Coherent Detection Method for Moving Platform Based Distributed Aperture Radar and Experimental Verification
-
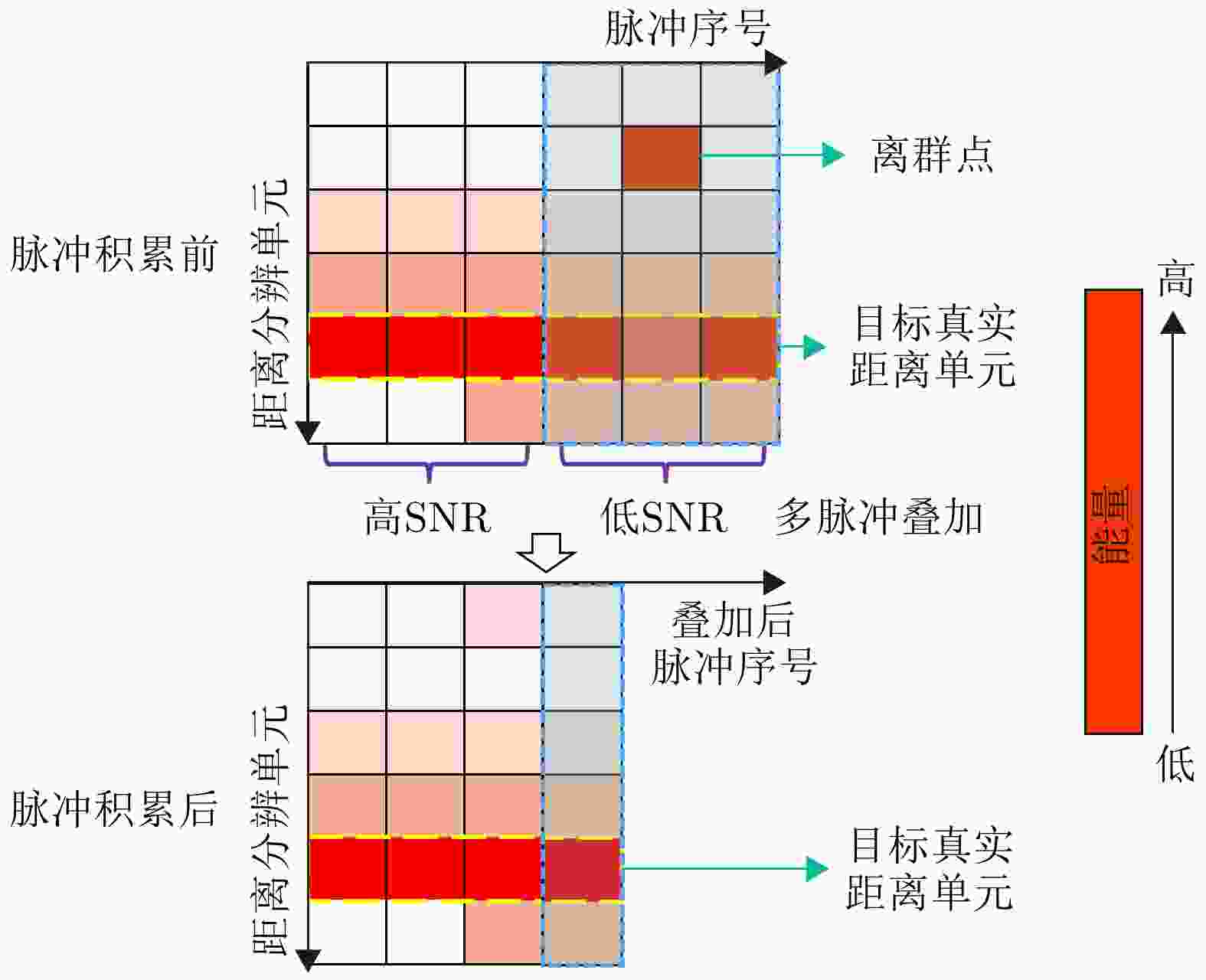
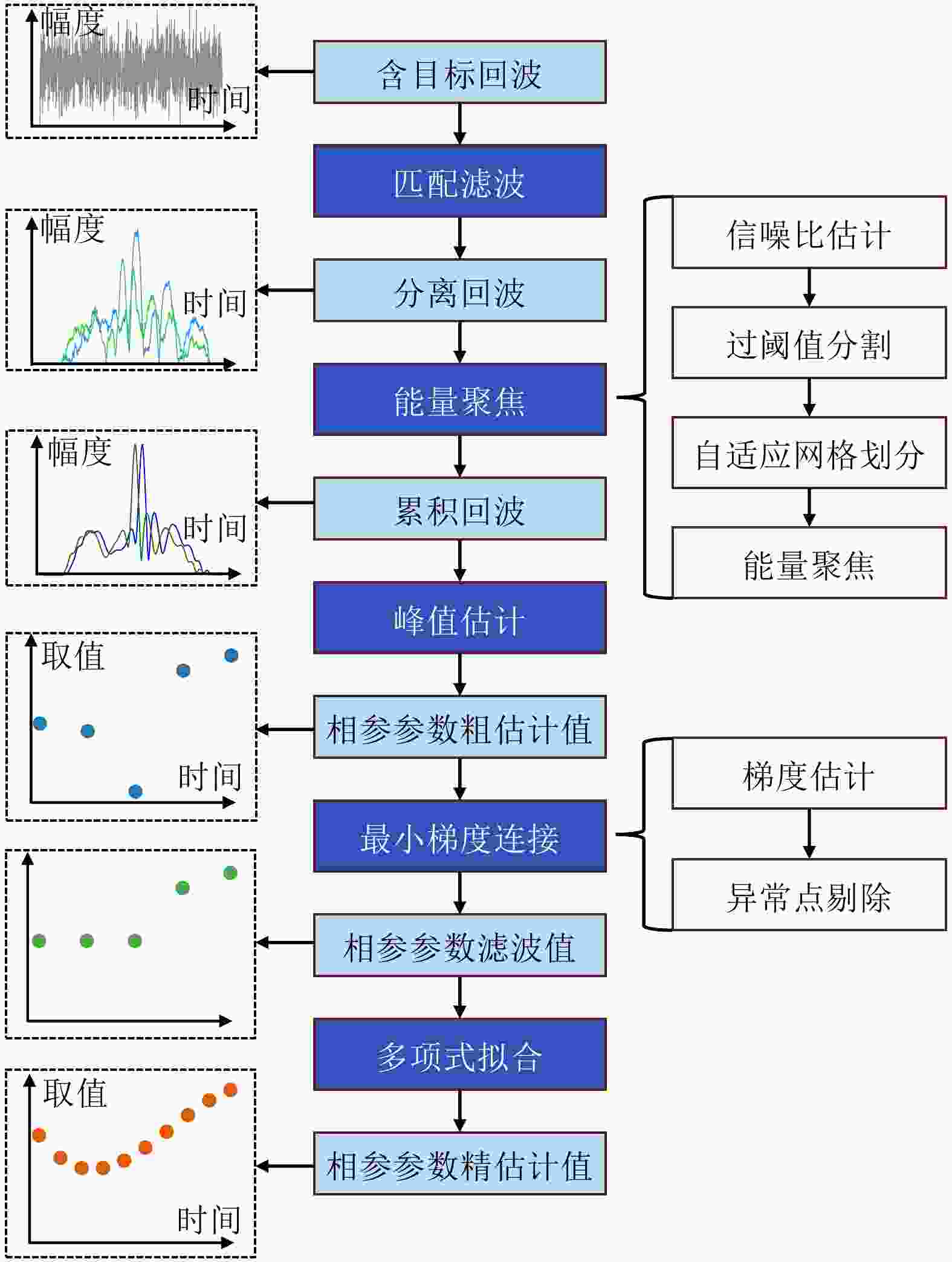
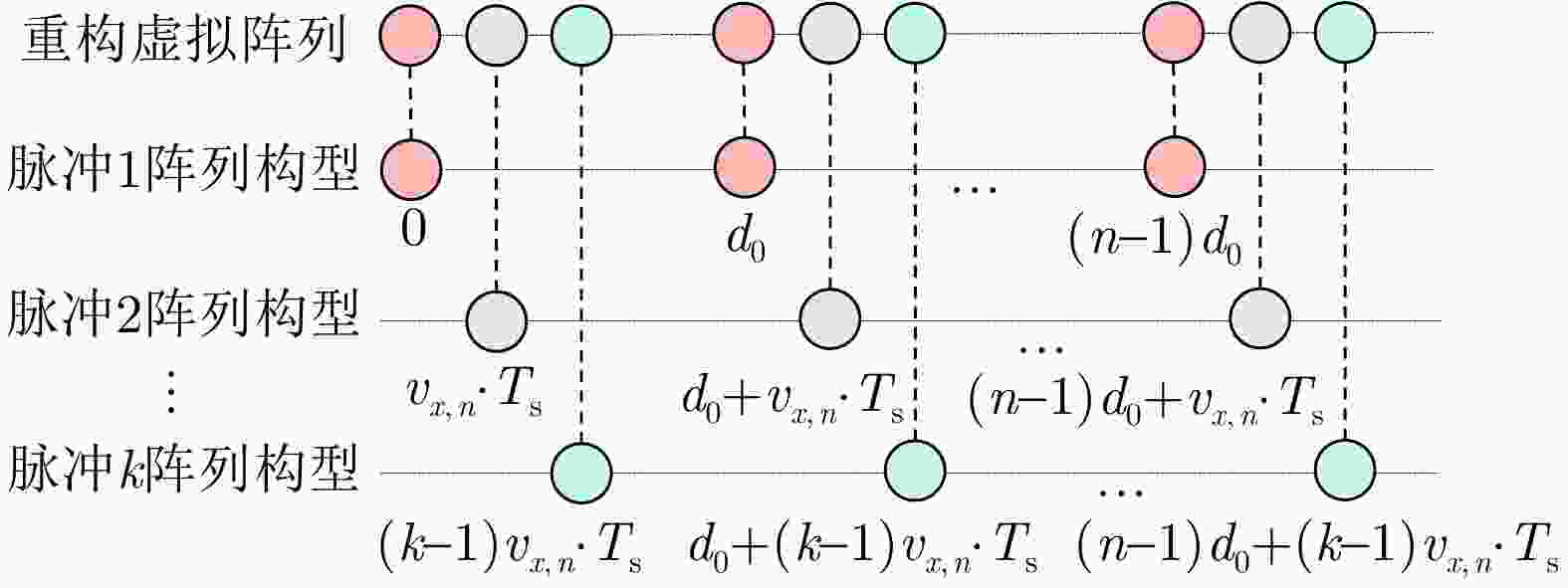
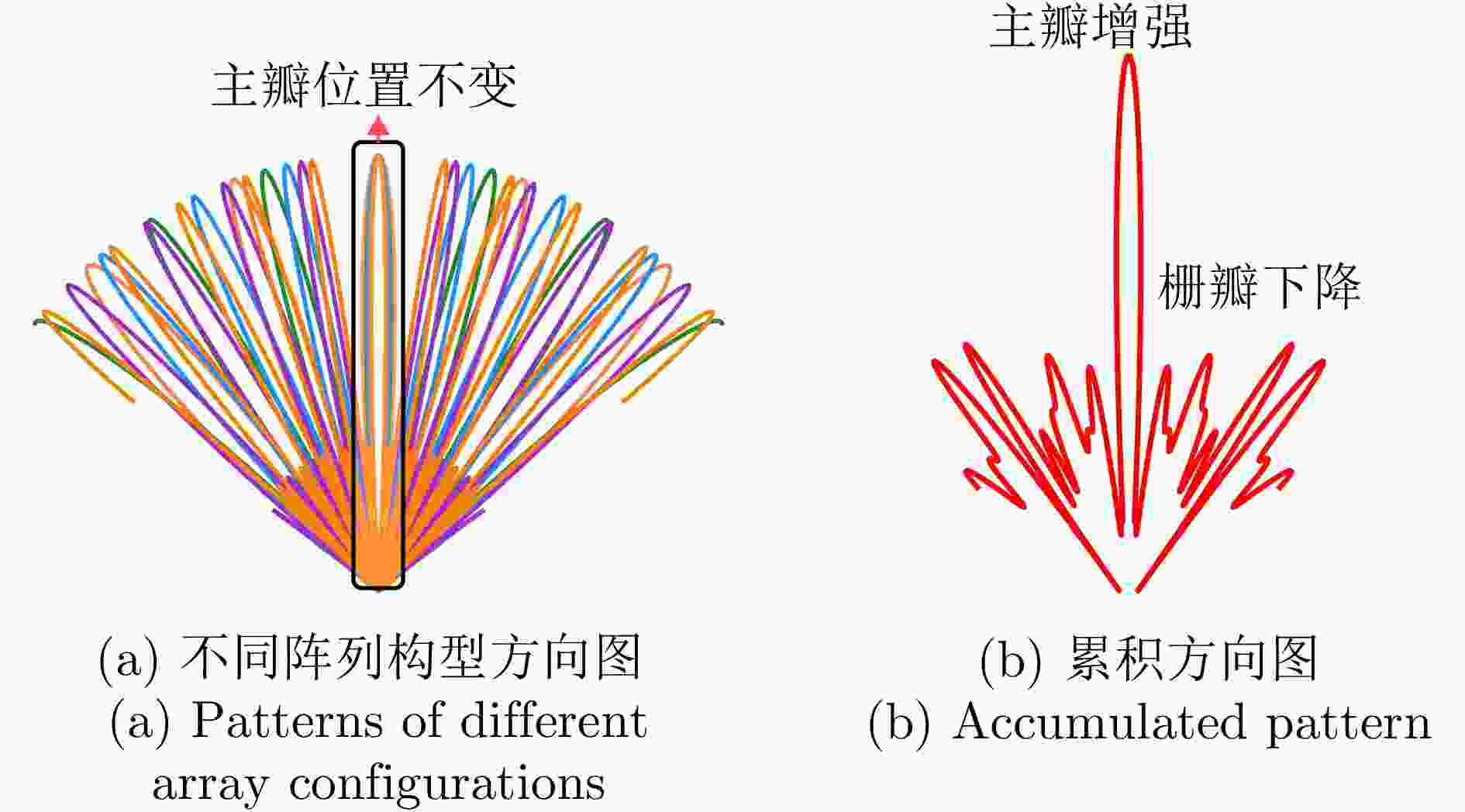
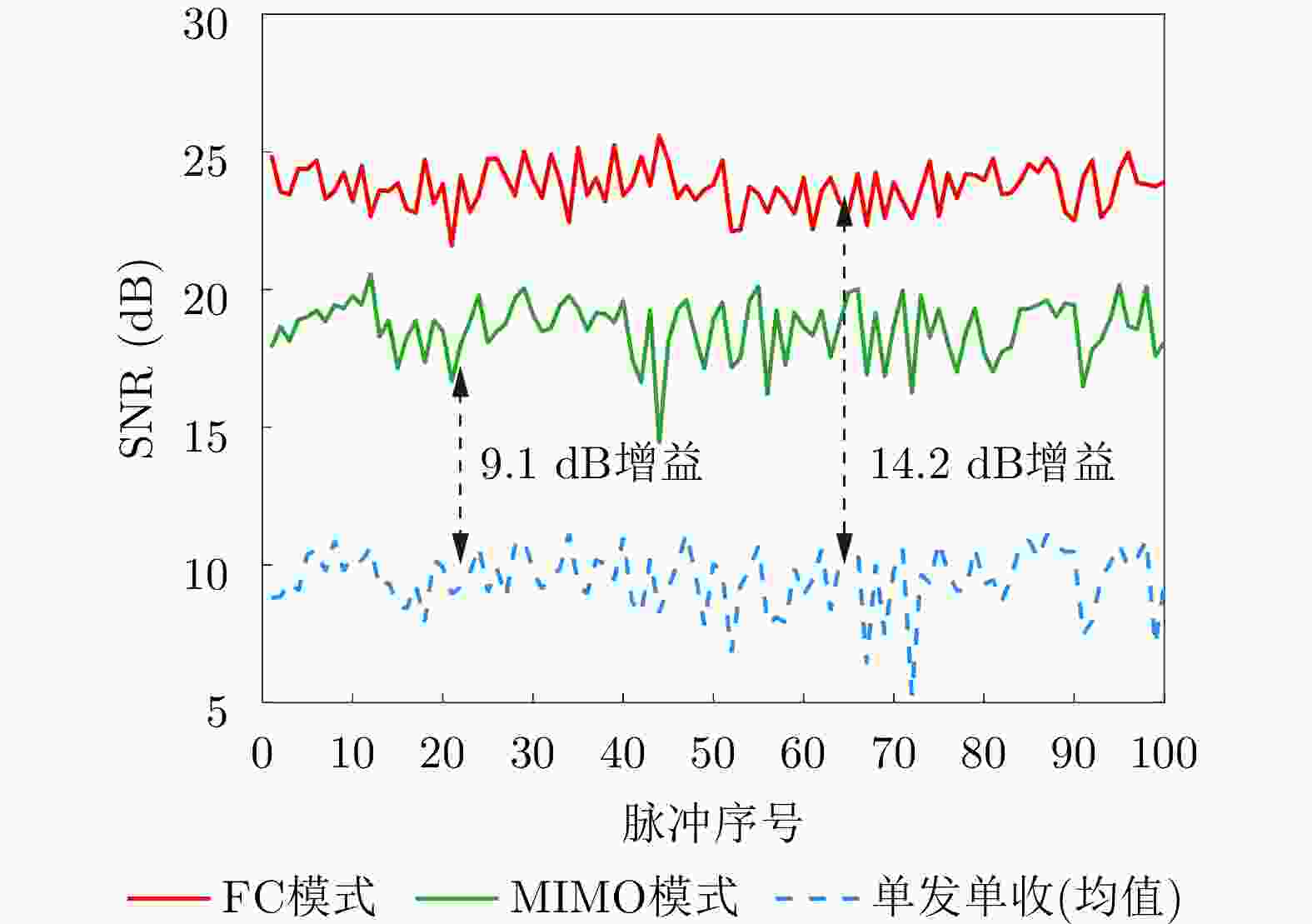
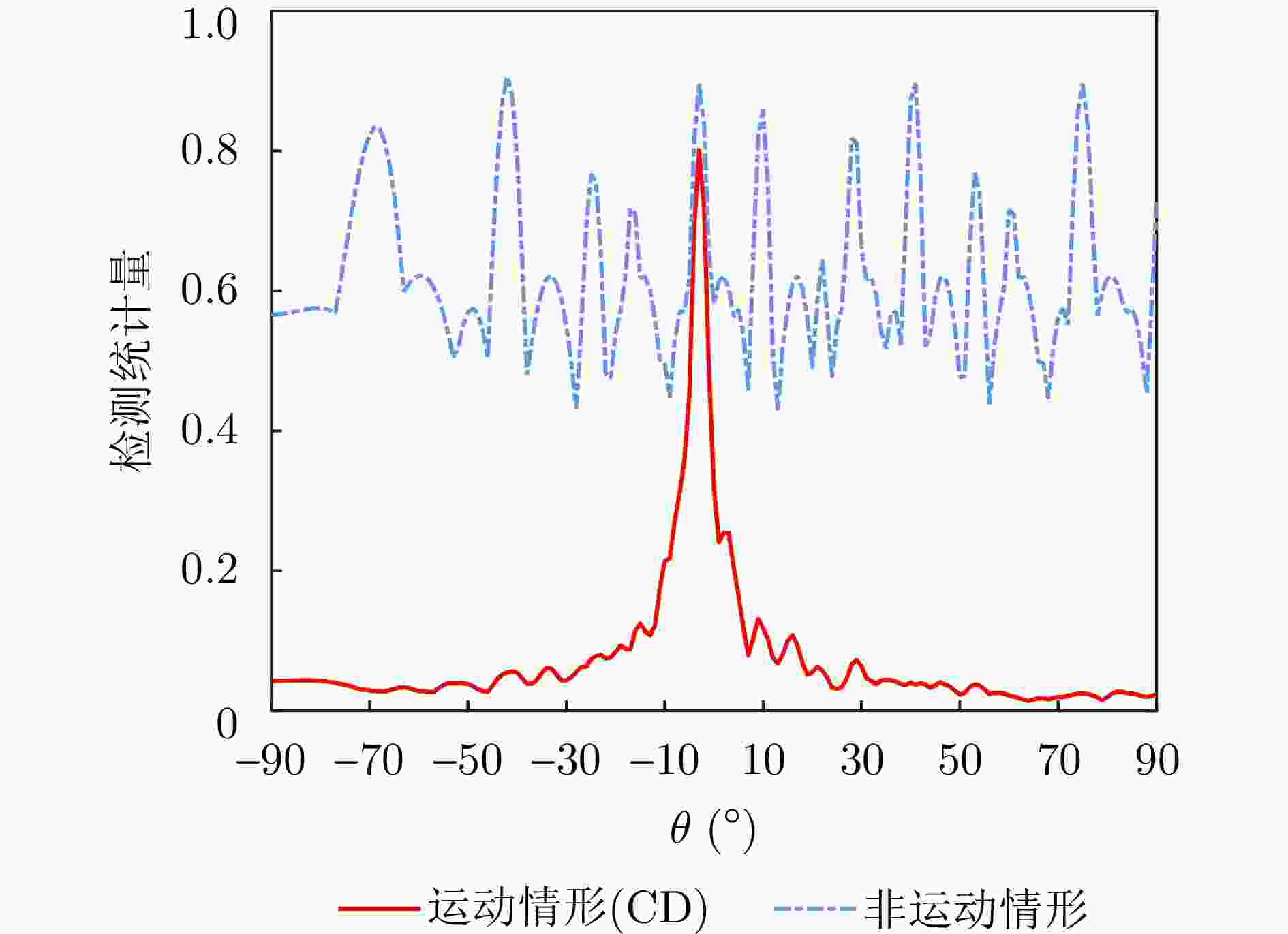
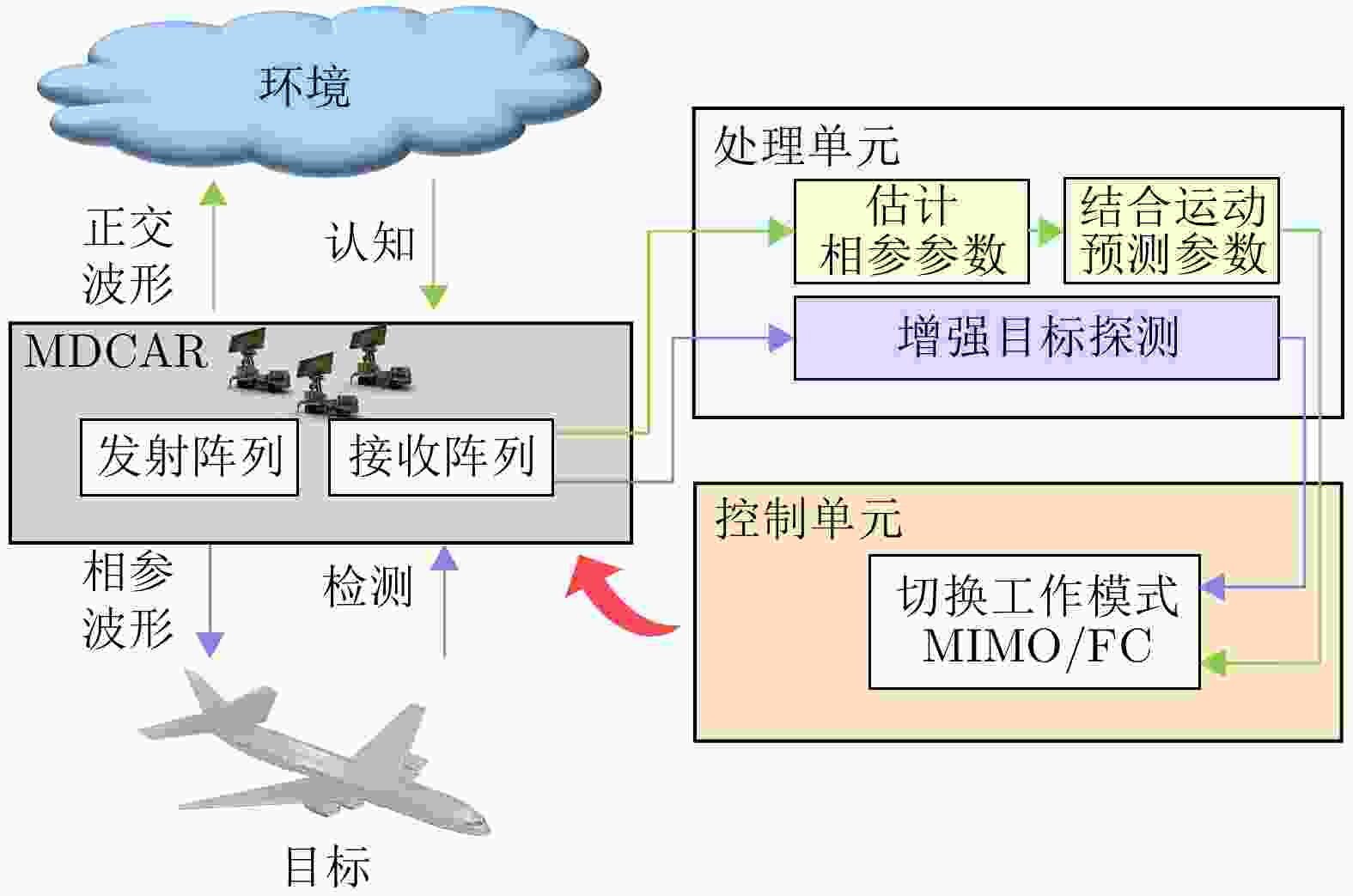
摘要: 动平台分布孔径雷达不仅可以通过多部小孔径雷达相参合成等效获得大孔径雷达的探测性能,也可进一步通过机动性和灵活部署增强探测与抗毁伤能力,是未来雷达重要发展方向之一。但由于多雷达间存在内部钟差和外部传播路径差,各雷达发射信号无法直接相参合成,需进行必要的时间和相位相参参数校正,且分布孔径雷达间距通常远超半波长,合成方向图将存在栅瓣问题,影响目标角度估计。为获得相参参数,该文以闭环式框架为基础,给出动平台分布孔径雷达认知相参框架,并结合运动条件下相参参数的变化规律,提出多脉冲关联相参参数估计方法以提升参数估计精度。同时,针对栅瓣问题,结合平台运动特性提出一种基于阵列构型累积的无模糊角度估计方法。最后,在仿真验证基础上基于所提框架设计了3节点地面动平台分布孔径雷达原理样机并开展了试验验证,试验结果表明在运动场景下,相比单部孔径雷达可以实现最高14.2 dB的信噪比增益,从而提升了目标的测距精度,同时在一定条件下实现了目标角度的无模糊测量,证明了所提方法和框架的有效性。该文工作将对未来分布孔径雷达的工程化实现及发展起到一定的引导作用。Abstract: As one of the most promising next-generation radars, Moving platform based Distributed Aperture Radar (MDAR) cannot only coherently combining distributed apertures to obtain the same detection performance of a large aperture, but also enhance the detection and anti-damage capabilities through mobility and flexible deployment. However, time and phase synchronization among radars should be done before coherently combining due to internal clock differences and external propagation path differences. Moreover, grating lobes will generate as the distance between multiple radars usually exceeds half a wavelength, which affects the estimation accuracy of target angle. To obtain Coherent Parameters (CPs), this paper established a cognitive framework for MDAR based on closed-loop structure. And a multi-pulse correlation CPs estimation method considering motion conditions is proposed to improve estimation accuracy. In the meanwhile, an unambiguous angle estimation method based on array configuration accumulation is proposed considering platform motion characteristics. Finally, based on the simulation verification and the proposed framework, a prototype of a 3-node ground Moving platform based Distributed Coherent Aperture Radar (MDCAR) system is designed and experiments are conducted. Compared to a single radar, a maximum value of 14.2 dB signal-to-noise ratio improvement can be achieved, which can further enhance range detection accuracy. Besides, unambiguous angle estimation is also realized under certain conditions. This work is expected to provide support for the research and development of MDCAR.
-
表 1 相参参数估计仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of CPs estimation
参数 数值 节点数目 2 信号波形 正负线性调频信号 节点初始位置 [0, 0; 0, 50] m 发射中心频率 300 MHz 发射带宽 10 MHz 脉冲重复频率 2000 Hz 仿真持续时间 1 s 节点运动速度 [0, 10] m/s 目标初始位置 [ 10000 ,8000 ] m目标运动速度 [–200, 0] m/s 初始内部相位误差 0° 表 2 角度估计主要仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters of angle estimation
参数 数值 节点数目 3 节点初始位置 [0, 0; 0, 1.5; 0, 3.0] m 发射中心频率 300 MHz 节点运动速度(相参情形) [0, 10; 0, 10; 0, 10] m/s 节点运动速度(非相参情形) [0, 10; 0, 20; 0, 30] m/s 脉冲重复间隔 25 ms 目标角度 10° 所用脉冲个数 3 表 3 雷达参数
Table 3. Radar parameters
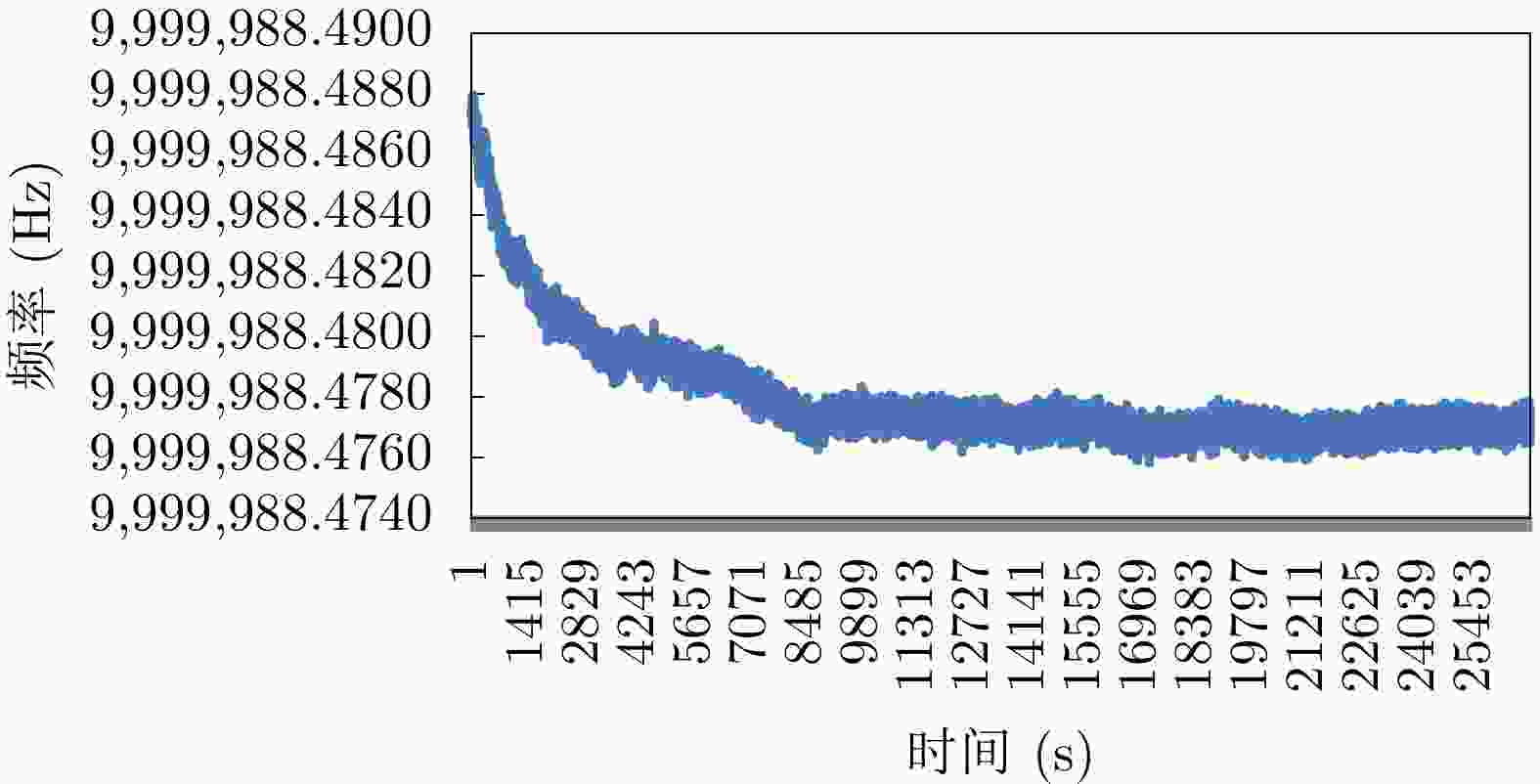
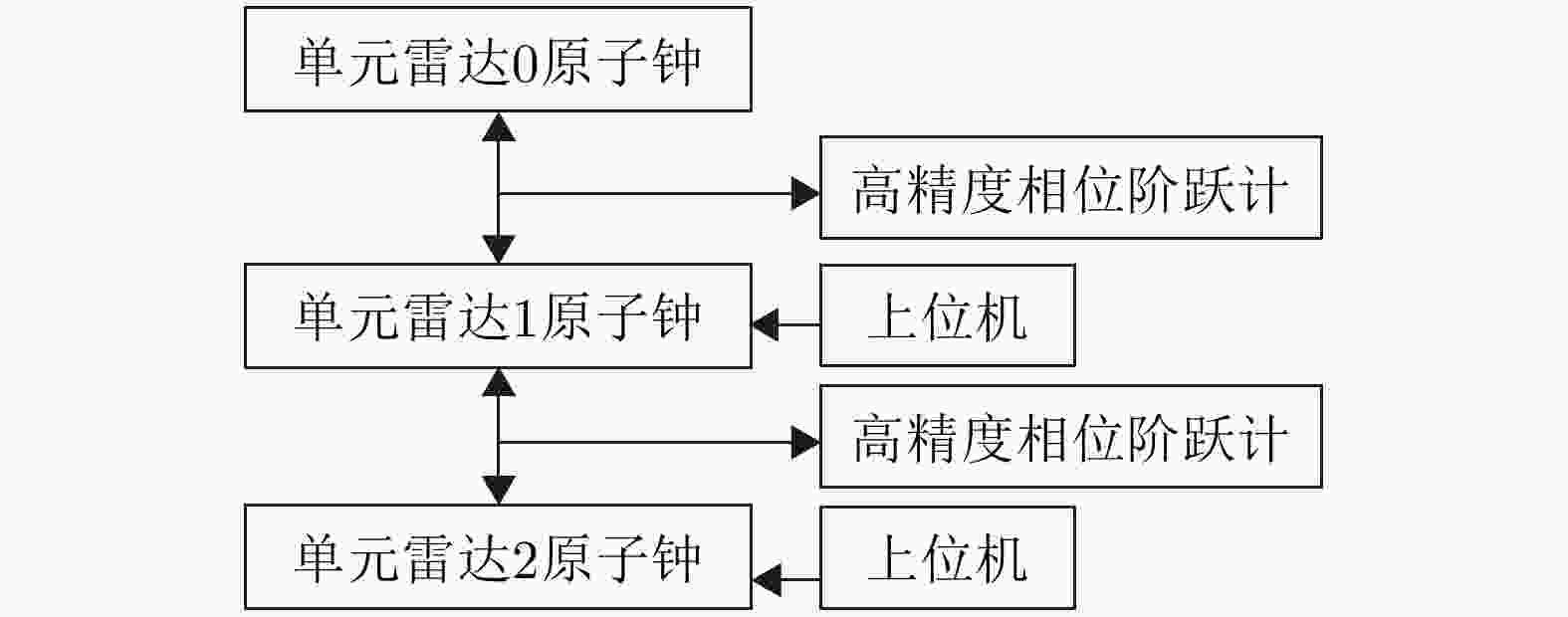
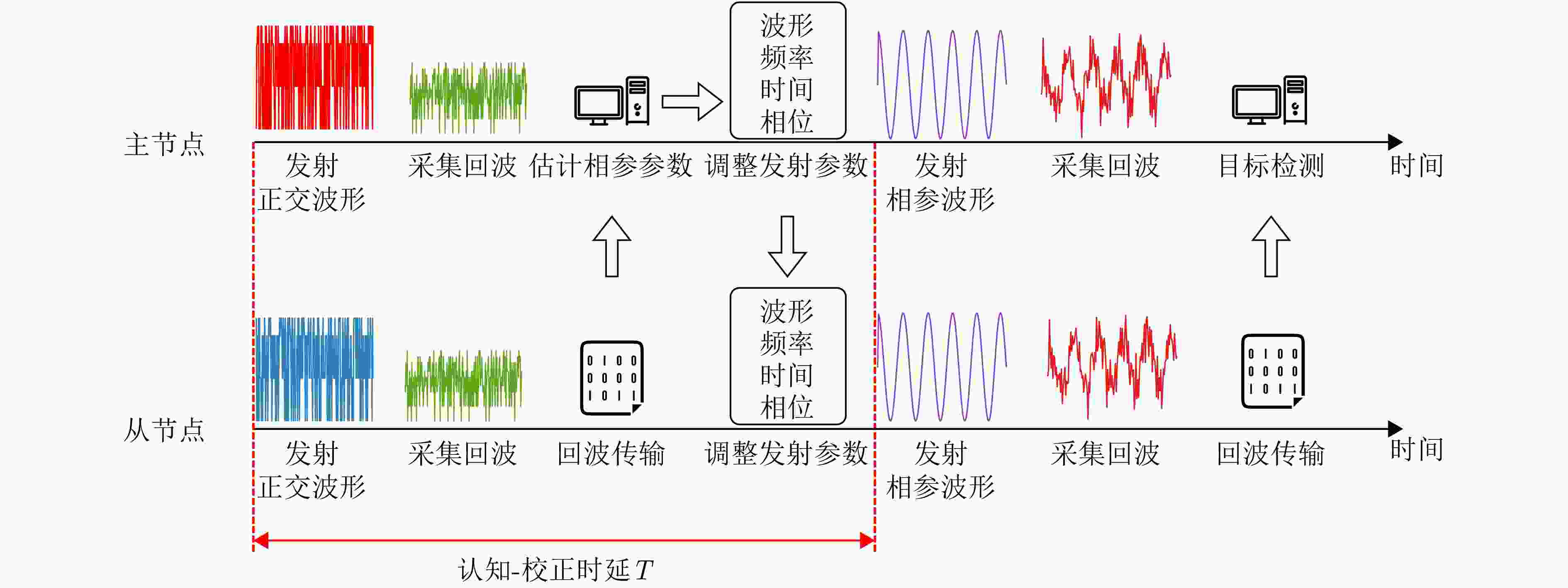
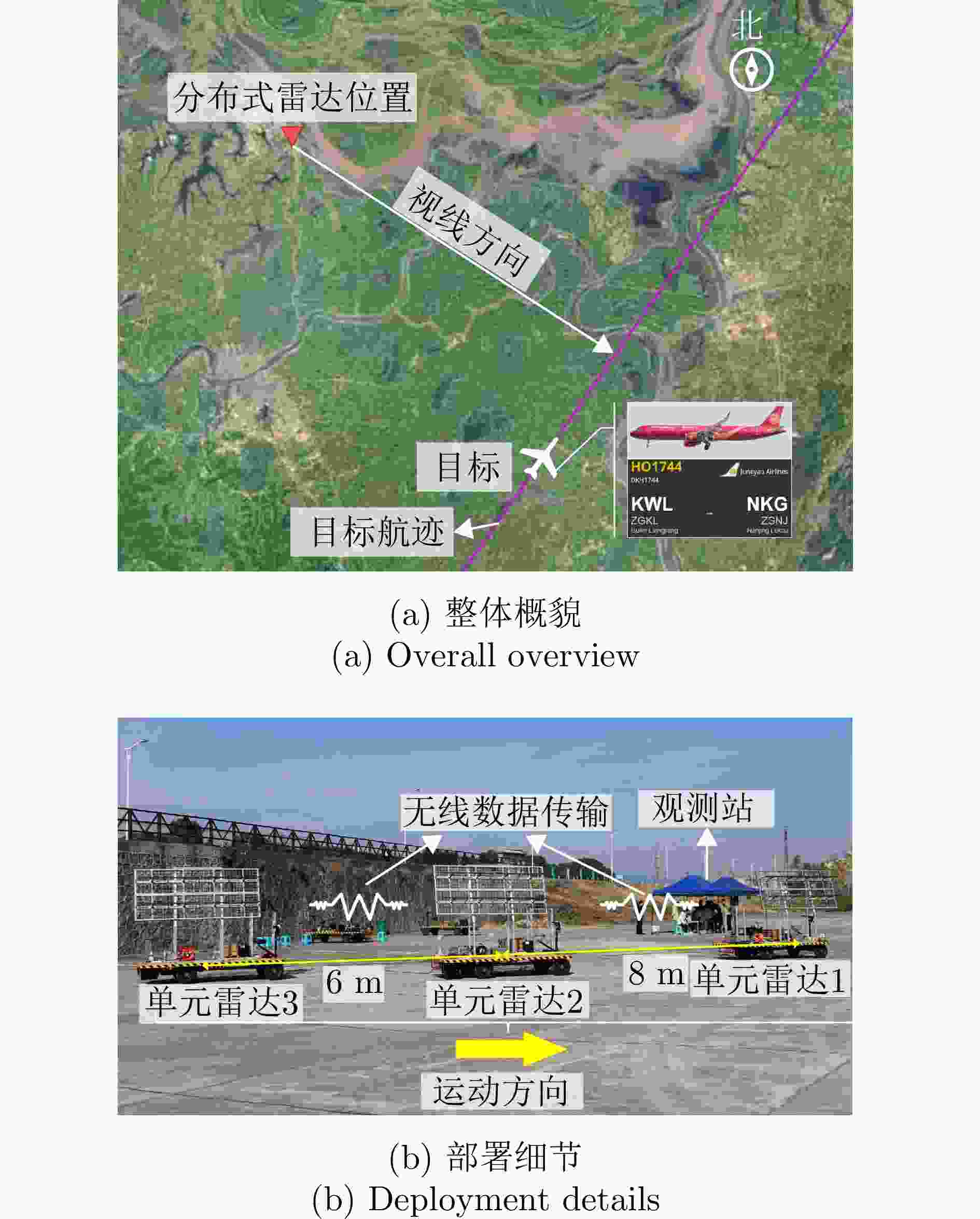
参数 数值 节点数目 3 发射中心频率 230 MHz 信号带宽 1 MHz 脉冲宽度 30 μs 脉冲重复频率 2000 Hz 认知-校正时延 0.5 s -
[1] CUOMO K M, COUTTS S D, MCHARG J C, et al. Wideband aperture coherence processing for next generation radar (NexGen)[R]. MIT Lincoln Laboratory Report NG-3, 2004. [2] 鲁耀兵, 高红卫. 分布孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 216–217.LU Yaobing and GAO Hongwei. Distributed Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 216–217. [3] KORDIK A M, METCALF J G, CURTIS D D, et al. Graceful performance degradation and improved error tolerance via mixed-mode distributed coherent radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(5): 5251–5262. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3236487. [4] NANZER J A, MGHABGHAB S R, ELLISON S M, et al. Distributed phased arrays: Challenges and recent advances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4893–4907. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3092401. [5] 刘泉华, 张凯翔, 梁振楠, 等. 地基分布式相参雷达技术研究综述[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(12): 2443–2459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.12.001.LIU Quanhua, ZHANG Kaixiang, LIANG Zhennan, et al. Research overview of ground-based distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(12): 2443–2459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.12.001. [6] 刘兴华, 王国玉, 徐振海, 等. 分布式孔径相参合成原理、发展与技术实现综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1229–1248. doi: 10.12000/JR23195.LIU Xinghua, WANG Guoyu, XU Zhenhai, et al. Review of principles, development and technical implementation of coherently combining distributed apertures[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1229–1248. doi: 10.12000/JR23195. [7] 卢佳欣, 刘飞峰, 缪颖杰, 等. 动平台分布式相参雷达系统分析[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(5): 825–830. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.05.013.LU Jiaxin, LIU Feifeng, MIAO Yingjie, et al. Analysis on distributed coherent radar system with moving platforms[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(5): 825–830. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.05.013. [8] MUDUMBAI R, BARRIAC G, and MADHOW U. On the feasibility of distributed beamforming in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2007, 6(5): 1754–1763. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2007.360377. [9] GAO Hongwei, ZHOU Baoliang, ZHOU Dongming, et al. Performance analysis and experimental study on distributed aperture coherence-synthetic radar[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059191. [10] SUN Palin, TANG Jun, HE Qian, et al. Cramer-Rao bound of parameters estimation and coherence performance for next generation radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2013, 7(5): 553–567. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0139. [11] 宋靖, 周青松, 张剑云. 基于相关法的分布式全相参雷达相干参数估计及相参性能[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(7): 1710–1715. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141339.SONG Jing, ZHOU Qingsong, and ZHANG Jianyun. Coherent parameters estimation by cross-correlation for distributed aperture fully coherent radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(7): 1710–1715. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141339. [12] 张洪纲, 雷子健, 刘泉华. 基于MUSIC法的宽带分布式全相参雷达相参参数估计方法[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(2): 208–214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.02.011.ZHANG Honggang, LEI Zijian, and LIU Quanhua. Coherent parameters estimation method based on MUSIC in wideband distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(2): 208–214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.02.011. [13] 刘兴华, 徐振海, 王罗胜斌, 等. 基于信号重建的分布式相参雷达相参参数估计算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(9): 1931–1938. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.06.LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, WANG Luoshengbin, et al. Coherent parameters estimation algorithm for distributed coherent aperture radar based on signal reconstruction[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1931–1938. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.06. [14] LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, LIU Xiang, et al. A clean signal reconstruction approach for coherently combining multiple radars[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2018, 2018(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s13634-018-0569-1. [15] 殷丕磊, 张洪纲, 翟腾普, 等. 基于Kalman滤波的分布式全相参雷达相参参数估计方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2016, 36(3): 282–288. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2016.03.012.YIN Pilei, ZHANG Honggang, ZHAI Tengpu, et al. Coherent parameters estimation using Kalman filter in distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016, 36(3): 282–288. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2016.03.012. [16] LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, WANG Luoshengbin, et al. Dual-radar coherently combining: Generalised paradigm and verification example[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(5): 689–699. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5089. [17] 陈金铭, 王彤, 吴建新, 等. 基于特显点的机载分布式相参雷达同步误差校正方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 356–363. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190694.CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, WU Jianxin, et al. Airborne distributed coherent aperture radar synchronization error calibration method based on prominent points[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 356–363. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190694. [18] CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. Time and phase synchronization using clutter observations in airborne distributed coherent aperture radars[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(3): 432–449. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.040. [19] CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. Identifiability analysis of positioning and synchronization errors in airborne distributed coherence aperture radars[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5978–5993. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3144481. [20] LIU Xiaoyu, WANG Tong, CHEN Jinming, et al. Efficient configuration calibration using ground auxiliary receivers at inaccurate locations[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 129: 103675. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103675. [21] ZHANG Yuxuan, WU Jianxin, and ZHANG Lei. Joint multierror calibration by merging errors in distributed coherent aperture radar using strong scatter echoes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(1): 1148–1158. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3335186. [22] ZENG Tao, YIN Pilei, and LIU Quanhua. Wideband distributed coherent aperture radar based on stepped frequency signal: Theory and experimental results[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(4): 672–688. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0221. [23] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, LI Linghao, et al. First demonstration of single-pass distributed SAR tomographic imaging with a P-band UAV SAR prototype[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5238618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3221859. [24] LIU Ruitao, ZHANG Wei, YU Xianxiang, et al. Transmit-receive beamforming for distributed phased-MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(2): 1439–1453. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3133596. [25] FENG Bokai and DAVID C J. Two-way pattern grating lobe control for distributed digital subarray antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(10): 4375–4383. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2465863. [26] MASSA A, ROCCA P, and OLIVERI G. Compressive sensing in electromagnetics—a review[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2015, 57(1): 224–238. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2015.2397092. [27] LIU Yanhui, NIE Zaiping, and LIU Qinghuo. Reducing the number of elements in a linear antenna array by the matrix pencil method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(9): 2955–2962. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.928801. [28] LIU Yanhui, LIU Qinghuo and NIE Zaiping. Reducing the number of elements in multiple-pattern linear arrays by the extended matrix pencil methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(2): 652–660. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2292529. [29] PINCHERA D, MIGLIORE M D, and PANARIELLO G. Synthesis of large sparse arrays using IDEA (inflating-deflating exploration algorithm)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(9): 4658–4668. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2846777. [30] YAN Chuang, YANG Peng, XING Zhiyu, et al. Synthesis of planar sparse arrays with minimum spacing constraint[J] IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(6): 1095–1098. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2833962. [31] MOHAN A and RAJ A A B. Array thinning of Beamformers using simple genetic algorithm[C]. 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Smart Power System and Sustainable Energy, Keonjhar, India: IEEE, 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CISPSSE49931.2020.9212258. [32] OLIVERI G, ROCCA P, and MASSA A. Reliable diagnosis of large linear arrays-a Bayesian compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(10): 4627–4636. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2207344. [33] HU Liubo, WU Jianxin, and ZHANG Lei. Efficient transceiving search scheme and implementation method for collocated distributed coherent aperture radar via grating lobes exploitation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(9): 2262. doi: 10.3390/rs15092262. [34] NANZER J A. Spatial filtering of grating lobes in mobile sparse arrays[C]. 2016 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Austin, USA: IEEE, 2016: 26–28. doi: 10.1109/RWS.2016.7444354. [35] CHATTERJEE P and NANZER J A. Using platform motion for improved spatial filtering in distributed antenna arrays[C]. 2018 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Anaheim, USA, 2018: 253–255. doi: 10.1109/RWS.2018.8305002. [36] WANG Yuanhao, YANG Qi, Wang Hongqiang, et al. Grating lobe suppression for distributed phased array via accumulated array pattern synthesis[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2023, 22(7): 1527–1531. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2023.3249908. [37] MA Penghui, LI Jianfeng, PAN Jingjing, et al. Enhanced DOA estimation with augmented CADiS by exploiting array motion strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 4713–4727. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3224908. [38] LUO Shuai, WANG Yuexian, LI Jianying, et al. Angle estimation for bistatic MIMO radar with a sparse moving array in the presence of position errors and gain-phase perturbation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(12): 16006–16020. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3294605. [39] 刘兴华, 徐振海, 肖顺平. 分布式相参雷达几何布置约束条件[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09.LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, and XIAO Shunping. Geometric arrangement constraints of distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09. [40] CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873. [41] KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745. [42] XU Luzhou, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Target detection and parameter estimation for MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 927–939. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655353. [43] MGHABGHAB S and NANZER J A. Ranging requirements for open-loop coherent distributed arrays with wireless frequency synchronization[C]. 2020 IEEE USNC-CNC-URSI North American Radio Science Meeting, Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2020: 69–70. doi: 10.23919/USNC/URSI49741.2020.9321643. [44] CHATTERJEE P and NANZER J A. Effects of time alignment errors in coherent distributed radar[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 727–731. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378649. [45] CHALLA S, MORELANDE M R, MUŠICKID, et al. Fundamentals of Object Tracking[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2011. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511975837. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: