Structured Low-rankness Method of Joint Neighboring Pixels for Tomographic SAR 3D Imaging
-
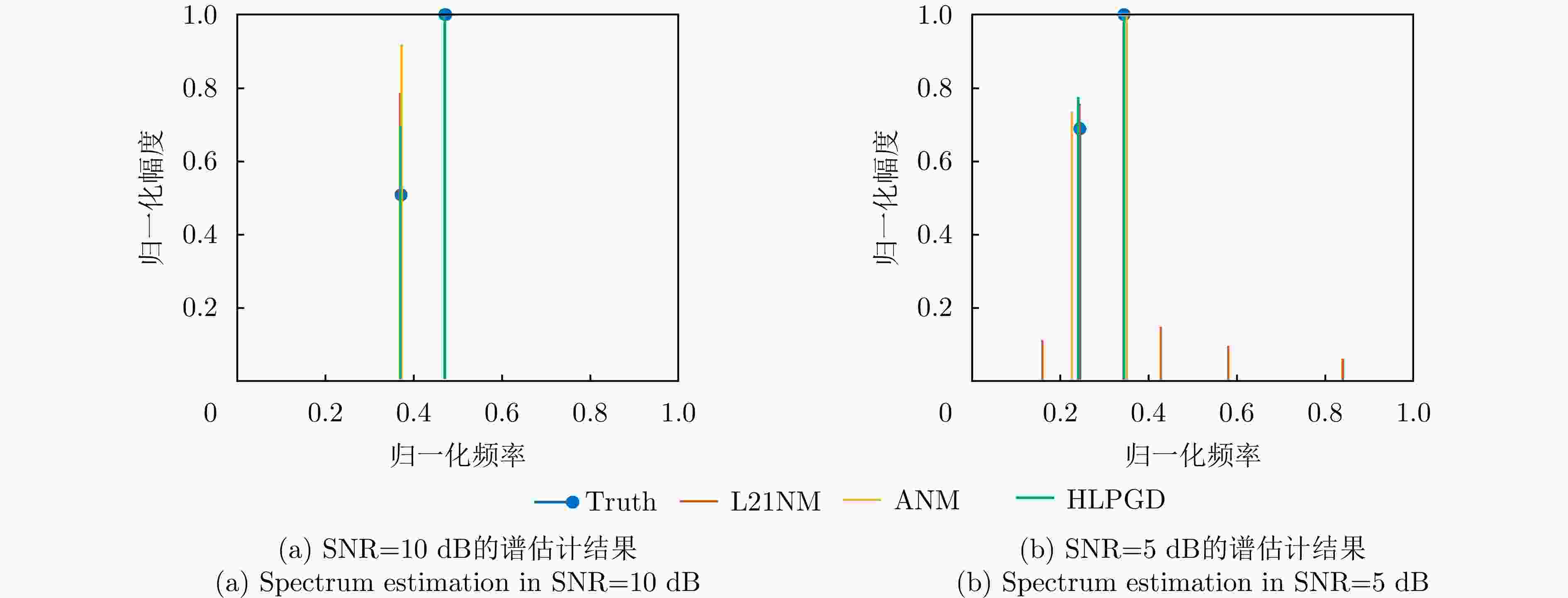
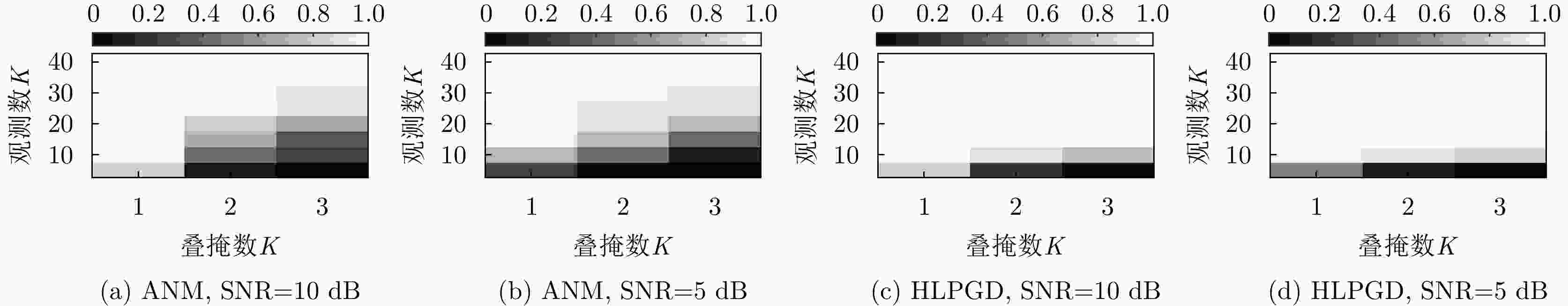
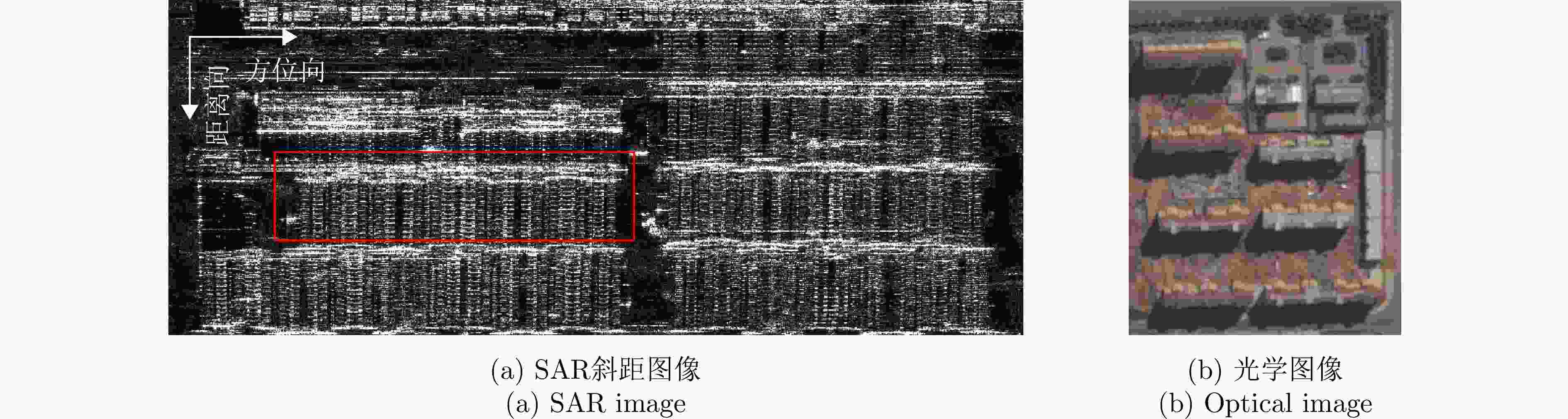
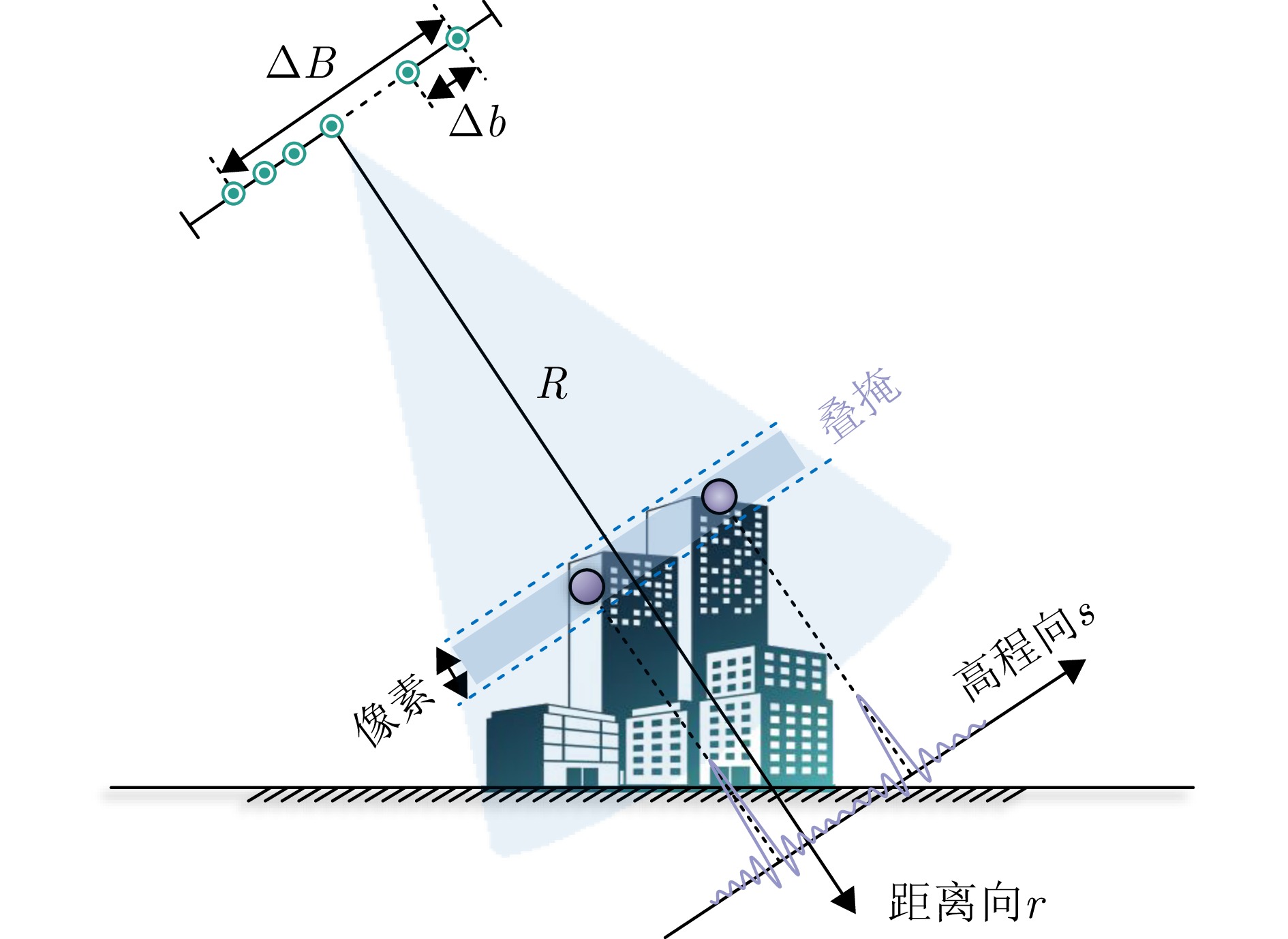
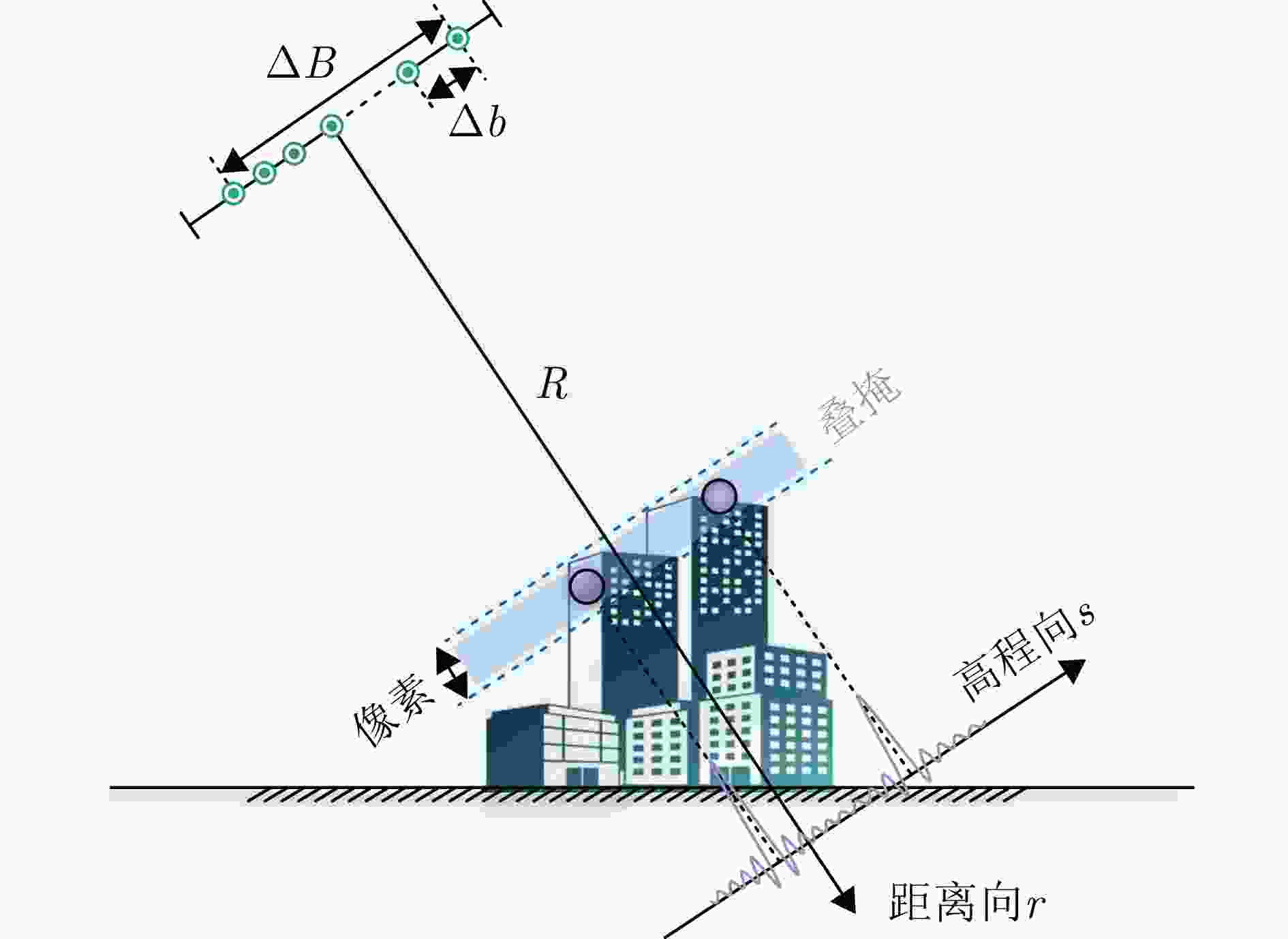
摘要: 层析合成孔径雷达(TomoSAR)三维成像能够克服场景叠掩、投影几何失真等问题,具有重要的科学研究和应用价值。由于TomoSAR高程分辨率受到高程向孔径限制,通常利用压缩感知等超分辨算法提升三维成像性能。然而,传统压缩感知方法需预先划分离散网格导致存在网格失配等问题,同时在通道数少、信噪比低等限制条件下,成像分辨精度受限。针对以上问题,该文提出了一种基于联合邻域像素结构化低秩的层析SAR超分辨三维成像方法,通过增强信号内部结构性表征以增加有效样本数量,提高三维重建性能。具体而言,基于邻域像素高程一致性假设,可联合邻域像素稀疏特性构建无网格结构化低秩非凸优化模型,以增强信号内部结构表征并克服传统稀疏网格化的缺陷。此外采用投影梯度下降算法进行高效求解,引入非相干可行域约束,有效降低重构性能对采样位置的依赖性。最后,利用仿真数据、实测SARMV3D-1.0机载阵列数据和陆地探测一号卫星数据进行了验证。实验结果表明,所提方法在三维重建精度和稳定性方面均显著优于现有大多数主流方法。Abstract: Tomographic SAR (TomoSAR) has significant value in scientific research and applications, as it enables three-dimensional (3D) imaging to address limitations such as scene overlay and projection geometric distortion. The elevation resolution of TomoSAR is limited by the aperture in the elevation direction. Consequently, super-resolution algorithms such as Compressive Sensing (CS) are generally used to enhance the performance of 3D imaging. However, conventional CS methods suffer from grid mismatch issues due to predefined discrete grids, which lead to limited resolution under practical constraints, such as limited channels and low signal-to-noise ratios. To address these limitations, a novel, gridless, super-resolution algorithm based on the structured low-rankness of joint neighboring pixels is proposed herein for tomographic 3D SAR Imaging. By enhancing the intrinsic structural observation, the efficacy of the model for 3D reconstruction can be effectively improved by increasing the number of valid observations. Specifically, a gridless, structured, low-rank, non-convex optimization model is constructed by leveraging the joint sparse characteristics of neighboring pixels, overcoming the limitations of traditional sparse grid-based approaches. Furthermore, an efficient solution is achieved using a projected gradient descent algorithm, and the dependence of the reconstruction performance on the sampling positions is reduced by introducing an incoherent feasible region constraint. Finally, the superiority of the proposed algorithm is validated through both simulation and analysis of real measured datasets, including the SARMV3D-1.0 airborne array dataset and spaceborne LuTan-1 dataset. The proposed algorithm achieves superior 3D reconstruction accuracy and stability compared to most existing state-of-the-art methods.
-
Key words:
- 3D SAR /
- Joint neighboring pixels /
- Super-resolution /
- Structured low-rankness /
- LuTan-1
-
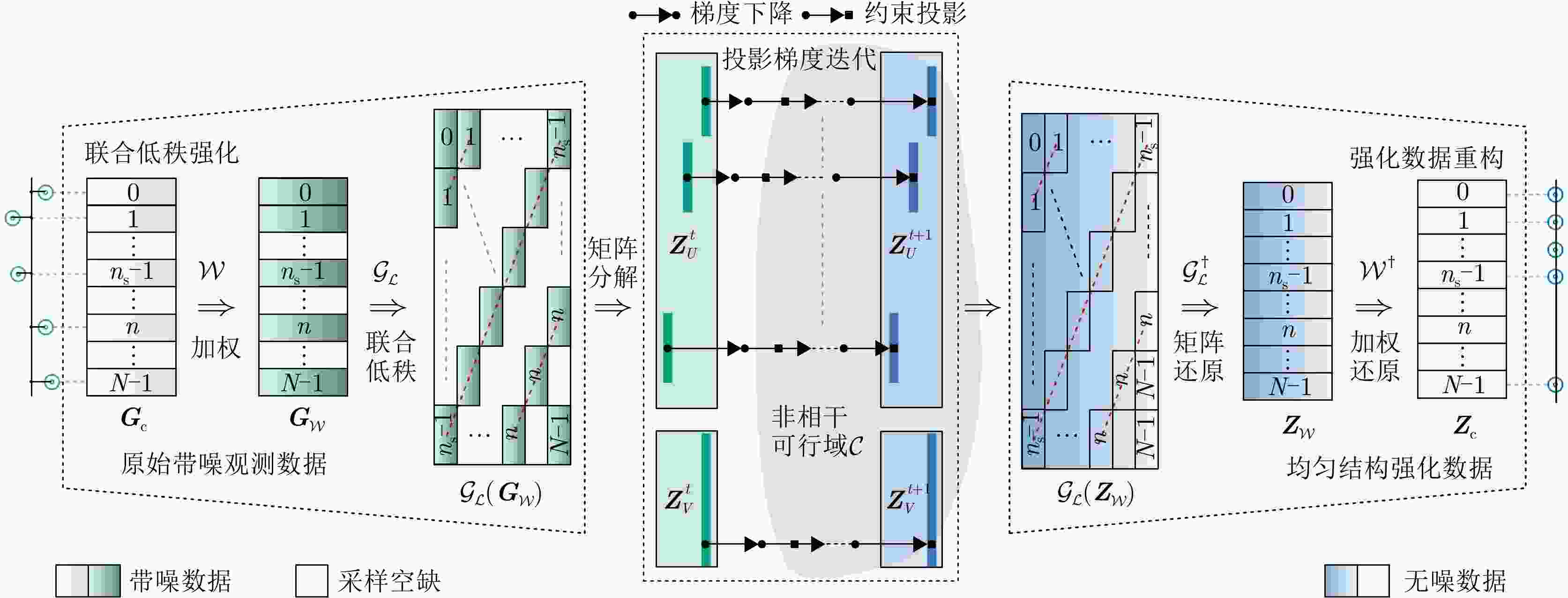
1 HLPGD超分辨算法流程
1. The process of HLPGD super-resolution algorithm
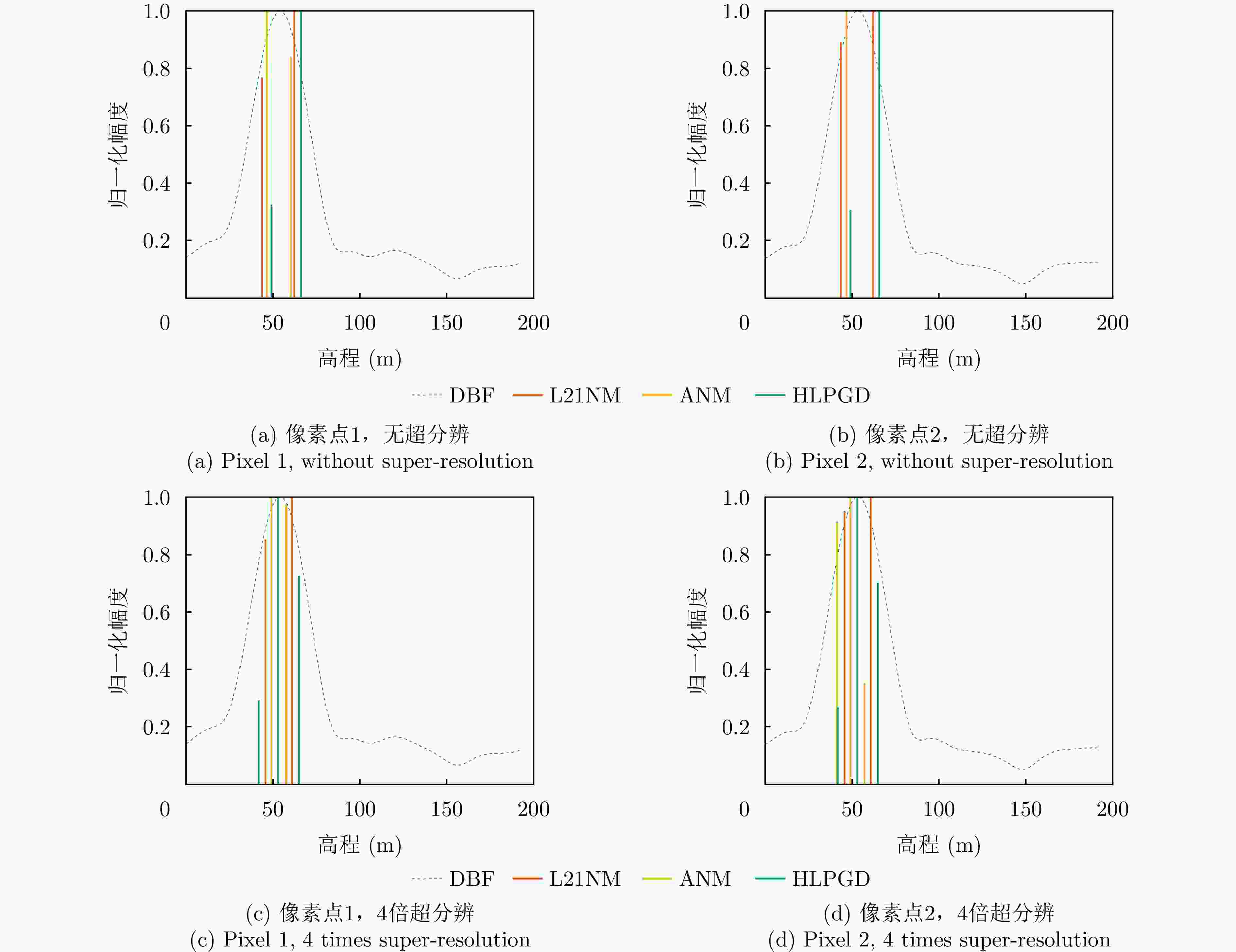
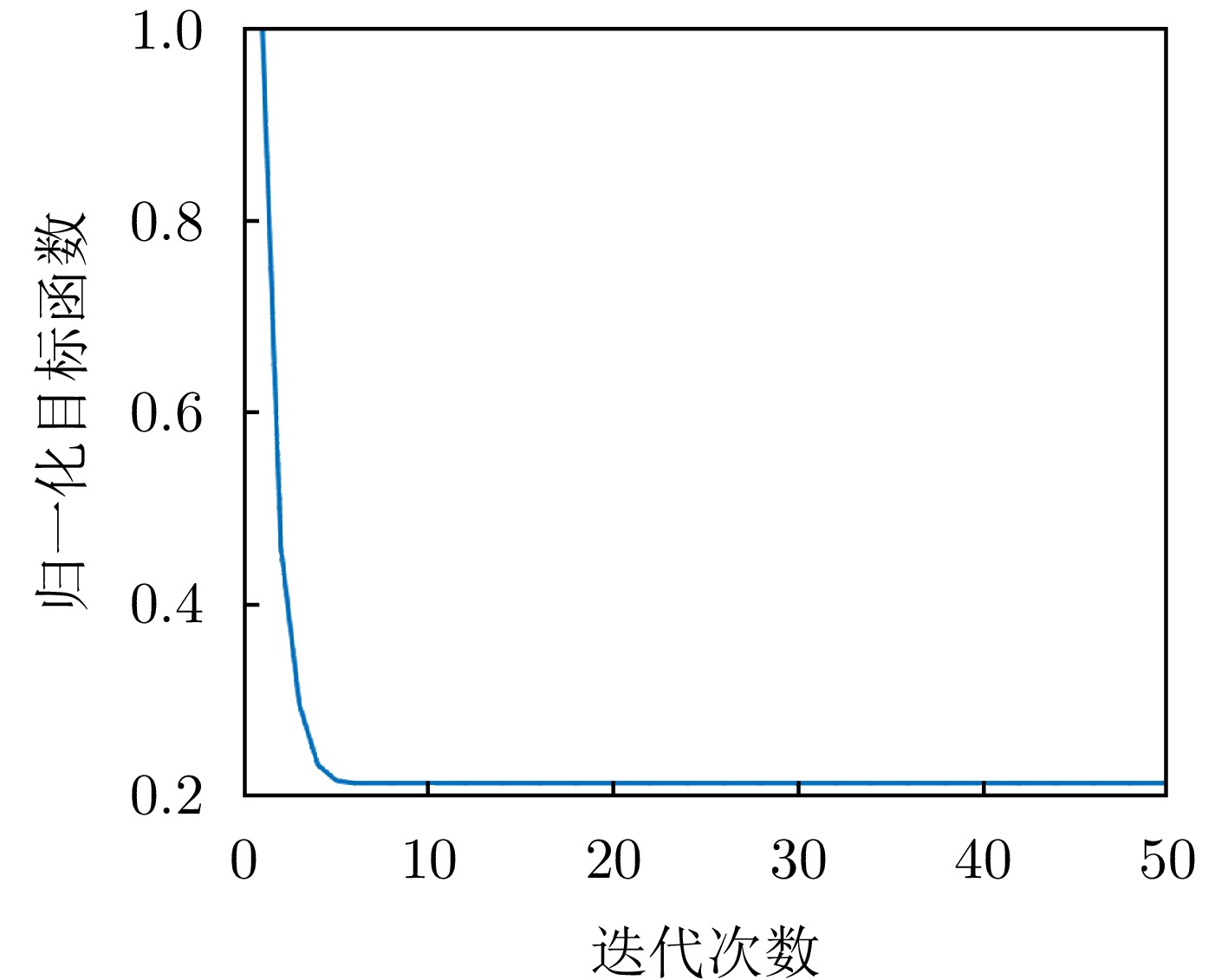
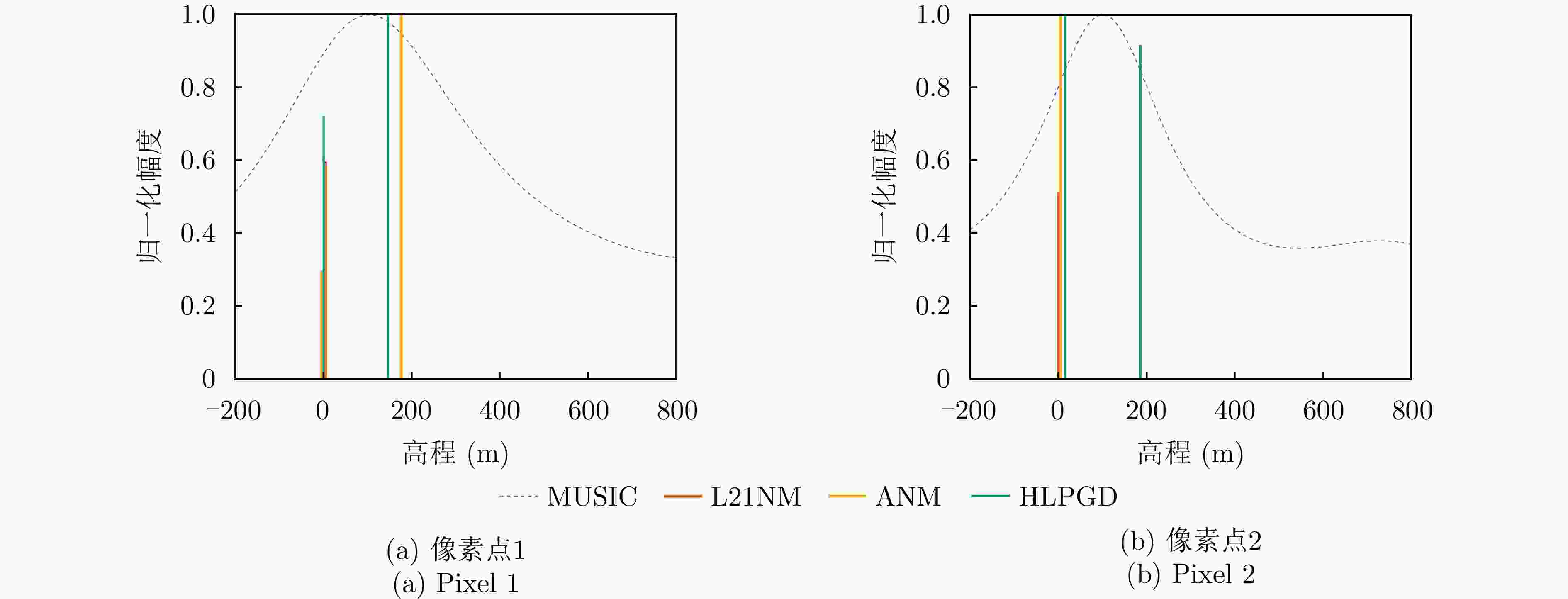
输入:邻域多像素观测矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\text{c}}} $,采样算子$ {P_\Omega } $,梯度下降步长$ \eta $,最大迭代次数${T_{\max }}$; (1) 变量初值:$ [{\boldsymbol{U}},{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} ,{\boldsymbol{V}}] = {{\mathrm{SVD}}} ({{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\text{c}}}) $, $ {\boldsymbol{Z}}_U^0 = {\boldsymbol{U}}{{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} ^{\tfrac{1}{2}}} $, $ {\boldsymbol{Z}}_V^0 = {\boldsymbol{V}}{{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} ^{\tfrac{1}{2}}} $; (2) 迭代求解:For count $t = 1:{T_{\max }}$ $ {\boldsymbol{Z}}_U^{t + 1} = {{\boldsymbol{P}}_\mathcal{C}}({\boldsymbol{Z}}_U^t - \eta \nabla F({\boldsymbol{Z}}_U^t)) $ $ {\boldsymbol{Z}}_V^{t + 1} = {P_\mathcal{C}}({\boldsymbol{Z}}_V^t - \eta \nabla F({\boldsymbol{Z}}_V^t)) $ end (3) 数据重构:得到收敛值$ \tilde {\boldsymbol{Z}}_U $和$ \tilde {\boldsymbol{Z}}_V $,并根据$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\text{c}}} = \mathcal{W}_{}^\dagger (\mathcal{G}_\mathcal{L}^\dagger ({\tilde {\boldsymbol{Z}}_U}\tilde {\boldsymbol{Z}}_V^{\text{H}})) $重构无噪声多像素信号矩阵; (4) 频率估计:对$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\text{c}}} $使用Root-MUSIC算法进行高程频率超分辨估计; (5) 点云滤波:利用式(21)进行超分辨模型定阶实现有效点筛选; 输出:高程频率$\{ {f_1},{f_2},\cdots\} $。 表 1 机载数据集雷达系统参数
Table 1. Radar system parameters of airborne data
参数 数值 参数 数值 阵列通道数 8 信号波长 0.021 m 图像大小 1200 ×3100 方位分辨率 0.073 m 下视角 32.00° 距离分辨率 0.150 m 平台高度 1.67 km 高程分辨率 26.73 m 表 2 星载陆探一号卫星数据集雷达系统参数
Table 2. Radar system parameters of spaceborne data of LuTan-1 satellites
参数 数值 参数 数值 观测航过数 12 信号波长 0.238 m 图像大小 2880 ×3200 方位分辨率 1.67 m 下视角 51.67° 距离分辨率 1.87 m 轨道高度 607 km 高程分辨率 182.4 m 表 3 实测数据超分辨成像指标汇总
Table 3. Summary of super-resolution imaging metrics of measured data
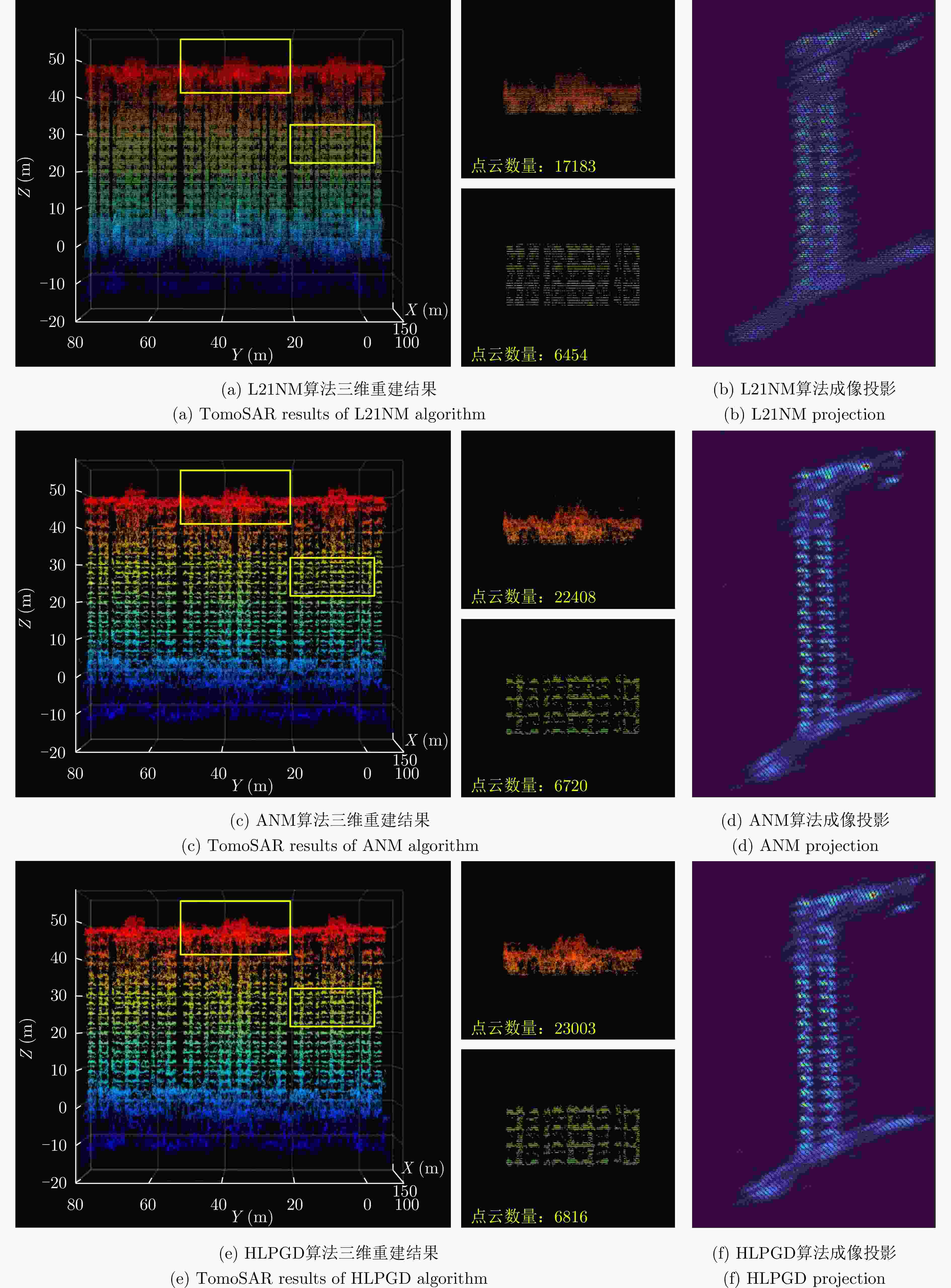
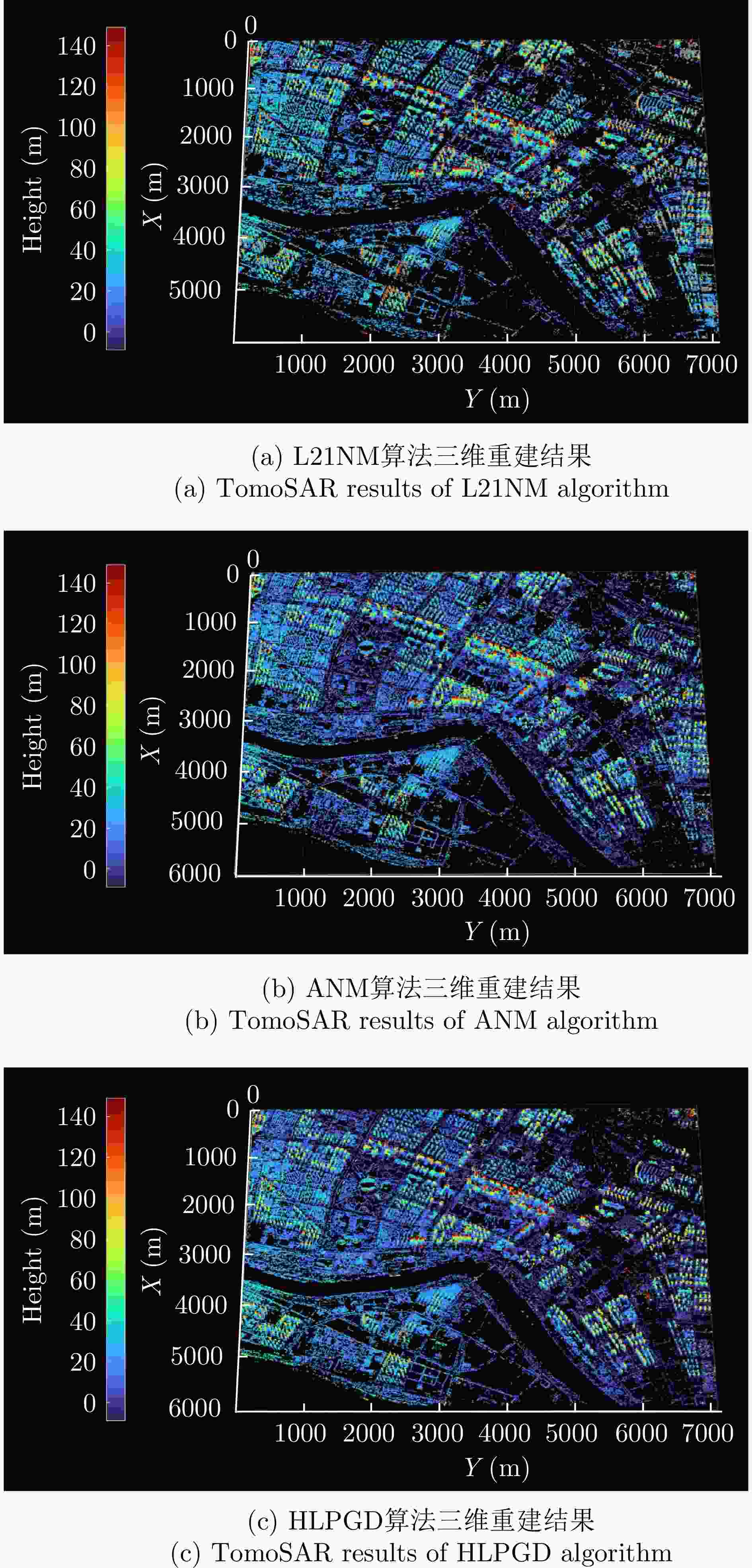
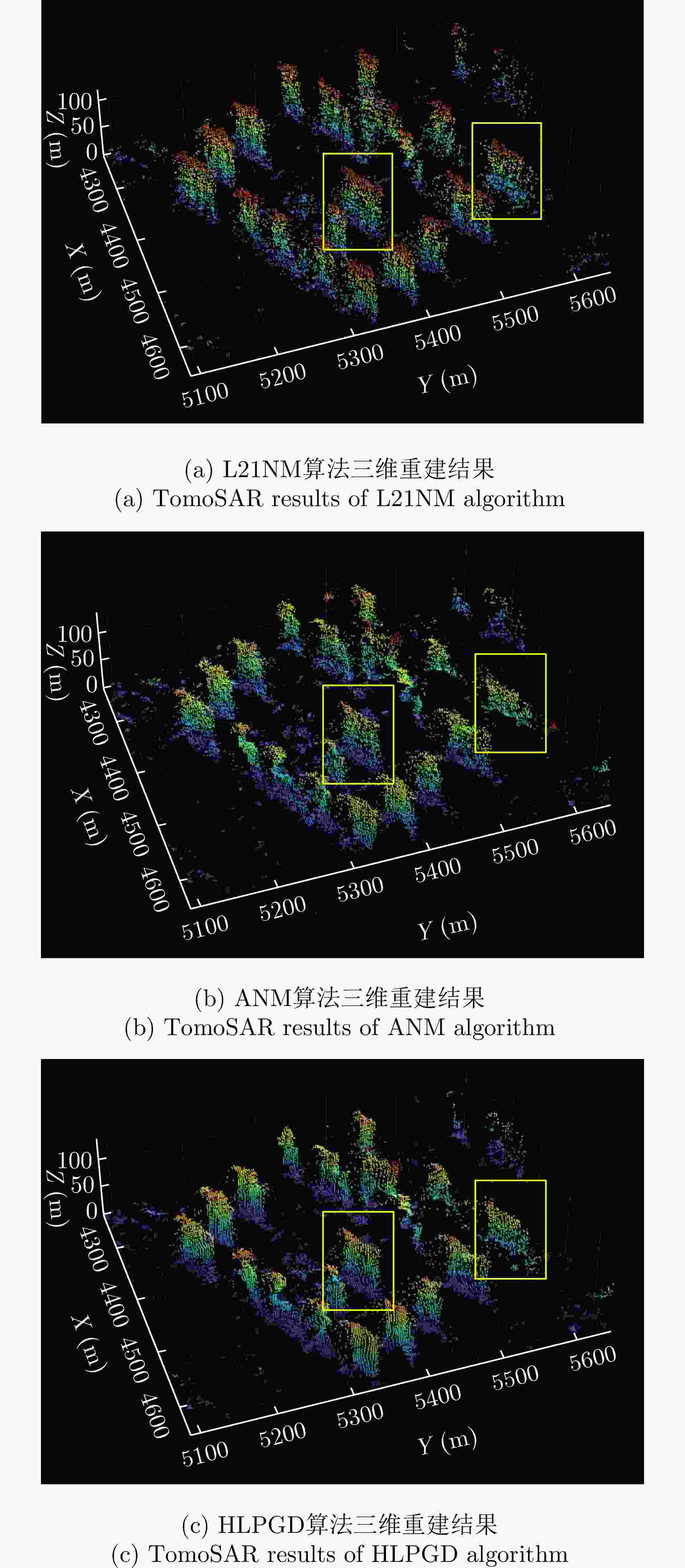
算法 Ku波段机载数据集(运城) L波段星载数据集(南京) 处理时间(min) 三维点云重建数 处理时间(min) 三维点云重建数 L21NM 284.14 232181 5705.5 657863 ANM 11.12 247352 851.3 772789 HLPGD 8.98 276915 709.5 823788 -
[1] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567. [2] REIGBER A, MOREIRA A, and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 1999: 44–46. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1999.773395. [3] FORNARO G and SERAFINO F. Imaging of single and double scatterers in urban areas via SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(12): 3497–3505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.881748. [4] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. [5] WANG Chaodong, LI Zhongyu, HAI Yu, et al. Multistatic TomoSAR 3-D imaging technique via matrix completion for structured targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5215716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3563481. [6] 毕辉, 金双, 王潇, 等. 基于高分三号SAR数据的城市建筑高分辨率高维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113.BI Hui, JIN Shuang, WANG Xiao, et al. High-resolution high-dimensional imaging of urban building based on GaoFen-3 SAR data[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113. [7] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487. [8] ZHU Xiaoxinag and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098. [9] RAMBOUR C, DENIS L, TUPIN F, et al. Introducing spatial regularization in SAR tomography reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8600–8617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921756. [10] YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3139–3153. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2420541. [11] LI Yuanxin and CHI Yuejie. Off-the-grid line spectrum denoising and estimation with multiple measurement vectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(5): 1257–1269. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2496294. [12] 杜邦, 仇晓兰, 张柘, 等. 基于扰动的结合Off-grid目标的层析SAR三维成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 62–70. doi: 10.12000/JR21093.DU Bang, QIU Xiaolan, ZHANG Zhe, et al. L1 minimization with perturbation for Off-grid tomographic SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 62–70. doi: 10.12000/JR21093. [13] CANDÈS E J and FERNANDEZ-GRANDA C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2014, 67(6): 906–956. doi: 10.1002/cpa.21455. [14] CHI Yuejie and FERREIRA DA COSTA M. Harnessing sparsity over the continuum: Atomic norm minimization for superresolution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(2): 39–57. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2962209. [15] YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222378. [16] TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR B N, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451. [17] WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Tomographic SAR inversion by atomic-norm minimization—the gridless compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3223524. [18] WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Efficient ADMM algorithm for atomic norm minimization in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5211415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3395510. [19] GAO Silin, WANG Wenlong, WANG Muhan, et al. A robust super-resolution gridless imaging framework for UAV-borne SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5210917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3393972. [20] ZHANG Bangjie, XU Gang, YU Hanwen, et al. Array 3-D SAR tomography using robust gridless compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5205013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3259980. [21] LIU Minkun, WANG Yan, DING Zegang, et al. Atomic norm minimization based fast off-grid tomographic SAR imaging with nonuniform sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358863. [22] SHAO Mingxiao, ZHANG Zhe, LI Jie, et al. TADCG: A novel gridless tomographic SAR imaging approach based on the alternate descent conditional gradient algorithm with robustness and efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5201213. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3345454. [23] ZHANG Shuai, HAO Yingshuai, WANG Meng, et al. Multichannel Hankel matrix completion through nonconvex optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(4): 617–632. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2827299. [24] CHEN Yuxin and CHI Yuejie. Robust spectral compressed sensing via structured matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(10): 6576–6601. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2343623. [25] CAI Jianfeng, WANG Tianming, and WEI Ke. Spectral compressed sensing via projected gradient descent[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2018, 28(3): 2625–2653. doi: 10.1137/17M1141394. [26] LI Jinsheng, CUI Wei, and ZHANG Xu. Projected gradient descent for spectral compressed sensing via symmetric Hankel factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 1590–1606. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3378004. [27] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112.QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112. [28] ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646. [29] XU Gang, ZHANG Bangjie, YU Hanwen, et al. Sparse synthetic aperture radar imaging from compressed sensing and machine learning: Theories, applications, and trends[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(4): 32–69. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2022.3218801. [30] 杨磊, 王腾腾, 陈英杰, 等. 低秩矩阵补全高分辨SAR成像特征重建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 2965–2974. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220992.YANG Lei, WANG Tengteng, CHEN Yingjie, et al. Feature reconstruction of high resolution SAR imagery based on low rank matrix completion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 2965–2974. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220992. [31] MAO Sihan and CHEN Jinchi. Blind super-resolution of point sources via projected gradient descent[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4649–4664. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3209006. [32] VU T and RAICH R. On asymptotic linear convergence of projected gradient descent for constrained least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4061–4076. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3192142. [33] RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of Root-MUSIC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939–1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540. [34] BUDILLON A and SCHIRINZI G. GLRT based on support estimation for multiple scatterers detection in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1086–1094. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2494376. [35] 任烨仙, 徐丰. 若干层析SAR成像方法在解叠掩性能上的对比分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139.REN Yexian and XU Feng. Comparative experiments on separation performance of overlapping scatterers with several tomography imaging methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139. [36] 姬昂, 裴昊, 张邦杰, 等. 阵列SAR高分辨三维成像与点云聚类研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 2087–2094. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231223.JI Ang, PEI Hao, ZHANG Bangjie, et al. Research on high-resolution 3D imaging and point cloud clustering of array SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 2087–2094. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231223. [37] 任子帅, 张照, 高雨欣, 等. 基于自适应高程约束的TomoSAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1056–1068. doi: 10.12000/JR23111.REN Zishuai, ZHANG Zhao, GAO Yuxin, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of tomographic SAR based on adaptive elevation constraint[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1056–1068. doi: 10.12000/JR23111. [38] LI Tao, TANG Xinming, ZHANG Xiang, et al. First application demonstrations of Lu Tan-1 SAR satellites[C]. 2023 SAR in Big Data Era (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 2023: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA59007.2023.10294711. [39] XU Gang, CHEN Yuzhi, JI Ang, et al. 3-D high-resolution imaging and array calibration of ground-based millimeter-wave MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(8): 4919–4931. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3352406. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: