The Design and Joint Positioning Method of an ultra-wideband Through-wall Radar System for Distributed Wireless Networking
-
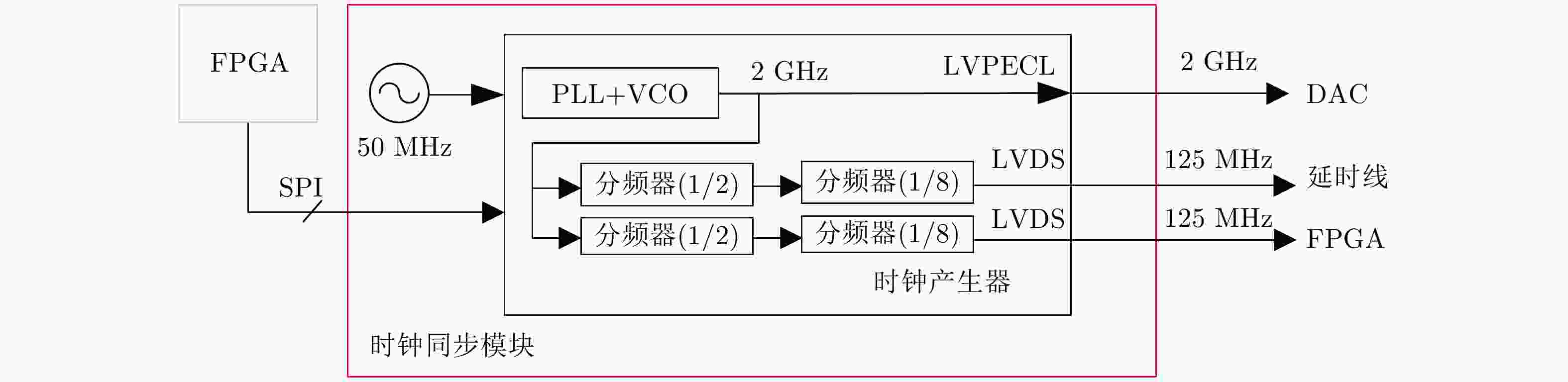
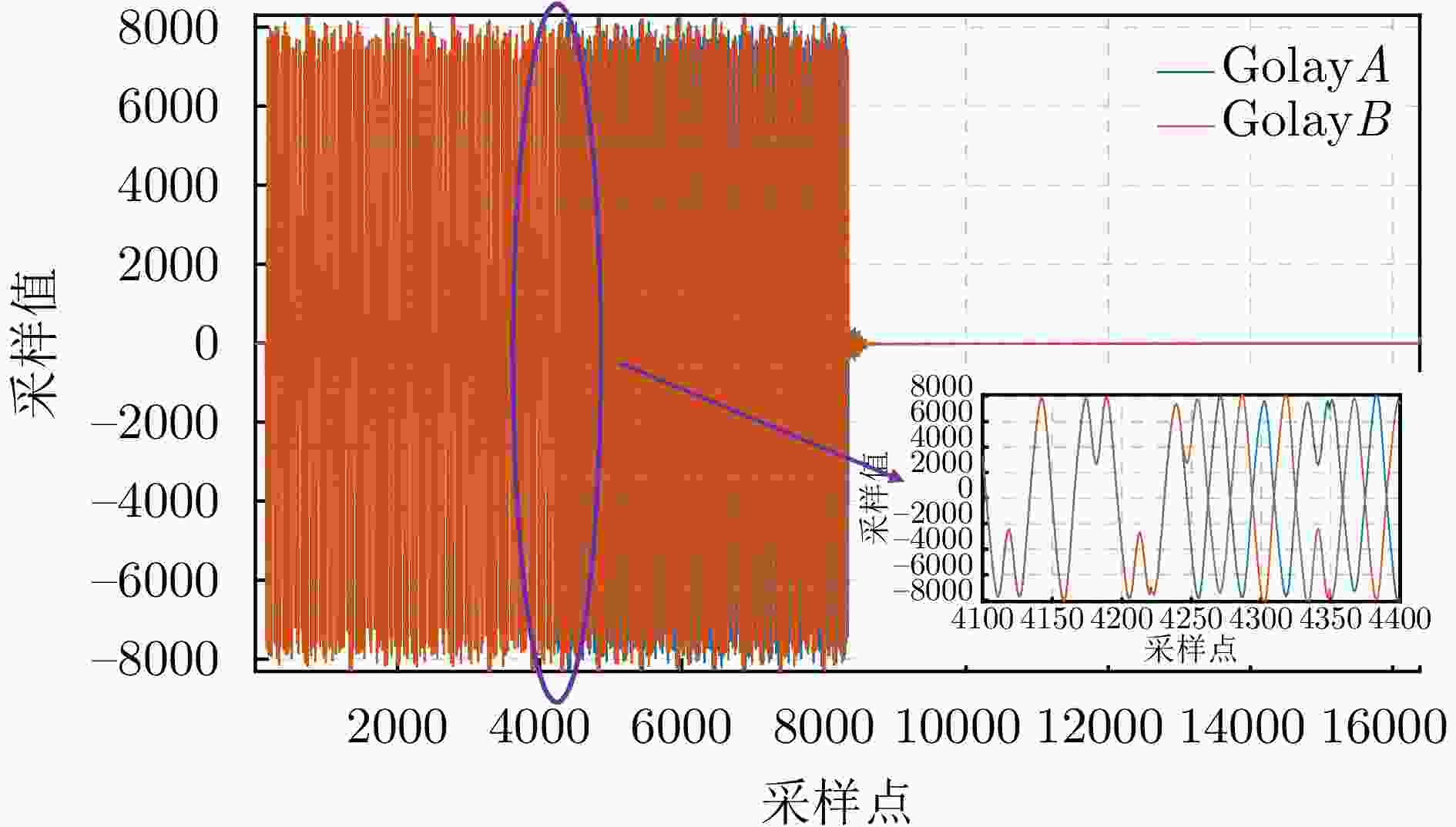
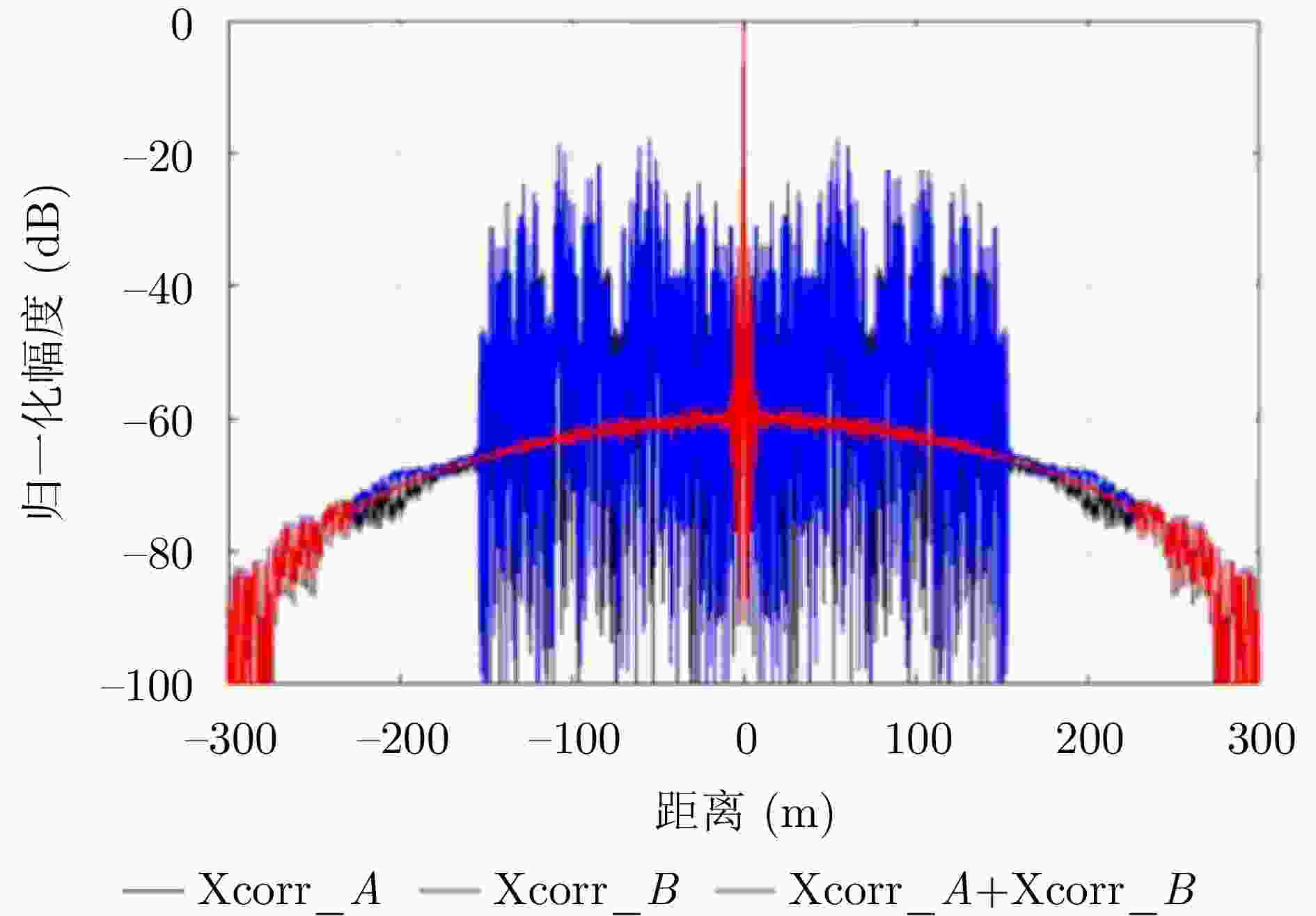
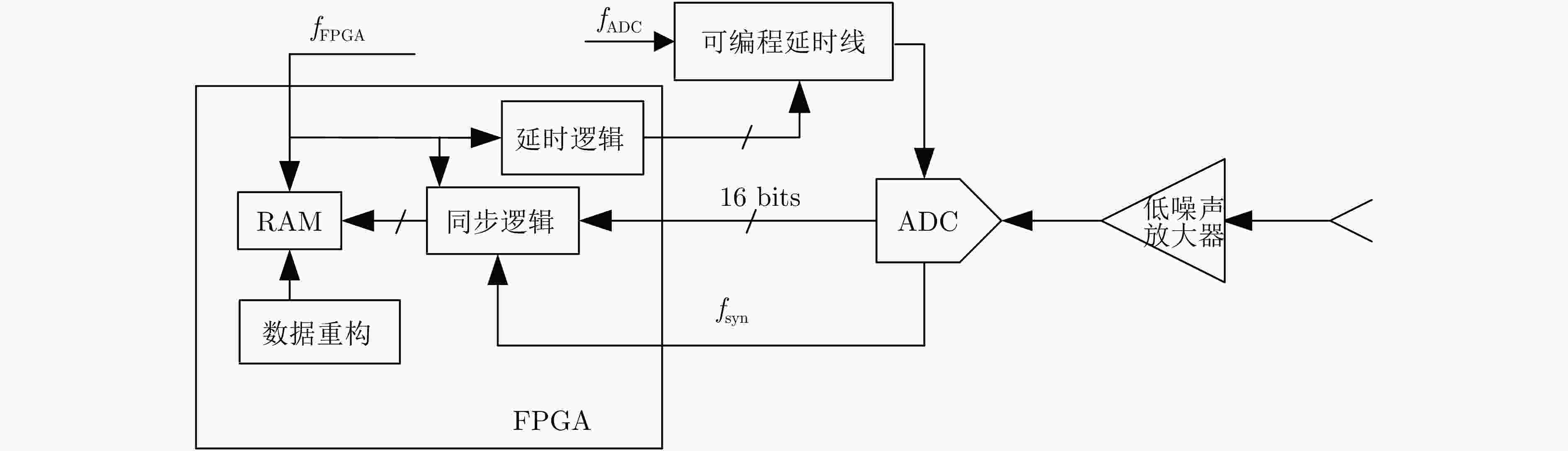
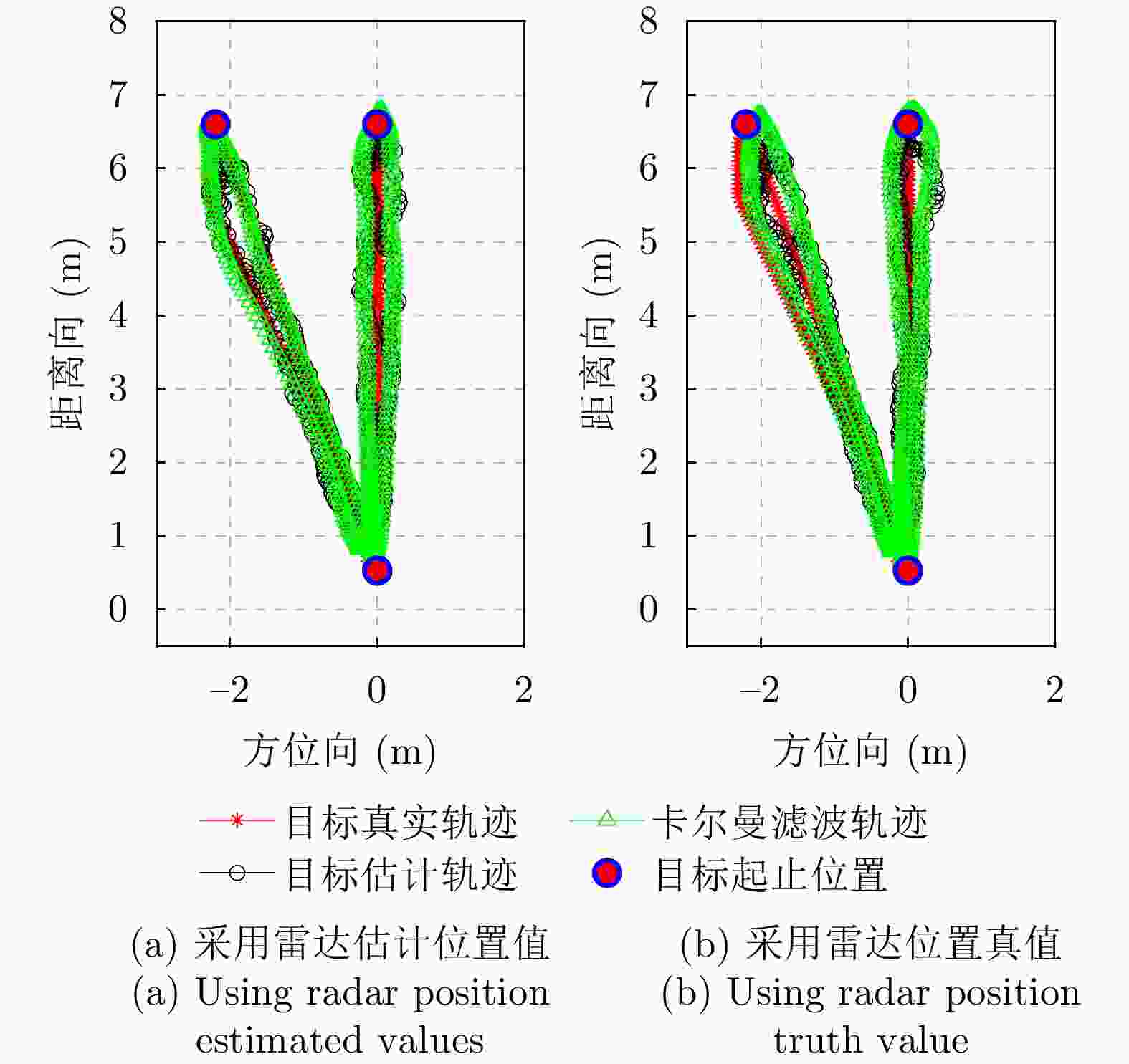
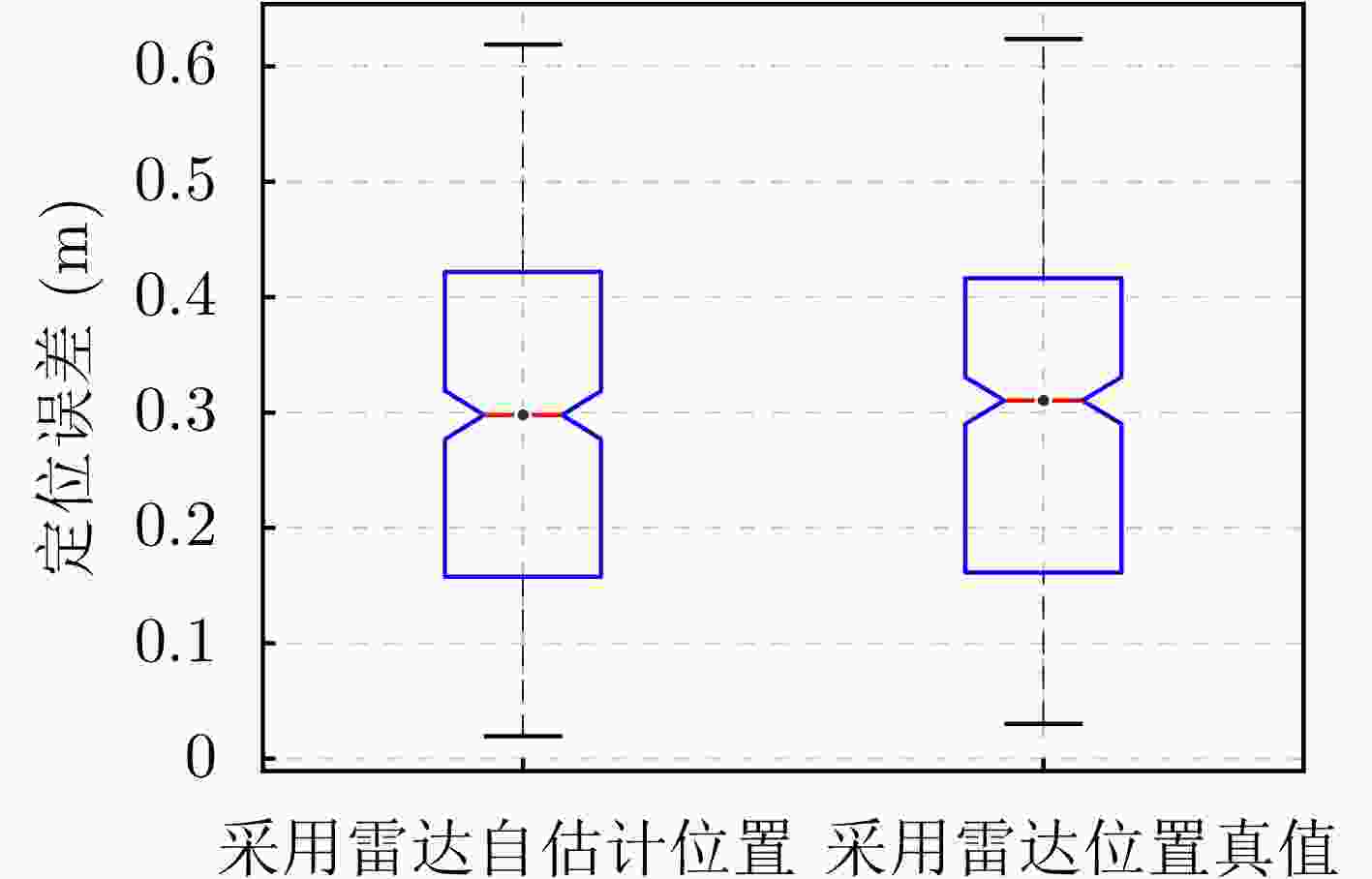
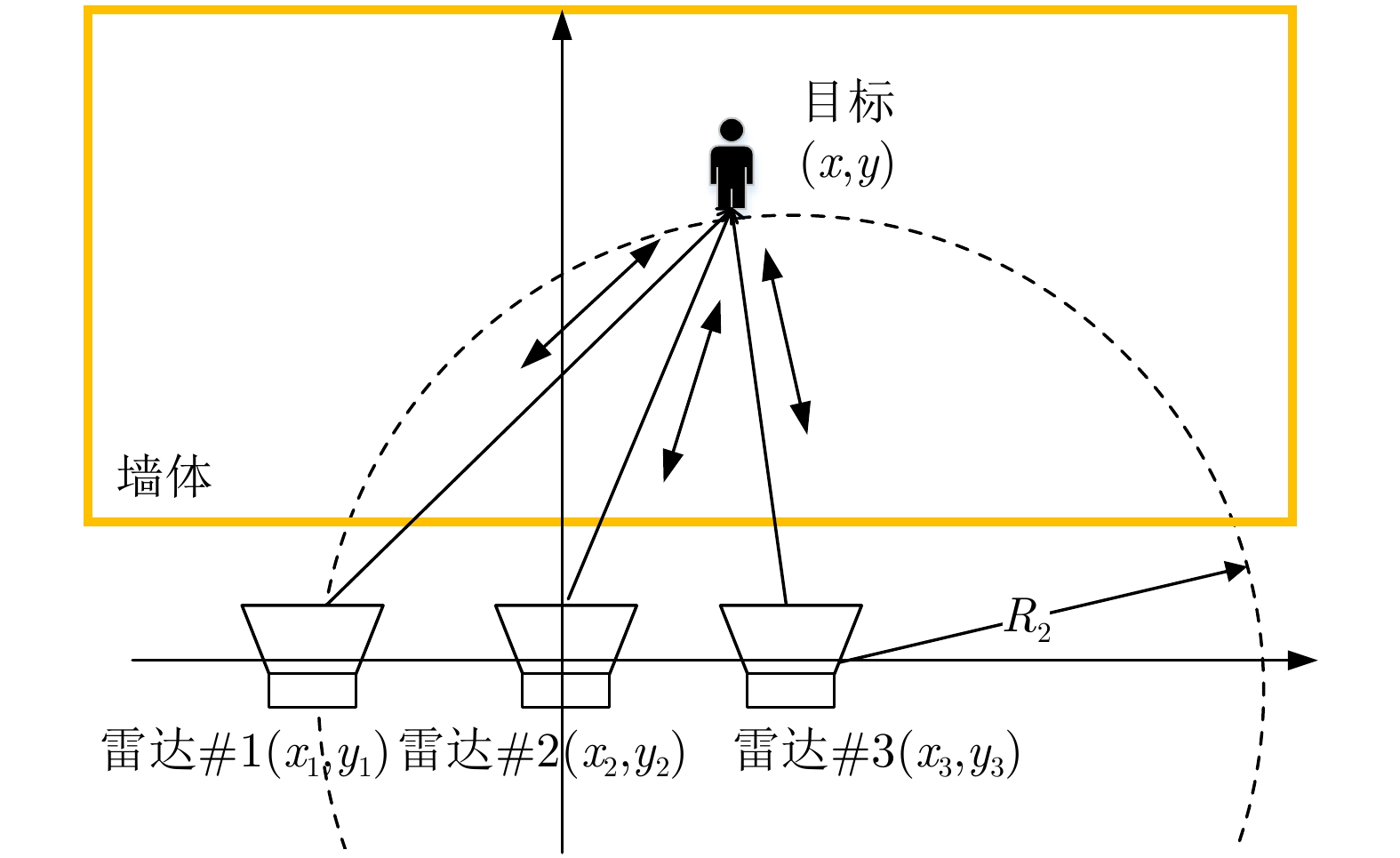
摘要: 单发单收穿墙雷达具备便携、系统简单、可独立工作等优势,但难以实现目标二维定位与跟踪。该文基于便携式单发单收雷达设计了一套分布式无线组网穿墙雷达系统,同时提出了一种目标联合定位方法,能够兼顾系统便携、低成本和目标二维信息估计。首先,设计了基于互补格雷码发射波形的超宽带雷达系统,解决了同频段多台雷达同时工作互相干扰的问题;分布式无线组网超宽带穿墙雷达系统包括3个雷达节点,并通过无线模块与数据处理中心通信。其次,提出了一种基于行为认知理论和模板匹配相结合的数据同步方法,通过识别各雷达数据中的相同运动状态来解决无线组网雷达慢时同步问题,摆脱了传统同步方法对硬件的苛刻要求。最后,提出基于Levenberg-Marquardt (L-M)最优化算法的雷达位置自估计和目标位置求解方法,实现了无先验雷达节点位置信息下的目标快速定位与跟踪。通过仿真分析与实验验证,该文设计的无线组网雷达系统可以实现目标二维定位与实时跟踪,雷达自身位置的估计精度优于0.06 m,对运动人体目标定位精度优于0.62 m。Abstract: Through-wall radar systems with single transmitter and receiver have the advantages of portability, simplicity, and independent operation; however, they cannot accomplish two-dimensional (2D) localization and tracking of targets. This paper proposes distributed wireless networking for through-wall radar systems based on a portable single transmitter and single receiver radar. Moreover, a target joint positioning method is proposed in this study, which can balance system portability, low cost, and target 2D information estimation. First, a complementary Gray code transmission waveform is utilized to overcome the issue of mutual interference when multiple radars operate simultaneously in the same frequency band, and each radar node communicates with the processing center via wireless modules, forming a distributed wireless networking radar system. In addition, a data synchronization method combines the behavioral cognition theory and template matching, which identifies identical motion states in data obtained from different radars, realizing slow-time synchronization among distributed radars and thereby eliminating the strict hardware requirements of conventional synchronization methods. Finally, a joint localization method based on Levenberg-Marquardt is proposed, which can simultaneously estimate the positions of radar nodes and targets without requiring prior radar position information. Simulation and field experiments are performed, and the results reveal that the distributed wireless networking radar system developed in this study can obtain 2D target positions and track moving targets in real time. The estimation accuracy of the radar’s own position is less than 0.06 m, and the positioning accuracy of moving human targets is less than 0.62 m.
-
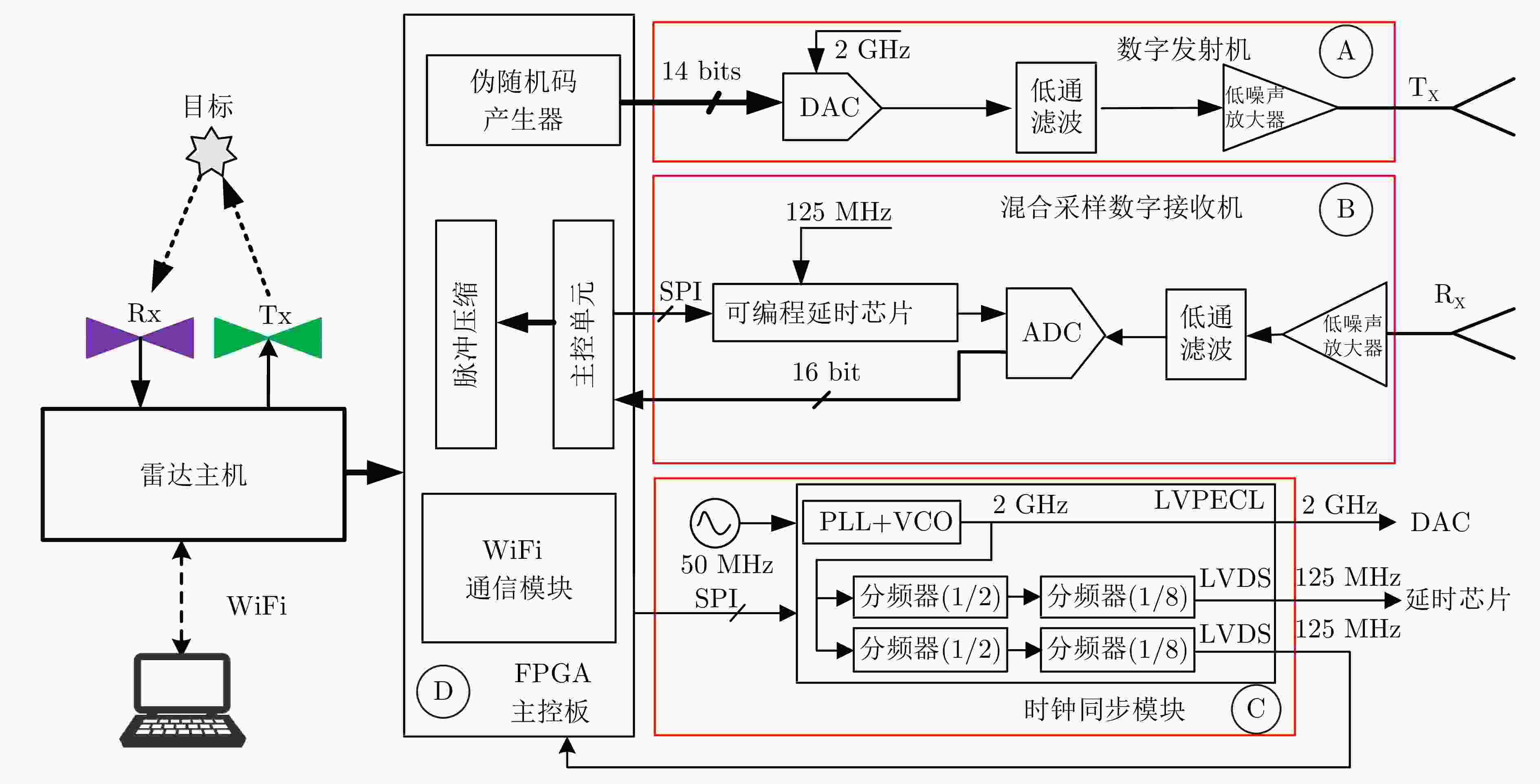
表 1 伪随机编码穿墙雷达系统关键参数
Table 1. Key parameters of pseudo random coded through-wall radar system
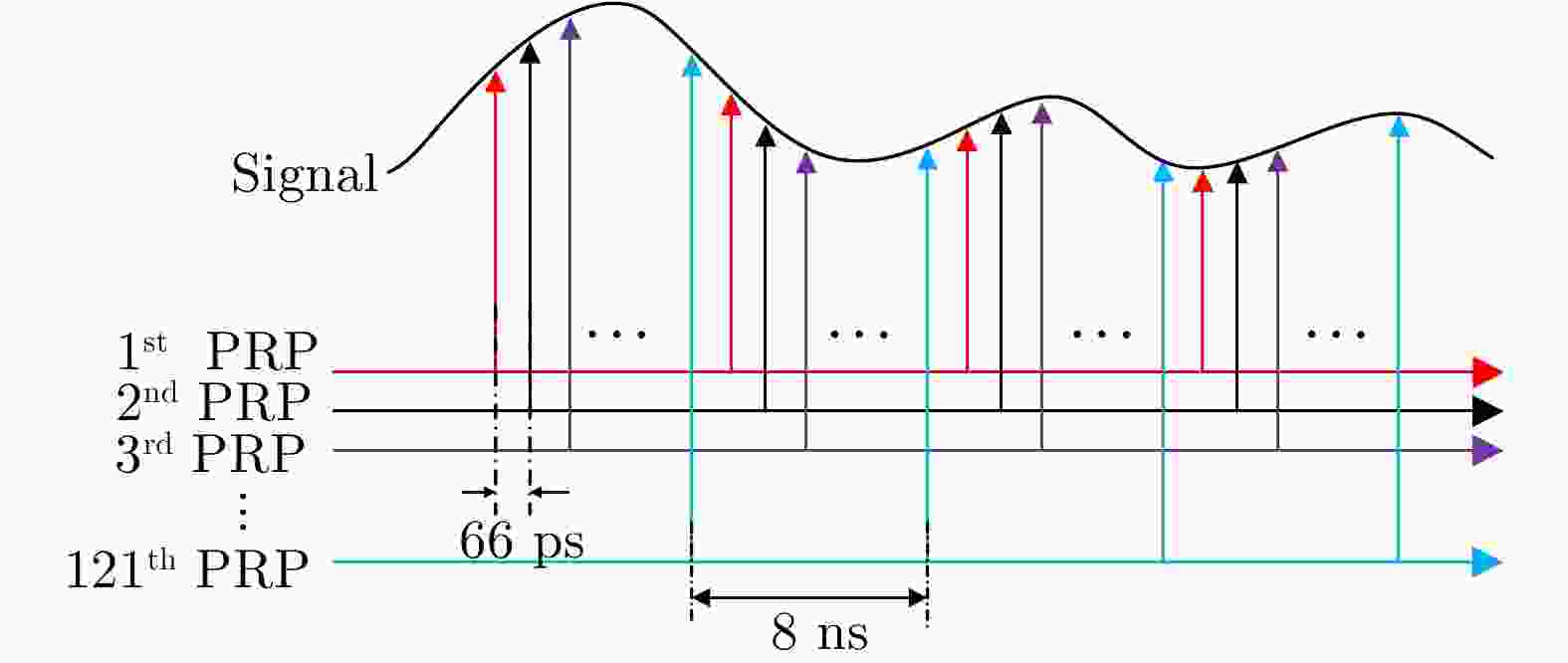
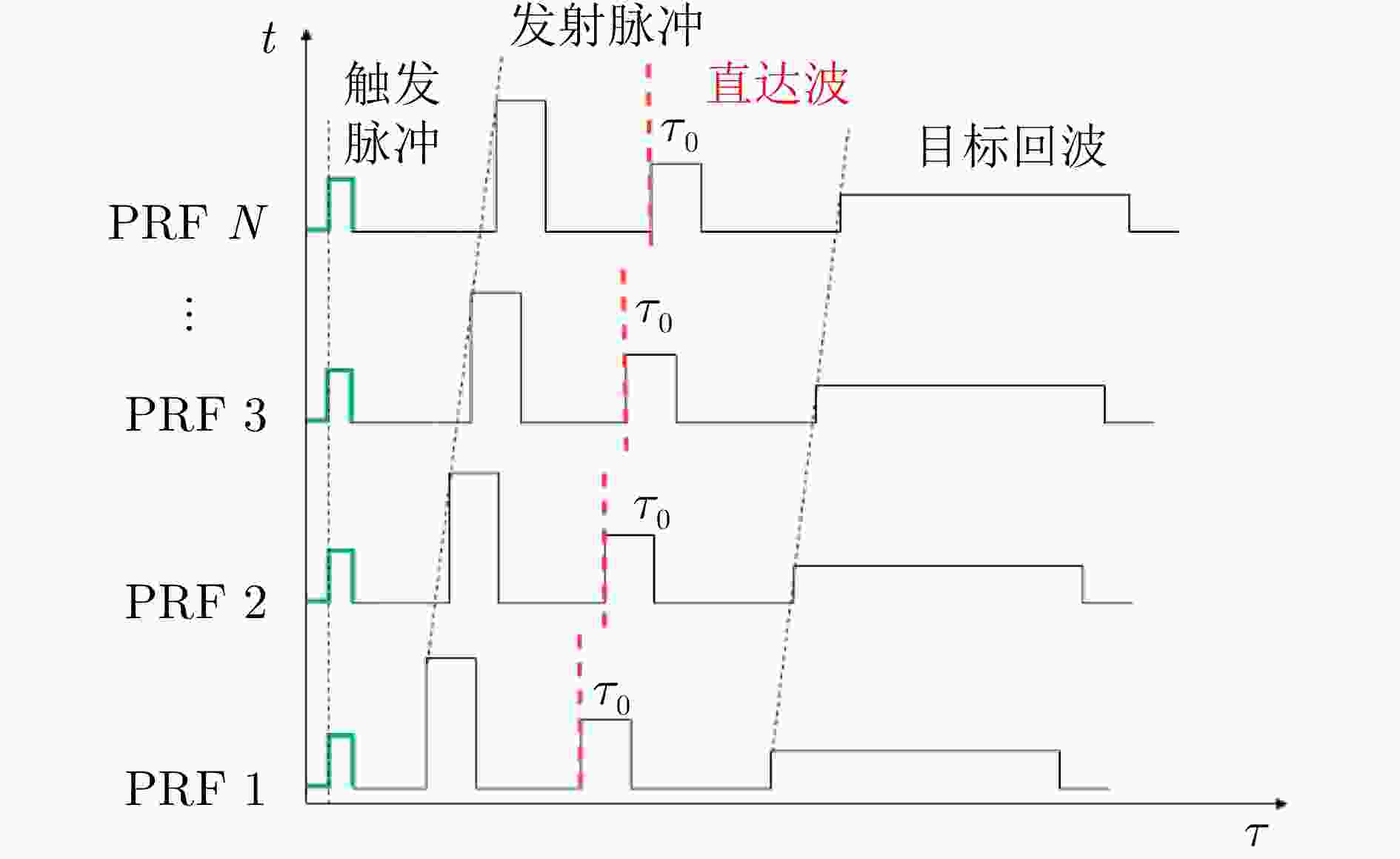
参数 指标 中心频率 1 GHz 带宽 1 GHz 码型 Golay互补码 累加次数 16 ADC位数 16 bit 等效采样率 16 GHz 扫描率 8 道/s 发射功率 17 dBm 重量 0.6 kg 表 2 无测距误差下雷达位置最优化估计结果(m)
Table 2. The optimization estimation results of radar position without range error (m)
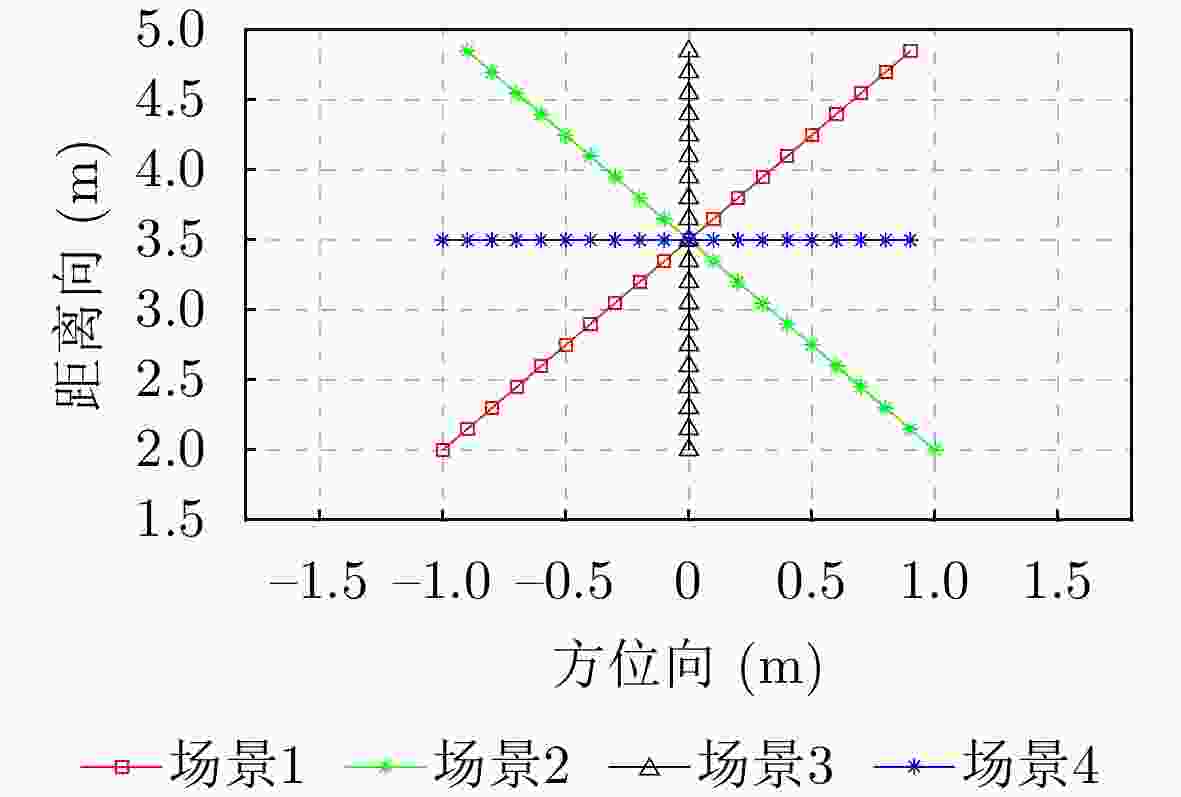
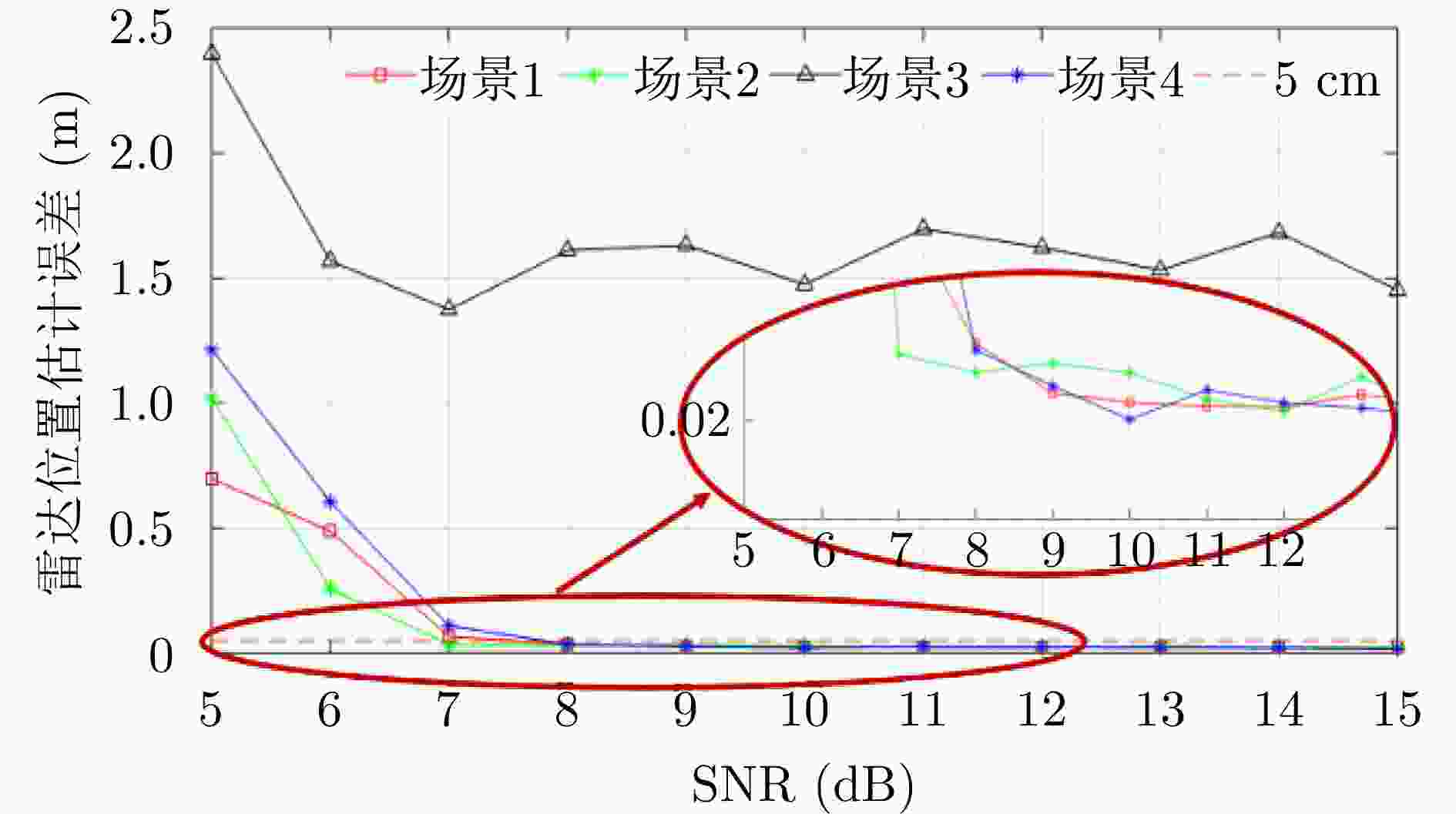
雷达放置位置 场景1 场景2 场景3 场景4 (–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+1.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+1.0,0)(–2.0,0)
(+1.0,0)(–1.95,0)
(+1.05,0)(–2.0,0)
(+1.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–1.05,0)
(+1.95,0)(–1.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–0.5,0)
(+1.0,0)(–0.5,0)
(+1.0,0)(–0.5,0)
(+1.0,0)(–0.52,0)
(+0.97,0)(–0.5,0)
(+1.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+3.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+3.0,0)(–1.0,0)
(+3.0,0)(–1.08,0)
(+2.91,0)(–1.0,0)
(+3.0,0)注:红色为雷达位置估计误差最大的情形。 表 3 含测距误差下雷达位置最优化估计结果(m)
Table 3. The optimization estimation results of radar position with range error (m)
雷达放置位置 场景1 场景2 场景3 场景4 (–2.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–2.03,0)
(+2.00,0)(–1.99,0)
(+2.02,0)(–2.19,0)
(+1.83,0)(–2.02,0)
(+1.99,0)(–2.0,0)
(+1.0,0)(–2.07,0)
(+0.97,0)(–1.98,0)
(+0.99,0)(–2.31,0)
(+0.79,0)(–2.05,0)
(+0.97,0)(–1.0,0)
(+2.0,0)(–0.99,0)
(+2.02,0)(–0.98,0)
(+2.00,0)(–1.03,0)
(+1.99,0)(–1.02,0)
(+2.01,0)(–0.5,0)
(+1.0,0)(–0.57,0)
(+1.00,0)(–0.48,0)
(+1.03,0)(–0.34,0)
(+1.29,0)(–0.50,0)
(+0.95,0)(–1.0,0)
(+3.0,0)(–1.01,0)
(+2.99,0)(–0.97,0)
(+3.02,0)(–1.21,0)
(+2.82,0)(–0.99,0)
(+3.00,0)注:红色为雷达位置估计误差最大的情形。 表 4 雷达位置最优化估计结果 (m)
Table 4. The estimation results of radar position optimization (m)
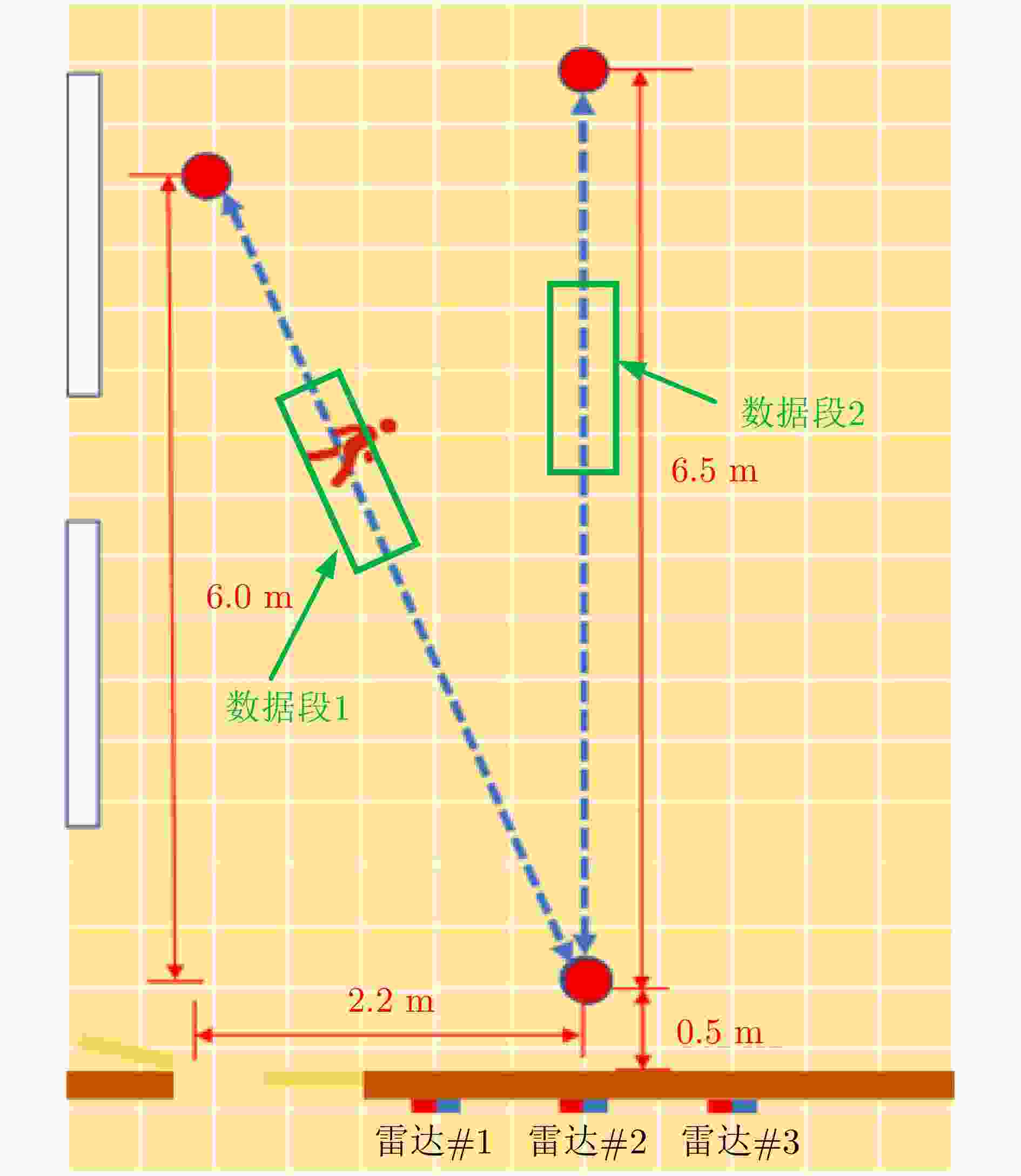
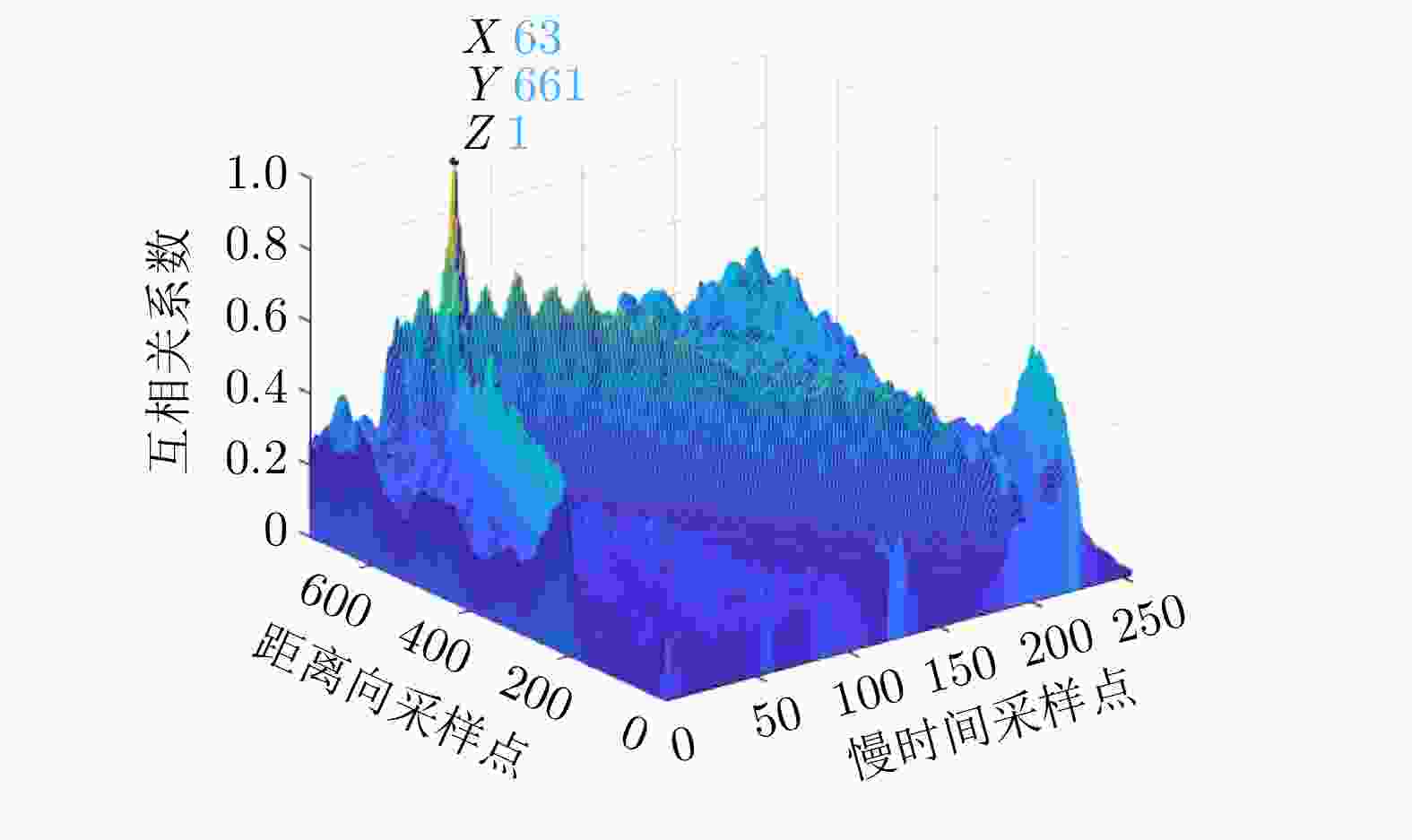
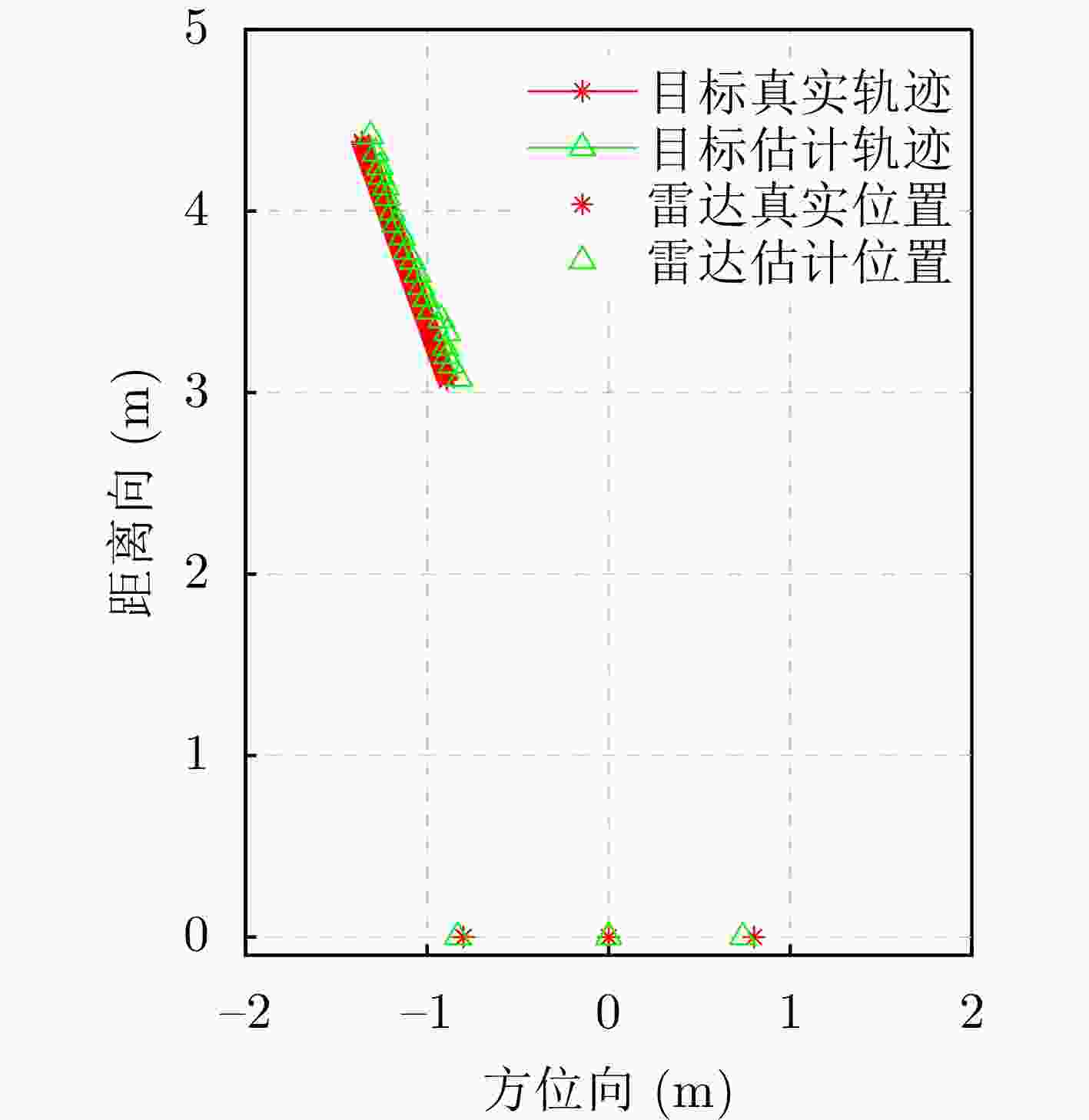
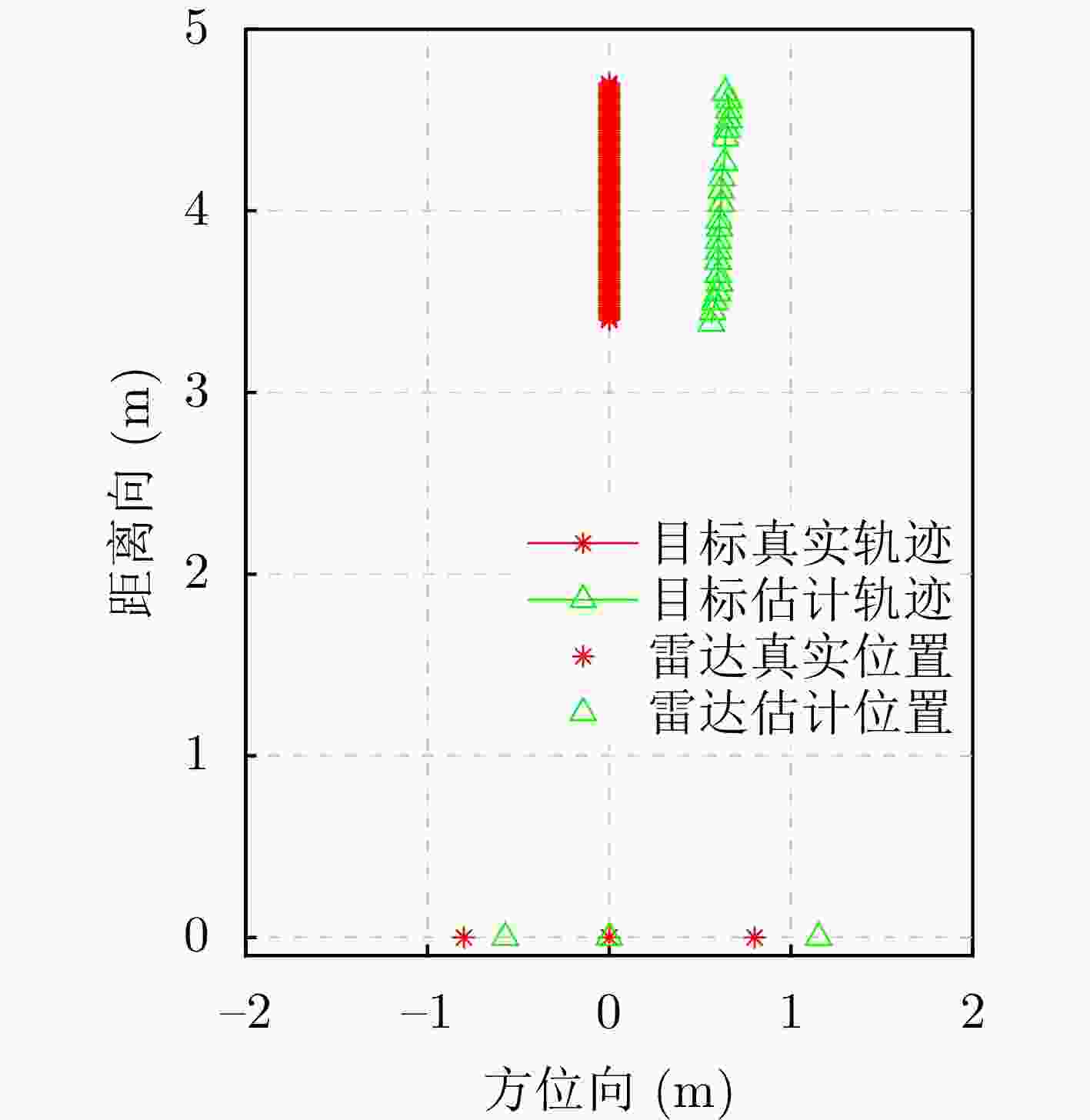
雷达放置位置 数据段1 数据段2 雷达#1(–0.8,0)
雷达#3(+0.8,0)(– 0.8328 ,0 )
(+0.7382 ,0)(– 0.5721 ,0)
(+1.1519 ,0) -
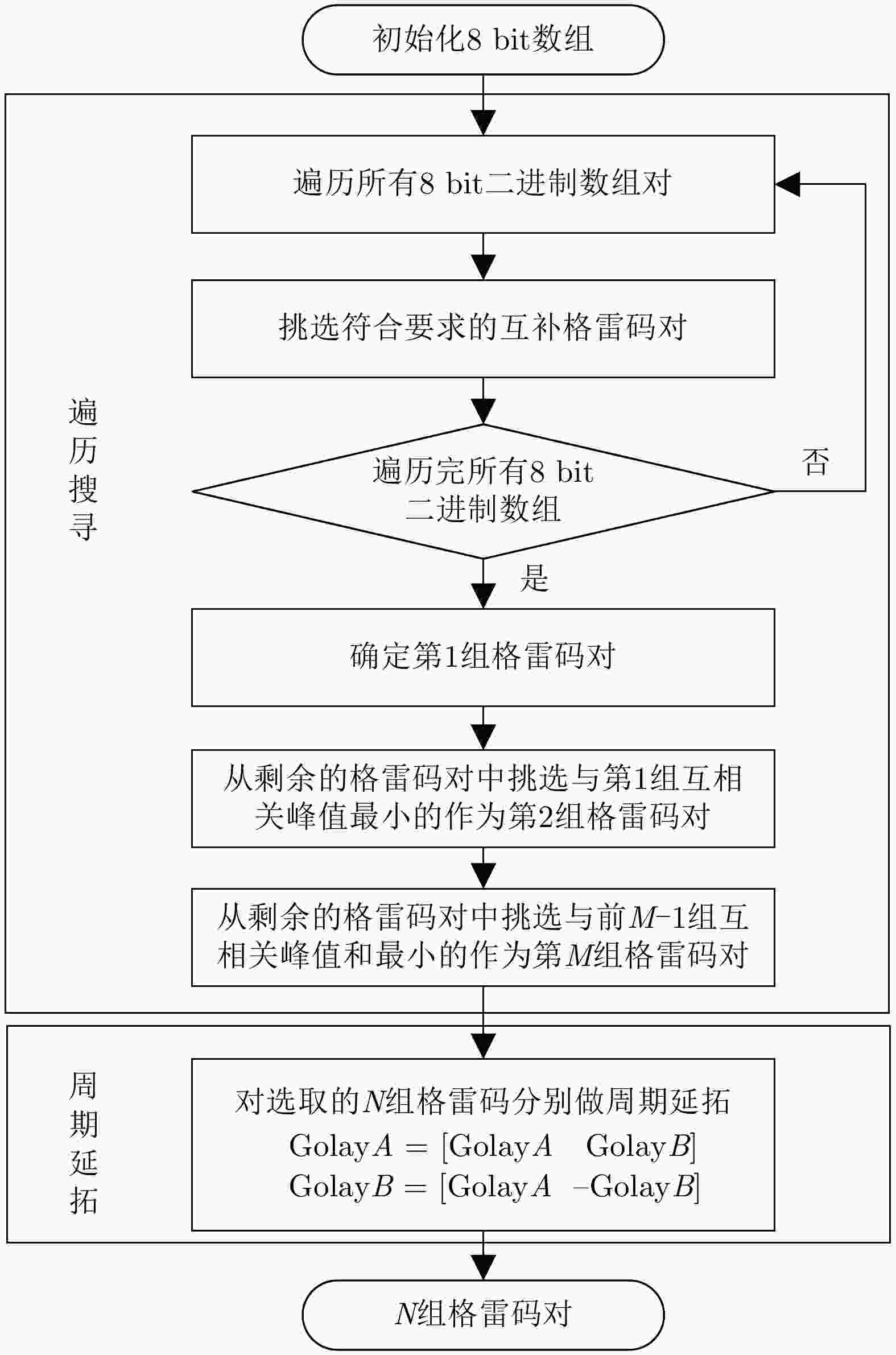
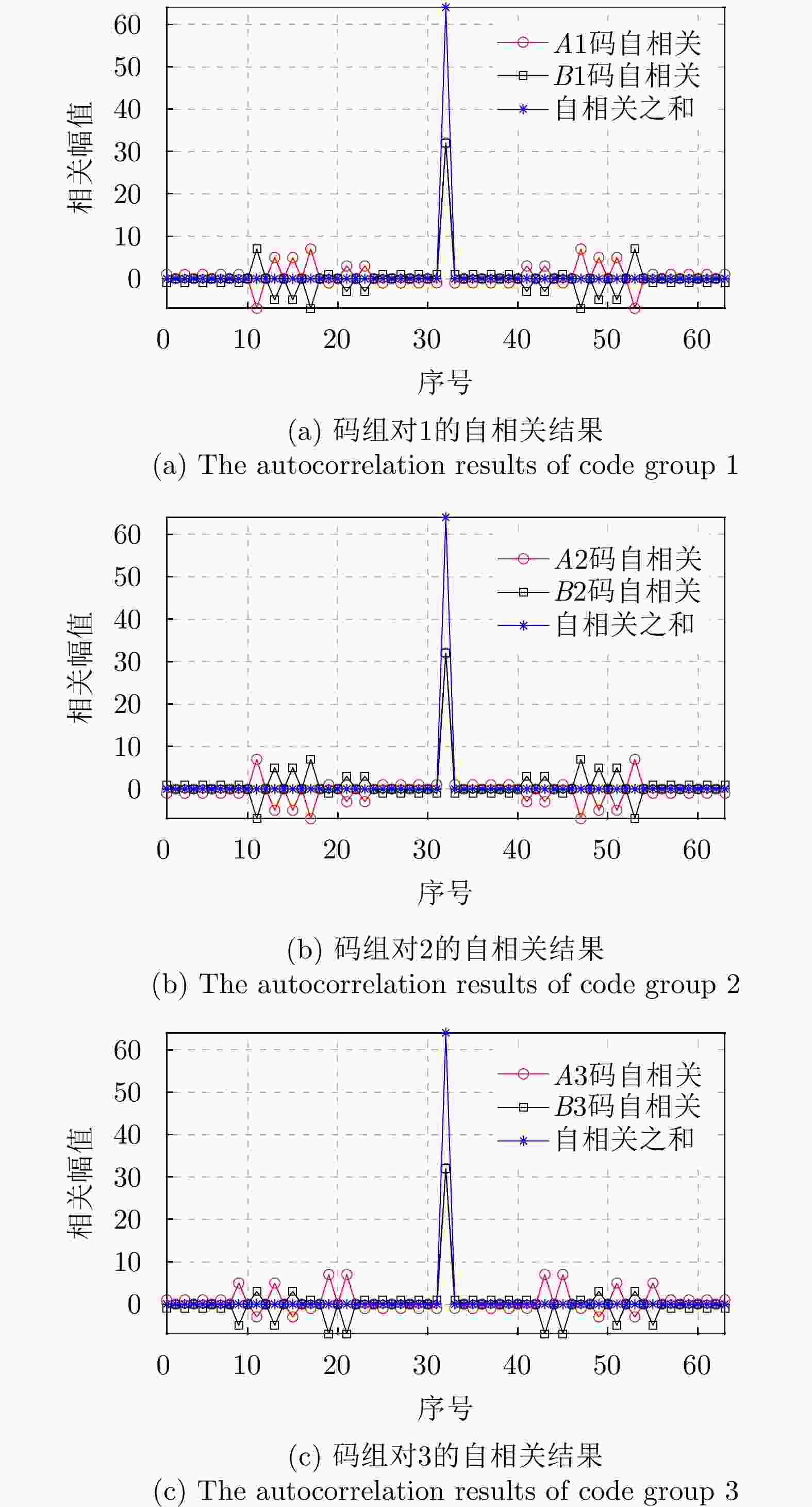
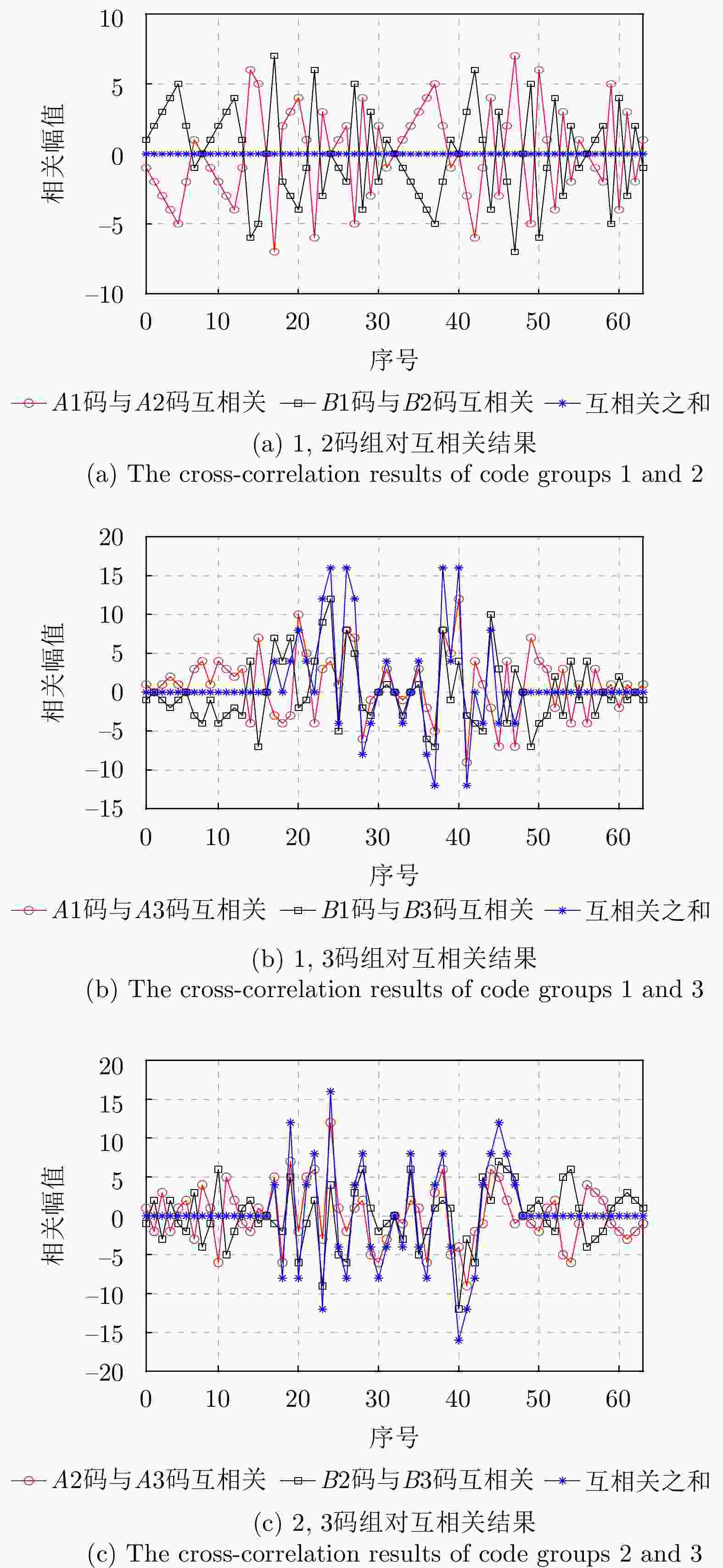
[1] AMIN M G, 朱国富, 陆必应, 金添, 等译. 穿墙雷达成像[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014: 100−110.AMIN M G, ZHU Guofu, LU Biying, JIN Tian, et al. translation. Through-The-Wall Radar Imaging[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014: 100−110. [2] 夏正欢, 张群英, 叶盛波, 等. 一种便携式伪随机编码超宽带人体感知雷达设计[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027.XIA Zhenghuan, ZHANG Qunying, YE Shengbo, et al. Design of a handheld pseudo random coded uwb radar for human sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027. [3] WANG J, DU H, NIYATO DT, et al. Through the wall detection and localization of autonomous mobile device in indoor scenario.[J] IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2024, 42: 161−176. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3322819. [4] 金添, 宋勇平. 超宽带雷达建筑物结构稀疏成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031.JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Sparse imaging of building layouts in ultra-wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031. [5] ZHENG Zhijie, PAN Jun, NI Zhikang, et al. Recovering human pose and shape from through-the-wall radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5112015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3162333. [6] LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Improved vital signal extraction algorithm for through the wall radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2020, 56(2): 89–91. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.2853. [7] QU Xiaodong, GAO Weicheng, MENG Haoyu, et al. Indoor human behavior recognition method based on wavelet scattering network and conditional random field model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5104815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3276023. [8] 张杨, 吕昊, 于霄, 等. 基于超宽谱雷达多目标穿墙探测定位技术的研究[J]. 医疗卫生装备, 2016, 37(8): 10–13. doi: 10.7687/J.ISSN1003-8868.2016.08.010.ZHANG Yang, LYU Hao, YU Xiao, et al. Research of through-wall detection and location technique for multihuman targets using ultra wideband radar[J]. Chinese Medical Equipment Journal, 2016, 37(8): 10–13. doi: 10.7687/J.ISSN1003-8868.2016.08.010. [9] MOHAMMED I, COLLINGS I B, and HANLY S V. Multiple target localization through-the-wall using non-coherent Bi-static radar[C]. 2019 13th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Gold Coast, Australia, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCS47537.2019.9008415. [10] LIU Xin, ZHANG Jingwei, GUO Ruijie, et al. A novel interferometry positioning and tracking method with short baseline for UWB through-the-wall radar system[C]. 2018 17th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), Rapperswil, Switzerland, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICGPR.2018.8441520. [11] PAN Jun, YE Shengbo, SHI Cheng, et al. 3D imaging of moving targets for ultra-wideband MIMO through-wall radar system[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(3): 261–273. doi: 10.1049/RSN2.12035. [12] 刘新, 阎焜, 杨光耀, 等. UWB-MIMO穿墙雷达三维成像与运动补偿算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356.LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Study on 3D imaging and motion compensation algorithm for UWB-MIMO through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. [13] 郭冠斌, 方青. 雷达组网技术的现状与发展[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2005, 3(4): 193–197, 202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2005.04.001.GUO Guanbin and FANG Qing. Current status and development of radar netting technique[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2005, 3(4): 193–197, 202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2005.04.001. [14] 史城, 叶盛波, 潘俊, 等. 一种基于分布式穿墙雷达的复杂条件下人体目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203.SHI Cheng, YE Shengbo, PAN Jun, et al. A human target detection method under complex conditions by distributed through-wall radar system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203. [15] 曾涛, 殷丕磊, 杨小鹏, 等. 分布式全相参雷达系统时间与相位同步方案研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 105–110. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20104.ZENG Tao, YIN Pilei, YANG Xiaopeng, et al. Time and phase synchronization for distributed aperture coherent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 105–110. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20104. [16] KOCUR D A, ŠVECOVÁ M, and ROVNÁKOVÁ J. Through-the-wall localization of a moving target by two independent ultra wideband (UWB) radar systems[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(9): 11969–11997. doi: 10.3390/s130911969. [17] ZHANG Jun, JIN Tian, HE Yuan, et al. A centralized processing framework for foliage-penetration human tracking in multistatic radar[J]. Radioengineering, 2016, 25(1): 98–105. doi: 10.13164/RE.2016.0098. [18] HE Yuan, AUBRY P, and LE CHEVALIER F. Ultra-wideband multistatic tracking of human targets[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/CP.2013.0406. [19] PRAGER S, HAYNES M S, and MOGHADDAM M. Wireless subnanosecond RF synchronization for distributed ultrawideband software-defined radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(11): 4787–4804. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3014876. [20] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Low probability of intercept-based collaborative power and bandwidth allocation strategy for multi-target tracking in distributed radar network system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(12): 6367–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2977328. [21] NIU Ruixin, BLUM R S, VARSHNEY P K, et al. Target localization and tracking in noncoherent multiple-input multiple-output radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1466–1489. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178073. [22] ROVNÁKOVÁ J and KOCUR D. TOA estimation and data association for through-wall tracking of moving targets[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2010, 2010: 420767. doi: 10.1155/2010/420767. [23] 李虎泉, 郭世盛, 陈家辉, 等. 分布式穿墙成像雷达空间配准方法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2023, 52(1): 30–37. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022162.LI Huquan, GUO Shisheng, CHEN Jiahui, et al. Radar registration algorithm for distributed through-the-wall imaging radar[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023, 52(1): 30–37. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022162. [24] REN Wei, QI Fugui, FOROUGHIAN F, et al. Vital sign detection in any orientation using a distributed radar network via modified independent component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4774–4790. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3101655. [25] YANG Shixing, YI Wei, and JAKOBSSON A. Multitarget detection strategy for distributed MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5113516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3175046. [26] XIA Zhenghuan, WU Shiyou, LIU Xin, et al. Through-floor vital sign searching for trapped person using wireless-netted UWB radars[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(22): 10538. doi: 10.3390/app112210538. [27] SAKAMOTO T and SATO T. A method of estimating a room shape using a single antenna in a multipath environment[C]. Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 2010: 1–5. [28] GOLAY M. Complementary series[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1961, 7(2): 82–87. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1961.1057620. [29] 何东健. 数字图像处理[M]. 3版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2015: 207–209.HE Dongjian. Digital Image Processing[M]. 3rd ed. Xi’an: XIDIAN UNIVERSIY PRESS, 2015: 207–209. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: