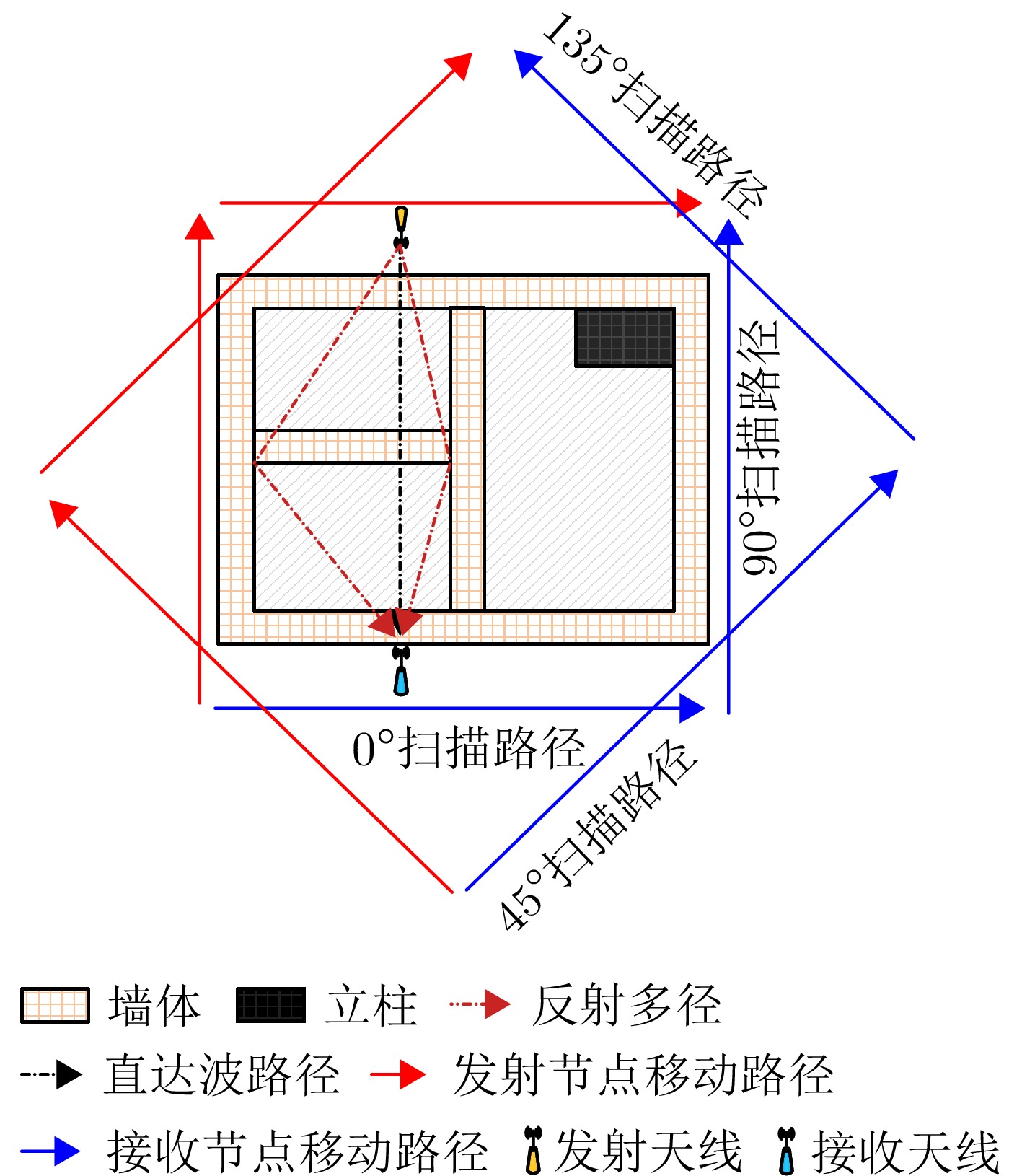
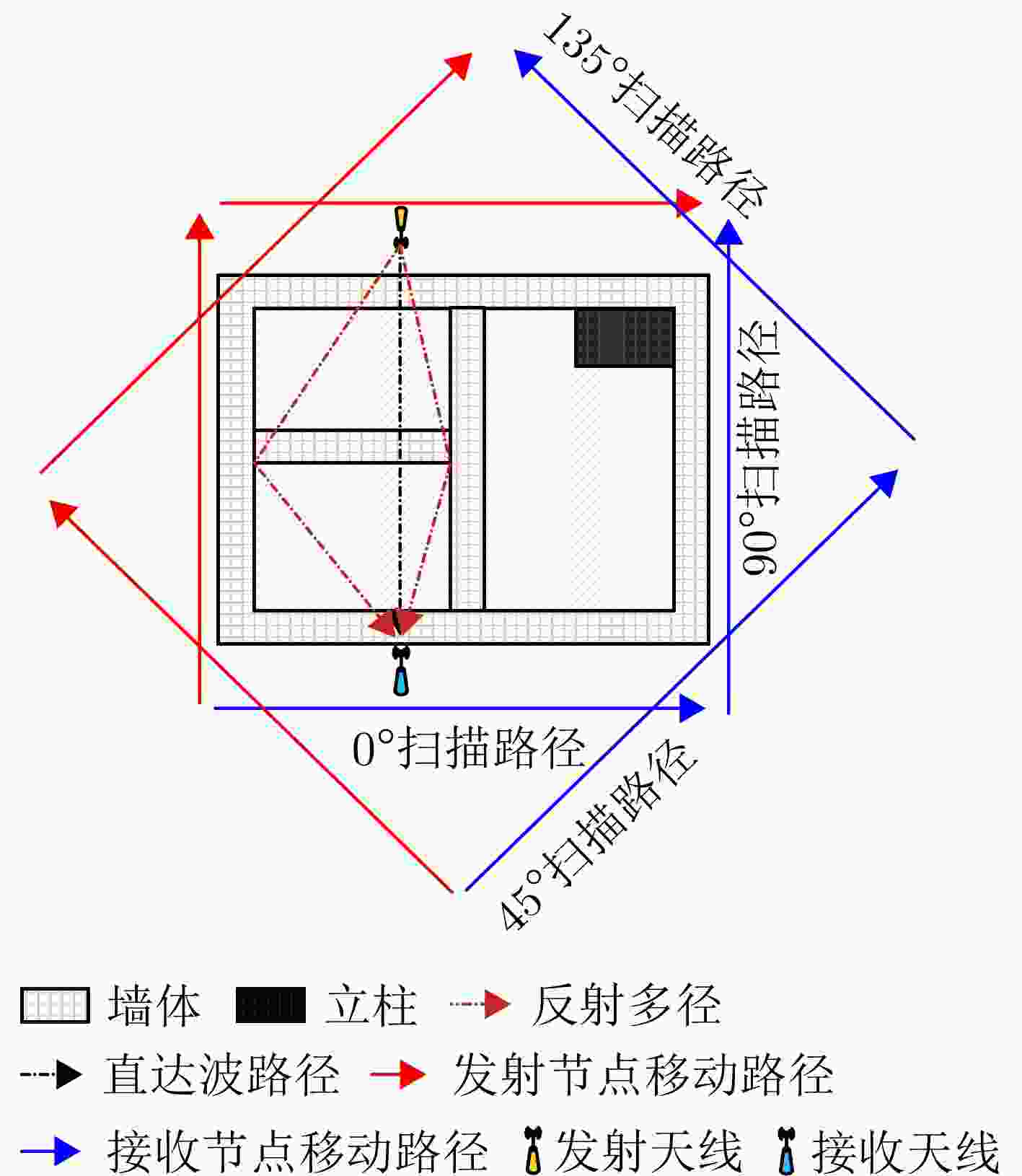
Building Layout Tomography Method Based on Joint Multidomain Direct Wave Estimation
-
摘要: 在进入陌生建筑物之前掌握其内部结构信息,能够为反恐作战、灾害救援、监视管控等多种应用提供支持,具有重要的现实意义和研究价值。为实现建筑布局结构信息获取,该文开展了基于多域联合直达波估计的建筑布局层析成像方法研究。首先,建立了线性近似模型,实现了直达波信号传播时延与未知建筑布局图像之间的映射关系;在此模型基础上,分析了在层析成像模式下直达波信号与多径信号在快时间域、慢时间域与多普勒域中的分布特性,提出了一种基于多域联合的直达波估计算法,实现了多径干扰抑制与直达波信号精确估计;此外,提出了一种总变分约束的投影矩阵自适应修正代数重建算法,提升了有限数据下的建筑布局反演质量;最后,电磁仿真与实测实验结果证明了所提出的建筑布局层析成像方法的有效性,其重建结果的结构相似性指标分别可达到91.2%和81.7%,显著优于现有建筑布局层析成像方法。Abstract: Obtaining internal layout information before entering unfamiliar buildings is crucial for various applications, such as counter-terrorism operations, disaster relief, and surveillance, highlighting its great practical significance and research value. To enable the acquisition of the building layout information, this paper presents a building layout tomography method based on joint multidomain direct wave estimation. First, a linear approximation model is established to map the relationship between the propagation delay of direct wave signals and the layout of the unknown building. Using this model, the distribution characteristics of direct wave and multipath signals in the fast-time, slow-time, and Doppler domains are analyzed in the tomographic imaging mode. A joint multidomain direct wave estimation algorithm is then proposed to achieve the suppression of multipath interference and precise estimation of direct wave signals. Additionally, a projection matrix adaptive correction algebraic reconstruction algorithm with total variation constraints is proposed, which enhances building layout inversion quality under limited data scenarios. Finally, electromagnetic simulation and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed building layout tomography method, with structural similarity indices of 91.2% and 81.7% for the reconstructed results, significantly outperforming existing building layout tomography methods.
-
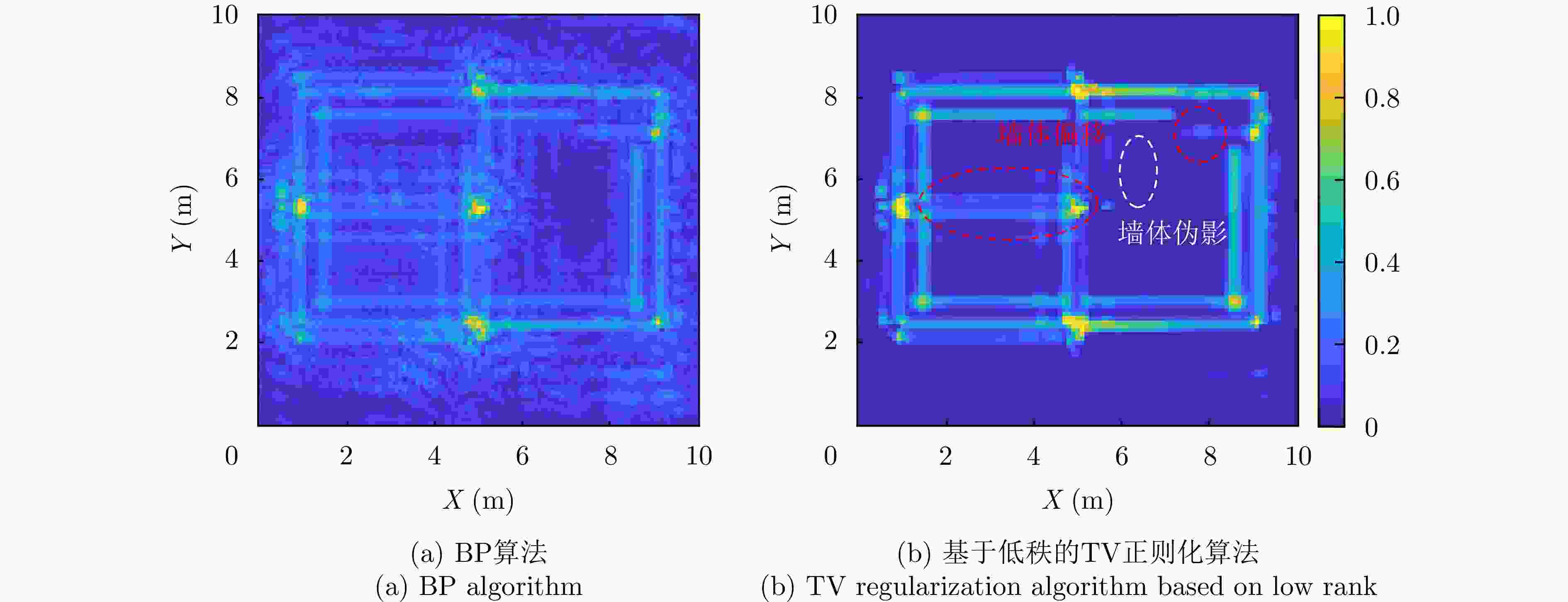
1 PMAM-ART-TV算法流程
1. PMAM-ART-TV algorithm flow
输入: P, A,初始化$ {\boldsymbol{O}}=0 $,外部停止标准${\varepsilon _o}$,内部停止标准
${\varepsilon _i}$,外部迭代次数$t = 0$,外部最大迭代次数$ {T_o} $,内部最大迭代
次数${T_i}$输出: $ \tilde{{\boldsymbol{O}}}={\boldsymbol{O}}^{t} $ repeat 1、代数重建迭代: $k = 0$ 求解式(16)、式(17)更新$ \Delta C_{}^{k + 1} $ 求解式(18)更新$ {{O}}_n^{k + 1} $ $ k = k + 1 $ 直到$k = {T_i}$或者$ \Vert {{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{k+1}-{{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{k}\Vert \le {\varepsilon }_{i} $,输出$ {{{\boldsymbol{O}}}_{{\mathrm{ART}}}} $ 2、总变分约束迭代: $k = 0$, $ {{\boldsymbol{O}}} = {{{\boldsymbol{O}}}_{{\mathrm{ART}}}} $, $ {{{\boldsymbol{u}}}^k} = 0 $ 求解式(23)更新$ {{{\boldsymbol{u}}}^{k + 1}} $ 求解式(24)更新${{\boldsymbol{b}}}_x^{k + 1}$, ${{\boldsymbol{b}}}_y^{k + 1}$ 求解式(25)更新$ {{\boldsymbol{d}}}_x^{k + 1} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{d}}}_y^{k + 1} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{O}}} = {{{\boldsymbol{u}}}^{k + 1}} $, $ k = k + 1 $ 直到$k = {T_i}$或者$ \Vert {{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{k+1}-{{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{k}\Vert \le {\varepsilon }_{i} $,输出O 3、更新投影矩阵 求解式(28)更新A, $ {{{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{t + 1}} $, $t = t + 1$ until 直到$t = {T_o}$或者$ \Vert {{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{t+1}-{{\boldsymbol{O}}}^{t}\Vert \le {\varepsilon }_{o} $ 表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
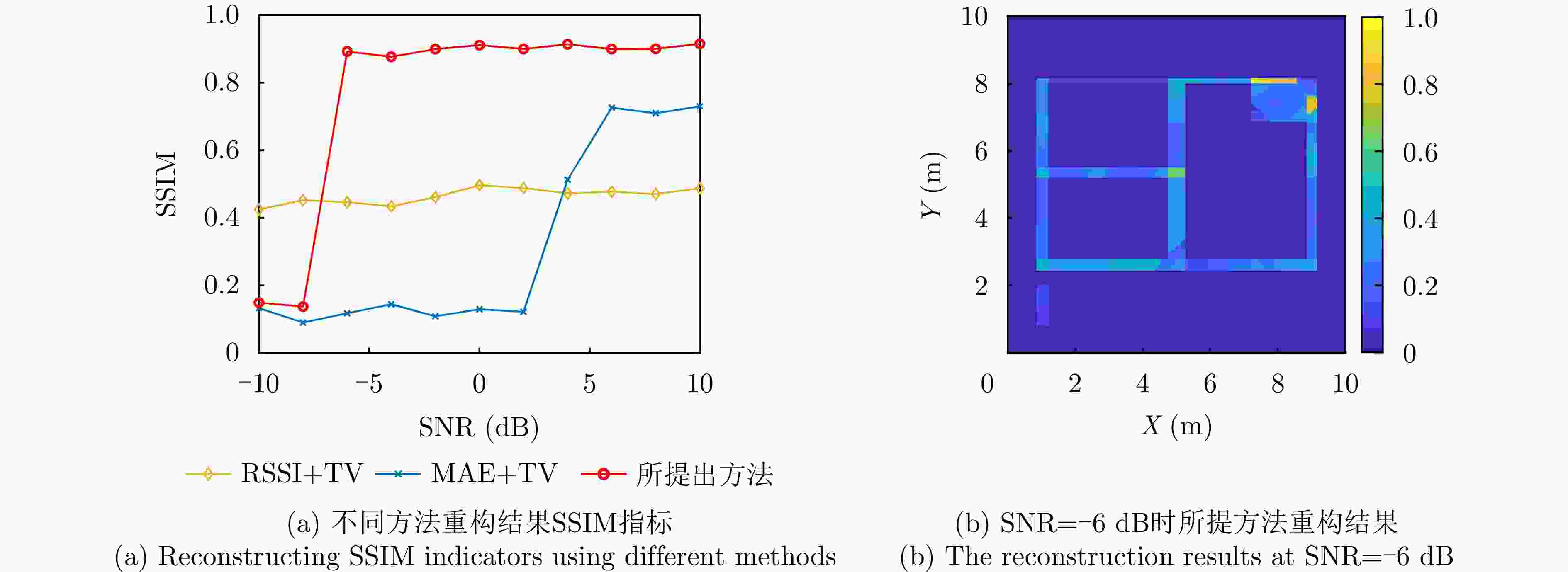
类型 仿真参数 数值 信号参数 发射信号 步进频信号 中心频率 1.5 GHz 带宽 600 MHz 单频点持续时间 100 μs 扫描参数 采样路径长度 10 m 采样路径数目 4组 采样间隔 0.05 m 场景参数 场景尺寸 2 m×2 m 墙体厚度 0.20 m 相对介电常数 4 电导率 0.01 S/m 表 2 观测数据误差对比
Table 2. Comparison of observation data errors
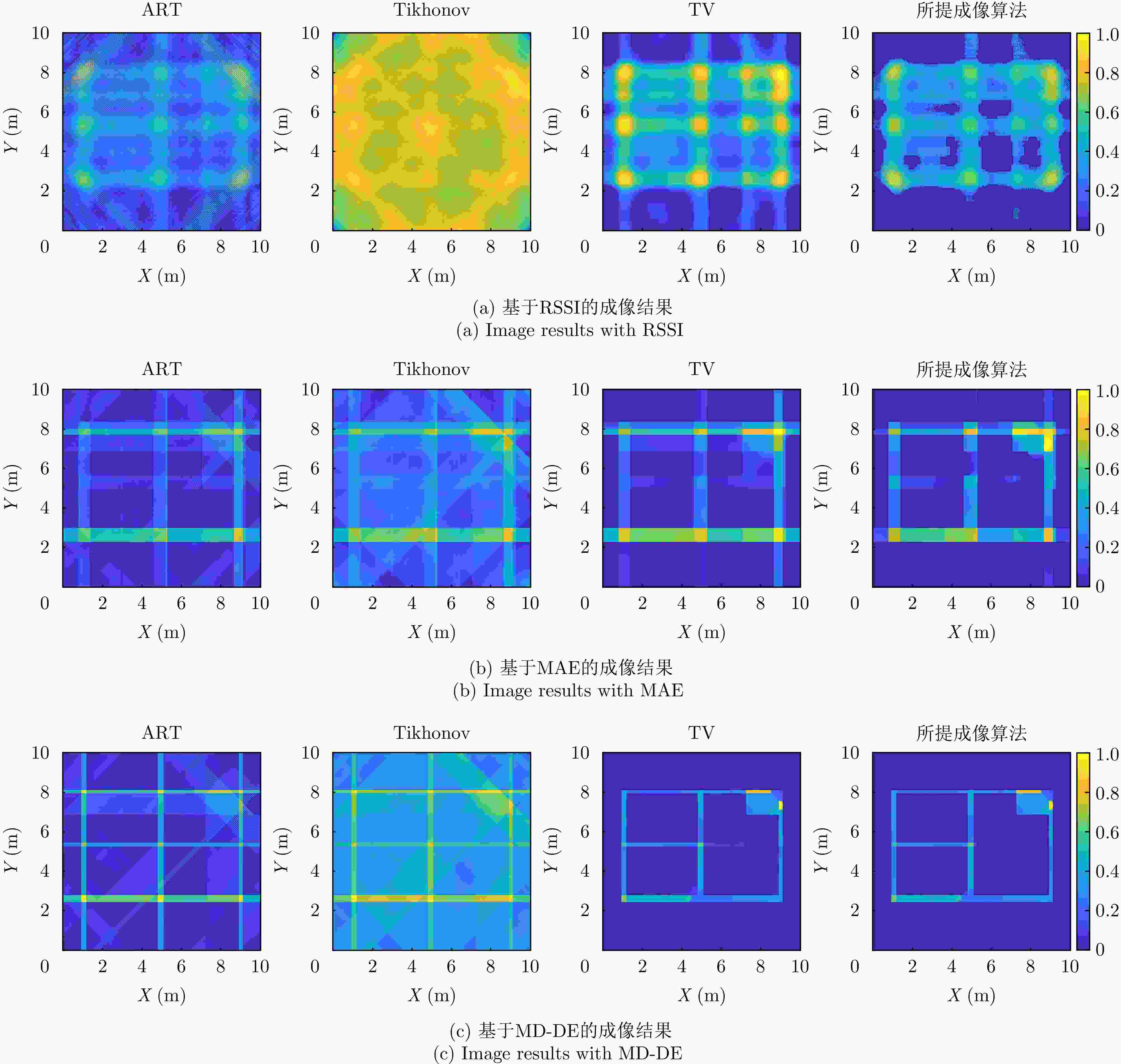
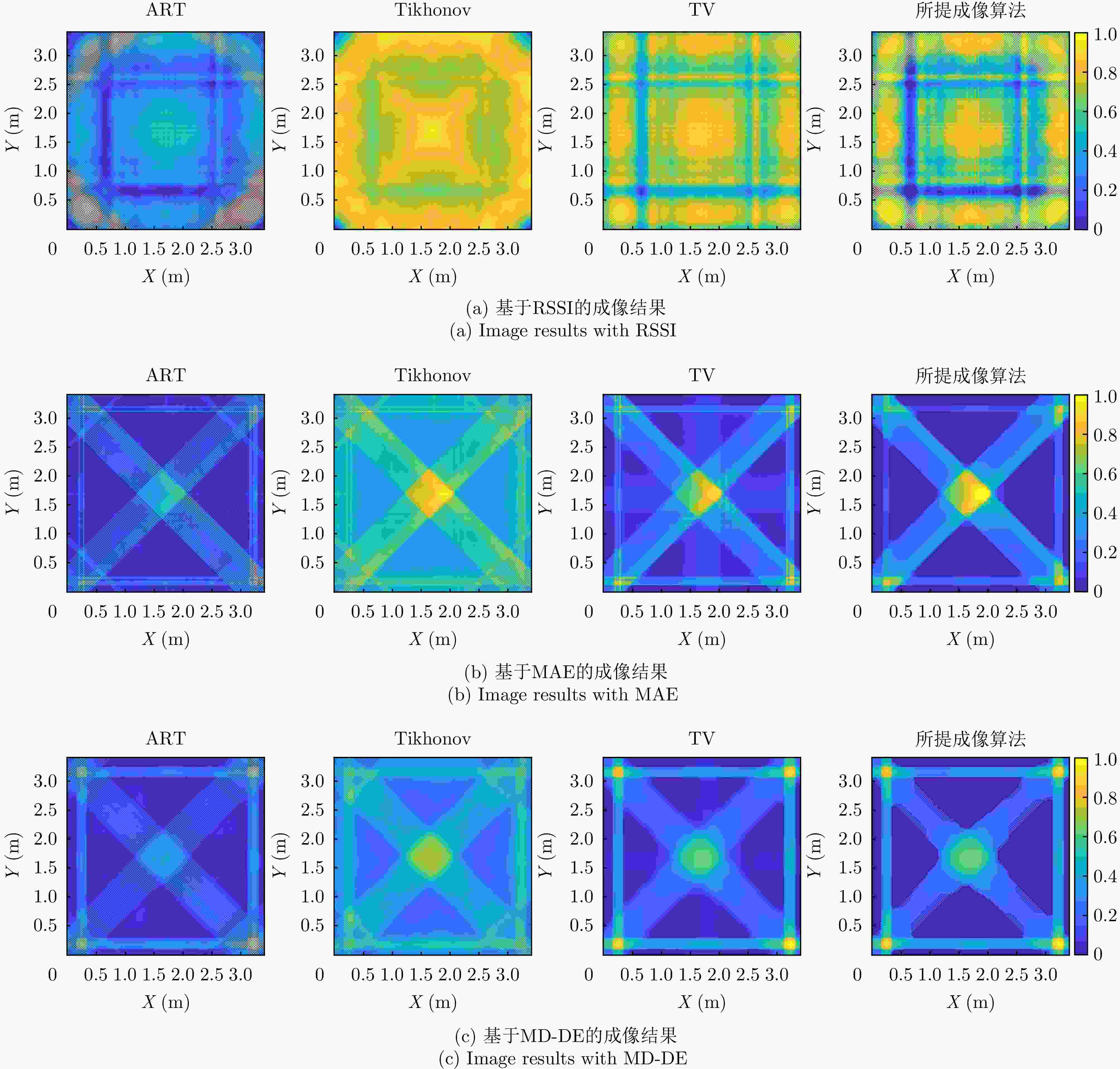
表 3 仿真成像结果SSIM指标对比(%)
Table 3. Comparison of SSIM indicators in simulation imaging results (%)
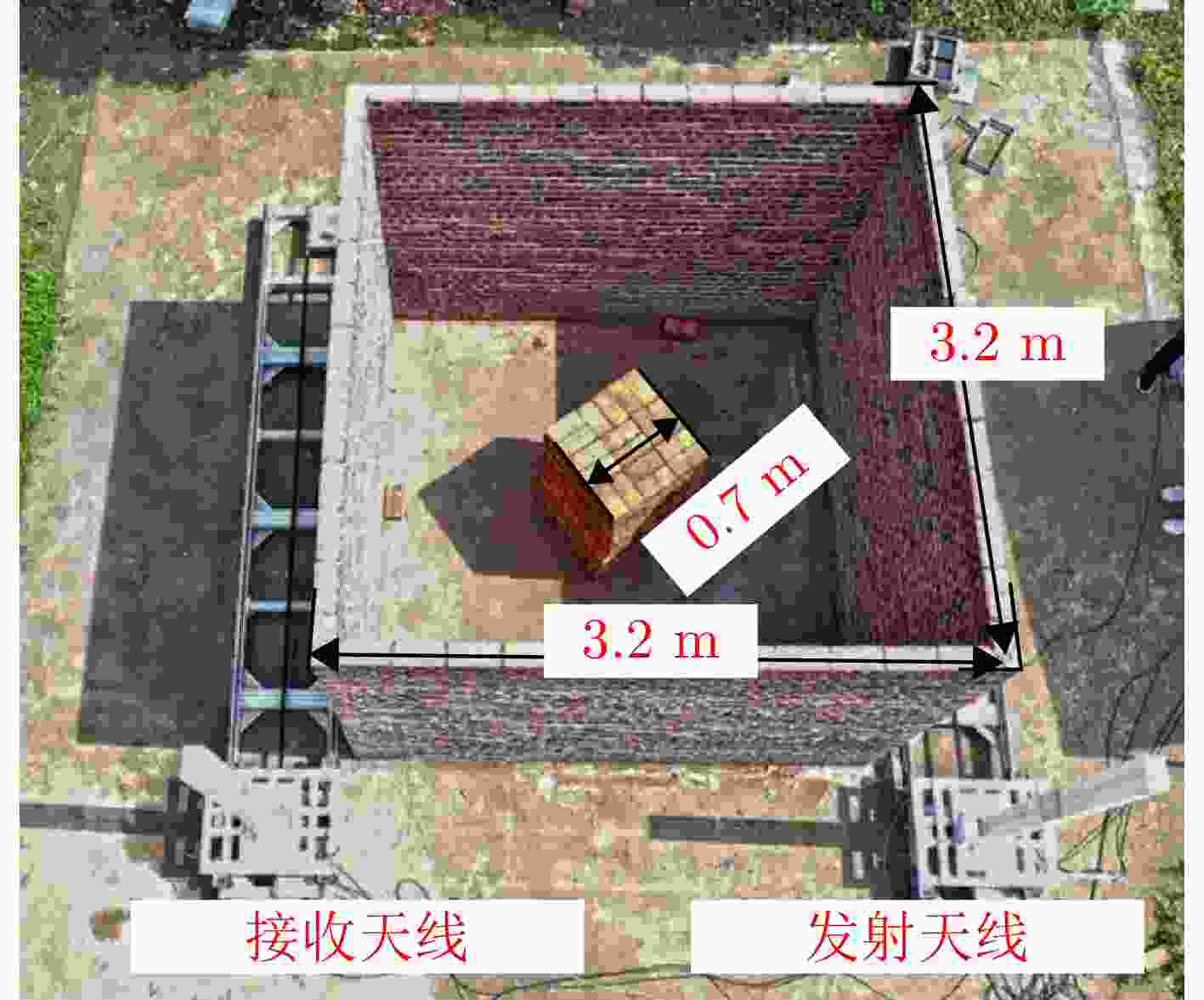
方法 ART Tikhonov TV PMAM-ART-TV RSSI 30.8 28.7 48.9 68.5 MAE 34.1 51.4 72.8 86.2 MD-DE 40.6 58.9 88.9 91.2 表 4 雷达系统参数
Table 4. Radar system parameters
参数名称 数值 中心频率 1.9 GHz 带宽 600 MHz 频率步进 2 MHz 频点持续时间 100 μs 表 5 实测成像结果SSIM指标对比(%)
Table 5. Comparison of SSIM indicators in actual imaging results (%)
方法 ART Tikhonov TV PMAM-ART-TV RSSI 31.4 30.6 31.2 31.7 MAE 43.9 49.8 73.6 75.5 MD-DE 46.3 56.6 78.6 81.7 -
[1] 金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119.JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. [2] AHMAD F and AMIN M G. Noncoherent approach to through-the-wall radar localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(4): 1405–1419. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.314581. [3] 崔国龙. 超宽带穿墙雷达合成孔径成像算法研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008: 6–16.CUI Guolong. Research and implementation of synthetic aperture imaging algorithm for ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008: 6–16. [4] NKWARI P K M, SINHA S, and FERREIRA H C. Through-the-wall radar imaging: A review[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2018, 35(6): 631–639. doi: 10.1080/02564602.2017.1364146. [5] GUO Shisheng, CUI Guolong, KONG Lingjiang, et al. An imaging dictionary based multipath suppression algorithm for through-wall radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 269–283. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756298. [6] CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, LUO Haolan, et al. Non-line-of-sight multi-target localization algorithm for driver-assistance radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5332–5337. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3227971. [7] CHEN Jiahui, LI Nian, GUO Shisheng, et al. Enhanced 3-D building layout tomographic imaging via tensor approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5105614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3391282. [8] LI Nian, CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, et al. Building layout tomographic imaging based on MIMO-UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5108713. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3435831. [9] NGUYEN L, RESSLER M, and SICHINA J. Sensing through the wall imaging using the Army Research Lab ultra-wideband synchronous impulse reconstruction (UWB SIRE) radar[C]. SPIE 6947, Radar Sensor Technology XII, Orlando, USA, 2008: 69470B. doi: 10.1117/12.776869. [10] LE C, DOGARU T, NGUYEN L, et al. Ultrawideband (UWB) radar imaging of building interior: Measurements and predictions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2016653. [11] 金添, 宋勇平. 超宽带雷达建筑物结构稀疏成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031.JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Sparse imaging of building layouts in ultra-wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031. [12] ZHANG Yang, CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, et al. Building layout tomographic reconstruction via commercial WiFi signals[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(20): 15500–15511. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3073912. [13] MOSTOFI Y. Cooperative wireless-based obstacle/object mapping and see-through capabilities in robotic networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(5): 817–829. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.32. [14] DEPATLA S, BUCKLAND L, and MOSTOFI Y. X-ray vision with only WiFi power measurements using Rytov wave models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(4): 1376–1387. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2397446. [15] DEPATLA S, KARANAM C R, and MOSTOFI Y. Robotic through-wall imaging: Radio-frequency imaging possibilities with unmanned vehicles[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2017, 59(5): 47–60. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2017.2731302. [16] KARANAM C R and MOSTOFI Y. 3D through-wall imaging with unmanned aerial vehicles using WiFi[C]. The 16th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Pittsburgh, USA, 2017: 131–142. doi: 10.1145/3055031.3055084. [17] 张扬. 建筑布局结构透视微波层析成像理论与方法[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022: 20–82.ZHANG Yang. Theory and method of perspective microwave tomography of building layout structure[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 20–82. [18] GUO Qichang, LI Yanlei, LIANG Xingdong, et al. A novel CT-mode through-the-wall imaging method based on time delay estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(8): 1381–1385. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3000423. [19] CHEN Jiahui, ZHANG Yang, LI Huquan, et al. Ultrawideband tomographic imaging in multipath-rich environment[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8016305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.30961830. [20] YASWANTH K, BHATTACHARYA S, and KHANKHOJE U K. Algebraic reconstruction techniques for inverse imaging[C]. 2016 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Cairns, Australia, 2016: 756–759. doi: 10.1109/ICEAA.2016.7731509. [21] ANDREU F, CASELLES V, DÍAZ J I, et al. Some qualitative properties for the total variation flow[J]. Journal of Functional Analysis, 2002, 188(2): 516–547. doi: 10.1006/jfan.2001.3829. [22] LI Nian, ZHAN Yang, CHEN Jiahui, et al. Building layout tomographic imaging method with sparse scan angles[C]. The 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2022: 2128–2132. doi: 10.1109/ICCC56324.2022.10066042. [23] GOLDSTEIN T and OSHER S. The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 323–343. doi: 10.1137/080725891. [24] OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076. [25] WARREN C, GIANNOPOULOS A, and GIANNAKIS I. GprMax: Open source software to simulate electromagnetic wave propagation for ground penetrating radar[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2016, 209: 163–170. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2016.08.020. [26] HAMILTON B R, MA Xiaoli, BAXLEY R J, et al. Radio frequency tomography in mobile networks[C]. 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Ann Arbor, USA, 2012: 508–511. doi: 10.1109/SSP.2012.6319745. [27] CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, CUI Guolong, et al. Building layout reconstruction with transmissive and reflective signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3199270. [28] ZHAO Jifang, JIN Liangnian, and LIU Qinghua. Through-the-wall radar sparse imaging for building walls[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7403–7405. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0541. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: