Active Blanket Jamming Suppression Method for Spaceborne SAR Images Based on Regional Feature Refinement Perceptual Learning
-
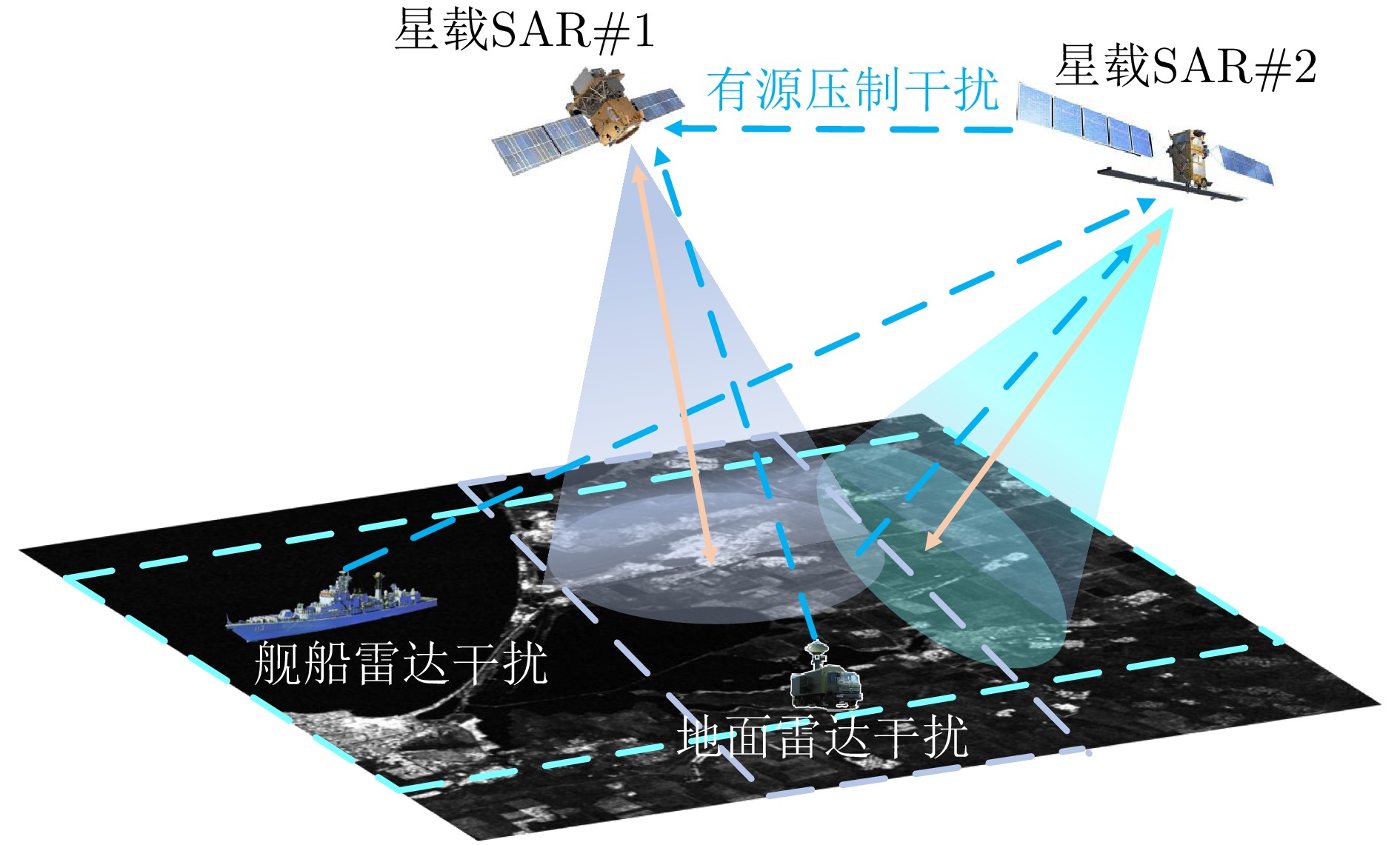
摘要: 星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)系统常受到强电磁干扰而导致成像质量下降,但现有基于图像域的干扰抑制方法易造成图像失真、纹理细节信息丢失等难题。针对上述问题,该文提出了一种基于区域特征细化感知学习的星载SAR图像有源压制干扰抑制方法。首先,建立了星载SAR图像域有源压制干扰信号和图像模型;其次,设计一种基于区域特征感知的高精度干扰识别网络,利用高效通道注意力机制,提取SAR图像有源压制干扰图样特征,可以有效识别SAR图像干扰区域;然后,构建一种基于SAR图像和压制干扰特征联合学习的多元区域特征细化干扰抑制网络,将SAR图像切分为多元区域,采用多模块协同处理多元区域上的压制干扰特征,实现复杂场景条件下SAR图像有源压制干扰的精细化抑制。最后,构建SAR图像有源压制干扰仿真数据集,且采用哨兵1号实测数据进行实验验证分析。实验结果表明所提方法能有效识别和抑制星载SAR图像多种典型有源压制干扰。Abstract: Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems are often subject to strong electromagnetic interference, resulting in imaging quality degradation. However, existing image domain-based interference suppression methods are prone to image distortion and loss of texture detail information, among other difficulties. To address these problems, this paper proposes a method for suppressing active suppression interferences inspaceborne SAR images based on perceptual learning of regional feature refinement. First, an active suppression interference signal and image model is established in the spaceborne SAR image domain. Second, a high-precision interference recognition network based on regional feature perception is designed to extract the active suppression interference pattern features of the involved SAR image using an efficient channel attention mechanism, consequently resulting in effective recognition of the interference region of the SAR image. Third, a multivariate regional feature refinement interference suppression network is constructed based on the joint learning of the SAR image and suppression interference features, which are combined to form the SAR image and suppression interference pattern. A feature refinement interference suppression network is then constructed based on the joint learning of the SAR image and suppression interference feature. The network slices the SAR image into multivariate regions, and adopts multi-module collaborative processing of suppression interference features on the multivariate regions to realize refined suppression of the active suppression interference of the SAR image under complex conditions. Finally, a simulation dataset of SAR image active suppression interference is constructed, and the evaluated Sentinel-1 data are used for experimental verification and analysis. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively recognize and suppress various typical active suppression interferences in spaceborne SAR images.
-
表 1 干扰参数设置
Table 1. Jamming parameters configuration
参数 移频干扰及噪声卷积调制干扰 射频噪声干扰 中心频率 4 GHz 10 GHz 采样率 120 MHz 120 MHz 脉冲持续时间 3 μs 10 μs 调频斜率 1.6655 $ \times $1013 Hz/s5$ \times $1013 Hz/s 脉冲重复频率 1000 Hz1000 Hz场景中心最近斜距 1136 m8485 m表 2 5种网络识别性能比较(%)
Table 2. Comparison of recognition performance of five networks (%)
测试集 方法 射频噪声干扰 卷积调制干扰 移频干扰 无干扰 OA
Test_1SpnasNet100 95.208 88.125 93.375 94.750 92.865 FBNetc100 97.750 83.750 94.620 97.083 93.301 ResNet18 82.604 73.750 80.067 81.625 79.512 MnasNet 96.250 92.500 95.625 97.060 95.359 IRRFPNet 99.806 99.628 99.760 99.905 99.775 Test_2 SpnasNet100 95.833 78.625 89.500 91.792 88.938 FBNetc100 96.235 84.375 94.125 93.958 92.173 ResNet18 81.460 72.165 77.250 82.500 78.344 MnasNet 98.750 91.875 96.250 95.625 96.625 IRRFPNet 99.875 99.792 99.840 99.925 99.858
Test_3SpnasNet100 92.315 82.583 96.250 89.255 90.101 FBNetc100 95.000 85.250 90.402 94.750 91.351 ResNet18 80.572 74.500 81.267 79.875 79.054 MnasNet 97.372 85.625 98.125 96.958 94.520 IRRFPNet 99.790 99.895 99.370 100.00 99.764
Test_4SpnasNet100 94.875 81.015 92.000 92.583 90.118 FBNetc100 93.750 80.625 91.535 95.000 90.228 ResNet18 79.708 72.250 78.375 80.917 77.813 MnasNet 98.125 87.500 97.500 97.002 95.032 IRRFPNet 99.885 99.680 99.792 99.950 99.827 表 3 不同方法仿真实验的IEN, ISH及ICO指标计算结果
Table 3. Calculation of IEN, ISH and ICO for simulation experiments with different methods
场景(图10) 方法 IEN ISH ICO 场景1 真值图像 5.2194 – 17.6613 3.0279 陷波滤波方法 5.3487 – 19.6172 4.2246 RESCAN 5.2284 – 14.7195 1.5356 DRDNet 5.2154 – 17.6395 3.0118 DRFRISNet 5.2195 – 17.6701 3.0127 场景2 真值图像 5.9682 – 15.2466 1.7486 陷波滤波方法 5.4960 – 19.9296 3.5259 RESCAN 5.9116 – 14.1725 1.3188 DRDNet 5.9688 – 15.2465 1.7455 DRFRISNet 5.9678 – 15.2465 1.7480 场景3 真值图像 6.9088 – 9.6839 1.1570 陷波滤波方法 6.6281 – 13.7598 1.7738 RESCAN 7.1879 – 8.9641 1.0095 DRDNet 7.0350 – 9.3704 1.2169 DRFRISNet 6.8098 – 9.7194 1.1240 场景4 真值图像 6.9806 – 10.5063 1.6968 陷波滤波方法 6.9089 – 12.4531 1.6764 RESCAN 7.0970 – 8.9138 1.2965 DRDNet 6.9258 – 10.1447 1.6503 DRFRISNet 6.9495 – 10.2587 1.6625 表 4 不同方法仿真实验的PSNR及SSIM指标计算结果
Table 4. Calculation of PSNR and SSIM for simulation experiments with different methods
场景(图10) 陷波滤波方法 RESCAN DRDNet DRFRISNet PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM 场景1 16.3777 0.0386 27.7221 0.8847 31.2742 0.9459 37.9279 0.9889 场景2 16.2330 0.4063 29.2225 0.8790 33.7739 0.9582 38.4685 0.9905 场景3 13.8495 0.3880 26.3501 0.8551 30.8176 0.9351 33.5751 0.9818 场景4 15.0873 0.5388 26.6142 0.8661 31.9454 0.9405 34.2852 0.9872 表 5 不同方法实测实验的IEN, ISH及ICO指标计算结果
Table 5. Calculation of IEN, ISH and ICO for simulation experiments with different methods
场景(图14) 方法 IEN ISH ICO 场景(图14) 方法 IEN ISH ICO 场景5 真值图像 4.2833 – 15.9504 4.8074 场景8 真值图像 6.4156 – 12.9350 1.6968 陷波滤波方法 5.4302 – 16.9256 3.9217 陷波滤波方法 5.2377 – 22.1863 1.6764 RESCAN 2.0471 – 16.5179 4.7079 RESCAN 5.8306 – 14.1303 1.2965 DRDNet 2.1126 – 16.3571 4.9755 DRDNet 5.8738 – 14.5922 1.6503 DRFRISNet 4.5146 – 16.0021 4.8075 DRFRISNet 5.8820 – 12.8447 1.6625 场景6 真值图像 7.6337 – 6.8687 1.7486 场景9 真值图像 4.7258 – 13.1804 1.1027 陷波滤波方法 6.9500 – 12.0783 3.5259 陷波滤波方法 5.7357 – 18.7759 1.2968 RESCAN 7.5334 – 7.1883 1.3188 RESCAN 3.0881 – 16.2433 0.9492 DRDNet 7.5670 – 6.7022 1.7455 DRDNet 5.3006 – 13.4509 1.0238 DRFRISNet 7.6074 – 6.9875 1.7480 DRFRISNet 4.3446 – 13.0803 1.0785 场景7 真值图像 6.6716 – 10.5940 1.1570 场景10 真值图像 7.0936 – 9.2369 1.0057 陷波滤波方法 5.8949 – 18.3770 1.7738 陷波滤波方法 6.1757 – 16.8893 1.8313 RESCAN 6.3696 – 9.1933 1.0095 RESCAN 6.6451 – 11.9947 0.9725 DRDNet 6.3970 – 9.5748 1.2169 DRDNet 6.6612 – 10.5871 1.0673 DRFRISNet 6.4196 – 10.5294 1.1240 DRFRISNet 6.8497 – 10.0975 1.0162 表 6 不同方法实测实验的PSNR及SSIM指标计算结果
Table 6. Calculation of PSNR and SSIM for simulation experiments with different methods
场景(图14) 干扰图像 陷波滤波方法 RESCAN DRDNet DRFRISNet PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM 场景5 30.4133 0.9762 23.7897 0.8769 29.8113 0.9709 30.4442 0.9777 33.8496 0.9895 场景6 17.0048 0.8226 10.8052 0.2450 19.7852 0.8897 22.0794 0.9336 24.2911 0.9615 场景7 17.4517 0.5136 11.2595 0.1435 23.8517 0.7756 24.4211 0.8170 25.1023 0.8409 场景8 20.6213 0.6646 14.5254 0.1686 22.9472 0.7413 24.4636 0.7874 26.4066 0.9075 场景9 20.1741 0.8653 15.3698 0.3536 22.1510 0.8895 30.3326 0.9860 31.6360 0.9910 场景10 16.5528 0.5407 11.5139 0.1652 18.8683 0.6463 20.3926 0.7298 30.9412 0.9693 表 7 对LLFE单元进行消融实验的PSNR及SSIM指标计算结果
Table 7. Calculation of PSNR and SSIM metrics for ablation experiments on LLFE-Moudle
场景(图16) 无LLFE单元 有LLFE单元 PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM 场景11 23.7820 0.8988 30.5310 0.9815 场景12 19.0430 0.8691 24.1102 0.9586 场景13 24.3205 0.7932 25.2305 0.8490 场景14 21.5722 0.7218 26.7804 0.9118 -
[1] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099. [2] 吴一戎, 朱敏慧. 合成孔径雷达技术的发展现状与趋势[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2000, 15(2): 121–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012.WU Yirong and ZHU Minhui. The developing status and trends of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2000, 15(2): 121–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012. [3] 邓云凯, 禹卫东, 张衡, 等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008.DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008. [4] 王谋, 韦顺军, 沈蓉, 等. 基于自学习稀疏先验的三维SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101.WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHEN Rong, et al. 3D SAR imaging method based on learned sparse prior[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101. [5] ZHANG Hao, WEI Shunjun, WANG Mou, et al. FUAS-Net: Feature-oriented unsupervised network for FMCW radar interference suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(4): 2602–2619. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3318669. [6] WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, et al. Efficient ADMM framework based on functional measurement model for mmW 3-D SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5226417. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3165541. [7] WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, et al. CTV-Net: Complex-valued TV-driven network with nested topology for 3-D SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(4): 5588–5602. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3208252. [8] 林晓烘. 星载合成孔径雷达干扰与抗干扰技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.LIN Xiaohong. Study on jamming and anti-jamming techniques for spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [9] 黄岩, 赵博, 陶明亮, 等. 合成孔径雷达抗干扰技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113.HUANG Yan, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. Review of synthetic aperture radar interference suppression[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113. [10] LAMONT-SMITH T, HILL R D, HAYWARD S D, et al. Filtering approaches for interference suppression in low-frequency SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(4): 338–344. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20050092. [11] 韩朝赟, 岑熙, 崔嘉禾, 等. 纹理异常感知SAR自监督学习干扰抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168.HAN Zhaoyun, CEN Xi, CUI Jiahe, et al. Self-supervised learning method for SAR interference suppression based on abnormal texture perception[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168. [12] ZHOU Feng, WU Renbiao, XING Mengdao, et al. Eigensubspace-based filtering with application in narrow-band interference suppression for SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(1): 75–79. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.887033. [13] LIU Zhiling, LIAO Guisheng, and YANG Zhiwei. Time variant RFI suppression for SAR using iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1424–1428. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2259575. [14] SU Jia, TAO Haihong, TAO Mingliang, et al. Narrow-band interference suppression via RPCA-based signal separation in time-frequency domain[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(11): 5016–5025. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2727520. [15] HUANG Yan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Narrowband RFI suppression for SAR system via efficient parameter-free decomposition algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3311–3322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2797946. [16] REIGBER A and FERRO-FAMIL L. Interference suppression in synthesized SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(1): 45–49. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.838419. [17] YANG Huizhang, LI Kun, LI Jie, et al. BSF: Block subspace filter for removing narrowband and wideband radio interference artifacts in single-look complex SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3096538. [18] YANG Huizhang, HE Yaomin, DU Yanlei, et al. Two-dimensional spectral analysis filter for removal of LFM radar interference in spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5219016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3132495. [19] YANG Huizhang, LANG Ping, LU Xingyu, et al. Robust block subspace filtering for efficient removal of radio interference in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5206812. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3369021. [20] 陈爽. 基于深度学习的雷达有源欺骗干扰识别方法[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2023. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2023.001330.CHEN Shuang. Identification method of radar active deception jamming based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2023.001330. [21] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143.CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143. [22] 张顺生, 陈爽, 陈晓莹, 等. 面向小样本的多模态雷达有源欺骗干扰识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104.ZHANG Shunsheng, CHEN Shuang, CHEN Xiaoying, et al. Active deception jamming recognition method in multimodal radar based on small samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104. [23] FAN Weiwei, ZHOU Feng, TAO Mingliang, et al. Interference mitigation for synthetic aperture radar based on deep residual network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(14): 1654. doi: 10.3390/rs11141654. [24] CHEN Shengyi, SHANGGUAN Wangyi, TAGHIA J, et al. Automotive radar interference mitigation based on a generative adversarial network[C]. 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2020: 728–730. doi: 10.1109/APMC47863.2020.9331379. [25] SHEN Jiayuan, HAN Bing, PAN Zongxu, et al. Radio frequency interference suppression in SAR system using prior-induced deep neural network[C]. 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 943–946. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883464. [26] WEI Yanyan, ZHANG Zhao, ZHANG Haijun, et al. A coarse-to-fine multi-stream hybrid deraining network for single image deraining[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Beijing, China, 2019: 628–637. doi: 10.1109/ICDM.2019.00073. [27] WU Haiyan, QU Yanyun, LIN Shaohui, et al. Contrastive learning for compact single image dehazing[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10546–10555. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01041. [28] HONG Ming, XIE Yuan, LI Cuihua, et al. Distilling image dehazing with heterogeneous task imitation[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3459–3468. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00352. [29] CUI Xin, WANG Cong, REN Dongwei, et al. Semi-supervised image deraining using knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(12): 8327–8341. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3190516. [30] LI Ning, LV Zongsen, and GUO Zhengwei. Observation and mitigation of mutual RFI between SAR satellites: A case study between Chinese GaoFen-3 and European Sentinel-1A[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5112819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3170363. [31] YANG Huizhang, TAO Mingliang, CHEN Shengyao, et al. On the mutual interference between spaceborne SARs: Modeling, characterization, and mitigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(10): 8470–8485. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3036635. [32] 曲婧华. 有源噪声调制干扰的仿真及性能分析[J]. 空军工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 8(1): 44–46.QU Jinghua. Simulation and analysis of complex active noise modulation jamming[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2007, 8(1): 44–46. [33] 殷加鹏, 李健兵, 庞晨, 等. 一种极化-多普勒气象雷达的射频干扰滤波方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 905–918. doi: 10.12000/JR21102.YIN Jiapeng, LI Jianbing, PANG Chen, et al. A radio frequency interference mitigation method for polarimetric Doppler weather radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 905–918. doi: 10.12000/JR21102. [34] 房明星, 王杰贵, 雷磊. SAR雷达二维噪声卷积调制干扰研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2014, 42(2): 139–144, 160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.02.025.FANG Mingxing, WANG Jiegui, and LEI Lei. Study on 2D noise convolution modulation jamming to SAR[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2014, 42(2): 139–144, 160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.02.025. [35] 黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的移频干扰研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2006, 27(3): 463–468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.03.027.HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. A study on the shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2006, 27(3): 463–468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.03.027. [36] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155. [37] OYEDOTUN O K, AL ISMAEIL K, and AOUADA D. Why is everyone training very deep neural network with skip connections?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 5961–5975. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3131813. [38] ZHANG Hongguang, DAI Yuchao, LI Hongdong, et al. Deep stacked hierarchical multi-patch network for image deblurring[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5971–5979. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00613. [39] ZAMIR S W, ARORA A, KHAN S, et al. Multi-stage progressive image restoration[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14816–14826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01458. [40] BARRON J T. A general and adaptive robust loss function[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4326–4334. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00446. [41] SEIF G and ANDROUTSOS D. Edge-based loss function for single image super-resolution[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 1468–1472. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461664. [42] 朱铮涛, 黎绍发, 陈华平. 基于图像熵的自动聚焦函数研究[J]. 光学精密工程, 2004, 12(5): 537–542. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2004.05.014.ZHU Zhengtao, LI Shaofa, and CHEN Huaping. Research on auto-focused function based on the image entropy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2004, 12(5): 537–542. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2004.05.014. [43] 王凡, 倪晋平, 董涛, 等. 结合视觉注意力机制和图像锐度的无参图像质量评价方法[J]. 应用光学, 2018, 39(1): 51–56. doi: 10.5768/JAO201839.0102002.WANG Fan, NI Jinping, DONG Tao, et al. No-reference image quality assessment method based on visual attention mechanism and sharpness metric approach[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2018, 39(1): 51–56. doi: 10.5768/JAO201839. 0102002. [44] 王俊平, 李锦. 图像对比度增强研究的进展[J]. 电子科技, 2013, 26(5): 160–165. doi: 10.16180/j.cnki.issn1007-7820.2013.05.045.WANG Junping and LI Jin. Development and prospect of image contrast enhancement[J]. Electronic Science & Technology, 2013, 26(5): 160–165. doi: 10.16180/j.cnki.issn1007-7820.2013.05.045. [45] HORÉ A and ZIOU D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM[C]. 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 2010: 2366–2369. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2010.579. [46] BAKUROV I, BUZZELLI M, SCHETTINI R, et al. Structural similarity index (SSIM) revisited: A data-driven approach[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 189: 116087. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116087. [47] GUPTA N and AGARWAL B B. Suspicious activity classification in classrooms using deep learning[J]. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 2023, 13(6): 12226–12230. doi: 10.48084/etasr.6228. [48] WU Bichen, DAI Xiaoliang, ZHANG Peizhao, et al. FBNet: Hardware-aware efficient ConvNet design via differentiable neural architecture search[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10726–10734. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01099. [49] CHEN Zhao, JIANG Yin, ZHANG Xiaoyu, et al. ResNet18DNN: Prediction approach of drug-induced liver injury by deep neural network with ResNet18[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2022, 23(1): bbab503. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab503. [50] TAN Mingxing, CHEN Bo, PANG Ruoming, et al. MnasNet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2815–2823. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00293. [51] 张晓明, 王莎莎. 针对窄带干扰抑制的数字陷波器设计[J]. 无线电工程, 2008, 38(5): 24–25, 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2008.05.008.ZHANG Xiaoming and WANG Shasha. Methods for IIR digital notch filter to suppress narrow-band interference[J]. Radio Engineering, 2008, 38(5): 24–25, 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2008.05.008. [52] 刘江, 李健聪, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于自适应陷波滤波的列车卫星定位窄带干扰防护[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(5): 49–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.05.007.LIU Jiang, LI Jiancong, CAI Bogen, et al. Narrow-band interference protection for satellite-based train positioning based on adaptive notch filter[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(5): 49–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.05.007. [53] LI Xia, WU Jianlong, LIN Zhouchen, et al. Recurrent squeeze-and-excitation context aggregation net for single image deraining[C]. 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 2018: 262–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_16. [54] DENG Sen, WEI Mingqiang, WANG Jun, et al. Detail-recovery image deraining via context aggregation networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 14548–14557. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01457. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: