Three-dimensional Imaging of Tomographic SAR Based on Adaptive Elevation Constraint
-
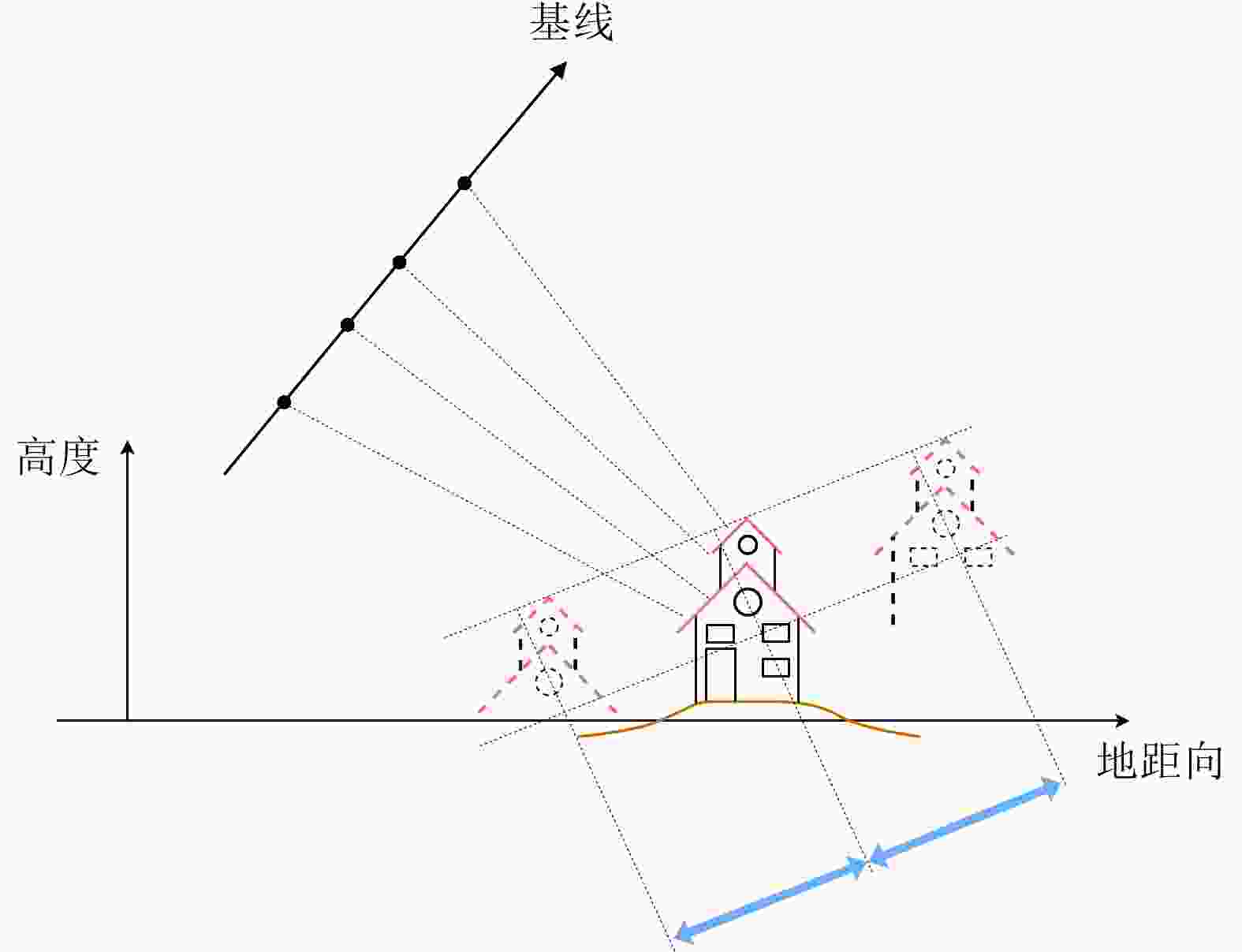
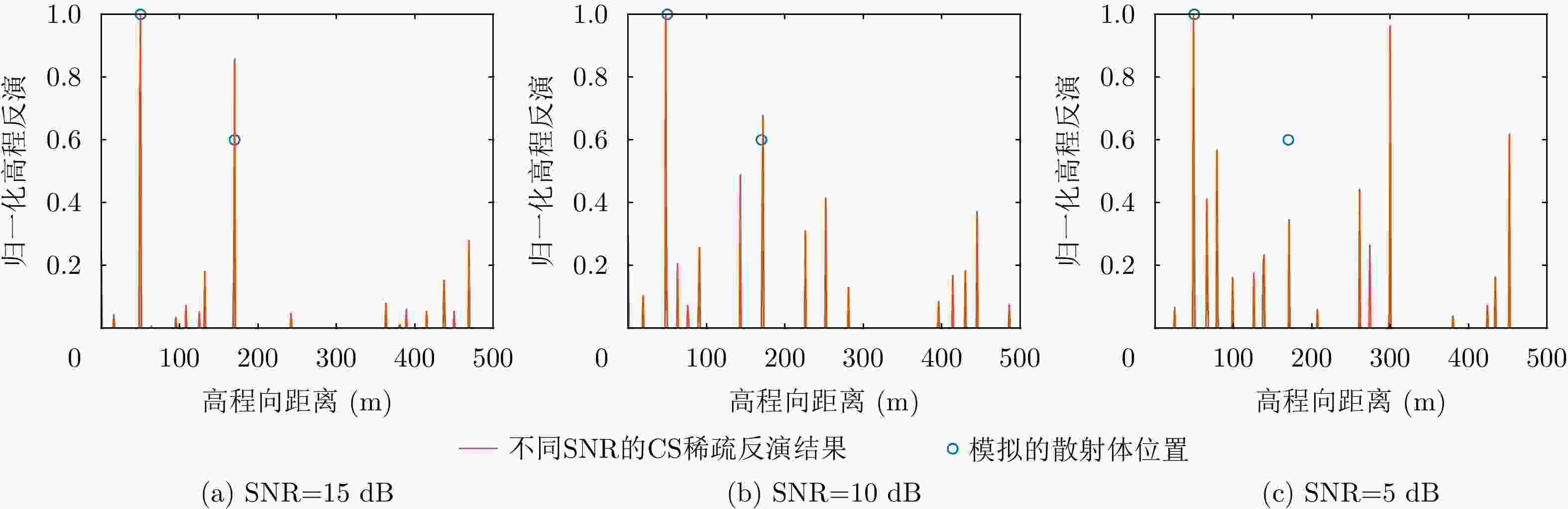
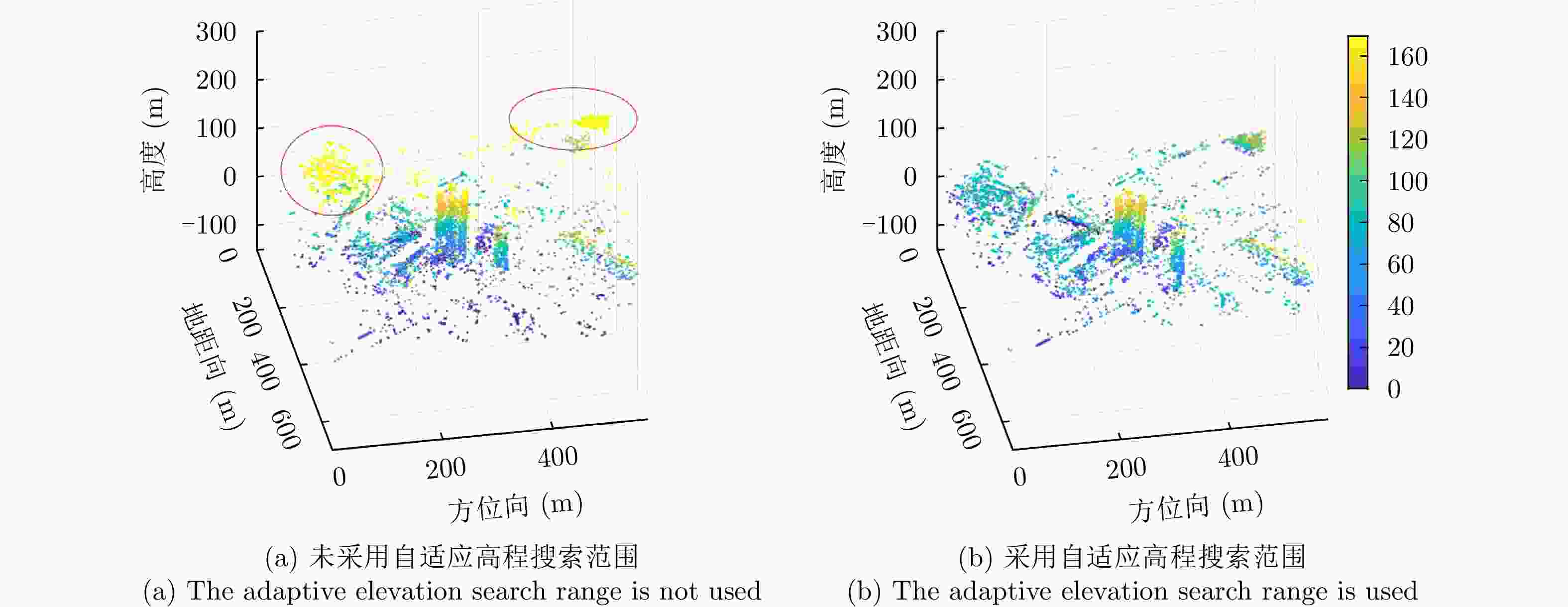
摘要: 层析合成孔径雷达成像(TomoSAR)是2010年以来SAR成像领域尤其是城市三维成像的热门研究方向。但在TomoSAR三维重建中,相位缠绕会引起高程散射剖面的周期性谱峰,并导致散射体高程向位置的错误估计和三维成像结果中建筑点云的分层,即高程模糊。该文针对这一现象,提出一种自适应调整高程搜索范围的方法,以提升散射体高程估计的准确度,并改善高程模糊。该方法首先进行场景的高度预估计,然后根据高度预估计构建高程采样中心线性函数并计算搜索半径,从而确定并更新各像素的高程搜索范围,保留真实谱峰并隔离模糊峰值。机载和星载的实测数据实验表明所提方法明显改善了高程模糊和伪影问题,提高了三维点云的空间集中度和连续性。
-
关键词:
- 层析合成孔径雷达成像(TomoSAR) /
- 相位缠绕 /
- 高程模糊 /
- 散射体 /
- 高程搜索范围
Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar Tomography (TomoSAR) has emerged as a hot research topic in the field of SAR imaging, particularly for three-dimensional (3D) urban imaging in recent years. However, in TomoSAR 3D reconstruction, due to the phase unwrapping difficulty, periodic spectral peaks appear in the reconstruction results of the reflectivity profile along the elevation. This results in errors in estimating the elevation locations of the scatterers and causing layering effects in 3D imaging results, which is the elevation ambiguity. In light of this phenomenon observed in TomoSAR, a method for the adaptive adjustment of the elevation search range is proposed to improve the accuracy of the elevation estimation and reduce elevation ambiguity. In this method, the height of the scene is first estimated, the linear function of the elevation sampling center is subsequently constructed based on the height pre-estimations, and the search radius is finally calculated. Thereafter, the elevation search range of each pixel in the SAR image is determined and updated, preserving the true spectral peaks while isolating the ambiguity peaks. The experimental results for airborne and spaceborne measured data demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves elevation ambiguity and artifacts-related issues while also improving the spatial concentration and continuity of 3D point clouds.-
Key words:
- TomoSAR /
- Phase unwrapping /
- Elevation ambiguity /
- Scatterers /
- Elevation sample range
-
表 1 仿真实验1参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters for the first simulation data
参数 数值 参数 数值 通道数 11 波长 0.02 m 基线跨度 1 m 下视角 45° 最小基线间隔 0.1 m 高程模糊间隔 100 m 斜距 1000 m 高程瑞利分辨率 10 m 表 2 仿真实验2参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters for the second simulation data
参数 数值 参数 数值 航过数 11 波长 0.03 m 基线跨度 450 m 下视角 45° 最小基线间隔 21 m 最大不模糊高程 428.6 m 斜距 600 km 高程瑞利分辨率 20 m 表 3 峨眉数据参数
Table 3. Parameters of Emei data
参数 数值 载波频率 14.5 GHz 最小基线间隔 0.1115 m 最大基线长度 1.1274 m 载机航线海拔 2157 m 场景海拔 420 m 中心斜距 2040.1 m 中心下视角 31.6° 距离向像素尺寸 0.1362 m 方位向像素尺寸 0.1051 m 表 4 峨眉数据的平均邻域高度差(m)
Table 4.
$\Delta {{\boldsymbol{h}}_{\bf{E}}}$ of Emei data (m)未采用自适应高程搜索范围$\Delta {h_{\text{E}}}$ 采用自适应高程搜索范围$\Delta {h_{\text{E}}}$ 12.6512 7.5453 表 5 巴塞罗那数据参数
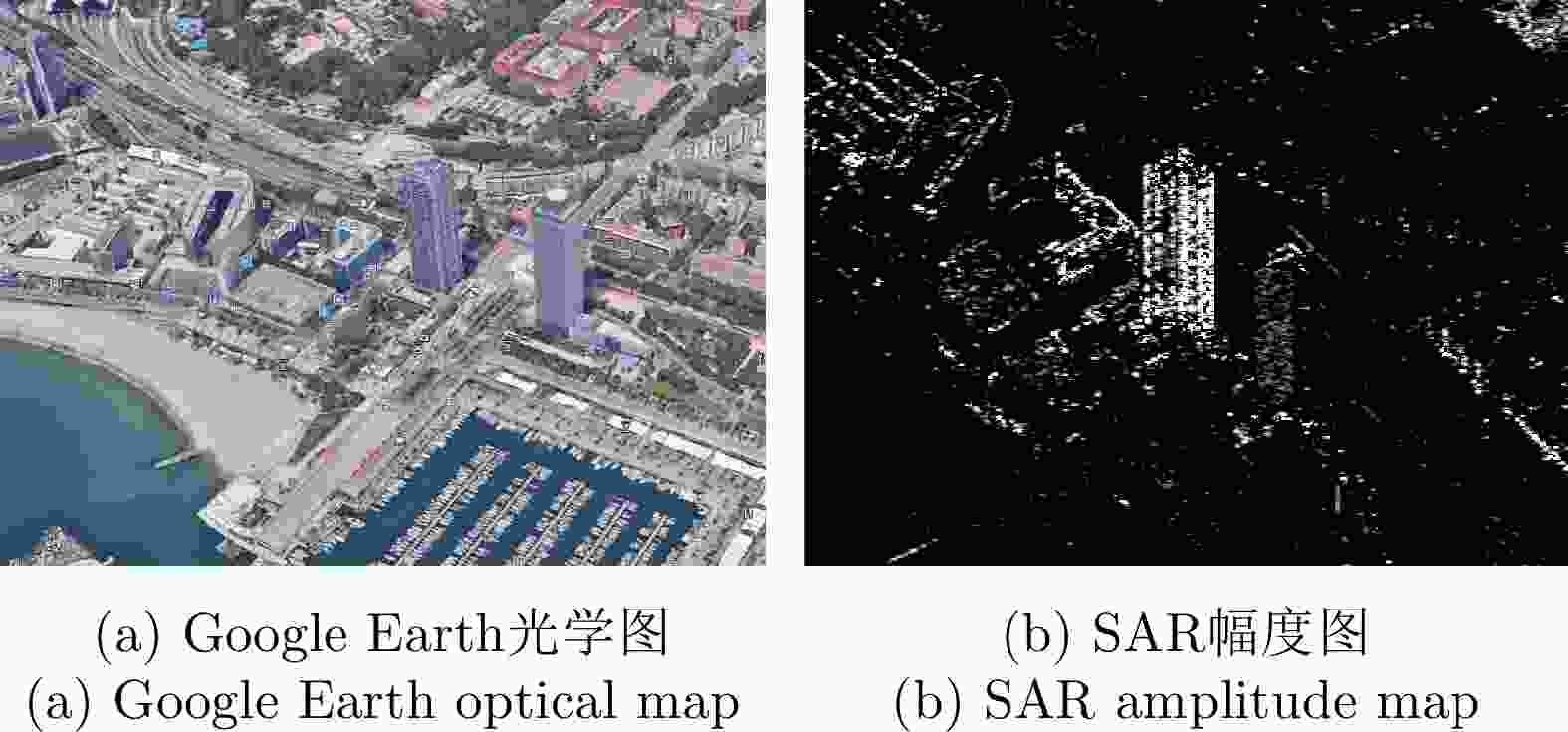
Table 5. Parameters of Barcelona data
参数 数值 载波频率 9.65 GHz 最小基线间隔 7.98 m 最大基线长度 246.4 m 中心斜距 621.6 km 中心下视角 35.7° 距离向像素尺寸 0.91 m 方位向像素尺寸 1.88 m 表 6 巴塞罗那数据的平均邻域高度差(m)
Table 6.
$\Delta {{\boldsymbol{h}}_{\mathbf{E}}}$ of Barcelona data (m)未采用自适应高程搜索范围$\Delta {h_{\text{E}}}$ 采用自适应高程搜索范围$\Delta {h_{\text{E}}}$ 22.5561 14.3084 -
[1] MUNSON D C, O’BRIEN J D, and JENKINS W K. A tomographic formulation of spotlight-mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1983, 71(8): 917–925. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1983.12698 [2] 张斌, 韦立登, 胡庆荣, 等. 基于四阶累积量的机载多基线SAR谱估计解叠掩方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 740–749. doi: 10.12000/JR18087ZHANG Bin, WEI Lideng, HU Qingrong, et al. Solution to layover problemin airborne multi-baseline SAR based on spectrum estimation with fourth-order cumulant[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 740–749. doi: 10.12000/JR18087 [3] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [4] FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 [5] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [6] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, PAUCIULLO A, et al. Tomographic processing of interferometric SAR data: Developments, applications, and future research perspectives[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 41–50. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312073 [7] 张红, 江凯, 王超, 等. SAR层析技术的研究与应用[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2010, 25(2): 282–287. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.2.282ZHANG Hong, JIANG Kai, WANG Chao, et al. The current status of SAR tomography[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2010, 25(2): 282–287. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.2.282 [8] EL MOUSSAWI I, MINH D H T, BAGHDADI N, et al. L-band UAVSAR tomographic imaging in dense forests: Gabon forests[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 475. doi: 10.3390/rs11050475 [9] EL MOUSSAWI I, MINH D H T, BAGHDADI N, et al. Monitoring tropical forest structure using SAR tomography at L- and P-band[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(16): 1934. doi: 10.3390/rs11161934 [10] PIAU P, BRUNIQUEL J, CAEL J C, et al. Analysis of the resolution of a multitemporal SAR System[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 1993: 1196–1199. [11] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1 norm regularization—the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [12] 魏恋欢, 廖明生, BALZ T, 等. 高分辨率SAR层析成像建筑物叠掩散射体提取[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2014, 39(5): 536–540. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20120460WEI Lianhuan, LIAO Mingsheng, BALZ T, et al. Layover building scatterers extraction via high-resolution spaceborne SAR tomography[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(5): 536–540. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20120460 [13] 毕辉, 金双, 王潇, 等. 基于高分三号SAR数据的城市建筑高分辨率高维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113BI Hui, JIN Shuang, WANG Xiao, et al. High-resolution high-dimensional imaging of urban building based on GaoFen-3 SAR data[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113 [14] LOMBARDINI F and REIGBER A. Adaptive spectral estimation for multibaseline SAR tomography with airborne L-band data[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 2014–2016. [15] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [16] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 [17] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 [18] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [19] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 [20] ZHANG Bangjie, XU Gang, YU Hangwen, et al. Array 3-D SAR tomography using robust gridless compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5205013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3259980 [21] 林赟, 张琳, 韦立登, 等. 无先验模型复杂结构设施SAR全方位三维成像方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 909–919. doi: 10.12000/JR22148LIN Yun, ZHANG Lin, WEI Lideng, et al. Research on full-aspect three-dimensional SAR imaging method for complex structural facilities without prior model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 909–919. doi: 10.12000/JR22148 [22] REN Yexian, XIAO Aoran, HU Fengming, et al. Coprime sensing for airborne array interferometric SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5229615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3182980 [23] LI Xiaowan, ZHANG Fubo, LI Yanlei, et al. An elevation ambiguity resolution method based on segmentation and reorganization of TomoSAR point cloud in 3D mountain reconstruction[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5118. doi: 10.3390/rs13245118 [24] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027 [25] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Sparse reconstruction techniques for SAR tomography[C]. 17th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Corfu, Greece, 2011: 1–8. [26] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013 [27] WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Tomographic SAR inversion by atomic-norm minimization—the gridless compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3223524 [28] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [29] CHEN S S, DONOHO D L, and SAUNDERS M A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J]. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1): 129–159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [30] 王金峰, 皮亦鸣, 曹宗杰. 一种机载SAR层析三维成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(5): 1029–1033. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00737WANG Jinfeng, PI Yiming, and CAO Zongjie. An algorithm for airborne SAR tomography 3D imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(5): 1029–1033. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00737 [31] GUO Rui, WANG Fan, ZANG Bo, et al. High-rise building 3D reconstruction with the wrapped interferometric phase[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(6): 1439. doi: 10.3390/s19061439 [32] GUO Rui, GAO Yuxin, ZHANG Zhao, et al. Efficient tomographic inversion based on refined scatterer pre-estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4513305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3203037 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: