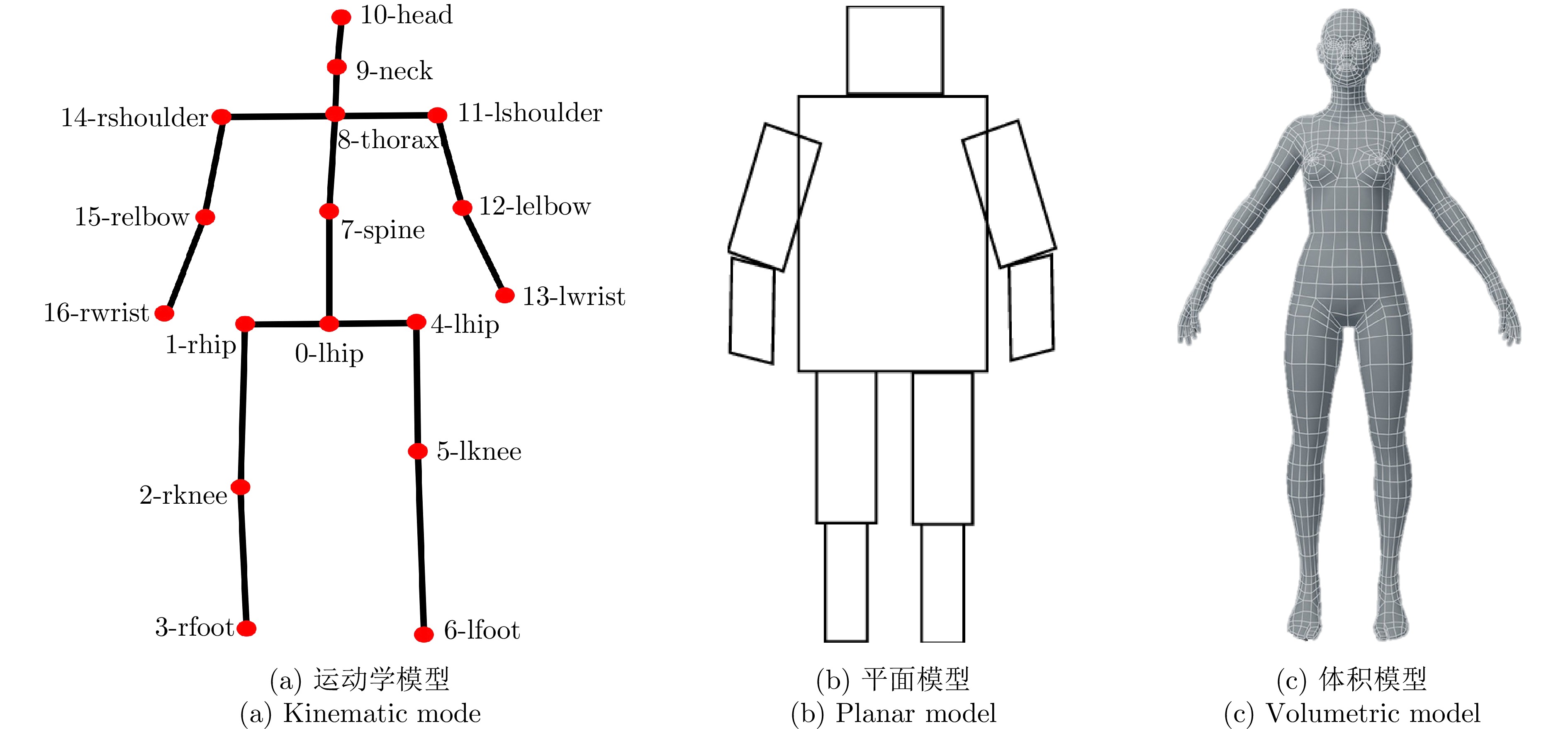
-
摘要: 人体姿态估计在人机交互、动作捕捉和虚拟现实等领域具有广泛的应用前景,一直是人体感知研究的重要方向。然而,基于光学图像的姿态估计方法往往受限于光照条件和隐私问题。因此,利用可在各种光照遮挡下工作,且具有隐私保护性的无线信号进行人体姿态估计获得了更多关注。根据无线信号的工作频率,现有技术可分为高频方法和低频方法,且不同的信号频率对应硬件系统、信号特性、噪声处理和深度学习算法设计等方面均有所不同。该文将以毫米波雷达、穿墙雷达和WiFi信号为代表,回顾其在人体姿态重建研究中的进展和代表性工作,分析各类信号模式的优势与局限,并对潜在研究难点以及未来发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: Human pose estimation holds tremendous potential in fields such as human-computer interaction, motion capture, and virtual reality, making it a focus in human perception research. However, optical image-based pose estimation methods are often limited by lighting conditions and privacy concerns. Therefore, the use of wireless signals that can operate under various lighting conditions and obstructions while ensuring privacy is gaining increasing attention for human pose estimation. Wireless signal-based pose estimation technologies can be categorized into high-frequency and low-frequency methods. These methods differ in their hardware systems, signal characteristics, noise processing, and deep learning algorithm design based on the signal frequency used. This paper highlights research advancements and notable works in human pose reconstruction using millimeter-wave radar, through-wall radar, and WiFi. It analyzes the advantages and limitations of each signal type and explores potential research challenges and future developments in the field.
-
Key words:
- Human pose estimation /
- Wireless sensing /
- Deep learning /
- Millimeter-wave radar /
- Through-Wall Radar (TWR) /
- WiFi
-
表 1 基于无线信号的人体姿态估计研究现状总结
Table 1. Summary of research status on pose estimation based on wireless signals
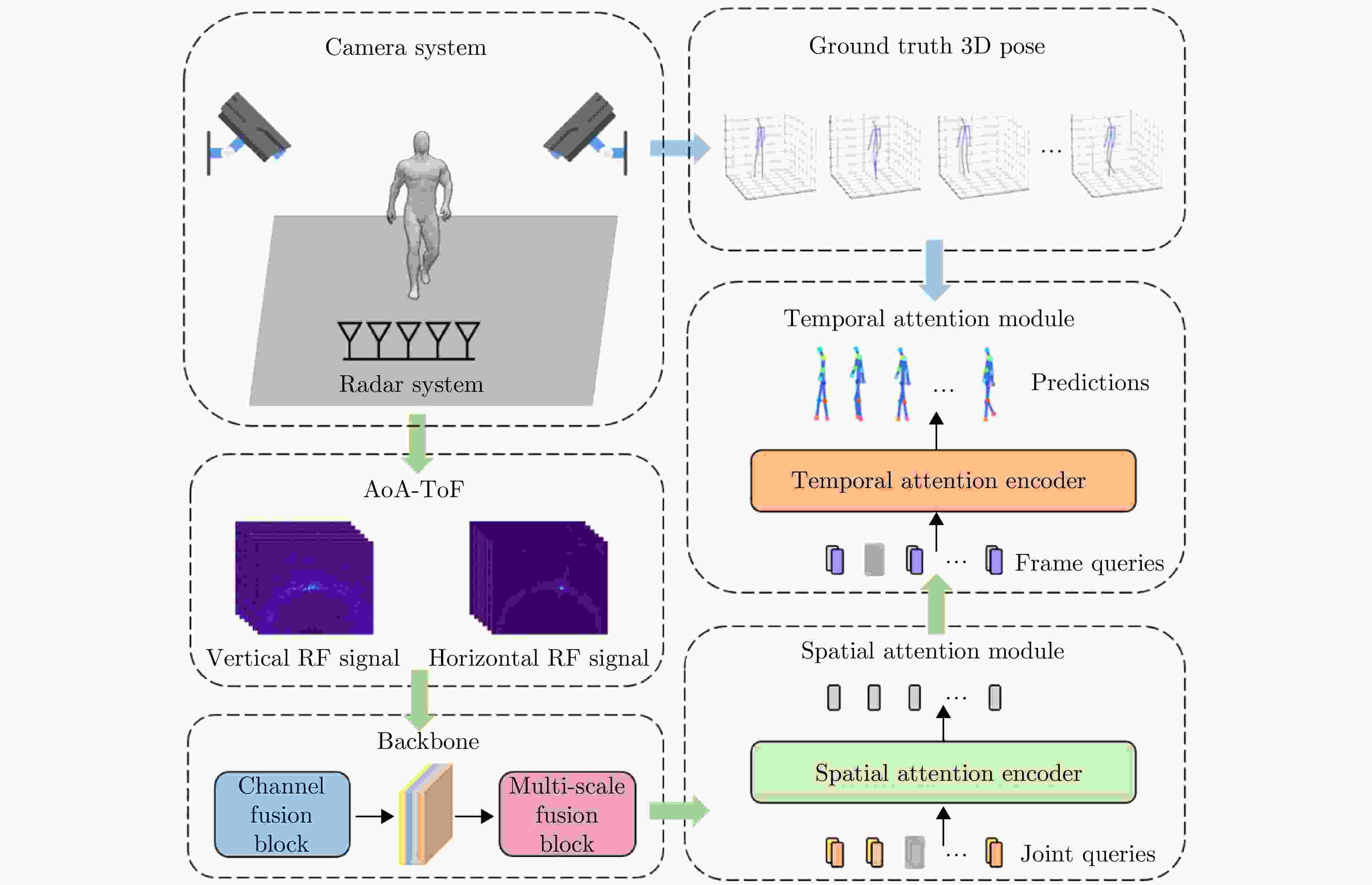
基于频率的分类 设备 雷达特征信息 代表性工作 基于高频无线信号的
人体姿态估计毫米波雷达
(30~300 GHz)3D point cloud mmPose[29] Heatmap RPM[18] Heatmap RPM 2.0[14] Heatmap MobiRFPose[19] 基于低频无线信号的
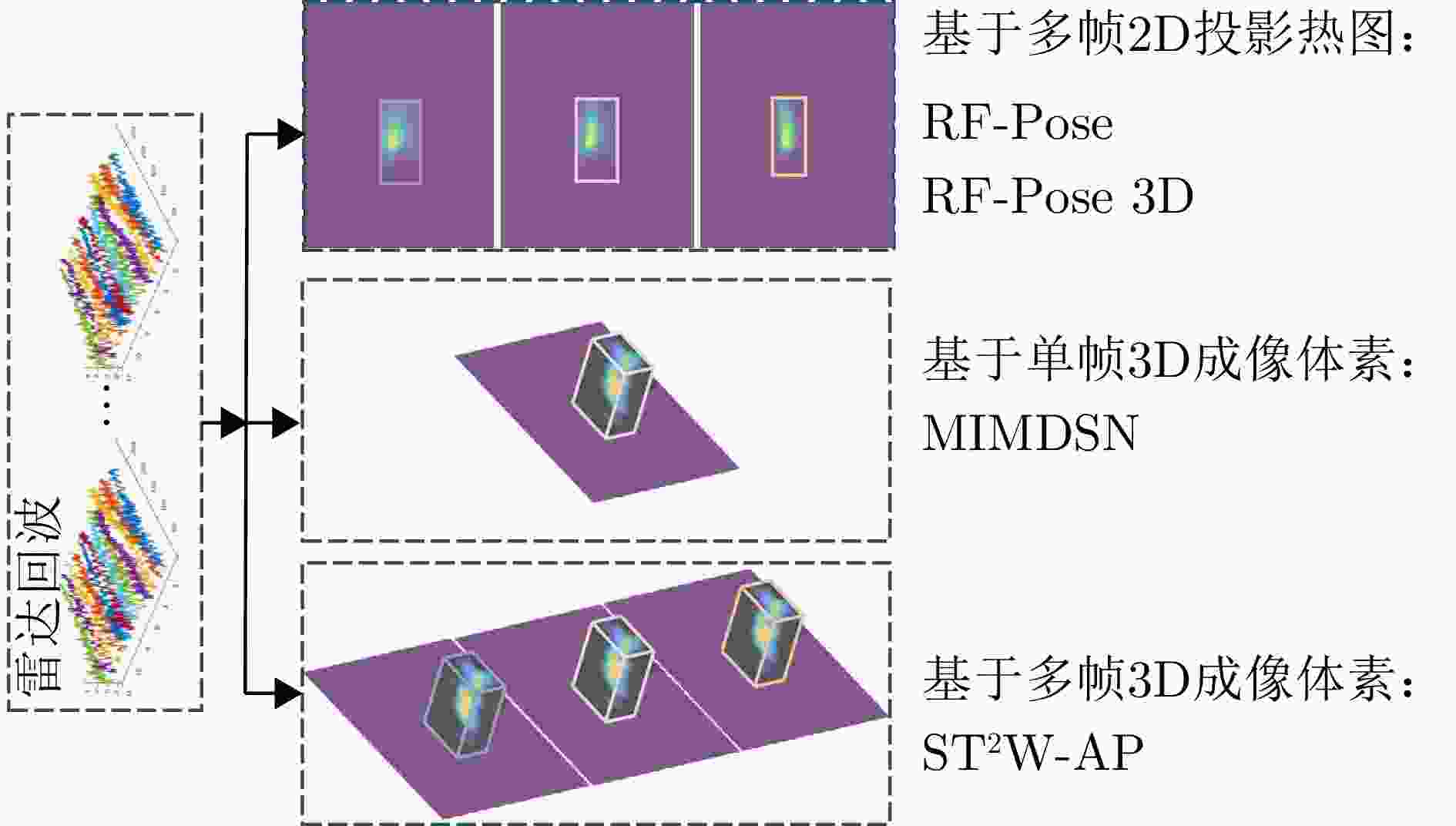
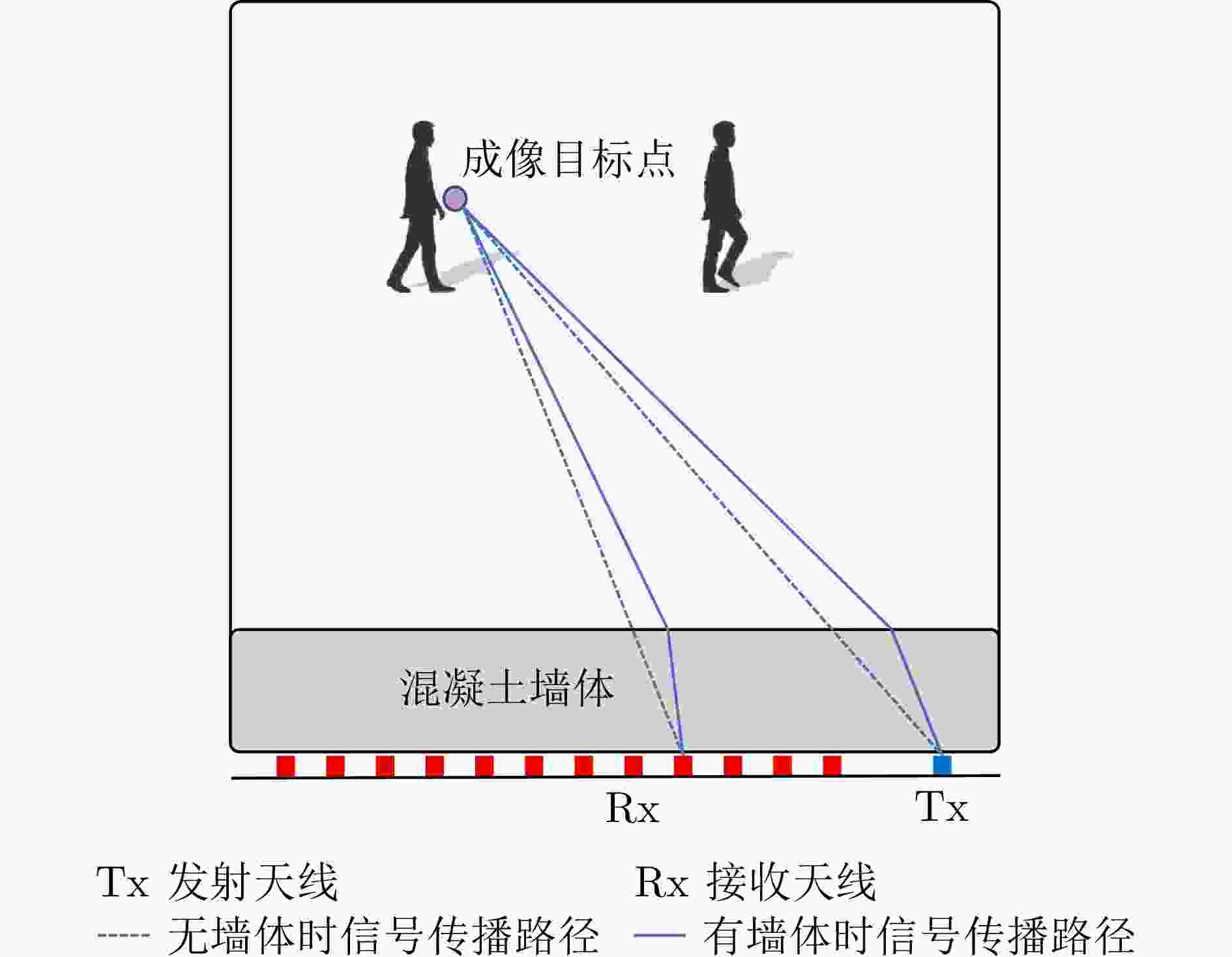
人体姿态估计穿墙雷达
(300 MHz~10 GHz)Heatmap RF-Pose[34] Heatmap RF-Pose3D[36] 单帧3D成像体素 MIMDSN[37] 多帧3D成像体素 ST2W-AP[38] Heatmap和3D成像体素 Dual-task Net[39] 多帧雷达回波 RadarFormer[40] WiFi
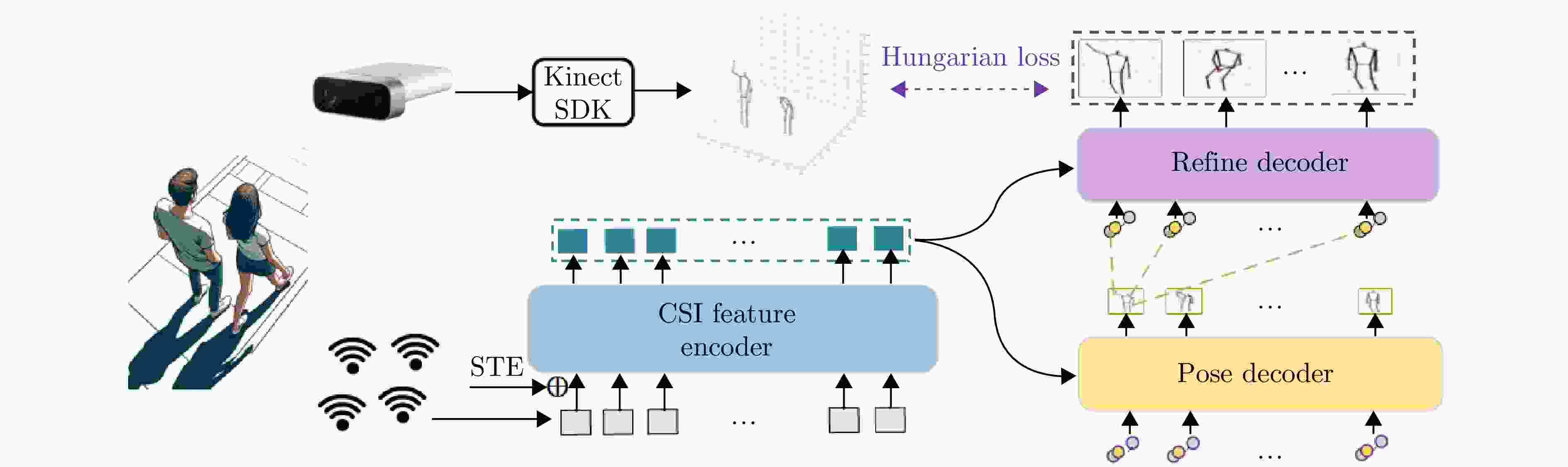
(2.400~5.825 GHz)Channel state information Person-in-WiFi[41] Channel state information Person-in-WiFi 3D[42] Channel state information DensePose From WiFi[43] 表 2 基于无线信号的人体姿态估计数据集对比
Table 2. Summary of dataset on pose estimation based on wireless signals
数据集 无线设备 真值采集设备 场景数量 行为种类 用户数量 总样本数(帧) UWB-HA4D-1.0 穿墙雷达 RGB 3 10 11 110280 HIBER 毫米波雷达 RGB 10 4 10 402380 RT-Pose 毫米波雷达 RGB
LiDAR40 6 10 72000 mRI 毫米波雷达 RGB-D
IMU1 12 20 160000 mmBody 毫米波雷达 RGB 100 7 20 >20万 HuPR 毫米波雷达 RGB 1 3 6 141000 -
[1] ZHAO Zhongqiu, ZHENG Peng, XU Shoutao, et al. Object detection with deep learning: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(11): 3212–3232. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2876865. [2] CHEN Yucheng, TIAN Yingli, and HE Mingyi. Monocular human pose estimation: A survey of deep learning-based methods[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2020, 192: 102897. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2019.102897. [3] MUNEA T L, JEMBRE Y Z, WELDEGEBRIEL H T, et al. The progress of human pose estimation: A survey and taxonomy of models applied in 2D human pose estimation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 133330–133348. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010248. [4] JIAO Licheng, ZHANG Ruohan, LIU Fang, et al. New generation deep learning for video object detection: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 3195–3215. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3053249. [5] 杨小鹏, 高炜程, 渠晓东. 基于微多普勒角点特征与Non-Local机制的穿墙雷达人体步态异常终止行为辨识技术[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 68–86. doi: 10.12000/JR23181.YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Weicheng, and QU Xiaodong. Human anomalous gait termination recognition via through-the-wall radar based on micro-Doppler corner features and Non-Local mechanism[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 68–86. doi: 10.12000/JR23181. [6] 金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119.JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. [7] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [8] 夏正欢, 张群英, 叶盛波, 等. 一种便携式伪随机编码超宽带人体感知雷达设计[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027.XIA Zhenghuan, ZHANG Qunying, YE Shengbo, et al. Design of a handheld pseudo random coded UWB radar for human sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027. [9] ZHANG Dongheng, HU Yang, and CHEN Yan. MTrack: Tracking multiperson moving trajectories and vital signs with radio signals[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(5): 3904–3914. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3025820. [10] LI Yadong, ZHANG Dongheng, CHEN Jinbo, et al. Towards domain-independent and real-time gesture recognition using mmWave signal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(12): 7355–7369. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3207570. [11] ZHANG Binbin, ZHANG Dongheng, LI Yadong, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for RF-based gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(23): 21026–21038. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3284496. [12] SONG Ruiyuan, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RF-URL: Unsupervised representation learning for RF sensing[C]. The 28th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Sydney, Australia, 2022: 282–295. doi: 10.1145/3495243.3560529. [13] GONG Hanqin, ZHANG Dongheng, CHEN Jinbo, et al. Enabling orientation-free mmwave-based vital sign sensing with multi-domain signal analysis[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2024: 8751–8755. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10448323. [14] XIE Chunyang, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RPM 2.0: RF-based pose machines for multi-person 3D pose estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(1): 490–503. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3287329. [15] YANG Shuai, ZHANG Dongheng, SONG Ruiyuan, et al. Multiple WiFi access points co-localization through joint AoA estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(2): 1488–1502. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3239377. [16] WU Zhi, ZHANG Dongheng, XIE Chunyang, et al. RFMask: A simple baseline for human silhouette segmentation with radio signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023, 25: 4730–4741. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3181455. [17] GENG Ruixu, HU Yang, LU Zhi, et al. Passive non-line-of-sight imaging using optimal transport[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 110–124. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3128312. [18] XIE Chunyang, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RPM: RF-based pose machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 637–649. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3268376. [19] YU Cong, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. MobiRFPose: Portable RF-based 3D human pose camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 3715–3727. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3314979. [20] YU Cong, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. Fast 3D human pose estimation using RF signals[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10094778. [21] MU Kangle, LUAN T H, ZHU Lina, et al. A survey of handy see-through wall technology[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 82951–82971. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991201. [22] SONG Yongkun, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction via UWB MIMO radar and 3D CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 241. doi: 10.3390/rs13020241. [23] VASISHT D, JAIN A, HSU C Y, et al. Duet: Estimating user position and identity in smart homes using intermittent and incomplete RF-data[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 2(2): 84. doi: 10.1145/3214287. [24] HSU C Y, HRISTOV R, LEE G H, et al. Enabling identification and behavioral sensing in homes using radio reflections[C]. 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, Scotland UK, 2019: 548. doi: 10.1145/3290605.3300778. [25] FAN Lijie, LI Tianhong, YUAN Yuan, et al. In-home daily-life captioning using radio signals[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 105–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_7. [26] TIAN Yonglong, LEE G H, HE Hao, et al. RF-based fall monitoring using convolutional neural networks[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 2(3): 137. doi: 10.1145/3264947. [27] AYYALASOMAYAJULA R, ARUN A, WU Chenfeng, et al. Deep learning based wireless localization for indoor navigation[C]. The 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, London, United Kingdom, 2020: 17. doi: 10.1145/3372224.3380894. [28] CAO Zhongping, DING Wen, CHEN Rihui, et al. A joint global-local network for human pose estimation with millimeter wave radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(1): 434–446. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3201005. [29] SENGUPTA A, JIN Feng, ZHANG Renyuan, et al. mm-Pose: Real-time human skeletal posture estimation using mmWave radars and CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(17): 10032–10044. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2991741. [30] ADIB F, HSU C Y, MAO Hongzi, et al. Capturing the human figure through a wall[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(6): 219. doi: 10.1145/2816795.2818072. [31] AHMAD F, ZHANG Yimin, and AMIN M G. Three-dimensional wideband beamforming for imaging through a single wall[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(2): 176–179. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915742. [32] KONG Lingjiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Xiaobo, et al. Three-dimensional human imaging for through-the-wall radar[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2009.4976932. [33] HOLL P M and REINHARD F. Holography of Wi-Fi radiation[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 118(18): 183901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.183901. [34] ZHAO Mingmin, LI Tianhong, ABU ALSHEIKH M, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation using radio signals[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7356–7365. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00768. [35] JIANG Wenjun, XUE Hongfei, MIAO Chenglin, et al. Towards 3D human pose construction using WiFi[C]. The 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, London, United Kingdom, 2020: 23. doi: 10.1145/3372224.3380900. [36] ZHAO Mingmin, TIAN Yonglong, ZHAO Hang, et al. RF-based 3D skeletons[C]. 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 2018: 267–281. doi: 10.1145/3230543.3230579. [37] ZHENG Zhijie, PAN Jun, ZHANG Diankun, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation by mutual information maximizing deeply supervised nets[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(2): 3190–3205. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3294955. [38] 张锐, 龚汉钦, 宋瑞源, 等. 基于4D成像雷达的隔墙人体姿态重建与行为识别研究[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 44–61. doi: 10.12000/JR24132.ZHANG Rui, GONG Hanqin, SONG Ruiyuan, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction and action recognition using four-dimensional imaging radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 44–61. doi: 10.12000/JR24132. [39] SONG Yongkun, DAI Yongpeng, JIN Tian, et al. Dual-task human activity sensing for pose reconstruction and action recognition using 4-D imaging radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(19): 23927–23940. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3308788. [40] ZHENG Zhijie, ZHANG Diankun, LIANG Xiao, et al. RadarFormer: End-to-end human perception with through-wall radar and transformers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 35(10): 4319–4332. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3314031. [41] WANG Fei, ZHOU Sanping, PANEV S, et al. Person-in-WiFi: Fine-grained person perception using WiFi[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 5452–5461. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00555. [42] YAN Kangwei, WANG Fei, QIAN Bo, et al. Person-in-WiFi 3D: End-to-end multi-person 3D pose estimation with Wi-Fi[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 969–978. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00098. [43] GENG Jiaqi, HUANG Dong, and DE LA TORRE F. DensePose from WiFi[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00250. 2022. [44] CAO Zhe, SIMON T, WEI S E, et al. Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7291–7299. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.143. [45] JOHNSON S and EVERINGHAM M. Clustered pose and nonlinear appearance models for human pose estimation[C]. 2010 British Machine Vision Conference, Aberystwyth, UK, 2010: 1–11. [46] CHEN Xianjie and YUILLE A. Parsing occluded people by flexible compositions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3945–3954. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299020. [47] LI Wenbo, WANG Zhicheng, YIN Binyi, et al. Rethinking on multi-stage networks for human pose estimation[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.00148. 2019. [48] BOULIC R, THALMANN N M, and THALMANN D. A global human walking model with real-time kinematic personification[J]. The Visual Computer, 1990, 6(6): 344–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01901021. [49] BOULIC R, REZZONICO S, and THALMANN D. Multi-finger manipulation of virtual objects[C]. ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Hong Kong, China, 1996: 67–74. doi: 10.1145/3304181.3304195. [50] JU S X, BLACK M J, and YACOOB Y. Cardboard people: A parameterized model of articulated image motion[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Killington, USA, 1996: 38–44. doi: 10.1109/AFGR.1996.557241. [51] JIANG Hao. Finding human poses in videos using concurrent matching and segmentation[C]. The 10th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Queenstown, New Zealand, 2011: 228–243. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-19315-6_18. [52] COOTES T F, TAYLOR C J, COOPER D H, et al. Active shape models-their training and application[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 1995, 61(1): 38–59. doi: 10.1006/cviu.1995.1004. [53] FREIFELD O, WEISS A, ZUFFI S, et al. Contour people: A parameterized model of 2D articulated human shape[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 639–646. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540154. [54] URTASUN R and FUA P. 3D human body tracking using deterministic temporal motion models[C]. The 8th European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 2004: 92–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24672-5_8. [55] LOPER M, MAHMOOD N, ROMERO J, et al. SMPL: A skinned multi-person linear model[J]. Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries, 2023, 2: 88. doi: 10.1145/3596711.3596800. [56] SAITO Shunsuke, HUANG Zeng, NATSUME Ryota, et al. PIFu: Pixel-aligned implicit function for high-resolution clothed human digitization[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 2304–2314. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00239. [57] PONS-MOLL G, ROMERO J, MAHMOOD N, et al. Dyna: A model of dynamic human shape in motion[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(4): 120. doi: 10.1145/2766993. [58] ZUFFI S and BLACK M J. The stitched puppet: A graphical model of 3D human shape and pose[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3537–3546. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298976. [59] JOO H, SIMON T, and SHEIKH Y. Total capture: A 3D deformation model for tracking faces, hands, and bodies[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8320–8329. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00868. [60] XU Hongyi, BAZAVAN E G, ZANFIR A, et al. GHUM & GHUML: Generative 3D human shape and articulated pose models[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6184–6193. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00622. [61] CHEN V C, LI Fayin, HO S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402. [62] 李柯蒙, 戴永鹏, 宋勇平, 等. 单通道超宽带雷达人体姿态增量估计技术[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 16–27. doi: 10.12000/JR24109.LI Kemeng, DAI Yongpeng, SONG Yongping, et al. Single-channel ultrawideband radar human pose-incremental estimation technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 16–27. doi: 10.12000/JR24109. [63] 金添, 宋永坤, 戴永鹏, 等. UWB-HA4D-1.0: 超宽带雷达人体动作四维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008.JIN Tian, SONG Yongkun, DAI Yongpeng, et al. UWB-HA4D-1.0: An ultra-wideband radar human activity 4D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008. [64] HO Y H, CHENG J H, KUAN Shengyao, et al. RT-Pose: A 4D radar tensor-based 3D human pose estimation and localization benchmark[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.13930. 2024. [65] AN Sizhe, LI Yin, and OGRAS U. mRI: Multi-modal 3D human pose estimation dataset using mmwave, RGB-D, and inertial sensors[C]. 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1988. [66] CHEN Anjun, WANG Xiangyu, ZHU Shaohao, et al. mmBody benchmark: 3D body reconstruction dataset and analysis for millimeter wave radar[C]. 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 2022: 3501–3510. doi: 10.1145/3503161.3548262. [67] LEE S P, KINI N P, PENG W H, et al. HuPR: A benchmark for human pose estimation using millimeter wave radar[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 5715–5724. doi: 10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00567. [68] GADRE A, VASISHT D, RAGHUVANSHI N, et al. MiLTOn: Sensing product integrity without opening the box using non-invasive acoustic vibrometry[C]. 21st ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Milano, Italy, 2022: 390–402. doi: 10.1109/IPSN54338.2022.00038. [69] LI Yang, LIU Yutong, WANG Yanping, et al. The millimeter-wave radar SLAM assisted by the RCS feature of the target and IMU[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(18): 5421. doi: 10.3390/s20185421. [70] CARUANA R. Multitask learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1997, 28(1): 41–75. doi: 10.1023/A:1007379606734. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: