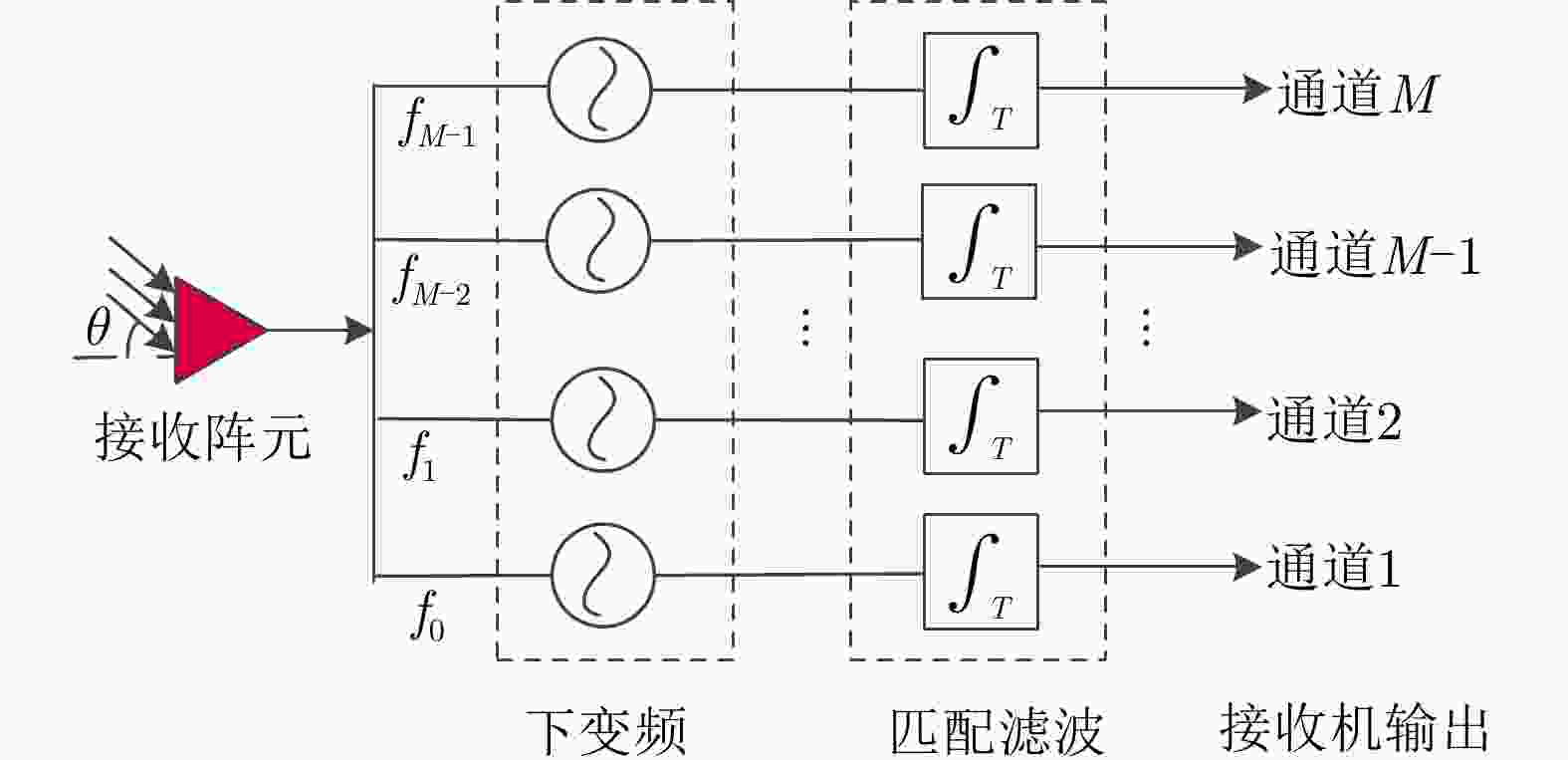
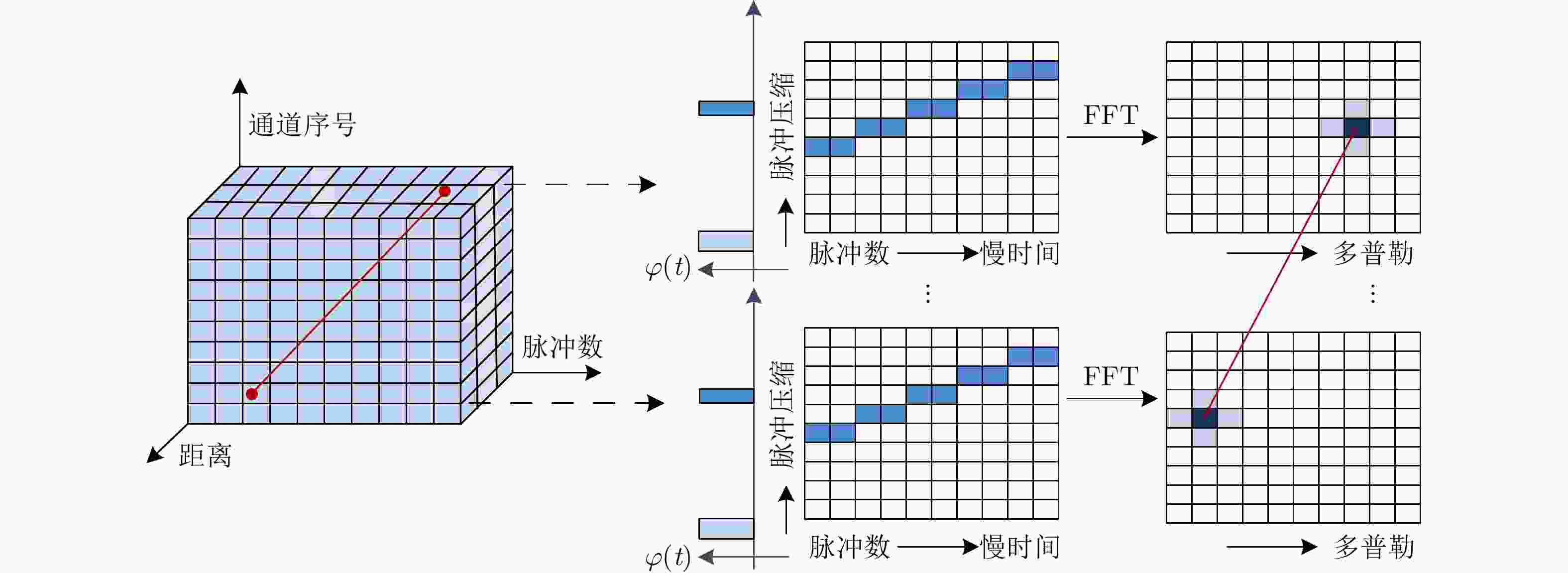
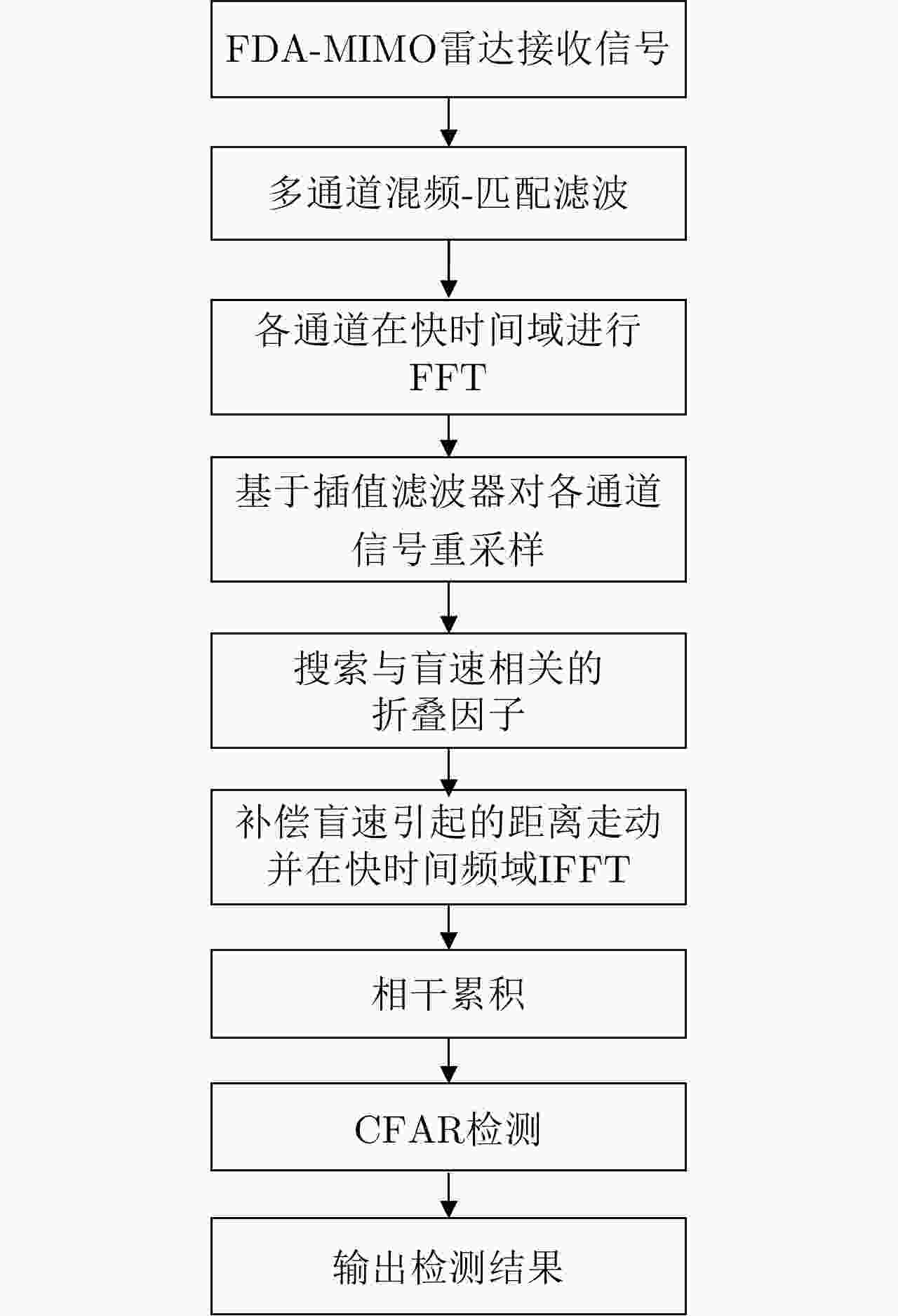
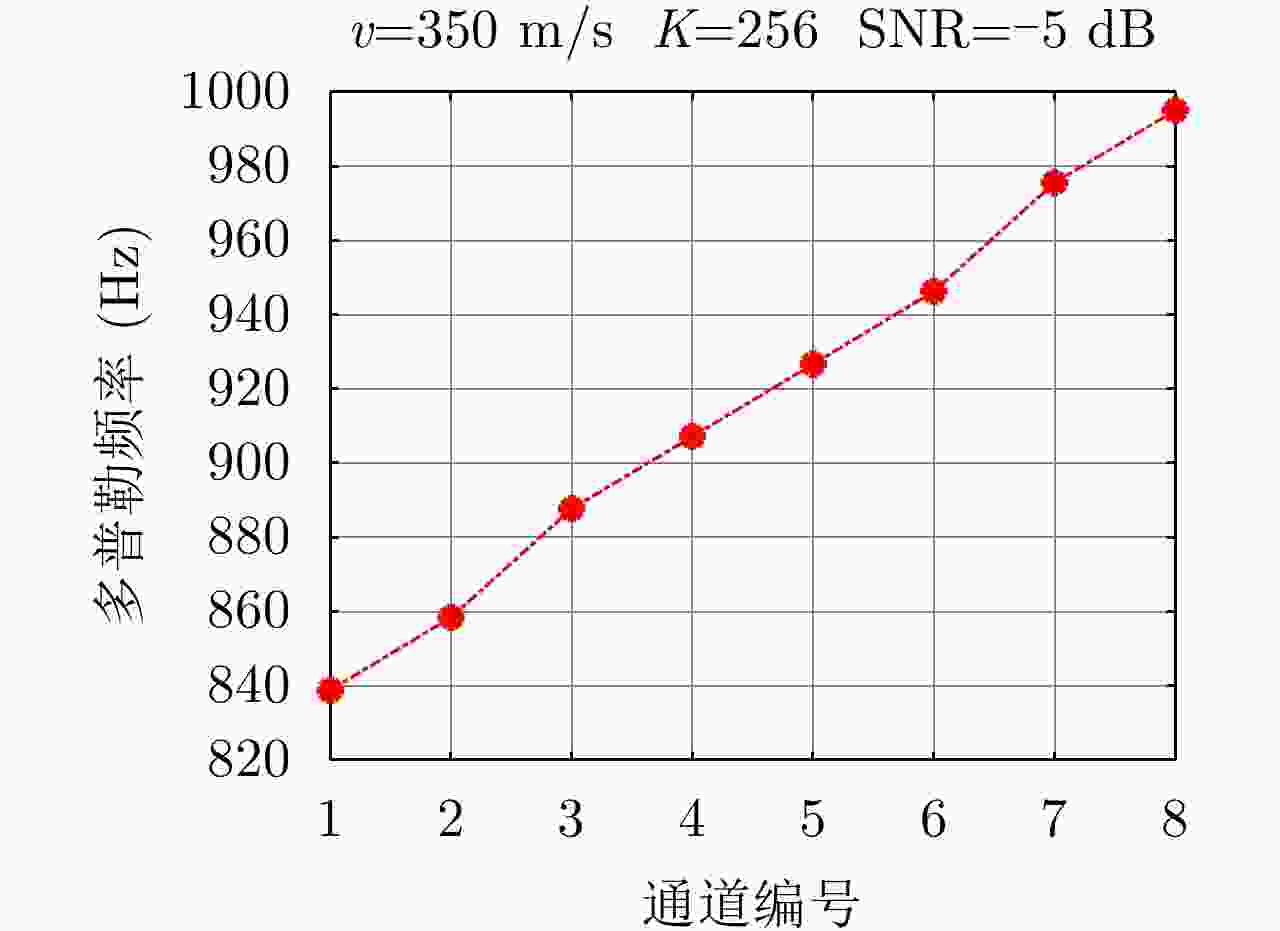
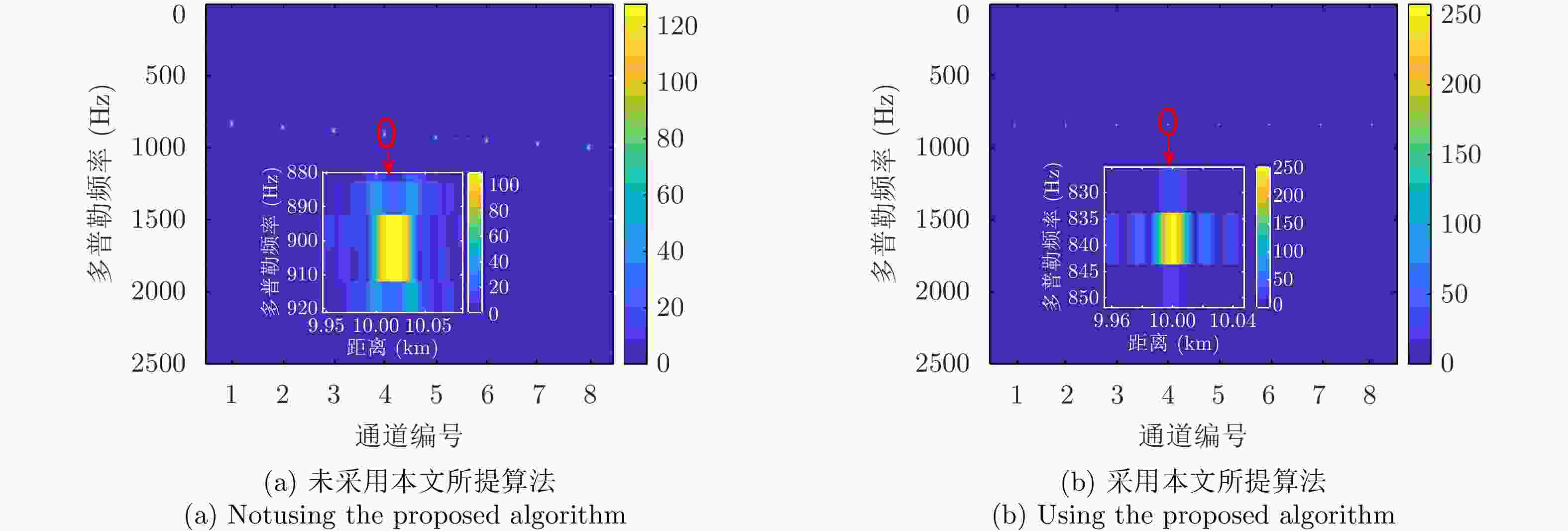
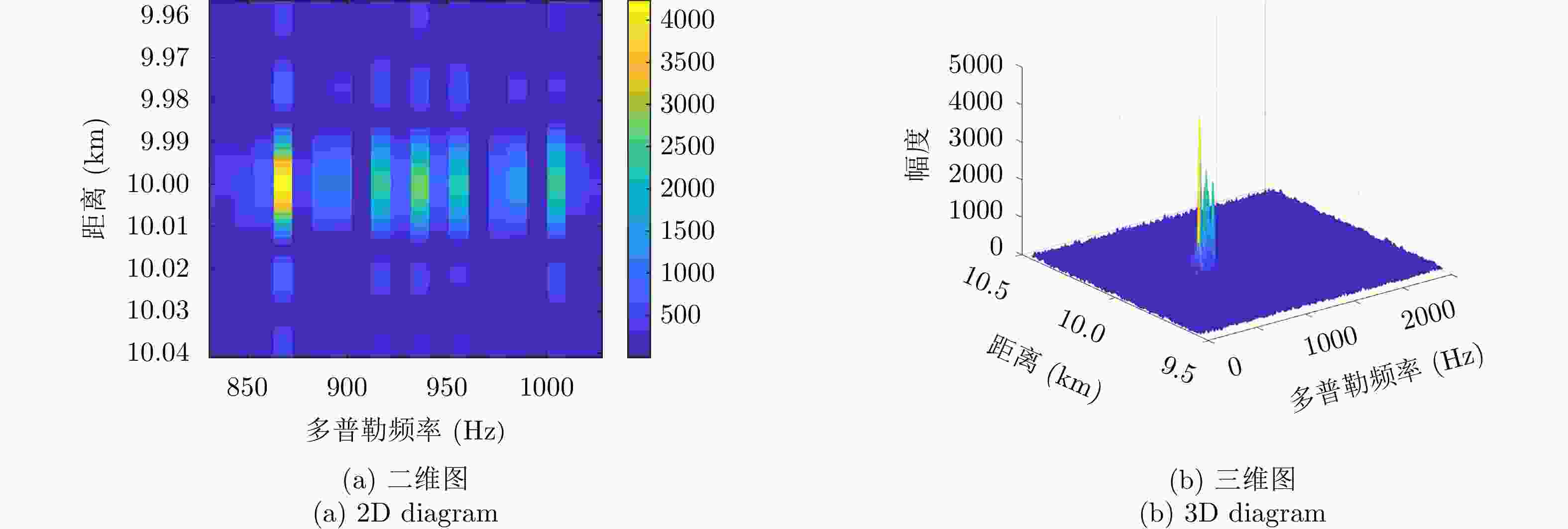
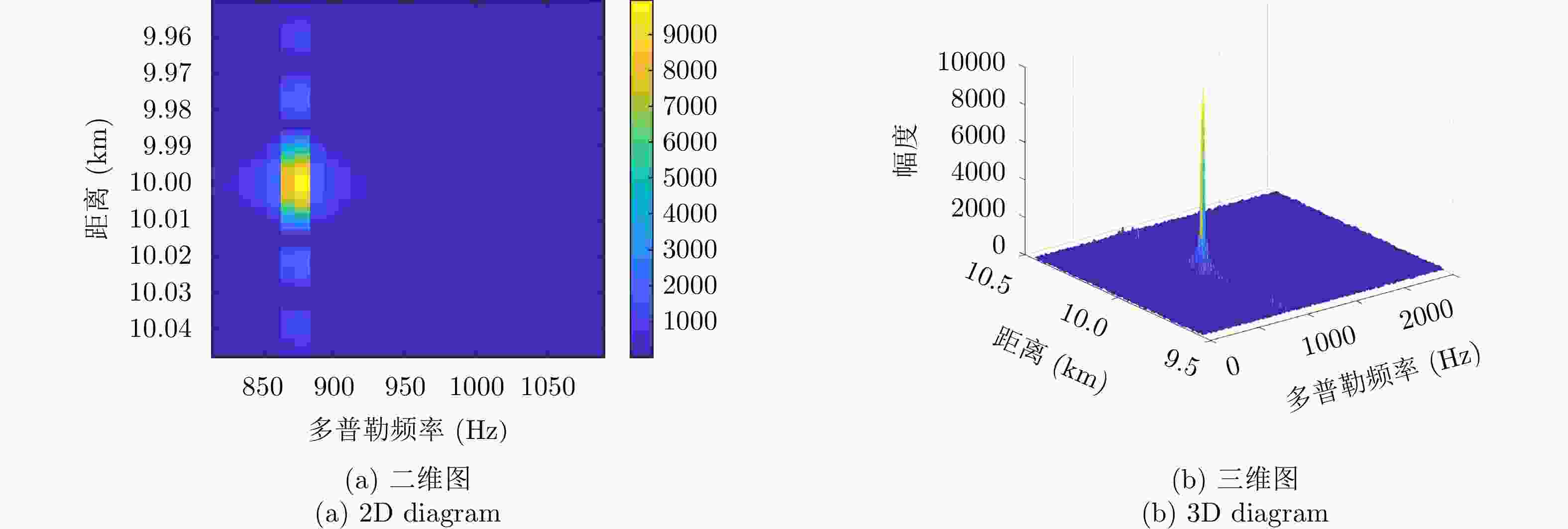
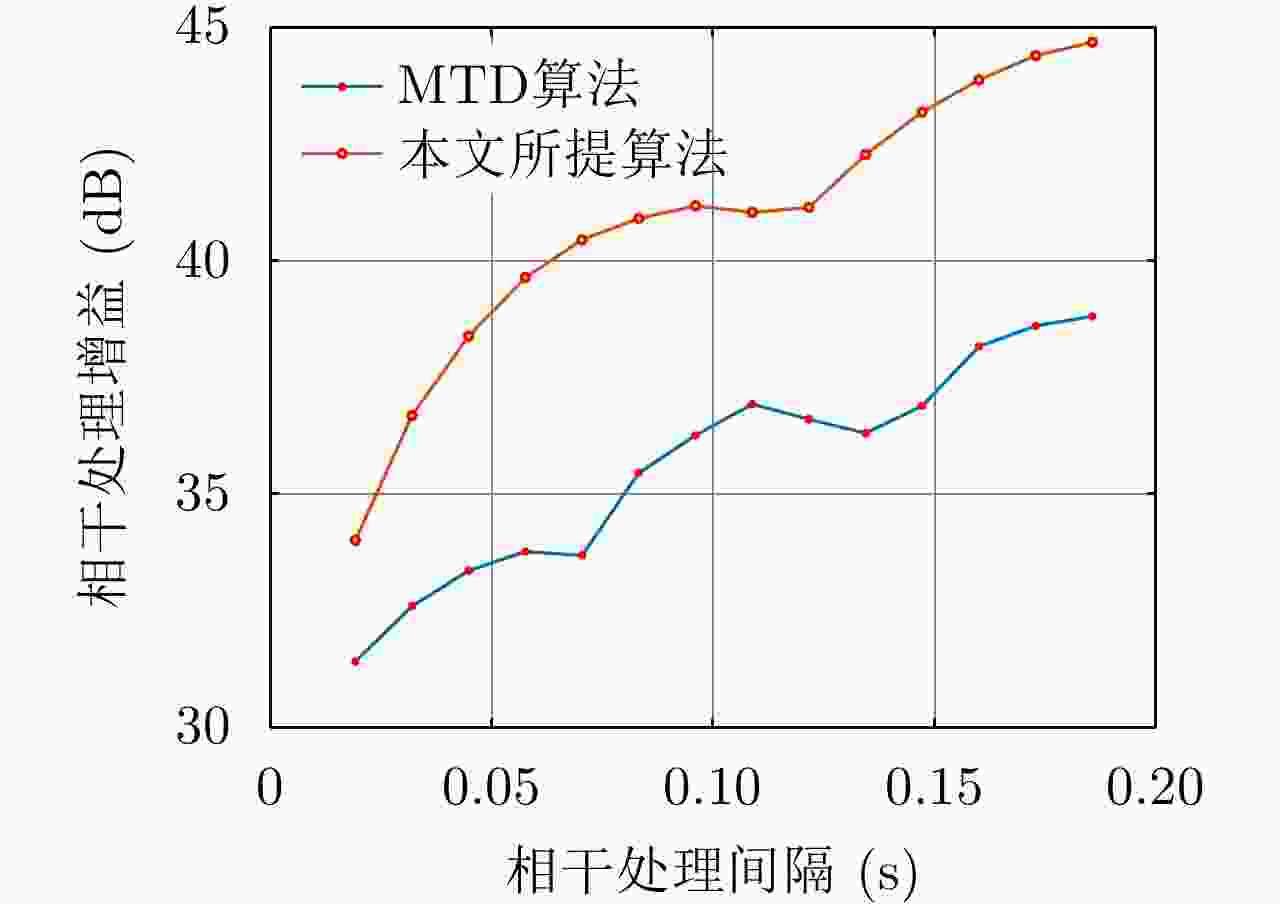
| [1] |
ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 215–217.
|
| [2] |
王文钦, 陈慧, 郑植, 等. 频控阵雷达技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029WANG Wenqin, CHEN Hui, ZHENG Zhi, et al. Advances on frequency diverse array radar and its applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029
|
| [3] |
LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Suppression of mainbeam deceptive jammer with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11584–11598. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014689
|
| [4] |
LIAO Yi, TANG Hu, CHEN Xiaolong, et al. Frequency diverse array beampattern synthesis with taylor windowed frequency offsets[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(11): 1901–1905. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2020.3024710
|
| [5] |
WANG Wenqin, SO H C, and FARINA A. An overview on time/frequency modulated array processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 228–246. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627182
|
| [6] |
熊杰. 频控阵发射波束形成及其应用方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018.XIONG Jie. Research on transmitting beamforming technology and its applications of frequency diverse array[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018.
|
| [7] |
ZHU Yu, LIU Lei, LU Zheng, et al. Target detection performance analysis of FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164276–164285. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943082
|
| [8] |
CHENG Jie, CHEN Hui, GUI Ronghua, et al. Persymmetric adaptive detector for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference. Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5.
|
| [9] |
LAN L, MARINO A, AUBRY A, et al. Design of adaptive detectors for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2020 IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5.
|
| [10] |
LAN Lan, MARINO A, AUBRY A, et al. GLRT-based adaptive target detection in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 597–613. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3028485
|
| [11] |
XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, and SO H C. Space-time adaptive processing with vertical frequency diverse array for range-ambiguous clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5352–5364. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2561308
|
| [12] |
XU Jian, WANG Wenqin, CUI Can, et al. Joint range, angle and Doppler estimation for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2018 IEEE 10th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Sheffield, UK, 2018: 499–503.
|
| [13] |
陈小龙, 陈宝欣, 黄勇, 等. 频控阵雷达空距频聚焦信号处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 183–193. doi: 10.12000/JR18018CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, HUANG Yong, et al. Frequency diverse array radar signal processing via Space-Range-Doppler focus (SRDF) method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 183–193. doi: 10.12000/JR18018
|
| [14] |
程婕, 王文钦, 侯宇典, 等. 基于FDA雷达的多径干扰抑制及目标检测[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(1): 28–34. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.004CHENG Jie, WANG Wenqin, HOU Yudian, et al. Multipath jamming suppression and target detection based on FDA radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(1): 28–34. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.004
|
| [15] |
HUANG Bang, WANG Wenqin, BASIT A, et al. Bayesian detection in Gaussian clutter for FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 2655–2667. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3139894
|
| [16] |
HUANG Bang, BASIT A, GUI Ronghua, et al. Adaptive moving target detection without training data for FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(1): 220–232. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3126781
|
| [17] |
桂荣华. 频控阵雷达自适应处理关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.GUI Ronghua. Research on adaptive processing technology for frequency diverse array radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020.
|
| [18] |
CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, and HE You. High resolution extraction of radar micro-Doppler signature using sparse time-frequency distribution[C]. 32nd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science, Montreal, Canada, 2017: 1–4.
|
| [19] |
CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, GUAN Jian, et al. Space-range-Doppler focus-based low-observable moving target detection using frequency diverse array MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 43892–43904. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2863745
|
| [20] |
XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, HUANG Lei, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming for fast-moving target detection with FDA-STAP radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(4): 973–984. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2628340
|
| [21] |
GUI Ronghua, WANG Wenqin, CUI Can, et al. Coherent pulsed-FDA radar receiver design with time-variance consideration: SINR and CRB analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(1): 200–214. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2764860
|
| [22] |
GUI Ronghua, WANG Wenqin, and SHAO Huaizong. General receiver design for FDA radar[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma, USA, 2018: 280–285.
|
| [23] |
林洋, 张顺生, 王文钦, 等. LFM正交调制的FDA-MIMO雷达运动目标检测[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(11): 1888–1894. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.11.014LIN Yang, ZHANG Shunsheng, WANG Wenqin, et al. FDA-MIMO radar moving target detection with LFM orthogonal modulation[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(11): 1888–1894. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.11.014
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: