Joint Design of LPI Transmit Waveform and Receive Beamforming Based on Neural Networks for FDA-MIMO
-
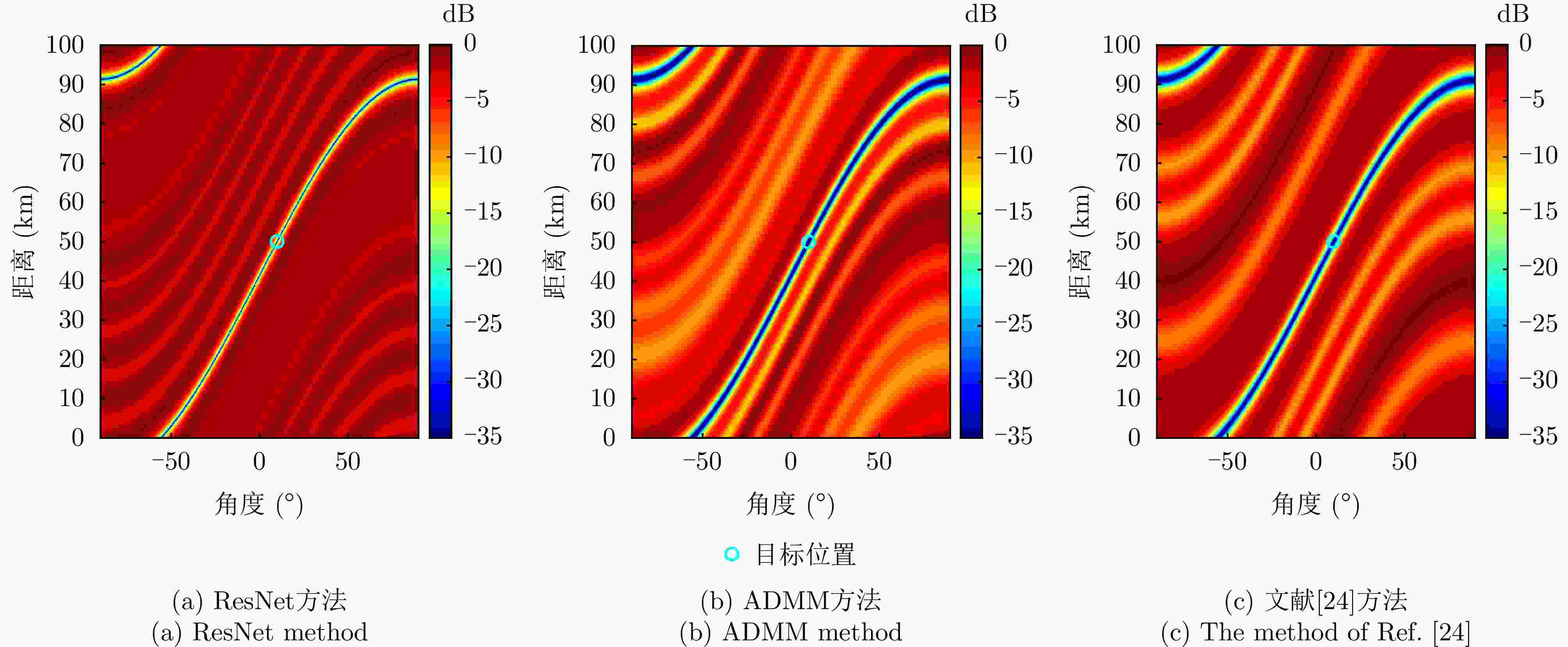
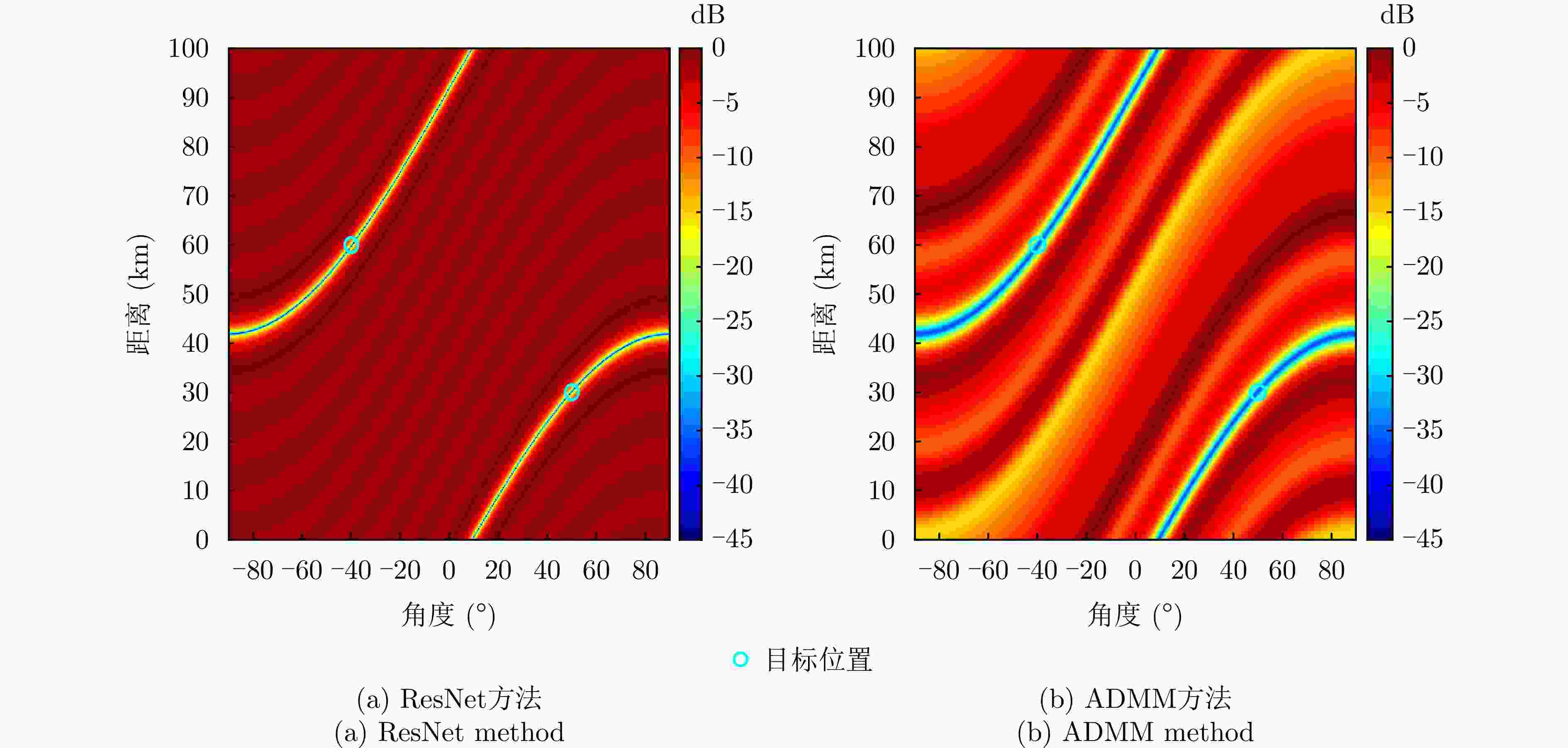
摘要: 针对传统相控阵或多输入多输出(MIMO)体制的低截获概率(LPI)阵列雷达仅能控制特定角度的辐射能量,而无法实现特定区域(距离、角度)能量控制的问题,该文提出一种基于神经网络的频控阵-多输入多输出(FDA-MIMO)雷达低截获概率发射波形设计方法。该方法通过对FDA-MIMO雷达的发射波形和接收波束形成联合设计,在确保雷达对目标检测概率的情况下,将雷达辐射能量均匀地分散到空域当中,并尽可能降低辐射到目标位置的能量,从而减小雷达信号被截获的概率。首先,建立了最小化方向图匹配误差准则下LPI性能发射波形设计和接收波束形成的优化目标函数;然后,将目标函数作为神经网络的损失函数;最后,通过迭代训练最小化神经网络的损失函数,直至网络收敛,求解出发射信号波形和对应的接收加权矢量。仿真结果表明,该文所提方法能更好地控制雷达功率分布,相比于传统算法,控制发射方向图非目标区域的波束能量分布方面有5 dB的改善;此外,在接收端形成的接收方向图波束能量也更为集中,且在多个干扰位置均产生了–50 dB以下的零陷,具有很好的干扰抑制效果。
-
关键词:
- 频控阵-多输入多输出雷达 /
- 低截获概率阵列雷达 /
- 残差神经网络 /
- 波形设计 /
- 波束形成
Abstract: Traditional Low Probability of Intercept (LPI) array radars that use phased array or Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems face limitations in terms of controlling radiation energy only at specific angles and cannot achieve energy control over specific areas of range and angle. To address these issues, this paper proposes an LPI waveform design method for Frequency Diverse Array (FDA)-MIMO radar utilizing neural networks. This method jointly designs the transmit waveform and receive beamforming in FDA-MIMO radars to ensure target detection probability while uniformly distributing radar energy across the spatial domain. This minimizes energy directed toward the target, thereby reducing the probability of the radar signal being intercepted. Initially, we formulate an optimization objective function aimed at LPI performance for transmitting waveform design and receiving beamforming by focusing on minimizing pattern matching errors. This function is then used as the loss function in a neural network. Through iterative training, the neural network minimizes this loss function until convergence, resulting in optimized transmit signal waveforms and solving the corresponding receive weighting vectors. Simulation results indicate that our proposed method significantly enhances radar power distribution control. Compared to traditional methods, it shows a 5 dB improvement in beam energy distribution control across nontarget regions of the transmit beam pattern. Furthermore, the receiver beam pattern achieves more concentrated energy, with deep nulls below −50 dB at multiple interference locations, demonstrating excellent interference suppression capabilities. -
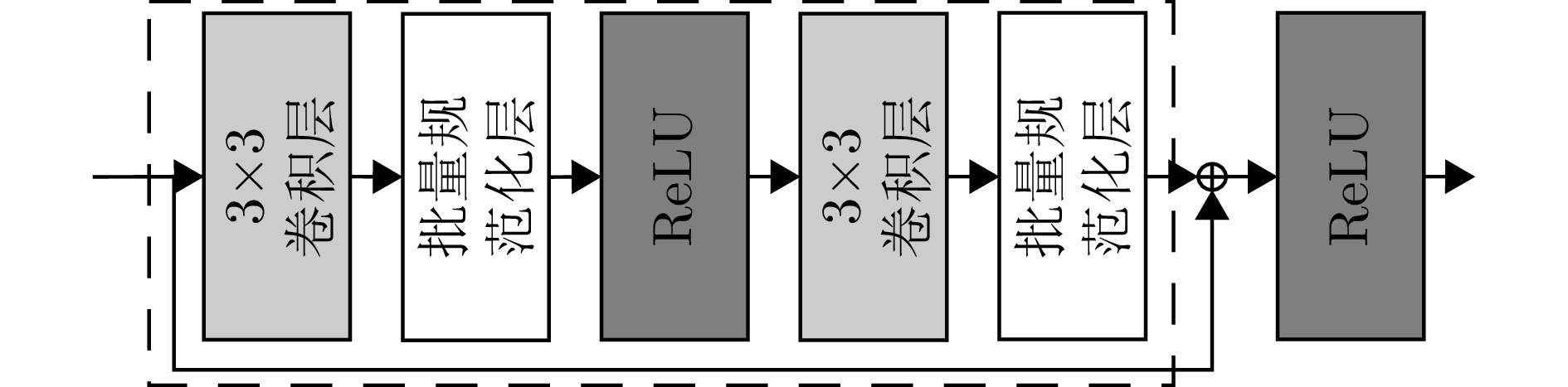
1 基于ResNet的优化算法伪代码
1. Pseudocode for optimization algorithm based on ResNet
1. ResNet I训练 网络输入:随机噪声矩阵 while未达到最大迭代次数or网络未收敛do 根据网络输出计算损失函数: $ \mathcal{L}_{1}(\boldsymbol{S}) \leftarrow\left\{\operatorname{Re}\left(\boldsymbol{S}^{\mathrm{H}} {\boldsymbol{a}}(r, \theta)\right), \operatorname{Im}\left(\boldsymbol{S}^{\mathrm{H}} {\boldsymbol{a}}(r, \theta)\right)\right\} $
$ \leftarrow\{\operatorname{Re}(\boldsymbol{S}), \operatorname{Im}(\boldsymbol{S})\} \leftarrow \boldsymbol{x}_{\text {outI }} $使用自适应优化算法(Adaptive Moment Estimation, Adam)
更新网络参数end while 输出波形$ {\boldsymbol{s}} $
$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}}=\operatorname{vec}(\boldsymbol{S})={\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}} {\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\mathrm{outI}}}} $2. ResNet II训练 网络输入:随机噪声矩阵 while未达到最大迭代次数or网络未收敛do 根据网络输出计算损失函数:
${\mathcal{L}}_{{\mathrm{II}}}({\boldsymbol{w}}) \leftarrow \left\{ {\mathrm{Re}}\left({\boldsymbol{w}}^{\mathrm{H}}\tilde {\boldsymbol{S}} {\boldsymbol{v}}(r,\theta) \right),\;{\mathrm{Im}}\left({\boldsymbol{w}}^{\mathrm{H}}\tilde {\boldsymbol{S}}{\boldsymbol{v}}(r,\theta) \right)\right\} $
$\leftarrow {\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\mathrm{outII}}} $使用自适应优化算法Adam更新网络参数 end while 输出接收加权矢量w ${\boldsymbol{w}}={\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\mathrm{outII}}}(1:NL)+{\mathrm{j}} {\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\mathrm{outII}}} (NL+1:2NL)$ 表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameter setting
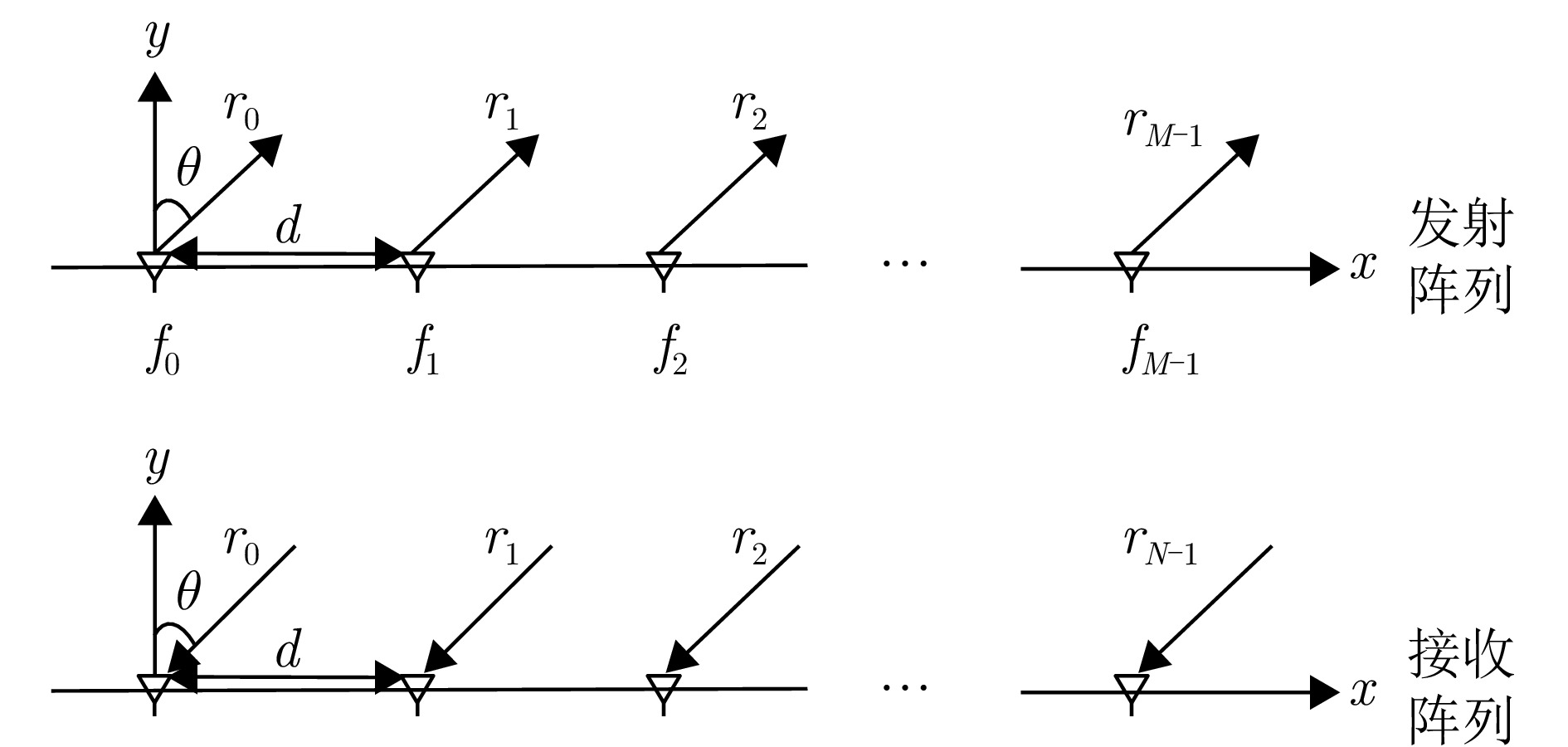
参数名称 符号 数值 发射阵元数 $ M $ $ 10 $ 接收阵元数 $ N $ $ 10 $ 发射波形样本数 $ L $ $ 8 $ 参考载频 $ f_{0} $ $ \text { 10 GHz } $ 频偏增量 $ \Delta f $ $ 3 \;\mathrm{kHz} $ 带宽 $ { B } $ $ 3\; \mathrm{kHz} $ 光速 $ \rm{c} $ $ 3 \times 10^{8} \;\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s} $ 阵元间距 $ d $ $ {\mathrm{c}} /\left(2 f_{0}\right) $ 距离观测范围 $ r$ $ [0: 0.1: 100] \;\mathrm{km} $ 角度观测范围 $ \theta $ $ \left[-90^{\circ}: 0.5^{\circ}: 90^{\circ}\right] $ 目标权重 $ \omega_{k} $ $ 1 $ 旁瓣区域权重 $ \omega_{p, q} $ $ 1 $ 干扰区域权重 $ \omega_{i} $ $ 1 $ 方向图主瓣调节参数 $ \mu $ $ 4 $ -
[1] ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. The 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 215–217. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631800. [2] WANG Wenqin. Overview of frequency diverse array in radar and navigation applications[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(6): 1001–1012. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0464. [3] 朱圣棋, 余昆, 许京伟, 等. 波形分集阵列新体制雷达研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188.ZHU Shengqi, YU Kun, XU Jingwei, et al. Research progress and prospect for the noval waveform diverse array radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188. [4] 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 廖桂生, 等. 频率分集阵雷达技术探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023.XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, LIAO Guisheng, et al. An overview of frequency diverse array radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023. [5] 王文钦, 张顺生. 频控阵雷达技术研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 830–849. doi: 10.12000/JR22141.WANG Wenqin and ZHANG Shunsheng. Recent advances in frequency diverse array radar techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 830–849. doi: 10.12000/JR22141. [6] CHEN Kejin, YANG Shiwen, CHEN Yikai, et al. Accurate models of time-invariant beampatterns for frequency diverse arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(5): 3022–3029. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2896712. [7] TAN Ming, WANG Chunyang, and LI Zhihui. Correction analysis of frequency diverse array radar about time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(2): 834–847. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3016508. [8] SAMMARTINO P F, BAKER C J, and GRIFFITHS H D. Frequency diverse MIMO techniques for radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 201–222. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404099. [9] ZHONG Tiantian, TAO Haihong, CAO Han, et al. Multiparameter estimation for monostatic FDA-MIMO radar with polarimetric antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2024, 72(3): 2524–2539. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2024.3353345. [10] 张顺生, 刘美慧, 王文钦. 基于多普勒扩展补偿的FDA-MIMO雷达运动目标检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 666–675. doi: 10.12000/JR22042.ZHANG Shunsheng, LIU Meihui, and WANG Wenqin. FDA-MIMO radar moving target detection based on Doppler spread compensation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 666–675. doi: 10.12000/JR22042. [11] BASIT A, WANG Wenqin, NUSENU S Y, et al. Cognitive FDA-MIMO with channel uncertainty information for target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(4): 963–975. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2928799. [12] LAN Lan, MARINO A, AUBRY A, et al. GLRT-based adaptive target detection in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 597–613. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3028485. [13] ZHU Jingjing, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Discrimination of target and mainlobe jammers with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 583–587. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3276630. [14] 林洋, 张顺生, 王文钦. FDA-MIMO雷达主瓣距离模糊杂波抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(1): 84–92. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.011.LIN Yang, ZHANG Shunsheng, and WANG Wenqin. Main-beam range-ambiguous clutter suppression method with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(1): 84–92. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.011. [15] LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Suppression approach to main-beam deceptive jamming in FDA-MIMO radar using nonhomogeneous sample detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34582–34597. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2850816. [16] CHEN Kejin, YANG Shiwen, CHEN Yikai, et al. Transmit beamforming based on 4-D antenna arrays for low probability of intercept systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(5): 3625–3634. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2963593. [17] 万环, 余显祥, 全智, 等. 基于交替方向惩罚法的低精度量化MIMO雷达恒模波形设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 557–569. doi: 10.12000/JR22072.WAN Huan, YU Xianxiang, QUAN Zhi, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for low-resolution quantization MIMO radar based on an alternating direction penalty method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 557–569. doi: 10.12000/JR22072. [18] HE Qin, HE Zishu, WANG Zhihang, et al. Co-design of transmit-receive weights for MIMO system with LPI and multi-targets[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(8): 1863–1867. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3176011. [19] DENG Hai. Waveform design for MIMO radar with low probability of intercept (LPI) property[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, USA, 2011: 305–308. doi: 10.1109/APS.2011.5996703. [20] SHI Chenguang, WANG Fei, SELLATHURAI M, et al. Low probability of intercept-based distributed MIMO radar waveform design against barrage jamming in signal-dependent clutter and coloured noise[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2019, 13(4): 415–423. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2018.5212. [21] WANG Liu, WANG Wenqin, GUAN Haoliang, et al. LPI property of FDA transmitted signal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3905–3915. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3083402. [22] XIONG Jie, WANG Wenqin, CUI Can, et al. Cognitive FDA-MIMO radar for LPI transmit beamforming[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1574–1580. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0551. [23] GONG Pengcheng, JIANG Panke, and WU Yuntao. Transmit beamforming design for LPI of frequency diverse array MIMO radar[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar, Haikou, China, 2021: 1910–1913. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028350. [24] GONG Pengcheng, ZHANG Zhuoyu, WU Yuntao, et al. Joint design of transmit waveform and receive beamforming for LPI FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 1938–1942. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3205206. [25] ZHANG Weijian, HU Jinfeng, WEI Zhiyong, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for MIMO radar transmit beampattern with residual network[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 177: 107735. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107735. [26] SALLAM T, ABDEL-RAHMAN A B, ALGHONIEMY M, et al. A neural-network-based beamformer for phased array weather radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5095–5104. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2554116. [27] ZHAO Zhonghui, ZHAO Huiling, WANG Zhaoping, et al. Radial basis function neural network optimal modeling for phase-only array pattern nulling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(11): 7971–7975. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2021.3083787. [28] 丁梓航, 谢军伟, 王博. 基于深度学习的FDA-MIMO雷达协方差矩阵缺失数据恢复方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1112–1124. doi: 10.12000/JR23002.DING Zihang, XIE Junwei, and WANG Bo. Missing covariance matrix recovery with the FDA-MIMO radar using deep learning method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1112–1124. doi: 10.12000/JR23002. [29] SALLAM T and ATTIYA A M. Convolutional neural network for 2D adaptive beamforming of phased array antennas with robustness to array imperfections[J]. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2021, 13(10): 1096–1102. doi: 10.1017/S1759078721001070. [30] WU Yue, CHEN Yinpeng, YUAN Lu, et al. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10183–10192. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01020. [31] JIA Wenkai, JAKOBSSON A, and WANG Wenqin. Designing FDA radars robust to contaminated shared spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 2861–2873. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3221030. [32] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, ZHANG Shengmiao, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for MIMO radar transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(18): 4912–4923. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2718976. [33] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: