Identification Method for Icosahedron Triangular Trihedral Corner Reflector and Vessels Based on Polarization Feature-range Joint Matrix
-
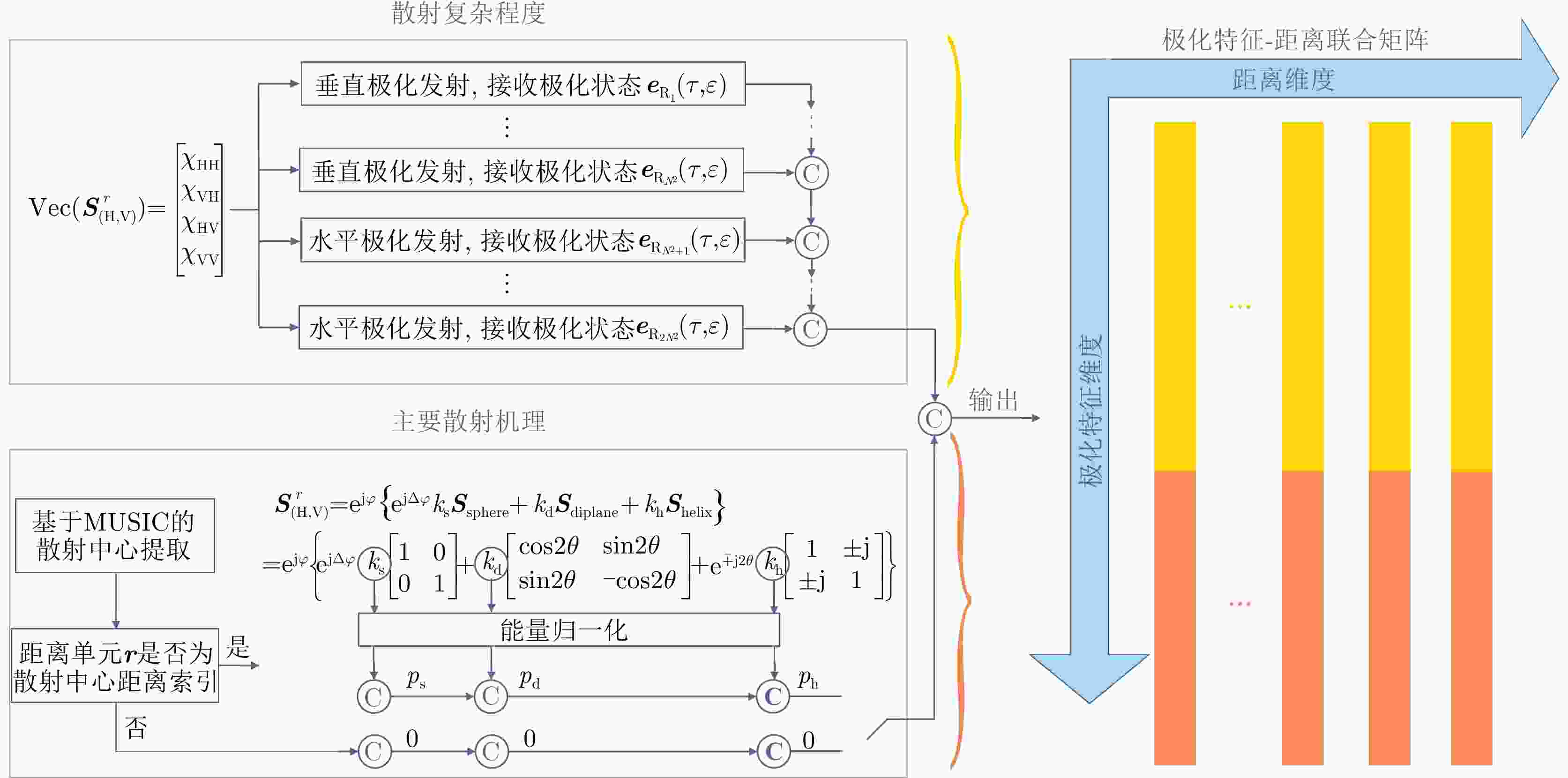
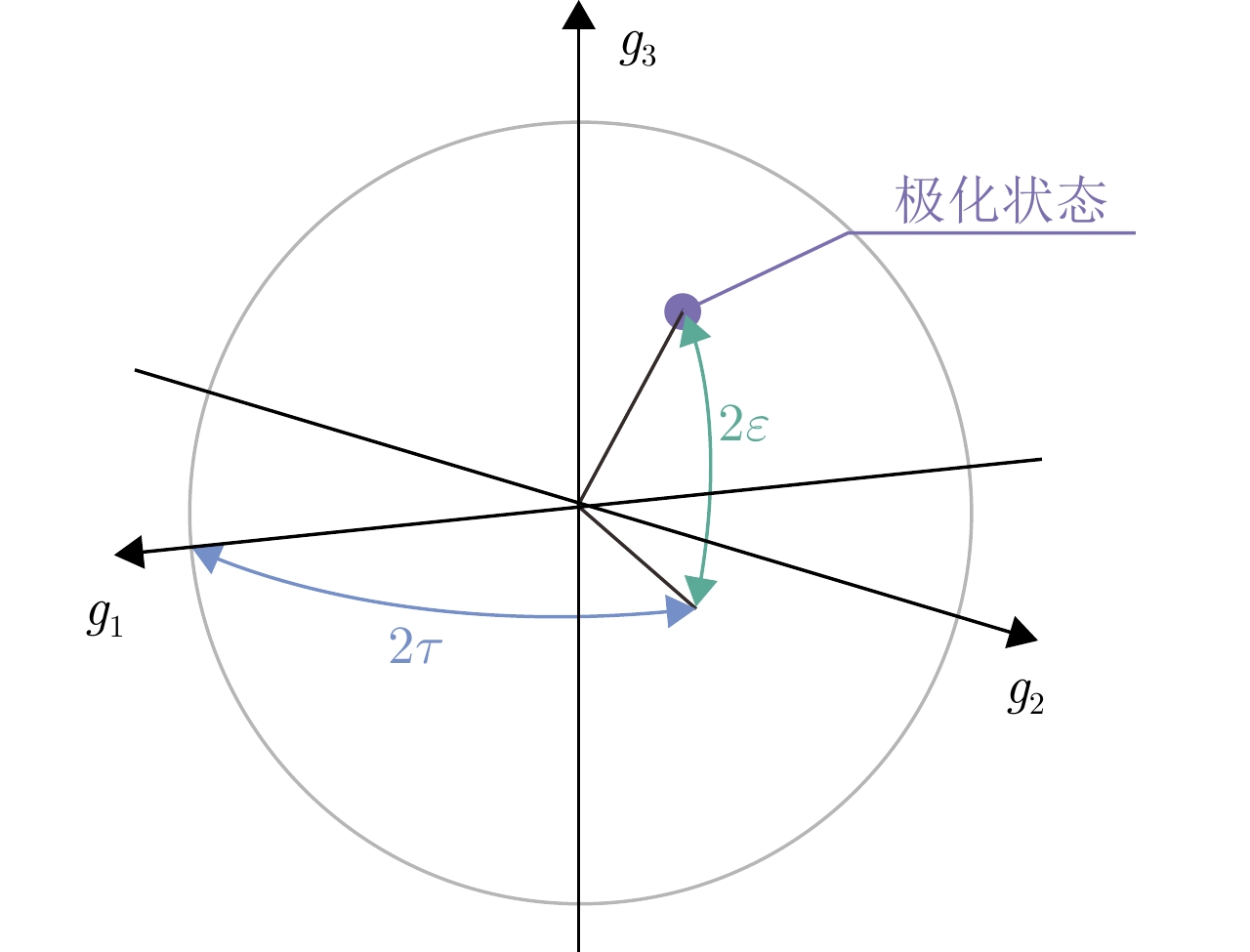
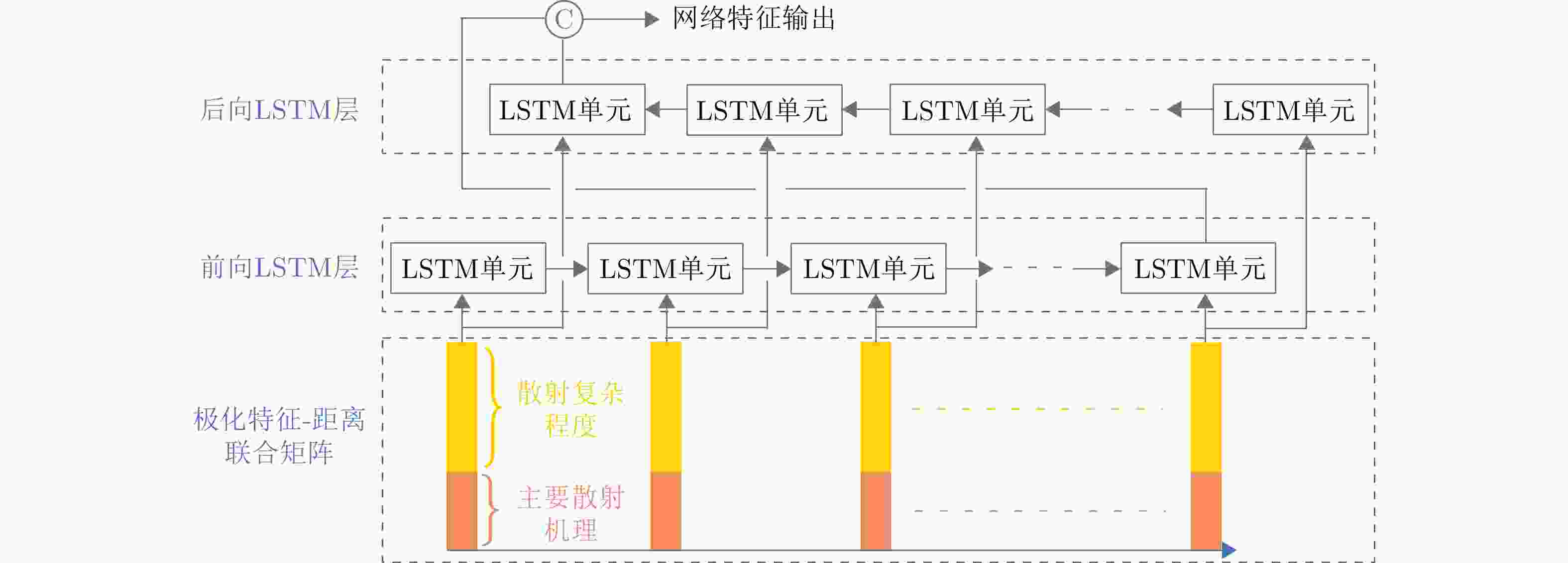
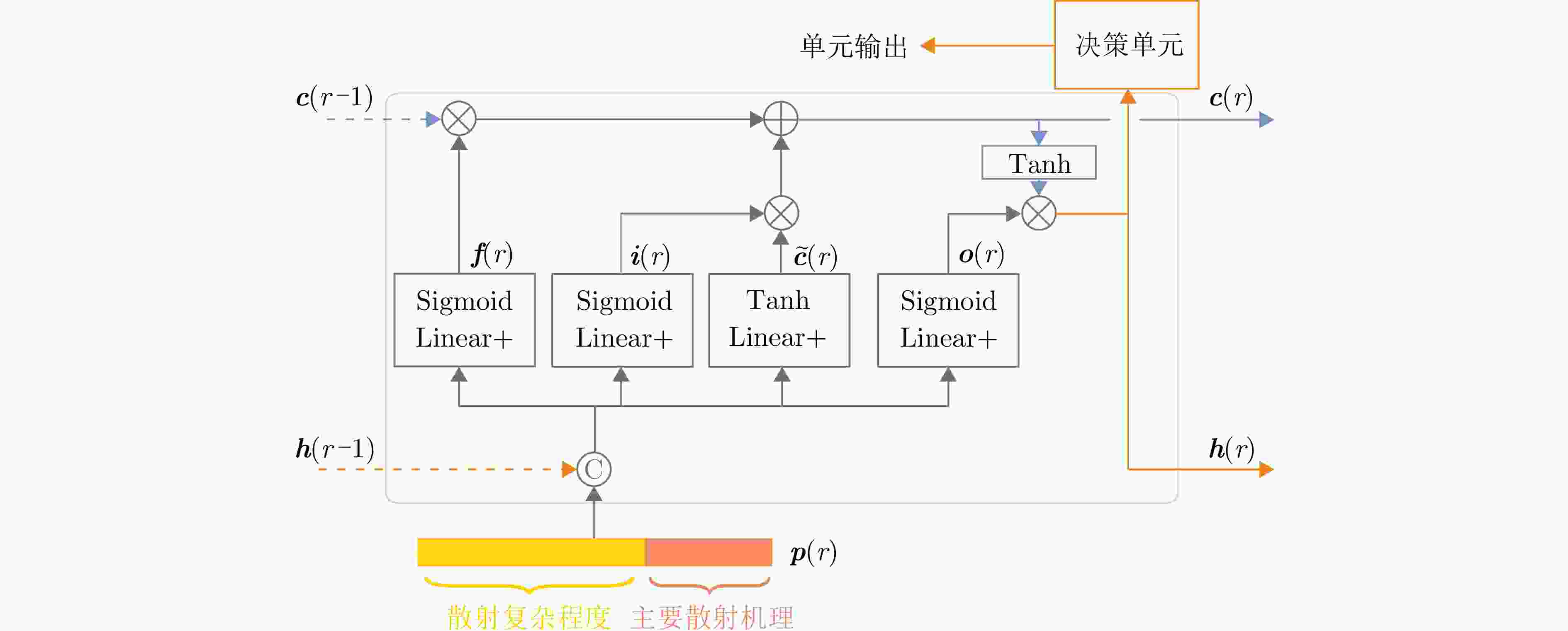
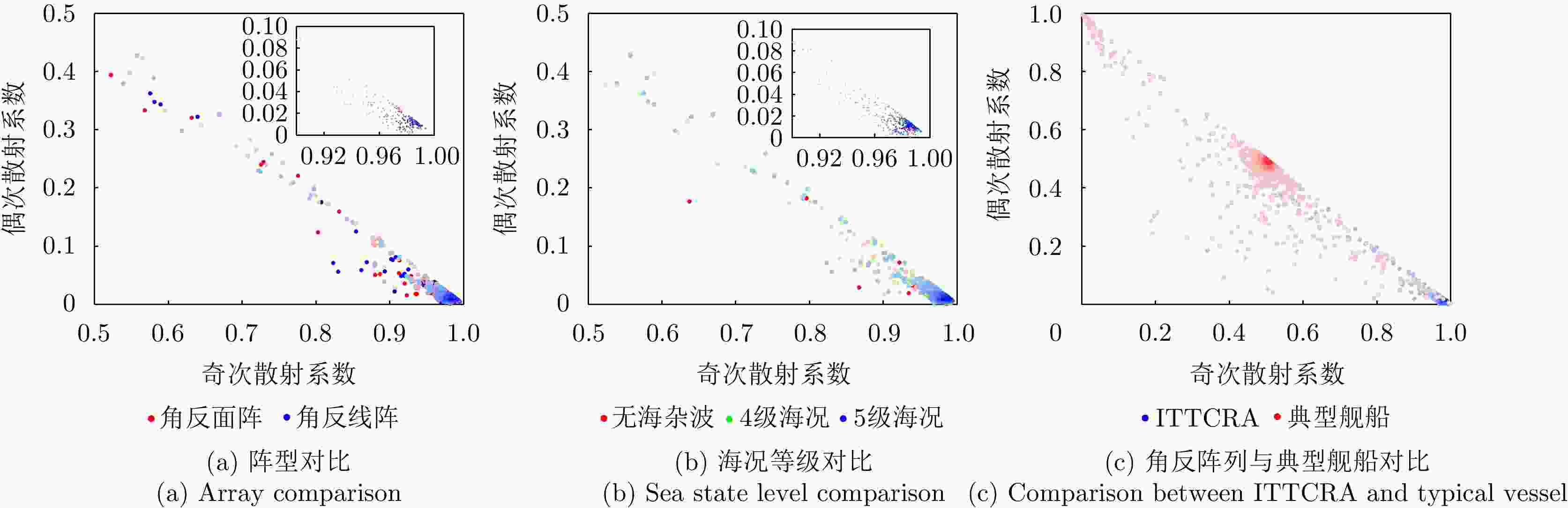
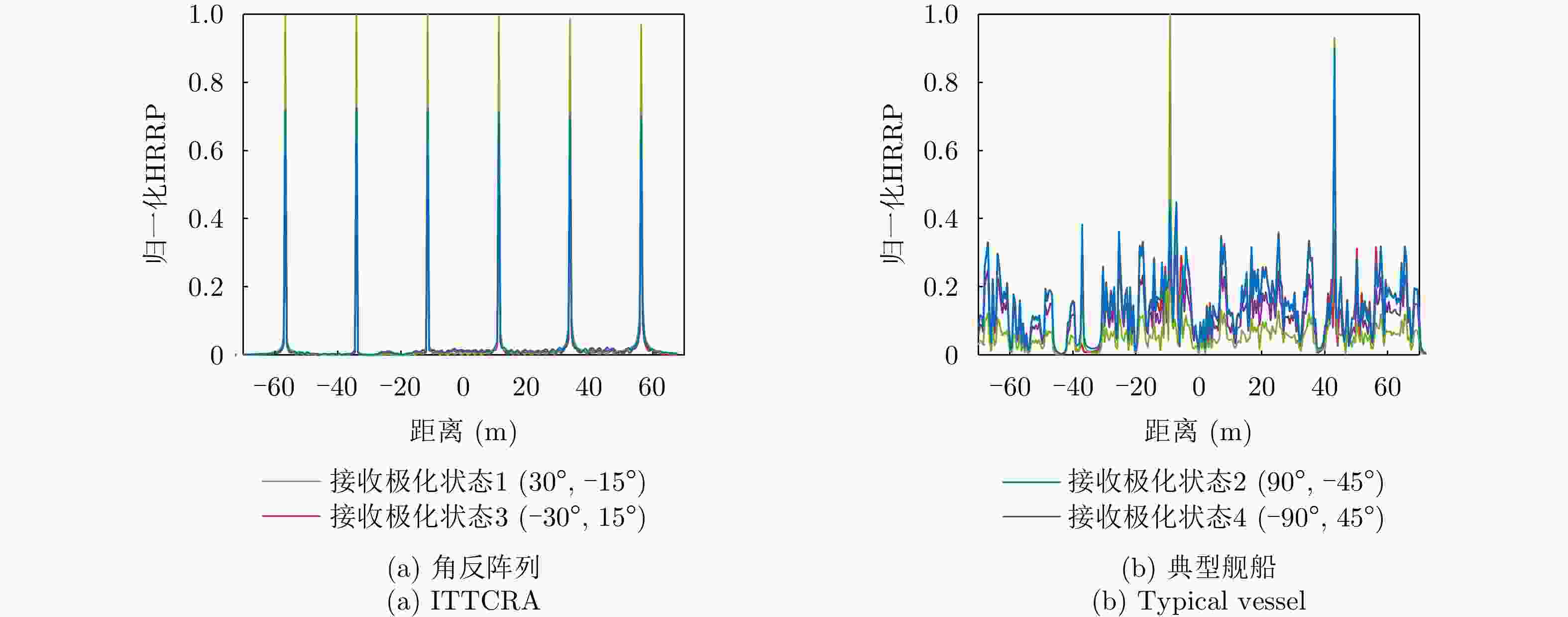
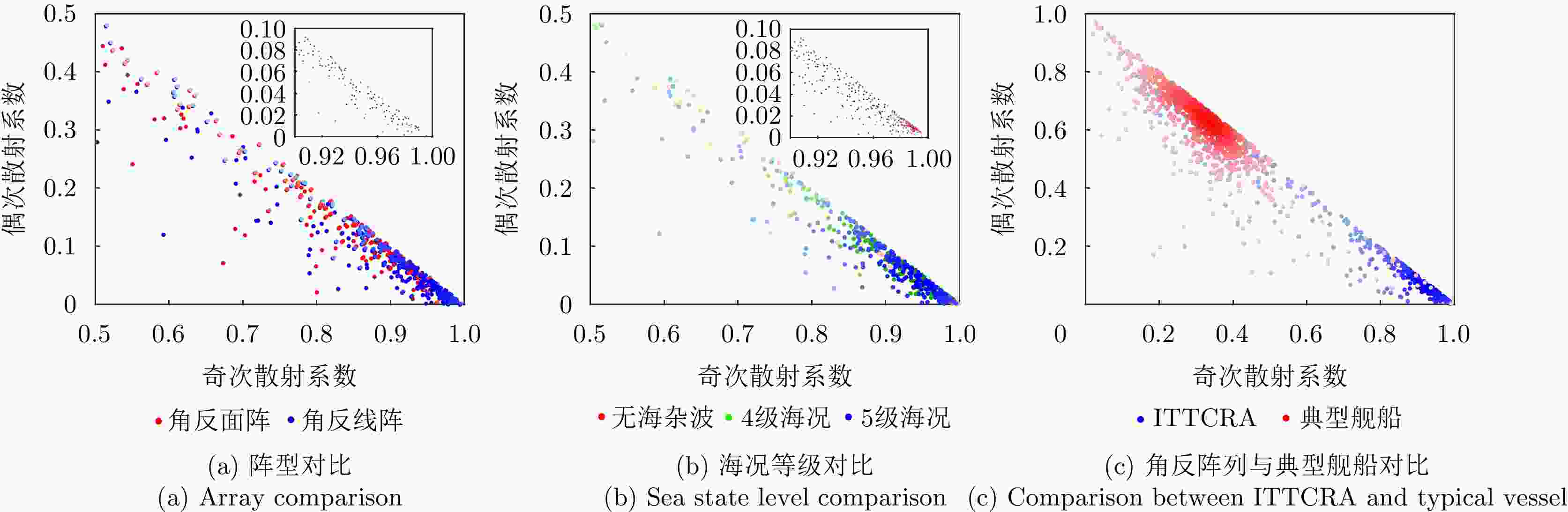
摘要: 在雷达目标识别领域,二十面体角反射器的引入无疑提升了目标辨识任务的难度。这种情况在中高海况下将尤为严重。剧烈起伏的海面将与二十面体角反射器形成耦合散射,这可能达到与目标相似的散射特性,从而导致传统目标辨识方法性能下降。针对中高海况下目标辨识难的问题,该文从主要散射机理和散射复杂程度两个方面,构建了极化特征-距离联合矩阵,表征中高海况下舰船与二十面体角反射器阵列之间的差异。然后,利用时序神经网络提取两者极化特征-距离联合矩阵的特征,以实现对目标的有效辨识。经数据集的验证,所提出的方法可以有效减少手工知识提取过程中的信息丢失。在中高海况条件下,相较于现有方法,该方法的准确率提升了10.14%,大幅降低了二十面体角反射器阵列造成的虚警。Abstract: In the field of radar target recognition, the introduction of Icosahedron Triangular Trihedral Corner Reflector (ITTCR) has increased the difficulty of target identification tasks, especially under moderate to high sea states. Under such conditions, the undulating sea surface can couple with an ITTCR to produce scattering characteristics similar to those of the target, resulting in a decline in the performance of traditional target identification methods. As a solution, a joint matrix of polarization features and range was constructed by considering the dominant scattering mechanisms and scattering complexity. This matrix characterizes the component-level differences between ships and ITTCR arrays in the presence of sea clutter. Subsequently, a temporal neural network extracts features from the joint matrices of the vessels and ITTCR arrays, achieving effective target identification. The performance of the proposed method was validated using a dataset. The proposed method effectively reduces information loss during manual knowledge refinement. Under moderate to high sea states, the proposed method has an accuracy higher than that of the existing methods by 10.14%. Furthermore, the proposed method considerably reduces false alarms caused by ITTCR arrays.
-
表 1 典型散射体极化散射矩阵
Table 1. Typical scatterer polarization scattering matrix
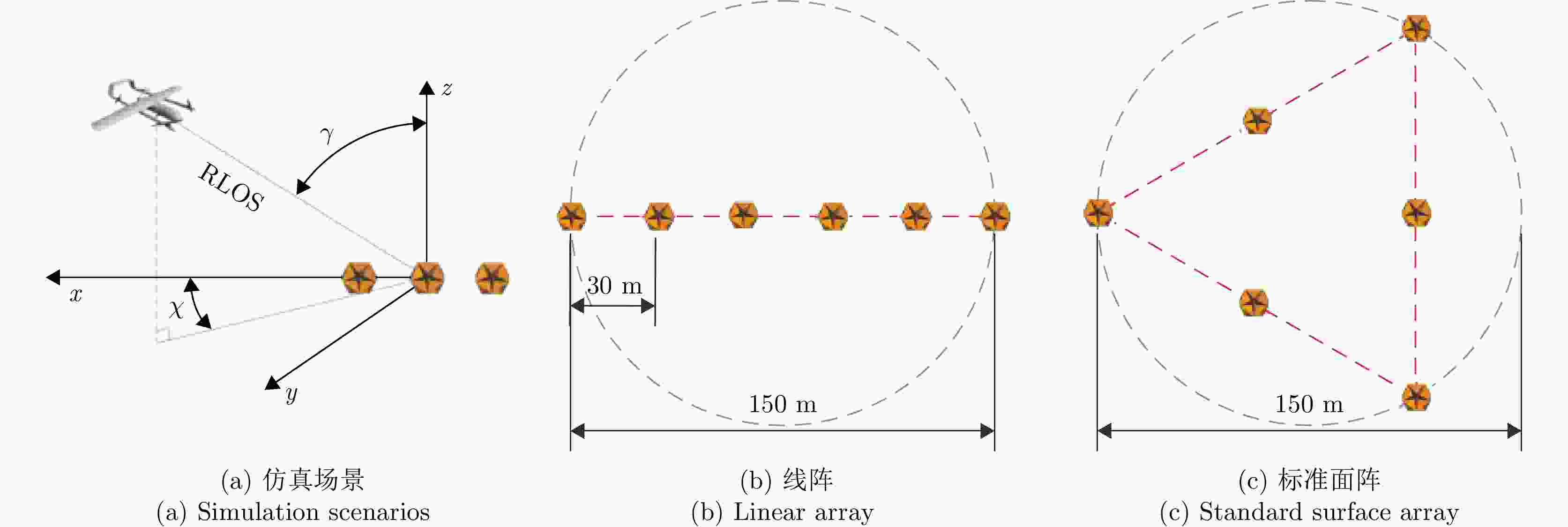
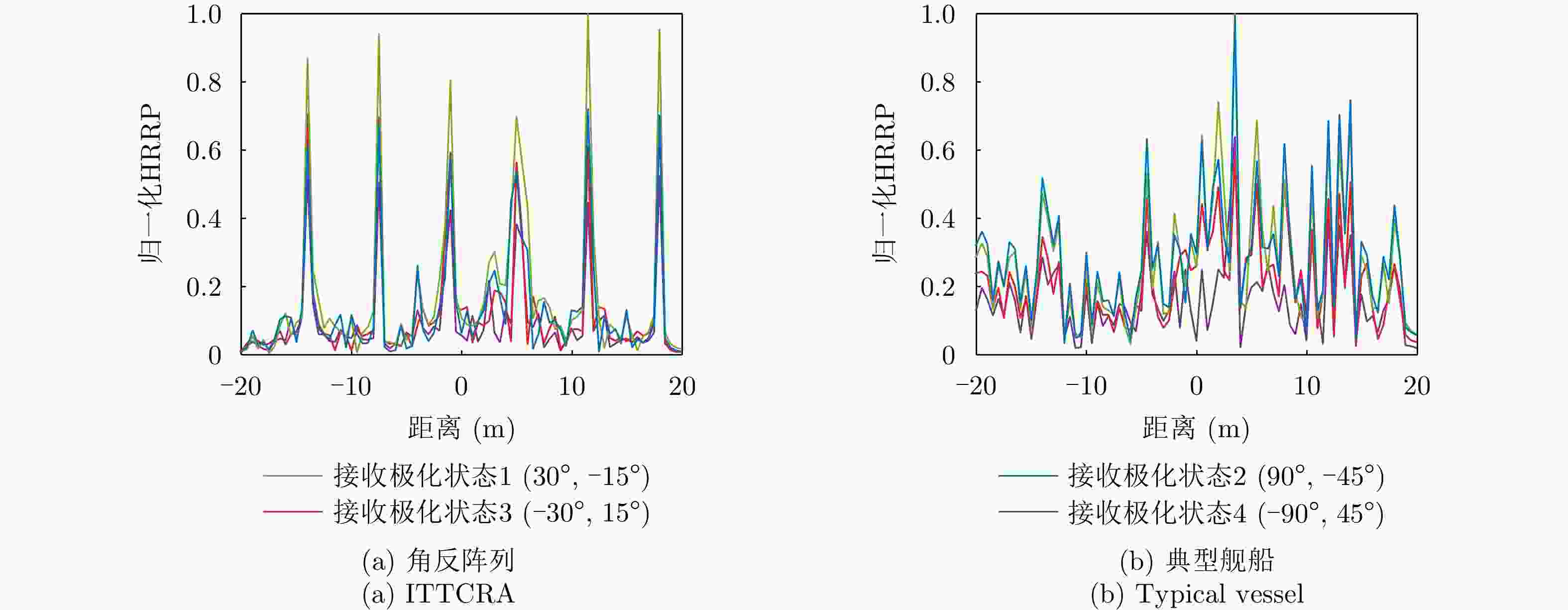
几何结构 PSM 二面角 $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\text{1}}&{\text{0}} \\ {\text{0}}&{{{ - 1}}} \end{array}} \right] $ 三面角 $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\text{1}}&{\text{0}} \\ {\text{0}}&{\text{1}} \end{array}} \right] $ 圆柱体 $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\text{1}}&{\text{0}} \\ {\text{0}}&{\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}} \end{array}} \right] $ 螺旋体 $ \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\text{1}}&{\text{j}} \\ {\text{j}}&{ - 1} \end{array}} \right] $ 窄二面角 $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\text{1}}&0 \\ 0&{ - \dfrac{1}{2}} \end{array}} \right] $ 表 2 海杂波背景角反阵列电磁仿真参数
Table 2. ITTCRA electromagnetic simulation parameters in sea clutter background
参数 指标 仿真目标 角反阵列、典型舰船 载频 16 GHz 带宽 300 MHz 方位角 0°~180°(线阵),0°~180°(面阵),间隔5° 俯仰角 15°, 90° 频点个数 601 表 3 实验雷达参数
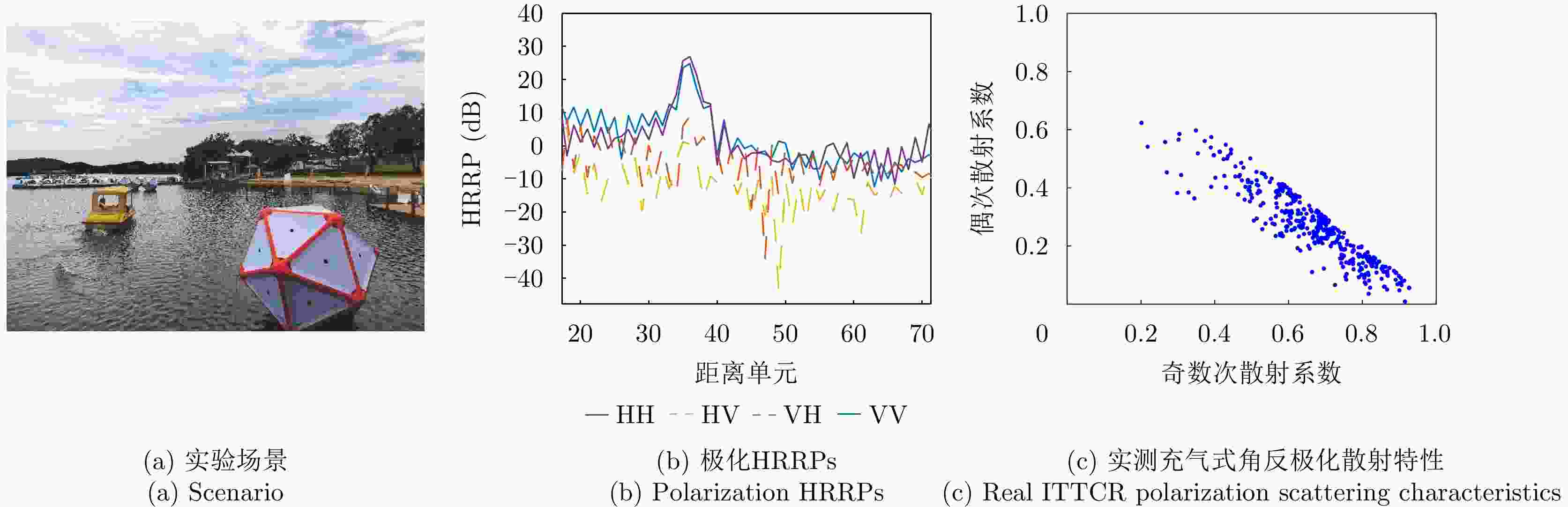
Table 3. Experimental radar parameters
编号 参数 指标 1 发射方式 水平极化、垂直极化分时发射 2 接收方式 水平极化和、垂直极化和
与垂直极化差同时接收3 工作中心频率 7 GHz 4 脉冲重复周期 50 μs 5 分时发射脉冲延时 25 μs 6 发射信号调制方式 线性调频 7 发射信号脉宽 20 μs 8 发射信号带宽 150 MHz 9 基带回波采样率 300 MHz 表 4 辨识方法性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of identification methods
表 5 采样点数N性能分析
Table 5. Performance analysis of sampling points N
N 准确度(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1 Score (%) 2 87.92 83.53 86.93 84.95 3 89.37 85.43 87.91 86.54 4 91.30 88.59 88.59 88.59 5 91.79 88.30 91.39 89.65 6 91.79 88.75 90.15 89.41 表 6 同海况各辨识网络性能对比
Table 6. Performance comparison of identification networks under the same sea states
辨识网络 准确度(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1 Score (%) ResNet18 90.34 87.04 87.94 87.47 BiGRU 90.82 87.80 88.26 88.03 所提方法 91.30 88.59 88.59 88.59 表 7 不同海况下各辨识网络性能对比
Table 7. Performance comparison of identification networks under different sea states
辨识网络 准确度(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1 Score (%) ResNet18 86.94 85.98 84.12 84.93 BiGRU 88.74 88.12 86.15 87.01 所提方法 89.19 88.25 87.16 87.67 表 8 网络输入性能对比分析
Table 8. Performance comparison analysis of network input
网络输入方式 准确度(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1 Score (%) PSM 79.71 73.34 72.75 73.03 Pauli分解 80.68 74.94 71.54 72.88 Krogager分解 84.54 80.02 78.47 79.19 所提方法 91.30 88.59 88.59 88.59 -
[1] 欧乃铭, 白明, 梁彬, 等. 三角板角反射器在RCS定标测试中的应用[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(2): 220–224. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.02.005.OU Naiming, BAI Ming, LIANG Bin, et al. Application of the trihedral corner reflector in RCS calibration test[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(2): 220–224. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.02.005. [2] 翁寅侃. SAR角反射器的优化设计及其应用[D]. [博士论文], 武汉大学, 2017: 1–20.WENG Yinkan. Optimization of corner reflector and its application in spaceborne SAR image[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Wuhan University, 2017: 1–20. [3] 张志远, 赵原源. 新型二十面体三角形角反射器的电磁散射特性分析[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2018, 40(4): 133–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.04.030.ZHANG Zhiyuan and ZHAO Yuanyuan. Analysis of electromagnetic scattering characteristic for new type icosahedrons triangular trihedral corner reflectors[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2018, 40(4): 133–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.04.030. [4] 赵非玉, 于群, 牛帅, 等. 异型多面体角反射器的电磁散射特性分析及应用[J]. 电波科学学报, 2023, 38(6): 982–988. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2023137.ZHAO Feiyu, YU Qun, NIU Shuai, et al. Analysis of electromagnetic scattering characteristics and application of heterotype polyhedron corner reflector[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2023, 38(6): 982–988. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2023137. [5] 骆颖. 基于TDSBR的海上目标与角反射器复合时域电磁散射及干扰分析研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021: 31–51. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.002354.LUO Ying. TDSBR-based time-domain electromagnetic scattering and jamming analysis of marine targets and corner reflectors[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021: 31–51. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.002354. [6] 丛洲, 丁大志, 樊振宏, 等. 基于绕射场修正快速迭代物理光学法的海面舰船与角反阵列电磁散射分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 2023, 38(6): 960–971. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2023142.CONG Zhou, DING Dazhi, FAN Zhenhong, et al. Analysis of RCS from sea surface ships and reflector arrays based on rapid iterative physical optics method with diffraction field correction[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2023, 38(6): 960–971. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2023142. [7] 汤广富, 李华, 甘荣兵, 等. 海战场环境下角反射器干扰分析[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2015, 30(5): 39–45, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2015.05.008.TANG Guangfu, LI Hua, GAN Rongbing, et al. Analysis of corner reflector under naval battlefield[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2015, 30(5): 39–45, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2015.05.008. [8] 孟凯, 马武举. 海面漂浮二十面角反射器电磁散射特性研究[J]. 数字海洋与水下攻防, 2020, 3(5): 437–442. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2020.05.013.MENG Kai and MA Wuju. Research on electromagnetic scattering characteristics of sea floating icosahedrons triangular trihedral corner reflectors[J]. Digital Ocean & Underwater Warfare, 2020, 3(5): 437–442. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2020.05.013. [9] 吴国庆, 王罗胜斌, 庞晨, 等. 雷达极化域变焦角反组合体对抗方法: 抗冲淡式干扰[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(12): 2969–2983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220979.WU Guoqing, WANG Luoshengbin, PANG Chen, et al. Radar polarization modulation countermeasures for combined corner reflector: Anti diluted jamming[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(12): 2969–2983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220979. [10] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 对海雷达目标识别中全极化HRRP的特征提取与选择[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722.FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. Feature extraction and selection of full polarization HRRP in target recognition process of maritime surveillance radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722. [11] 范学满, 胡生亮, 陈鹏, 等. 基于分类器联合的反舰导弹HRRP目标识别与拒判研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2017, 29(4): 14–20. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2017.04.003.FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, CHEN Peng, et al. HRRP recognition and rejection of anti-ship missile based on classifier combination[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2017, 29(4): 14–20. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2017.04.003. [12] 韩静雯, 杨勇, 连静, 等. 基于极化与距离像特征融合的雷达导引头角反射器鉴别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(11): 3658–3670. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.11.08.HAN Jingwen, YANG Yong, LIAN Jing, et al. Identification method of corner reflector based on polarization and HRRP feature fusion for radar seeker[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(11): 3658–3670. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.11.08. [13] 黄孟俊, 赵宏钟, 付强, 等. 一种基于微多普勒特征的海面角反射器干扰鉴别方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2012, 33(10): 1486–1491. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.10.018.HUANG Mengjun, ZHAO Hongzhong, FU Qiang, et al. A sea corner-reflector jamming identification method based on micro-Doppler feature[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(10): 1486–1491. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.10.018. [14] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039.WANG Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039. [15] 杨健, 曾亮, 马文婷, 等. 雷达目标极化散射特征提取的研究进展[J]. 电波科学学报, 2019, 34(1): 12–18. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2018091501.YANG Jian, ZENG Liang, MA Wenting, et al. Recent advances on extraction of polarimetric scattering features of radar target[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2019, 34(1): 12–18. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2018091501. [16] 李郝亮, 陈思伟, 王雪松. 海面角反射器的极化旋转域特性研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01.LI Haoliang, CHEN Siwei, and WANG Xuesong. Study on characterization of sea corner reflectors in polarimetric rotation domain[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01. [17] 刘涛, 杨子渊, 蒋燕妮, 等. 极化SAR图像舰船目标检测研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155.LIU Tao, YANG Ziyuan, JIANG Yanni, et al. Review of ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155. [18] 涂建华, 汤广富, 肖怀铁, 等. 基于极化分解的抗角反射器干扰研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2009, 7(2): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.02.002.TU Jianhua, TANG Guangfu, XIAO Huaitie, et al. A study of anti-corner reflector based on polarization decomposition[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2009, 7(2): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.02.002. [19] 朱珍珍, 汤广富, 程翥, 等. 基于极化分解的舰船和角反射器鉴别方法[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2010, 33(6): 15–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2010.06.003.ZHU Zhenzhen, TANG Guangfu, CHENG Zhu, et al. Discrimination method of ship and corner reflector based on polarization decomposition[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2010, 33(6): 15–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2010.06.003. [20] 吕方方. 海面目标动态回波仿真与特性分析[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019: 28–53. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2019.002034.LV Fangfang. Dynamic echo simulation and characteristic analysis of sea surface targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019: 28–53. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2019.002034. [21] WANG Miao, XIE Min, SU Qinning, et al. Identification of ship and corner reflector based on invariant features of the polarization[C]. The 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Wuxi, China, 2019: 545–549. doi: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2019.8868738. [22] LIANG Zhuorui, WANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaofeng, et al. Identification of ship and corner reflector in sea clutter environment[C]. The 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2020: 622–626. doi: 10.1109/ICSP48669.2020.9321063. [23] KROGAGER E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. doi: 10.1049/el:19900979. [24] KIM K T, SEO D K, and KIM H T. Efficient radar target recognition using the MUSIC algorithm and invariant features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(3): 325–337. doi: 10.1109/8.999623. [25] 王罗胜斌, 王雪松, 徐振海. 雷达极化域调控超分辨的原理与方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141.WANG Luoshengbin, WANG Xuesong, and XU Zhenhai. Principle and approach to polarization modulation for radar super-resolution[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141. [26] HUANG Zhiheng, XU Wei, and YU Kai. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.01991, 2015. [27] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.324. [28] DONG Chunlei, GUO Lixin, and MENG Xiao. An accelerated algorithm based on GO-PO/PTD and CWMFSM for EM scattering from the ship over a sea surface and SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(5): 3934–3944. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2963241. [29] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [30] CHUNG J, GÜLÇEHRE C, CHO K, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555, 2014. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: