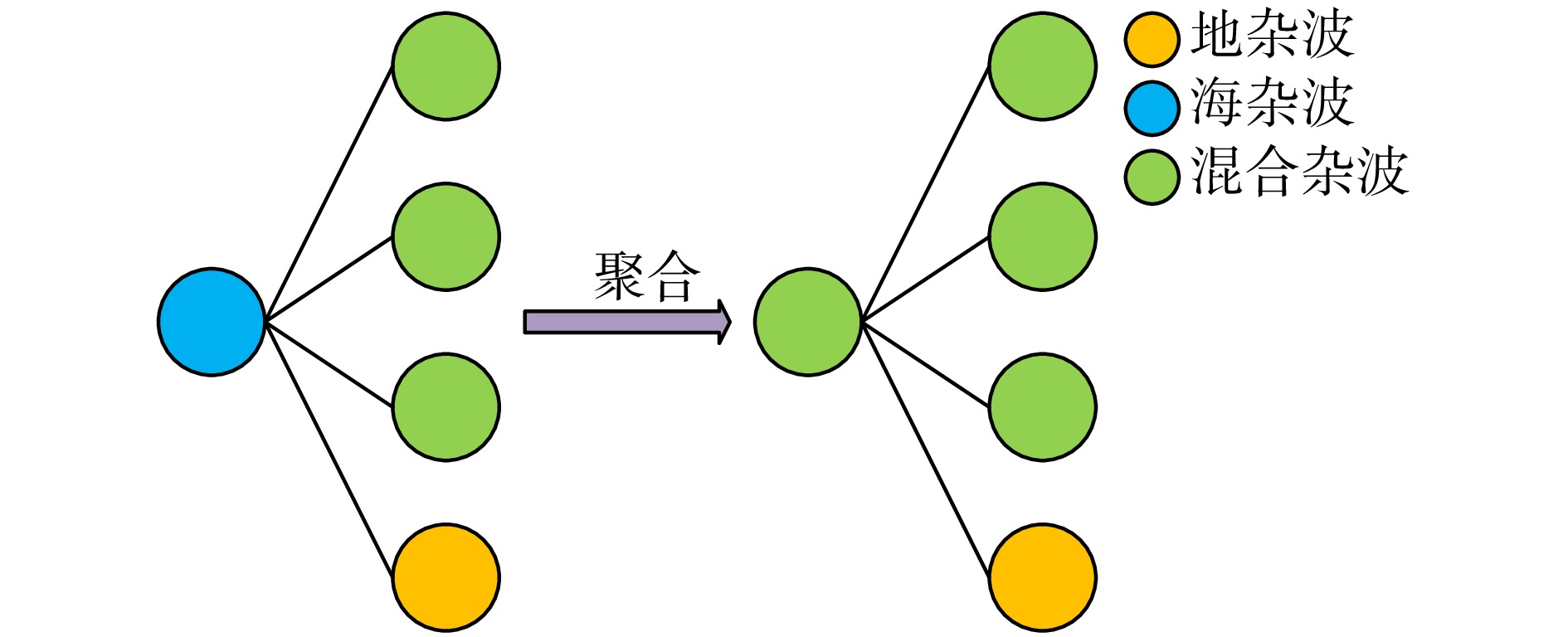
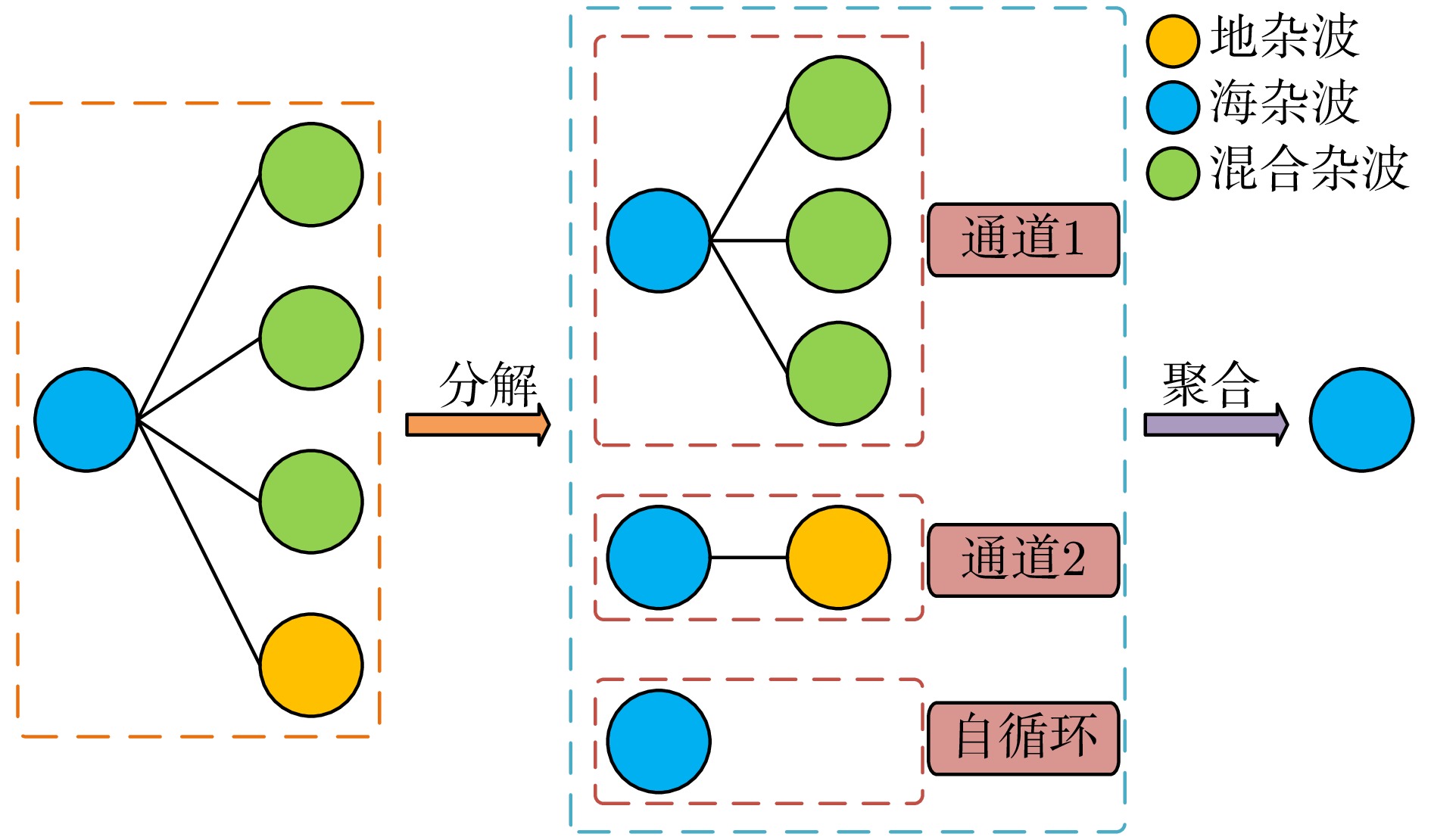
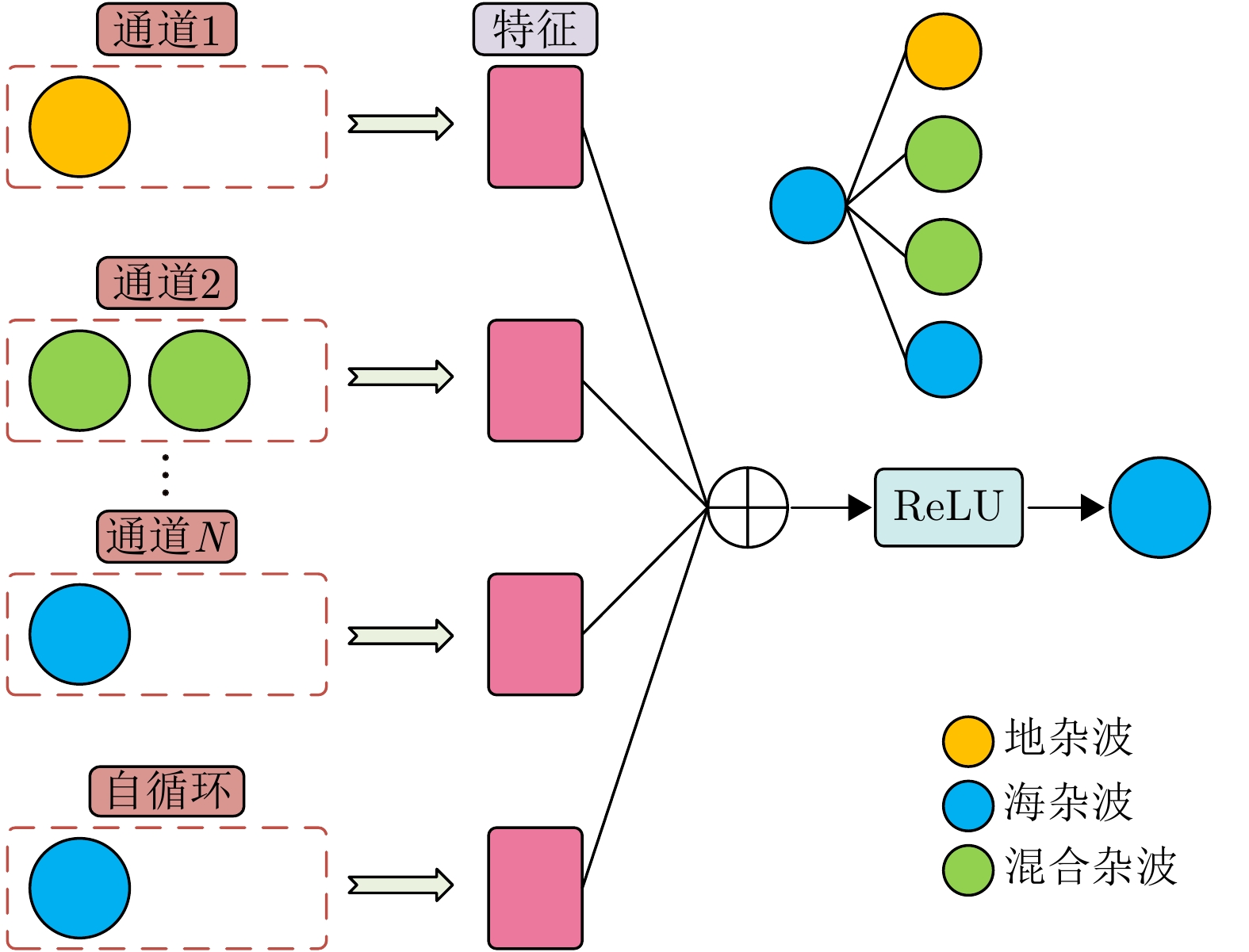
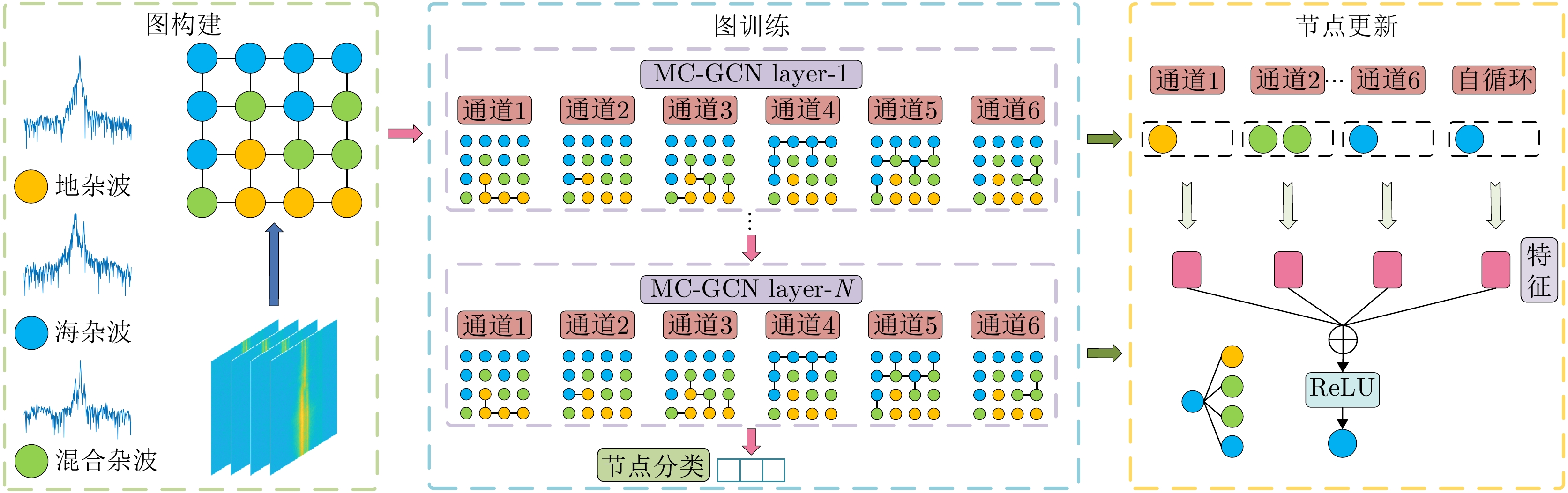
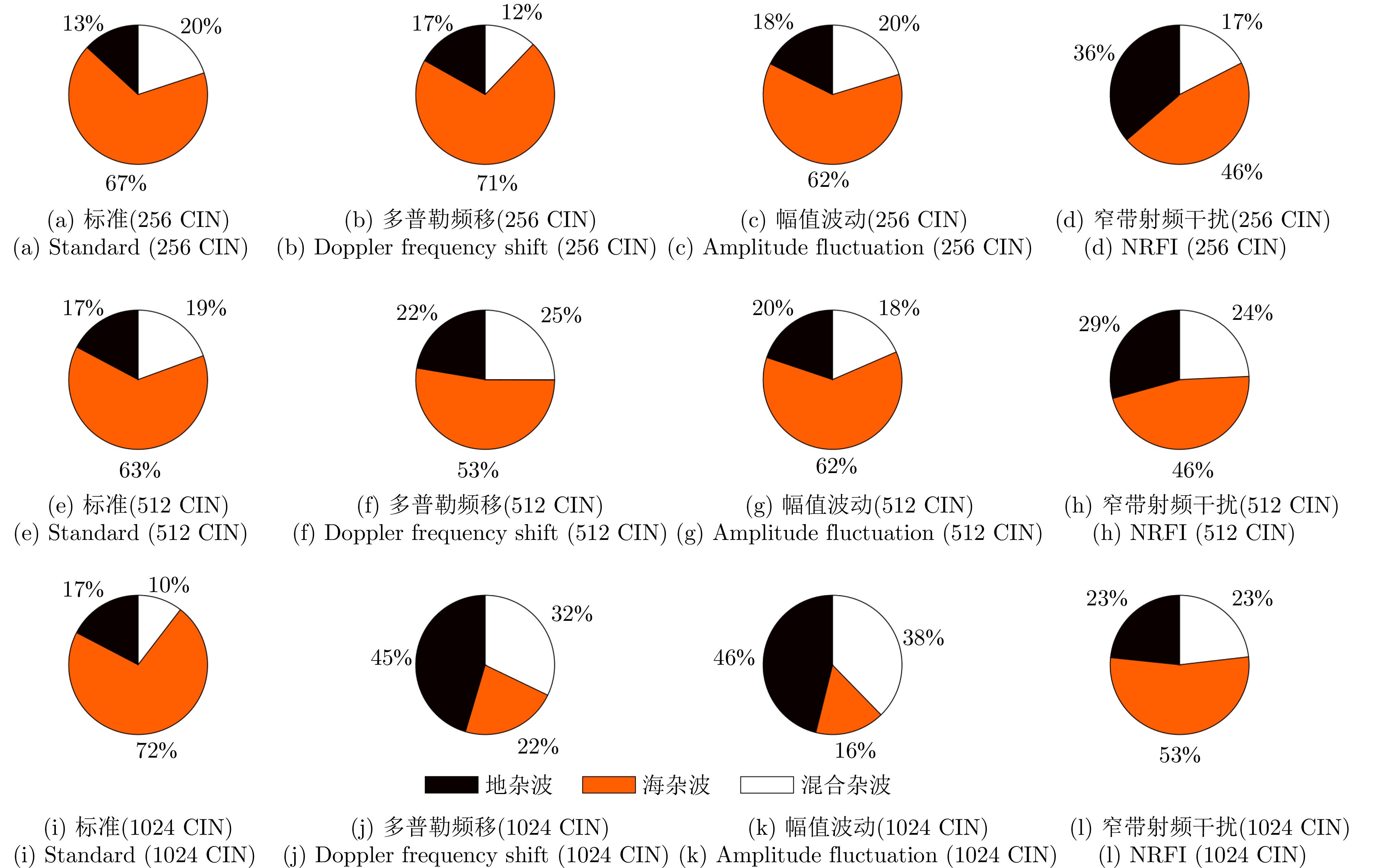
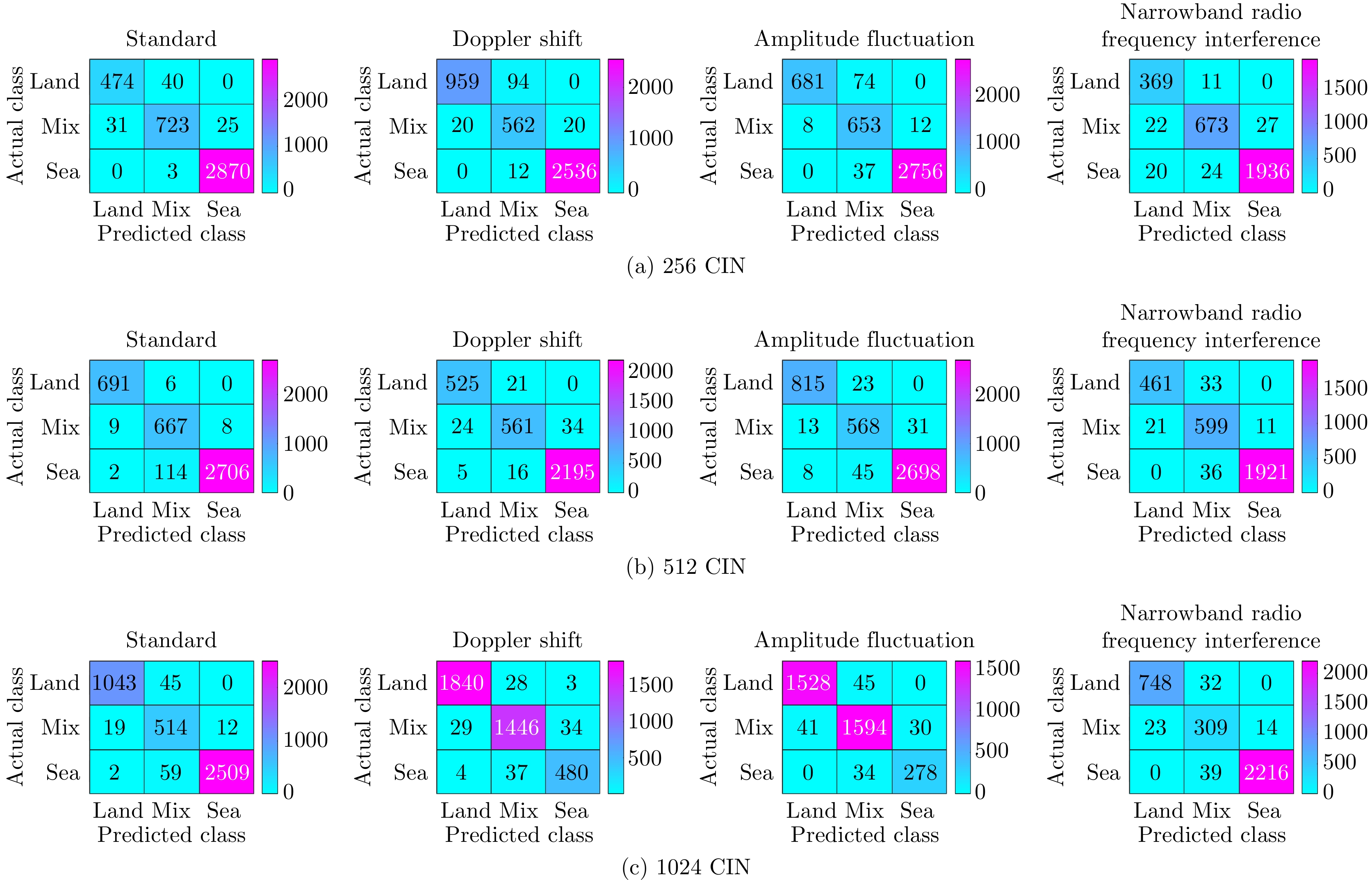
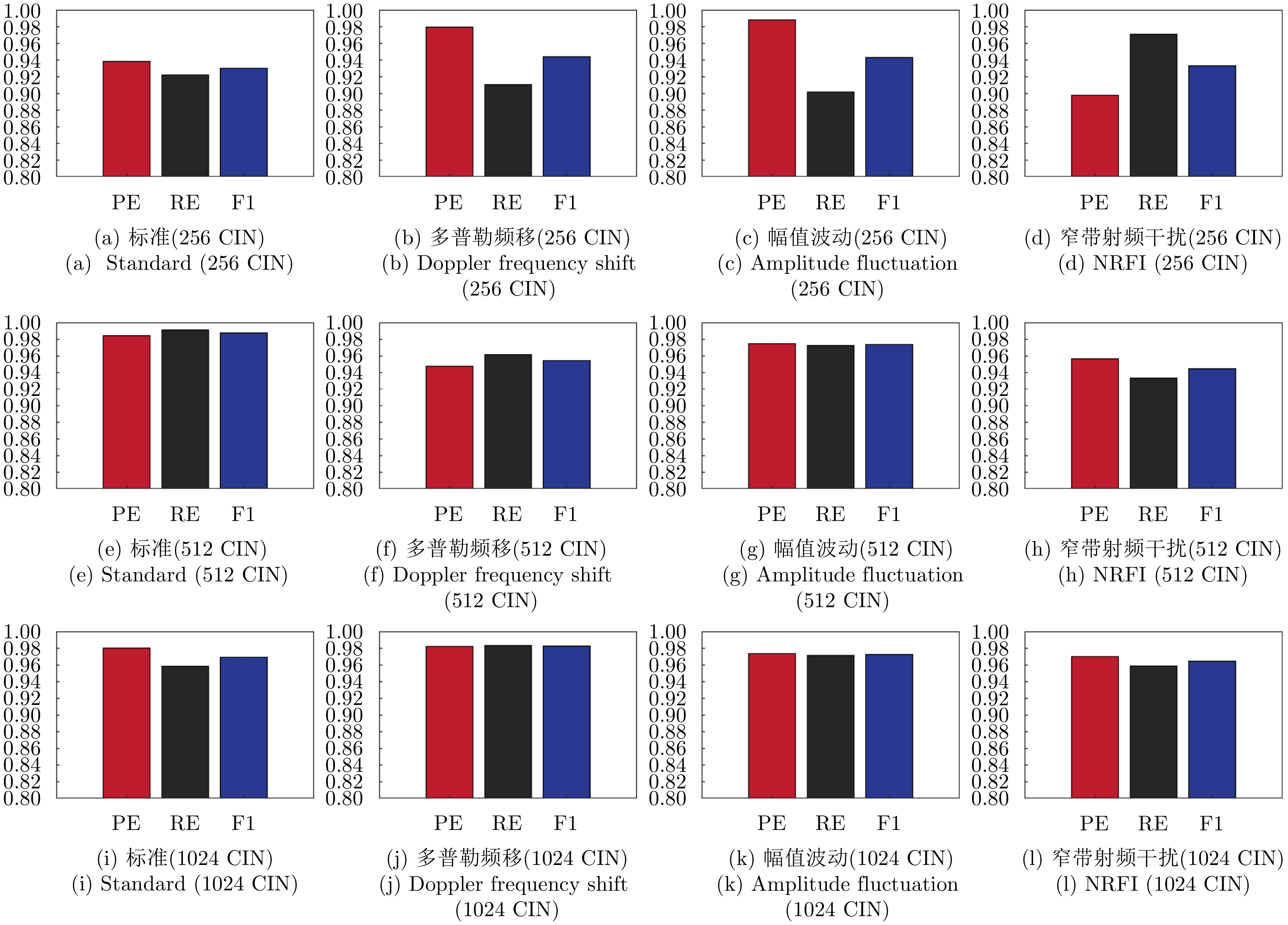
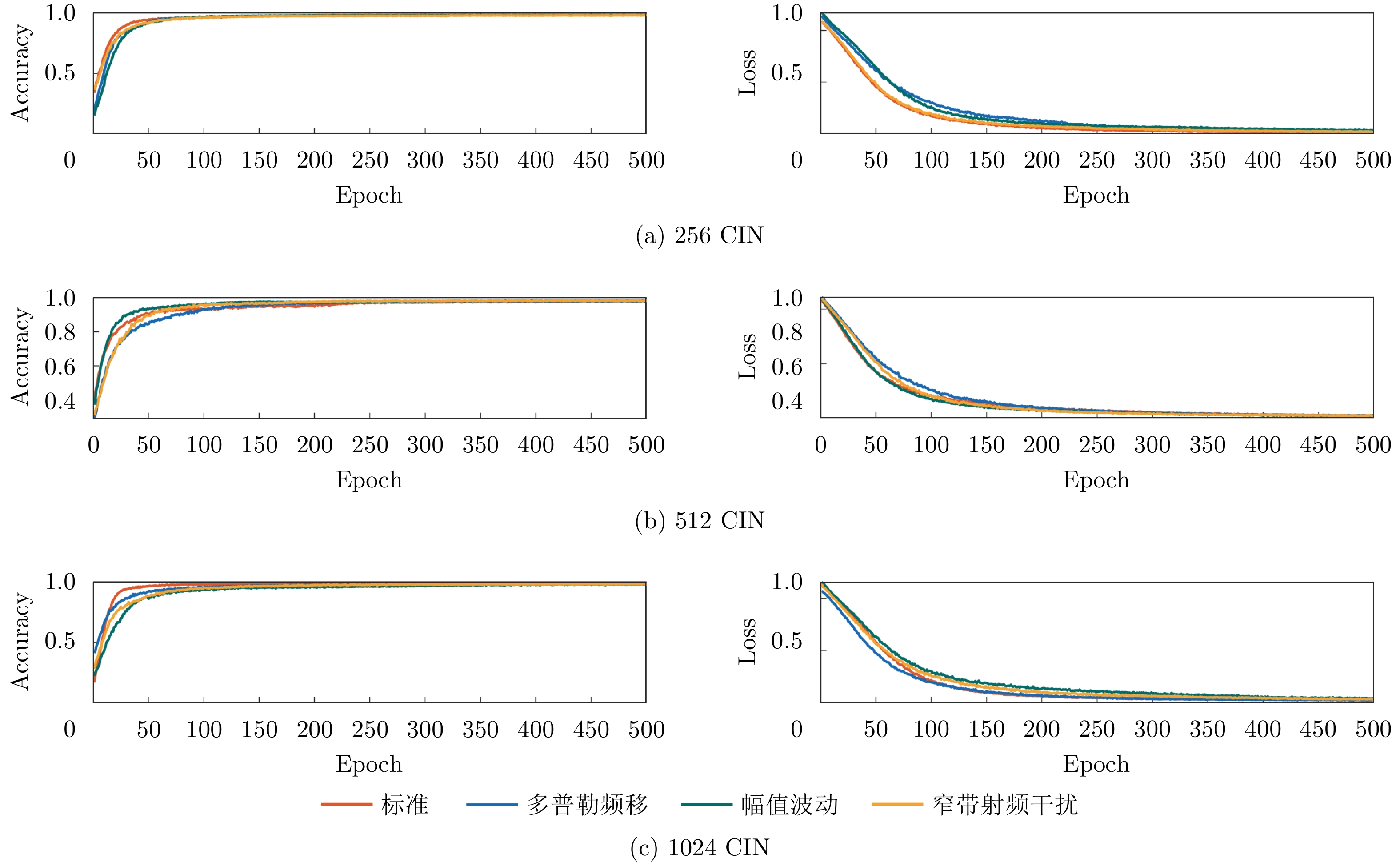
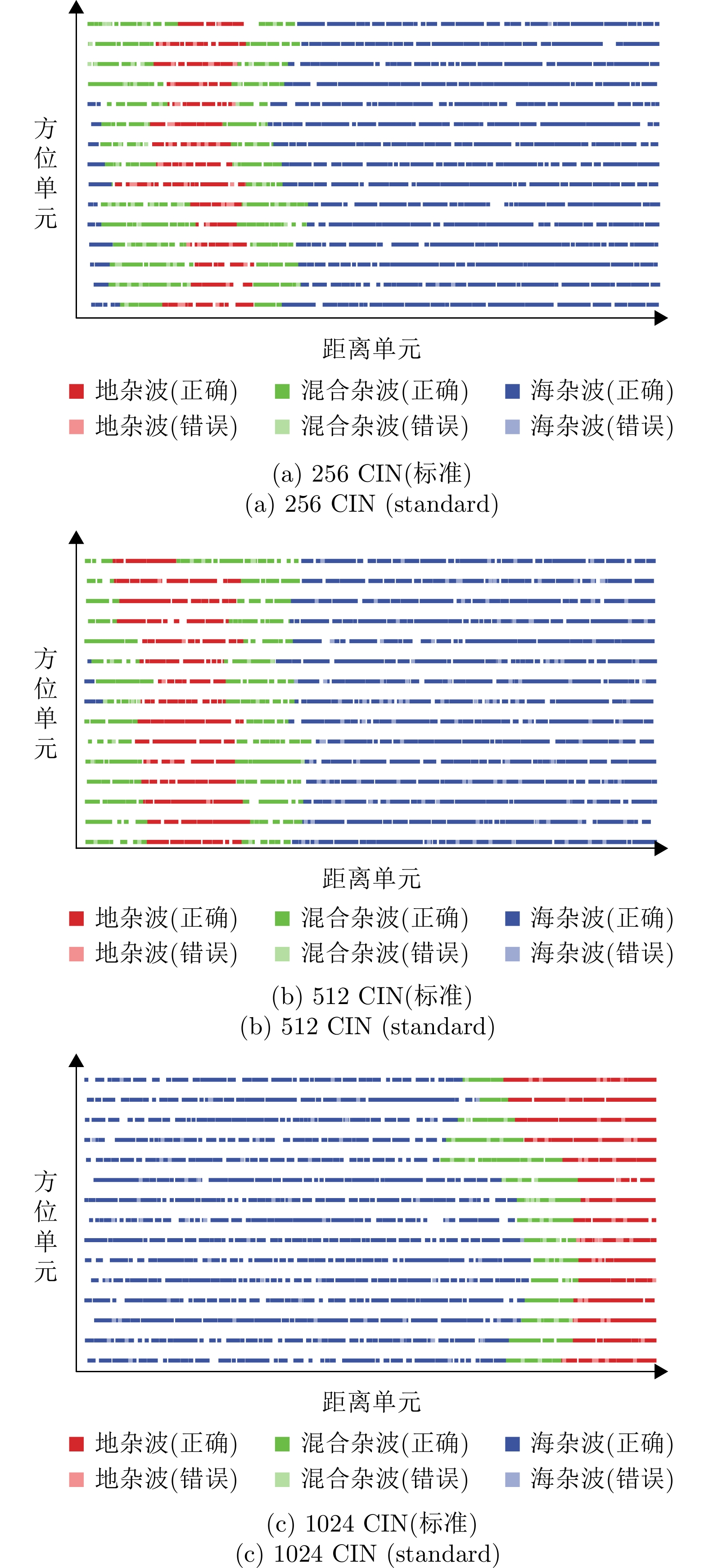
| [1] |
GUO Zhen, WANG Zengfu, LAN Hua, et al. OTHR multitarget tracking with a GMRF model of ionospheric parameters[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 182: 107940. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107940. |
| [2] |
LAN Hua, WANG Zengfu, BAI Xianglong, et al. Measurement-level target tracking fusion for over-the-horizon radar network using message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1600–1623. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3044109. |
| [3] |
GUO Zhen, WANG Zengfu, HAO Yuhang, et al. An improved coordinate registration for over-the-horizon radar using reference sources[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(24): 3086. doi: 10.3390/electronics10243086. |
| [4] |
WHEADON N S, WHITEHOUSE J C, MILSOM J D, et al. Ionospheric modelling and target coordinate registration for HF sky-wave radars[C]. 1994 Sixth International Conference on HF Radio Systems and Techniques, York, UK, 1994: 258–266. doi: 10.1049/cp:19940504. |
| [5] |
BARNUM J R and SIMPSON E E. Over-the-horizon radar target registration improvement by terrain feature localization[J]. Radio Science, 1998, 33(4): 1077–1093. doi: 10.1029/98RS00831. |
| [6] |
TURLEY M D E, GARDINER-GARDEN R S, and HOLDSWORTH D A. High-resolution wide area remote sensing for HF radar track registration[C]. 2013 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2013: 128–133. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6651973. |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040. WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040. |
| [9] |
何密, 平钦文, 戴然. 深度学习融合超宽带雷达图谱的跌倒检测研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169. HE Mi, PING Qinwen, and DAI Ran. Fall detection based on deep learning fusing ultrawideband radar spectrograms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169. |
| [10] |
CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. |
| [11] |
LI Can, WANG Zengfu, ZHANG Zhishan, et al. Sea/land clutter recognition for over-the-horizon radar via deep CNN[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCAIS46528.2019.9074545. |
| [12] |
LI Can, ZHANG Yu, WANG Zengfu, et al. Cross-scale land/sea clutter classification method for over-the-horizon radar based on algebraic multigrid[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(12): 3021–3029. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220389. |
| [13] |
ZHANG Xiaoxuan, WANG Zengfu, LU Kun, et al. Data augmentation and classification of sea-land clutter for over-the-horizon radar using AC-VAEGAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5104416. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3274296. |
| [14] |
ZHANG Xiaoxuan, LI Yang, PAN Quan, et al. Triple loss adversarial domain adaptation network for cross-domain sea-land clutter classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5110718. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3328302. |
| [15] |
ZHANG Xiaoxuan, WANG Zengfu, JI Mingyue, et al. A sea-land clutter classification framework for over-the-horizon radar based on weighted loss semi-supervised generative adversarial network[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 133: 108526. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108526. |
| [16] |
ZHOU Jie, CUI Ganqu, HU Shengding, et al. Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications[J]. AI Open, 2020, 1: 57–81. doi: 10.1016/j.aiopen.2021.01.001. |
| [17] |
WU Zonghan, PAN Shirui, CHEN Fengwen, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(1): 4–24. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2978386. |
| [18] |
WU Lingfei, CHEN Yu, SHEN Kai, et al. Graph neural networks for natural language processing: A survey[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2023, 16(2): 119–328. doi: 10.1561/2200000096. |
| [19] |
YUAN Hao, YU Haiyang, GUI Shurui, et al. Explainability in graph neural networks: A taxonomic survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(5): 5782–5799. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3204236. |
| [20] |
SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Maritime target detection based on radar graph data and graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133473. |
| [21] |
SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Radar maritime target detection via spatial-temporal feature attention graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5102615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358862. |
| [22] |
LANG Ping, FU Xiongjun, DONG Jian, et al. A novel radar signals sorting method via residual graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 753–757. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3287404. |
| [23] |
FENT F, BAUERSCHMIDT P, and LIENKAMP M. RadarGNN: Transformation invariant graph neural network for radar-based perception[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023: 182–191. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00023. |
| [24] |
VELIČKOVIĆ P. Everything is connected: Graph neural networks[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2023, 79: 102538. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102538. |
| [25] |
XIAO Shunxin, WANG Shiping, DAI Yuanfei, et al. Graph neural networks in node classification: Survey and evaluation[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2022, 33(1): 4. doi: 10.1007/s00138-021-01251-0. |
| [26] |
NIVEN E B and DEUTSCH C V. Calculating a robust correlation coefficient and quantifying its uncertainty[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2012, 40: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2011.06.021. |
| [27] |
KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907, 2017.
|
| [28] |
CAI Lei, LI Jundong, WANG Jie, et al. Line graph neural networks for link prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 5103–5113. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3080635. |
| [29] |
XIE Yu, LIANG Yanfeng, GONG Maoguo, et al. Semisupervised graph neural networks for graph classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(10): 6222–6235. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3164696. |
| [30] |
LIAO Wenlong, BAK-JENSEN B, PILLAI J R, et al. A review of graph neural networks and their applications in power systems[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2022, 10(2): 345–360. doi: 10.35833/MPCE.2021.000058. |
| [31] |
MCPHERSON M, SMITH-LOVIN L, and COOK J M. Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks[J]. Annual Review of Sociology, 2001, 27: 415–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.27.1.415. |
| [32] |
VELIČKOVIĆ P, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1710.10903, 2017.
|
| [33] |
DU Jian, ZHANG Shanghang, WU Guanhang, et al. Topology adaptive graph convolutional networks[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1710.10370, 2018.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

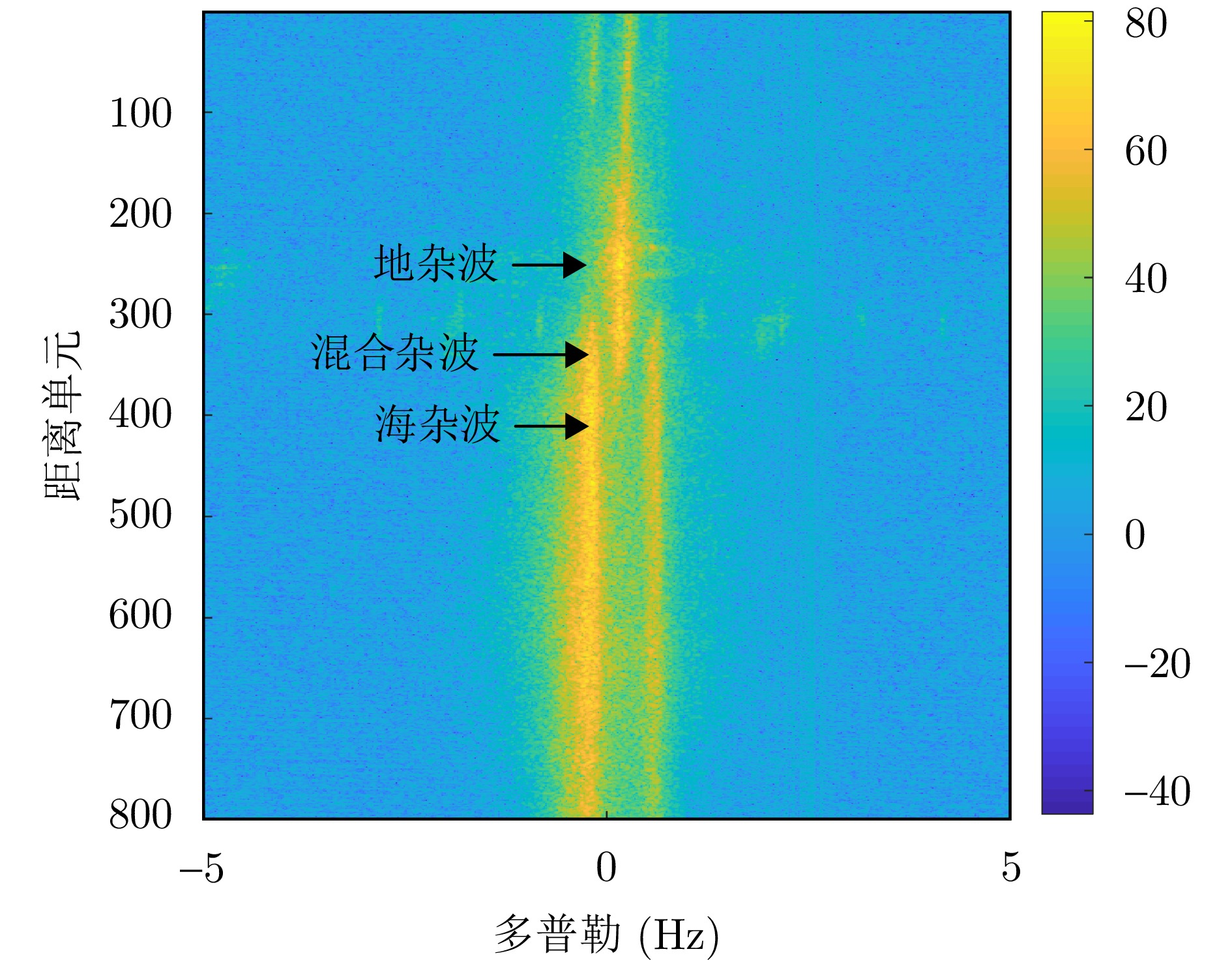



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: