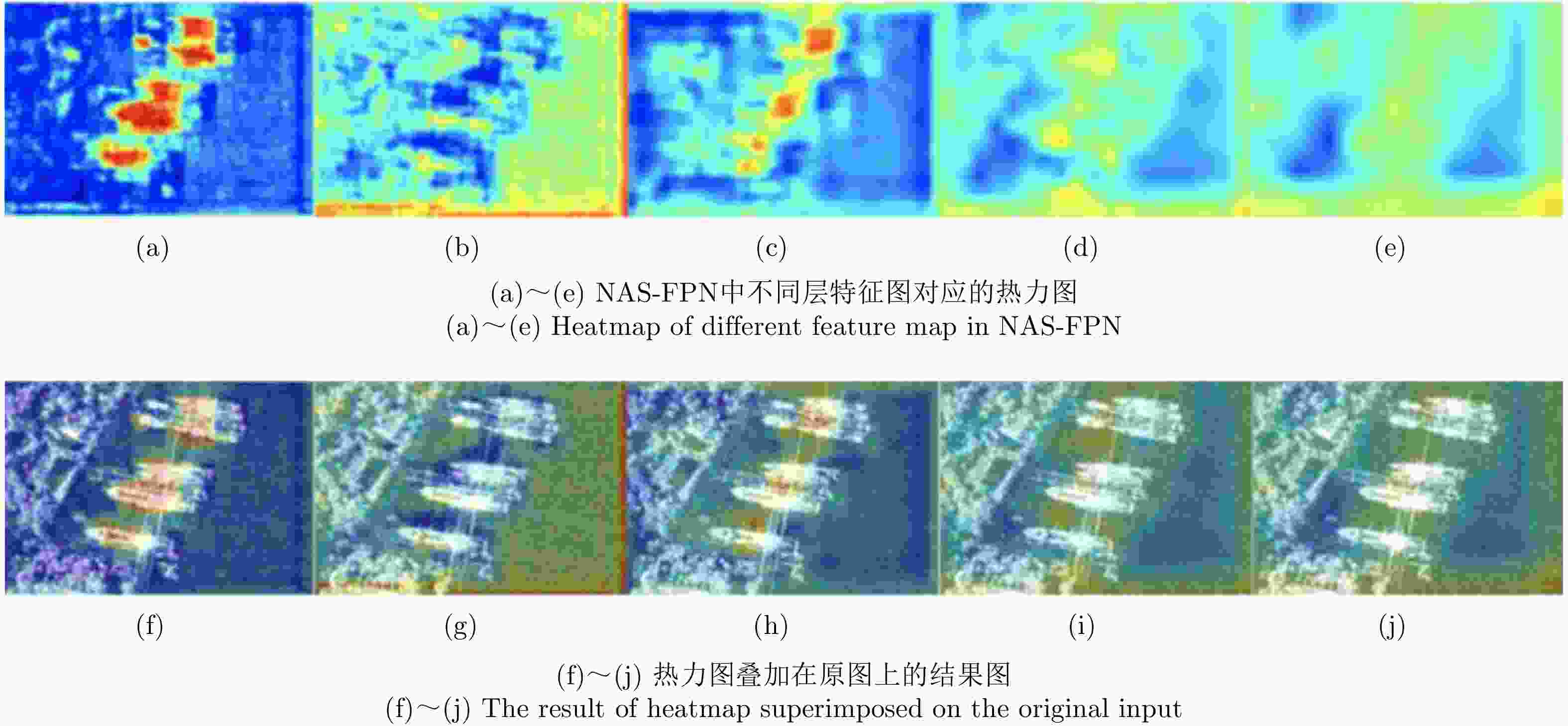
Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Multiscale Feature Fusion and Channel Relation Calibration of Features
-
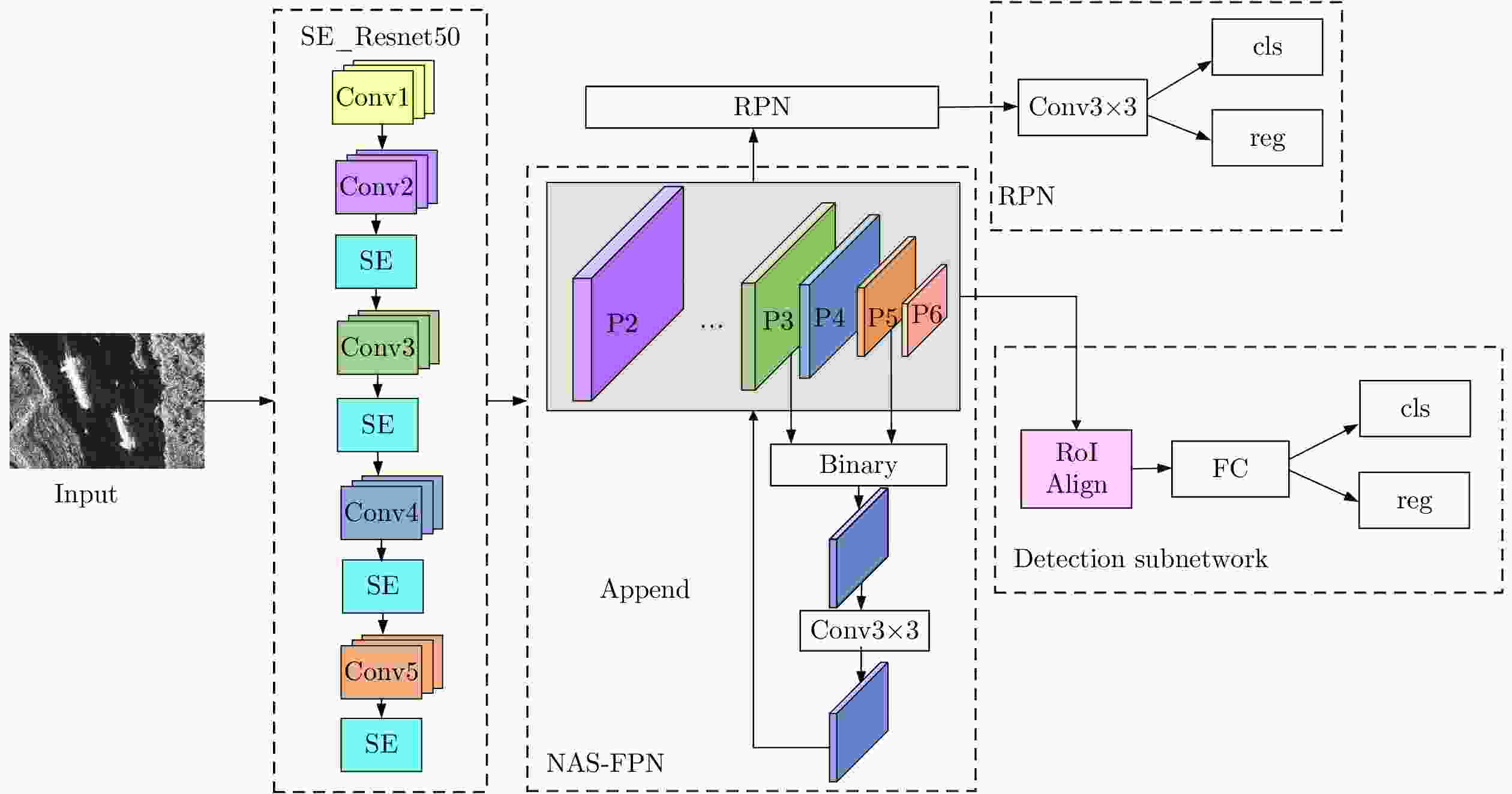
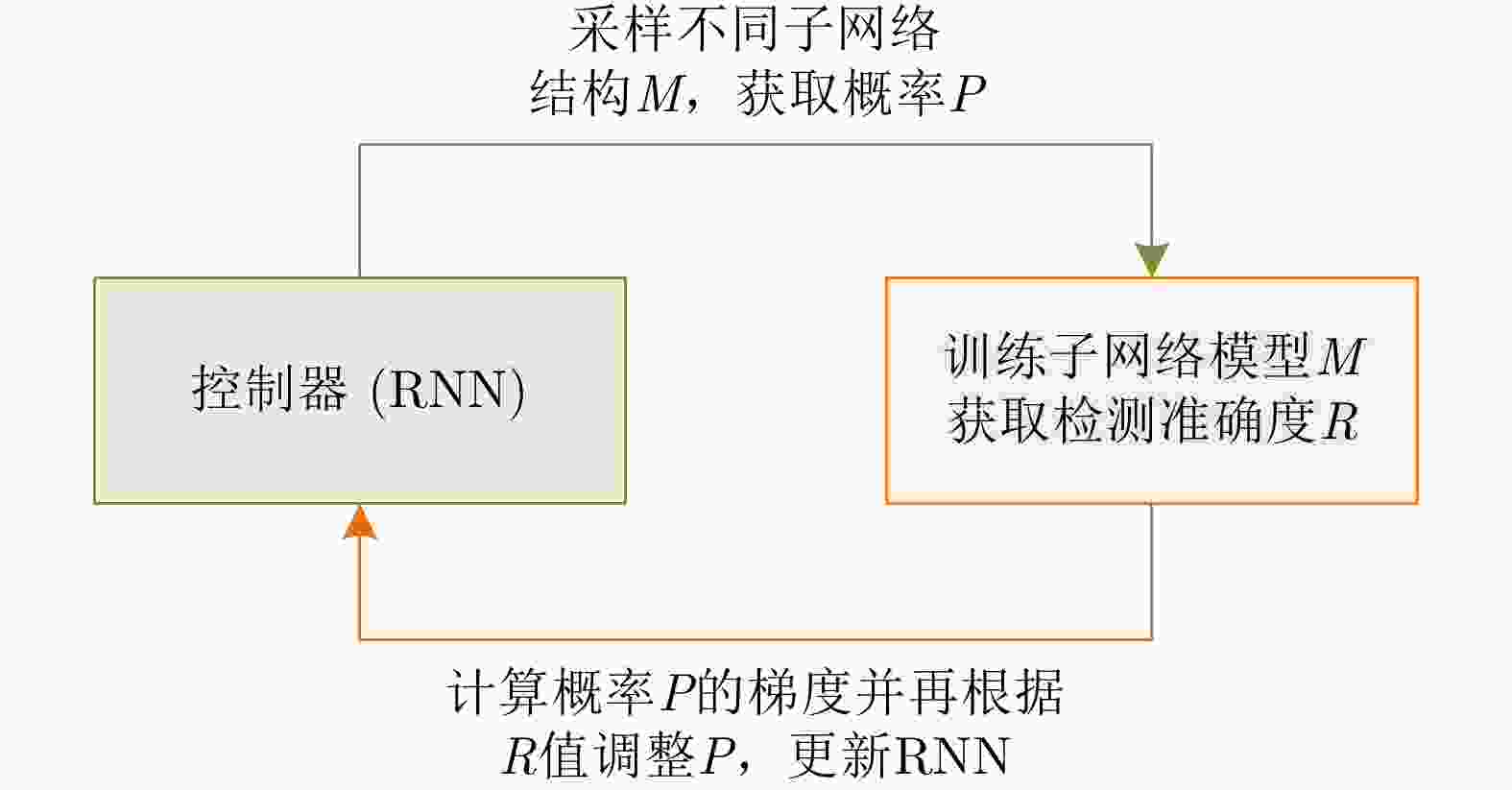
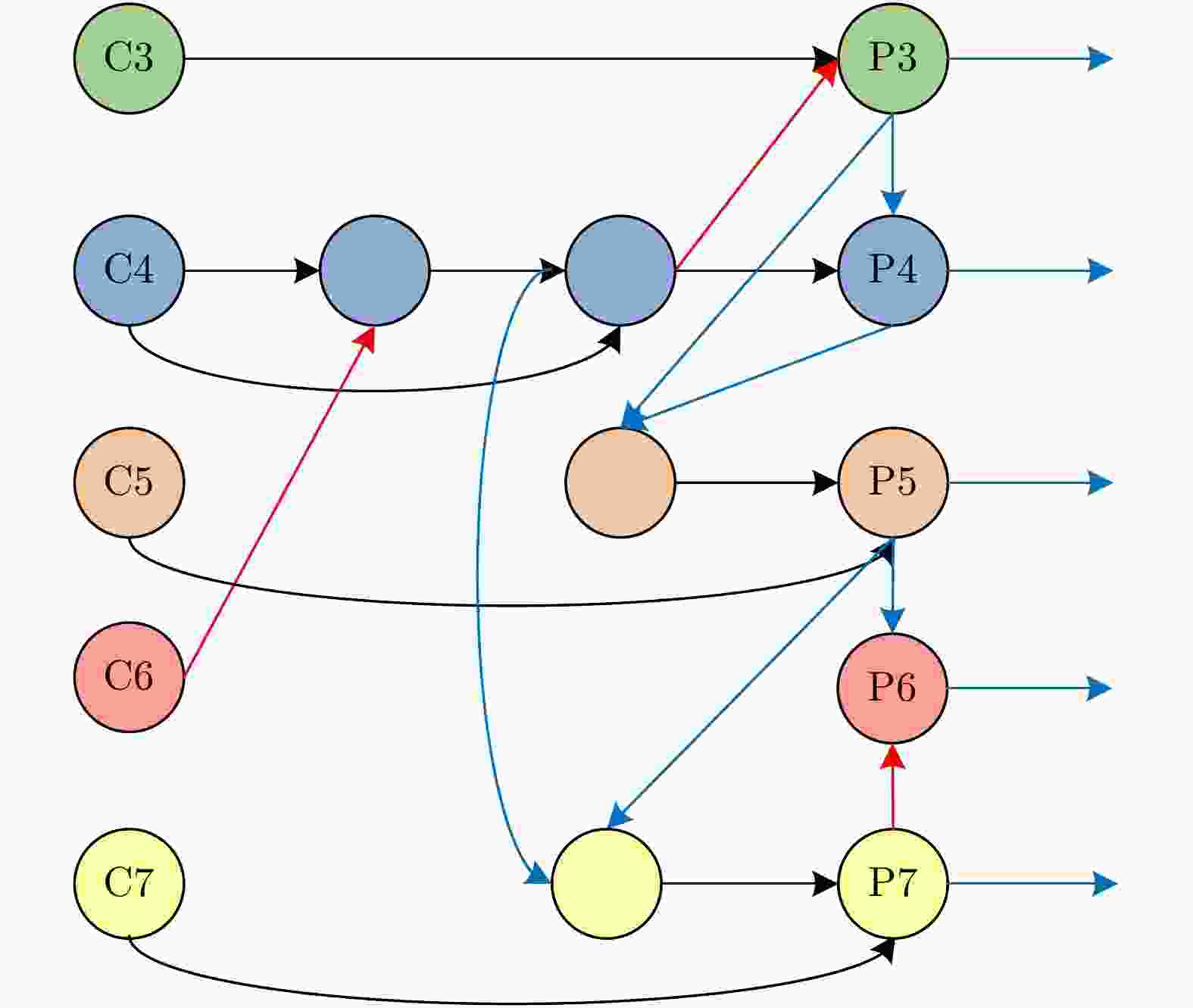
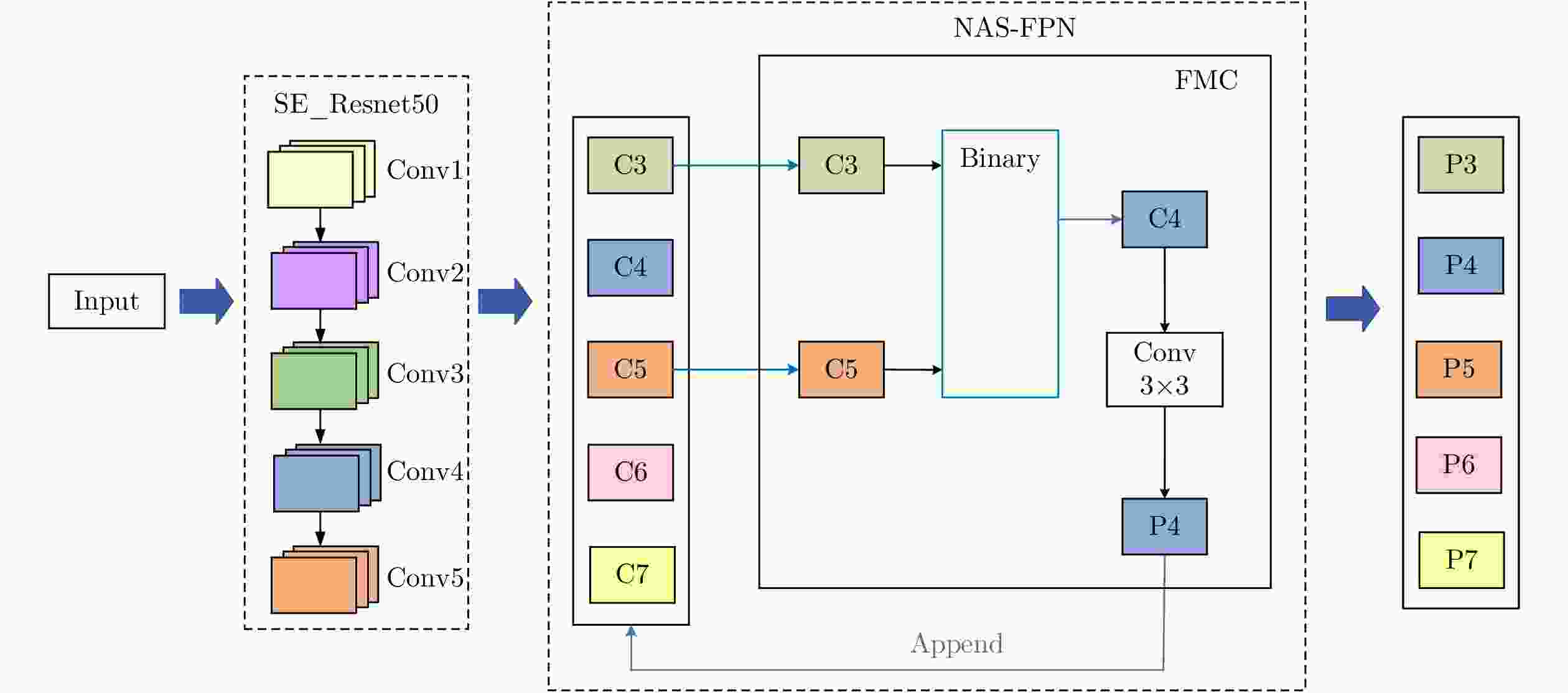
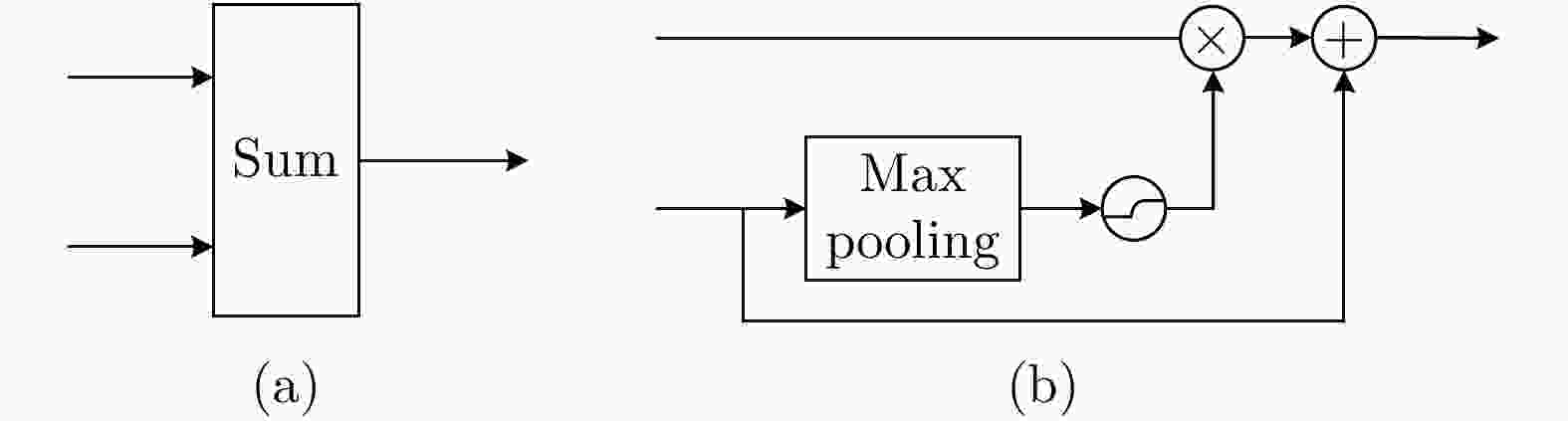
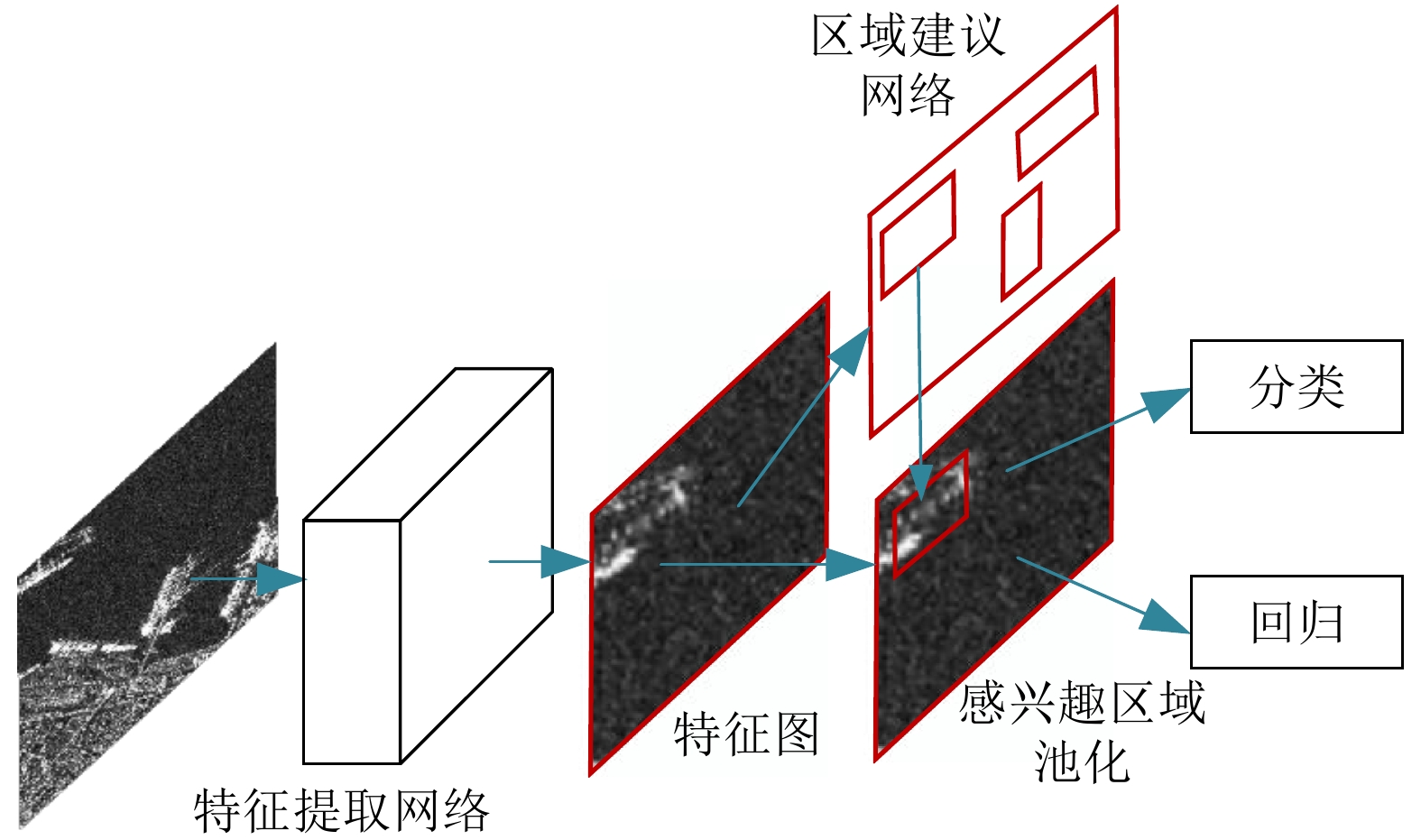
摘要: 目前深度学习技术在SAR图像的船舶检测中已取得显著的成果,但针对SAR船舶图像中复杂多变的背景环境,如何准确高效地提取目标特征,提升检测精度与检测速度仍存在着巨大的挑战。针对上述问题,该文提出了一种多尺度特征融合与特征通道关系校准的 SAR 图像船舶检测算法。在Faster R-CNN的基础上,首先通过引入通道注意力机制对特征提取网络进行特征间通道关系校准,提高网络对复杂场景下船舶目标特征提取的表达能力;其次,不同于原始的基于单一尺度特征生成候选区域的方法,该文基于神经架构搜索算法引入改进的特征金字塔结构,高效地将多尺度特征进行充分融合,改善了船舶目标中对小目标、近岸密集目标的漏检问题。最后,在SSDD数据集上进行对比验证。实验结果表明,相较原始的Faster R-CNN,检测精度从85.4%提高到89.4%,检测速率也从2.8 FPS提高到10.7 FPS。该方法能够有效实现高速与高精度的SAR图像船舶检测,具有一定的现实意义。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达 /
- Faster R-CNN /
- 船舶检测 /
- 特征融合 /
- 通道注意力
Abstract: Deep-learning technology has enabled remarkable results for ship detection in SAR images. However, in view of the complex and changeable backgrounds of SAR ship images, how to accurately and efficiently extract target features and improve detection accuracy and speed is still a huge challenge. To solve this problem, a ship detection algorithm based on multiscale feature fusion and channel relation calibration of features is proposed in this paper. First, based on Faster R-CNN, a channel attention mechanism is introduced to calibrate the channel relationship between features in the feature extraction network, so as to improve the network’s expression ability for extraction of ship features in different scenes. Second, unlike the original method of generating candidate regions based on single-scale features, this paper introduces an improved feature pyramid structure based on a neural architecture search algorithm, which helps improve the performance of the network. The multiscale features are effectively fused to settle the problem of missing detections of small targets and adjacent inshore targets. Experimental results on the SSDD dataset show that, compared with the original Faster R-CNN, the proposed algorithm improves detection accuracy from 85.4% to 89.4% and the detection rate from 2.8 FPS to 10.7 FPS. Thus, this method effectively achieves high-speed and high-accuracy SAR ship detection, which has practical benefits.-
Key words:
- SAR /
- Faster R-CNN /
- Ship detection /
- Features fusion /
- Channel attention
-
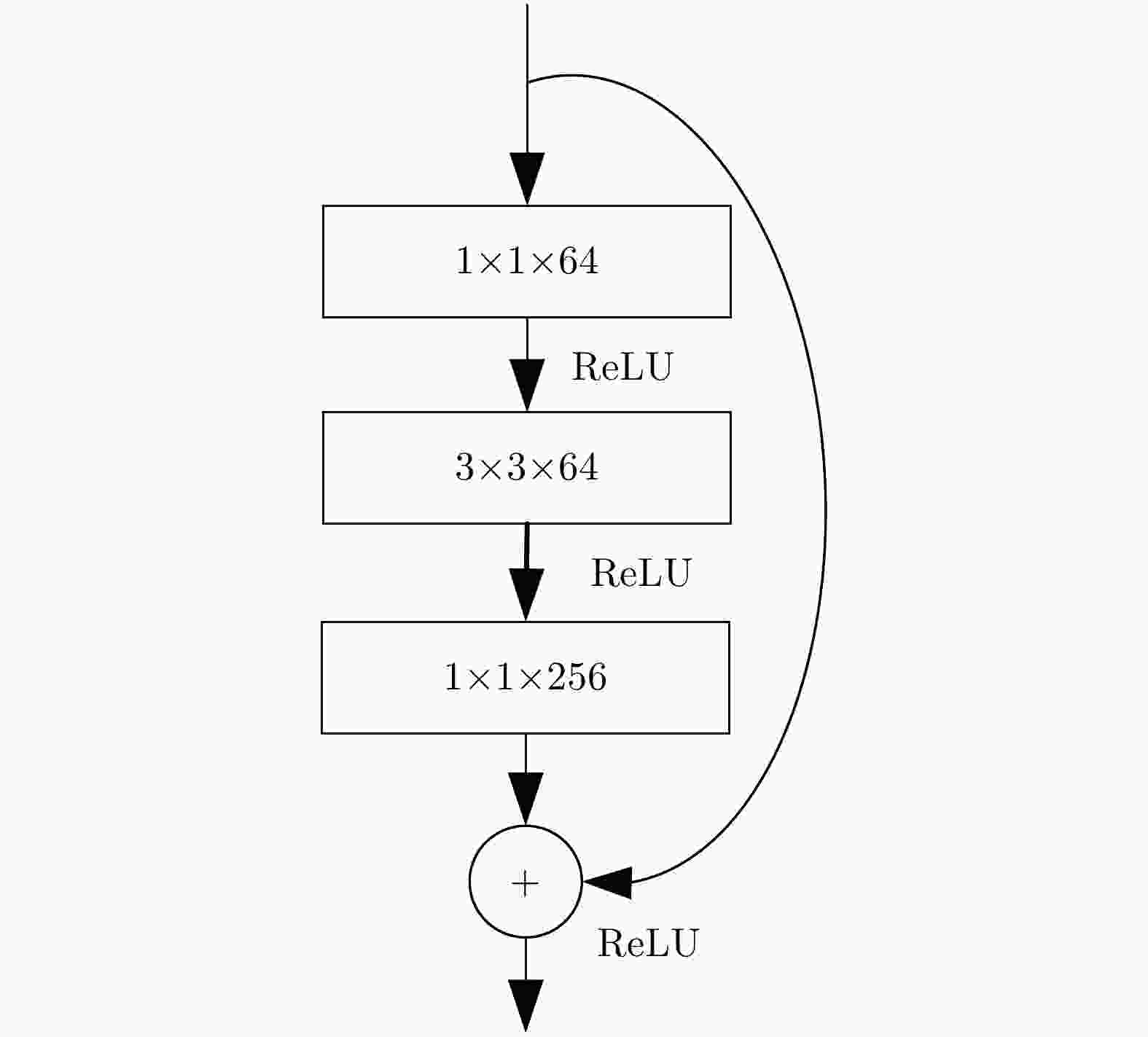
表 1 以Resnet50作为主干网络的特征提取网络参数
Table 1. The network parameters extraction with Resnet50 as the backbone network feature
网络层名称 类型 Resnet50 SE-Resnet50 卷积核(高度×宽度×通道数)/步长 卷积核(高度×宽度×通道数)/步长 Conv1 卷积层 $7 \times 7 \times 64/2$ $7 \times 7 \times 64/2$ max pool 池化层 $3 \times 3 \times 64/2$ $3 \times 3 \times 64/2$ Conv2_1—Conv2_9 残差结构 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1 \times 64/1} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 64/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 256/1} \end{array}} \right] \times 3$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } {1 \times 1 \times 64/1} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 64/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 256/1} \\ { {{{\rm{fc}}} },[16,256]} \end{array} } \right] \times 3$ Conv3_1—Conv3_12 残差结构 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1 \times 128/2} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 128/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 512/1} \end{array}} \right] \times 4$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } {1 \times 1 \times 128/2} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 128/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 512/1} \\ {{\rm{fc}},[32,512]} \end{array} } \right] \times 4$ Conv4_1—Conv4_18 残差结构 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1 \times 256/2} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 256/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 1024/1} \end{array}} \right] \times 6$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } {1 \times 1 \times 256/2} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 256/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 1024/1} \\ {{\rm{fc}},[64,1024]} \end{array} } \right] \times 6$ Conv5_1—Conv5_9 残差结构 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1 \times 512/1} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 512/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 2048/1} \end{array}} \right] \times 3$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } {1 \times 1 \times 512/1} \\ {3 \times 3 \times 512/1} \\ {1 \times 1 \times 2048/1} \\ {{\rm{fc}},[128,{\rm{2048} }]} \end{array} } \right] \times 3$ 表 2 基于Faster R-CNN的优化算法对比
Table 2. Comparison of optimization algorithms based on Faster R-CNN
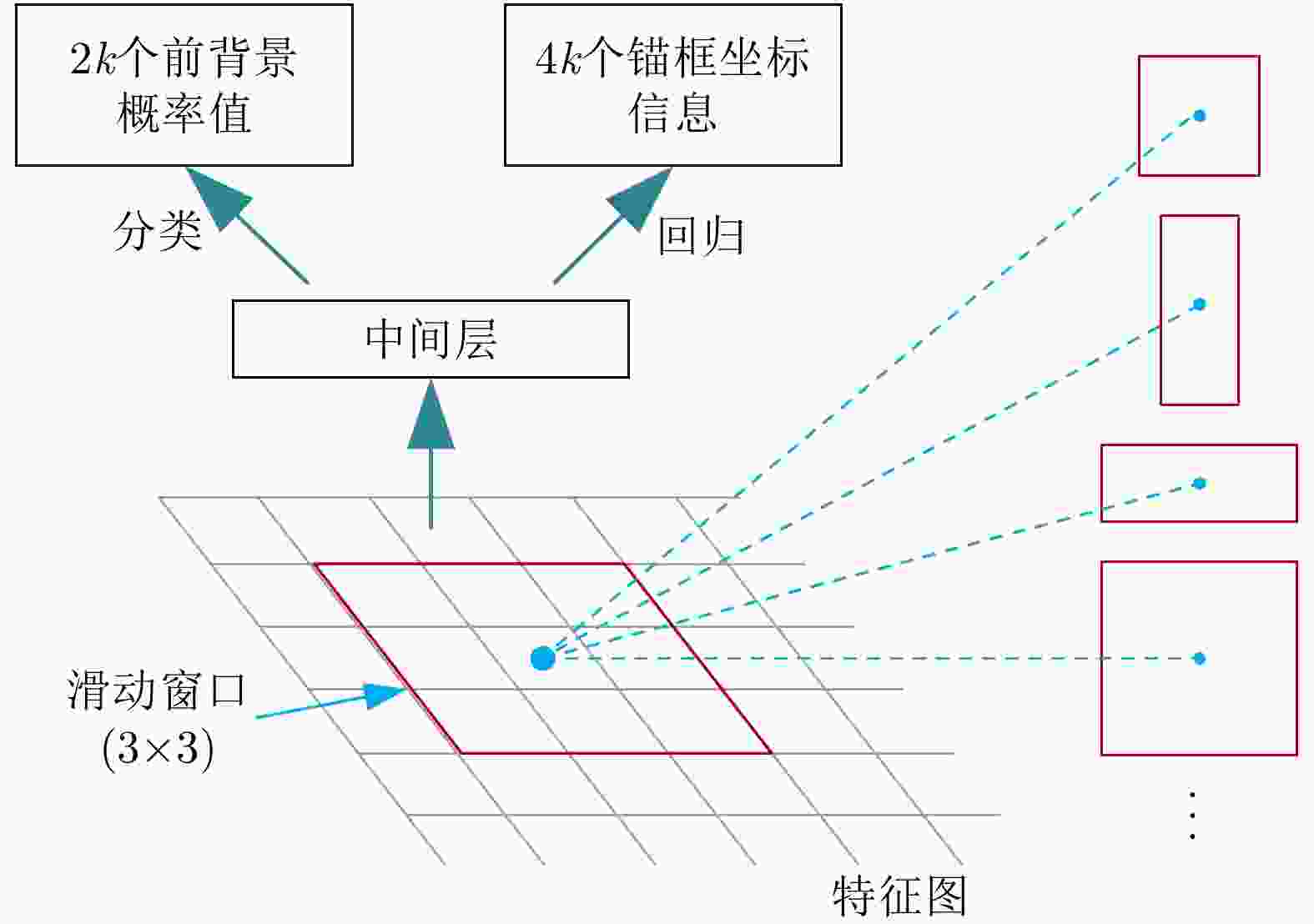
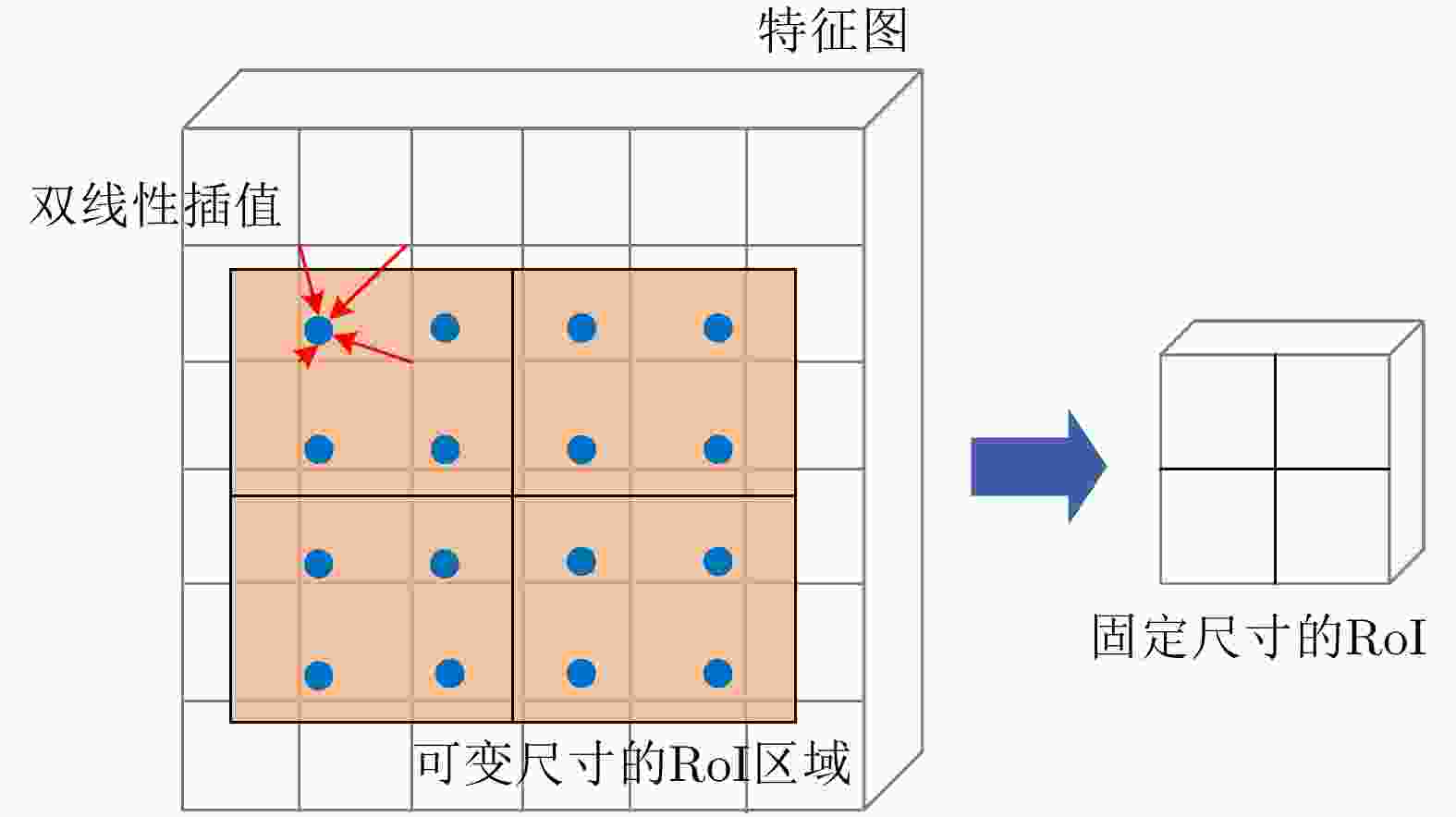
RoIAlign CA NAS-FPN AP (%) Time (s/iter) Speed (FPS) 85.4 0.667 2.80 √ 87.2 0.727 2.78 √ √ 88.2 0.741 2.67 √ √ 88.0 0.493 10.72 √ √ √ 89.4 0.535 10.70 表 3 不同检测算法的性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of different detection algorithms
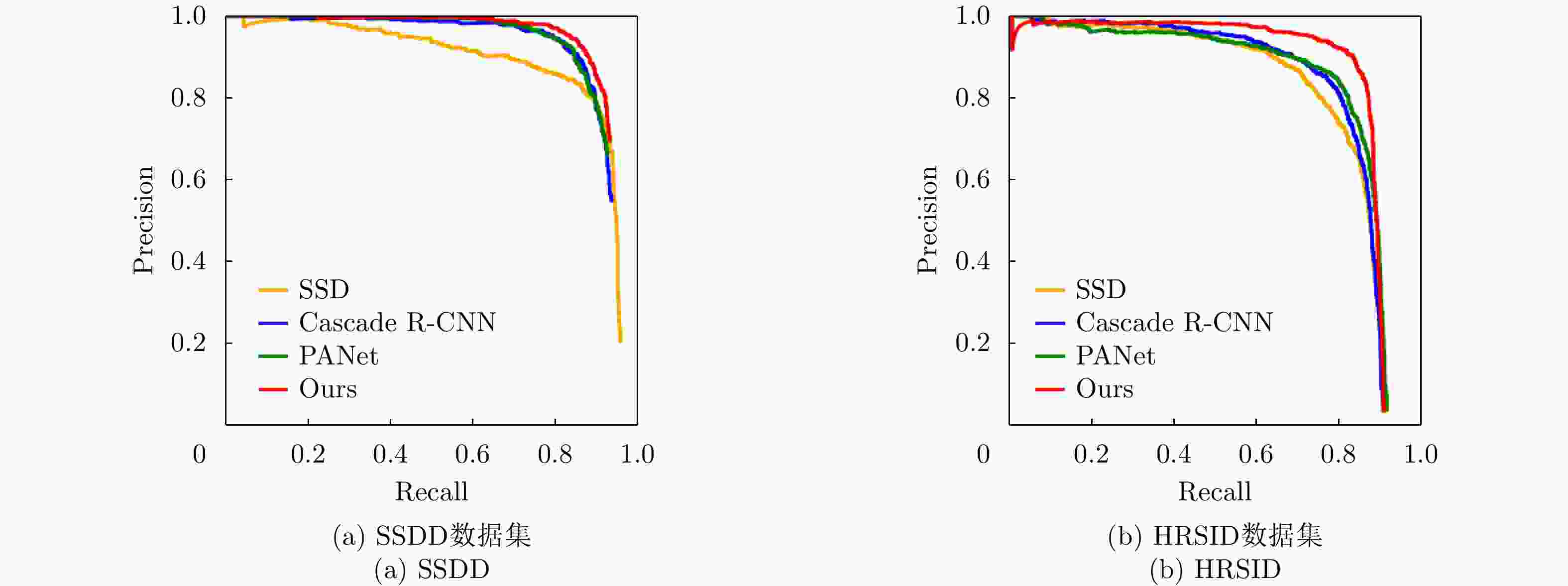
Method Image size FLOPs (230) Params (220) Time (s/iter) Speed (FPS) SSDD HRSID AP (%) AP (%) SSD 300×300 30.49 23.75 0.061 47.20 84.7 79.6 Cascade R-CNN 300×300 59.03 68.93 0.323 13.20 88.4 80.9 PANet 300×300 59.03 68.93 0.301 14.70 88.7 81.3 本文算法 300×300 33.66 70.27 0.535 10.70 89.4 82.8 表 4 不同检测算法基于SSDD在近岸与离岸场景下的性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of different detection algorithms in inshore and offshore scenes of SSDD
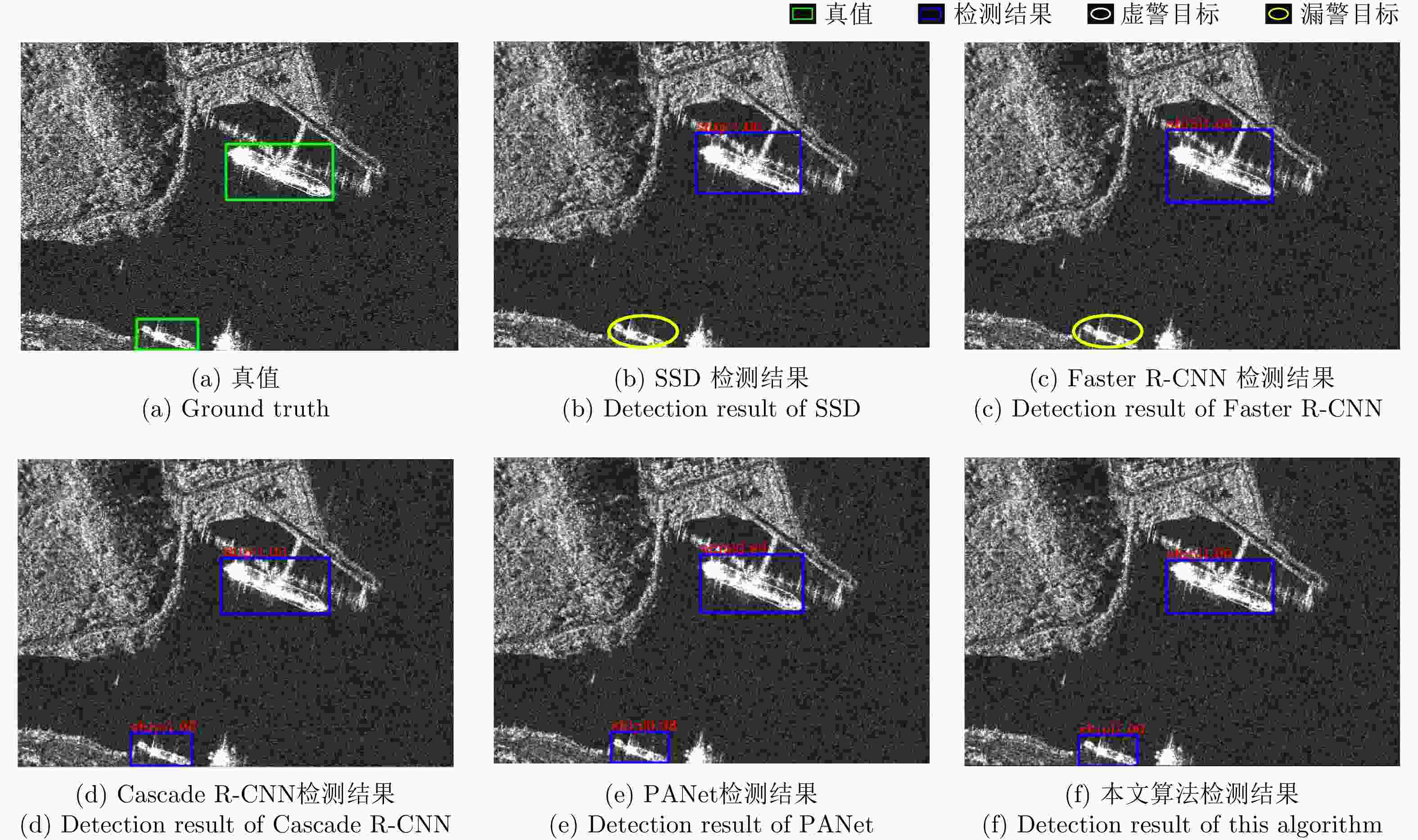
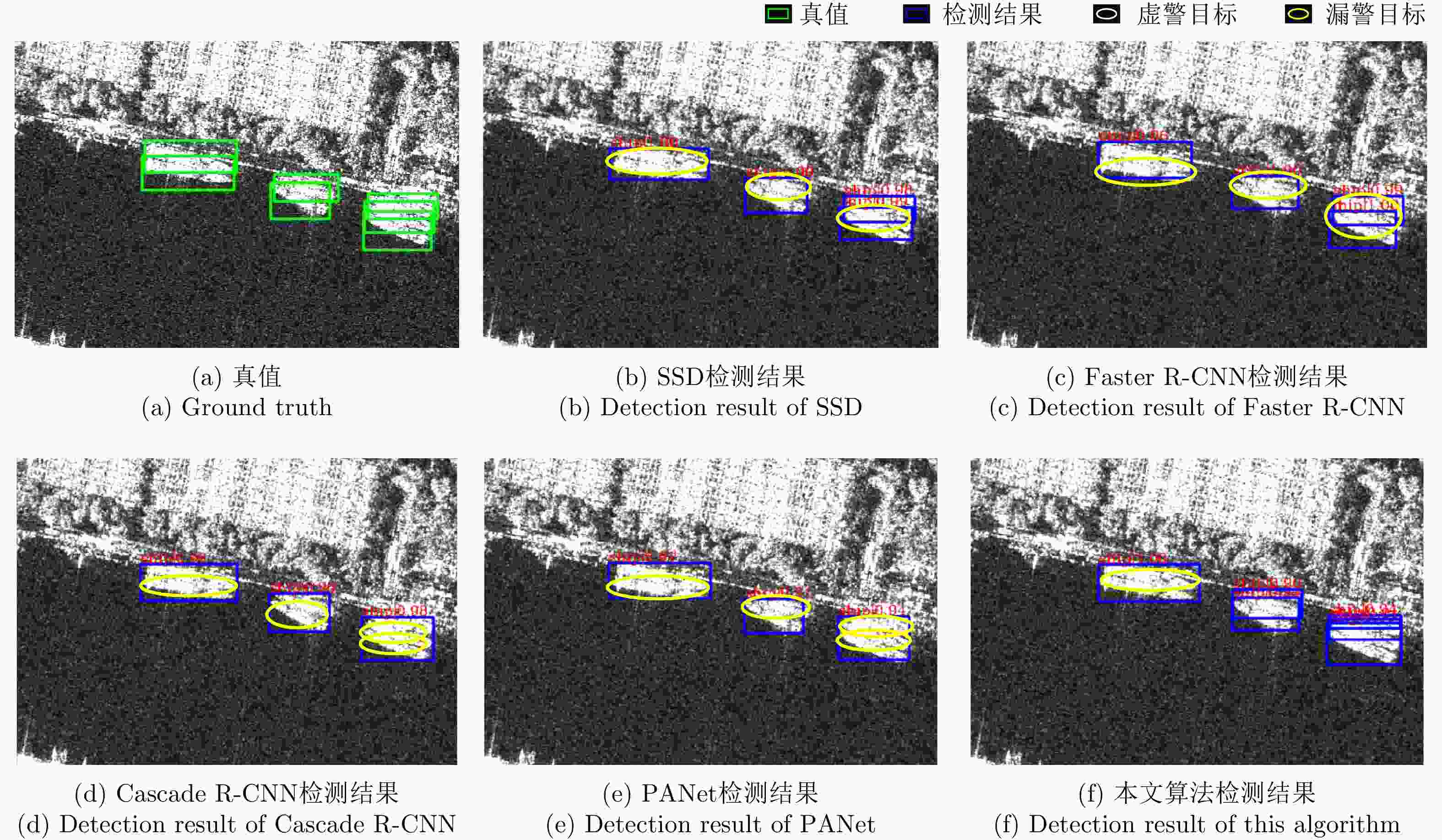
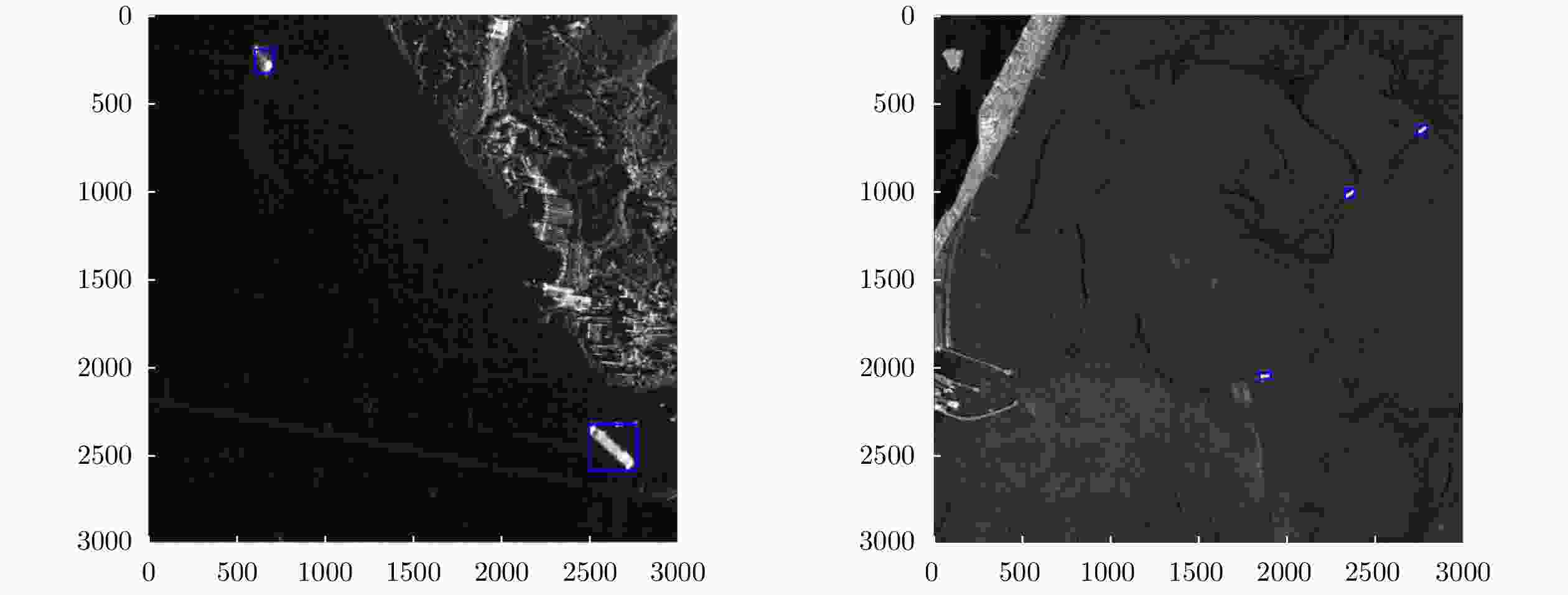
Method Inshore Offshore AP (%) R (%) AP (%) R (%) SSD 73.6 92.7 88.1 95.7 Cascade R-CNN 73.7 90.7 90.4 95.0 PANet 73.7 88.0 90.7 93.6 本文算法 74.3 90.7 90.7 94.1 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] 郭倩, 王海鹏, 徐丰. SAR图像飞机目标检测识别进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Research progress on aircraft detection and recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020 [3] WACKERMAN C C, FRIEDMAN K S, PICHEL W G, et al. Automatic detection of ships in RADARSAT-1 SAR imagery[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2001, 27(5): 568–577. doi: 10.1080/07038992.2001.10854896 [4] 陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 [5] 李健伟, 曲长文, 邵嘉琦, 等. 基于深度学习的SAR图像舰船检测数据集及性能分析[C]. 第五届高分辨率对地观测学术年会论文集, 西安, 2018: 180–201.LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, SHAO Jiaqi, et al. Dataset and performance analysis of ship detection methods based on deep learning[C]. The 5th China High Resolution Earth Observation Conference, Xi’an, China, 2018: 180–201. [6] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81. [7] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. [8] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [9] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [10] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [11] 李健伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟. 基于级联CNN的SAR图像舰船目标检测算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0168LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and PENG Shujuan. A ship detection method based on cascade CNN in SAR images[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0168 [12] 李广帅, 苏娟, 李义红. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的SAR图像飞机检测算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(1): 159–168. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0004LI Guangshuai, SU Juan, and LI Yihong. An aircraft detection algorithm in SAR image based on improved Faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(1): 159–168. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0004 [13] WANG Rui, SHAO Sihan, AN Mengyu, et al. Soft thresholding attention network for adaptive feature denoising in SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 29090–29105. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3059033 [14] ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. High-speed ship detection in SAR images based on a grid convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(10): 1206. doi: 10.3390/rs11101206 [15] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Depthwise separable convolution neural network for high-speed SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2483. doi: 10.3390/rs11212483 [16] ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. ShipDeNet-20: An only 20 convolution layers and <1-MB lightweight SAR ship detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, in press. [17] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. HyperLi-Net: A hyper-light deep learning network for high-accurate and high-speed ship detection from synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 167: 123–153. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.05.016 [18] GHIASI G, LIN T Y, and LE Q V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7029–7038. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00720. [19] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944, doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [20] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.322. [21] BODLA N, SINGH B, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Soft-NMS—Improving object detection with one line of code[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 5562–5570. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.593. [22] HU Jie, LI Shen, GANG Sun, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [23] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A deep learning dataset dedicated to small ship detection from large-scale sentinel-1 SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 2997. doi: 10.3390/rs12182997 [24] WEI Shunjun, ZENG Xiangfeng, QU Qizhe, et al. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234–120254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005861 [25] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097 [26] CAI Zhaowei and VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6154–6162, doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00644. [27] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759–8768. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00913. [28] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Balance scene learning mechanism for offshore and inshore ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, in press. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: