- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | |
Distributed Multi-target Localization System Based on Optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing Network
DOI: 10.12000/JR19028 CSTR: 32380.14.JR19028
More Information-
Abstract
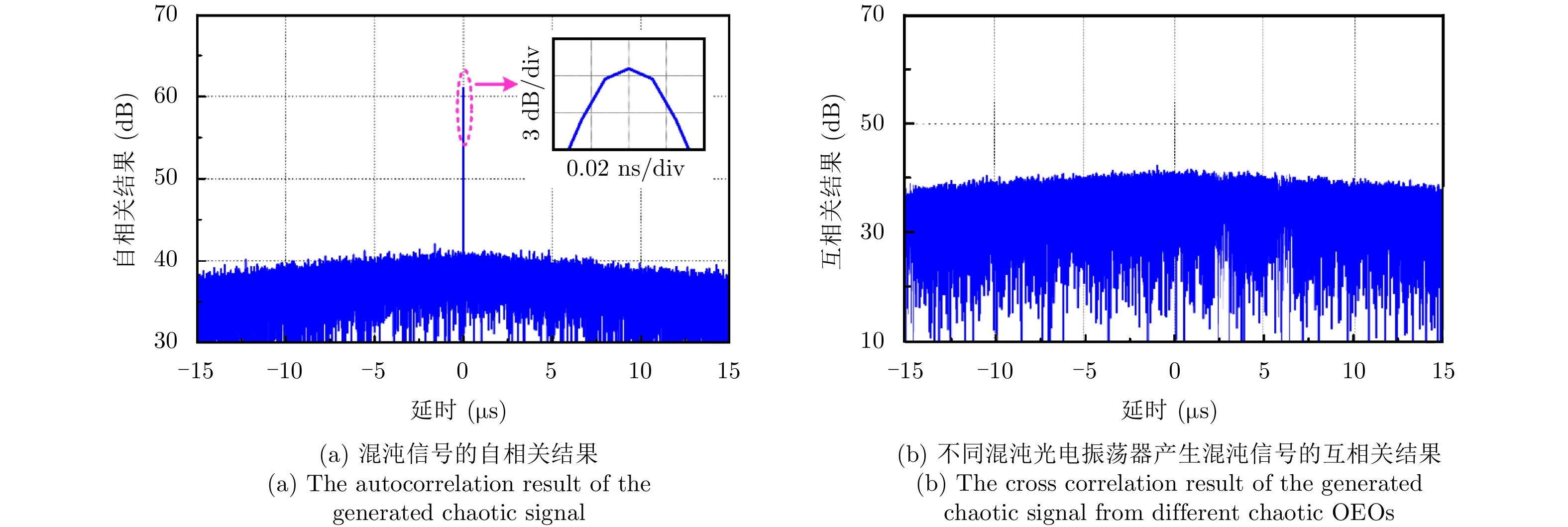
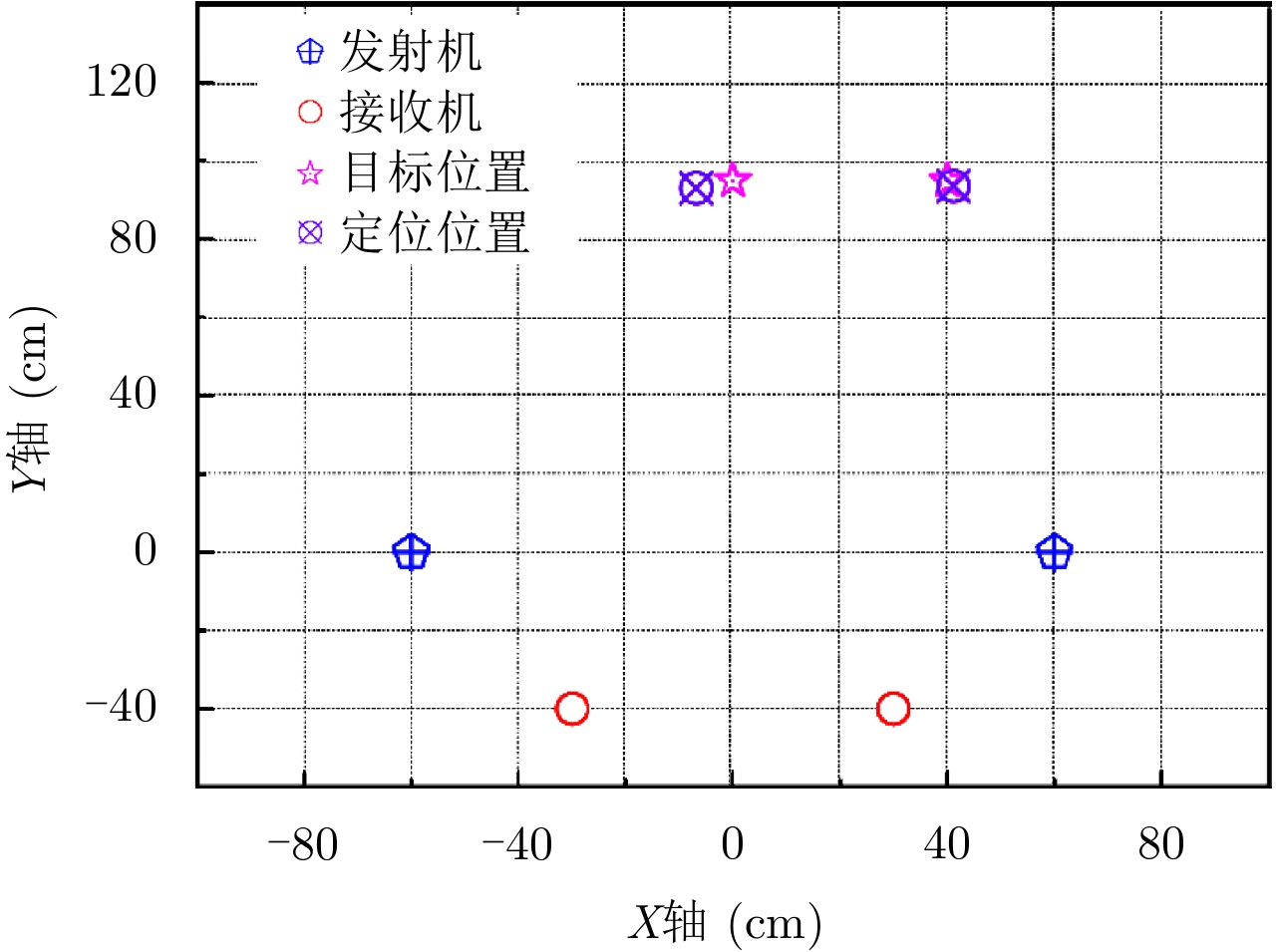
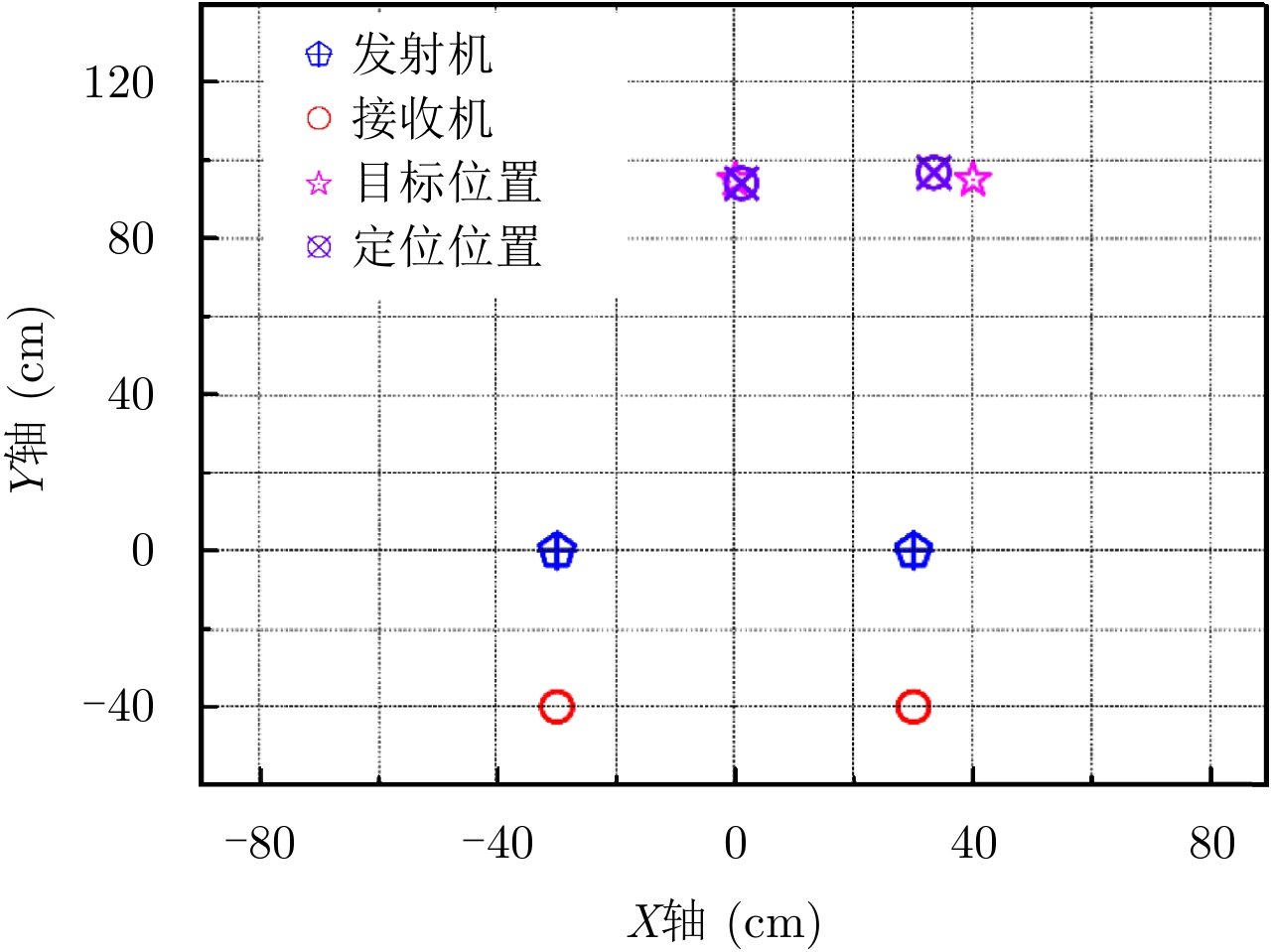
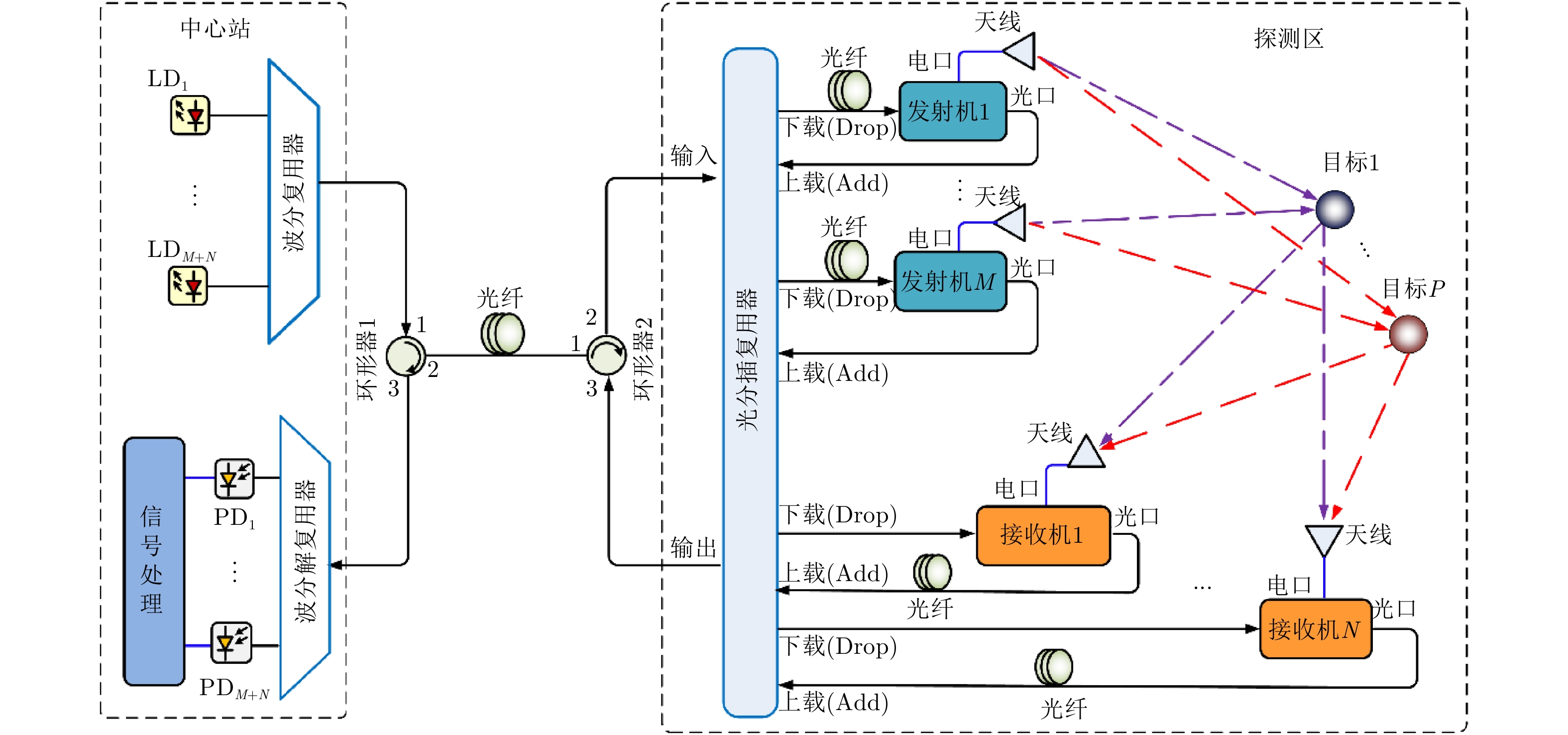
A distributed multi-target localization system based on optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) network is demonstrated. The wideband orthogonal waveforms are generated by introducing the chaotic OptoElectronic Oscillator (OEO). The optical WDM network is introduced to transmit the wideband signals from multiple distributed transmitting and receiving units to the central station for processing, and the accurate localization of multiple targets is achieved based on the time of arrival localization method. The multiple optical carriers are generated at the central station, the complex processing to achieve the high-precision of the target localization is supported by the resources at the central station, and the remote transmitting and receiving units are simplified. Moreover, a proof of concept of the distributed multi-target localization system based on optical WDM network is obtained. The localization system comprising two transmitters and two receivers is experimentally established. The orthogonal chaotic waveforms with the frequency range of 3.1~10.6 GHz are successfully generated from the chaotic OEOs. The two-dimensional localization of two targets is realized via the maximum positioning error of 7.09 cm. Additionally, the reconfiguration of the system is experimentally verified. -

-
References
[1] SHEN J Y, MOLISCH A F, and SALMI J. Accurate passive location estimation using TOA measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(6): 2182–2192. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.040412.110697[2] GRODENSKY D, KRAVITZ D, and ZADOK A. Ultra-wideband microwave-photonic noise radar based on optical waveform generation[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(10): 839–841. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2188889[3] ZHENG Jianyu, WANG Hui, FU Jianbin, et al. Fiber-distributed ultra-wideband noise radar with steerable power spectrum and colorless base station[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 4896–4907. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.004896[4] LLORENTE R, MORANT M, AMIOT N, et al. Novel photonic analog-to-digital converter architecture for precise localization of ultra-wide band radio transmitters[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(6): 1321–1327. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.110619[5] FU Jianbin and PAN Shilong. Fiber-connected UWB sensor network for high-resolution localization using optical time-division multiplexing[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(18): 21218–21223. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.021218[6] YAO Tingfeng, ZHU Dan, LIU Shifeng, et al. Wavelength-division multiplexed fiber-connected sensor network for SLource localization[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(18): 1874–1877. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2336796[7] ZHANG Mingjiang, JI Yongning, ZHANG Yongning, et al. Remote radar based on chaos generation and radio over fiber[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2014, 6(5): 7902412. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2014.2352628[8] KANNO A and KAWANISHI T. Broadband frequency-modulated continuous-wave signal generation by optical modulation technique[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(20): 3566–3572. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2318724[9] FU Jianbin, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHU Dan, et al. Fiber-distributed ultra-wideband radar network based on wavelength reusing transceivers[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 18457–18469. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.018457[10] YAO Tingfeng, ZHU Dan, BEN De, et al. Distributed MIMO chaotic radar based on wavelength-division multiplexing technology[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(8): 1631–1634. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.001631[11] 徐威远. 基于光纤网络架构的分布式多目标定位系统[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2017.XU Weiyuan. Research on distributed localization system based on optical fiber network[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017.[12] 姚汀峰. 基于微波光子技术的分布式雷达研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2015.YAO Tingfeng. Research on distributed radar based on microwave photonics technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015. -
Proportional views

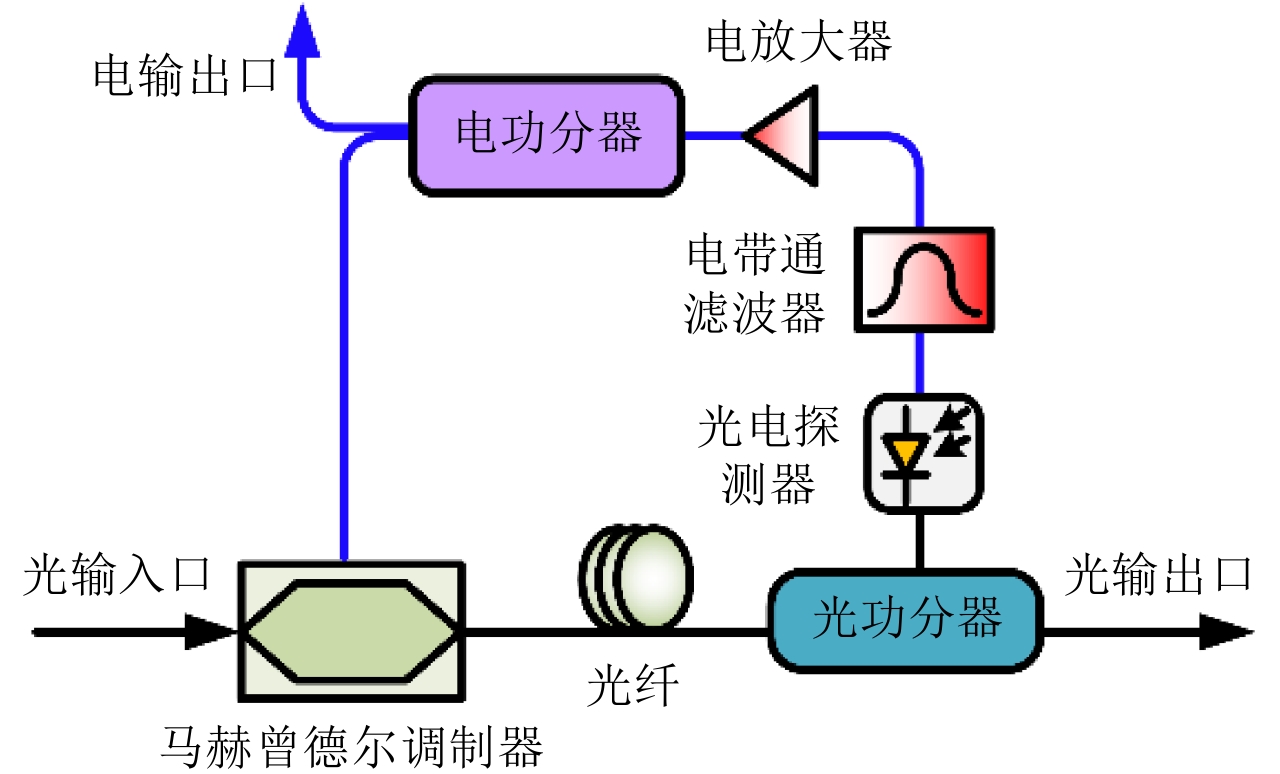
- Figure 1. Distributed multi-target localization system based on optical WDM network
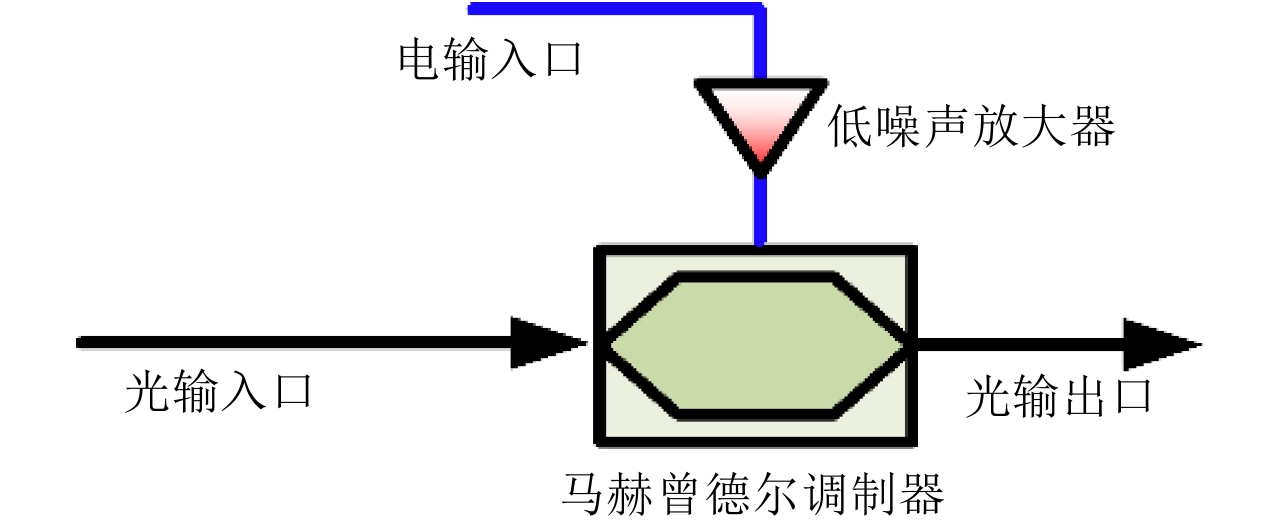
- Figure 2. The structure of the transmitter
- Figure 3. The structure of the receiver
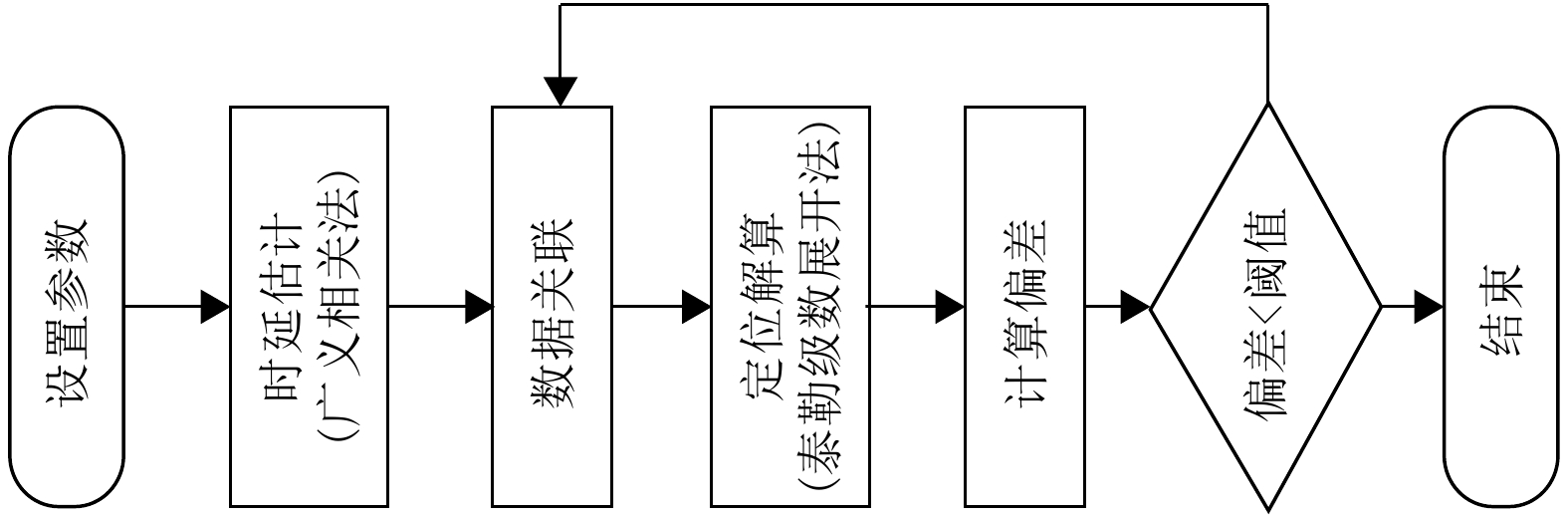
- Figure 4. The localization solution process
- Figure 5. Schematic diagram of TOA localization with the system composed of two transmitters and two receivers
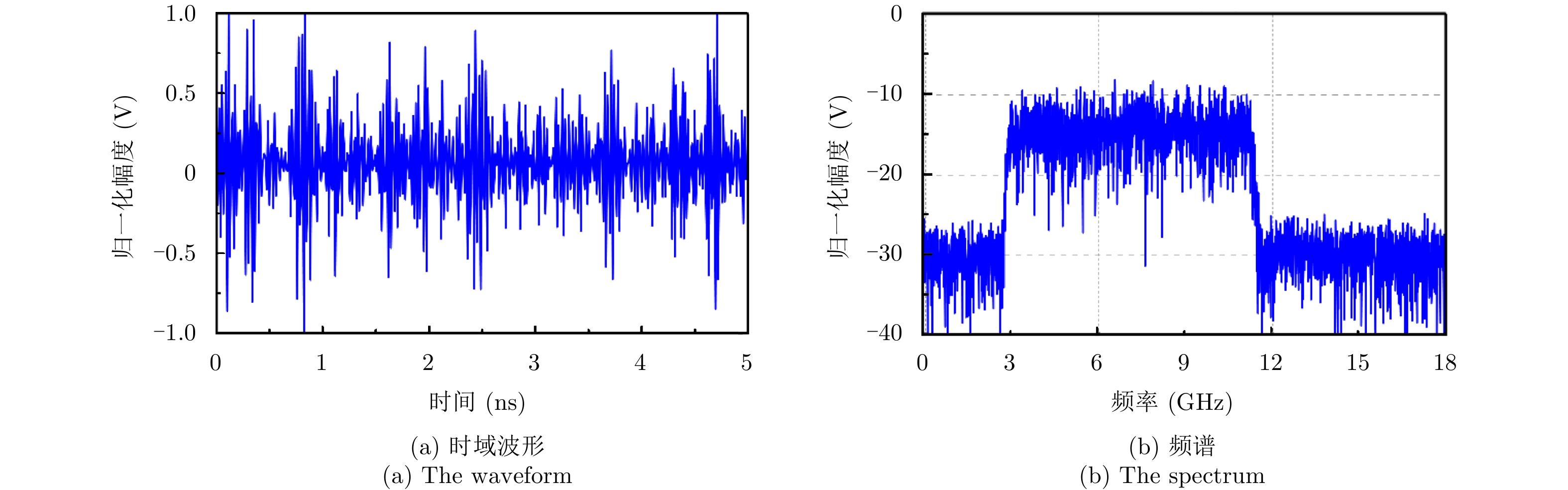
- Figure 6. The generated chaotic signal
- Figure 7. The results of the generated chaotic signal
- Figure 8. The received signal
- Figure 9. Experimental results of two targets localization
- Figure 10. Experimental results of two targets localization when changing the transmitter positions


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: