Joint Space-polarization Jamming Suppression Algorithm Based on Dimensional Decomposition for Digital Array Antenna
-
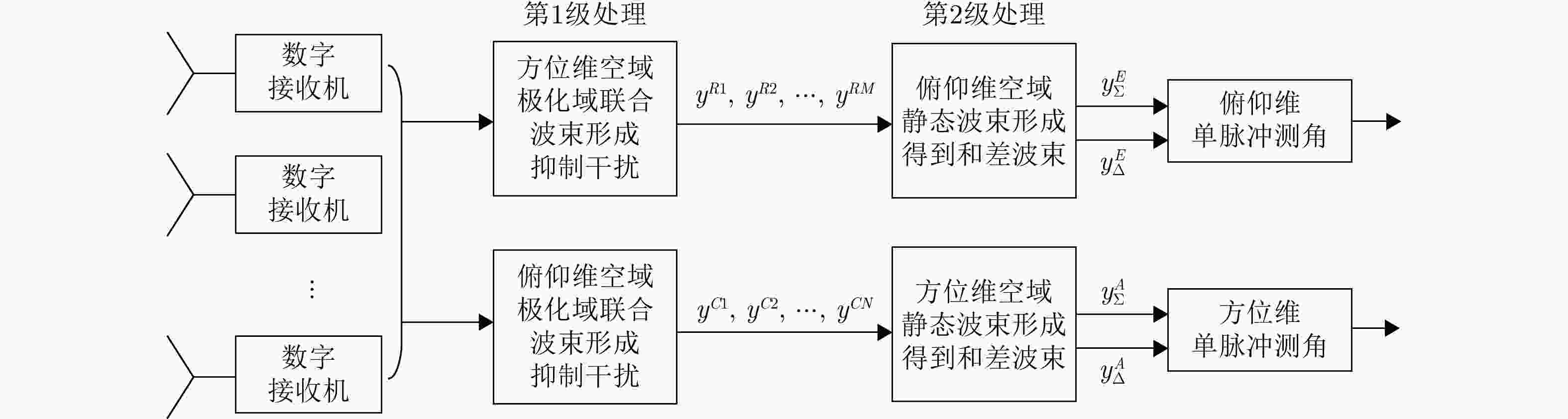
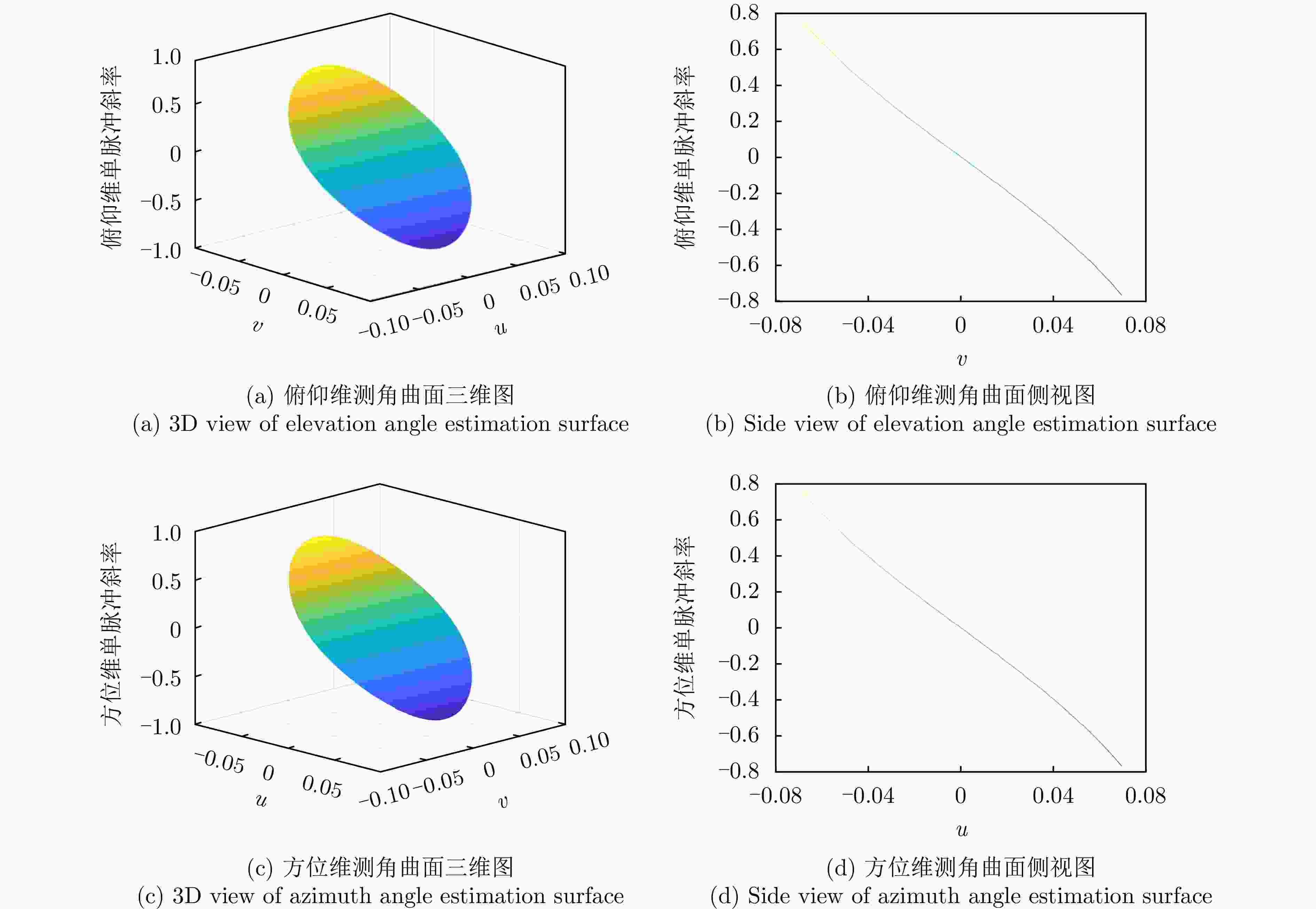
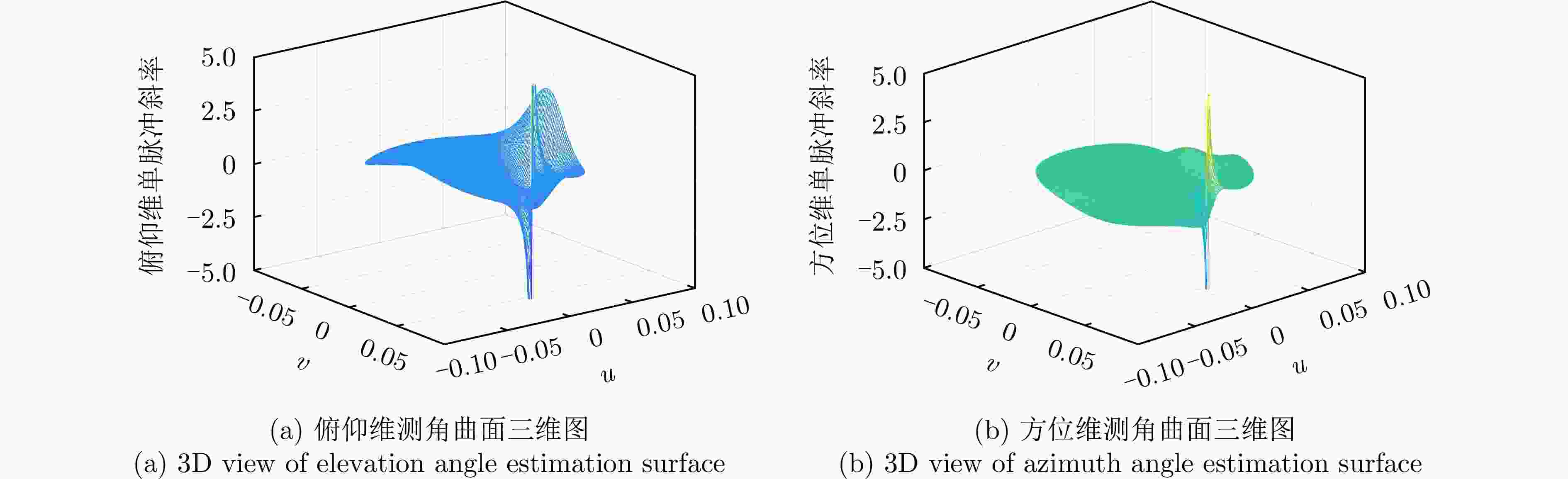
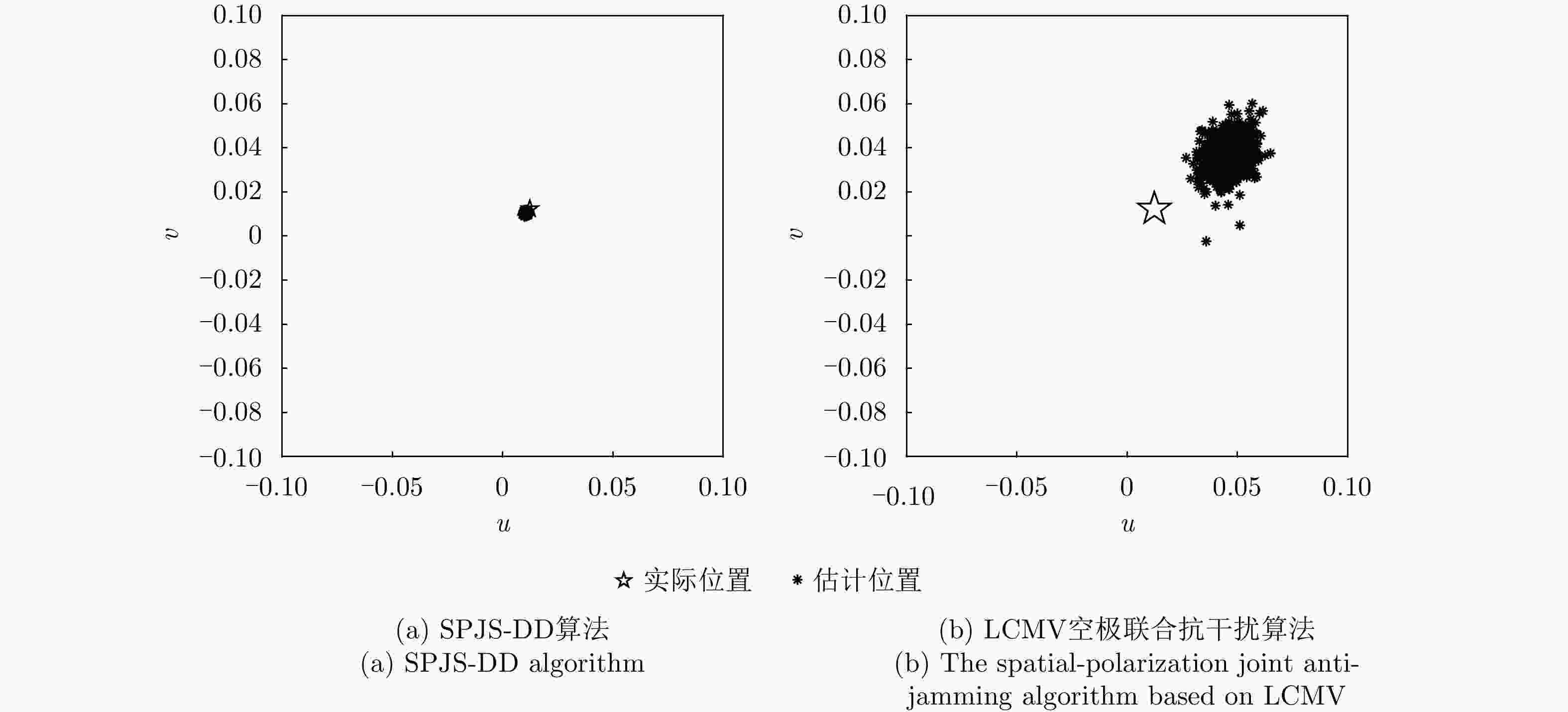
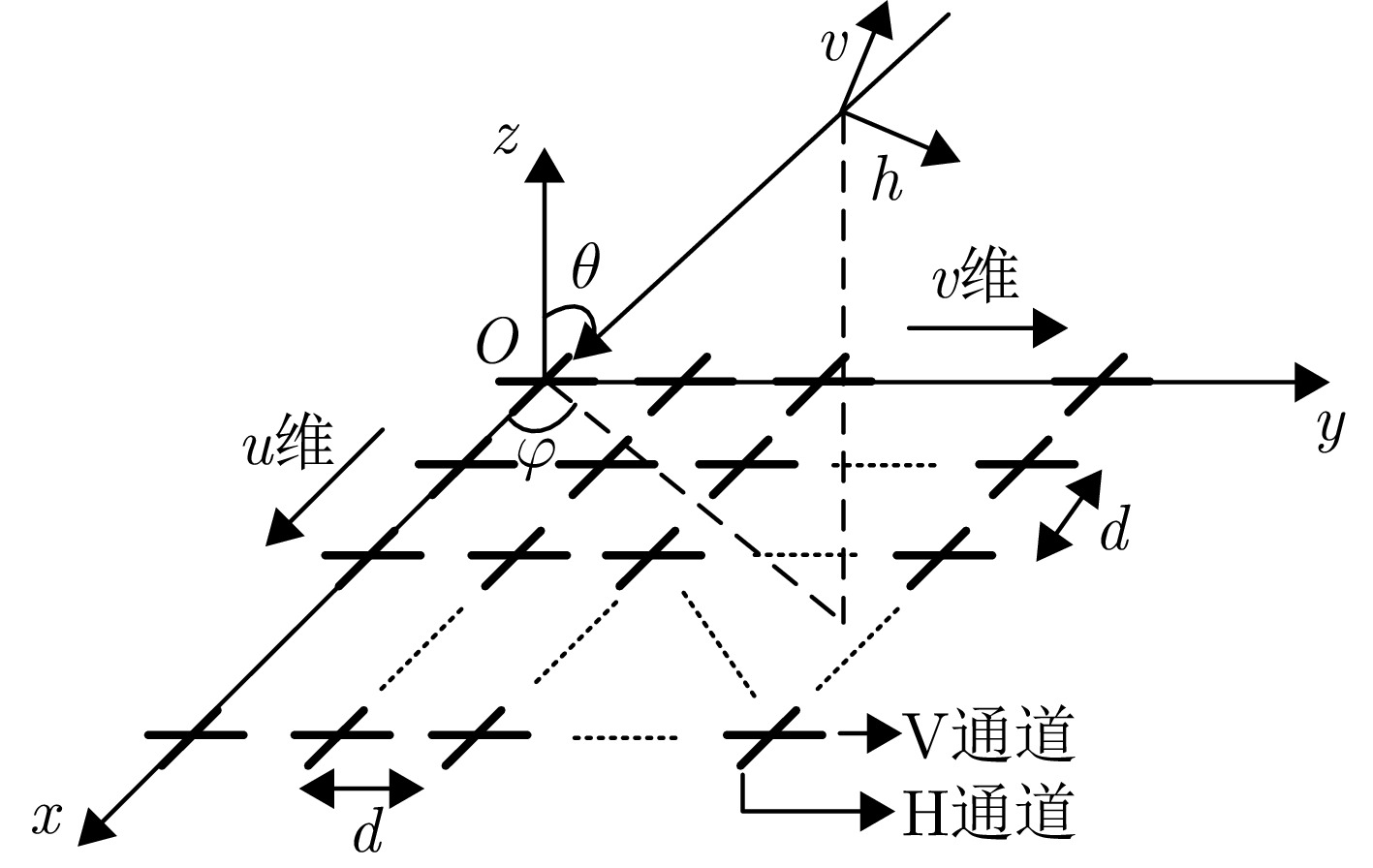
摘要: 针对数字阵列天线自适应对抗主瓣内的自卫式和伴飞式干扰时引起的波束畸变和单脉冲测角性能下降等问题,该文提出了一种基于分维的空域-极化域联合主瓣干扰抑制算法(SPJS-DD)。针对双极化矩形平面阵列天线,推导了空域-极化域联合阵列接收信号导向性矢量的方位维与俯仰维正交性。在此基础上,将方位维/俯仰维依次设置为测角维,另一维度为非测角维,SPJS-DD算法分为两级进行处理:第1级在非测角维进行,对波束方向图进行波束指向的空域-极化域联合约束,通过自适应处理完成非测角维的主瓣干扰抑制;第2级在测角维进行静态和、差波束形成。通过二维分级处理能够在测角维保持单脉冲波束形状不失真,并且在非测角维利用空域-极化域联合自由度抑制主瓣干扰。仿真结果表明,SPJS-DD算法能够有效抑制主瓣干扰,同时获得了良好的单脉冲测角性能。Abstract: To address beam pattern distortion and monopulse angle estimation precision degradation associated with adaptive beamforming processing in the presence of mainlobe self-defense or escort jamming, a joint Space-Polarization Jamming Suppression method based on Dimensional Decomposition (SPJS-DD) is proposed for digital phased array antennas. In SPJS-DD, the orthogonality between the spatial array steering vectors in the azimuth and elevation dimensions of a dual-polarized rectangular planar array antenna is derived first. The azimuth and elevation dimensions of the rectangular array are then alternately selected as the Angle Estimation Dimension (AED), with the other serving as the Non-Angle Estimation Dimension (NAED). The adaptive beamforming process in SPJS-DD is divided into two stages. The first-stage processing is applied in the NAED, where mainlobe jamming is adaptively suppressed using the degrees of freedom available in the joint spatial-polarized domain subject to a constraint on the desired steering direction. In the second stage, quiescent sum and difference weights are applied in the AED to preserve the monopulse beam pattern required for accurate angle estimation. Through this two-stage decomposition, SPJS-DD suppresses mainlobe jamming in the NAED while maintaining an undistorted monopulse beam pattern in the AED. Simulation results verify that the proposed SPJS-DD method effectively suppresses mainlobe jamming and achieves high-precision angle estimation.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameter of simulation
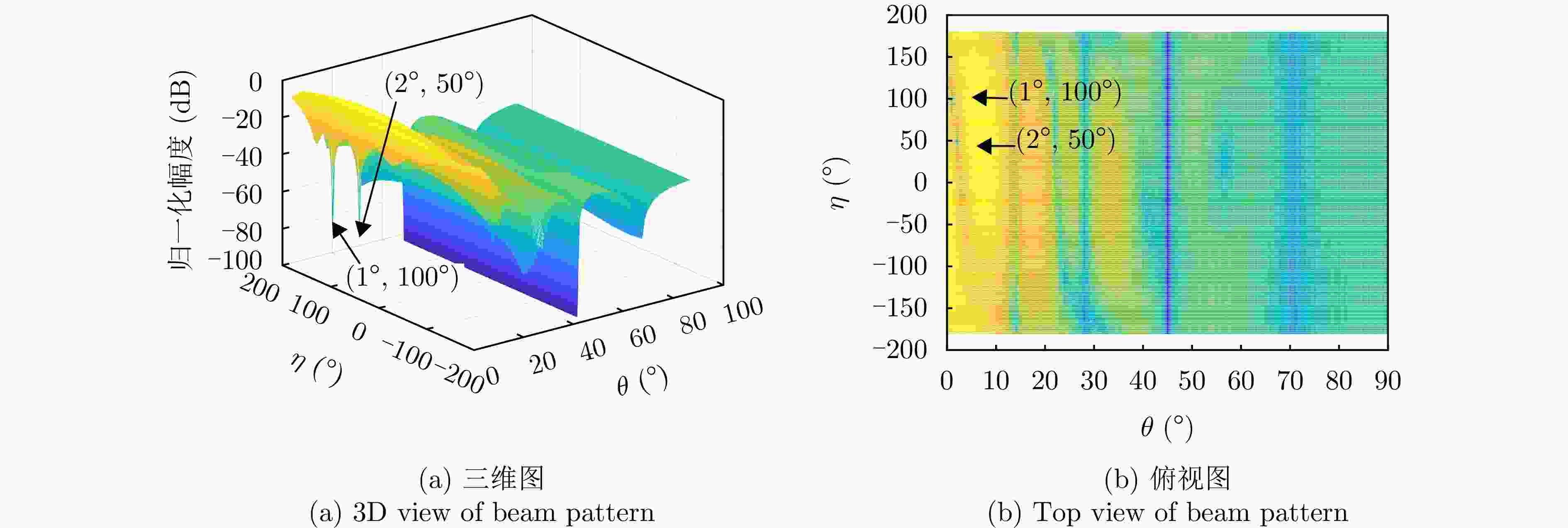
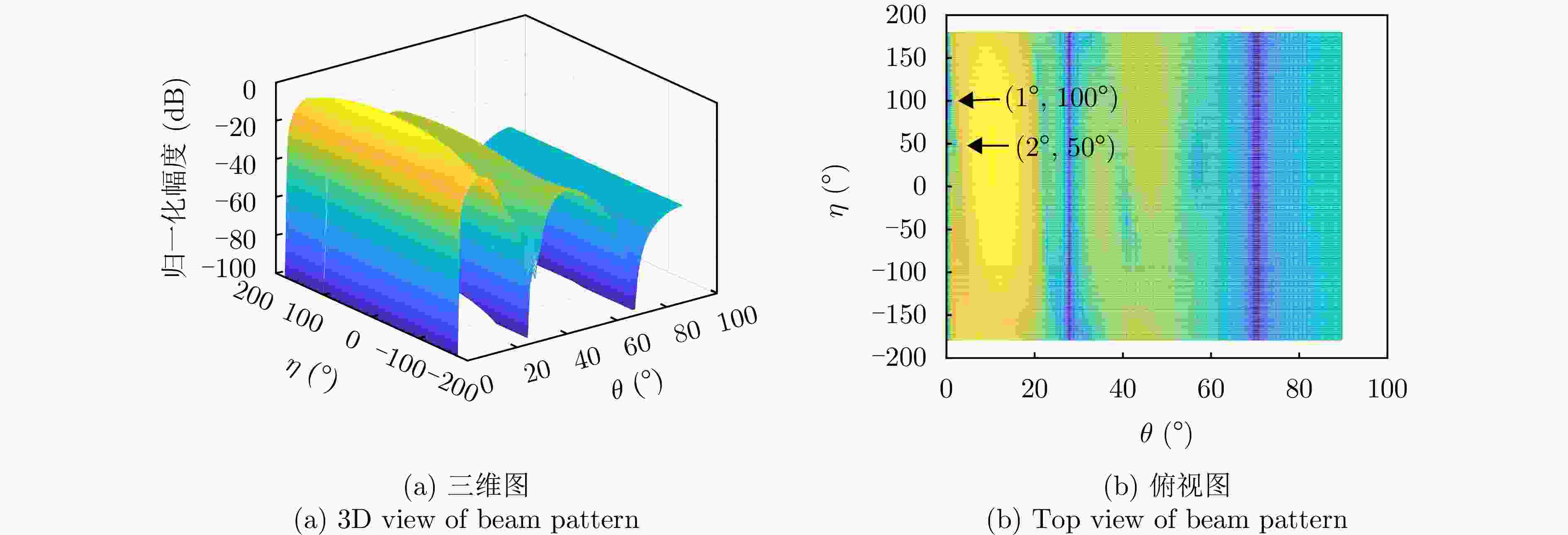
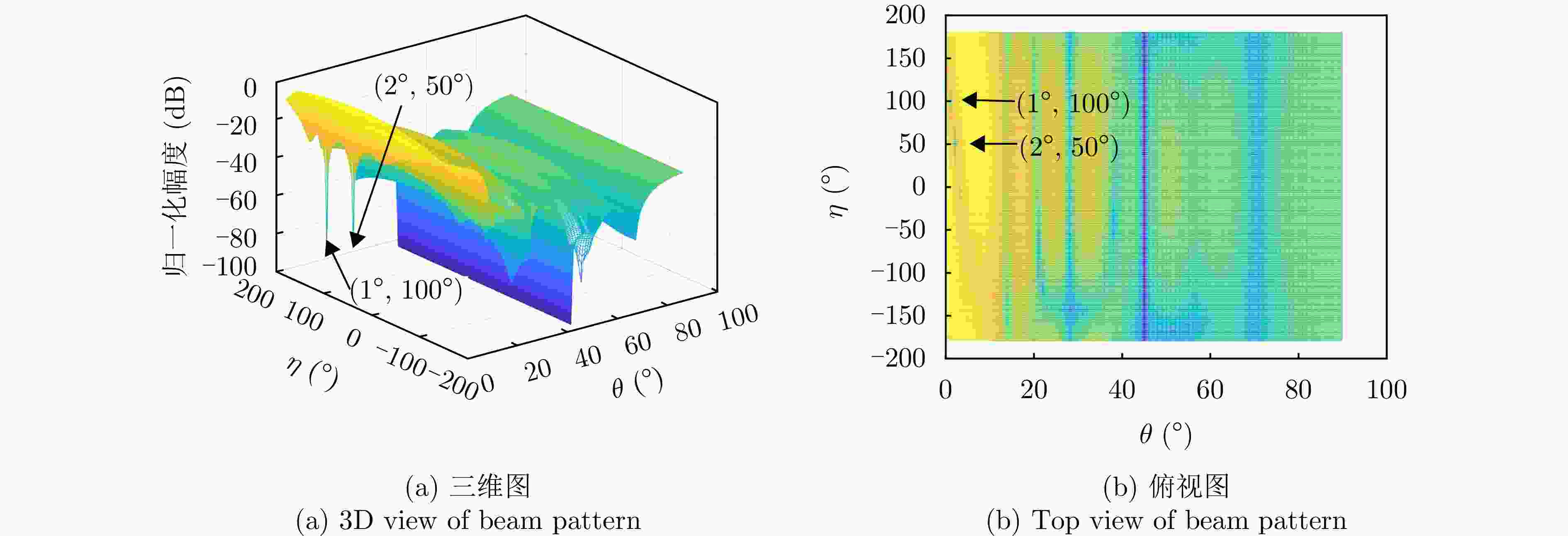
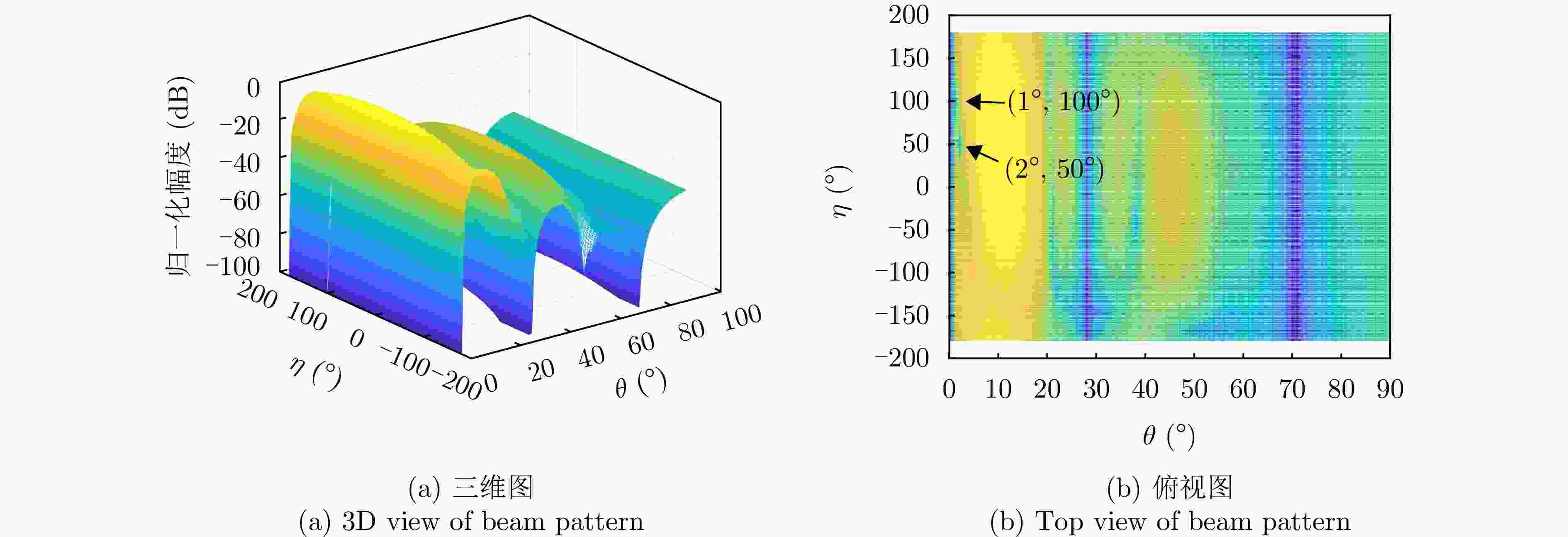
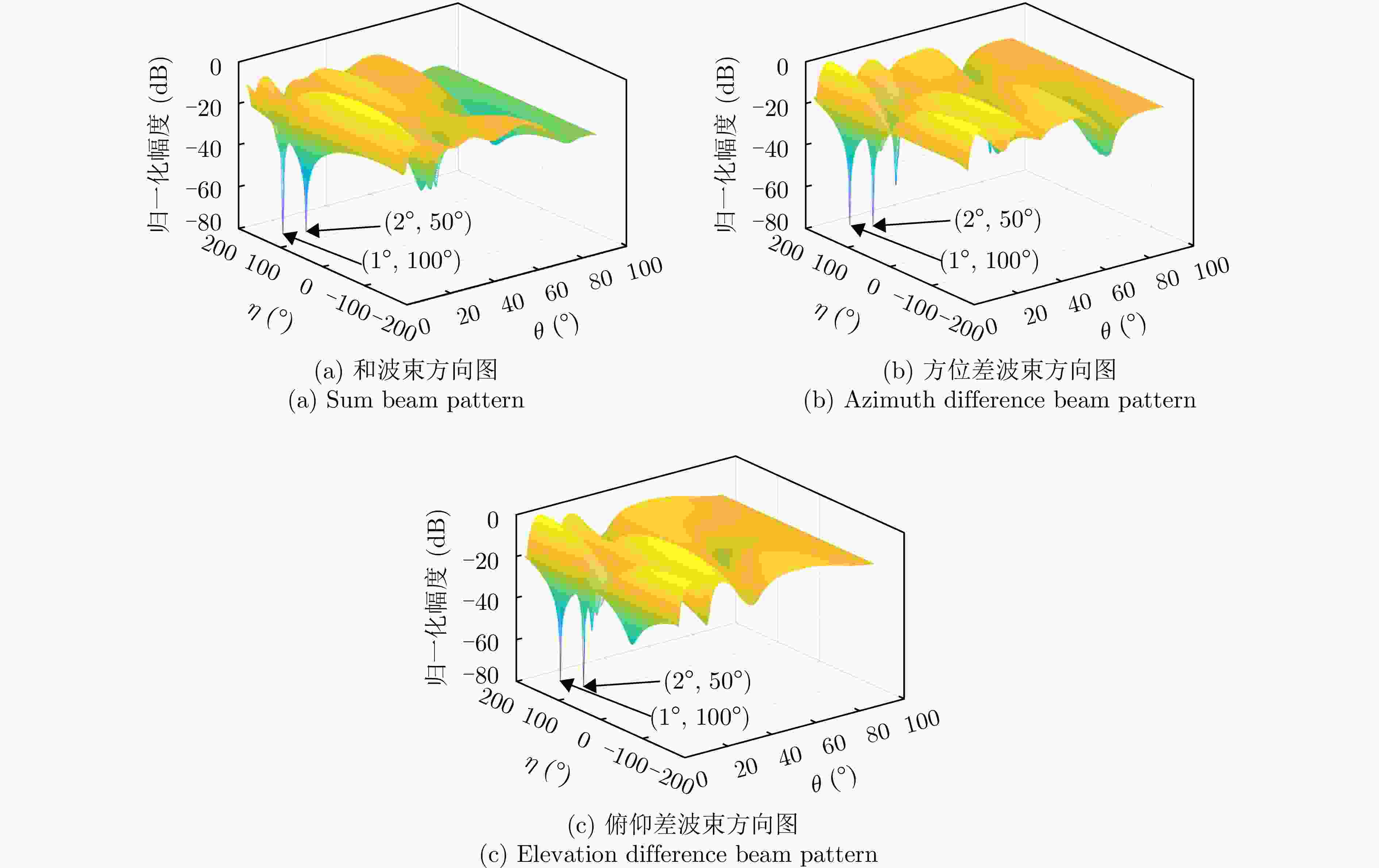
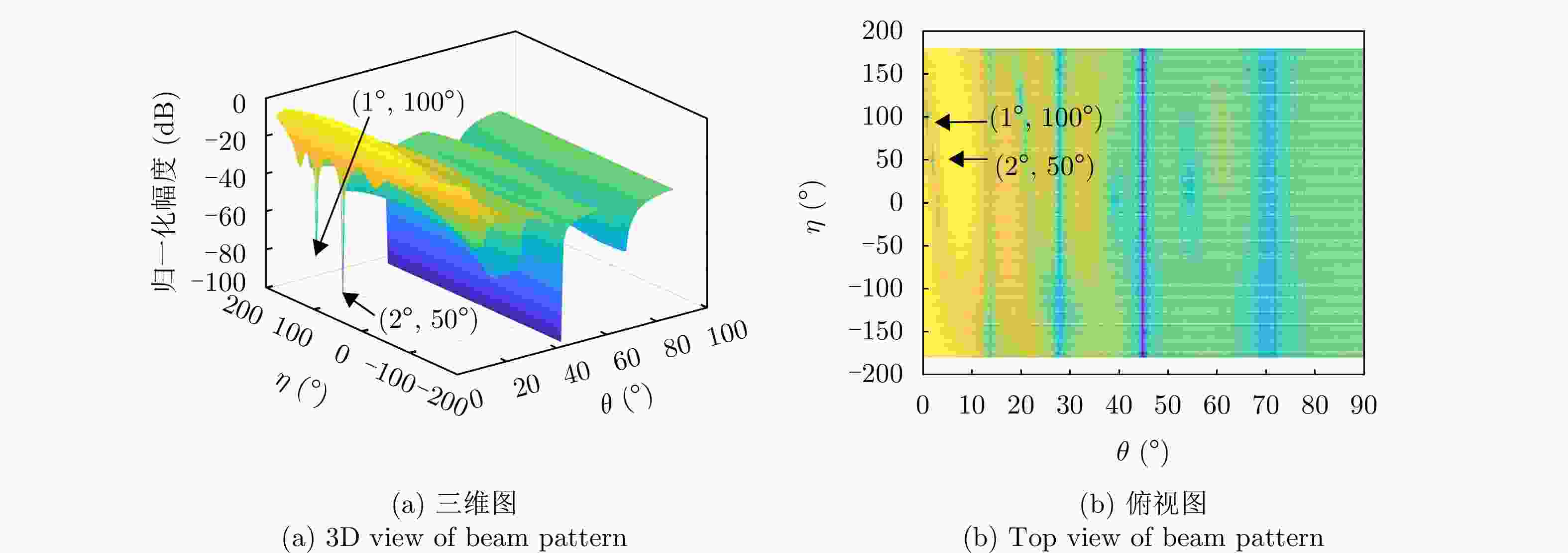
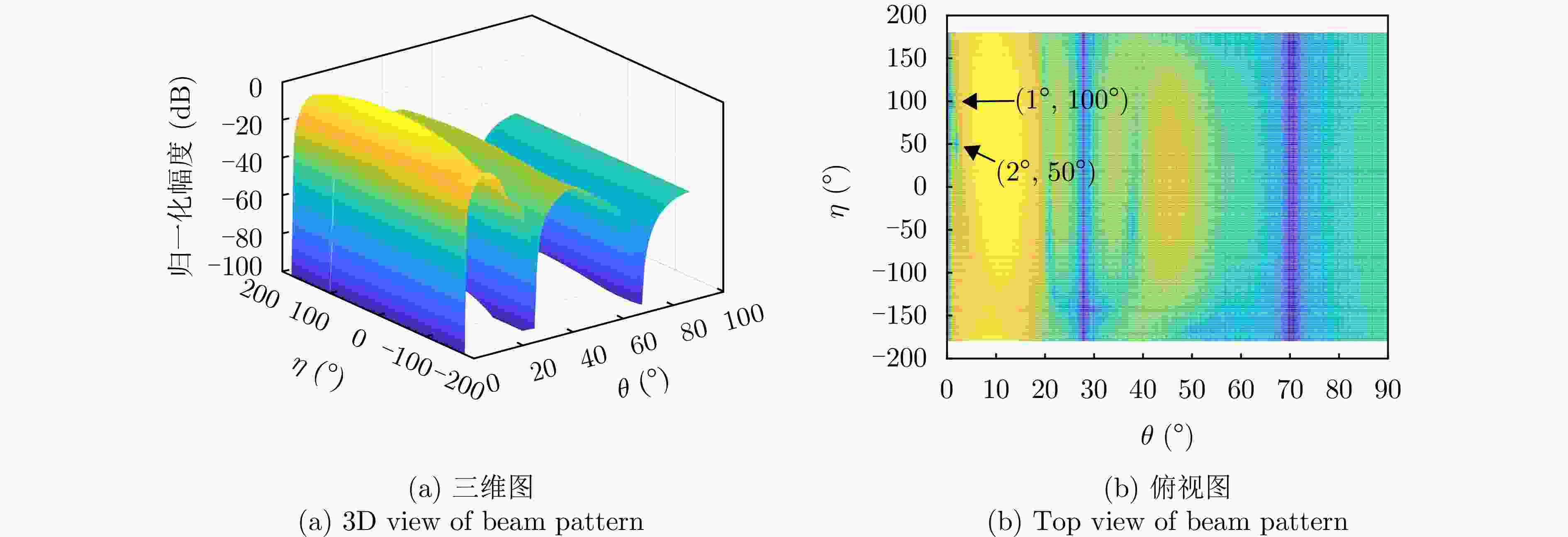
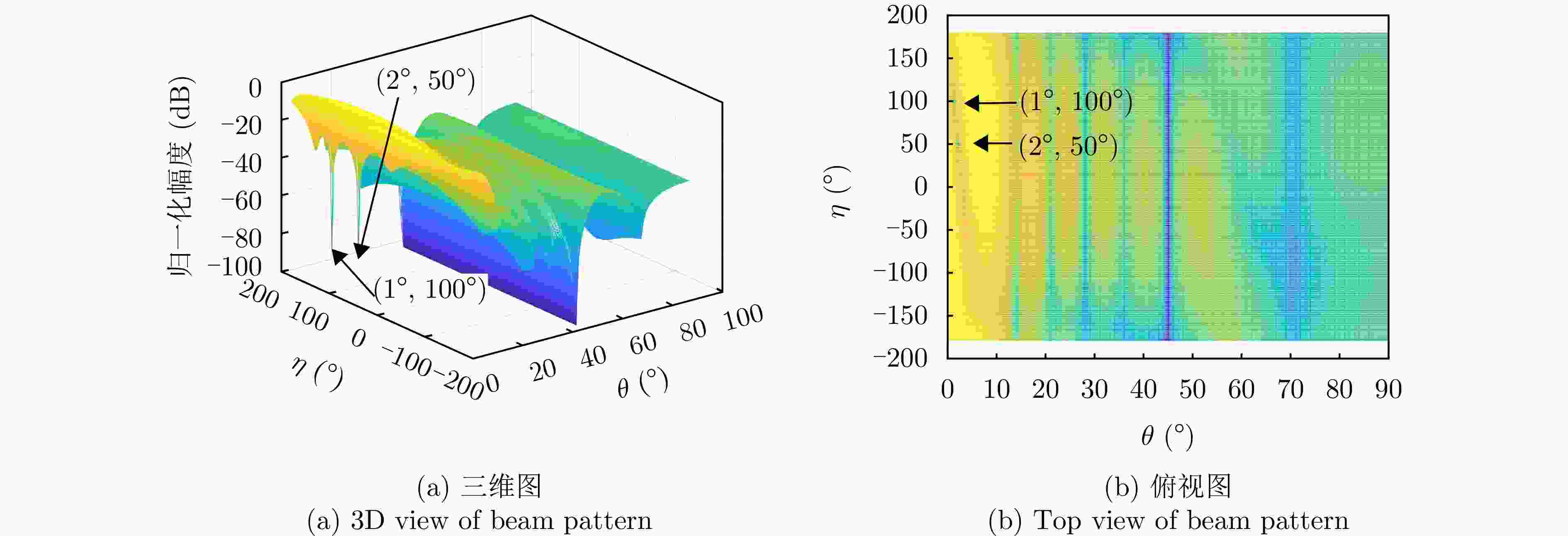
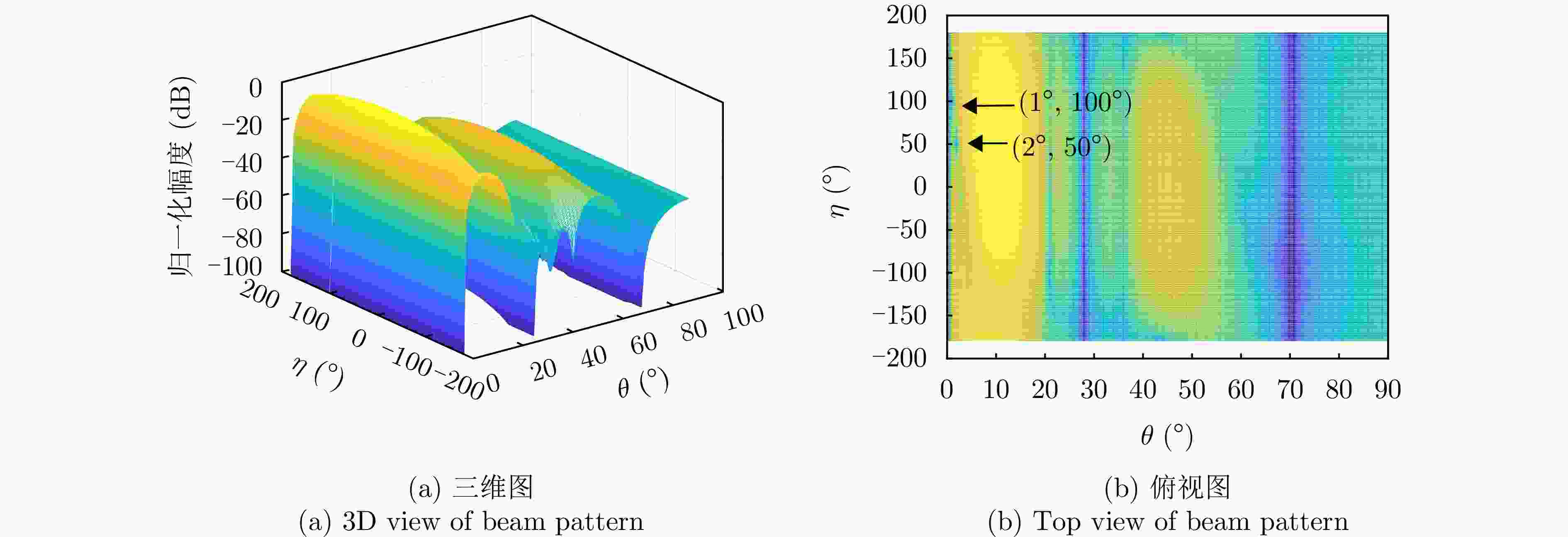
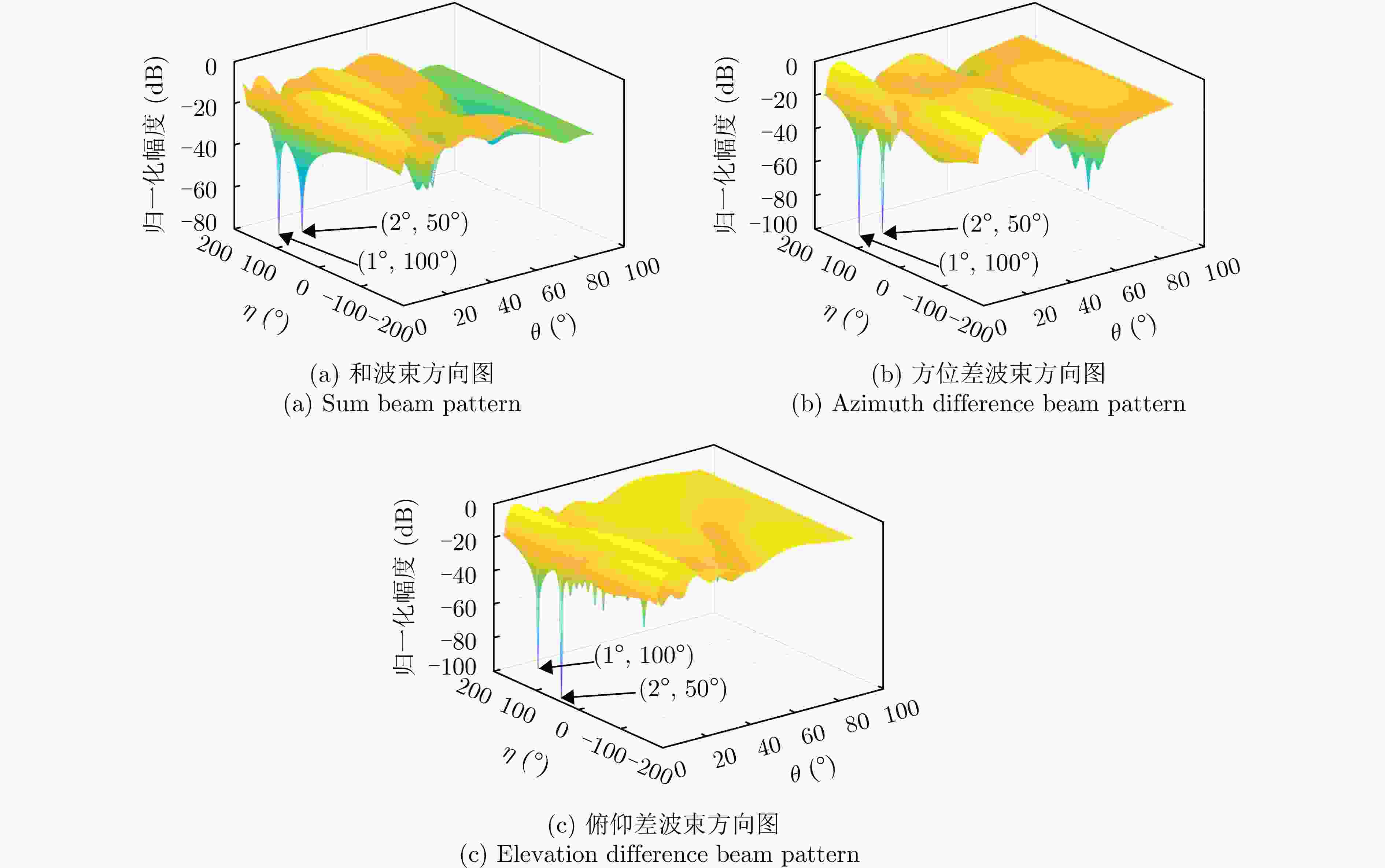
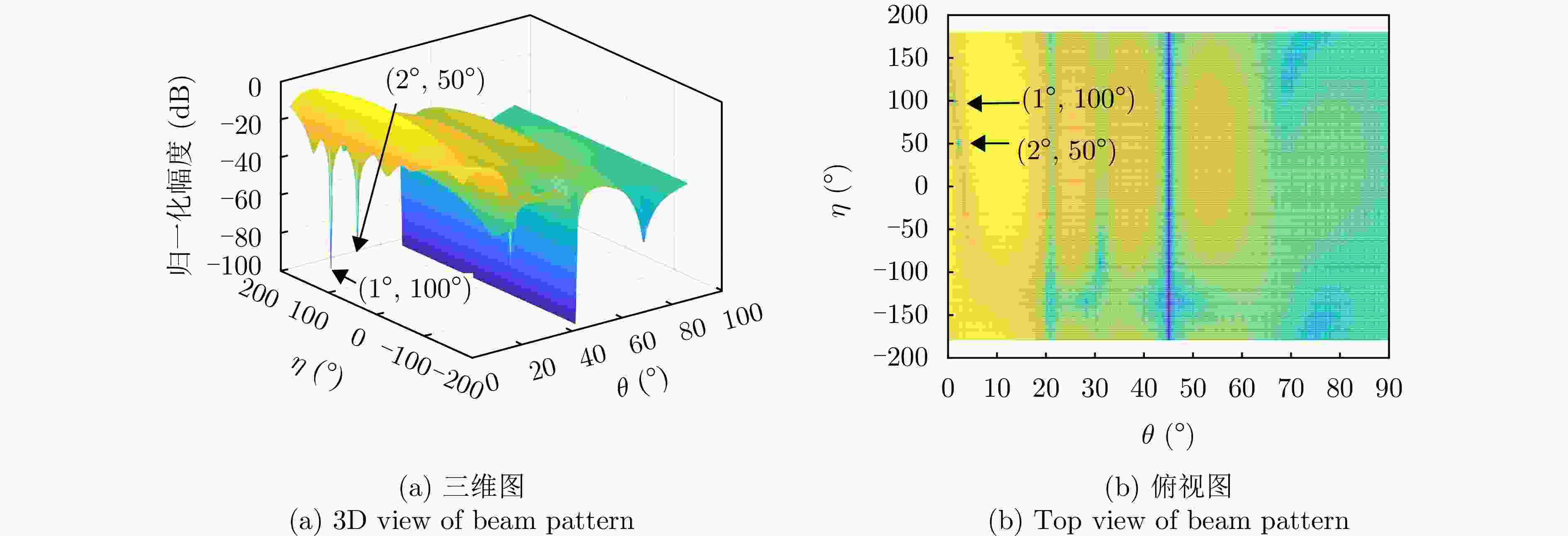
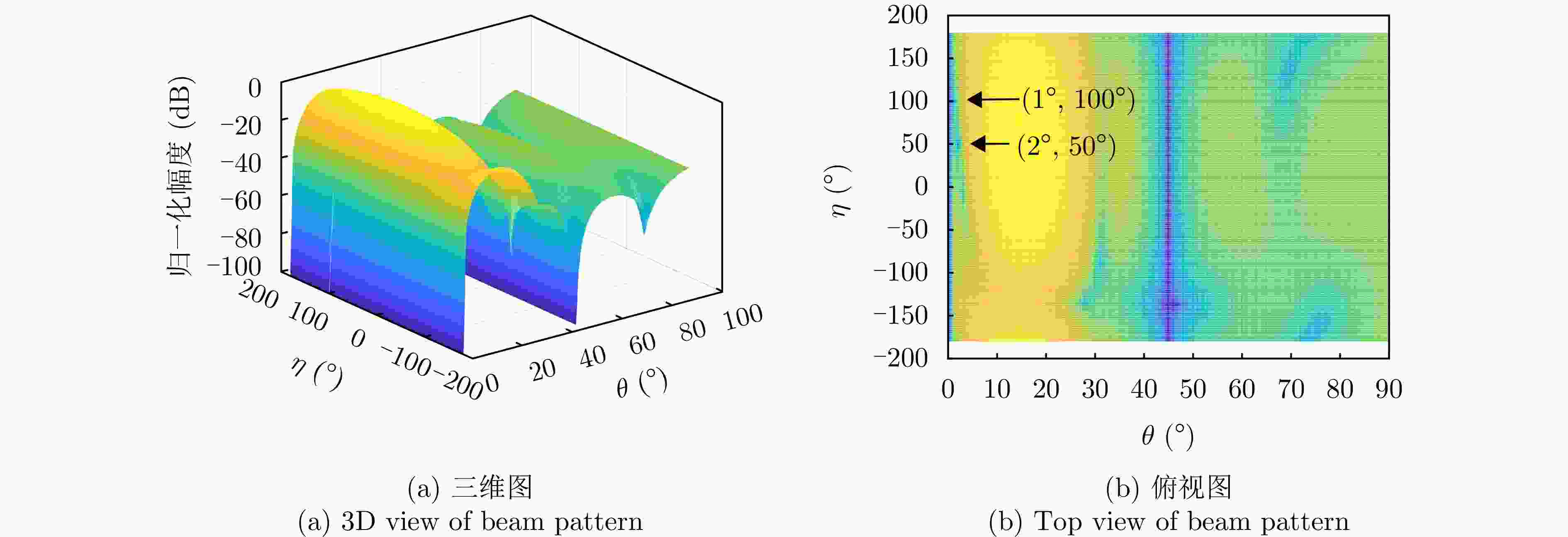
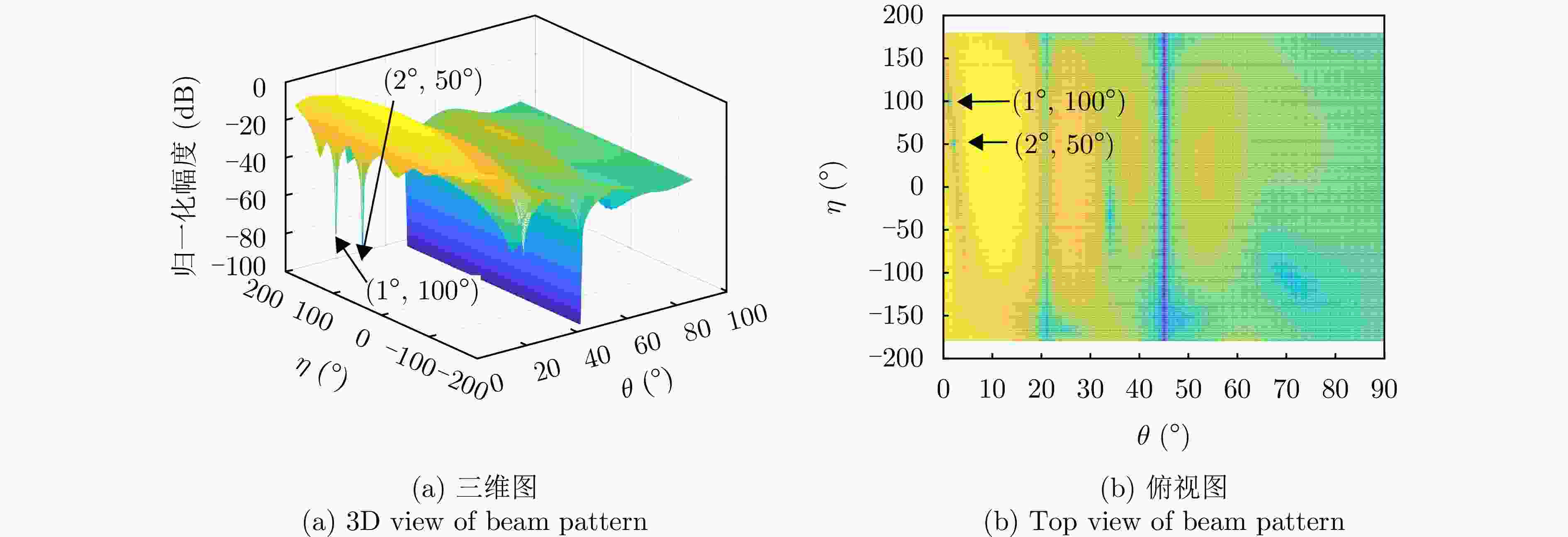
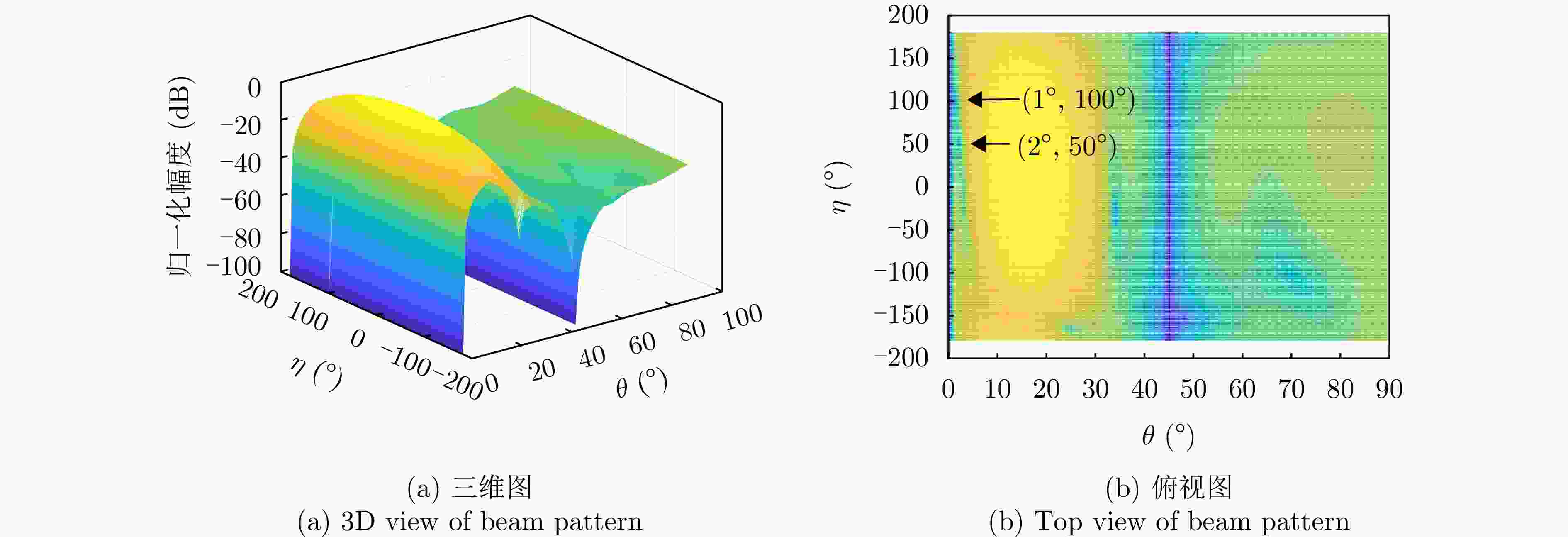
参数 数值 阵元间距 λ/2 波束指向$\left( {{\theta _0},{\varphi _0}} \right)$ (0°, 0°) 波束指向极化参数$({\eta _0},{\gamma _0})$ (90°, 0°) 目标信号方向$\left( {{\theta _{\mathrm{s}}},{\varphi _{\mathrm{s}}}} \right)$ (1°, 45°) 目标信号极化参数$({\eta _{\mathrm{s}}},{\gamma _{\mathrm{s}}})$ (80°, 0°) 目标SNR (dB) –10 主瓣干扰J1方向$\left( {\theta _1^{\rm J},\varphi _1^{\rm J}} \right)$ (1°, 45°) 主瓣干扰J1极化参数$(\eta _1^{\rm J},\gamma _1^{\rm J})$ (45°, 100°) 主瓣干扰J2方向$\left( {\theta _2^{\rm J},\varphi _2^{\rm J}} \right)$ (2°, 45°) 主瓣干扰J2极化参数$(\eta _2^{\rm J},\gamma _2^{\rm J})$ (45°, 50°) 表 2 仿真场景
Table 2. The environment of simulation
场景 参数 参数值 场景1 阵元数 M=N=12 干噪比 JSR1=40 dB, JSR2=40 dB 场景2 阵元数 M=N=12 干噪比 JSR1=60 dB, JSR2=60 dB 场景3 阵元数 M=N=8 干噪比 JSR1=40 dB, JSR2=40 dB 表 3 抗干扰前后信干噪比(dB)
Table 3. Comparison of SINR before and after anti-jamming (dB)
场景 指标 俯仰维测角时 方位维测角时 场景1 抗干扰前信干噪比 –53.18 –53.18 抗干扰后信干噪比 –3.04 –2.88 抗干扰改善因子 50.14 50.30 场景2 抗干扰前信干噪比 –73.40 –73.40 抗干扰后信干噪比 –2.10 –3.09 抗干扰改善因子 71.30 70.31 场景3 抗干扰前信干噪比 –52.96 –52.96 抗干扰后信干噪比 –9.29 –9.71 抗干扰改善因子 43.67 43.24 -
[1] LUO Weilin, JIN Hongbin, LI Hao, et al. Radar main-lobe jamming suppression based on adaptive opposite fireworks algorithm[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 2: 138–150. doi: 10.1109/OJAP.2020.3036878. [2] YUE Yaxing, ZHANG Zongyu, and SHI Zhiguo. Generalized widely linear robust adaptive beamforming: A sparse reconstruction perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 5663–5673. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3397240. [3] ZHANG Xuejun, FENG Dazheng, WANG Zhonggen, et al. A robust adaptive beamforming algorithm for mismatch and impulsive noise circumstance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2025, 22: 3502305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2025.3527696. [4] 胡海涛, 张剑云, 李小波, 等. 基于阻塞矩阵预处理的抗主瓣干扰算法[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2018, 40(5): 94–99.HU Haitao, ZHANG Jianyun, LI Xiaobo, et al. Anti-mainlobe interference algorithm based on blocking matrix preprocessing[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2018, 40(5): 94–99. [5] 李荣锋, 王永良, 万山虎. 主瓣干扰下自适应方向图保形方法的研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2002, 24(3): 50–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2002.03.015.LI Rongfeng, WANG Yongliang, and WAN Shanhu. Research of reshaping adapted pattern under mainlobe interference conditions[J]. Modern Radar, 2002, 24(3): 50–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2002.03.015. [6] 孟昊宇, 杨小鹏, 高升, 等. 基于特征值斜投影的主瓣干扰抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(2): 439–444. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.025.MENG Haoyu, YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Sheng, et al. Main lobe interference suppression method based on eigenvalue oblique projection[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(2): 439–444. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.025. [7] CHEN Xinzhu, SHU Ting, YU K B, et al. Joint adaptive beamforming techniques for distributed array radars in multiple mainlobe and sidelobe jammings[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(2): 248–252. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2958687. [8] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, DUAN Xiang, et al. Adaptive monopulse approach with joint linear constraints for planar array at subarray level[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1432–1441. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2793318. [9] LU Zukun, NIE Junwei, CHEN Feiqiang, et al. Adaptive time taps of STAP under channel mismatch for GNSS antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(11): 2813–2824. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2728420. [10] LEI Zhenshuo, QU Qizhe, CHEN Hao, et al. Mainlobe jamming suppression with space-time multichannel via blind source separation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(15): 17042–17053. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3278709. [11] DAI Huanyao, WANG Xuesong, LI Yongzhen, et al. Main-lobe jamming suppression method of using spatial polarization characteristics of antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 2167–2179. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237586. [12] QU Mingchao, LIU Ruizhi, DENG Zhian, et al. A direction-finding model with spatial polarization characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2025, 73(2): 1095–1109. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2024.3484180. [13] LU Yawei, MA Jiazhi, SHI Longfei, et al. Multiple interferences suppression with space-polarization null-decoupling for polarimetrie array[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(1): 44–52. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000006. [14] 周万幸. 一种新型极化抗干扰技术研究[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(3): 454–458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.03.005.ZHOU Wanxing. Research of a new type techniques for anti-interference using polarization[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(3): 454–458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.03.005. [15] 金鸣, 吕婷婷, 周曼丽, 等. 基于LCMV准则的空时极化联合抗干扰算法[J]. 无线电工程, 2022, 52(8): 1434–1440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.08.019.JIN Ming, LV Tingting, ZHOU Manli, et al. Joint anti-jamming algorithm for space-time polarization based on LCMV criterion[J]. Radio Engineering, 2022, 52(8): 1434–1440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.08.019. [16] WANG Haiyang, YAO Zhicheng, YANG Jian, et al. A novel beamforming algorithm for GNSS receivers with dual-polarized sensitive arrays in the joint space-time-polarization domain[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4506. doi: 10.3390/s18124506. [17] PARK K and SEO J. Single-antenna-based GPS antijamming method exploiting polarization diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(2): 919–934. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3034025. [18] WANG Meng, LUO Xiaoxuan, and DONG Jian. Anti-jamming algorithm of polarization-sensitive array based on improved constraint matrix and orthogonal subspace projection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(24): 30835–30846. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3329833. [19] GE Mengmeng, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Mainlobe jamming suppression with polarimetric multi-channel radar via independent component analysis[J] Digital Signal Processing, 2020, 106: 102806. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102806. [20] 杨书宁, 杨仲平, 张剑云, 等. 基于稀疏重构的空域-极化域联合抗主瓣干扰方法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(2): 401–409. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.020.YANG Shuning, YANG Zhongping, ZHANG Jianyun, et al. Space-polarization domain combined anti-mainlobe jamming method based on sparse reconstruction[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(2): 401–409. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.020. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: