-
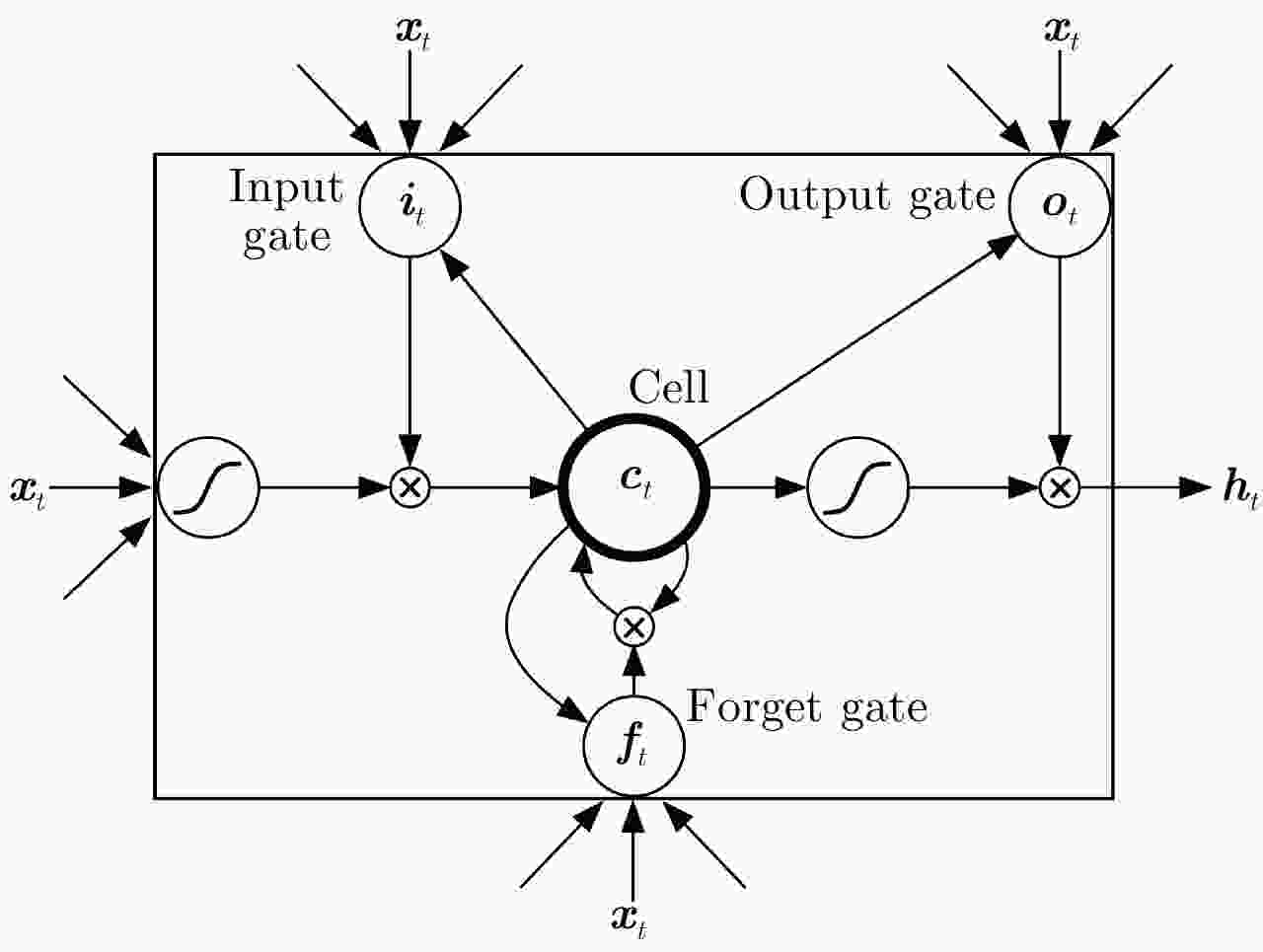
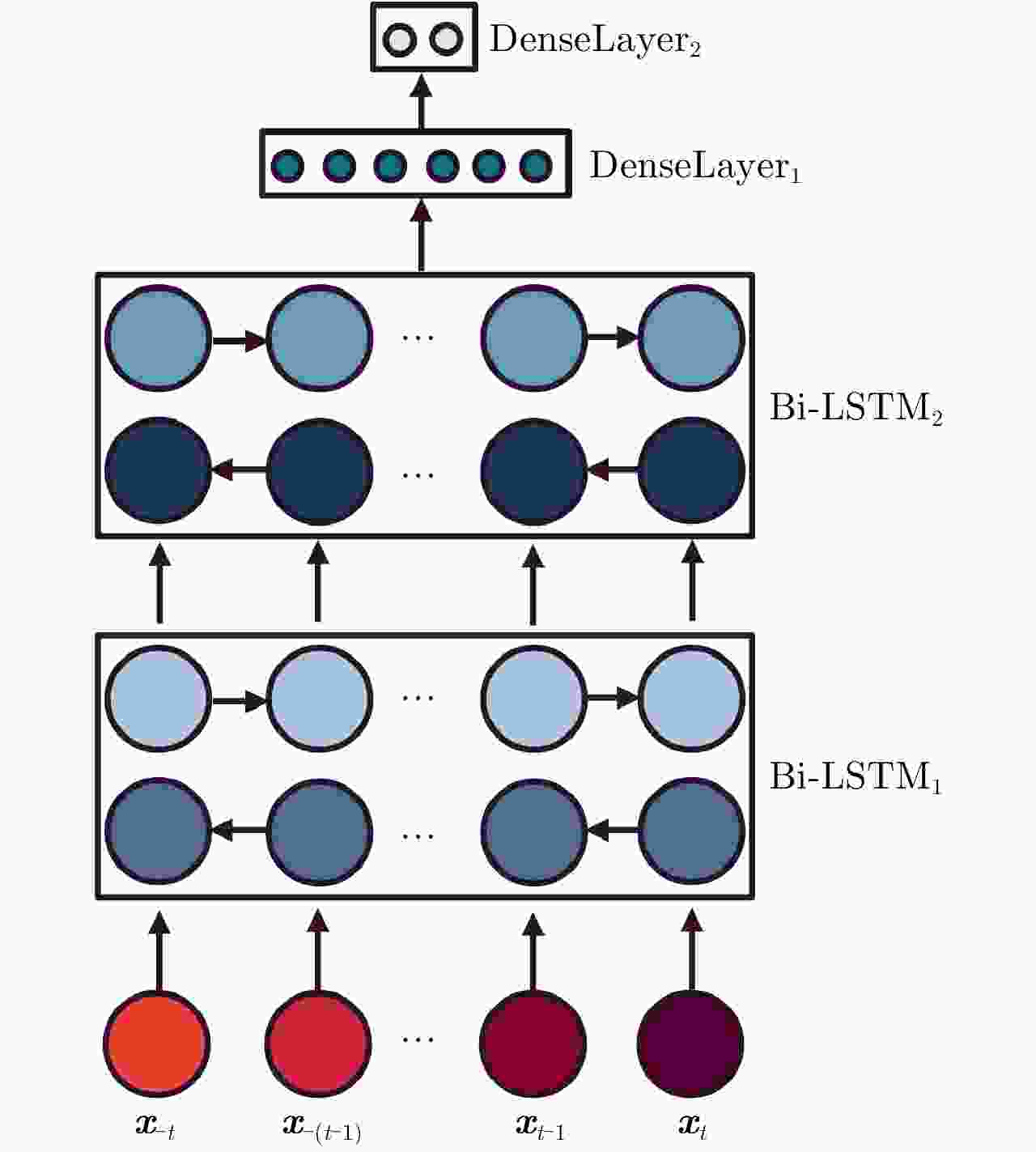
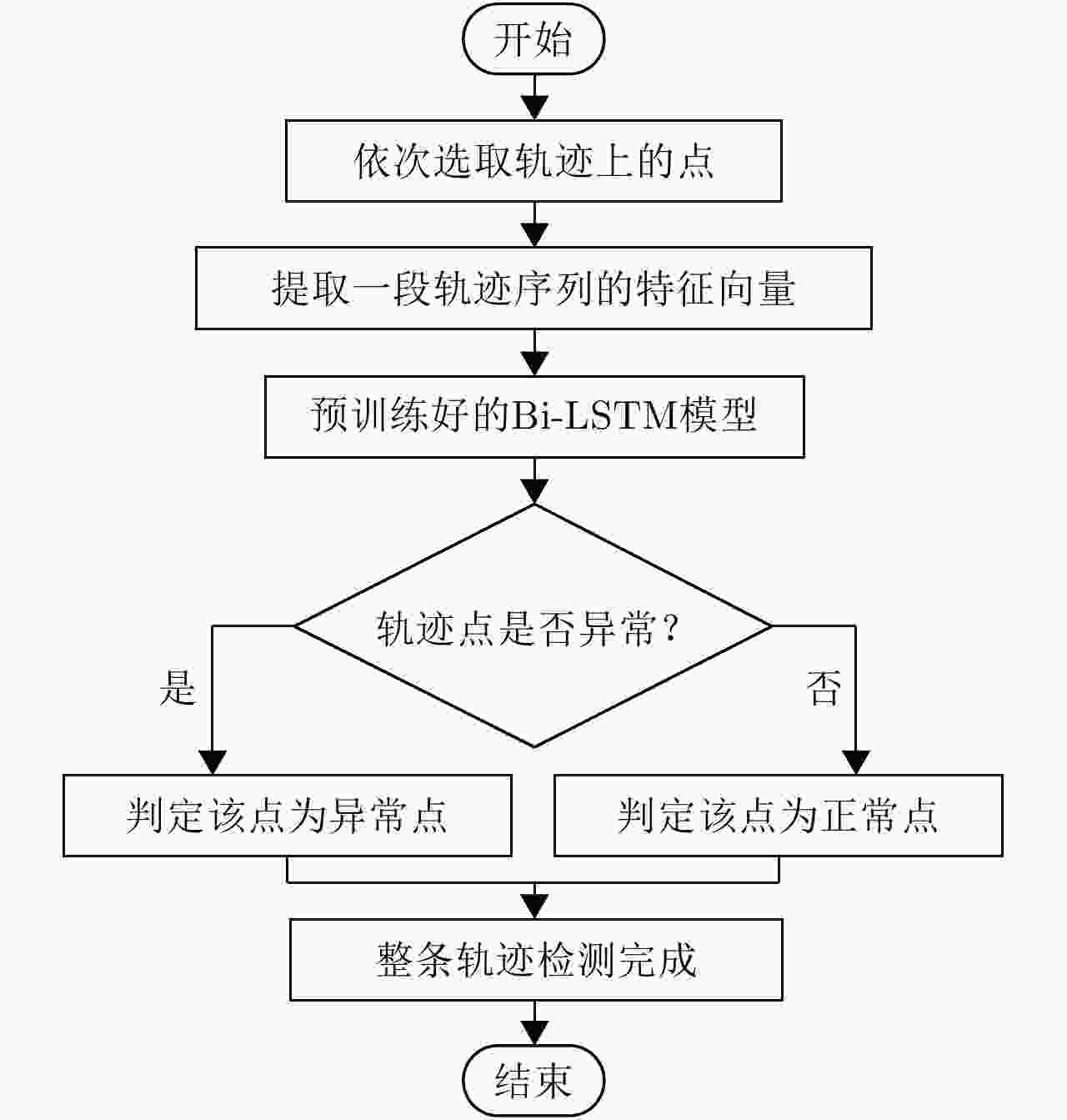
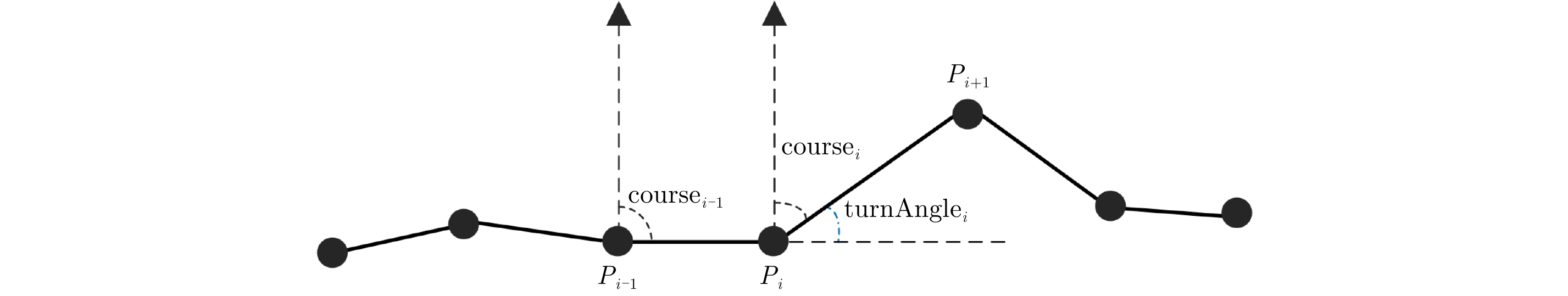
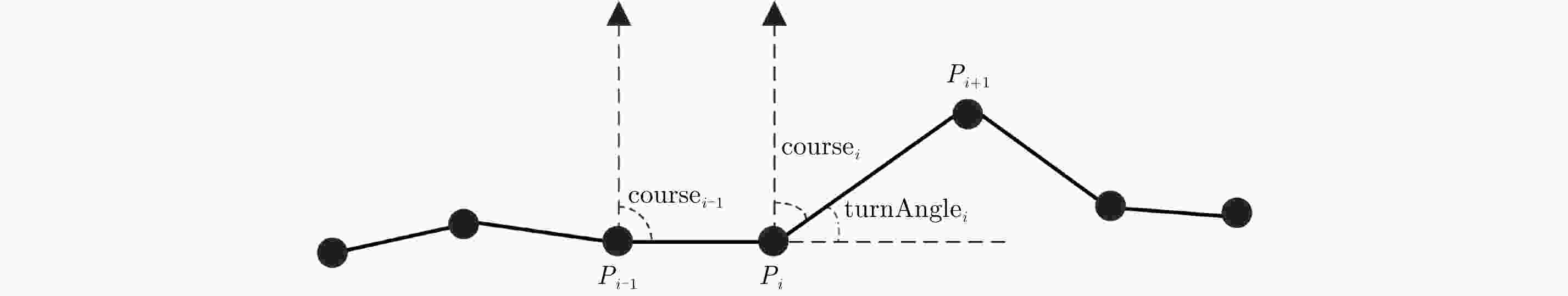
摘要: 定位技术的飞速发展催生了时空轨迹大数据,轨迹数据中往往存在着明显偏离轨迹的异常点。检测出轨迹中的异常点对提高数据质量和后续轨迹数据挖掘精度至关重要。该文提出了一种基于双向长短时记忆网络(Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory, Bi-LSTM)模型的轨迹异常点检测算法。首先对每个轨迹点提取一个6维的运动特征向量,然后构建了一个Bi-LSTM模型,模型输入为一定序列长度的轨迹数据特征向量,输出为轨迹点的类型结果。同时,算法采用了欠采样和过采样的组合方法缓解类别不平衡对检测性能的影响。融合了长短时记忆网络单元和双向网络,Bi-LSTM模型能够自动学习正常点和邻近异常点在运动特征上的差异。基于真实船舶轨迹标注数据的实验结果表明,该文算法的检测性能显著优于恒定速度阈值法、不考虑数据时序性的经典机器学习分类算法和卷积神经网络模型,尤其是召回率达到了0.902,验证了该文算法的有效性。Abstract: The rapid advances in positioning technology have created huge spatio-temporal trajectory data, and there are always obvious aberrant outliers in trajectory data. Detecting outliers in the trajectory is critical to improving data quality and the accuracy of subsequent trajectory data mining tasks. In this paper, we propose a trajectory outlier detection algorithm based on a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) model. First, a six-dimensional motion feature vector is extracted for each trajectory point, and then we construct a Bi-LSTM model. The model input is the trajectory data feature vector of a certain sequence length, and its output is the class type of the current track point. In addition, a combination method of undersampling and oversampling is applied to mitigate the effect of data distribution imbalance on detection performance. The Bi-LSTM model can automatically learn the difference between the normal points and adjacent abnormal points in the motion characteristics by combining the LSTM unit and the bidirectional network. Experimental results based on a real ship trajectory annotation data show that the detection performance of our proposed algorithm significantly exceeds those of the constant velocity threshold algorithm, non-sequential classical machine learning classification algorithms, and convolutional neural network model. Especially, the recall value of the proposed algorithm reaches 0.902, which verifies its effectiveness.
-
表 1 分类结果混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix of classification results
真实情况 预测结果 异常点 正常点 异常点 真正例(TP) 假反例(FN) 正常点 假正例(FP) 真反例(TN) 表 2 不同方法指标对比
Table 2. The performance of different models
模型 分类精度 准确率 召回率 F1值 AUC值 测试时长(s) CVTA 0.966 0.398 0.804 0.532 无 0.084 LR 0.981 0.857 0.101 0.180 0.550 1.603 DT 0.972 0.397 0.612 0.481 0.796 0.139 RF 0.989 0.811 0.623 0.705 0.810 0.317 XGBoost 0.980 0.517 0.640 0.572 0.813 0.398 CNN 0.983 0.828 0.268 0.405 0.633 4.069 Bi-LSTM 0.995 0.873 0.902 0.887 0.950 0.948 -
[1] LEE J G, HAN J W, and WHANG K Y. Trajectory clustering: A partition-and-group framework[C]. Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Beijing, China, 2007: 593–604. [2] 李万春, 黄成峰. 基于角度和多普勒频率的外辐射源定位系统的接收器最优航迹分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 660–665. doi: 10.12000/JR14118LI Wan-chun and HUANG Cheng-feng. Optimal trajectory analysis for the receiver of passive location systems using direction of arrival and Doppler measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 660–665. doi: 10.12000/JR14118 [3] 齐林, 王海鹏, 刘瑜. 基于统计双门限的中断航迹配对关联算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(3): 301–308. doi: 10.12000/JR14077QI Lin, WANG Hai-peng, and LIU Yu. Track segment association algorithm based on statistical binary thresholds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(3): 301–308. doi: 10.12000/JR14077 [4] ZHENG Y, LIU L K, WANG L H, et al. Learning transportation mode from raw GPS data for geographic applications on the web[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on World Wide Web, Beijing, China, 2008: 247–256. doi: 10.1145/1367497.1367532. [5] BAO J, ZHENG Y, and MOKBEL M F. Location-based and preference-aware recommendation using sparse geo-social networking data[C]. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Redondo Beach, California, 2012: 199–208. doi: 10.1145/2424321.2424348. [6] ZHANG D Q, LI N, ZHOU Z H, et al. iBAT: Detecting anomalous taxi trajectories from GPS traces[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Beijing, China, 2011: 99–108. doi: 10.1145/2030112.2030127. [7] ZHENG Y and ZHOU X F. Computing with Spatial Trajectories[M]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. [8] HAWKINS D M. Identification of Outliers[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1980. [9] HAN J W, KAMBER M, and PEI J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011. [10] ALVARES L O, OLIVEIRA G, and BOGORNY V. A framework for trajectory data preprocessing for data mining[C]. Proceedings of the 21st Interantional Conference on Software Engineering & Knowledge Engineering, SEKE, Boston, USA, 2009, 21: 698–702. [11] CHEN L, LV M Q, YE Q, et al. A personal route prediction system based on trajectory data mining[J]. Information Sciences, 2011, 181(7): 1264–1284. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2010.11.035 [12] ZHENG Y, XIE X, and MA W Y. Geolife: A collaborative social networking service among user, location and trajectory[J]. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 2010, 33(2): 32–39. [13] CHEN X J, CUI T T, FU J H, et al. Trend-residual dual modeling for detection of outliers in low-cost GPS trajectories[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(12): 2036. doi: 10.3390/s16122036 [14] 胡晶. 基于AIS的船舶轨迹分析与应用系统的设计与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 华中师范大学, 2015.HU Jing. Design and implementation of vessel trajectory analysis and application system based on AIS[D]. [Master dissertation], Central China Normal University, 2015. [15] 吴建华, 吴琛, 刘文, 等. 舶舶AIS轨迹异常的自动检测与修复算法[J]. 中国航海, 2017, 40(1): 8–12, 101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2017.01.003WU Jian-hua, WU Chen, LIU Wen, et al. Automatic detection and restoration algorithm for trajectory anomalies of ship AIS[J]. Navigation of China, 2017, 40(1): 8–12, 101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2017.01.003 [16] BESSA A, DE MESENTIER SILVA F, NOGUEIRA R F, et al. RioBusData: Outlier detection in bus routes of rio de janeiro[OL]. arXiv: 160106128, 2016. [17] FERNANDO T, DENMAN S, SRIDHARAN S, et al. Soft+ hardwired attention: An lstm framework for human trajectory prediction and abnormal event detection[OL]. arXiv: 1702.05552, 2017. [18] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [19] GRAVES A and SCHMIDHUBER J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures[J]. Neural Networks, 2005, 18(5/6): 602–610. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.06.042 [20] SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15: 1929–1958. [21] BATISTA G E A P A, PRATI R C, and MONARD M C. A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data[J]. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2004, 6(1): 20–29. doi: 10.1145/1007730.1007735 [22] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016.ZHOU Zhi-hua. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016. [23] FAWCETT T. An introduction to ROC analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(8): 861–874. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010 [24] PEDREGOSA F, VAROQUAUX G, GRAMFORT A, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2825–2830. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: