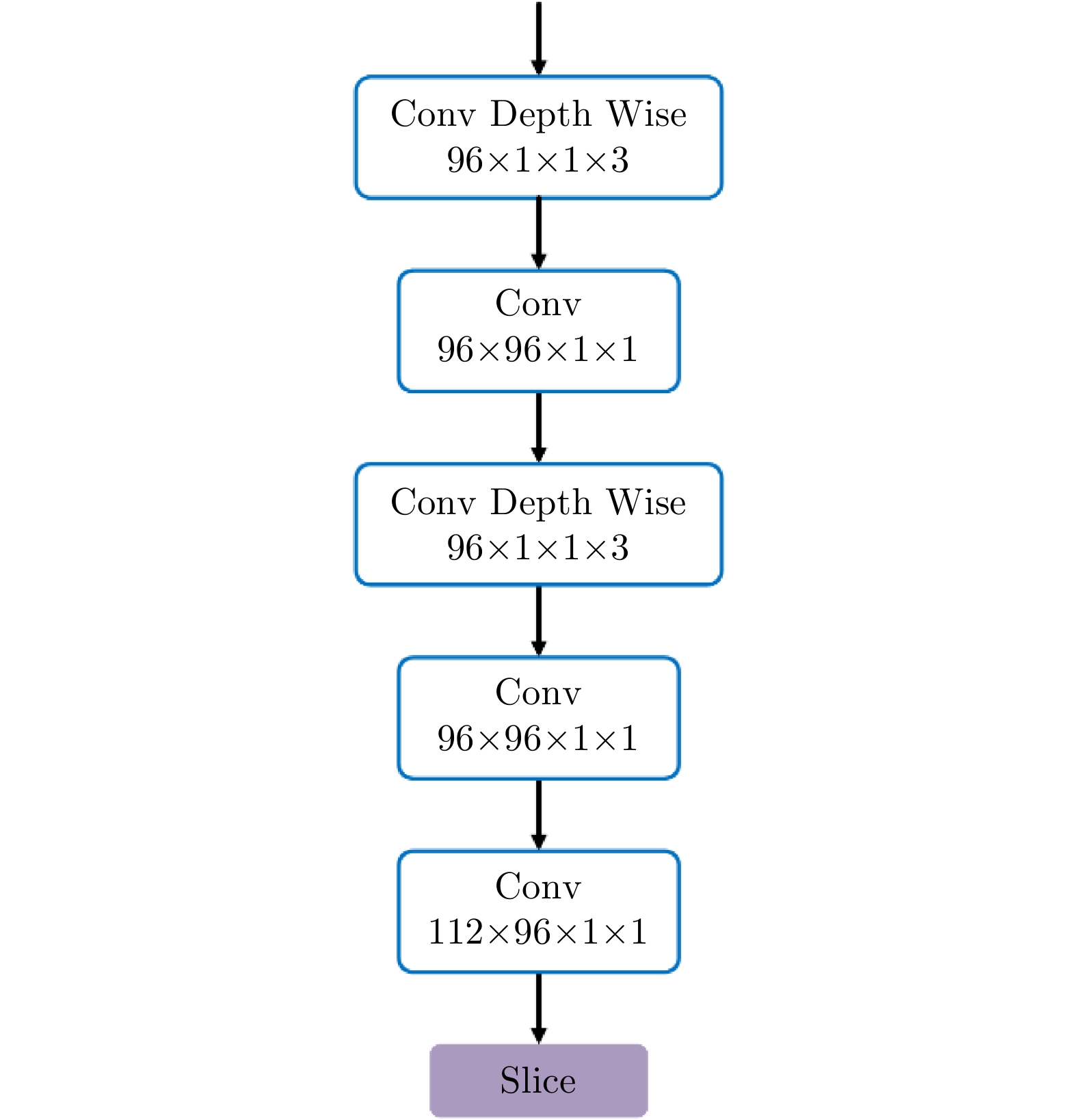
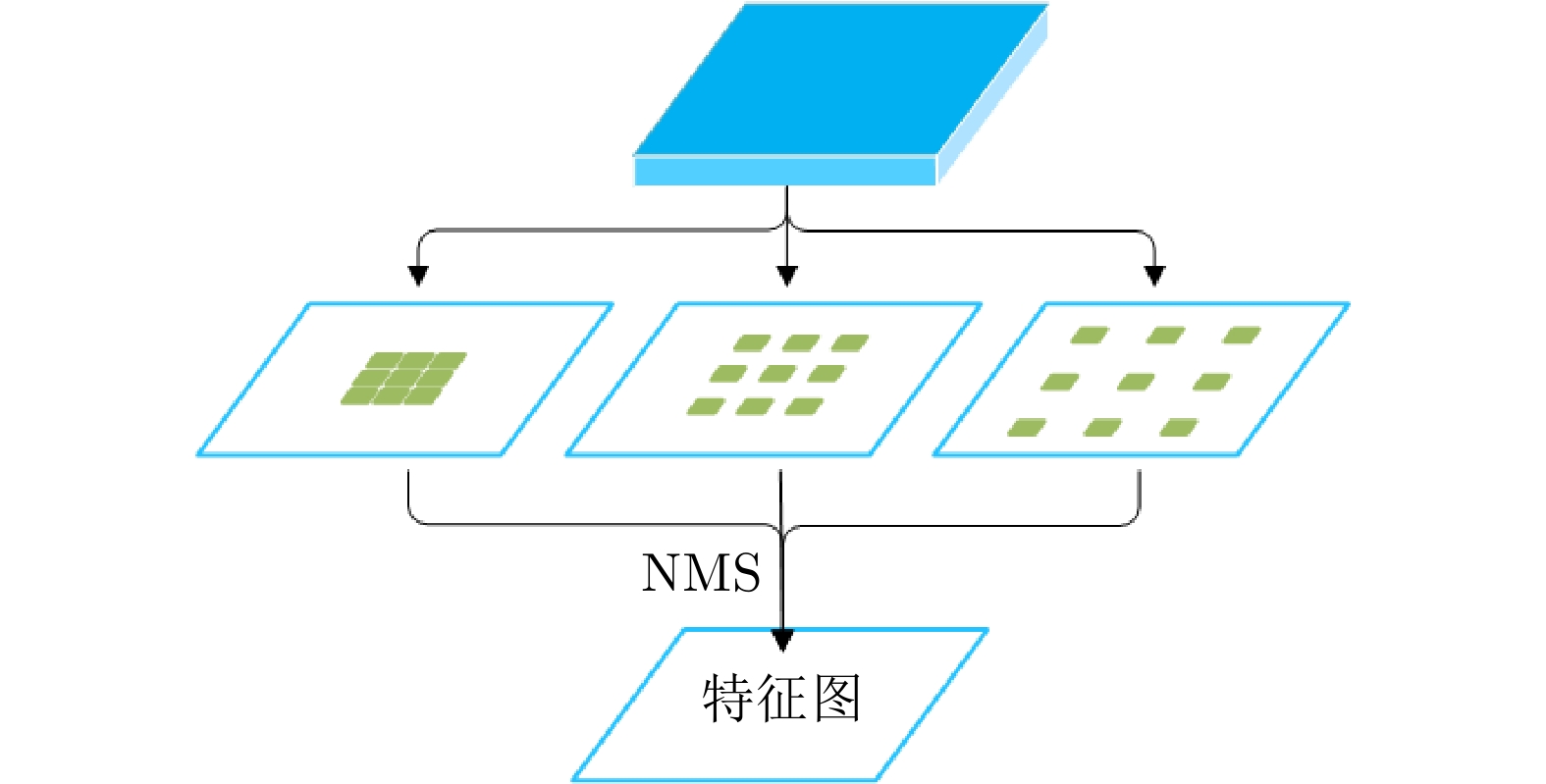
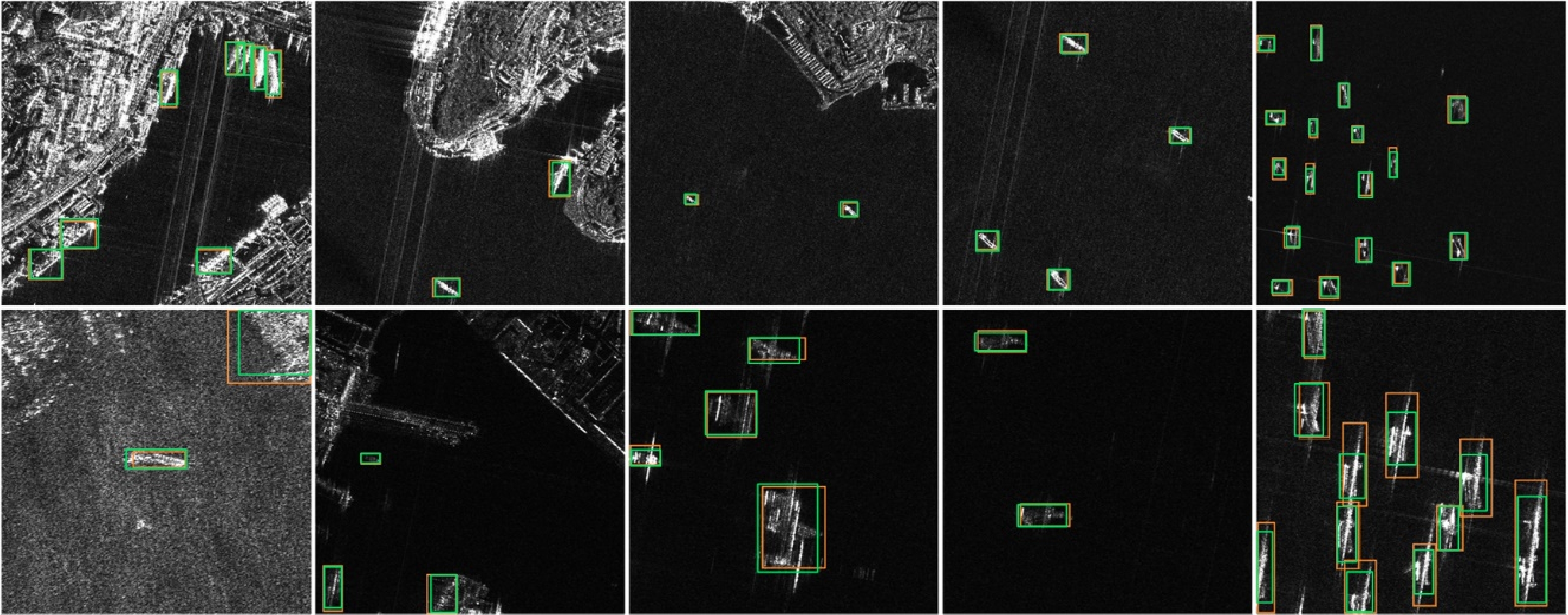
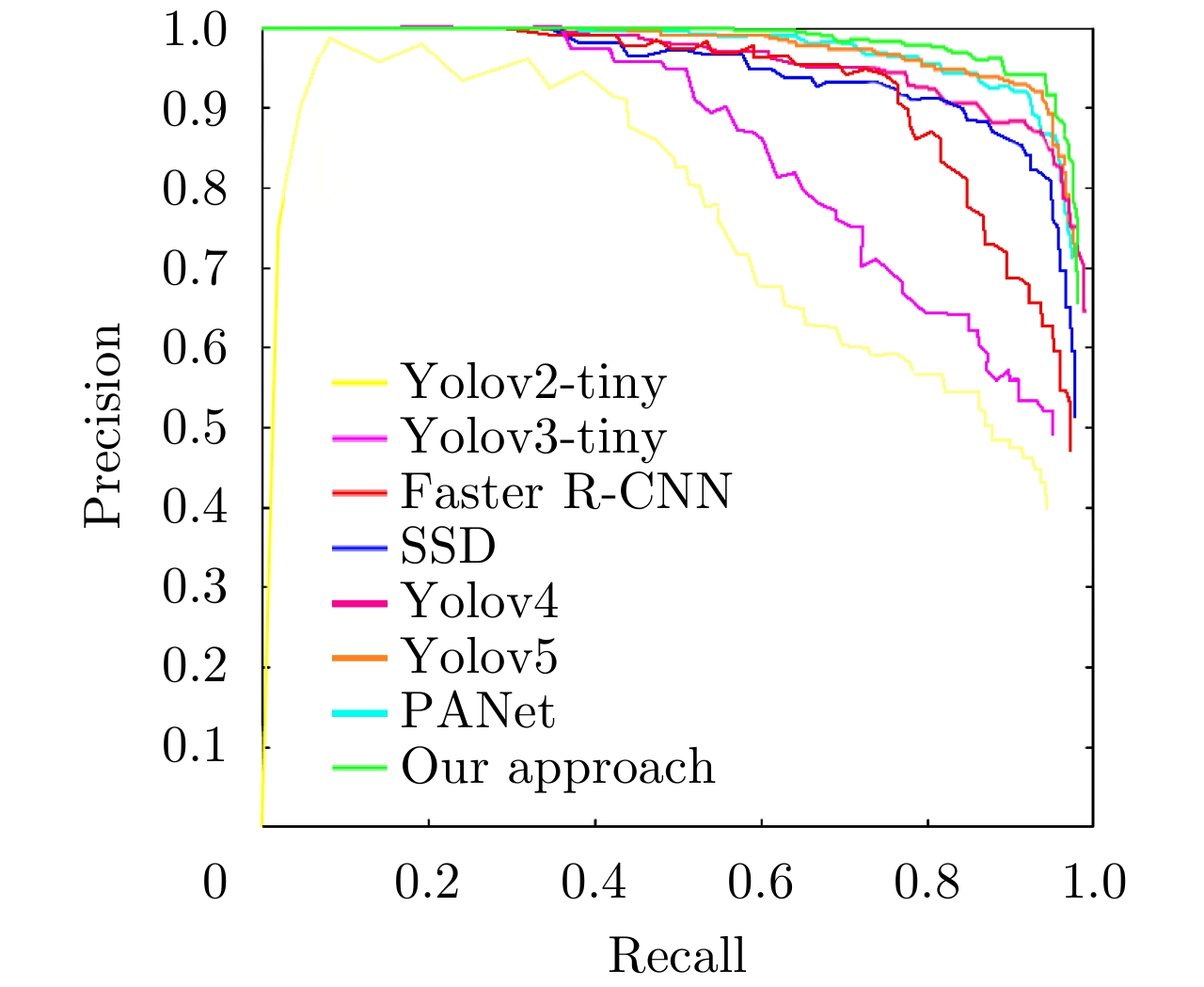
| [1] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [2] |
郭倩, 王海鹏, 徐丰. SAR图像飞机目标检测识别进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Research progress on aircraft detection and recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020 |
| [3] |
张杰, 张晰, 范陈清, 等. 极化SAR在海洋探测中的应用与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124ZHANG jie, ZHANG Xi, FAN Chenqing, et al. Discussion on application of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in marine surveillance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124 |
| [4] |
牟效乾, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于INet的雷达图像杂波抑制和目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Clutter suppression and marine target detection for radar images based on INet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090 |
| [5] |
WACKERMAN C C, FRIEDMAN K S, PICHEL W G, et al. Automatic detection of ships in RADARSAT-1 SAR imagery[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2001, 27(5): 568–577. doi: 10.1080/07038992.2001.10854896 |
| [6] |
陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 |
| [7] |
AUDEBERT N, LE SAUX B, and LEFÈVRE S. How useful is region-based classification of remote sensing images in a deep learning framework?[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 5091–5094. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730327. |
| [8] |
WANG Wenxiu, FU Yutian, DONG Feng, et al. Remote sensing ship detection technology based on DoG preprocessing and shape features[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2017: 1702–1706. doi: 10.1109/CompComm.2017.8322830. |
| [9] |
HOU Xiaodi and ZHANG Liqing. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2007.383267. |
| [10] |
GOFERMAN S, ZELNIK-MANOR L, and TAL A. Context-aware saliency detection[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2376–2383. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539929. |
| [11] |
LIU Zhi, ZOU Wenbin, and LE MEUR O. Saliency tree: A novel saliency detection framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(5): 1937–1952. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2307434 |
| [12] |
CHENG Gong, ZHOU Peicheng, and HAN Junwei. Learning rotation-invariant convolutional neural networks for object detection in VHR optical remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 7405–7415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2601622 |
| [13] |
LIU Li, OUYANG Wanli, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261–318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 |
| [14] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 |
| [15] |
GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587.
|
| [16] |
REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 |
| [17] |
NIE Xuan, DUAN Mengyang, DING Haoxuan, et al. Attention mask R-CNN for ship detection and segmentation from remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 9325–9334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964540 |
| [18] |
LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759–8768. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00913. |
| [19] |
LIU Yudong, WANG Yongtao, WANG Siwei, et al. Cbnet: A novel composite backbone network architecture for object detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 11653–11660. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6834 |
| [20] |
REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time objectdetection[C]. The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788.
|
| [21] |
LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. |
| [22] |
REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.690. |
| [23] |
REDMON J and FARHADI A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[C]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.
|
| [24] |
BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[C]. arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020.
|
| [25] |
IANDOLA F N, HAN Song, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size[C]. arXiv: 1602.07360, 2016.
|
| [26] |
MITTELMANN H and PENG Jiming. Estimating bounds for quadratic assignment problems associated with hamming and Manhattan distance matrices based on semidefinite programming[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2010, 20(6): 3408–3426. doi: 10.1137/090748834 |
| [27] |
LI Yanghao, CHEN Yuntao, WANG Naiyan, et al. Scale-aware trident networks for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6053–6062.
|
| [28] |
PASZKE A, GROSS S, MASSA F, et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library[C]. The 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 8026–8037.
|
| [29] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934. |
| [30] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and PENG Shujuan. A ship detection method based on cascade CNN in SAR images[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0168 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: