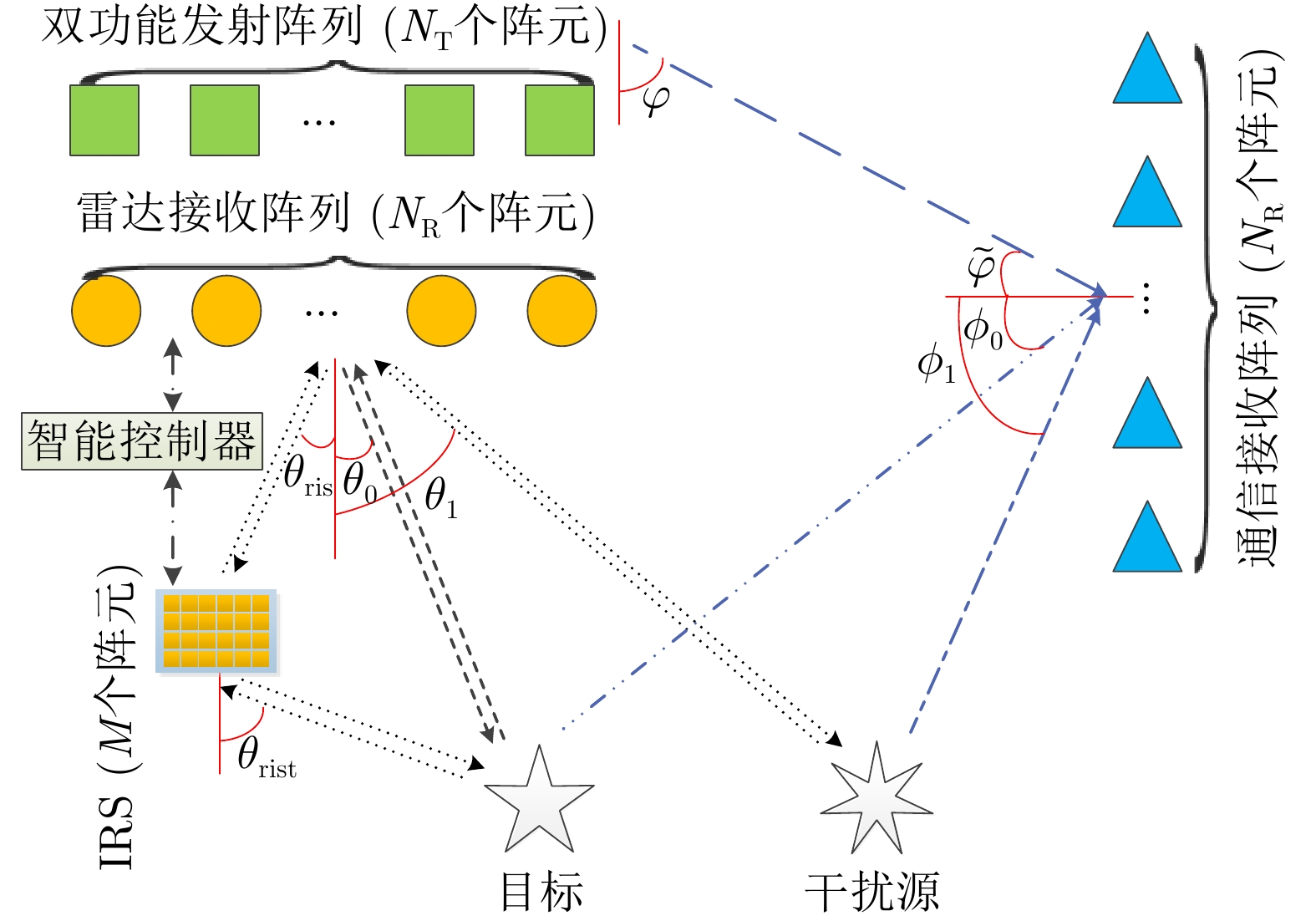
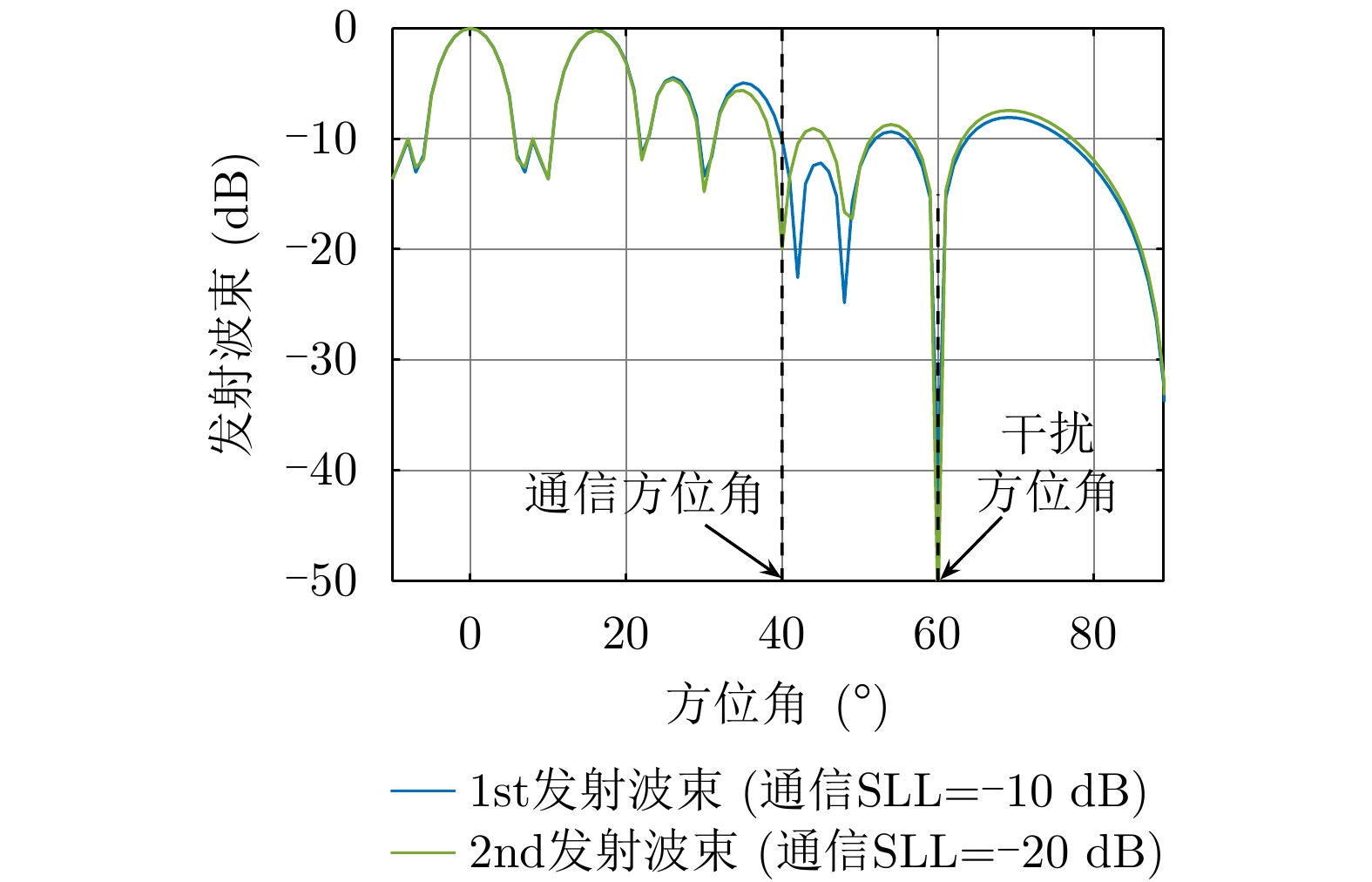
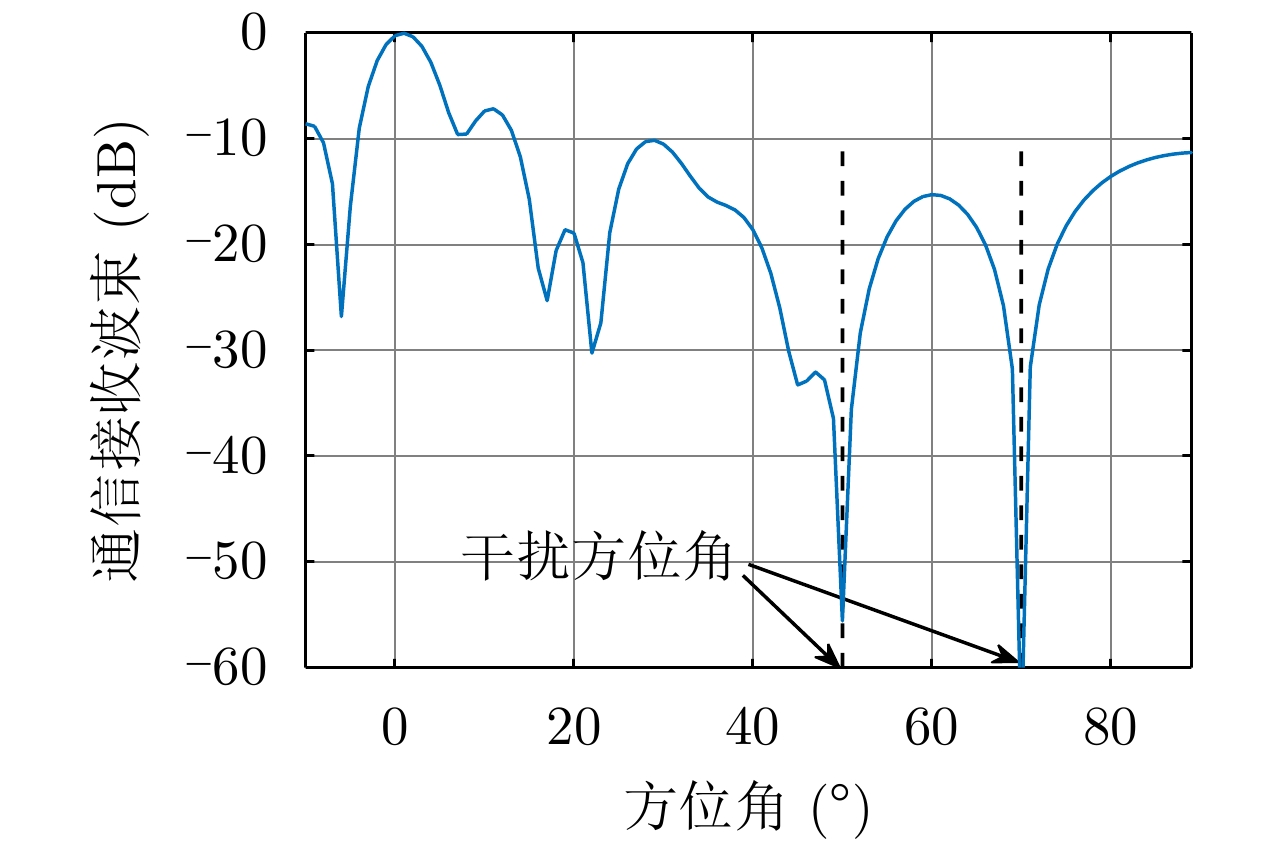
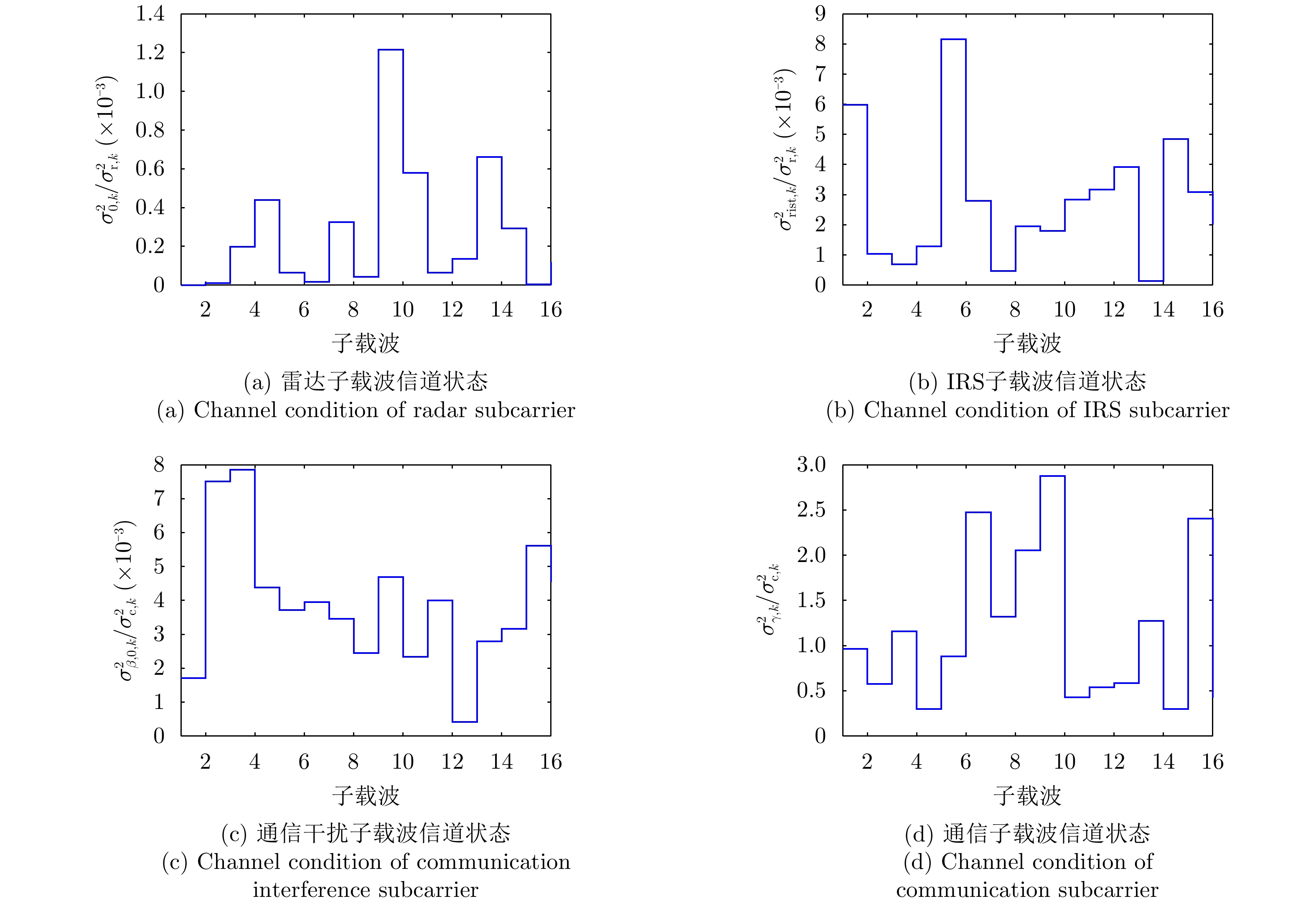
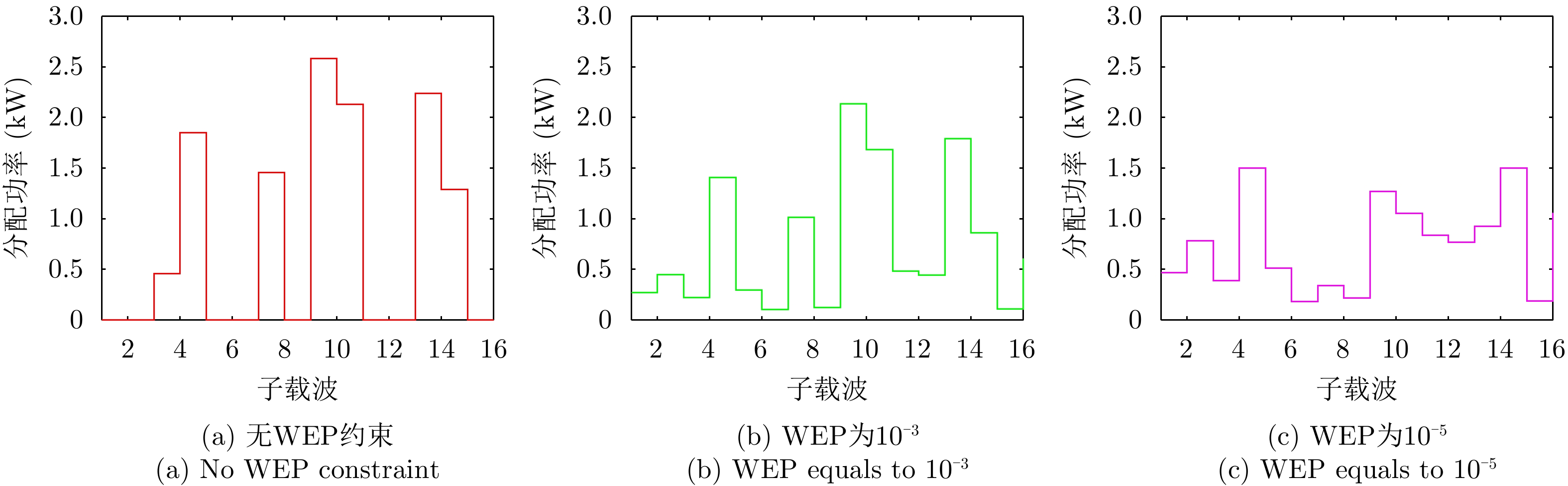
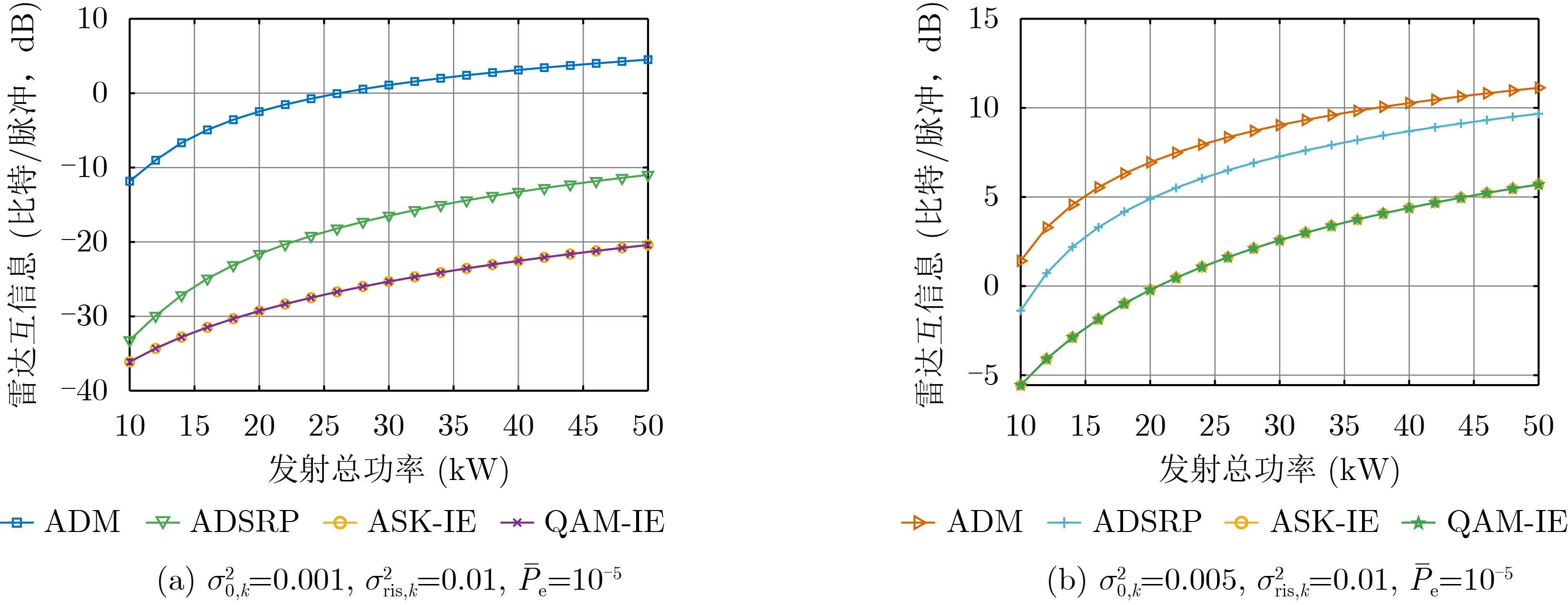
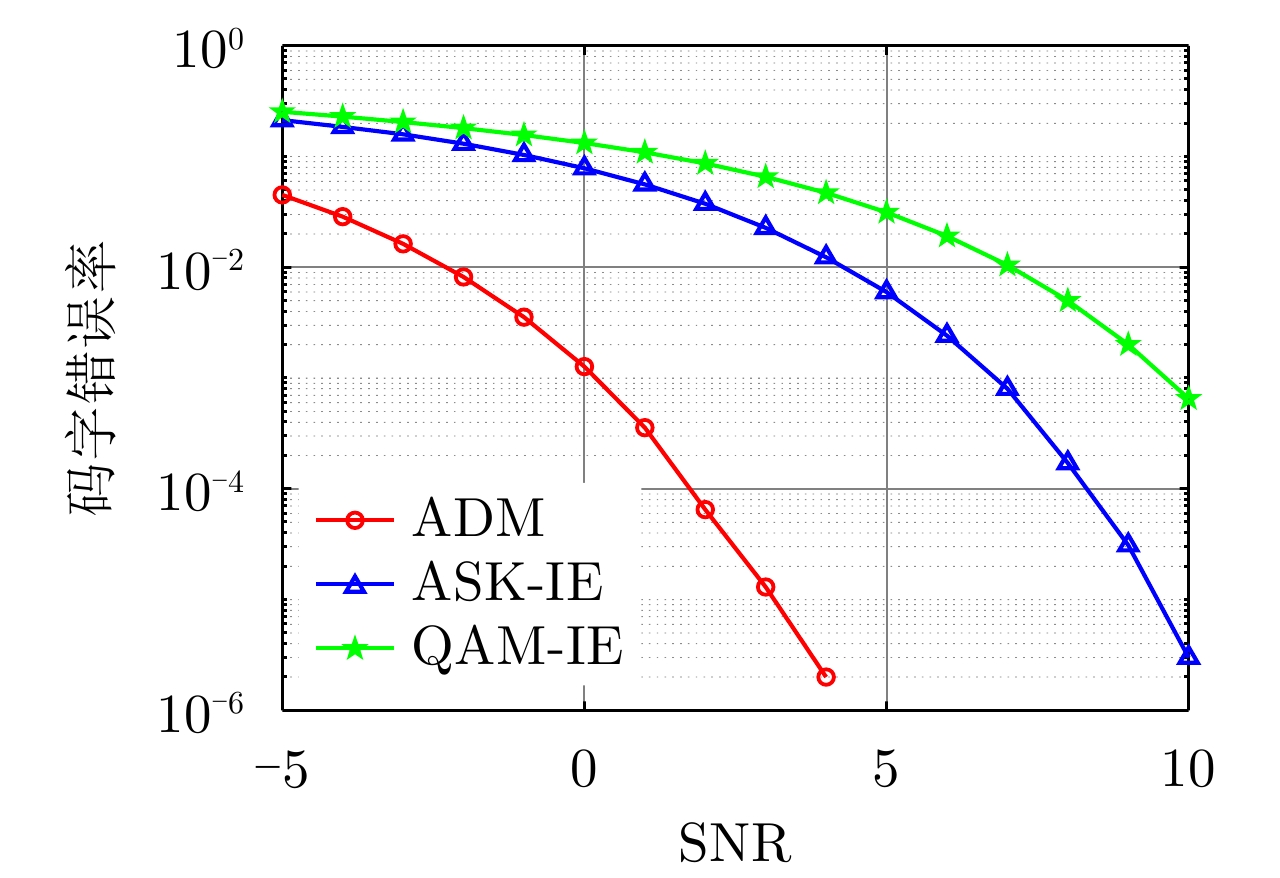
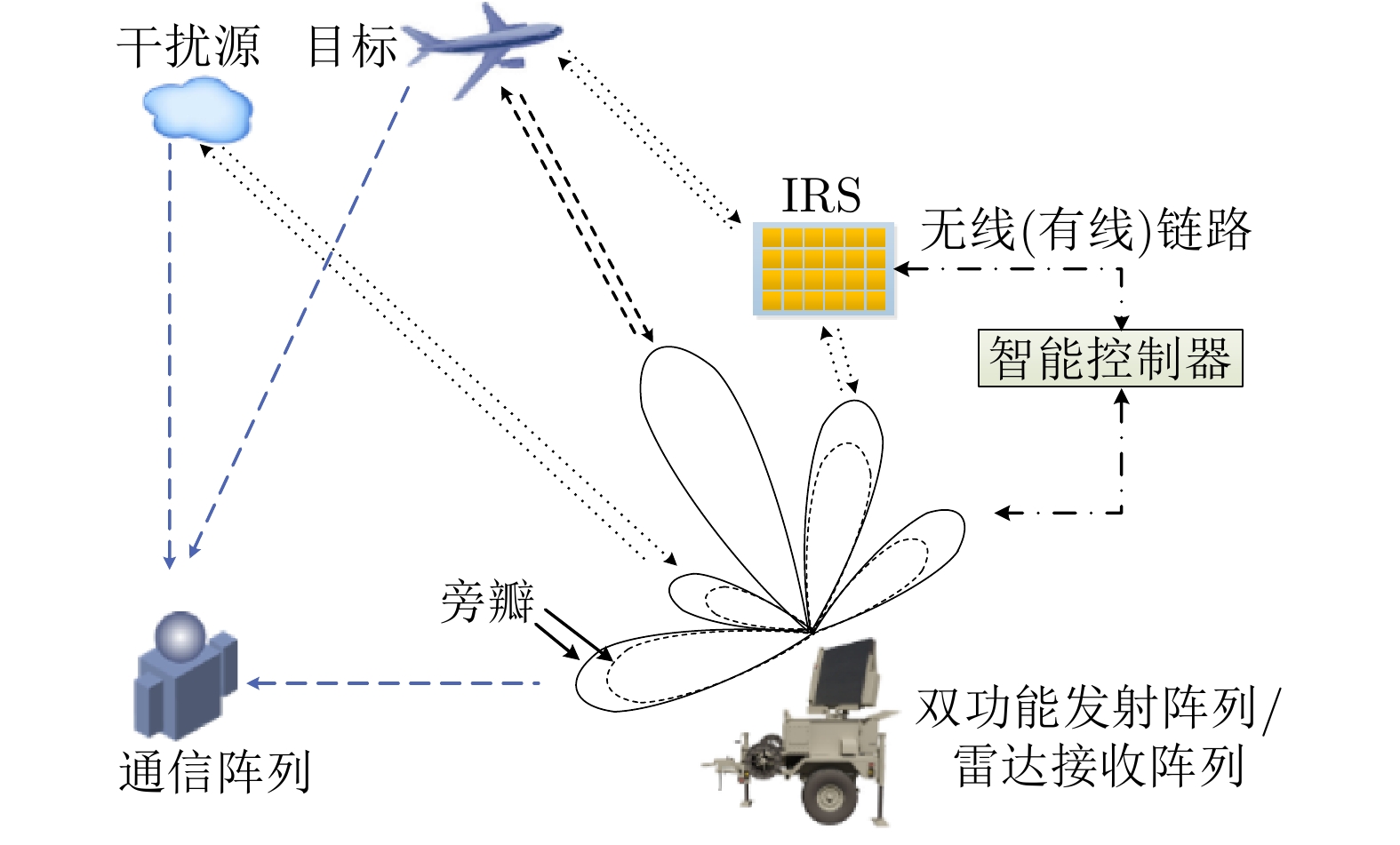
| [1] |
刘凡, 袁伟杰, 原进宏, 等. 雷达通信频谱共享及一体化: 综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113LIU Fan, YUAN Weijie, YUAN Jinhong, et al. Radar-communication spectrum sharing and integration: Overview and prospect[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
TAVIK G C, HILTERBRICK C L, EVINS J B, et al. The advanced multifunction RF concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(3): 1009–1020. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.843485 |
| [4] |
MAZUMDER S, DURAND J P, MEYER S L, et al. High-band digital preprocessor (HBDP) for the AMRFC test-bed[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(3): 1065–1071. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.843511 |
| [5] |
PAUL B, CHIRIYATH A R, and BLISS D W. Survey of RF communications and sensing convergence research[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 252–270. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2639038 |
| [6] |
OZKAPTAN C D, EKICI E, and ALTINTAS O. Adaptive waveform design for communication-enabled automotive radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3125924. |
| [7] |
MA Dingyou, SHLEZINGER N, HUANG Tianyao, et al. Joint radar-communication strategies for autonomous vehicles: Combining two key automotive technologies[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 85–97. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2983832 |
| [8] |
QUAN Siji, QIAN Weiping, GUO Junhai, et al. Radar-communication integration: An overview[C]. The 7th IEEE/International Conference on Advanced Infocomm Technology (ICAIT), Fuzhou, China, 2014: 98–103. doi: 10.1109/ICAIT.2014.7019537. |
| [9] |
刘永军. 基于OFDM的雷达通信一体化设计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.
LIU Yongjun. Study on integrated radar and communications design method based on OFDM[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019.
|
| [10] |
CAGER R, LAFLAME D, and PARODE L. Orbiter Ku-band integrated radar and communications subsystem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1978, 26(11): 1604–1619. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1978.1094004 |
| [11] |
HAN Liang and WU Ke. 24-GHz integrated radio and radar system capable of time-agile wireless communication and sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(3): 619–631. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2179552 |
| [12] |
HAN Liang and WU Ke. Multifunctional transceiver for future intelligent transportation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2011, 59(7): 1879–1892. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2138156 |
| [13] |
MOGHADDASI J and WU Ke. Multifunctional transceiver for future radar sensing and radio communicating data-fusion platform[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 818–838. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2530979 |
| [14] |
MISHRA A K and INGGS M. FOPEN capabilities of commensal radars based on whitespace communication systems[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies, Bangalore, India, 2014: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CONECCT.2014.6740313. |
| [15] |
WINKLER V and DETLEFSEN J. Automotive 24 GHz pulse radar extended by a DQPSK communication channel[C]. The 4th European Radar Conference, Munich, Germany, 2007: 138–141. doi: 10.1109/EURAD.2007.4404956. |
| [16] |
SURENDER S C, NARAYANAN R M, and DAS C R. Performance analysis of communications & radar coexistence in a covert UWB OSA system[C]. 2010 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Miami, USA, 2010: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2010.5683837. |
| [17] |
LI Xiaobai, YANG Ruijuan, and CHENG Wei. Integrated radar and communication based on multicarrier frequency modulation chirp signal[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(2): 406–412. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00567 |
| [18] |
TAKASE H and SHINRIKI M. A dual-use radar and communication system with complete complementary codes[C]. 2014 15th International Radar Symposium, Gdansk, Poland, 2014: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/IRS.2014.6869268. |
| [19] |
LI Xiaobai, YANG Ruijuan, ZHANG Zunquan, et al. Research of constructing method of complete complementary sequence in integrated radar and communication[C]. 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2012: 1729–1732. doi: 10.1109/ICoSP.2012.6491914. |
| [20] |
XU Shaojian, CHEN Yan, and ZHANG Peng. Integrated radar and communication based on DS-UWB[C]. 2006 3rd International Conference on Ultrawideband and Ultrashort Impulse Signals, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2006: 142–144. doi: 10.1109/UWBUS.2006.307182. |
| [21] |
GARMATYUK D, SCHUERGER J, MORTON Y T, et al. Feasibility study of a multi-carrier dual-use imaging radar and communication system[C]. The 37th European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 2007: 1473–1476. doi: 10.1109/EUMC.2007.4405484. |
| [22] |
RUGGIANO M and VAN GENDEREN P. Wideband ambiguity function and optimized coded radar signals[C]. The 4th European Radar Conference, Munich, Germany, 2007: 142–145. doi: 10.1109/EURAD.2007.4404957. |
| [23] |
LIU Shaohua and HUANG Zhixing. Design of integrated radar-communication signal based on spread spectrum[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2014, 12(1): 69–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2014.01.012 |
| [24] |
赵玉振, 陈龙永, 张福博, 等. 一种基于OFDM-chirp的雷达通信一体化波形设计与处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 453–466. doi: 10.12000/JR21028ZHAO Yuzhen, CHEN Longyong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. A new method of joint radar and communication waveform design and signal processing based on OFDM-chirp[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 453–466. doi: 10.12000/JR21028 |
| [25] |
GARMATYUK D, SCHUERGER J, KAUFFMAN K, et al. Wideband OFDM system for radar and communications[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2009.4977024. |
| [26] |
LIU Yongjun, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Multiobjective optimal waveform design for OFDM integrated radar and communication systems[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 331–342. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.06.026 |
| [27] |
SIT Y L, REICHARDT L, STURM C, et al. Extension of the OFDM joint radar-communication system for a multipath, multiuser scenario[C]. 2011 IEEE Radar Conference, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 718–723. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960632. |
| [28] |
LI Ziqi, MEI Jinjie, HU Dengpeng, et al. Peak-to-Average power ratio reduction for integration of radar and communication systems based on OFDM signals with block Golay coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 548–555. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14059 |
| [29] |
NOWAK M, WICKS M, ZHANG Zhiping, et al. Co-designed radar-communication using linear frequency modulation waveform[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(10): 28–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150236 |
| [30] |
GAGLIONE D, CLEMENTE C, ILIOUDIS C V, et al. Waveform design for communicating radar systems using fractional Fourier transform[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 80: 57–69. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.05.002 |
| [31] |
LIU Fan, ZHOU Longfei, MASOUROS C, et al. Toward dual-functional radar-communication systems: Optimal waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(16): 4264–4279. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2847648 |
| [32] |
EDARA I P, HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, et al. Ambiguity function analysis for dual-function radar communications using PSK signaling[C]. 2018 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2018: 900–904. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2018.8645328. |
| [33] |
HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, ZHANG Y D, et al. A dual function radar-communications system using sidelobe control and waveform diversity[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1260–1263. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131188. |
| [34] |
HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, ZHANG Y D, et al. Dual-function radar-communications: Information embedding using sidelobe control and waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(8): 2168–2181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2505667 |
| [35] |
HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, ZHANG Y D, et al. Dual-function radar-communications using phase-rotational invariance[C]. 2015 23rd European Signal Processing Conference, Nice, France, 2015: 1346–1350. doi: 10.1109/EUSIPCO.2015.7362603. |
| [36] |
AHMED A, ZHANG Y D, and GU Yujie. Dual-function radar-communications using QAM-based sidelobe modulation[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 82: 166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.06.018 |
| [37] |
TIAN Tuanwei, LI Guchong, and ZHOU Tao. Power distribution for an OFDM-based dual-function Radar-Communication sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(11): 5501504. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3033044 |
| [38] |
TIAN Tuanwei, ZHANG Tianxian, KONG Lingjiang, et al. Transmit/receive beamforming for MIMO-OFDM based dual-function radar and communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(5): 4693–4708. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3072094 |
| [39] |
WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 |
| [40] |
DI RENZO M, ZAPPONE A, DEBBAH M, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: How it works, state of research, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2450–2525. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007211 |
| [41] |
HU Jingzhi, ZHANG Hongliang, DI Boya, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface based rf sensing: Design, optimization, and implementation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2700–2716. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007041 |
| [42] |
HUANG Kewen and WANG Huiming. Passive beamforming for IRS aided wireless networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(12): 2035–2039. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3011596 |
| [43] |
DE JESUS TORRES A, SANGUINETTI L, and BJÖRNSON E. Electromagnetic interference in RIS-aided communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, in press, 2021. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3124584. |
| [44] |
WANG Jun, LIANG Yingchang, HAN Shiying, et al. Robust beamforming and phase shift design for IRS-enhanced multi-user MISO downlink communication[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9148947. |
| [45] |
ZHAO Jie, YANG Xi, DAI Junyan, et al. Programmable time-domain digital-coding metasurface for non-linear harmonic manipulation and new wireless communication systems[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(2): 231–238. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy135 |
| [46] |
DAI Junyan, TANG Wankai, ZHAO Jie, et al. Wireless communications through a simplified architecture based on time-domain digital coding metasurface[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(7): 1900044. doi: 10.1002/admt.201900044 |
| [47] |
TANG Wankai, DAI Junyan, CHEN Mingzheng, et al. MIMO transmission through reconfigurable intelligent surface: System design, analysis, and implementation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2683–2699. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007055 |
| [48] |
TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887 |
| [49] |
WANG Fangzhou, LI Hongbin, and FANG Jun. Joint active and passive beamforming for IRS-assisted radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021.
|
| [50] |
LU Wei, LIN Qiang, SONG Ningzhe, et al. Target detection in intelligent reflecting surface aided distributed MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2021, 5(3): 7000804. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2021.3061534 |
| [51] |
AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, and ROSAMILIA M. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for N-LOS radar surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 10735–10749. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3102315 |
| [52] |
施宏宇, 李国强, 刘康, 等. 基于反射型超表面的太赫兹偏折涡旋波束生成[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(5): 785–793. doi: 10.12000/JR21070SHI Hongyu, LI Guoqiang, LIU Kang, et al. Deflective vortex beams generation based on metasurfaces in the terahertz band[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(5): 785–793. doi: 10.12000/JR21070 |
| [53] |
BUZZI S, GROSSI E, LOPS M, et al. Foundations of MIMO radar detection aided by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.09250, 2021. |
| [54] |
WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, GUO Jing, et al. RIS-assisted spectrum sharing between MIMO radar and MU-MISO communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 594–598. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3039369 |
| [55] |
WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, ZHENG Zhong, et al. Joint Waveform design and passive beamforming for RIS-assisted dual-functional radar-communication system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(5): 5131–5136. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3075497 |
| [56] |
BELL M R. Information theory and radar waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(5): 1578–1597. doi: 10.1109/18.259642 |
| [57] |
AN Lin, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Multicontextual mutual information data for SAR image change detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1863–1867. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2432071 |
| [58] |
ZHANG Haowei, ZONG Binfeng, and XIE Junwei. Power and bandwidth allocation for multi-target tracking in collocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9795–9806. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3002899 |
| [59] |
WANG Lulu. Adaptive waveform design based on information theory[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015. doi: 10.7666/d.D01107893. |
| [60] |
ZHANG Yu. Study on the waveform design algorithm for cognitive radar based on maximum mutual information rule[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2012. doi: 10.7666/d.d216380. |
| [61] |
TANG Bo and LI Jian. Spectrally constrained MIMO radar waveform design based on mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(3): 821–834. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2887186 |
| [62] |
崔国龙, 余显祥, 杨婧, 等. 认知雷达波形优化设计方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. An overview of waveform optimization methods for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072 |
| [63] |
TIAN Tuanwei, ZHANG Tianxian, LI Guchong, et al. Mutual information-based power allocation and co-design for multicarrier radar and communication systems in coexistence[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 159300–159312. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950890 |
| [64] |
TIAN Tuanwei, ZHANG Tianxian, KONG Lingjiang, et al. Mutual information based partial band coexistence for joint radar and communication system[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835671. |
| [65] |
TKACENKO A and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Iterative greedy algorithm for solving the FIR paraunitary approximation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(1): 146–160. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.861054 |
| [66] |
OMIDVAR M N, YANG Ming, MEI Yi, et al. DG2: A faster and more accurate differential grouping for large-scale black-box optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(6): 929–942. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2694221 |
| [67] |
SUN Ying, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 794–816. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2601299 |
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 |
| [70] |
DU Xiaolin, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Hidden convexity in robust waveform and receive filter bank optimization under range unambiguous clutter[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 885–889. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2992323 |
| [71] |
CHEN Chunyang and VAIDYANATHAN P. MIMO radar waveform optimization with prior information of the extended target and clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(9): 3533–3544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2021632 |
| [72] |
LIU Jun, LI Hongbin, and HIMED B. Joint optimization of transmit and receive beamforming in active arrays[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 39–42. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2289325 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: