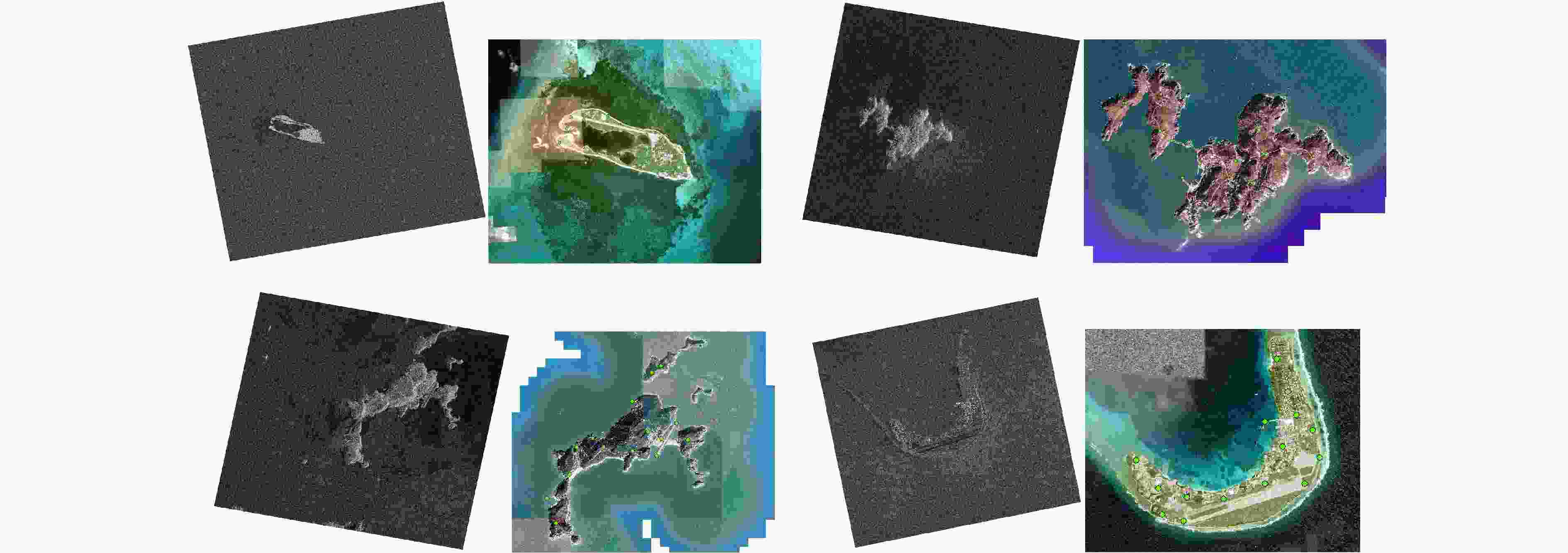
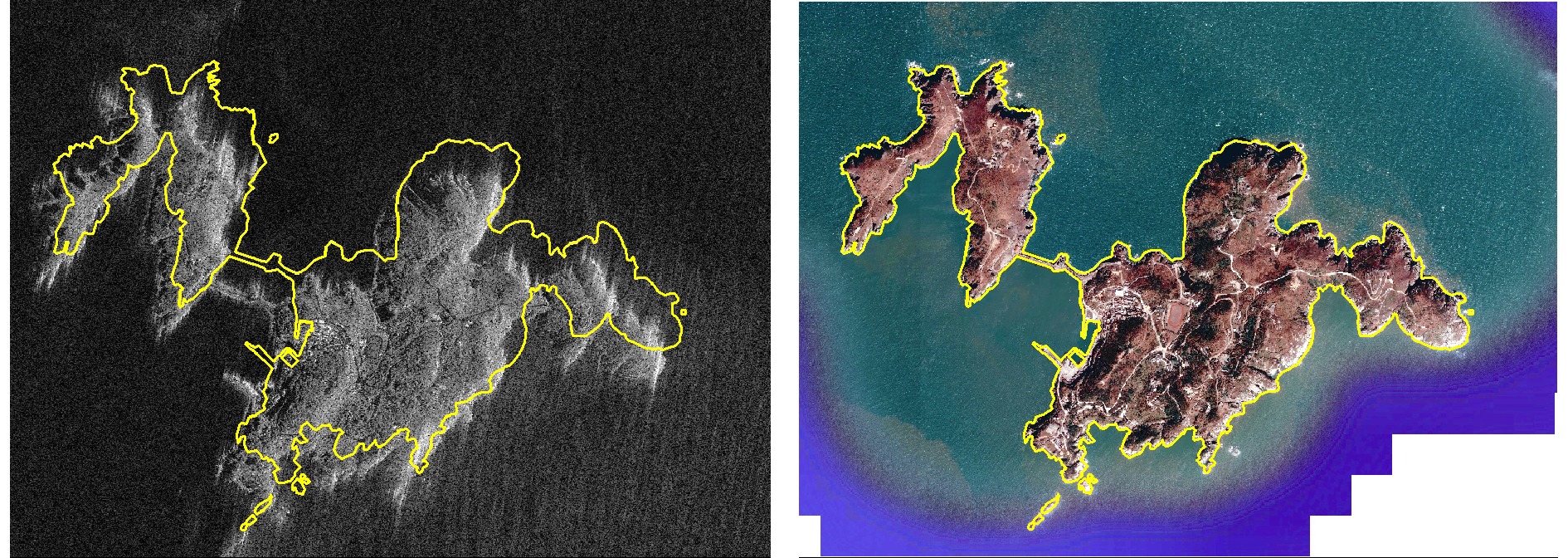
Orthorectification of High-resolution SAR Images in Island Regions Based on Fast Multimodal Registration
-
摘要: 随着高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)卫星的陆续发射,对天气条件多变的海岛区域进行全天候、全时段的高精度观测已变得可行。作为多种遥感应用的关键前置步骤正射校正,依赖于高精度控制点来纠正SAR影像的几何定位误差。然而,在海岛区域获取符合SAR校正要求的人工控制点不仅成本高,且风险大。为了应对这一挑战,该文首先提出了一种光学与SAR异源影像的快速配准算法,然后基于光学参考底图自动提取控制点,实现了海岛区域SAR影像的正射校正。所提出的配准算法分为两个阶段:首先构建异源影像的共性密集特征,然后在降采样后的特征上进行逐像素匹配,避免了异源影像特征点重复性低的问题。为了降低匹配复杂度,引入了海陆分割掩模以限定搜索范围。接着,对初步匹配点进行局部精细匹配,以减少降采样带来的不准确性。同时,引入海岸线均匀采样点以提升匹配结果的均匀性,并通过分段线性变换模型生成正射影像,确保了稀疏岛屿区域的整体校正精度。该算法在多景海岛区域的高分辨率SAR影像上表现出色,平均定位误差为3.2 m,整景校正时间仅需17.3 s,均优于现有多种先进的异源配准与校正算法,显示出其在工程应用中的巨大潜力。Abstract: With the successive launch of high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites, conducting all-weather, all-time high-precision observation of island regions with variable weather conditions has become feasible. As a key preprocessing step in various remote sensing applications, orthorectification relies on high-precision control points to correct the geometric positioning errors of SAR images. However, obtaining artificial control points that meet SAR correction requirements in island areas is costly and risky. To address this challenge, this study first proposes a rapid registration algorithm for optical and SAR heterogeneous images, and then automatically extracts control points based on an optical reference base map, achieving orthorectification of SAR images in island regions. The proposed registration algorithm consists of two stages: constructing dense common features of heterogeneous images; performing pixel-by-pixel matching on the down-sampled features, to avoid the issue of low repeatability of feature points in heterogeneous images. To reduce the matching complexity, a land sea segmentation mask is introduced to limit the search range. Subsequently, local fine matching is applied to the preliminary matched points to reduce inaccuracies introduced by down-sampling. Meanwhile, uniformly sampled coastline points are introduced to enhance the uniformity of the matching results, and orthorectified images are generated through a piecewise linear transformation model, ensuring the overall correction accuracy in sparse island areas. This algorithm performs excellently on the high-resolution SAR images of multiple scenes in island regions, with an average positioning error of 3.2 m and a complete scene correction time of only 17.3 s, both these values are superior to various existing advanced heterogeneous registration and correction algorithms, demonstrating the great potential of the proposed algorithm in engineering applications.
-
表 1 待校正的SAR影像成像参数信息
Table 1. The imaging parameter information of the SAR image to be rectified
测试区域 卫星型号 成像模式 成像视角(°) 波段 采样间隔(m) 影像尺寸(像素) A1 高分三号 滑动聚束 41.2 C 0.56/0.36 15616 ×29344 A2 高分三号 滑动聚束 21.4 C 0.56/0.31 8635 ×33560 B 高分三号 滑动聚束 39.3 C 0.56/0.34 13660 ×32208 C 高分三号 滑动聚束 29.7 C 0.56/0.33 10946 ×32032 D1 海丝一号 滑动聚束 28.0 C 0.31/0.17 9188 ×45875 D2 海丝一号 滑动聚束 28.8 C 0.31/0.32 12748 ×22937 表 2 所有算法在6组测试影像上的定位误差(m)
Table 2. The positioning errors of all algorithms on six sets of test images (m)
方法 A1 A2 B C D1 D2 平均处理时间(s) 本文算法 1.82 2.98 3.65 5.50 2.81 2.45 17.3 SFOC 2.10 / / 15.20 3.88 3.43 139.8 RIFT 2.93 3.87 7.09 6.54 5.90 4.33 194.3 3MRS 2.02 4.15 5.51 12.68 6.15 3.59 160.7 海岸线匹配 8.71 / / 9.44 12.15 6.04 172.1 注:/代表校正失败。 表 3 消融实验方法设置
Table 3. Setting of the ablation study
方法 基于海陆分割掩模的
逐像素匹配结合海岸线采样点的
分段线性变换GPU加速 T0(本文算法) √ √ √ T1 × √ √ T2 √ × √ T3 √ √ × 表 4 消融实验对比结果,包括定位误差(m)和平均处理时间(s)
Table 4. The comparison results of ablation study, including positioning error (m) and average processing time (s)
方法 A1 A2 B C D1 D2 平均处理时间(s) T0 1.82 2.98 3.65 5.50 2.81 2.45 17.3 T1 2.28 4.14 5.29 8.32 4.67 3.71 205.6 T2 2.24 3.71 7.31 5.63 3.95 3.38 16.9 T3 1.89 3.18 4.42 5.58 2.82 3.02 158.8 表 5 开源海岸线矢量与海陆分割的对比结果,包括定位误差(m)、平均处理时间(s)和采样点数量(个)
Table 5. The comparison results between open-source coastline vectors and land-sea segmentation, including positioning error (m), average processing time (s), and the number of sampling points (count)
测试区域 定位误差(m) 平均处理时间(s) 采样点数量(个) 开源海岸线矢量 海陆分割 开源海岸线矢量 海陆分割 开源海岸线矢量 海陆分割 A1 1.82 1.92 14.2 22.2 269 1451 A2 2.98 3.15 12.3 18.4 269 1451 B 3.65 4.67 15.0 20.25 783 1253 C 5.50 4.53 24.1 51.4 1119 3464 D1 2.81 3.28 15.5 20.91 157 824 D2 2.45 2.69 16.8 21.49 157 824 -
[1] 孙湫词, 谭勇华, 李家彪. 新时代我国海岛的生态保护和开发利用[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 35(8): 22–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.08.004.SUN Qiuci, TAN Yonghua, and LI Jiabiao. Ecological protection and exploitation of islands in China in new era[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 35(8): 22–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.08.004. [2] VASSILOPOULOU S, HURNI L, DIETRICH V, et al. Orthophoto generation using IKONOS imagery and high-resolution DEM: A case study on volcanic hazard monitoring of Nisyros Island (Greece)[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2002, 57(1/2): 24–38. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2716(02)00126-0. [3] 崔丹, 王辉, 刘君, 等. 海南岛沿岸海域砗磲资源调查及保护前景展望[J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(5): 527–532. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2019.05.006.CUI Dan, WANG Hui, LIU Jun, et al. The resources survey and conservation prospects of the giant clams in the coastal waters at Hainan Island[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 38(5): 527–532. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2019.05.006. [4] 李晓敏, 张杰, 孟俊敏, 等. 高分辨率SAR影像在海岛监视监测中的应用[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 35(2): 39–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.02.008.LI Xiaomin, ZHANG Jie, MENG Junmin, et al. Application of high spatial resolution SAR images in islands monitoring[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 35(2): 39–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.02.008. [5] 范剑超, 王德毅, 赵建华, 等. 高分三号SAR影像在国家海域使用动态监测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 456–472. doi: 10.12000/JR17080.FAN Jianchao, WANG Deyi, ZHAO Jianhua, et al. National sea area use dynamic monitoring based on GF-3 SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 456–472. doi: 10.12000/JR17080. [6] 孙学娇, 李俊杰, 陈卫荣, 等. 高分三号卫星助力海洋强国建设[J]. 卫星应用, 2023(12): 20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2023.12.007.SUN Xuejiao, LI Junjie, CHEN Weirong, et al. Gaofen-3 satellite aids in the construction of a maritime powerhouse[J]. Satellite Application, 2023(12): 20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2023.12.007. [7] 胡玉新, 王峰, 焦念刚, 等. 面向目标结构信息保持的SAR真正射遥感影像生成方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(10): 3767–3775. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221341.HU Yuxin, WANG Feng, JIAO Niangang, et al. True digital ortho maps production for target structure information of SAR remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(10): 3767–3775. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221341. [8] XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, and YOU Hongjian. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078–3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483. [9] XIANG Yuming, JIAO Niangang, WANG Feng, et al. A robust two-stage registration algorithm for large optical and SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5218615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3133863. [10] XIANG Yuming, WANG Xuanqi, WANG Feng, et al. A global-to-local algorithm for high-resolution optical and SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5215320. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3309855. [11] YE Yuanxin, ZHU Bai, TANG Tengfeng, et al. A robust multimodal remote sensing image registration method and system using steerable filters with first-and second-order gradients[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 188: 331–350. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.04.011. [12] MERKLE N, LUO Wenjie, AUER S, et al. Exploiting deep matching and SAR data for the geo-localization accuracy improvement of optical satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 586. doi: 10.3390/rs9060586. [13] FAN Zhongli, ZHANG Li, LIU Yuxuan, et al. Exploiting high geopositioning accuracy of SAR data to obtain accurate geometric orientation of optical satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3535. doi: 10.3390/rs13173535. [14] NIE Shanlan, ZHANG Haopeng, and JIANG Zhiguo. Sea-land segmentation based on template matching[C]. The Fifth International Conference on Network, Communication and Computing, Kyoto, Japan, 2016: 32–36. doi: 10.1145/3033288.3033309. [15] 尹航, 戚洪帅, 蔡锋, 等. 高分影像砂质海岸线精细提取及校正方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(4): 143–152. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2022084.YIN Hang, QI Hongshuai, CAI Feng, et al. Sandy coastline fine extraction and correction method based on high resolution image[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(4): 143–152. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2022084. [16] 李宁, 牛世林. 基于局部超分辨重建的高精度SAR图像水域分割方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096.LI Ning and NIU Shilin. High-precision water segmentation from synthetic aperture radar images based on local super-resolution restoration technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096. [17] KANG Wenchao, XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, et al. CFNet: A cross fusion network for joint land cover classification using optical and SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 1562–1574. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3144587. [18] WAN Ling, XIANG Yuming, and YOU Hongjian. An object-based hierarchical compound classification method for change detection in heterogeneous optical and SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9941–9959. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2930322. [19] LI Jiayuan, HU Qingwu, and AI Mingyao. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3296–3310. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2959244. [20] FAN Jianwei, YE Yuanxin, LI Jian, et al. A novel multiscale adaptive binning phase congruency feature for SAR and optical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235216. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3206804. [21] FAN Zhongli, WANG Mi, PI Yingdong, et al. A robust oriented filter-based matching method for multisource, multitemporal remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4703316. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3288531. [22] ZHU Bai, YANG Chao, DAI Jinkun, et al. R2FD2: Fast and robust matching of multimodal remote sensing images via repeatable feature detector and rotation-invariant feature descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5606115. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3264610. [23] XIONG Xin, JIN Guowang, XU Qing, et al. Robust registration algorithm for optical and SAR images based on adjacent self-similarity feature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5233117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3197357. [24] LIAO Yun, DI Yide, ZHOU Hao, et al. Feature matching and position matching between optical and SAR with local deep feature descriptor[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 448–462. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3134676. [25] XIANG Deliang, XIE Yuzhen, CHENG Jianda, et al. Optical and SAR image registration based on feature decoupling network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235913. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3211858. [26] QUAN Dou, WANG Shuang, GU Yu, et al. Deep feature correlation learning for multi-modal remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4708216. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3187015. [27] XU Wangyi, YUAN Xinhui, HU Qingwu, et al. SAR-optical feature matching: A large-scale patch dataset and a deep local descriptor[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 122: 103433. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2023.103433. [28] CUI Song, MA Ailong, ZHANG Liangpei, et al. MAP-Net: SAR and optical image matching via image-based convolutional network with attention mechanism and spatial pyramid aggregated pooling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1000513. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3066432. [29] 杨玉婷, 赵凌君, 赵路路, 等. 强化位置感知的光学与SAR图像一体化配准方法[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(3): 557–568. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.03.014.YANG Yuting, ZHAO Lingjun, ZHAO Lulu, et al. Integrated registration method for optical and SAR images by enhancing position awareness[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(3): 557–568. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.03.014. [30] 蓝朝桢, 卢万杰, 于君明, 等. 异源遥感影像特征匹配的深度学习算法[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(2): 189–202. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200048.LAN Chaozhen, LU Wanjie, YU Junming, et al. Deep learning algorithm for feature matching of cross modality remote sensing images[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(2): 189–202. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200048. [31] ZHANG Yongxian, LAN Chaozhen, ZHANG Haiming, et al. Multimodal remote sensing image matching via learning features and attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5603620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3348980. [32] 尤红建, 胡岩峰. SAR和光学图像精配准技术的研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 78–84. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13154.YOU Hongjian and HU Yanfeng. Investigation on fine registration for SAR and optical image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 78–84. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13154. [33] 王蒙蒙, 叶沅鑫, 朱柏, 等. 基于空间约束和结构特征的光学与SAR影像配准[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2022, 47(1): 141–148. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190354.WANG Mengmeng, YE Yuanxin, ZHU Bai, et al. An automatic registration method for optical and SAR images based on spatial constraint and structure features[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(1): 141–148. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190354. [34] YE Yuanxin, BRUZZONE L, SHAN Jie, et al. Fast and robust matching for multimodal remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9059–9070. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2924684. [35] XIANG Yuming, TAO Rongshu, WAN Ling, et al. OS-PC: Combining feature representation and 3-D phase correlation for subpixel optical and SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6451–6466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2976865. [36] ZHANG Han, LEI Lin, NI Weiping, et al. Explore better network framework for high-resolution optical and SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4704418. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3126939. [37] LIU Ming, ZHOU Gaoxiang, MA Lingfei, et al. SIFNet: A self-attention interaction fusion network for multisource satellite imagery template matching[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 118: 103247. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2023.103247. [38] FAN Zhongli, LIU Yuxian, LIU Yuxuan, et al. 3MRS: An effective coarse-to-fine matching method for multimodal remote sensing imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(3): 478. doi: 10.3390/rs14030478. [39] QUAN Dou, WEI Huiyuan, WANG Shuang, et al. A novel coarse-to-fine deep learning registration framework for multimodal remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5108316. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3306042. [40] CAO Fanzhi, SHI Tianxin, HAN Kaiyang, et al. RDFM: Robust deep feature matching for multimodal remote-sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 6009605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3309404. [41] EUGENIO F and MARQUÉS F. Automatic satellite image georeferencing using a contour-matching approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(12): 2869–2880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817226. [42] 刘善伟. 面向海岛海岸带的遥感影像几何精校正方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国石油大学, 2008.LIU Shanwei. Research on remote sensing image geometric precision correction method for island and costal zone[D]. [Master dissertation], China University of Petroleum, 2008. [43] DONG Yue, ZHANG Jinfang, and XU Fanjiang. Auto localization for coastal satellite imagery based on curve matching[C]. 2014 International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Information Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Beijing, China, 2014: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/MFI.2014.6997645. [44] MUTAQIN B W, ISNAIN M N, MARFAI M A, et al. Assessing the accuracy of open-source digital elevation models for the geomorphological analysis of very small islands of Indonesia[J]. Applied Geomatics, 2023, 15(4): 957–974. doi: 10.1007/s12518-023-00533-8. [45] 张靓, 孟婵媛, 李军, 等. 基于岸线配准的海岛礁遥感影像几何纠正方法[J]. 海洋测绘, 2011, 31(6): 24–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.06.007.ZHANG Liang, MENG Chanyuan, LI Jun, et al. Precision rectification method for island satellite image based on registration of coastline[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2011, 31(6): 24–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.06.007. [46] 张艳, 王涛, 冯伍法, 等. “天绘一号”海岛(礁)影像稀少控制下的定位技术研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2016, 41(5): 617–623. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140220.ZHANG Yan, WANG Tao, FENG Wufa, et al. Positioning technology study for mapping Satellite-1 islands (Reefs) imagery with scarce controls[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(5): 617–623. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140220. [47] MISRA I, ROHIL M K, MOORTHI S M, et al. MIRACLE: Multi-satellite Island image registration using anisotropic coherence locality enhanced nonlinear diffusion and Mahalanobis distance guided marginalization[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 44(12): 3753–3776. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2023.2225713. [48] OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076. [49] GOSHTASBY A. Piecewise linear mapping functions for image registration[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1986, 19(6): 459–466. doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(86)90044-0. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: