-
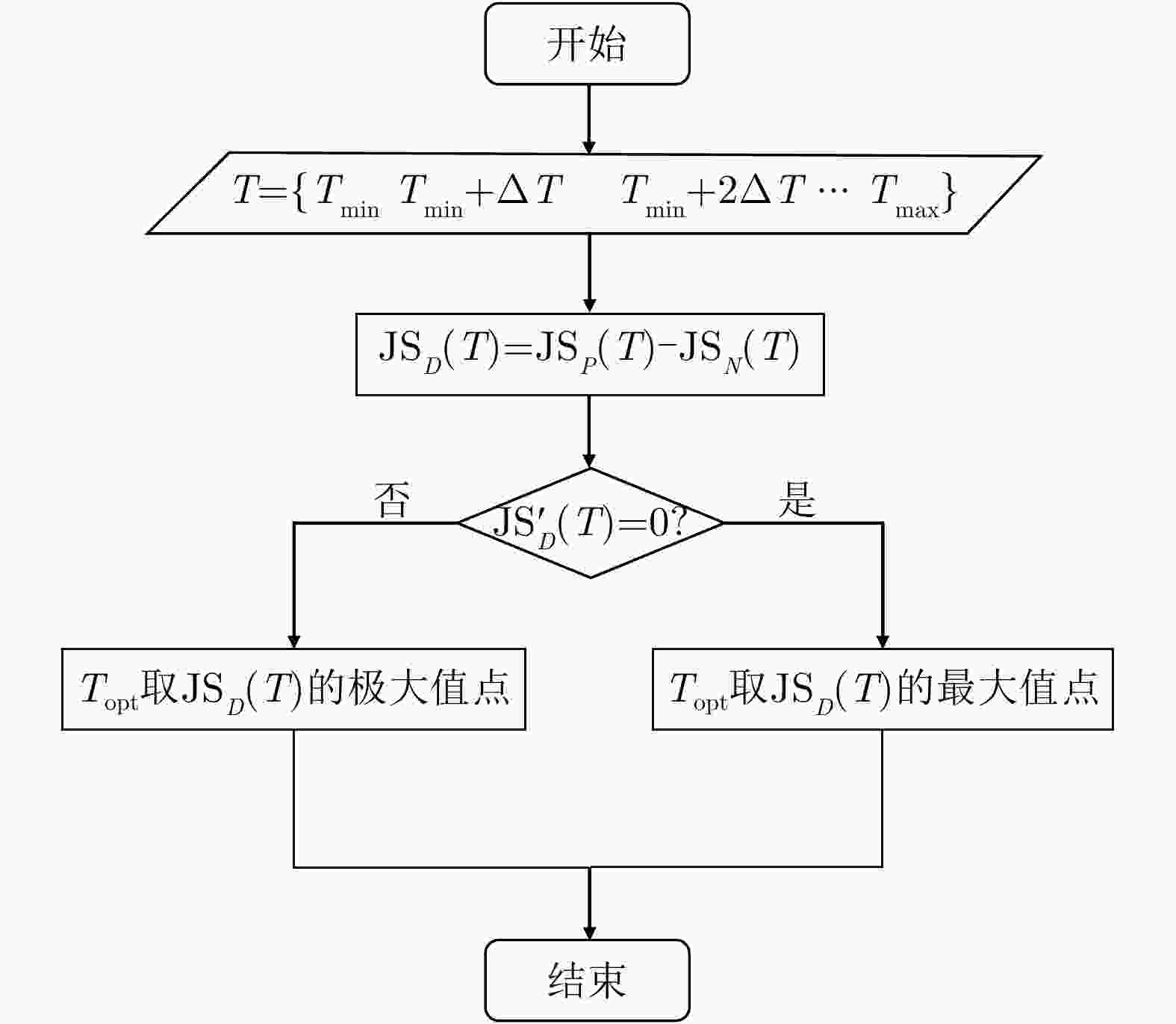
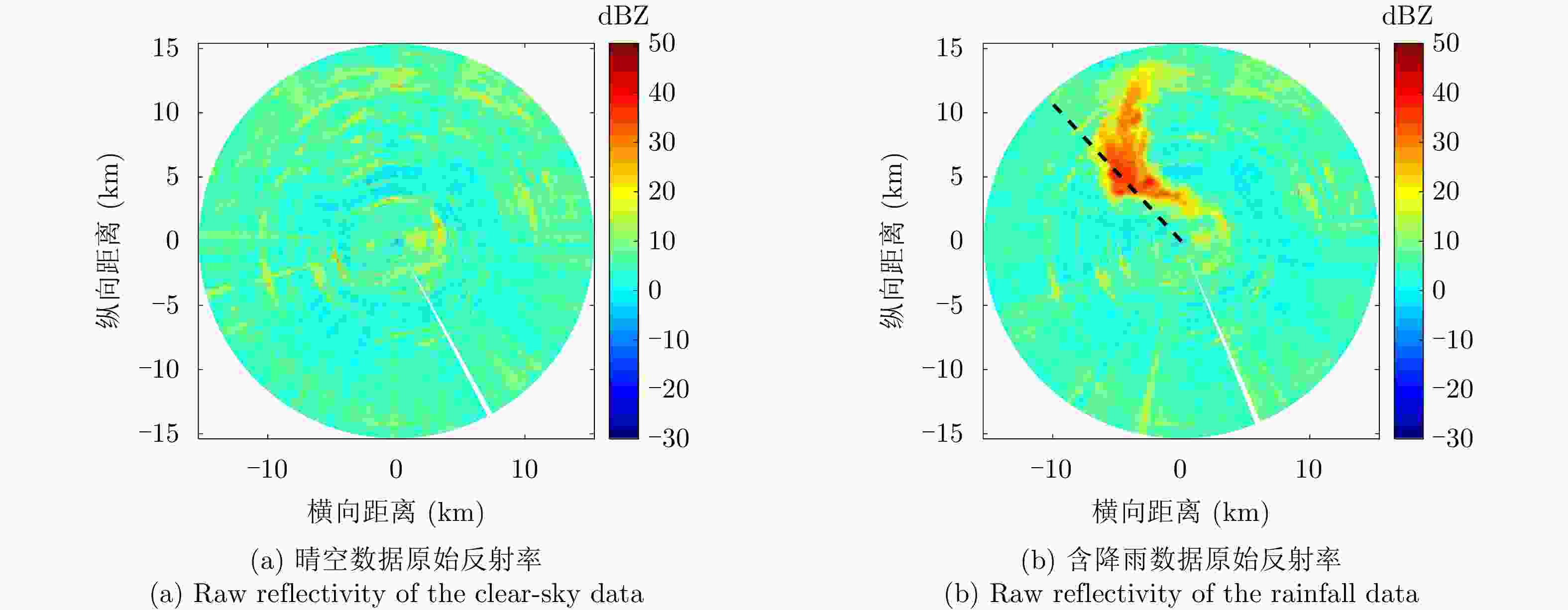
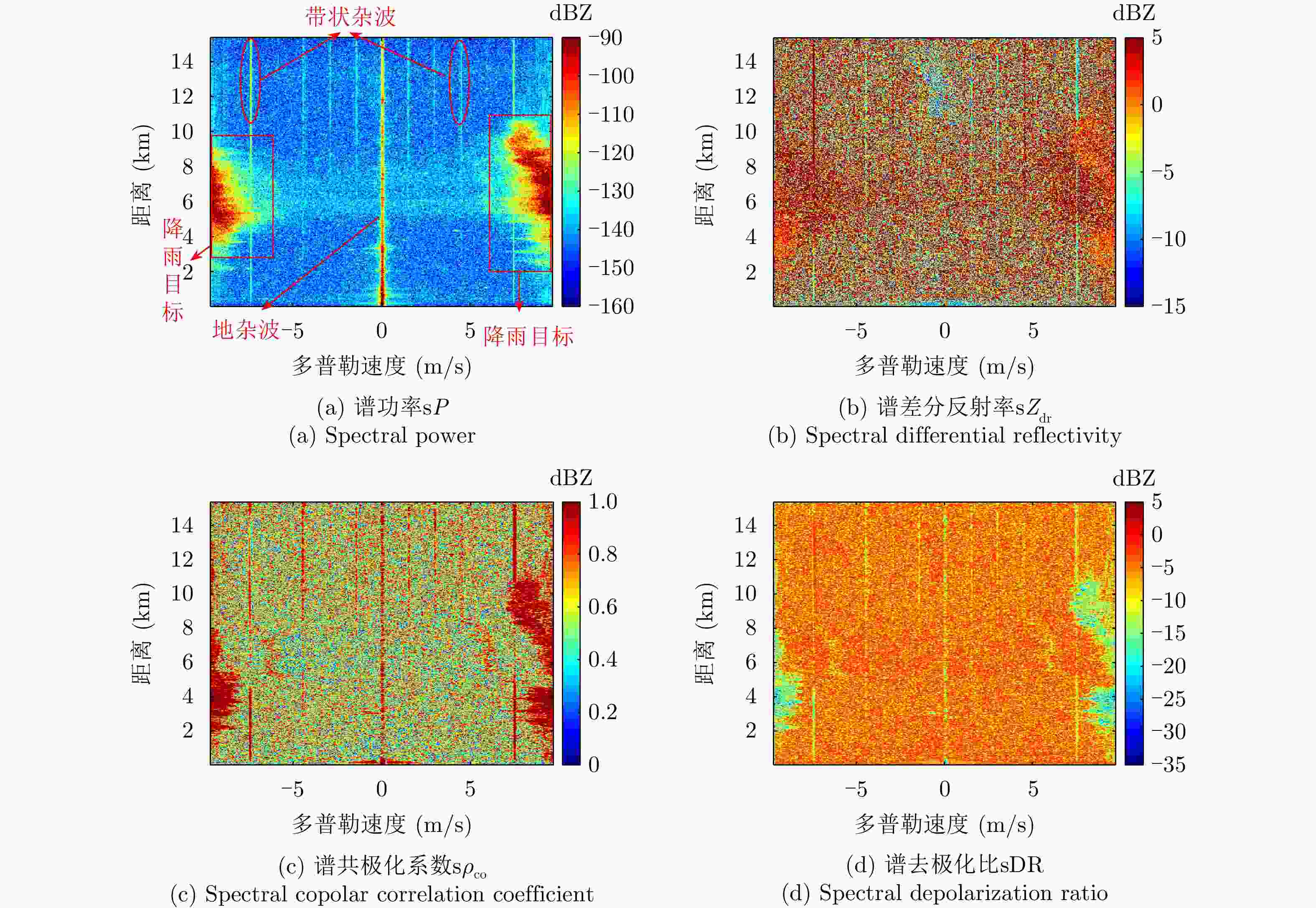
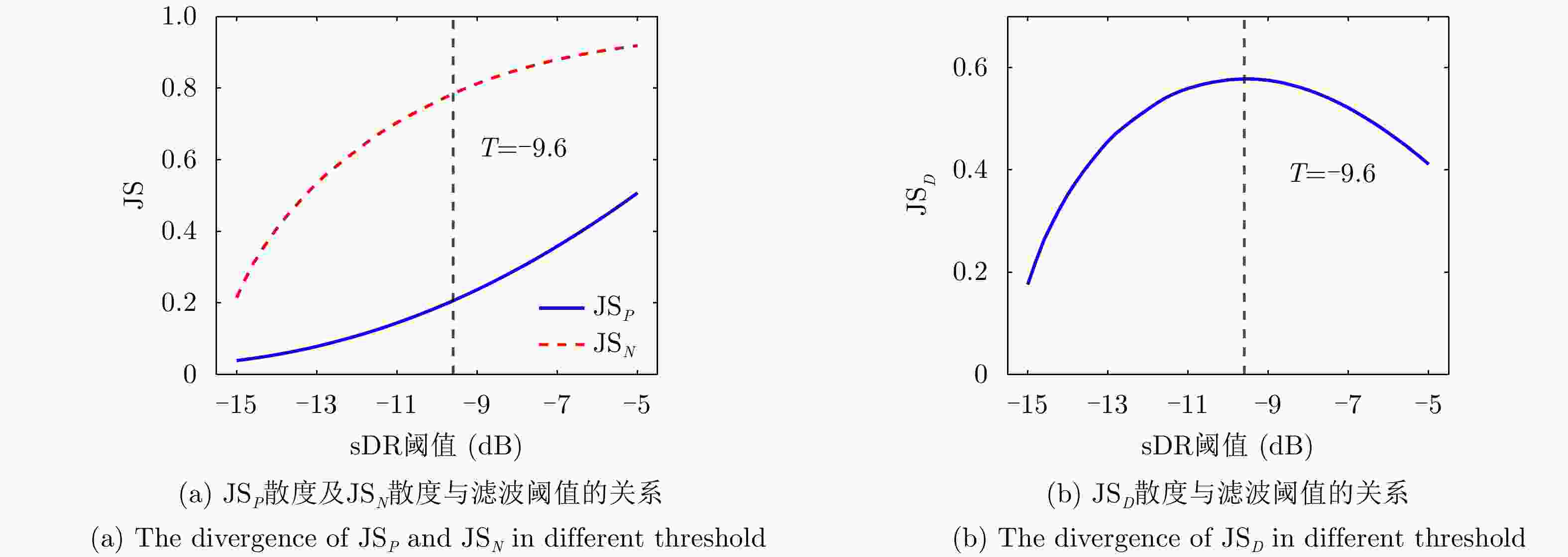
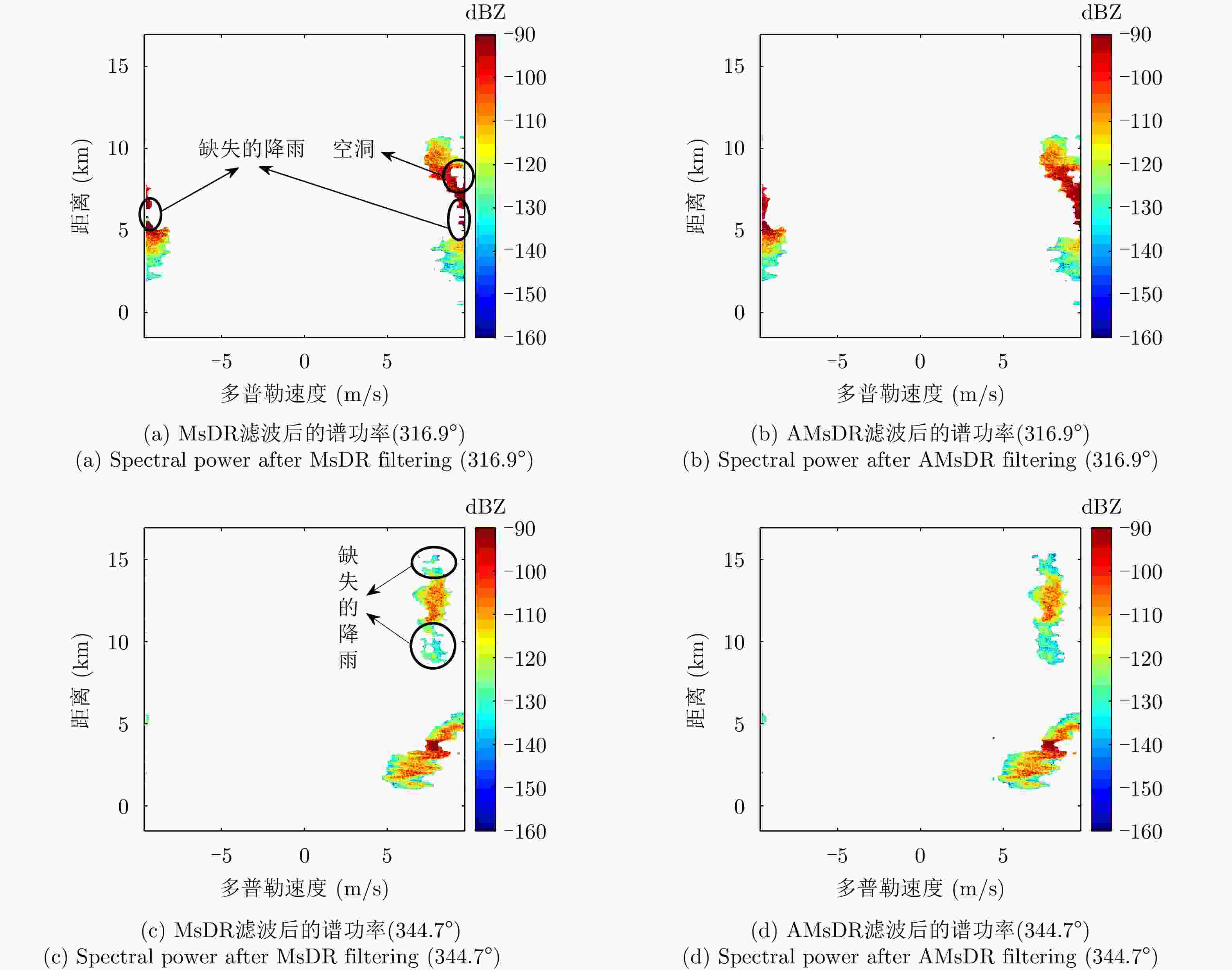
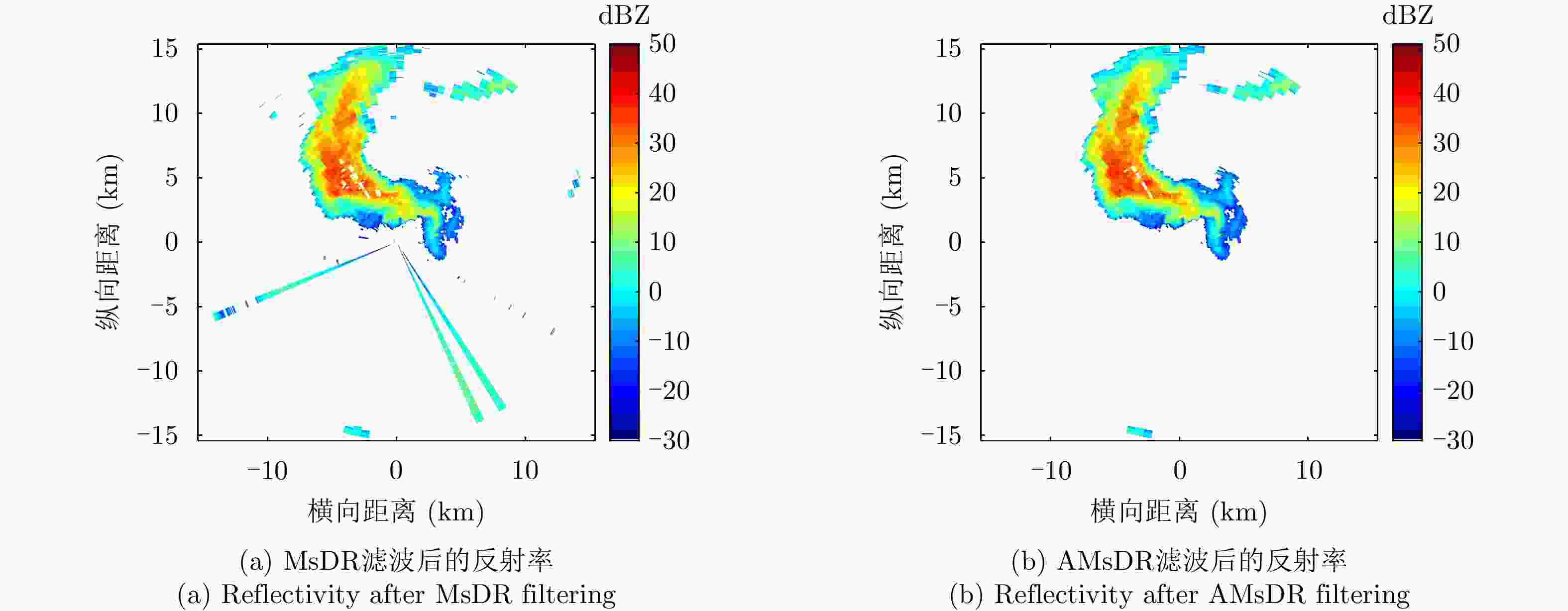
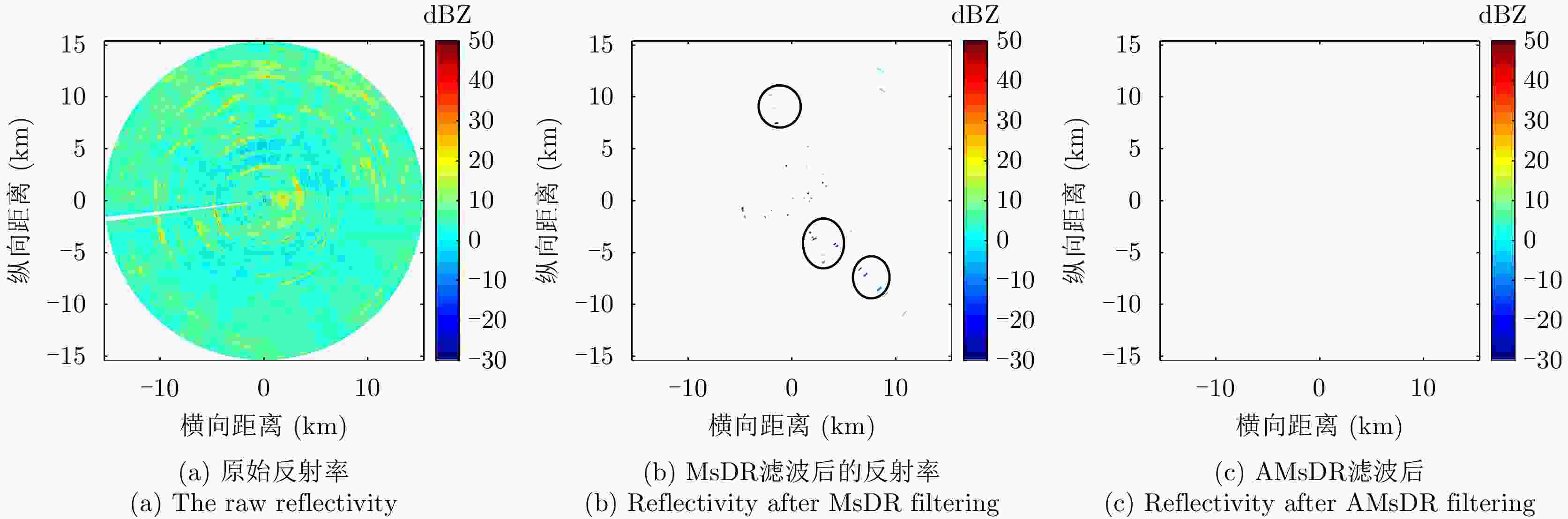
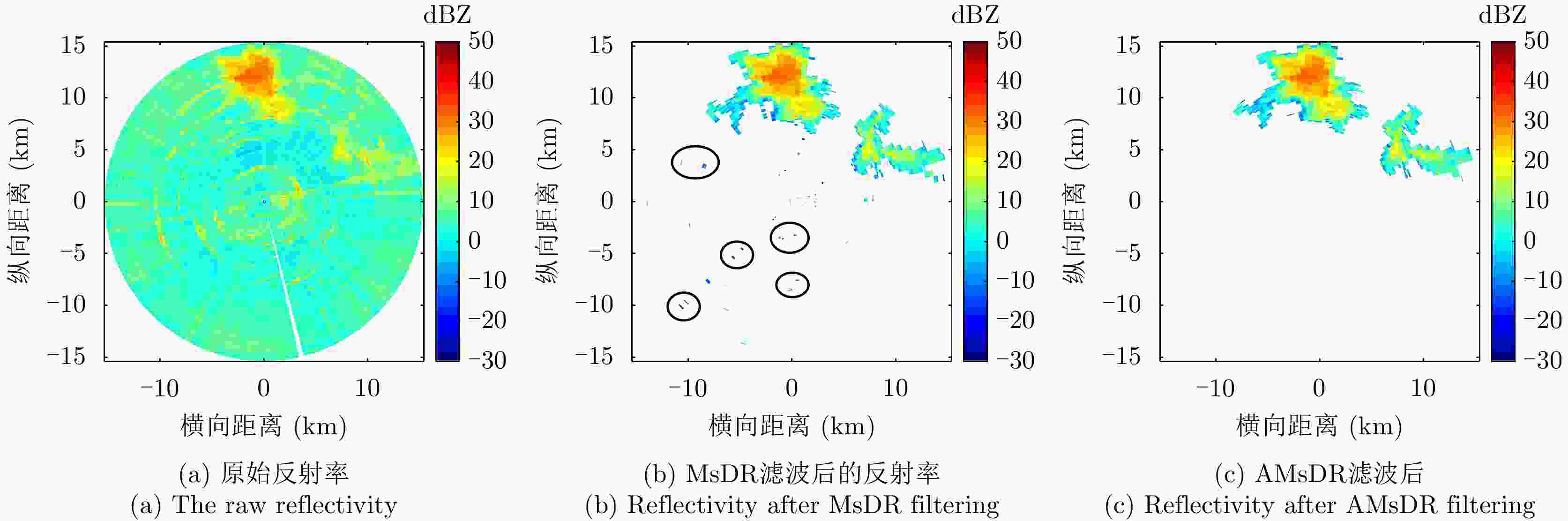
摘要: 针对双极化气象雷达中非气象回波的滤除问题,该文提出一种基于詹森-香农散度原理的自适应移动谱去极化比(AMsDR)滤波方法。该方法根据不同方位向回波的谱去极化比分布情况,利用气象回波和杂波在距离-多普勒图上的特征差异实现气象回波的保留和杂波的滤除。与现有固定阈值的移动谱去极化比滤波器相比,AMsDR滤波方法可根据不同方位向降雨和杂波的回波差异自适应地选择滤波阈值,提高杂波抑制与降雨保留性能。Abstract: This paper proposes an adaptive filtering method called the Adaptive Moving spectral Depolarization Ratio (AMsDR) filter to mitigate the clutter for dual-polarization weather radar based on Jensen-Shannon divergence principle. Specifically, the spectral depolarization ratio in the range-Doppler domain is the main variable distinguishing precipitation from clutter. The AMsDR filter can remove the clutter and noise and retain precipitation based on the difference of the spectral polarization feature and the spectral continuity of precipitation and clutter. The AMsDR filter can adaptively select the filter threshold depending on the echo difference between precipitation and clutter in different azimuths. Thus, the performance of the proposed filter is better than that of the current methods.
-
表 1 IDRA雷达参数
Table 1. IDRA radar specifications
参数 数值或属性 类型 线性FMCW 发射机类型 固态 极化类型 ATSR模式 中心频率 9.475 GHz 发射功率 20 W 扫描时间 409.6 μs 带宽 5 MHz 天线宽度 1.8° 扫描角 俯仰角0.5°
方位角0°~360°扫描周期 1圈/min -
[1] DOVIAK R J and ZRNIC D S. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations[M]. 2nd ed. Mineola: Dover Publications, 2006. [2] BRINGI V N and CHANDRASEKAR V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001. [3] MATROSOV S Y, CLARK K A, MARTNER B E, et al. X-Band polarimetric radar measurements of rainfall[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2002, 41(9): 941–952. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(2002)041<0941:XBPRMO>2.0.CO;2 [4] RYZHKOV A V, SCHUUR T J, BURGESS D W, et al. The joint polarization experiment: Polarimetric rainfall measurements and hydrometeor classification[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2005, 86(6): 809–824. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-86-6-809 [5] CHEN Haonan and CHANDRASEKAR V. The quantitative precipitation estimation system for Dallas-Fort Worth (DFW) urban remote sensing network[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 531: 259–271. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.05.040 [6] DIXON M and WIENER G. TITAN: Thunderstorm identification, tracking, analysis, and nowcasting—A radar-based methodology[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 1993, 10(6): 785–797. doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(1993)010<0785:TTITAA>2.0.CO;2 [7] STENSRUD D J, XUE Ming, WICKER L J, et al. Convective-scale warn-on-forecast system: A vision for 2020[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2009, 90(10): 1487–1500. doi: 10.1175/2009BAMS2795.1 [8] FUKAO S and HAMAZU K. Radar for Meteorological and Atmospheric Observations[M]. Tokyo: Springer, 2014. [9] 殷加鹏, 李健兵, 庞晨, 等. 一种极化-多普勒气象雷达的射频干扰滤波方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 905–918. doi: 10.12000/JR21102YIN Jiapeng, LI Jianbing, PANG Chen, et al. A radio frequency interference mitigation method for polarimetric Doppler weather radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 905–918. doi: 10.12000/JR21102 [10] YIN Jiapeng, UNAL C M H, and RUSSCHENBERG H W J. Narrow-band clutter mitigation in spectral polarimetric weather radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4655–4667. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2696263 [11] GROGINSKY H L and GLOVER K M. Weather radar canceller design[C]. The 19th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Boston, USA, 1980: 192–198. [12] SIGGIA A D and PASSARELLI R E. Gaussian model adaptive processing (GMAP) for improved ground clutter cancellation and moment calculation[C]. The 3rd European Conference on Radar Meteorology (ERAD 2004), Visby, Sweden, 2004: 67–73. [13] HUBBERT J C, DIXON M, ELLIS S M, et al. Weather radar ground clutter. Part I: Identification, modeling, and simulation[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2009, 26(7): 1165–1180. doi: 10.1175/2009JTECHA1159.1 [14] HUBBERT J C, DIXON M, and ELLIS S M. Weather radar ground clutter. Part II: Real-time identification and filtering[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2009, 26(7): 1181–1197. doi: 10.1175/2009JTECHA1160.1 [15] LI Yinguang, ZHANG Guifu, DOVIAK R J, et al. A new approach to detect ground clutter mixed with weather signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4): 2373–2387. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2209658 [16] LI Nan, WANG Zhenhui, SUN Kangyuan, et al. A quality control method of ground-based weather radar data based on statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2211–2219. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2776562 [17] WARDE D A and TORRES S M. The autocorrelation spectral density for Doppler-weather-radar signal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 508–518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2241775 [18] HUBBERT J C, MEYMARIS G, ROMATSCHKE U, et al. Using a regression ground clutter filter to improve weather radar signal statistics: Theory and simulations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2021, 38(8): 1353–1375. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-20-0026.1 [19] KRASNOV O A and YAROVOY A G. Polarimetric micro-Doppler characterization of wind turbines[C]. 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 2016: 1–5. [20] UNAL C. Spectral polarimetric radar clutter suppression to enhance atmospheric echoes[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2009, 26(9): 1781–1797. doi: 10.1175/2009JTECHA1170.1 [21] YIN Jiapeng, UNAL C, and RUSSCHENBERG H. Object-orientated filter design in spectral domain for polarimetric weather radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 2725–2740. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2876632 [22] YIN Jiapeng, CHEN Haonan, LI Yongzhen, et al. Clutter mitigation based on spectral depolarization ratio for dual-polarization weather radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6131–6145. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3088324 [23] BLOCH I and MAÎTRE H. Fuzzy mathematical morphology[J]. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 1994, 10(1/2): 55–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01530944 [24] SHANNON C E. Communication theory of secrecy systems[J]. Bell System Technical Journal, 1949, 28(4): 656–715. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1949.tb00928.x [25] LIN Jianhua. Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1991, 37(1): 145–151. doi: 10.1109/18.61115 [26] ENDRES D M and SCHINDELIN J E. A new metric for probability distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2003, 49(7): 1858–1860. doi: 10.1109/tit.2003.813506 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: