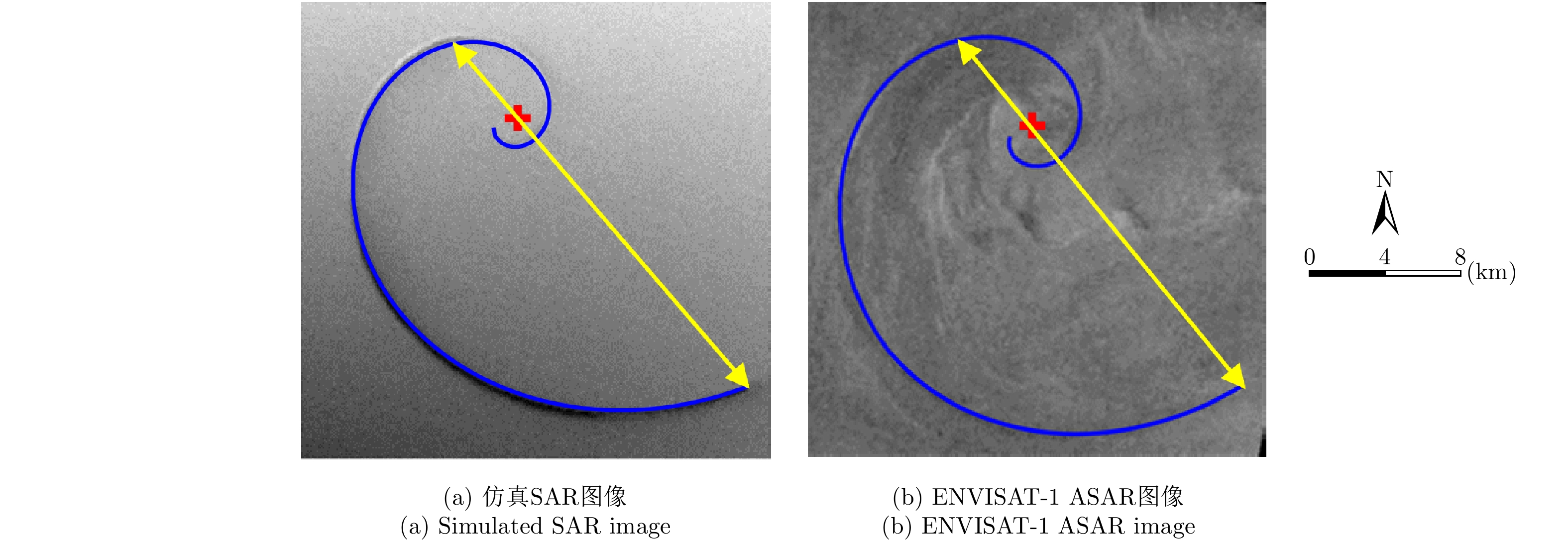
| [1] |
KARIMOVA S. Spiral eddies in the Baltic, Black and Caspian seas as seen by satellite radar data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 50(8): 1107–1124. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2011.10.027 |
| [2] |
IVANOV A Y and GINZBURG A I. Oceanic eddies in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2002, 111(3): 281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF02701974 |
| [3] |
KARIMOVA S and GADE M. Improved statistics of sub-mesoscale eddies in the Baltic Sea retrieved from SAR imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 37(10): 2394–2414. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2016.1145367 |
| [4] |
XU G J, YANG J S, DONG C M, et al. Statistical study of submesoscale eddies identified from synthetic aperture radar images in the Luzon Strait and adjacent seas[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(18): 4621–4631. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1084431 |
| [5] |
TAVRI A, SINGHA S, LEHNER S, et al. Observation of sub-mesoscale eddies over Baltic Sea using TerraSAR-X and Oceanographic data[C]. Proceedings of Living Planet Symposium 2016, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016.
|
| [6] |
LYZENGA D and WACKERMAN C. Detection and classification of ocean eddies using ERS-1 and aircraft SAR images[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd ERS Symposium on Space at the Service of our Environment, Florence, Italy, 1997: 1267–1271.
|
| [7] |
MITNIK L, DUBINA V, and LOBANOV V. Cold season features of the Japan Sea coastal zone revealed by ERS SAR[C]. Proceedings of ERS-Envisat Symposium " Looking Down to Earth in the New Millennium”, Noordwijk, Netherlands, 2000: 4232–4242.
|
| [8] |
LAVROVA O Y and MITYAGINA M I. Manifestation specifics of hydrodynamic processes in satellite images of intense phytoplankton bloom areas[J]. Izvestiya Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 2016, 52(9): 974–987. doi: 10.1134/S0001433816090176 |
| [9] |
YANG Min and CHONG Jing-song. A method based on logarithmic spiral edge fitting for information extraction of eddy in the SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 226–233. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13004 |
| [10] |
DRESCHLER-FISCHER L, LAVROVA O, SEPPKE B, et al. Detecting and tracking small scale eddies in the black sea and the Baltic Sea using high-resolution Radarsat-2 and TerraSAR-X imagery (DTeddie)[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1214–1217. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946650. |
| [11] |
KARIMOVA S. An approach to automated spiral eddy detection in SAR images[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, Texas, USA, 2017: 743–746. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8127059. |
| [12] |
HUANG D M, DU Y L, HE Q, et al. DeepEddy: A simple deep architecture for mesoscale oceanic eddy detection in SAR images[C]. Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Calabria, Italy, 2017: 673–678. DOI: 10.1109/ICNSC.2017.8000171. |
| [13] |
于祥祯. 顺轨干涉SAR对海洋表面流场监测的若干问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院研究生院, 2012: 30–34.
YU Xiang-zhen. Study on some problems of ocean surface current detection by along-track interferometric SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 30–34.
|
| [14] |
ROMEISER R, ALPERS W, and WISMANN V. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 1. Theory of the model and optimization/validation by scatterometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C11): 25237–25250. doi: 10.1029/97JC00190 |
| [15] |
ROMEISER R and ALPERS W. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 2. Model response to surface roughness variations and the radar imaging of underwater bottom topography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C11): 25251–25267. doi: 10.1029/97JC00191 |
| [16] |
ROMEISER R, SEIBT-WINCKLER A, HEINEKE M, et al. Validation of current and bathymetry measurements in the German Bight by airborne along-track interferometric SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2002 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 1822–1824. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1026266. |
| [17] |
OUYANG Y, CHONG J S, WU Y R, et al. Simulation studies of internal waves in SAR images under different SAR and wind field conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1734–1743. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2087384 |
| [18] |
朱克勤, 彭杰. 高等流体力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 132–138.
ZHU Ke-qin and PENG Jie. Advanced Fluid Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 132–138.
|
| [19] |
BURGERS J M. A mathematical model illustrating the theory of turbulence[J]. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1948, 1: 171–199. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2156(08)70100-5 |
| [20] |
ROTT N. On the viscous core of a line vortex[J]. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP, 1958, 9(5/6): 543–553. doi: 10.1007/BF02424773 |
| [21] |
LONGUET-HIGGINS M S and STEWART R W. Radiation stresses in water waves; a physical discussion, with applications[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1964, 11(4): 529–562. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(64)90001-4 |
| [22] |
YU Ying, WANG Xiao-qing, ZHU Min-hui, et al. Three-scale radar backscattering model of the ocean surface based on second-order scattering[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(9): 1771–1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.09.022 |
| [23] |
WHITHAM G B. A general approach to linear and non-linear dispersive waves using a Lagrangian[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1965, 22(2): 273–283. doi: 10.1017/S0022112065000745 |
| [24] |
ALPERS W R, ROSS D B, and RUFENACH C L. On the detectability of ocean surface waves by real and synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C7): 6481–6498. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC07p06481 |
| [25] |
ROMEISER R and THOMPSON D R. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 446–458. doi: 10.1109/36.823940 |
| [26] |
ROBINSON I S. Discovering the Ocean from Space: The Unique Applications of Satellite Oceanography[M]. Chichester, UK: Springer-Praxis, 2010: 76–78.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

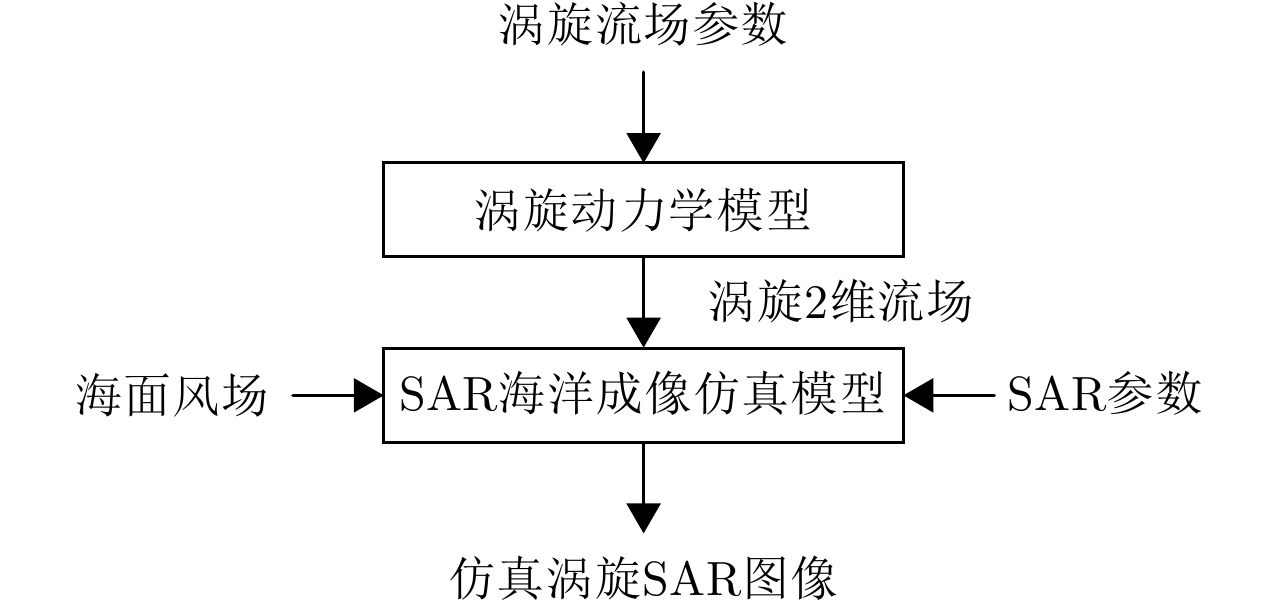



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: