Synthetic Aperture Passive Localization of a Single-satellite Multi-radar Emitter via Time-frequency Parameter Estimation
-
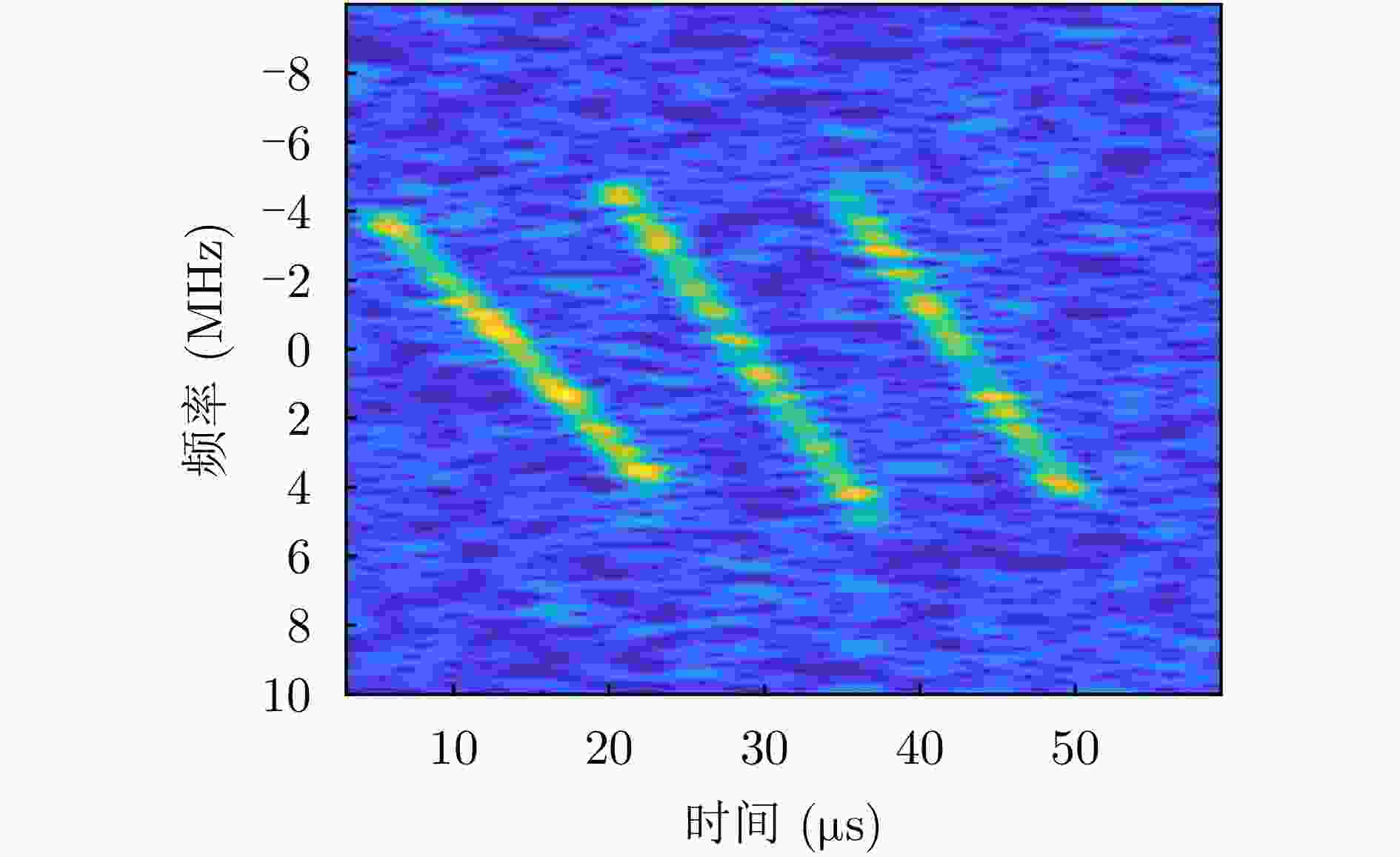
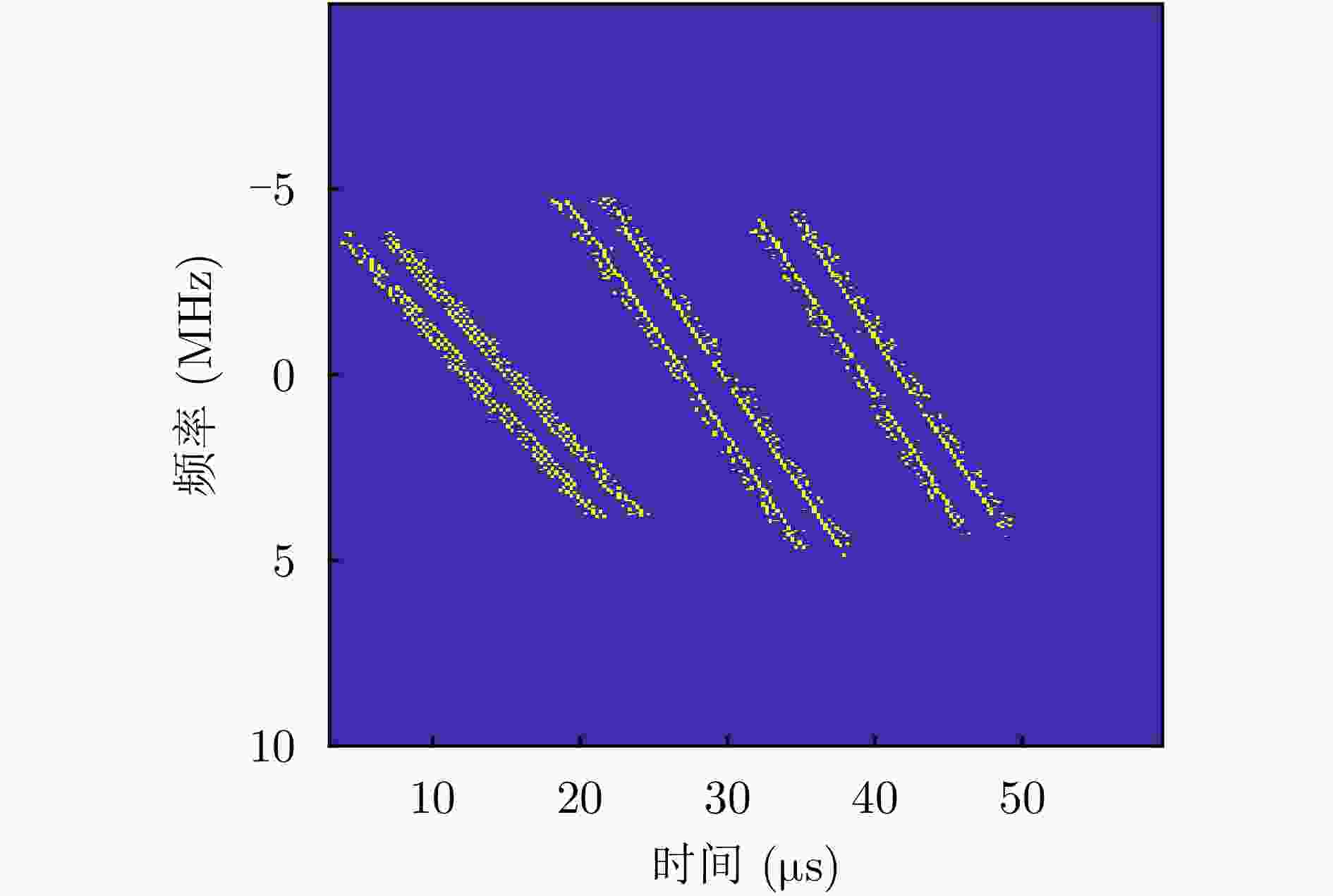
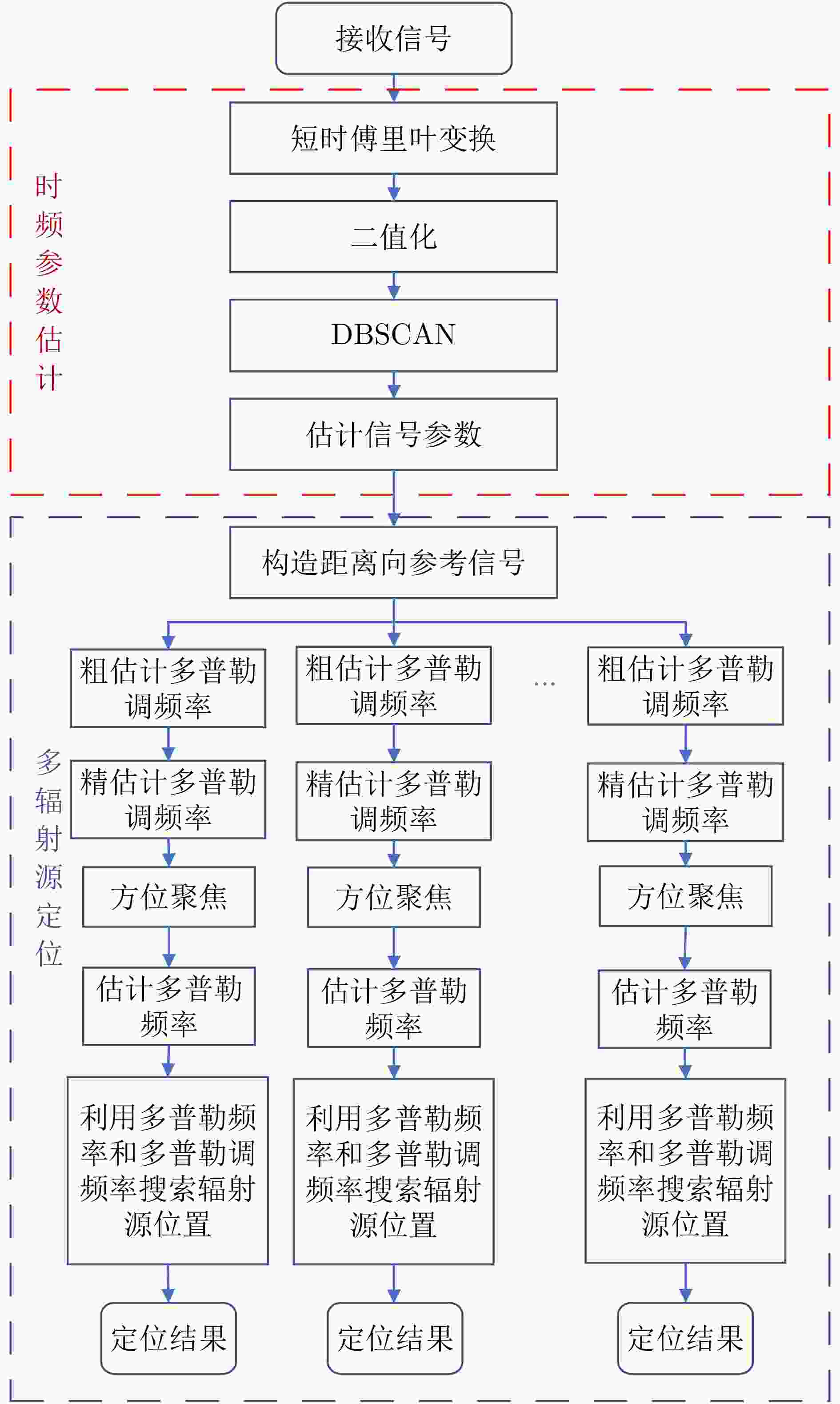
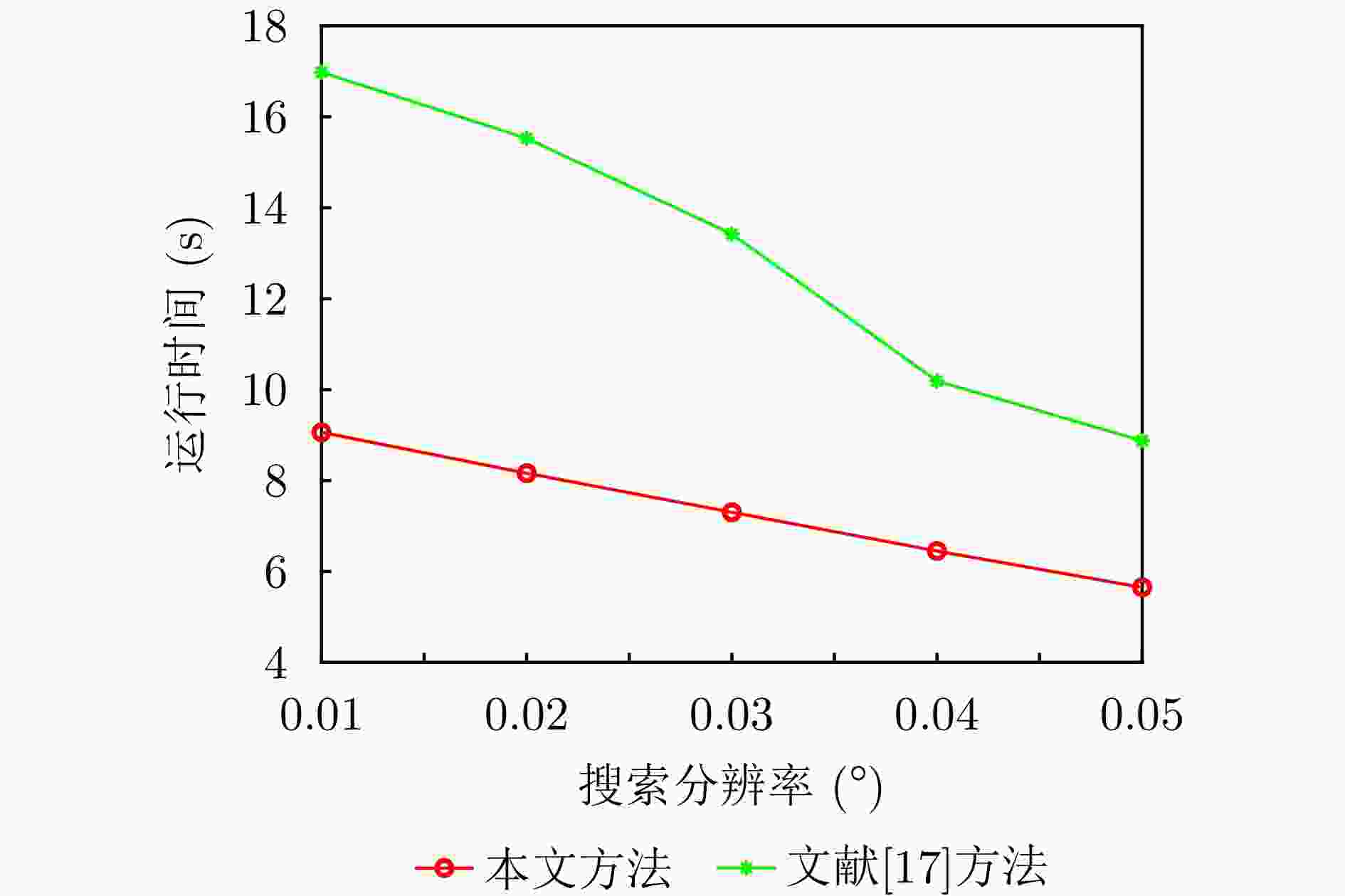
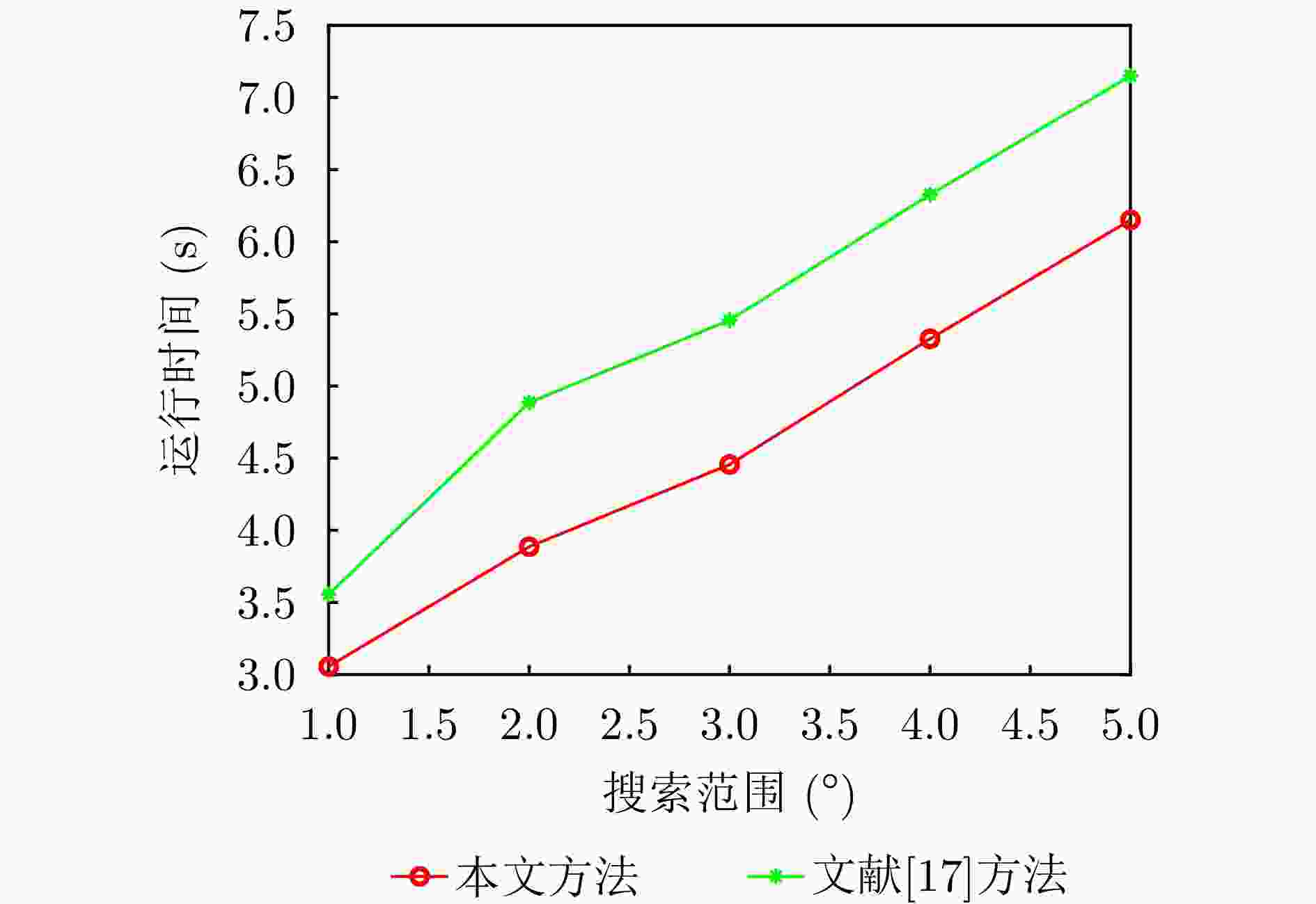
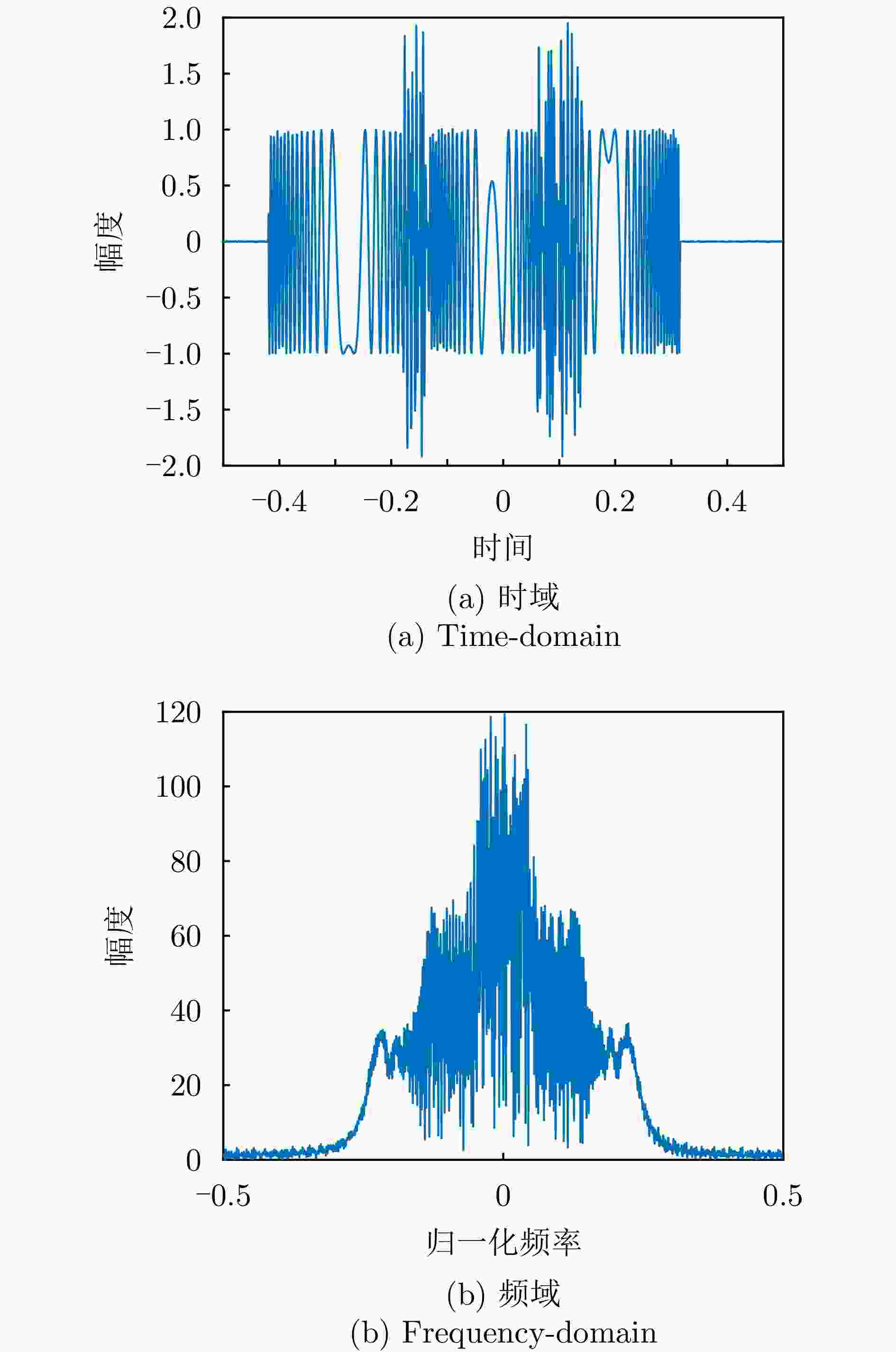
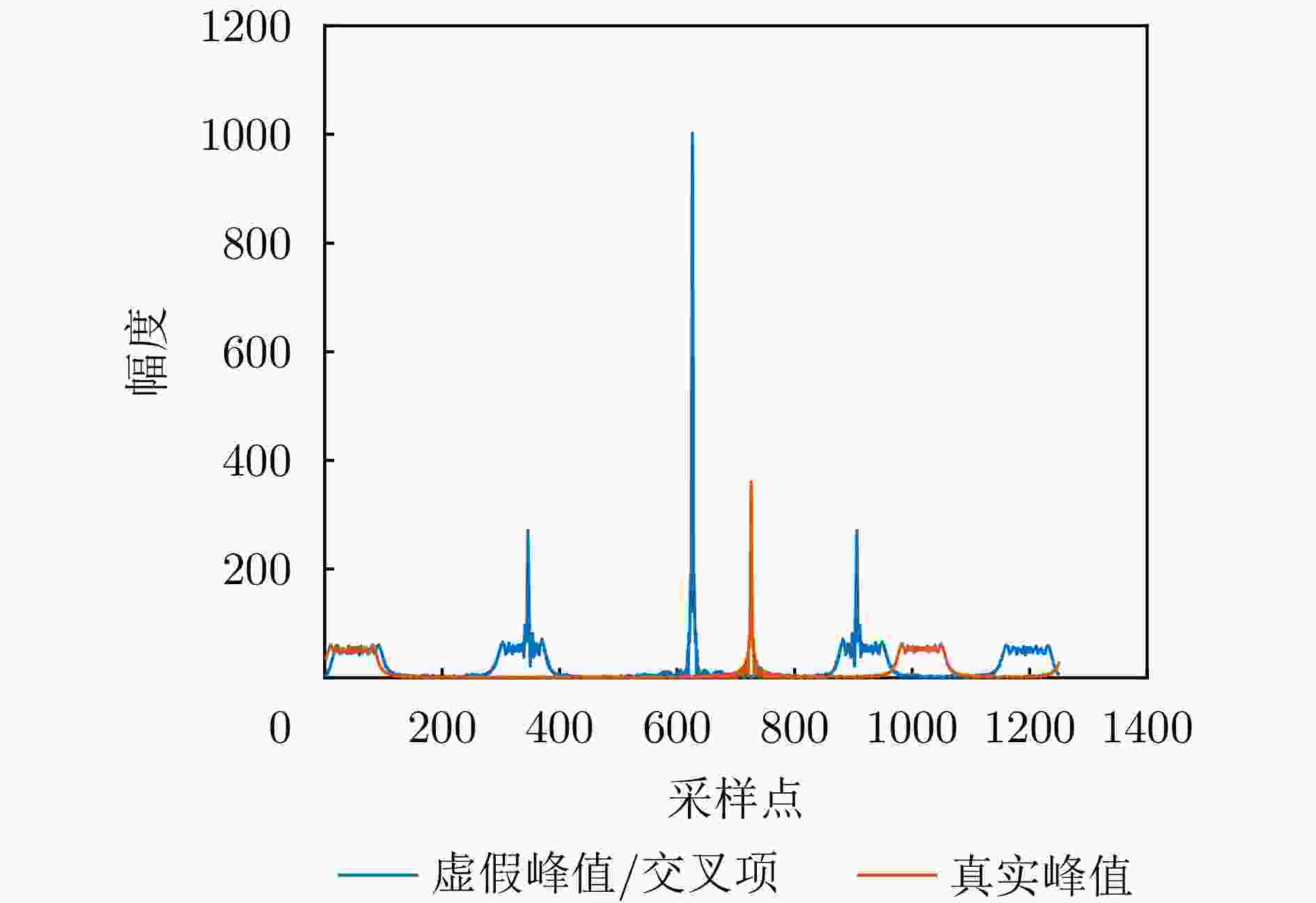
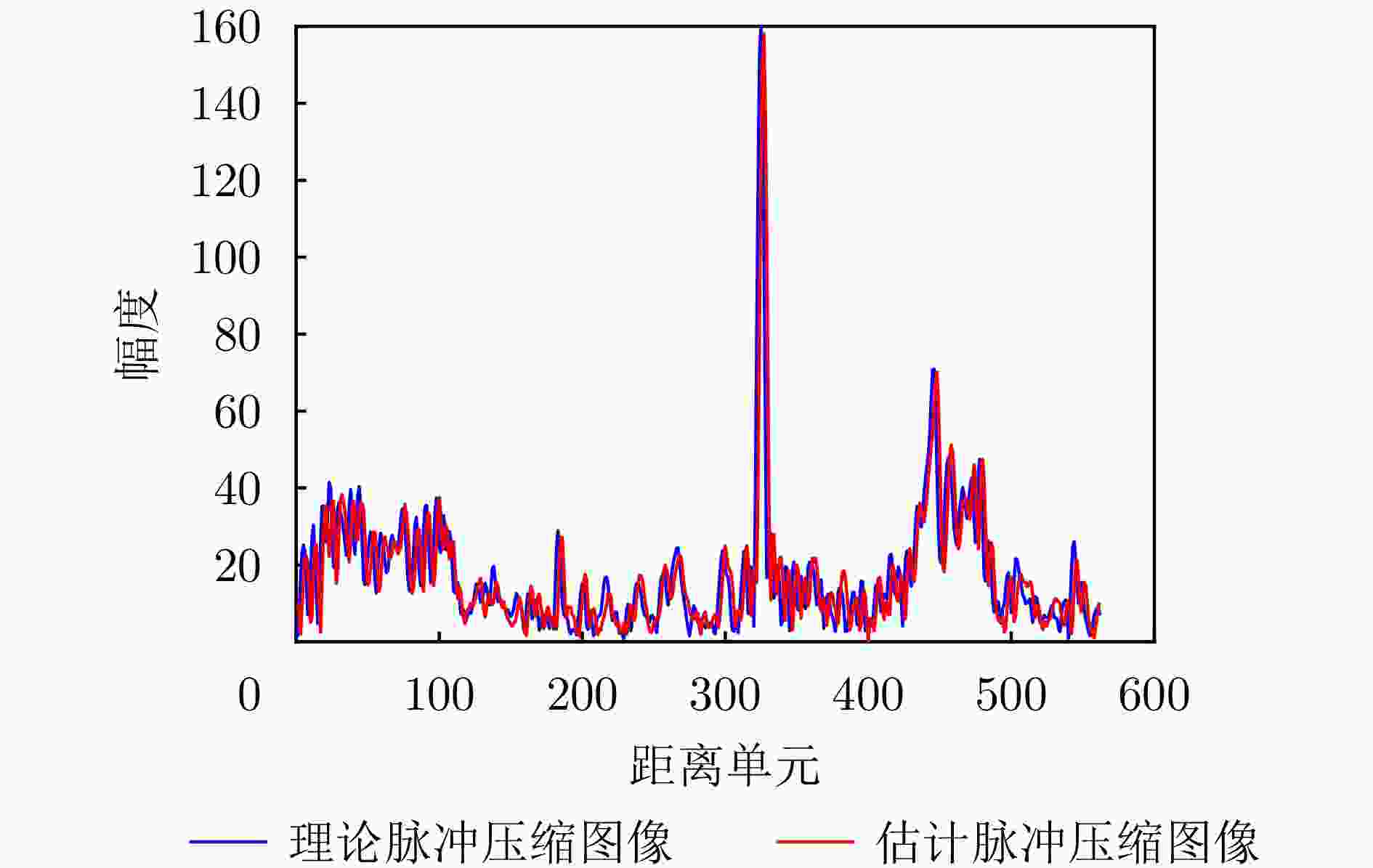
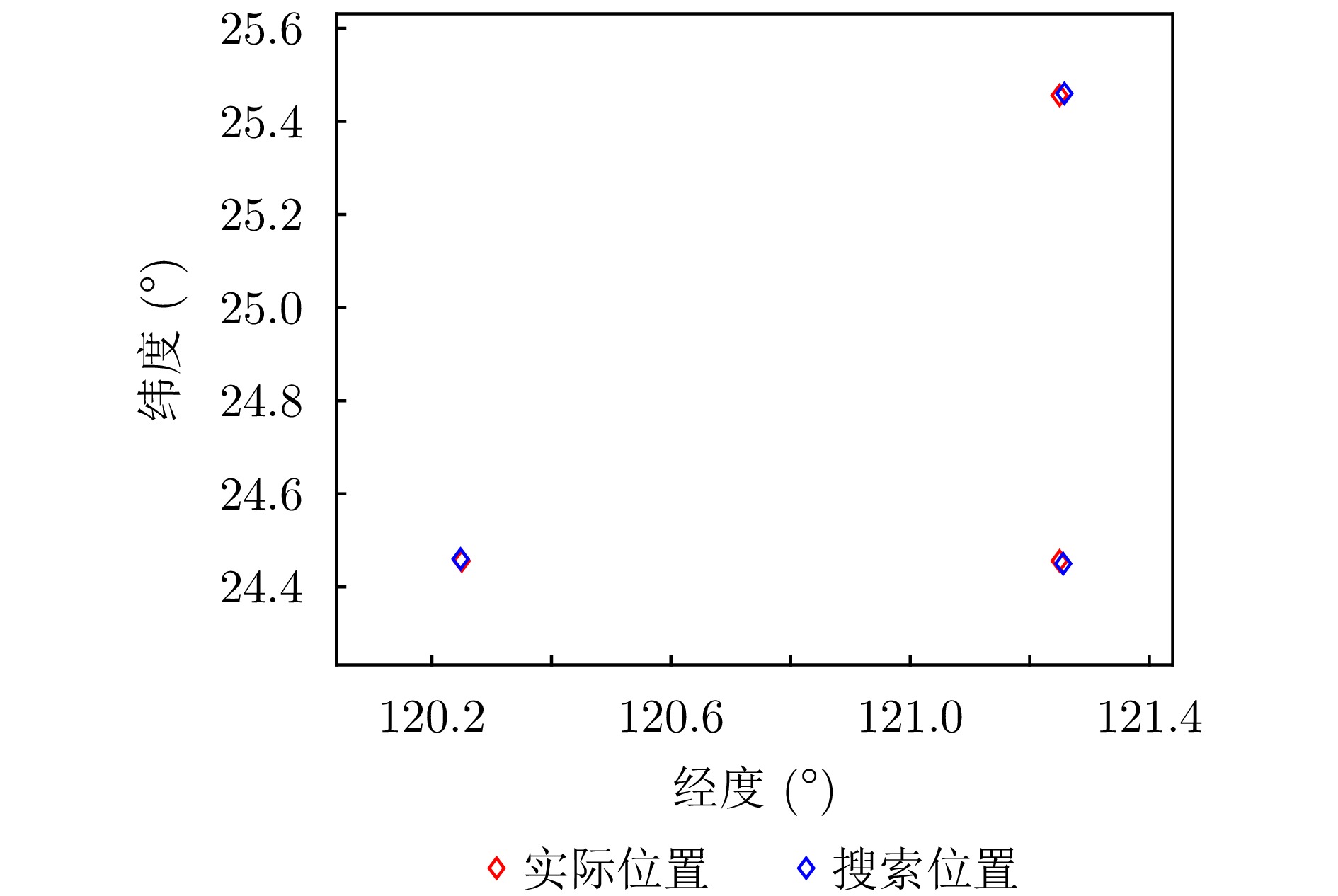
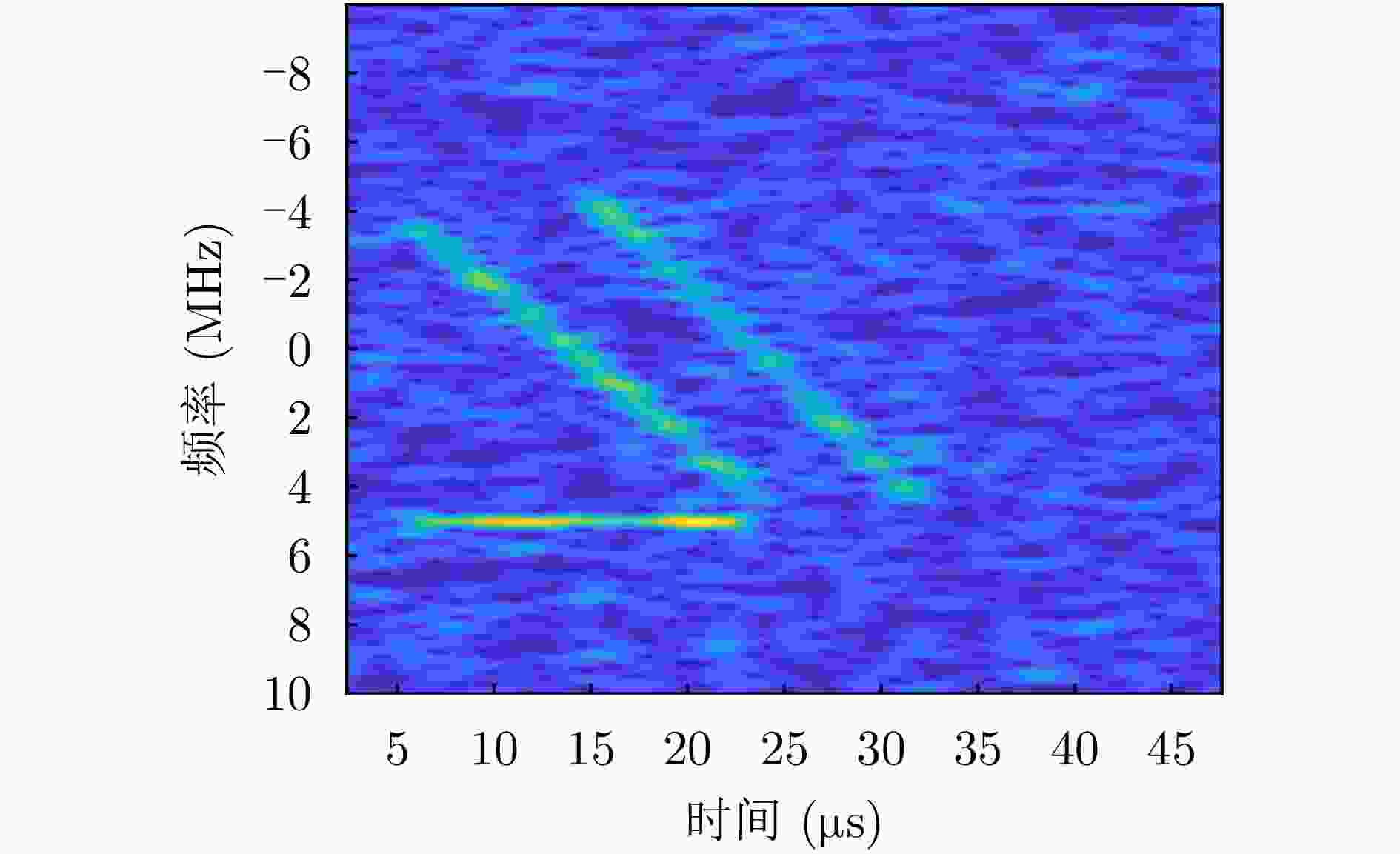
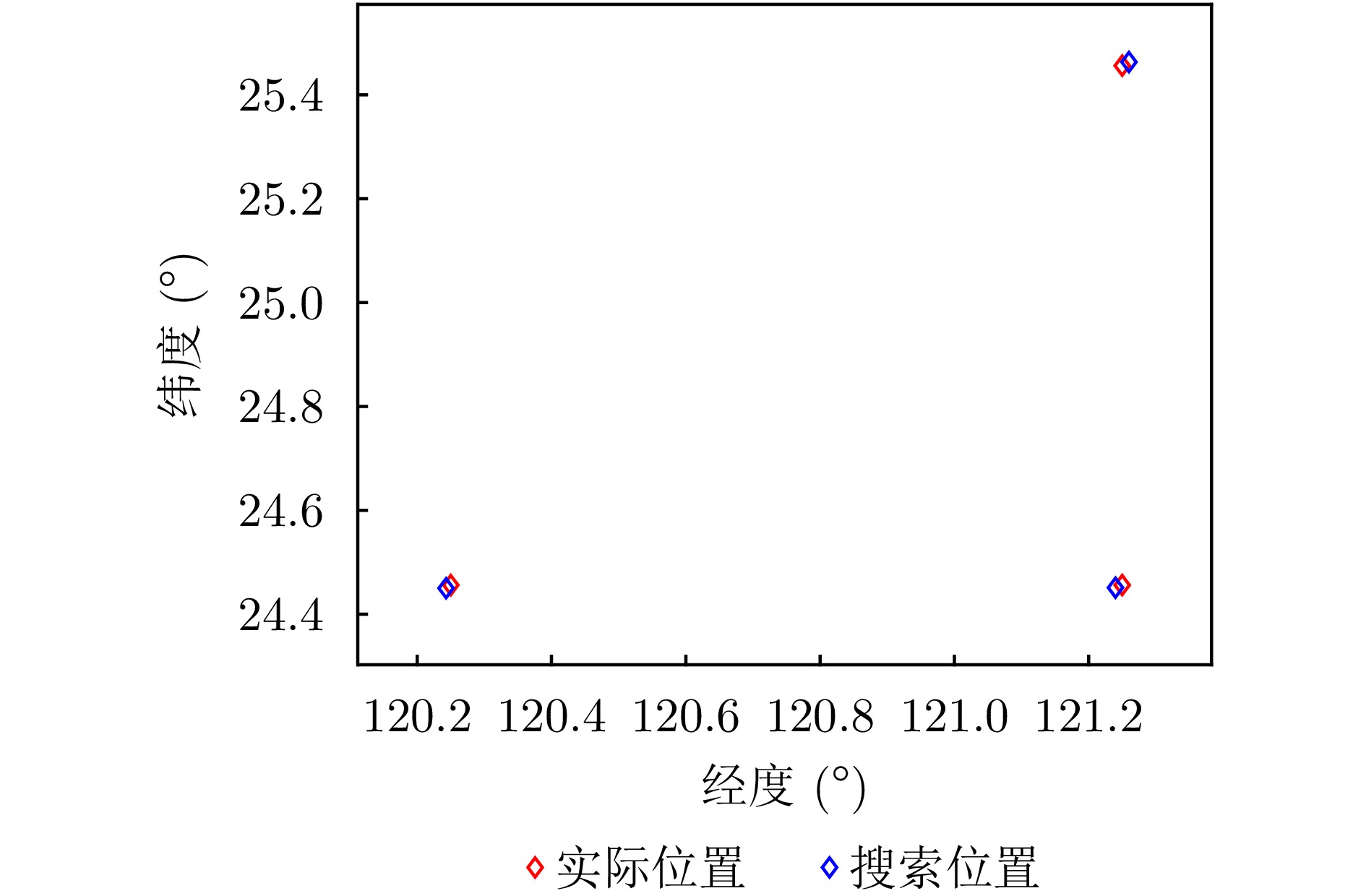
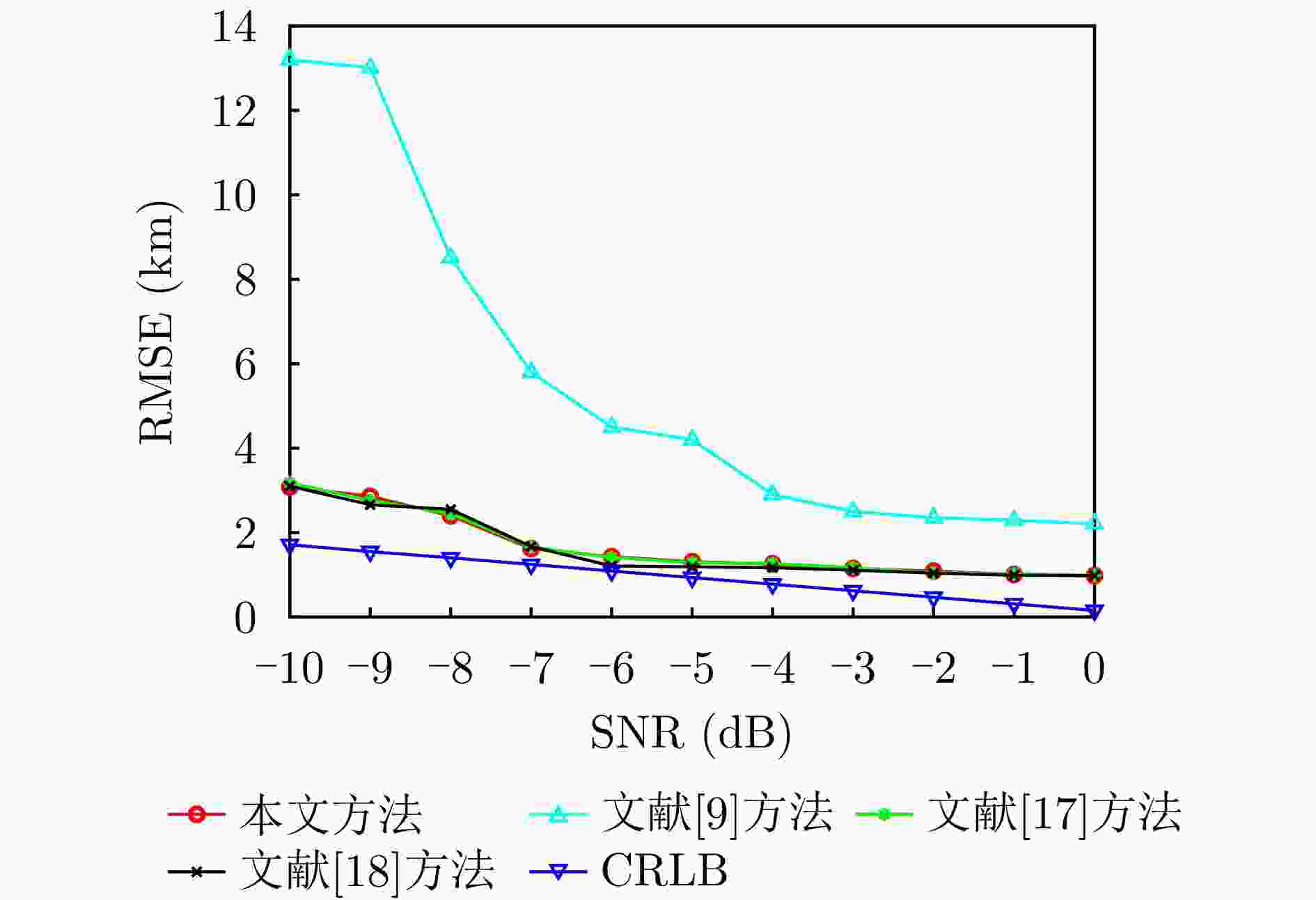
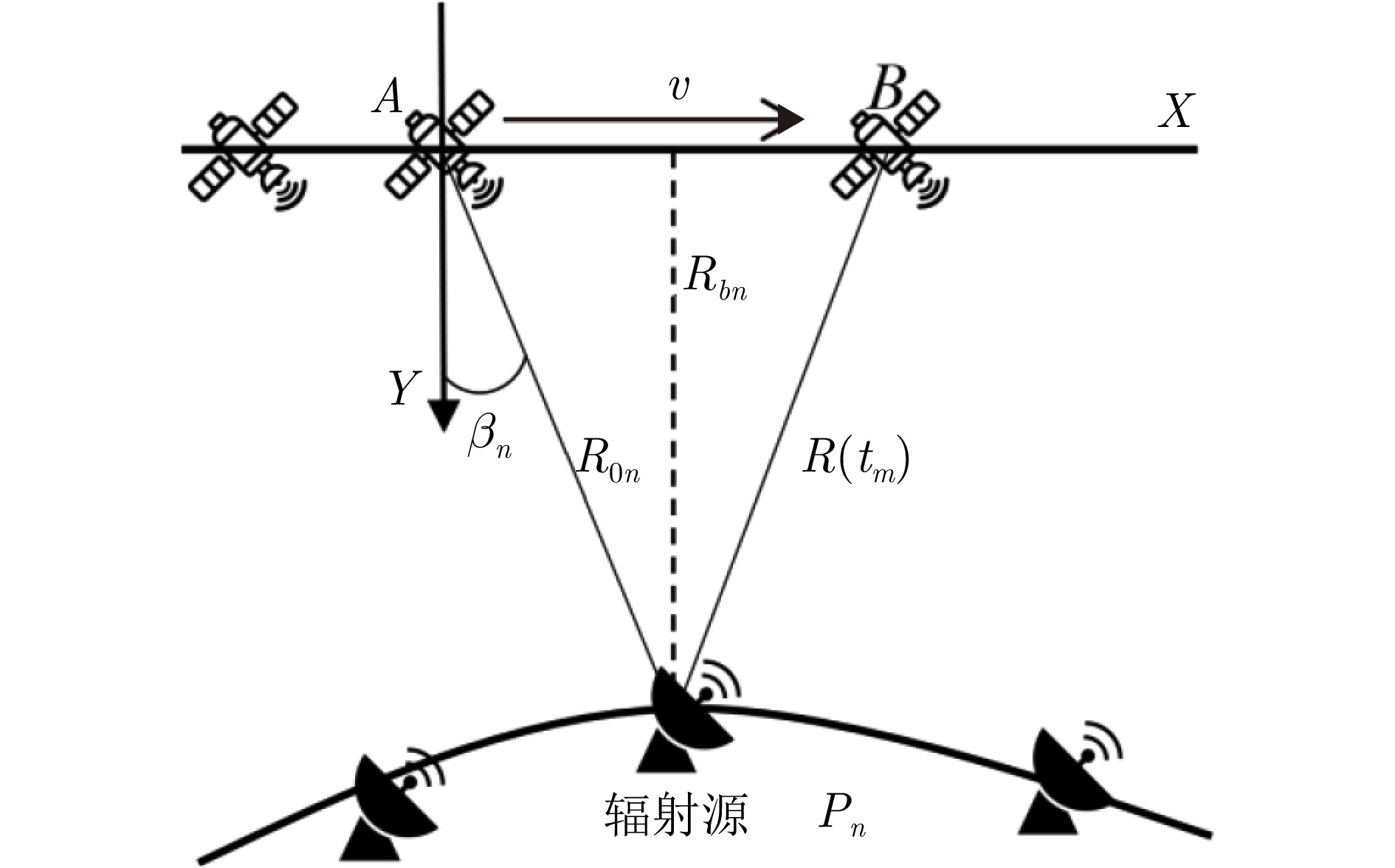
摘要: 基于合成孔径的无源定位方法具有高的定位精度,但对多个发射线性调频信号的雷达辐射源,由于难以分辨多个在时域和频域均混叠的信号,这会引起信号的相位重叠,导致其定位性能显著下降。针对这个问题,该文提出了一种基于时频参数估计的单星多雷达辐射源合成孔径无源定位方法。首先,构建了多个发射线性调频信号的雷达辐射源信号模型,采用短时傅里叶变换(STFT)与DBSCAN联合估计多个雷达辐射源信号的时频参数,通过STFT结合粗估计与精估计的搜索方式实现方位调频率的快速估计,最终通过距离和方位两维聚焦实现多个雷达辐射源的准确定位。在此基础上,推导了该文所提方法的克拉美罗下界(CRLB)。实验结果表明:与改进实值空时子空间数据融合的直接定位法相比,所提方法在信噪比–10 dB下定位精度提高了约10 km;与基于CLEAN的合成孔径多源定位方法相比,所提方法运算时间缩短一半。
-
关键词:
- 单星合成孔径定位 /
- 多雷达辐射源 /
- 时频混叠 /
- 时频参数估计 /
- 短时傅里叶变换-基于密度聚类
Abstract: Passive localization methods based on synthetic aperture imaging offer high positioning accuracy. However, in scenarios involving multiple radar emitters transmitting Linear Frequency-Modulated (LFM) signals, distinguishing signals that are overlapped in the time and frequency domains can be challenging. This phenomenon, known as phase overlap, results in a significant degradation of localization performance. To address this issue, the present paper proposes a single-satellite multi-radar-emitter passive localization method based on synthetic aperture imaging using time-frequency parameter estimation. First, a signal model for multiple radar emitters transmitting LFM signals is constructed. The time-frequency parameters of the multiple radar emitter signals are estimated concurrently via a combination of Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and DBSCAN. A rapid approximation of the azimuth chirp rate is attained through a coarse-to-fine search strategy founded upon the use of the STFT. The accurate localization of multiple radar emitters is ultimately realized through the implementation of two-dimensional focusing in the range and azimuth dimensions. The Cramer-Rao lower bound of the proposed method is derived on this basis. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed method enhances the localization accuracy by approximately 10 km at a signal-to-noise ratio of −10 dB, in comparison with the enhanced real-valued space-time subspace data fusion-based direct positioning method. Moreover, it reduces the computational time by half relative to the CLEAN-based synthetic aperture multi-source localization approach. -
表 1 实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters
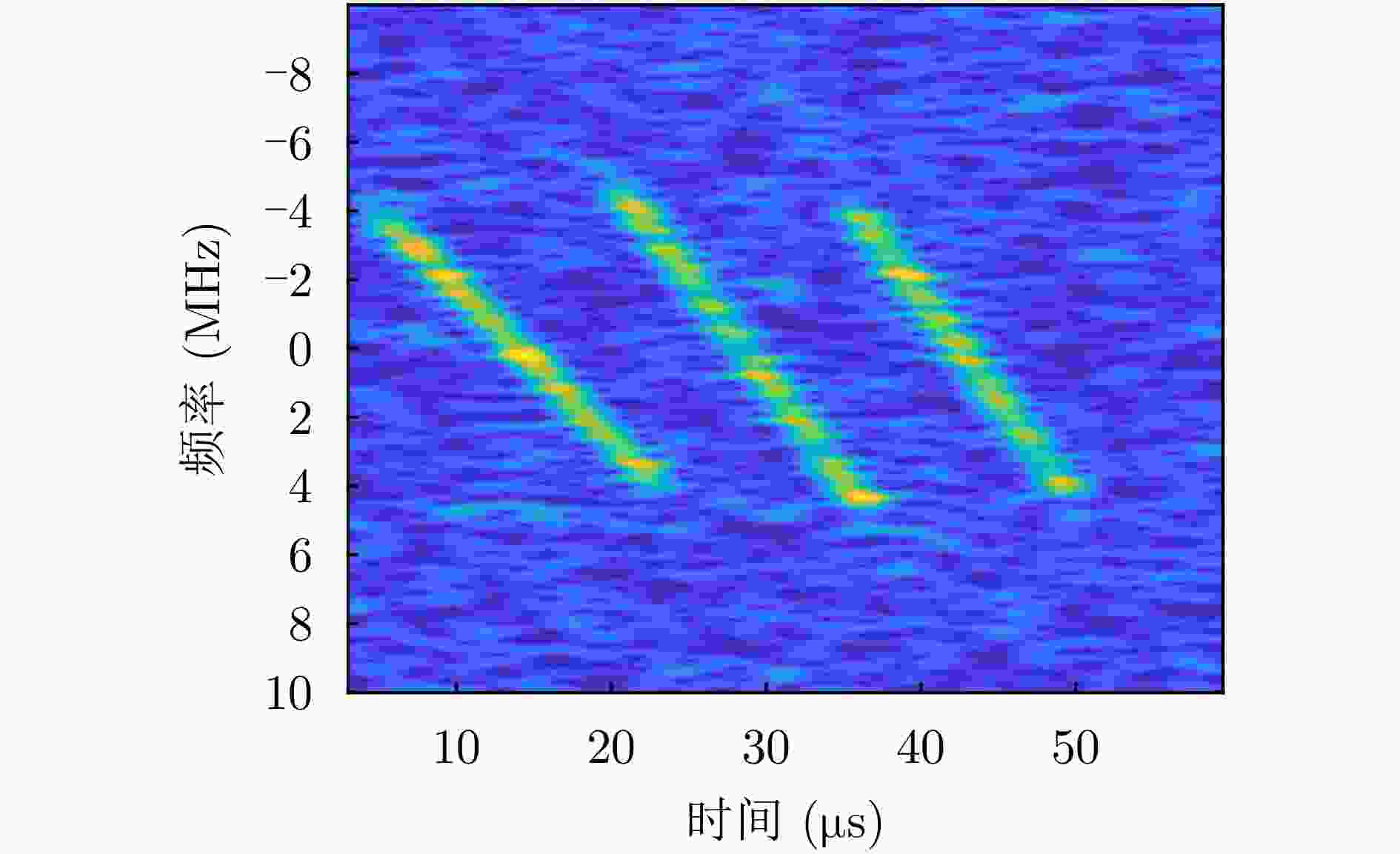
参数 数值 卫星高度(km) 550 卫星速度(m/s) 7500 采样率(MHz) 20 辐射源位置 (120.250°, 24.456°, 0)
(120.250°, 25.456°, 0)
(121.250°, 24.456°, 0)载频(GHz) 12 带宽(MHz) 8, 10, 9 脉冲持续时间(μs) 18, 17, 15 合成孔径时间(s) 1 -
[1] 马振洋, 周中华, 张帆, 等. 北斗三号仅用作追踪的机载设备适航要求分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(4): 1162–1175. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0452.MA Zhenyang, ZHOU Zhonghua, ZHANG Fan, et al. Analysis of airworthiness requirements of Beidou-3 airborne equipment only used for tracking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1162–1175. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0452. [2] 刘清, 谢坚, 王伶, 等. 卫星导航欺骗式干扰源高精度直接定位方法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(5): 1117–1122. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210527.LIU Qing, XIE Jian, WANG Ling, et al. High precision direct position determination method for satellite navigation spoofing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1117–1122. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210527. [3] ZHU Yifan and ZHANG Shunsheng.Passive location based on an accurate Doppler measurement by single satellite[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 1424–1427. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944430. [4] ELLIS P, VAN RHEEDEN D, and DOWLA F. Use of Doppler and Doppler rate for RF geolocation using a single LEO satellite[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 12907–12920. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965931. [5] 严航, 姚山峰. 低轨单星测频定位技术及其精度分析[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(18): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.18.002.YAN Hang and YAO Shanfeng. Localization technology of frequency measurement for single low earth orbit satellite and its precision analysis[J]. Computer Engineering, 2012, 38(18): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.18.002. [6] 吴顺华, 辛勤, 万建伟. 一种单星对星仅测角无源定轨跟踪方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2009, 21(12): 3701–3704.WU Shunhua, XIN Qin, and WAN Jianwei. Novel satellite-to-satellite passive orbit determination and tracking method with bearing-only measurements[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(12): 3701–3704. [7] 李腾, 郭福成, 姜文利. 星载干涉仪无源定位新方法及其误差分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032.LI Teng, GUO Fucheng, and JIANG Wenli. A novel method for satellite-borne passive localization using interferometer and its error analysis[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032. [8] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Direct position determination of multiple radio signals[C]. 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, Canada, 2004: ii–81. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2004.1326199. [9] 招乾民, 张顺生. 改进实值空时子空间数据融合的单星直接定位方法[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(6): 1111–1121. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.06.011.ZHAO Qianmin and ZHANG Shunsheng. Improved single-satellite direct position determination method via real-valued space-time subspace data fusion[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(6): 1111–1121. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.06.011. [10] 黄凯, 尤明懿, 陆安南, 等. 星载测向系统的测向误差及其定位误差计算方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2024, 45(9): 1488–1497. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.09.014.HUANG Kai, YOU Mingyi, LU Annan, et al. A calculation method of direction-finding errors and localization errors by a single satellite[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(9): 1488–1497. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.09.014. [11] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, XIANG Jixiang, et al. A imaging passive localization method for wideband signal based on SAR[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/APSAR46974.2019.9048398. [12] 张莉婷, 郇浩, 陶然. 基于被动合成孔径的单星无源高精度定位方法[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2020, 36(6): 43–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.06.010.ZHANG Liting, HUAN Hao, and TAO Ran. Highprecision emitter localization based on spaceborne passive synthetic aperture[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2020, 36(6): 43–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.06.010. [13] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Long synthetic aperture passive localization using azimuth chirp-rate contour map[C]. IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 928–931. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323154. [14] 王裕旗, 孙光才, 杨军, 等. 基于长合成孔径的辐射源成像定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080.WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, YANG Jun, et al. Passive localization algorithm for radiation source based on long synthetic aperture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080. [15] CHEN Bowei, WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, et al. A long synthetic aperture passive localization method using two planes[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 767–769. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028522. [16] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A high-resolution and high-precision passive positioning system based on synthetic aperture technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5230613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3186767. [17] WANG Yuqi, DONG Wenlong, SUN Guangcai, et al. A CLEAN-based synthetic aperture passive localization algorithm for multiple signal sources[J]. IEEE Journal on Miniaturization for Air and Space Systems, 2022, 3(4): 294–301. doi: 10.1109/JMASS.2022.3215982. [18] ZHANG Liting, HUAN Hao, RAN Tao, et al. A spaceborne passive localization algorithm based on MSD-HOUGH for multiple signal sources[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(22): 4303. doi: 10.3390/rs16224303. [19] ZHONG Qi, HE Zhiyi, and WEI Shaoren. Interrupted sampling repeater jamming recognition and suppression method based on DBSCAN algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 62597–62608. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3395537. [20] 李杨寰, 初翠强, 徐晖, 等. 一种新的脉冲重复频率估计方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2007, 22(2): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2007.02.005.LI Yanghuan, CHU Cuiqiang, XU Hui, et al. A novel algorithm for estimating pulse repetition frequency[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2007, 22(2): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2007.02.005. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: