-
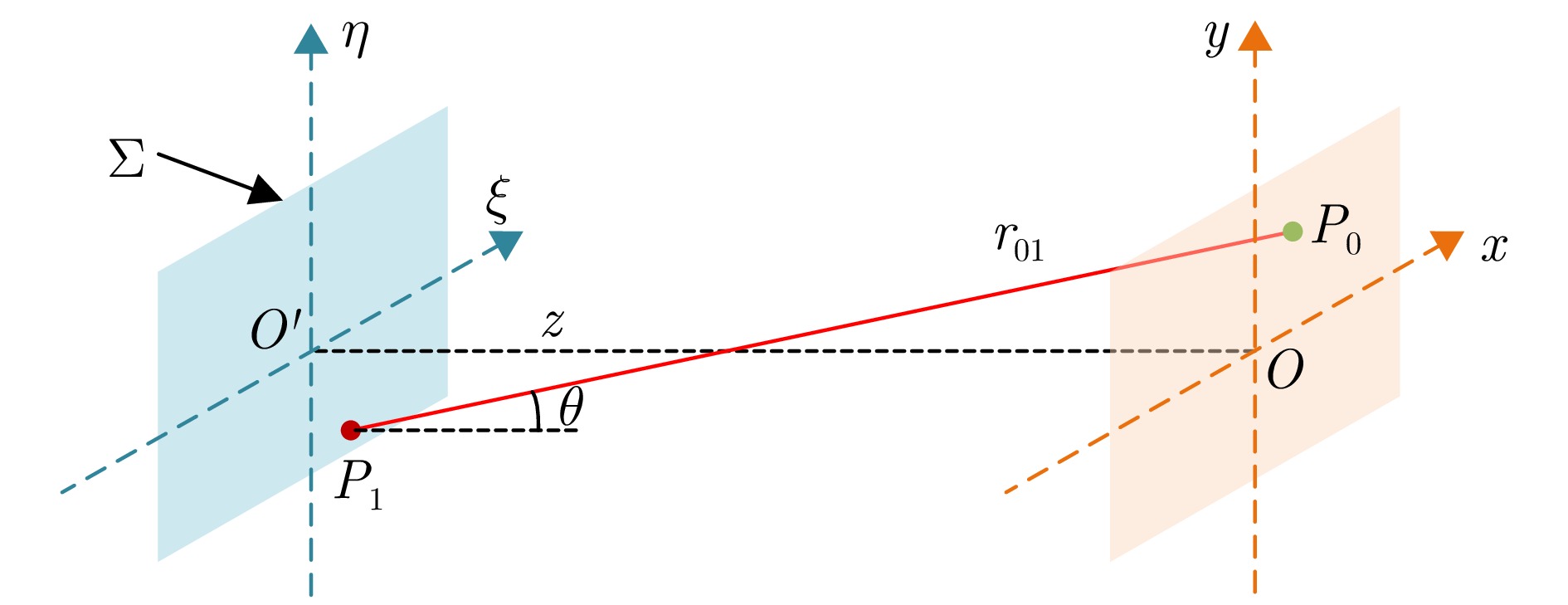
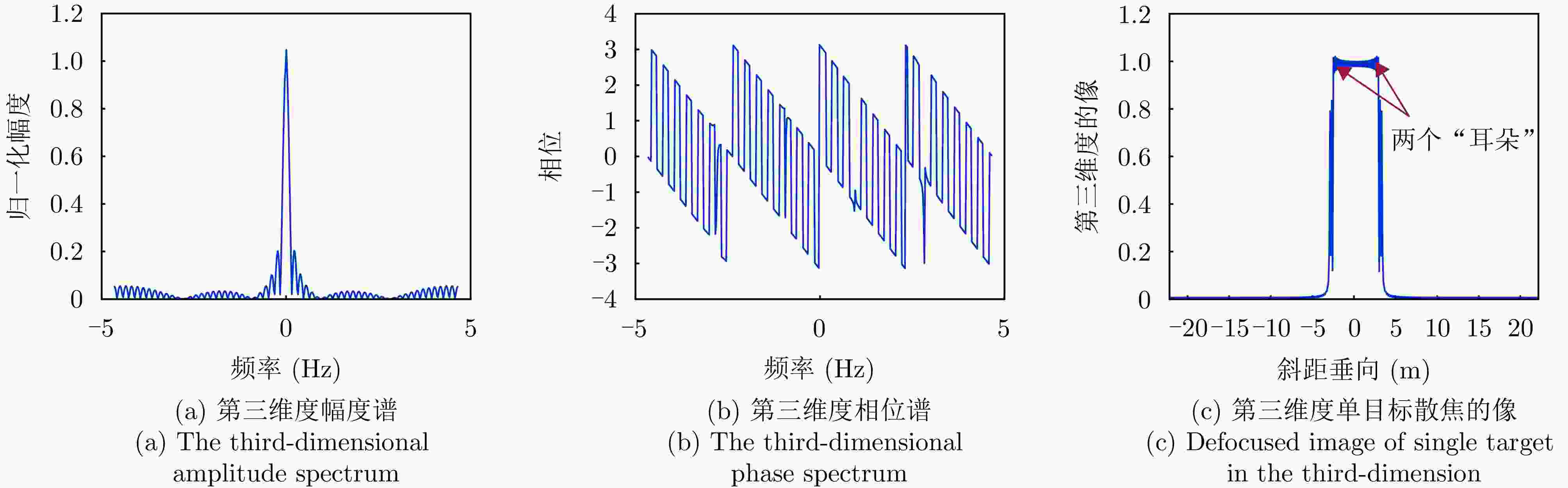
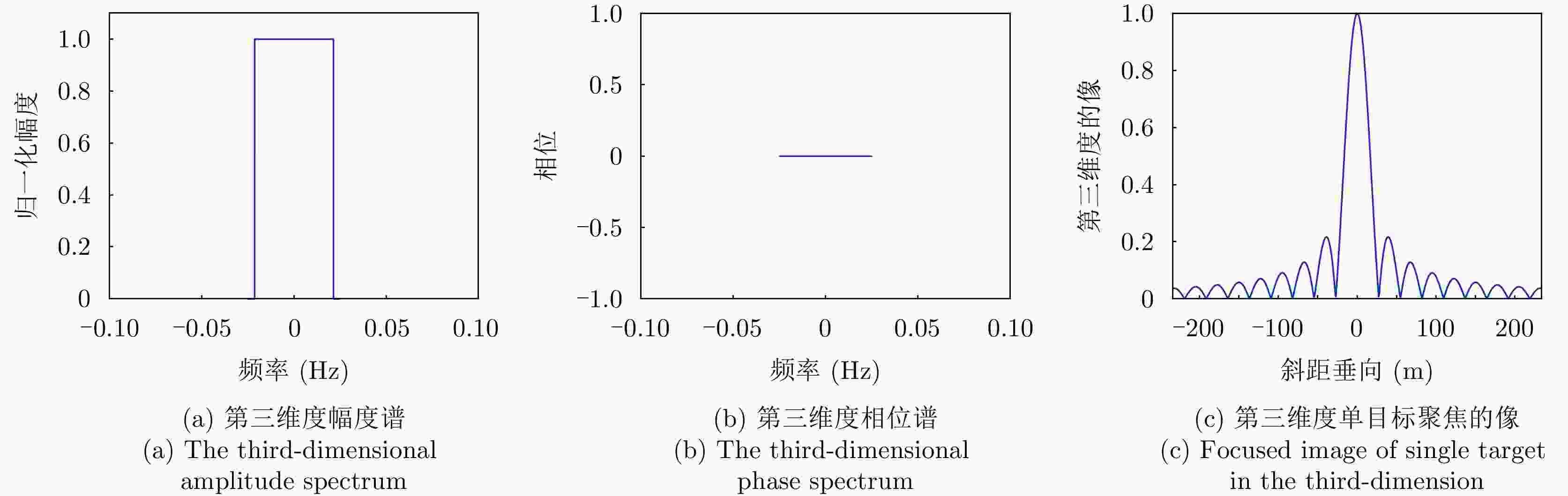
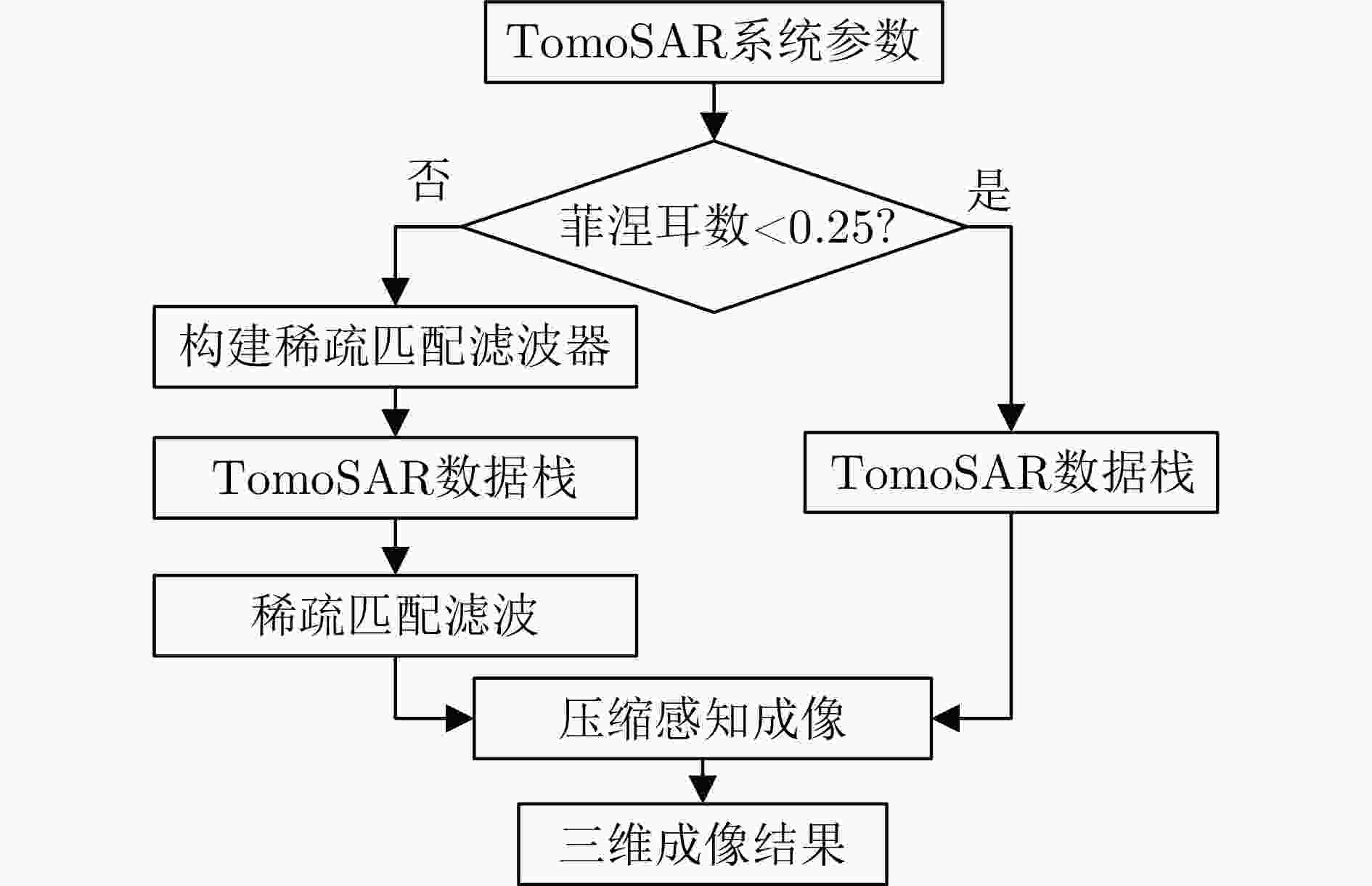
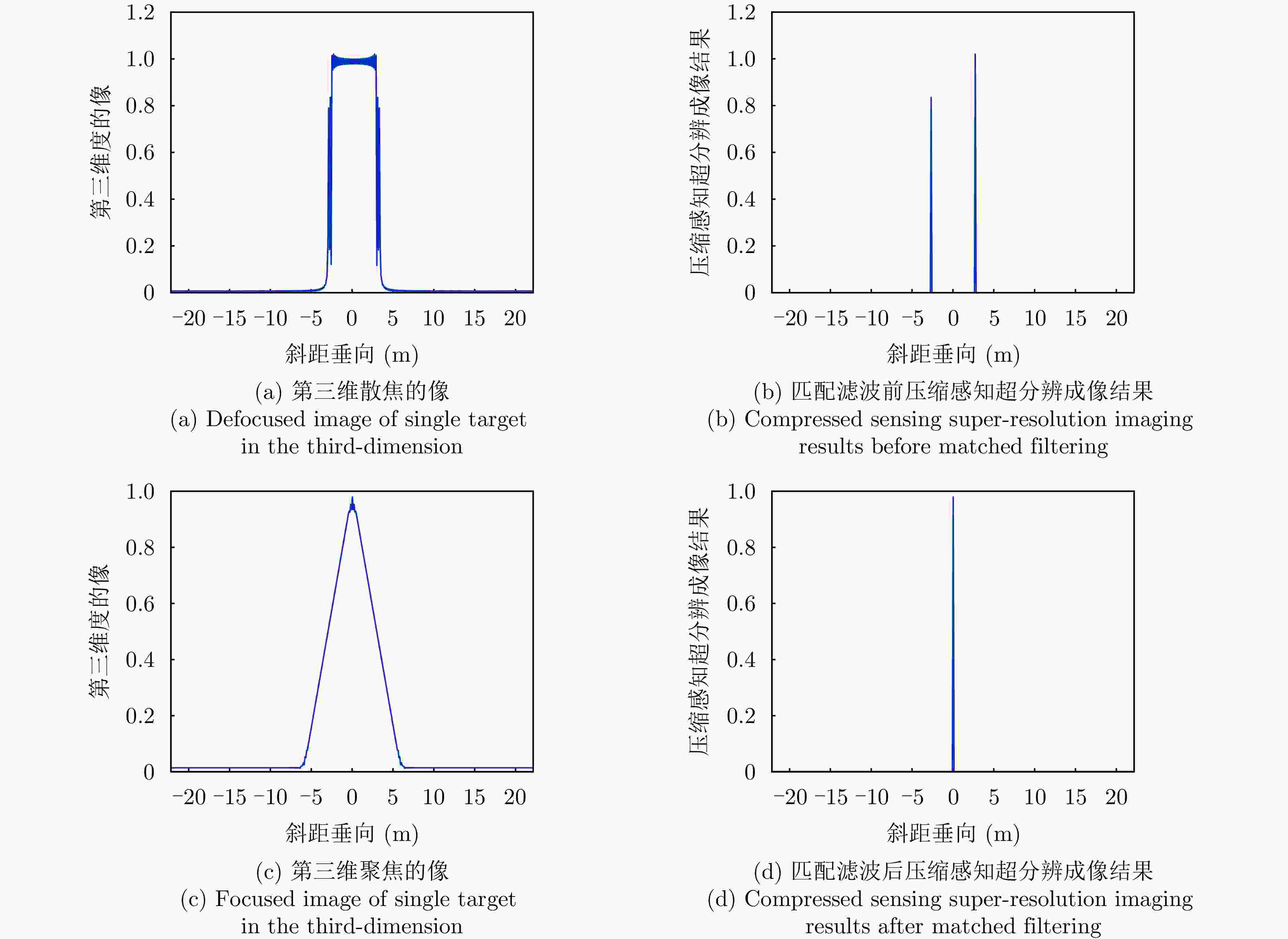
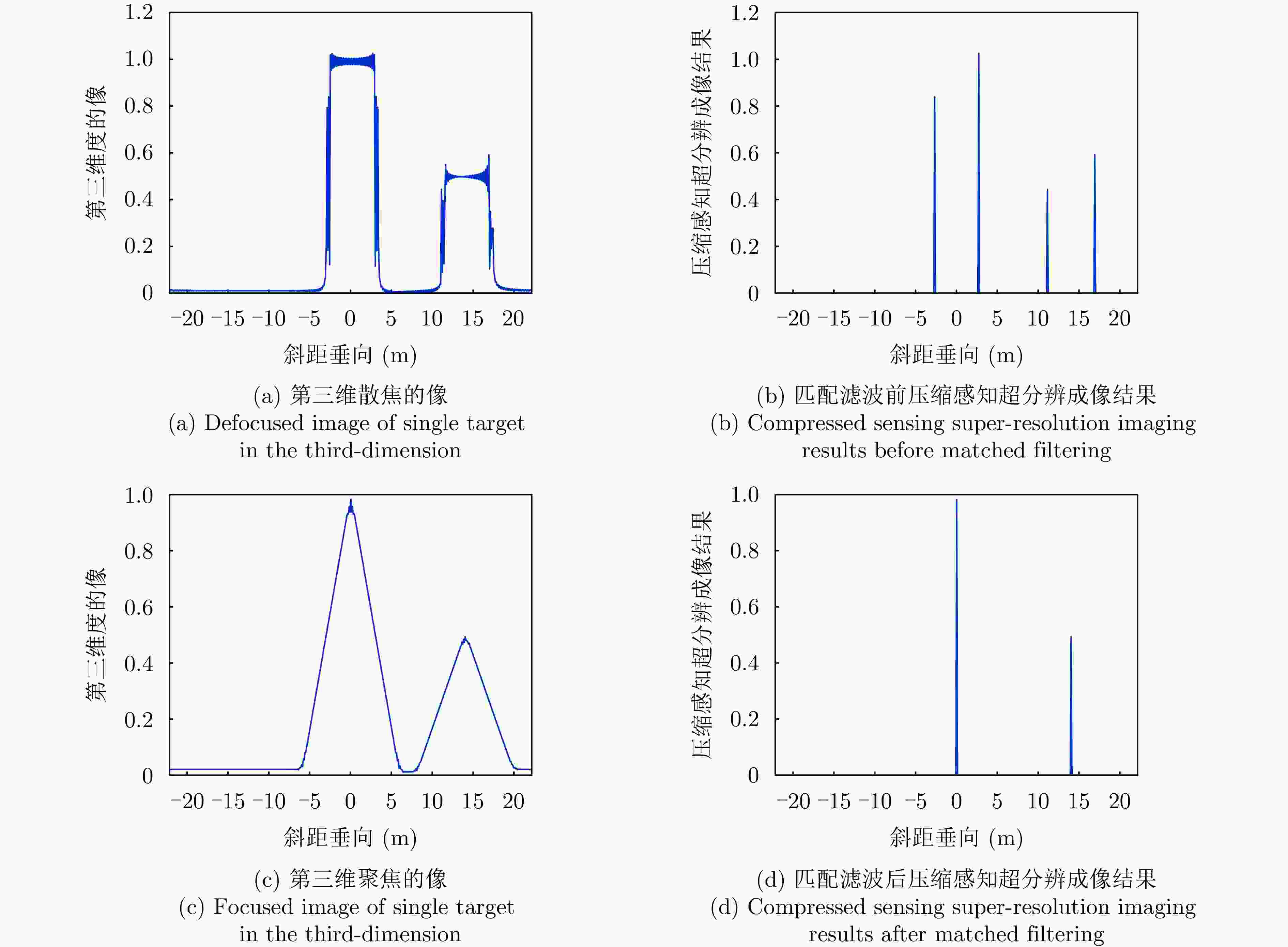
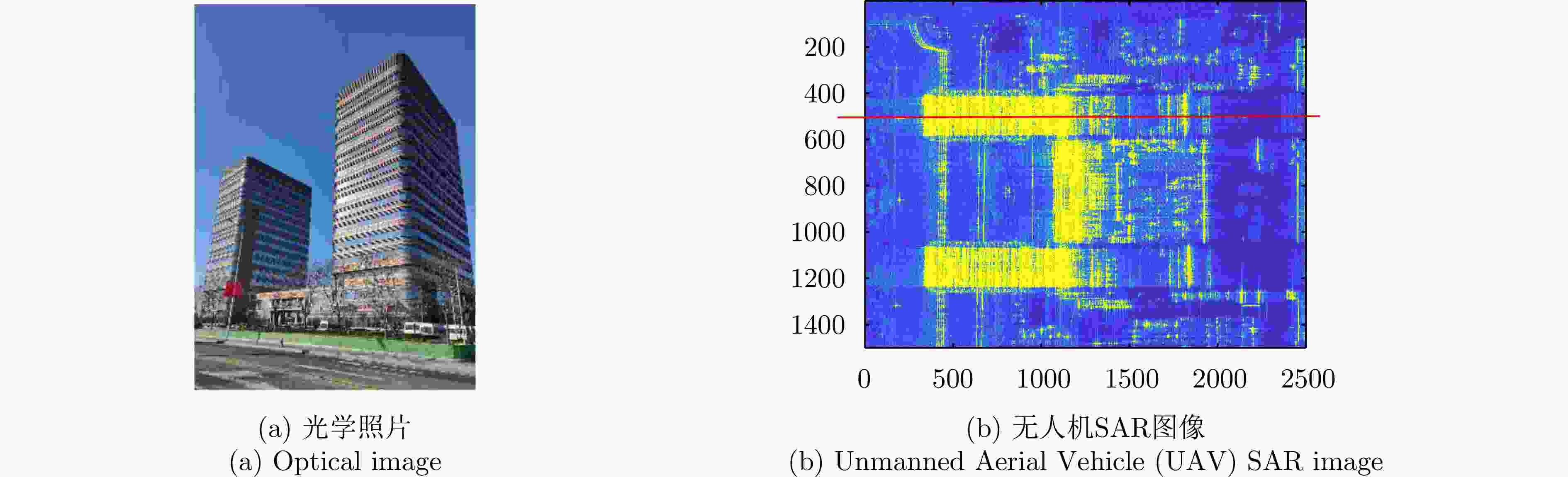
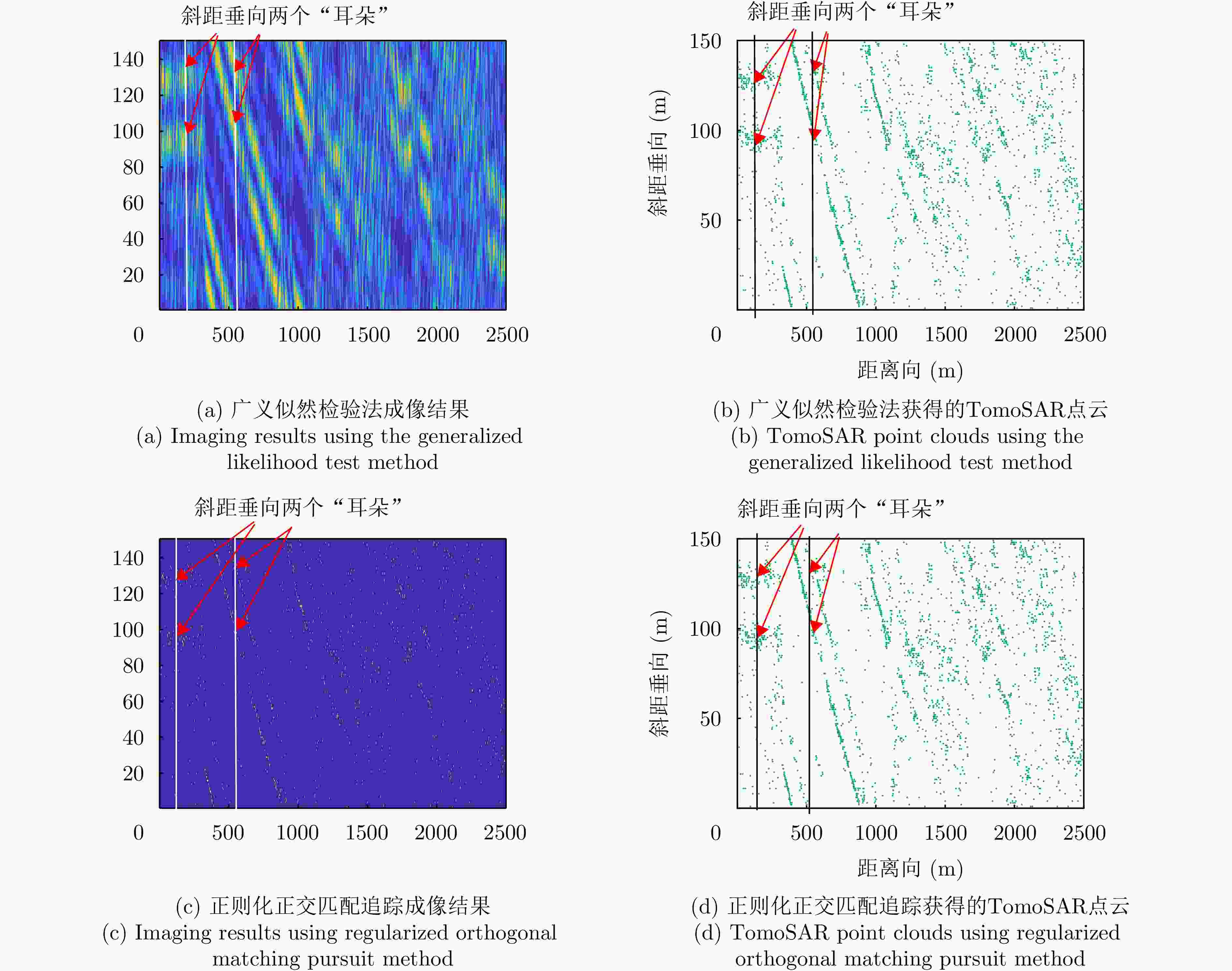
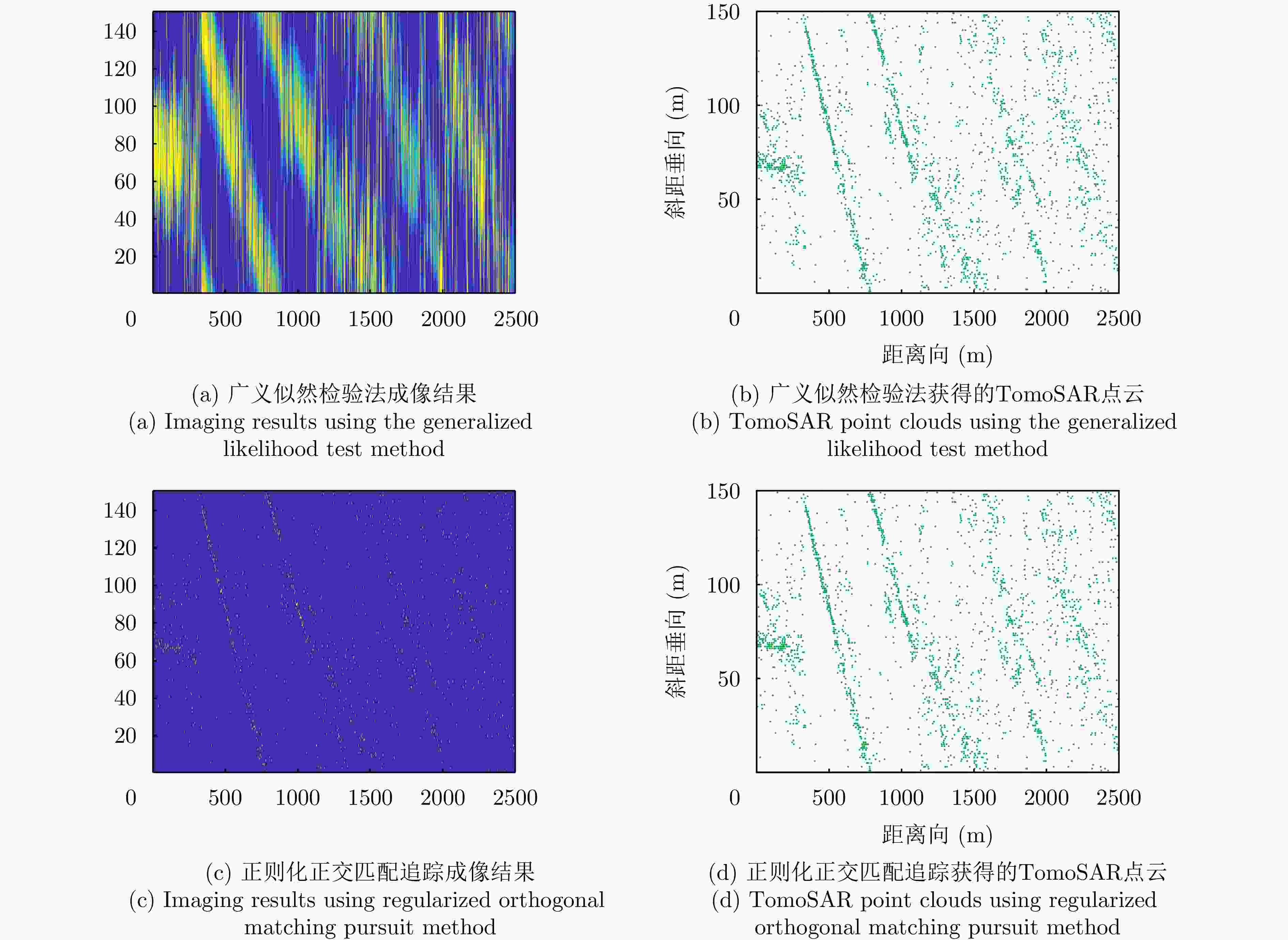
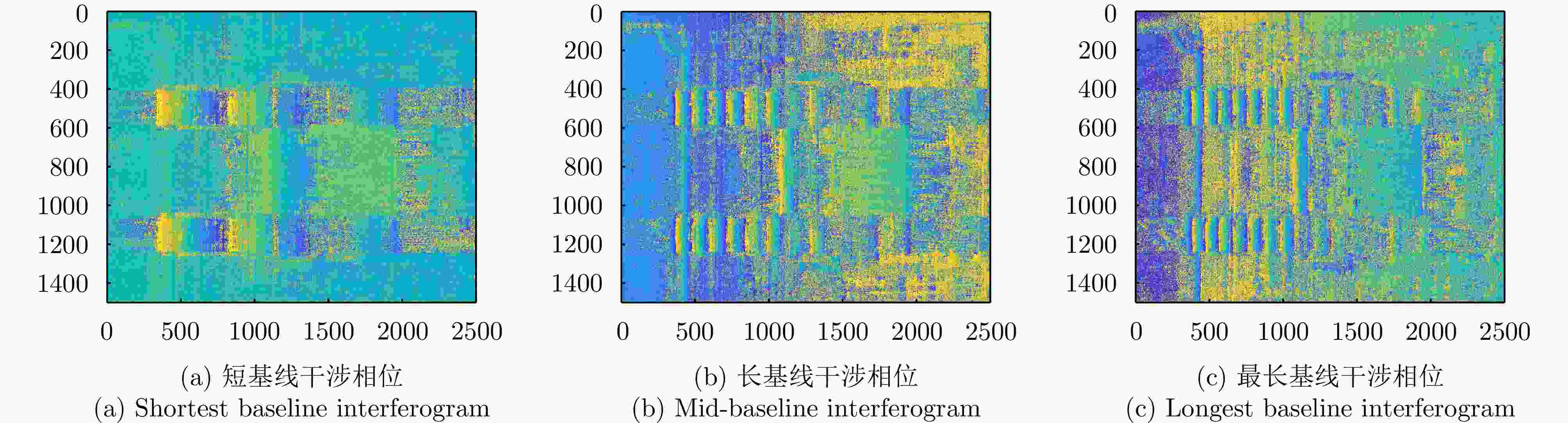
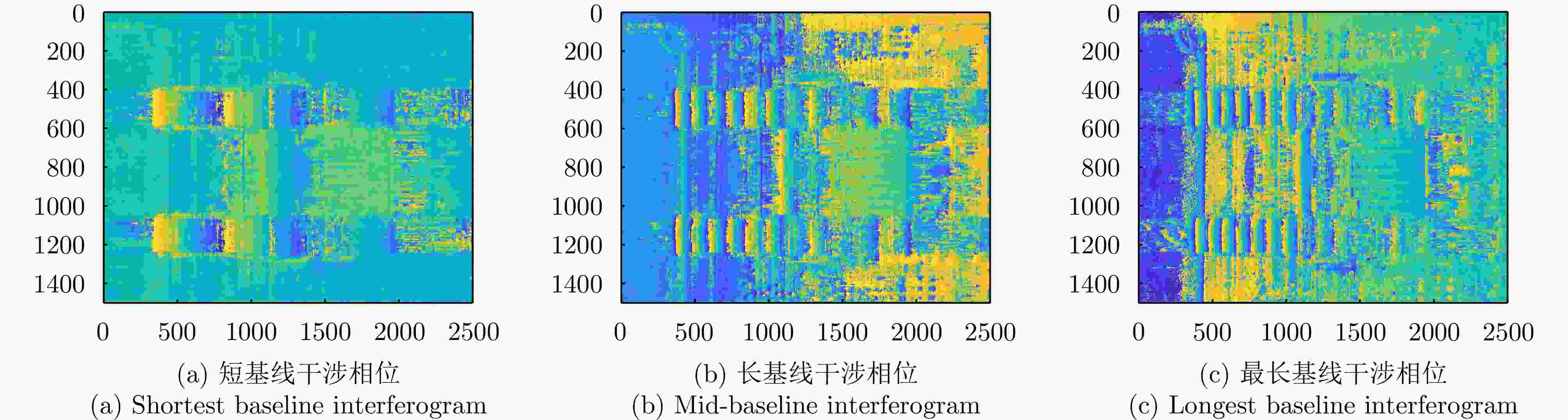
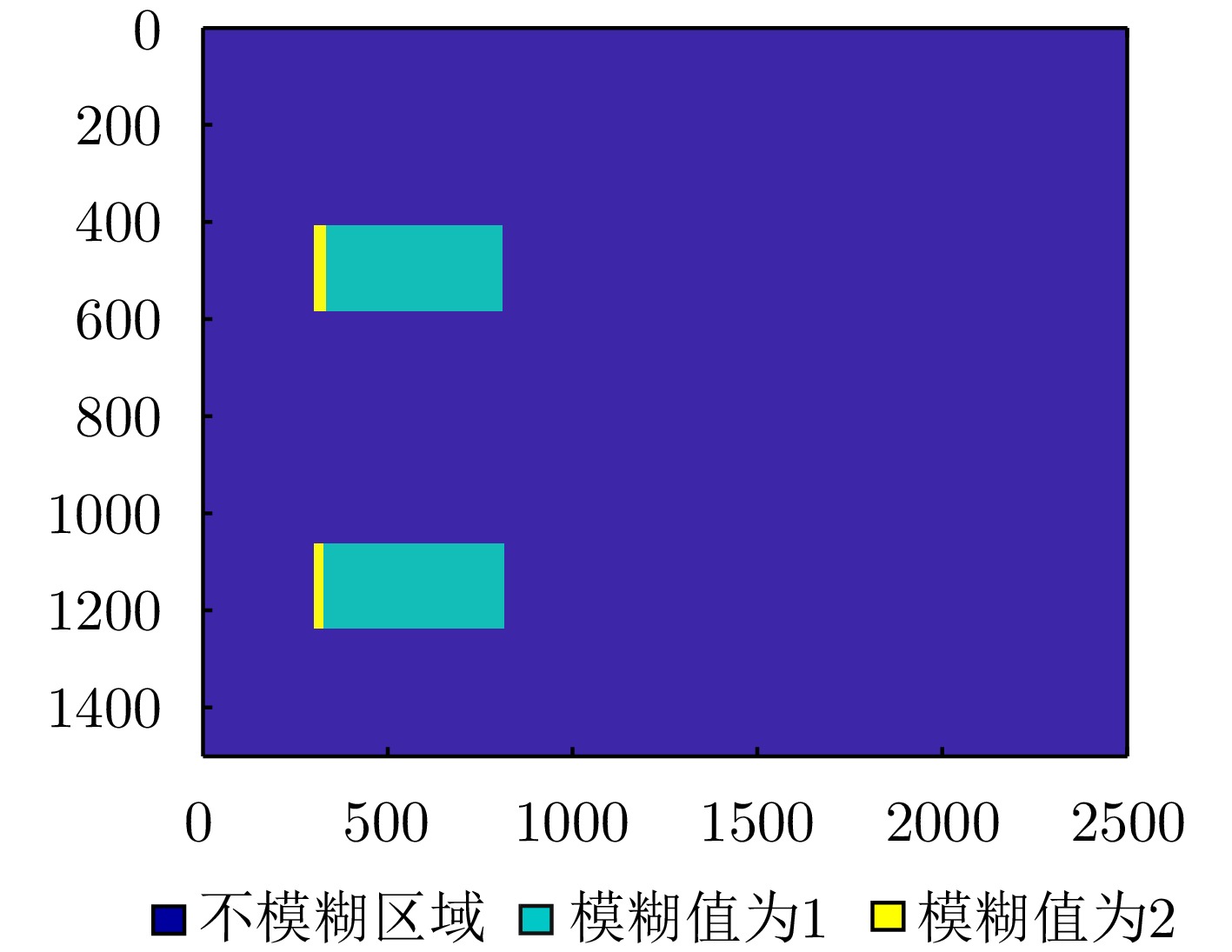
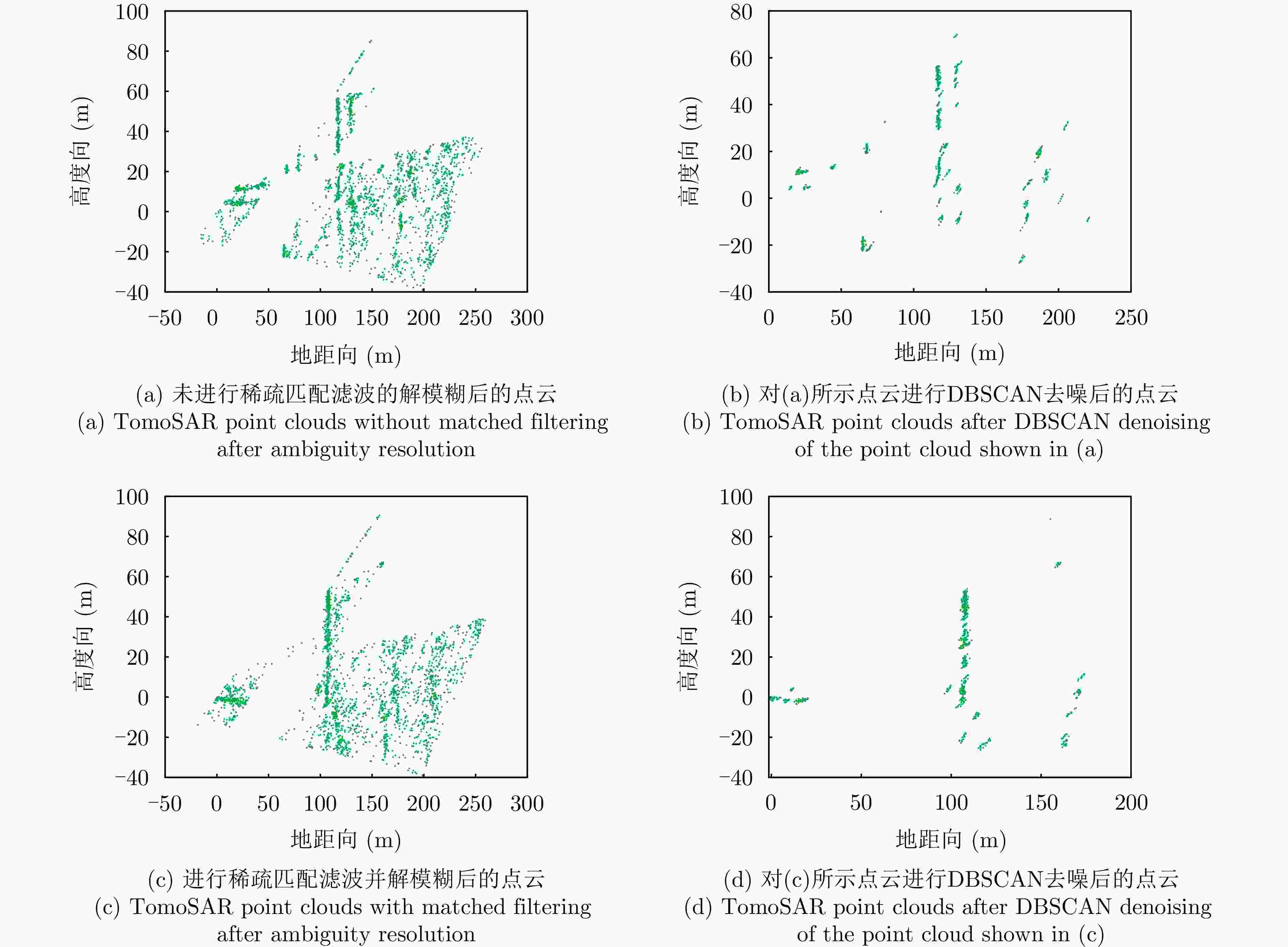
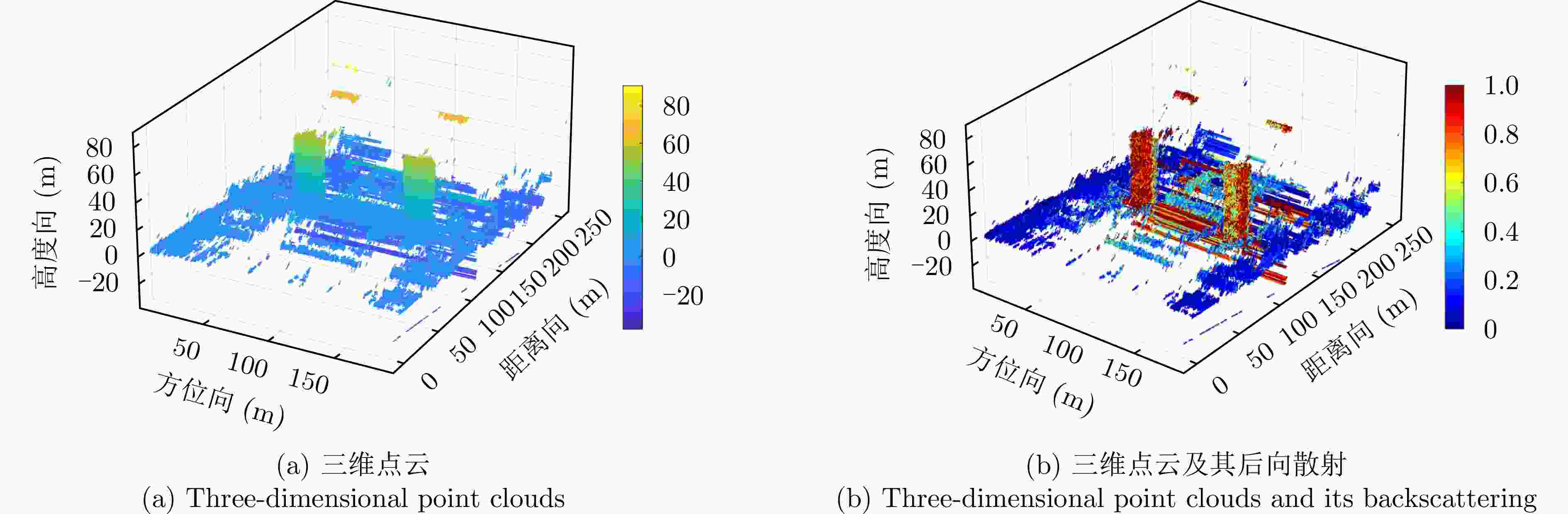
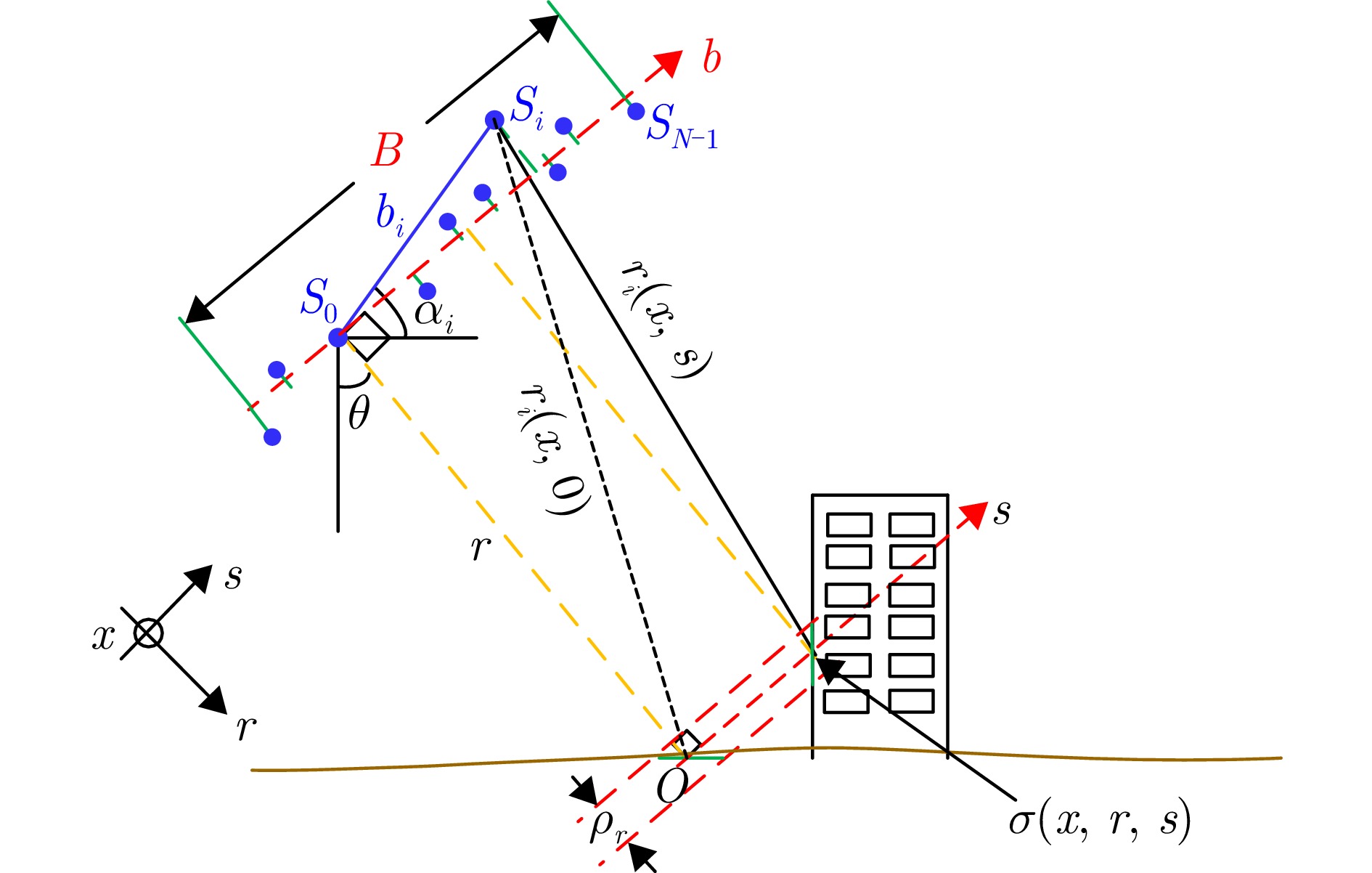
摘要: 层析SAR (TomoSAR)成像技术已经成为获取三维SAR点云的关键技术。然而,如果忽略斜距垂向的二次相位,可能会导致目标在高程方向的散焦问题,这是由于层析SAR成像中第三维也可能存在菲涅耳衍射所导致的。该文利用光学成像中的衍射原理解释了SAR成像中的衍射问题同样在第三维存在,并提出采用稀疏匹配滤波方法对第三维进行聚焦。第三维稀疏匹配滤波的关键在于构建稀疏相位补偿因子,进而构建稀疏匹配滤波器。首先根据TomoSAR影像的空间几何基线,构建第三维归一化的稀疏频率;然后,结合波长、距离、孔径等参数,根据菲涅耳积分特性构建频域稀疏匹配滤波器;最后,使用频域稀疏滤波器对稀疏采样的SAR图像进行相位补偿,再利用经典的稀疏成像算法(如压缩感知、似然比检测方法等)进行高程即第三维目标检测。该文采用中国科学院空天信息创新研究院的机载SAR数据,运用该文构建的频域稀疏匹配滤波器对其进行实验,实验结果验证了该文所提的方法能够解决层析SAR在菲涅耳衍射情况下导致的散焦问题,从而改善散焦引起的目标位置和后向散射信息不准确的问题。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar Tomography (TomoSAR) has emerged as the primary technique for generating 3D SAR point clouds. In practice, ignoring the quadratic phase distribution in the elevation dimension causes defocusing artifacts due to inherent Fresnel diffraction in tomographic SAR processing. By comparing with optical diffraction theory, this paper identifies similar diffraction effects in the third dimension of SAR images and introduces a sparse matched filtering technique for tomographic focusing. Our method is based on deriving a sparse phase compensation factor to construct the matched filter. The proposed processing chain includes three key steps. First, a normalized sparse frequency profile in the tomographic dimension is constructed using the spatial geometric baseline of TomoSAR acquisitions. Next, we derive a frequency-domain sparse matched filter based on Fresnel integral properties incorporating system parameters such as wavelength, range, and aperture size. Finally, phase compensation is applied through the designed sparse filter, enabling elevation target detection using established sparse imaging techniques, including compressed sensing and likelihood ratio detection. This study employs airborne SAR data acquired by the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, to validate the proposed frequency-domain sparse matched filter. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively reduces tomographic defocusing artifacts caused by Fresnel diffraction, substantially improving the accuracy of both target localization and backscattering coefficient estimation.
-
表 1 两组TomoSAR数据参数
Table 1. Two sets of TomoSAR data parameters
参数 符号 机载数据(m) 星载数据(m) 最小基线间隔 ${B_{\min }}$ 0.1071 20 最大基线长度 ${B_{\max }}$ 0.442 400 波长 $\lambda $ 0.0197 0.031 斜距 r 482.0413 603638.971 -
[1] BILJECKI F, STOTER J, LEDOUX H, et al. Applications of 3D city models: State of the art review[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2015, 4(4): 2842–2889. doi: 10.3390/ijgi4042842. [2] ELMQVIST T, ANDERSSON E, FRANTZESKAKI N, et al. Sustainability and resilience for transformation in the urban century[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2019, 2(4): 267–273. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0250-1. [3] WU Shengbiao, CHEN Bin, AN Jiafu, et al. The interplay of cloud cover and 3D urban structures reduces human access to sunlight[J]. Nature Cities, 2024, 1(10): 686–694. doi: 10.1038/s44284-024-00120-x. [4] MO Lidong, ZOHNER C M, REICH P B, et al. Integrated global assessment of the natural forest carbon potential[J]. Nature, 2023, 624(7990): 92–101. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06723-z. [5] BACCINI A, WALKER W, CARVALHO L, et al. Tropical forests are a net carbon source based on aboveground measurements of gain and loss[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6360): 230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.aam5962. [6] HUGONNET R, MCNABB R, BERTHIER E, et al. Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century[J]. Nature, 2021, 592(7856): 726–731. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03436-z. [7] ROUNCE D R, HOCK R, MAUSSION F, et al. Global glacier change in the 21st century: Every increase in temperature matters[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6627): 78–83. doi: 10.1126/science.abo1324. [8] PULLIAINEN J, LUOJUS K, DERKSEN C, et al. Patterns and trends of Northern Hemisphere snow mass from 1980 to 2018[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7808): 294–298. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2258-0. [9] PASQUALI P, PRATI C, ROCCA F, et al. A 3-D SAR experiment with EMSL data[C]. 1995 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’95. Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Firenze, Italy, 1995: 784–786. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1995.520585. [10] HOMER J, LONGSTAFF I D, and CALLAGHAN G. High resolution 3-D SAR via multi-baseline interferometry[C]. IGARSS’96. 1996 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, NE, USA, 1996: 796–798. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1996.516478. [11] FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934. [12] 李春升, 黄岩, 王璇, 等. 基于Chirp Scaling算法的星载SAR成像处理实现方法[J]. 电子学报, 1996, 24(6): 20–24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1996.06.005.LI Chunsheng, HUANG Yan, WANG Xuan, et al. A spaceborne SAR imaging processing algorithm using chip scaling[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1996, 24(6): 20–24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1996.06.005. [13] 黄岩, 李春升, 冯世章. 机载前斜视合成孔径雷达成像处理的精确Chirp Scaling算法[J]. 现代雷达, 1996, 18(5): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1996.05.001.HUANG Yan, LI Chunsheng, and FENG Shizhang. A precision Chirp Scaling algorithm for airborne SSAR imaging processing[J]. Modern Radar, 1996, 18(5): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1996.05.001. [14] 黄岩, 李春升, 陈杰, 等. 高分辨星载SAR改进Chirp Scaling成像算法[J]. 电子学报, 2000, 28(3): 35–38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.03.010.HUANG Yan, LI Chunsheng, CHEN Jie, et al. Refined Chirp Scaling algorithm for high resolution spaceborne SAR imaging[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2000, 28(3): 35–38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.03.010. [15] LAPRADE G L. An analytical and experimental study of stereo for radar[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering, 1963: 294–300. [16] GRAHAM L C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(6): 763–768. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9516. [17] 黄岩, 徐华平, 陈杰, 等. 干涉合成孔径雷达数据处理实现方法[J]. 电子科学学刊, 2000, 22(3): 373–378.HUANG Yan, XU Huaping, CHEN Jie, et al. An algorithm for interferometric sar data processing[J]. Journal of Electronics, 2000, 22(3): 373–378. [18] YAN Qiancheng, JIAO Zekun, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Comparison between different TomoSAR imaging models for airborne platform flying at low altitude[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(21): 5452. doi: 10.3390/rs14215452. [19] DONG Jie, ZHANG Lu, TANG Minggao, et al. Mapping landslide surface displacements with time series SAR interferometry by combining persistent and distributed scatterers: A case study of Jiaju landslide in Danba, China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 205: 180–198. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.11.022. [20] WANG Chao, TANG Yixian, ZHANG Hong, et al. First mapping of China surface movement using supercomputing interferometric SAR technique[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(16): 1608–1610. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.04.026. [21] SHI Xuguo, LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Teng, et al. Expressway deformation mapping using high-resolution TerraSAR-X images[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 5(2): 194–203. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.891774. [22] MUNSON D C, O’BRIEN J D, and JENKINS W K. A tomographic formulation of spotlight-mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1983, 71(8): 917–925. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1983.12698. [23] KNAELL K K and CARDILLO G P. Radar tomography for the generation of three-dimensional images[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1995, 142(2): 54–60. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19951791. [24] 韩冬, 周良将, 焦泽坤, 等. 基于改进三维后向投影的多圈圆迹SAR相干三维成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 131–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190945.HAN Dong, ZHOU Liangjiang, JIAO Zekun, et al. A coherent 3-D imaging method for multi-circular SAR based on an improved 3-D back projection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 131–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190945. [25] 张琳. 基于RD反投影的圆周SAR典型目标三维点云重建方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北方工业大学, 2023: 8–41.ZHANG Lin. Research on 3D point cloud reconstruction method of circular SAR typical target based on RD back projection[D]. [Master dissertation], North China University of Technology, 2023: 8–41. [26] ERTIN E, AUSTIN C D, SHARMA S, et al. GOTCHA experience report: Three-dimensional SAR imaging with complete circular apertures[C]. SPIE 6568, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIV, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2007: 656802. doi: 10.1117/12.723245. [27] 孙兵, 周荫清, 陈杰, 等. 广域观测圆轨迹环扫 SAR 成像模式研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(12): 2805–2808.SUN Bing, ZHOU Yinqing, CHEN Jie, et al. Operation mode of circular trace scanning SAR for wide observation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(12): 2805–2808. [28] GINI F, LOMBARDINI F, and MONTANARI M. Layover solution in multibaseline SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(4): 1344–1356. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1145755. [29] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873. [30] MEGLIO F, PANARIELLO G, and SCHIRINZI G. Three dimensional SAR image focusing from non-uniform samples[C]. 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007: 528–531. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2007.4422847. [31] LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M and FORTUNY-GUASCH J. 3-D radar imaging using range migration techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(5): 728–737. doi: 10.1109/8.855491. [32] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567. [33] MARTÍN-DEL-CAMPO-BECERRA G D, REIGBER A, NANNINI M, et al. Single-look SAR tomography of urban areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2555. doi: 10.3390/rs12162555. [34] BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, MA, USA, 2007: 128–133. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2007.374203. [35] BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. SAR tomography from sparse samples[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: IV-865–IV-868. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417514. [36] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization-the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117. [37] 刘慧, 郭馨宇, 郭子夜, 等. 基于交替方向乘子法的Capon层析SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2023, 21(3): 303–313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.03.009.LIU Hui, GUO Xinyu, GUO Ziye, et al. Capon tomographic SAR imaging method based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2023, 21(3): 303–313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.03.009. [38] ZHU Xiaoxiang. Spectral estimation for synthetic aperture radar tomography[D]. [Master dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2008: 11–14. [39] 张澄波. 综合孔径雷达 原理、系统分析与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 20–80.ZHANG Chengbo. Principles, System Analysis, and Applications of Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 20–80. [40] GOODMAN J W. Introduction to Fourier Optics[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005: 50–100. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: