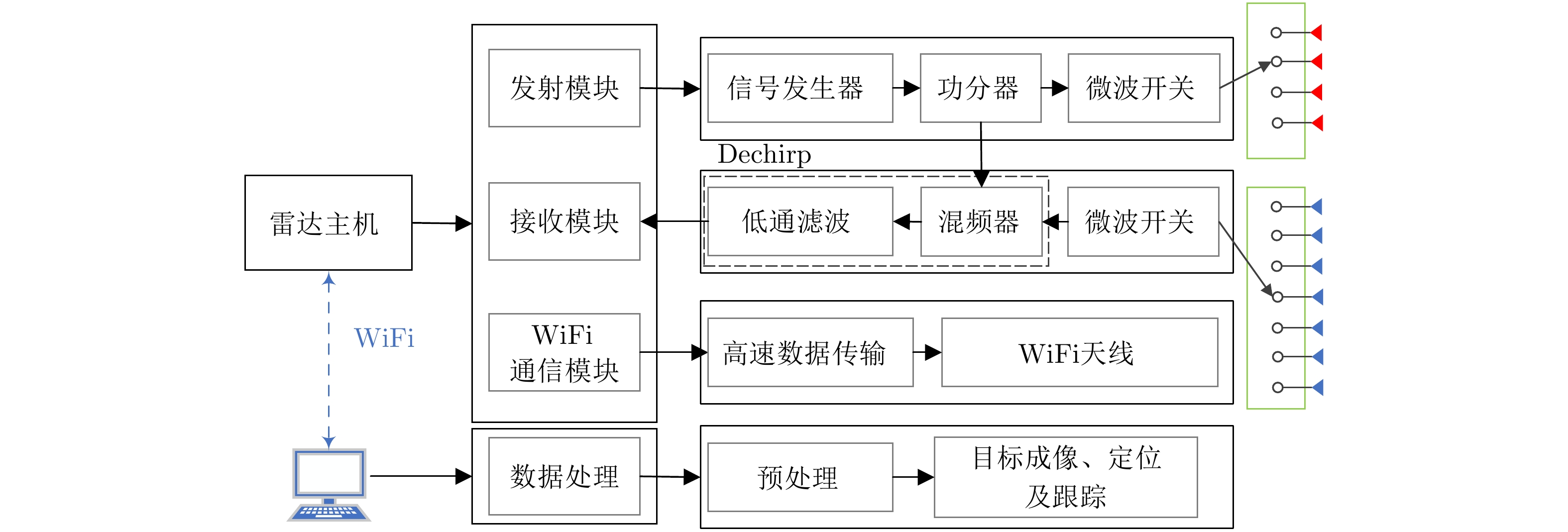
-
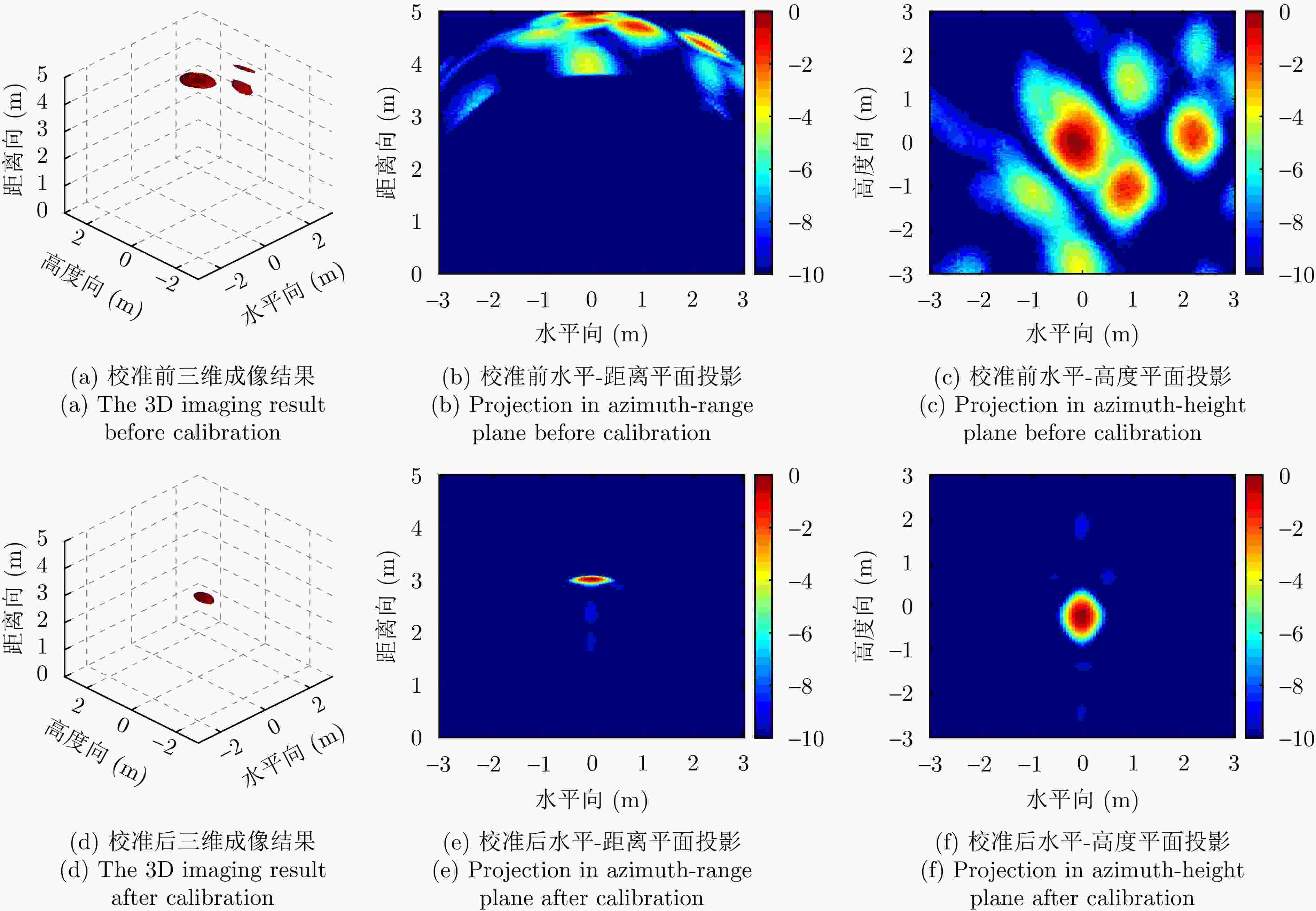
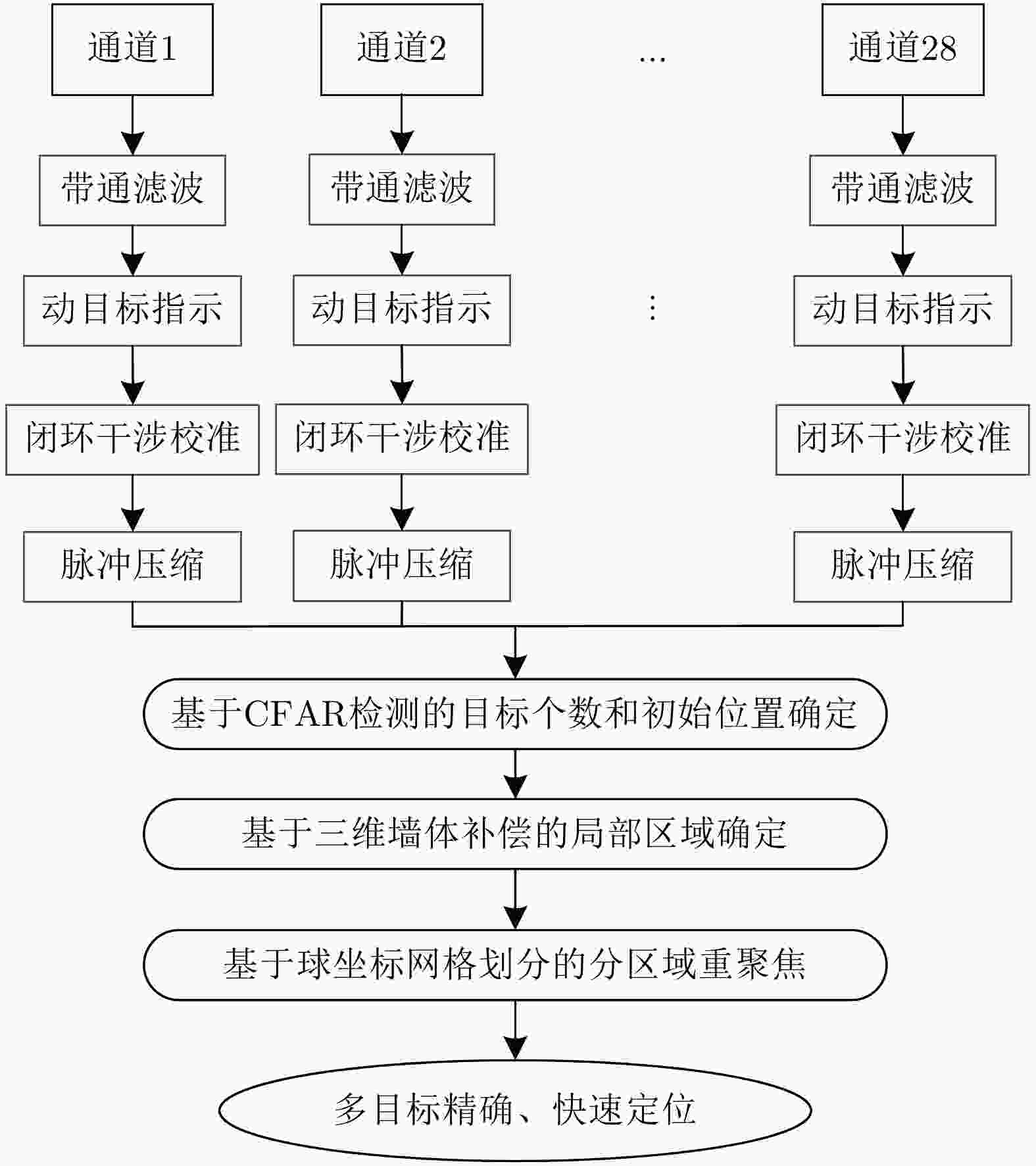
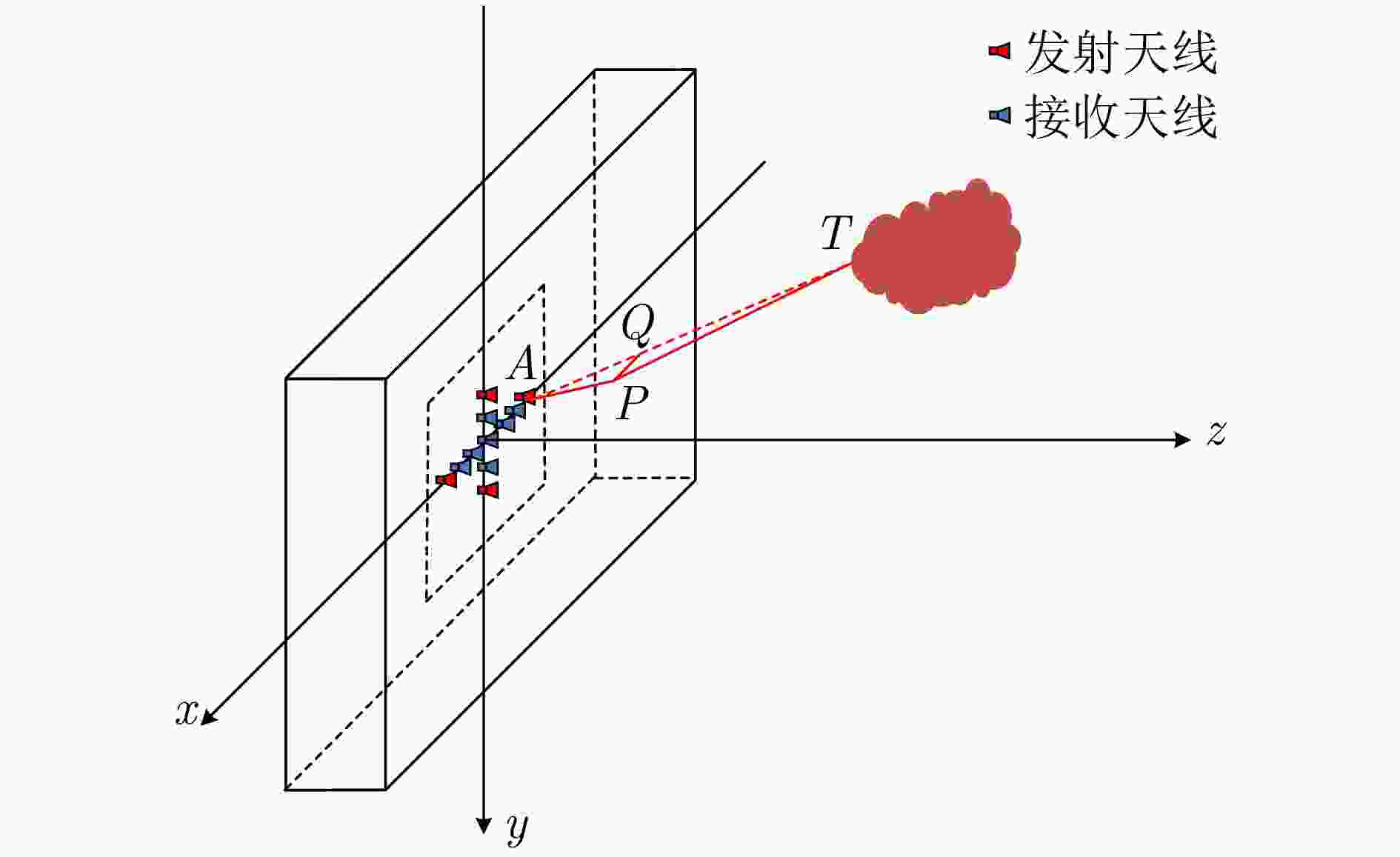
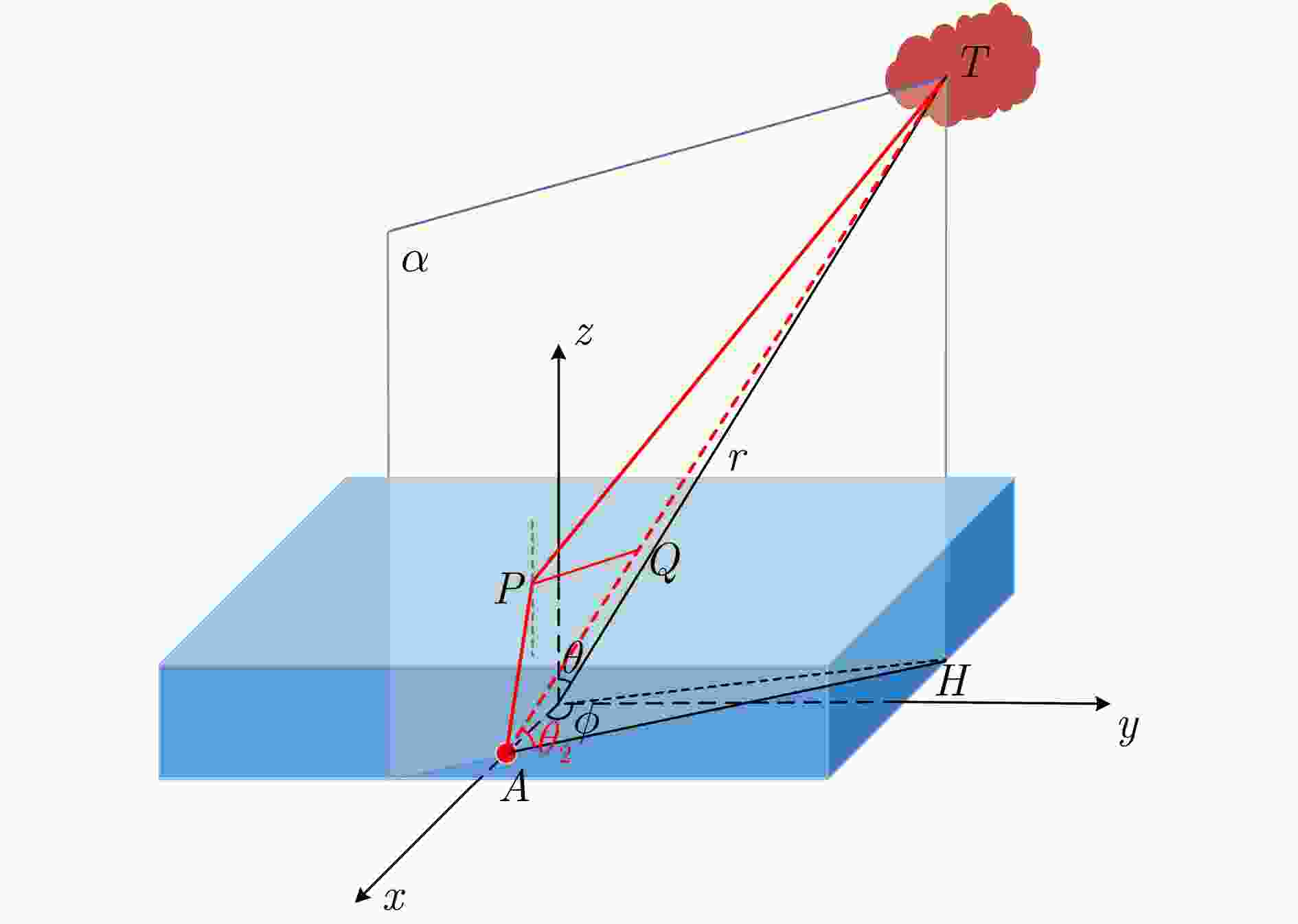
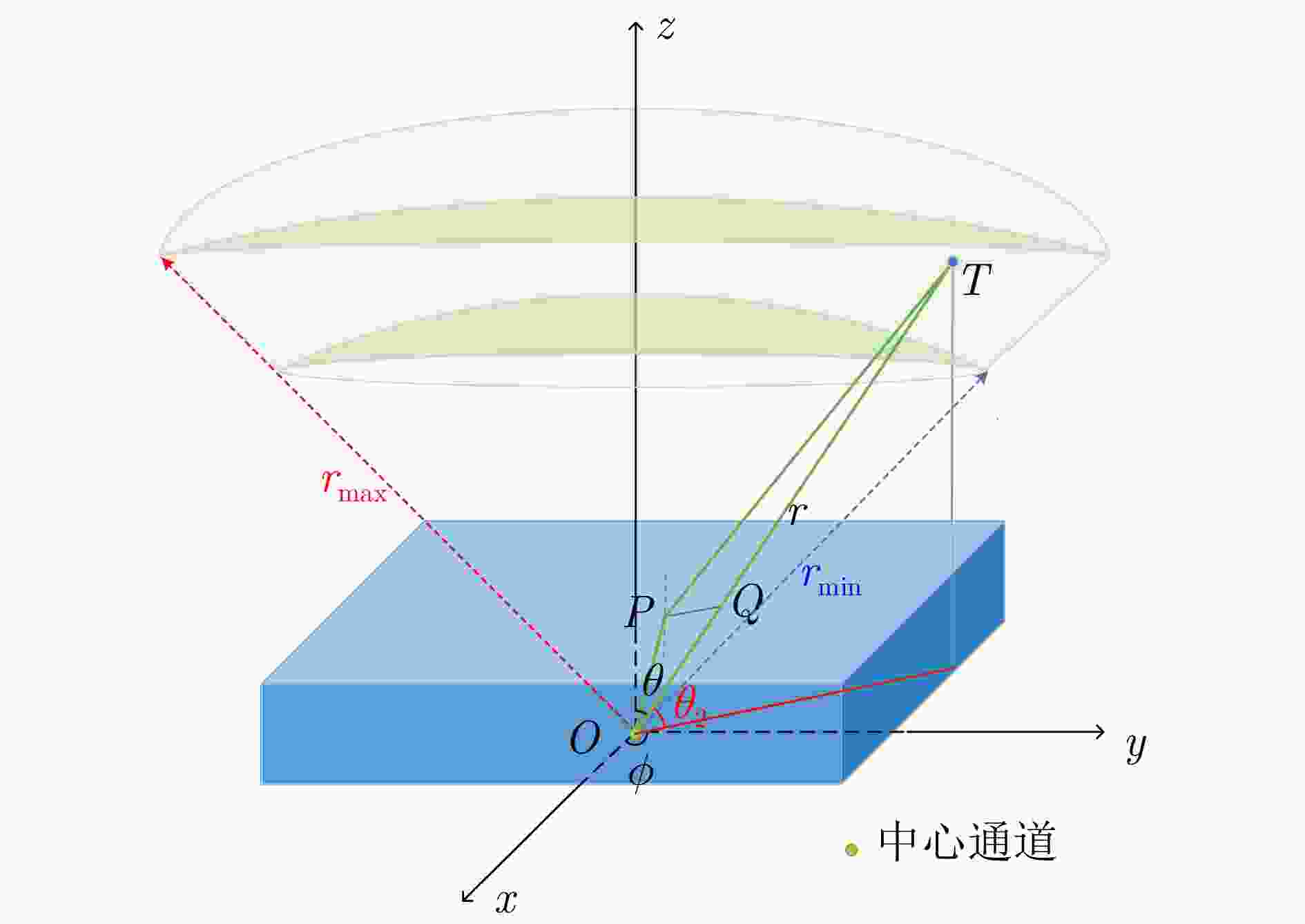
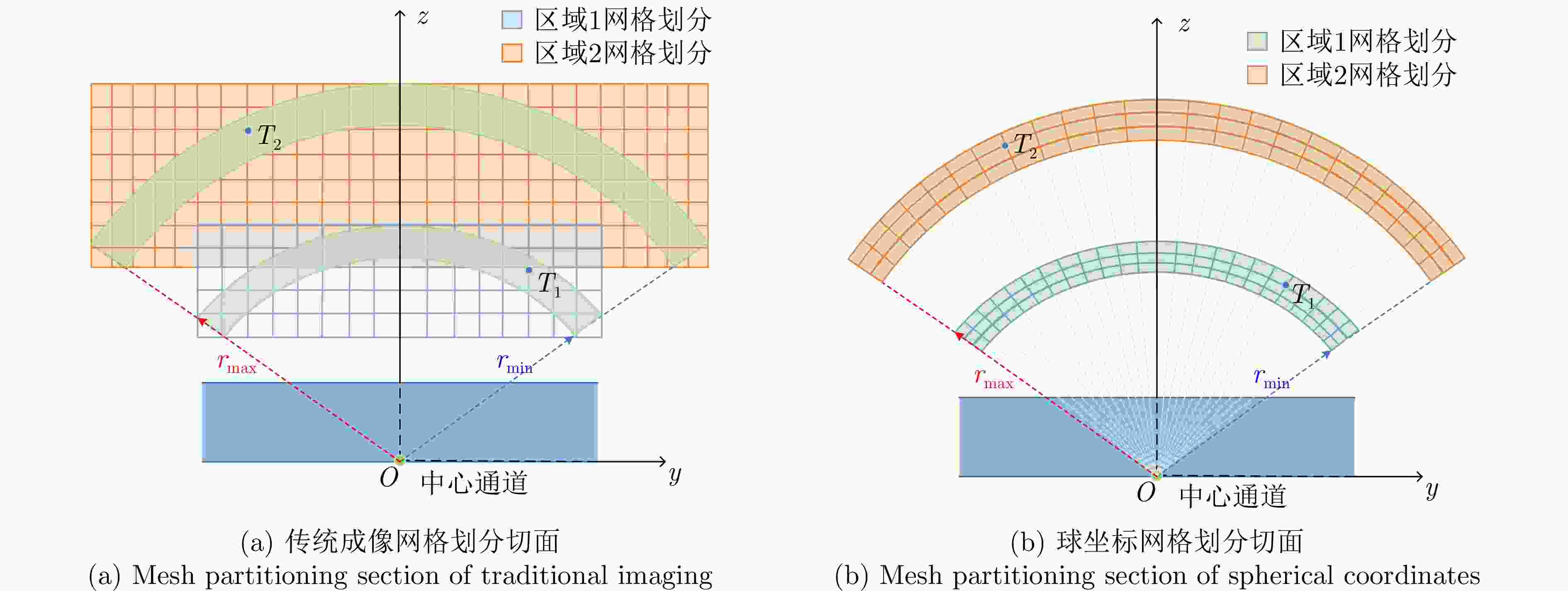
摘要: 超宽带穿墙雷达具备穿透墙体的能力,结合多输入多输出(MIMO)技术可以实现墙体后侧隐蔽目标的成像,为建筑物内人员检测和定位提供了丰富的信息。该文基于调频连续波(FMCW)体制下的多发多收超宽带穿墙雷达系统,提出了一种闭环干涉校准方法,校正了由系统内部误差产生的图像散焦。墙体的存在会导致目标成像位置偏离真实位置,该文推导了联合通道和像素点的三维墙体补偿算法,并基于其几何特性,提出快速重聚焦算法。首先去除墙体影响、确定目标存在区域;鉴于区域几何特性,选择适应区域形状的球坐标网格划分;分区域进行局部重聚焦,避免了因电磁波衰减导致成像结果中出现强目标掩盖弱目标的现象,并且球坐标形式的网格划分和局部成像大大缩减了算法耗时。通过仿真分析与实验验证,该文提出的系统校准方法能有效补偿系统误差,快速重聚焦算法可以实现墙后人体多目标三维定位,各维度定位精度优于10 cm,计算效率相对其余算法提升了5倍左右。从目标检测概率方面,所提算法相比其余算法不会出现弱目标的漏检。Abstract: Ultra-wideband through-wall radar, leveraging its ability to penetrate walls, can be used together with Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology to image hidden targets behind walls. This approach provides rich information for detecting and locating people within buildings. This paper introduces a closed-loop interferometric calibration method based on a multitransmitter multireceiver ultrawideband wall-penetrating radar system in the Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) regime. This method aims to correct scattering issues caused by internal system errors. The presence of walls causes the target imaging position to deviate from the real position. To address this, this paper derives a three-Dimensional (3D) wall compensation algorithm jointing channels and pixel points. Then, a fast refocusing algorithm is proposed based on the geometric properties of the imaging area. The first step involves removing the influence of walls on delay time and determining the presence of the target. Subsequently, in view of the geometric properties of the region, a spherical coordinate grid division adapted to the region shape is selected. Localized refocusing is then performed in the subregion. This avoids the issue of electromagnetic wave attenuation, causing strong targets to mask weak ones in the imaging results. At the same time, the adoption of spherical coordinates for gridding and localized imaging greatly reduces the overall time consumption by the algorithm. Through simulation analysis and experimental verification, the proposed calibration method can effectively compensate for system errors. The fast refocusing algorithm can be used to realize multitarget 3D localization of the human body behind walls, with the localization accuracy of each dimension surpassing 10 cm and computational speeds improving by five times compared with those of existing algorithms. In terms of target detection probability, the proposed algorithm consistently identifies weak targets that other algorithms may overlook.
-
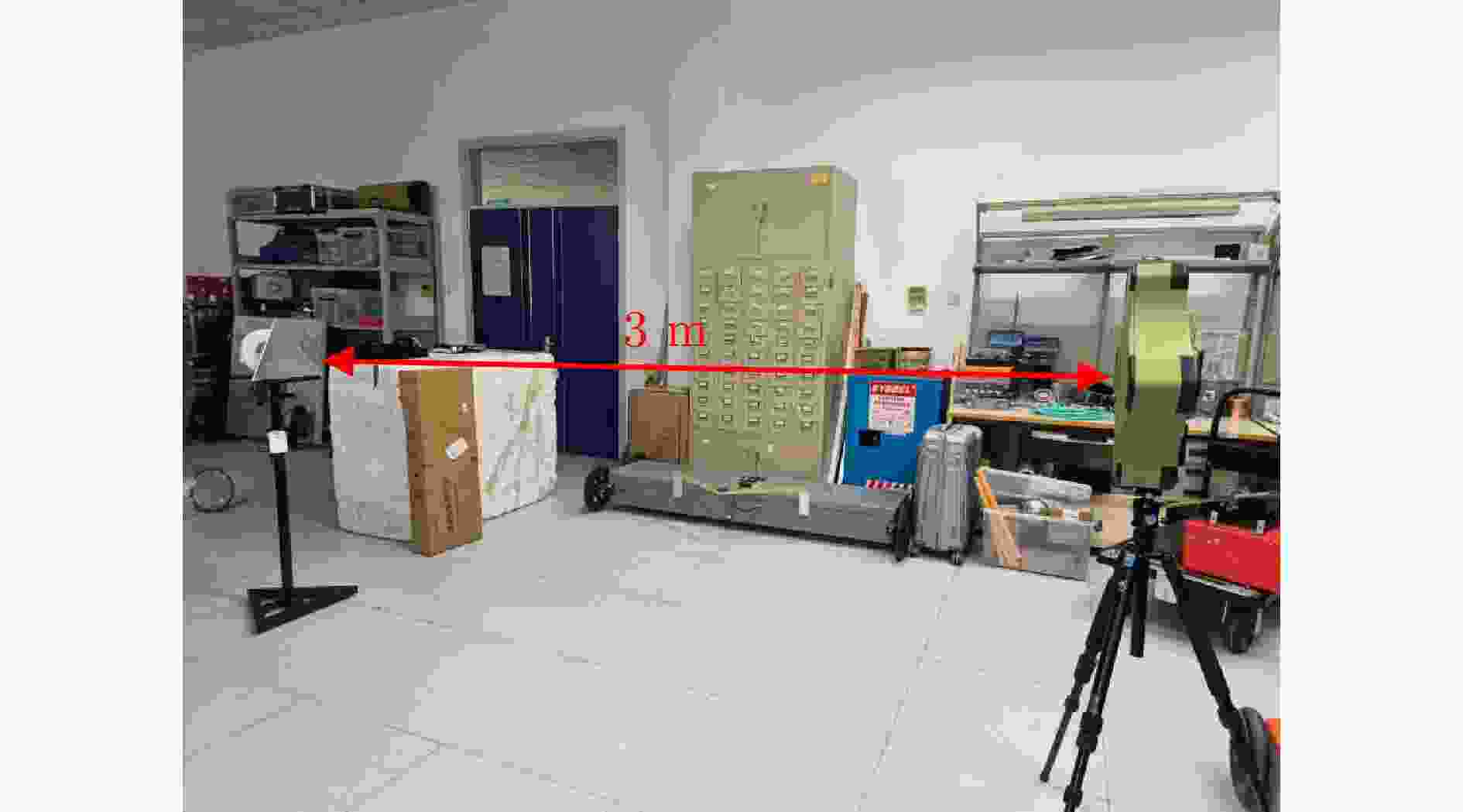
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1. Simulation parameter table
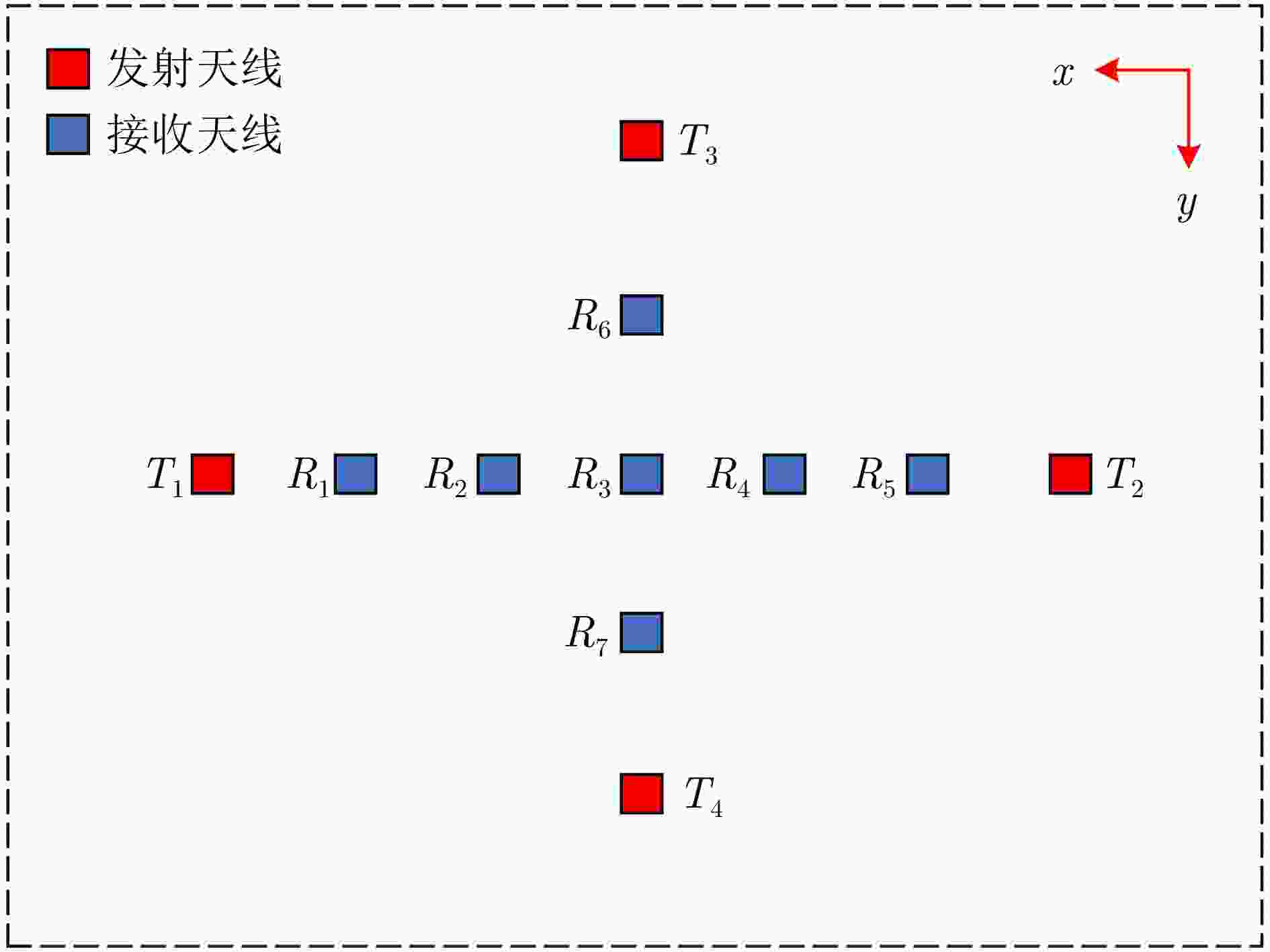
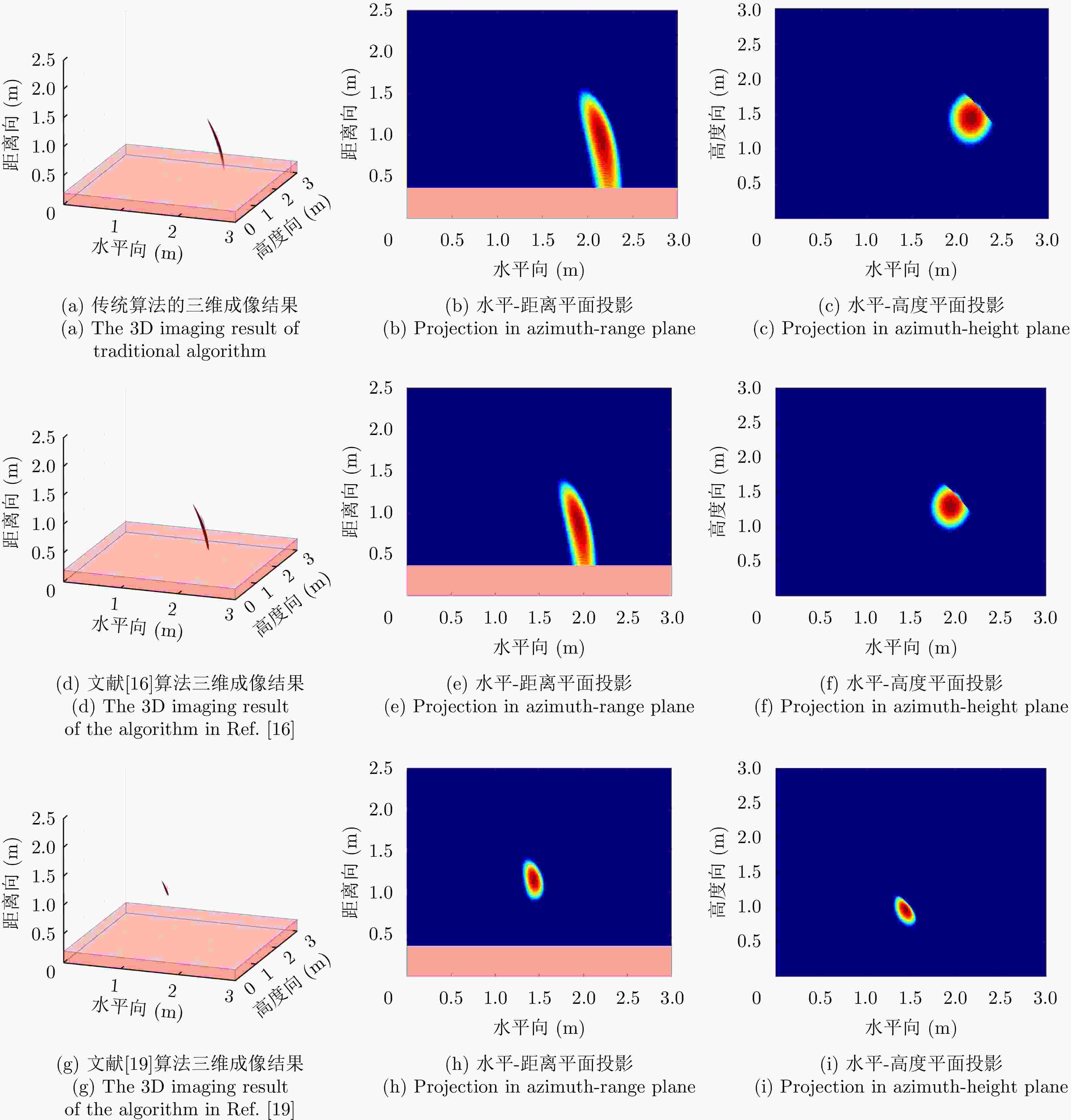
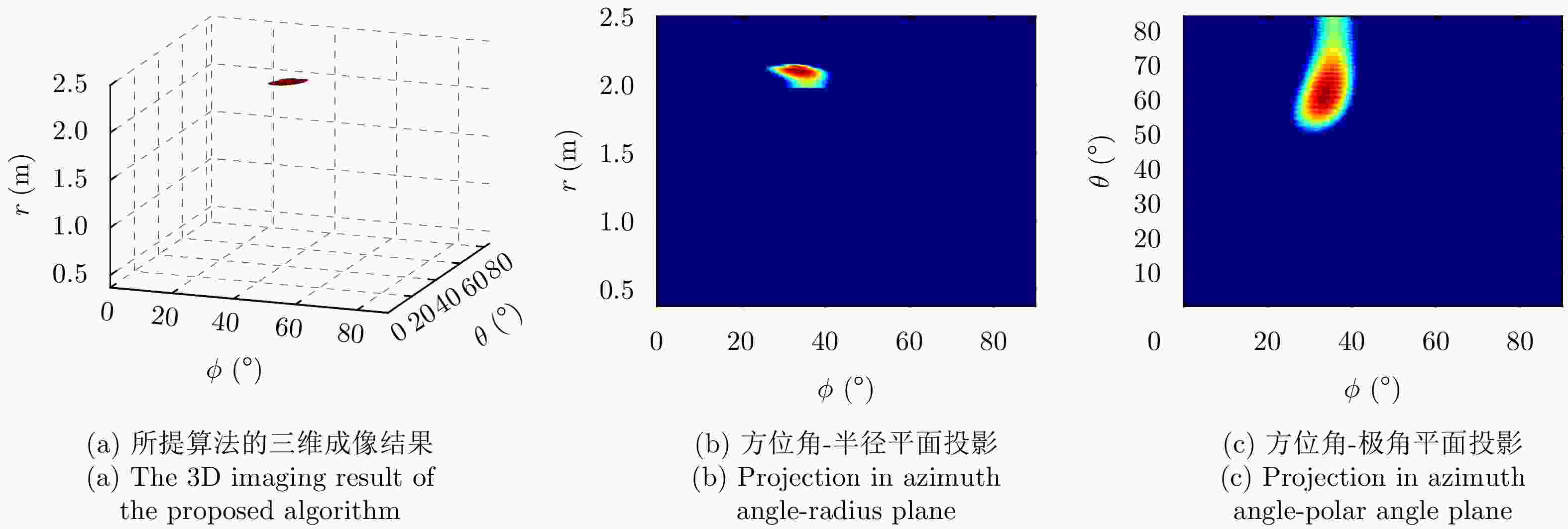
参数 指标 墙体厚度${D_{\mathrm{w}}}$ 37 cm 相对介电常数${\varepsilon _{\mathrm{r}}}$ 6 天线阵列 4发7收 信号波形 Ricker子波 目标位置 (1.5, 1.0, 1.0) 表 2 各方法定位精度对比(m)
Table 2. Comparison of positioning accuracy among various methods (m)
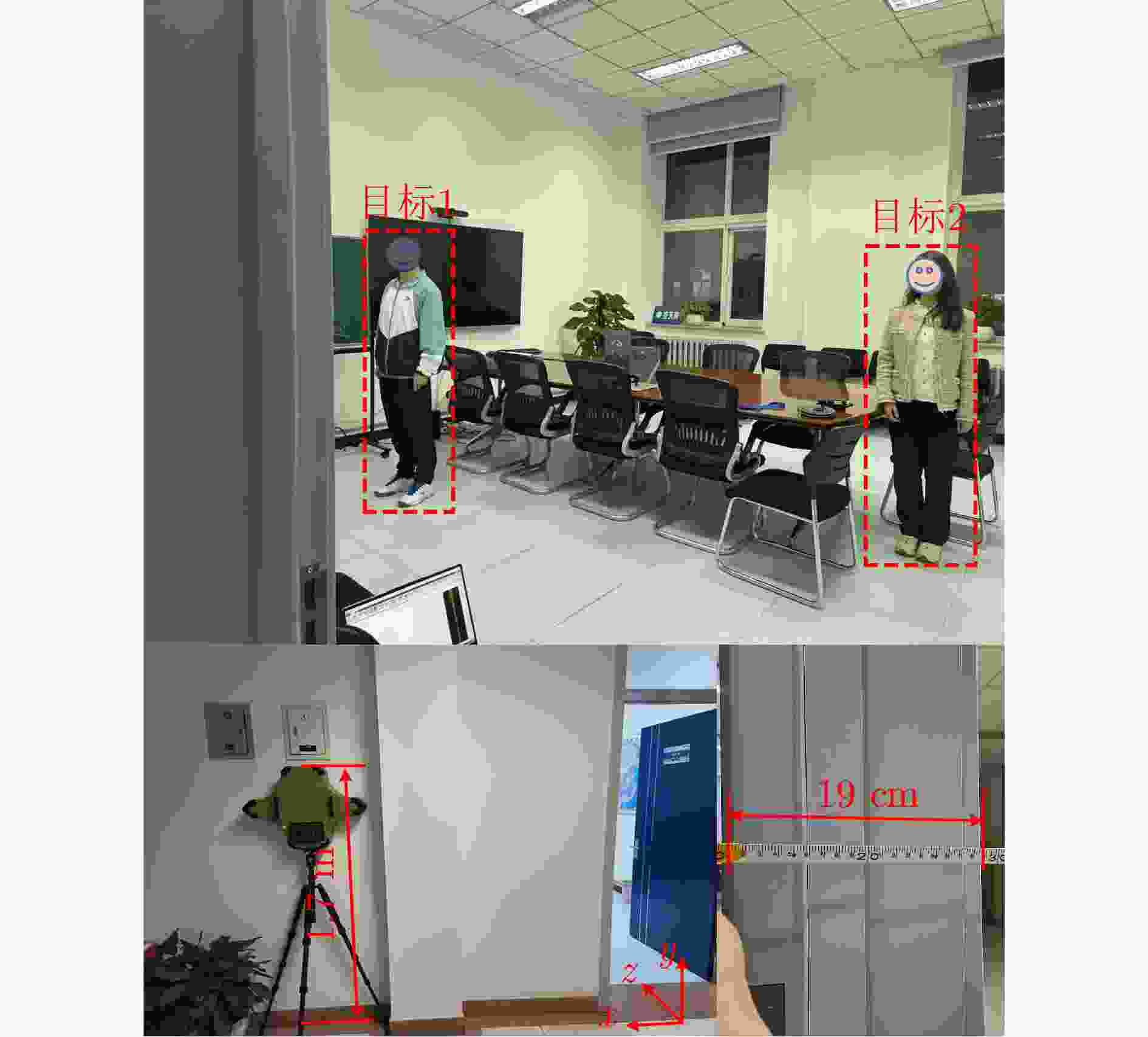
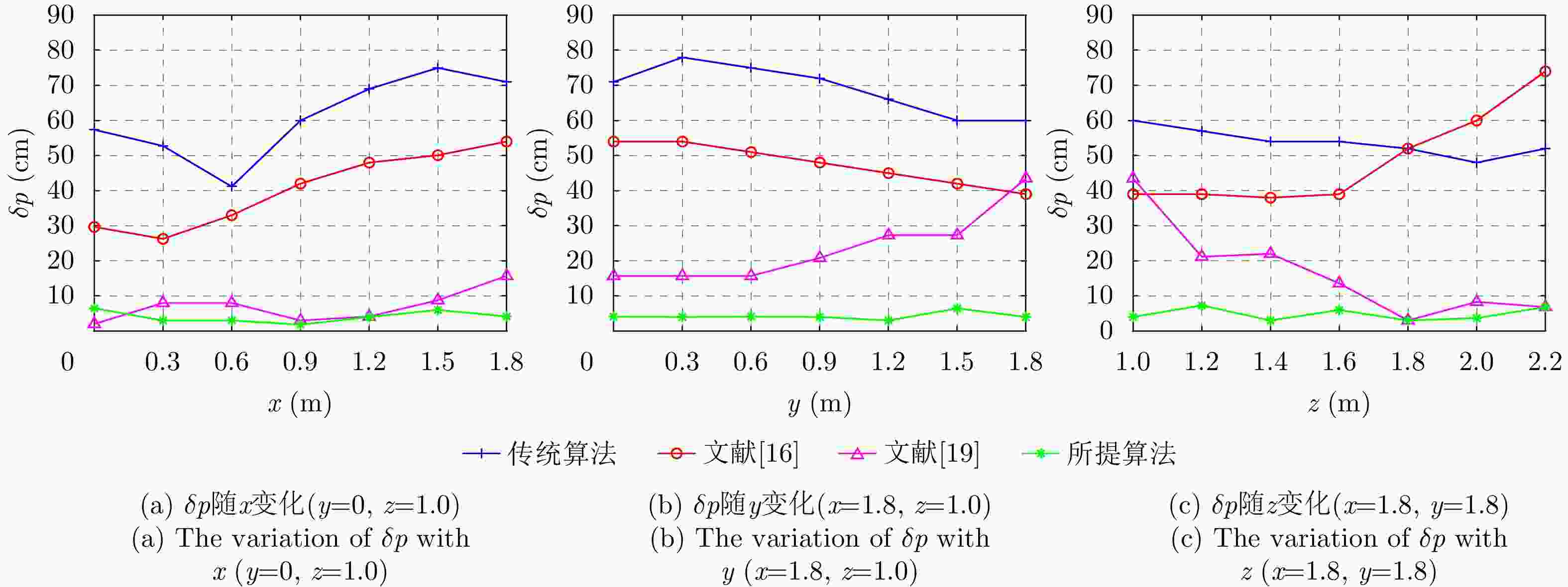
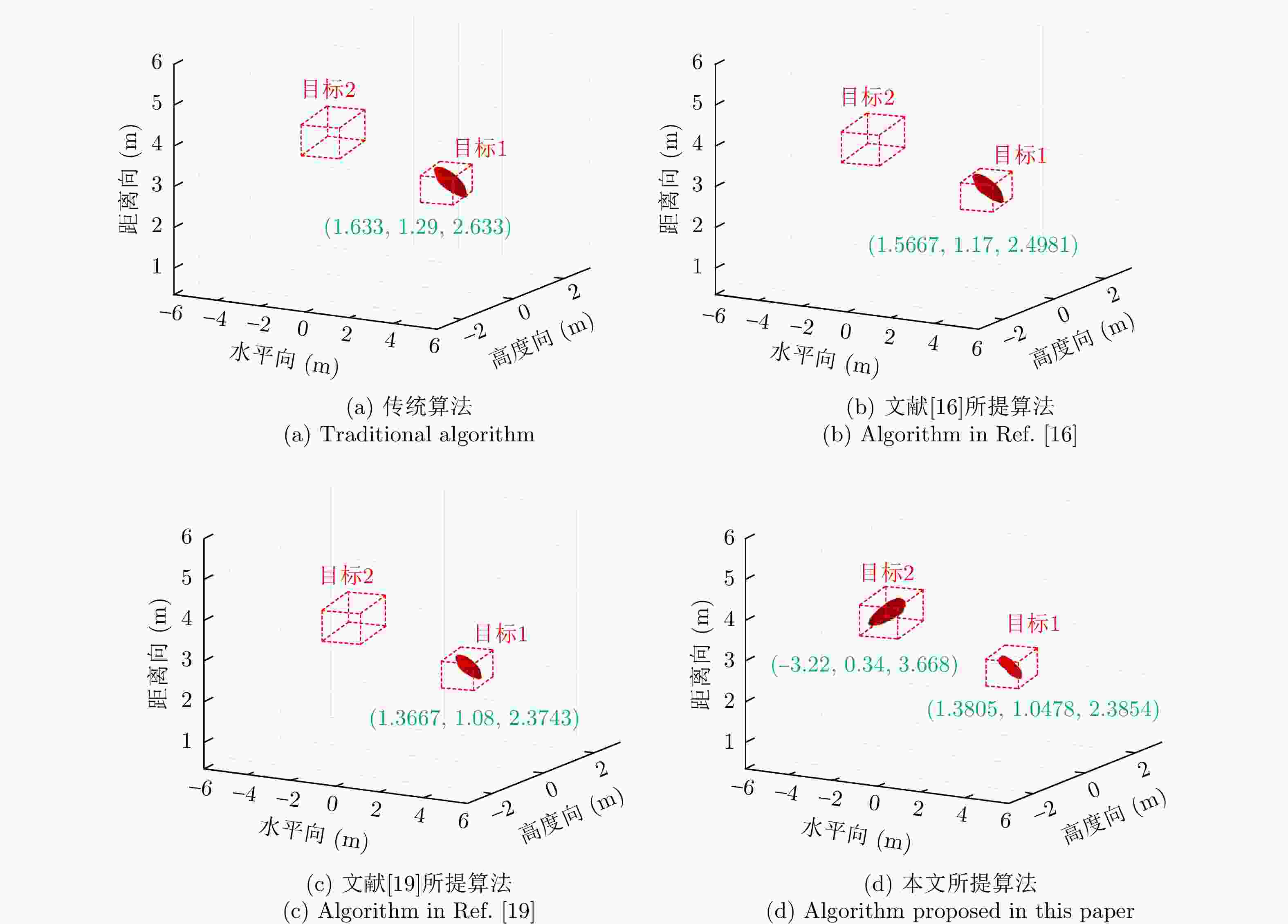
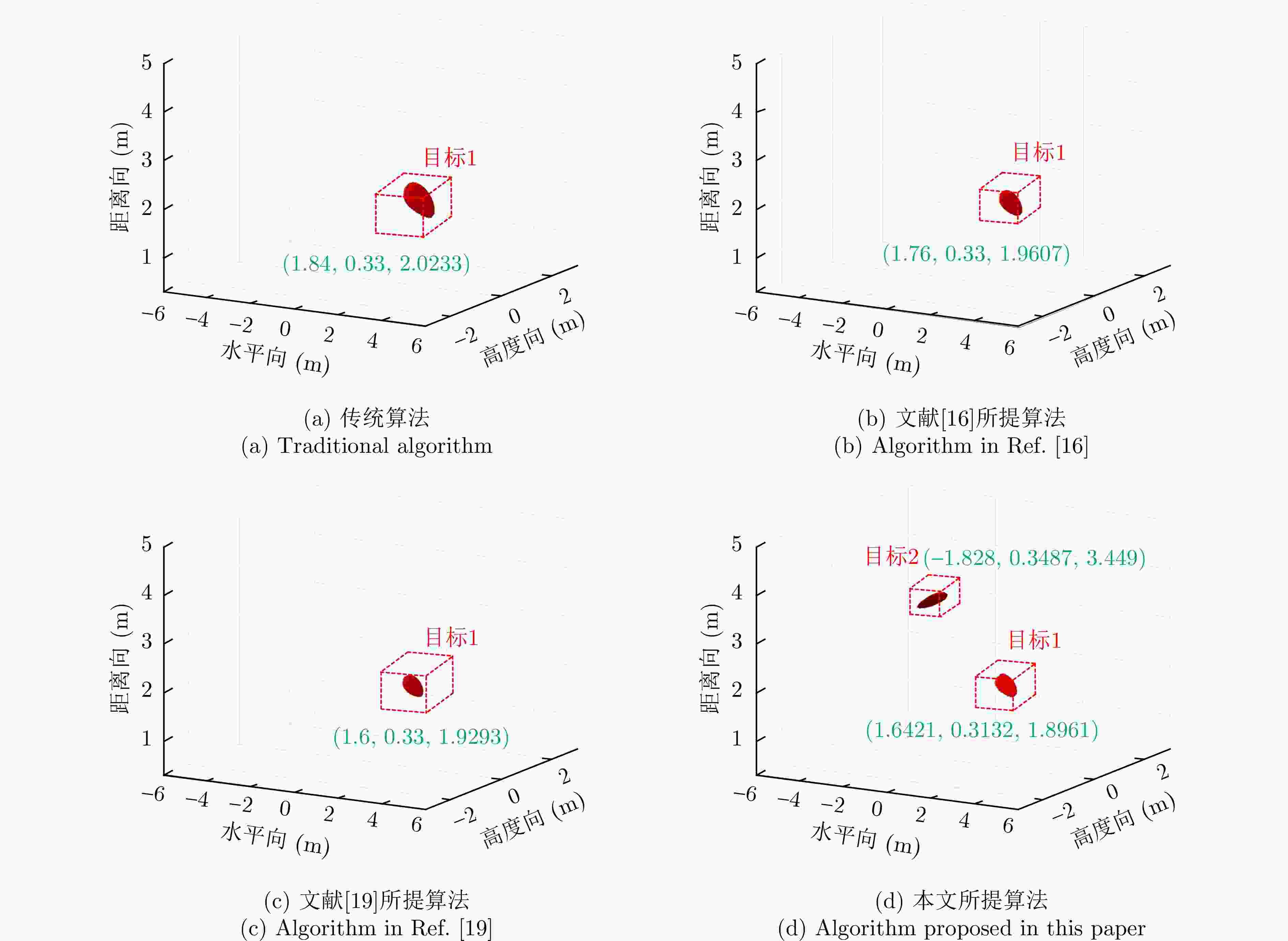
所用算法 x y z $|\Delta x|$ ($|\Delta x|/x$) $|\Delta y|$ ($\Delta y|/y$) $|\Delta z|$ ($|\Delta z|/z$) $\delta p$ 理想 1.5 1.0 1.0 — — — 传统算法 2.145 1.44 0.9877 0.645 (43%) 0.44 (44%) 0.0123 (1.23%)0.645 文献[16] 1.935 1.3 0.896 0.435 (22.48%) 0.3 (30%) 0.104 (10.4%) 0.435 文献[19] 1.4375 0.966 1.1634 0.0625 (4.17%)0.034 (3.4%) 0.1634 (16.34%)0.1634 所提算法 1.5408 1.0121 0.996 0.0408 (2.72%)0.0121 (1.21%)0.004 (0.4%) 0.0408 表 3 实验一各方法对目标1定位精度对比(m)
Table 3. Comparison of positioning accuracy of target 1 using various methods in the first experiment (m)
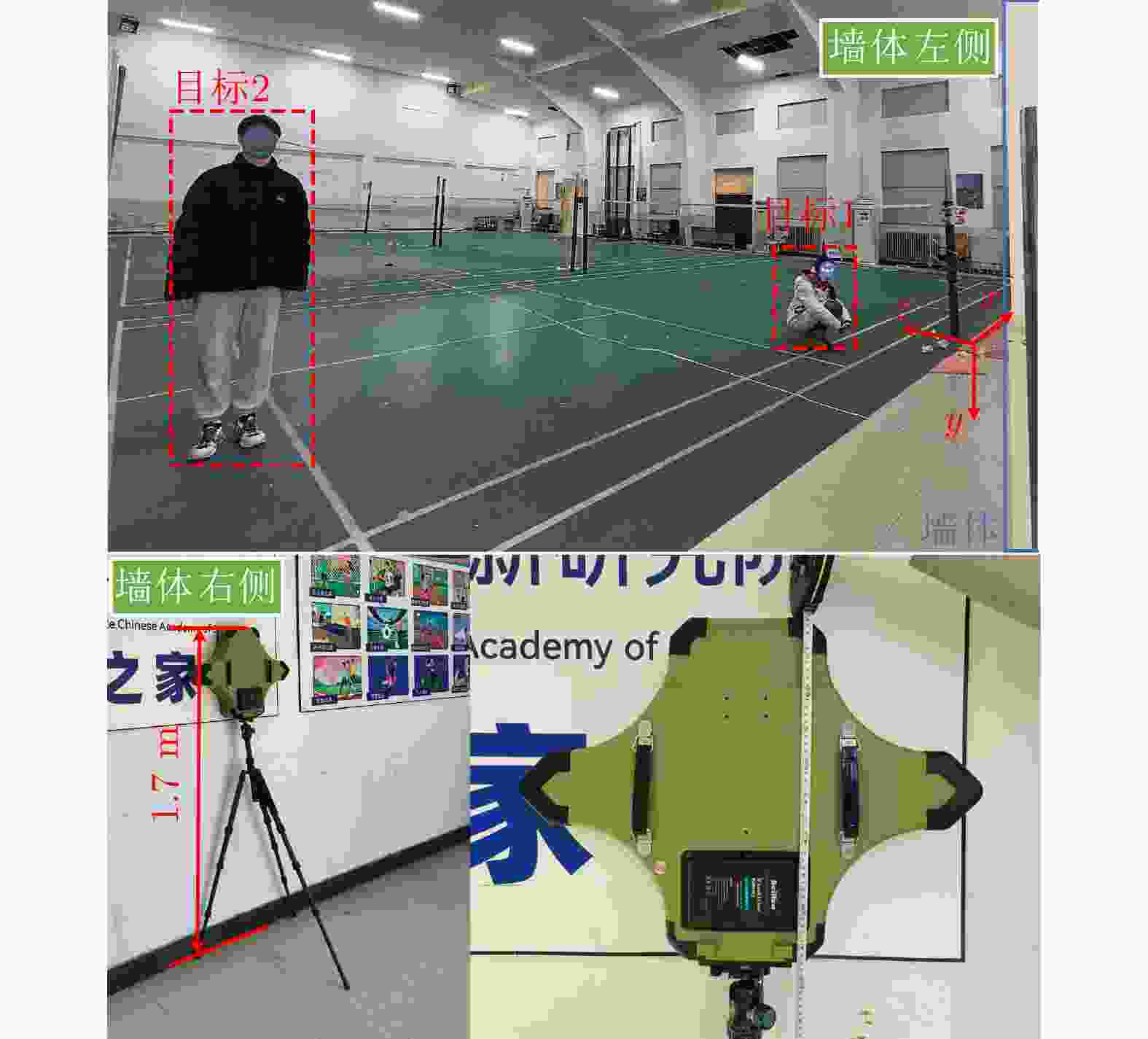
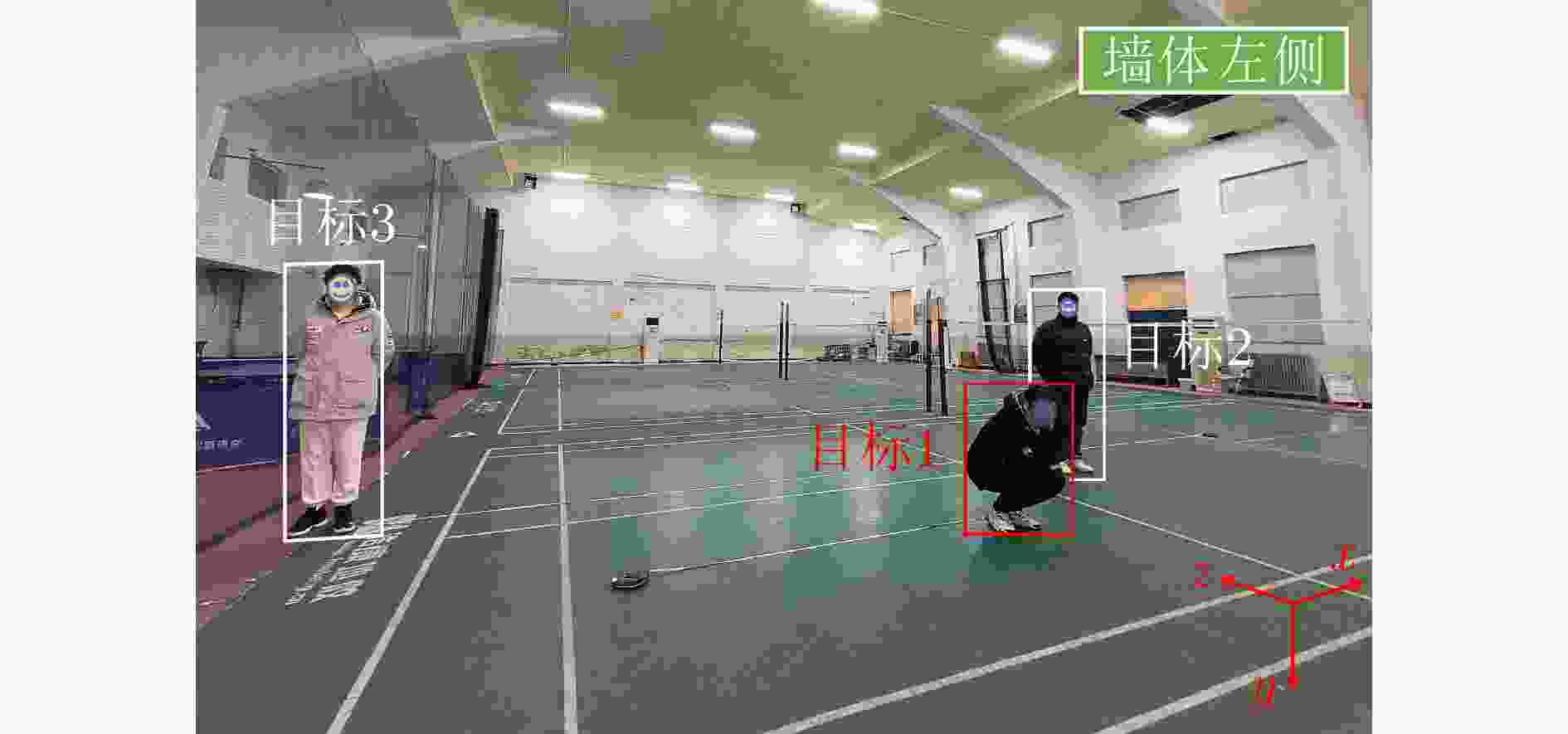
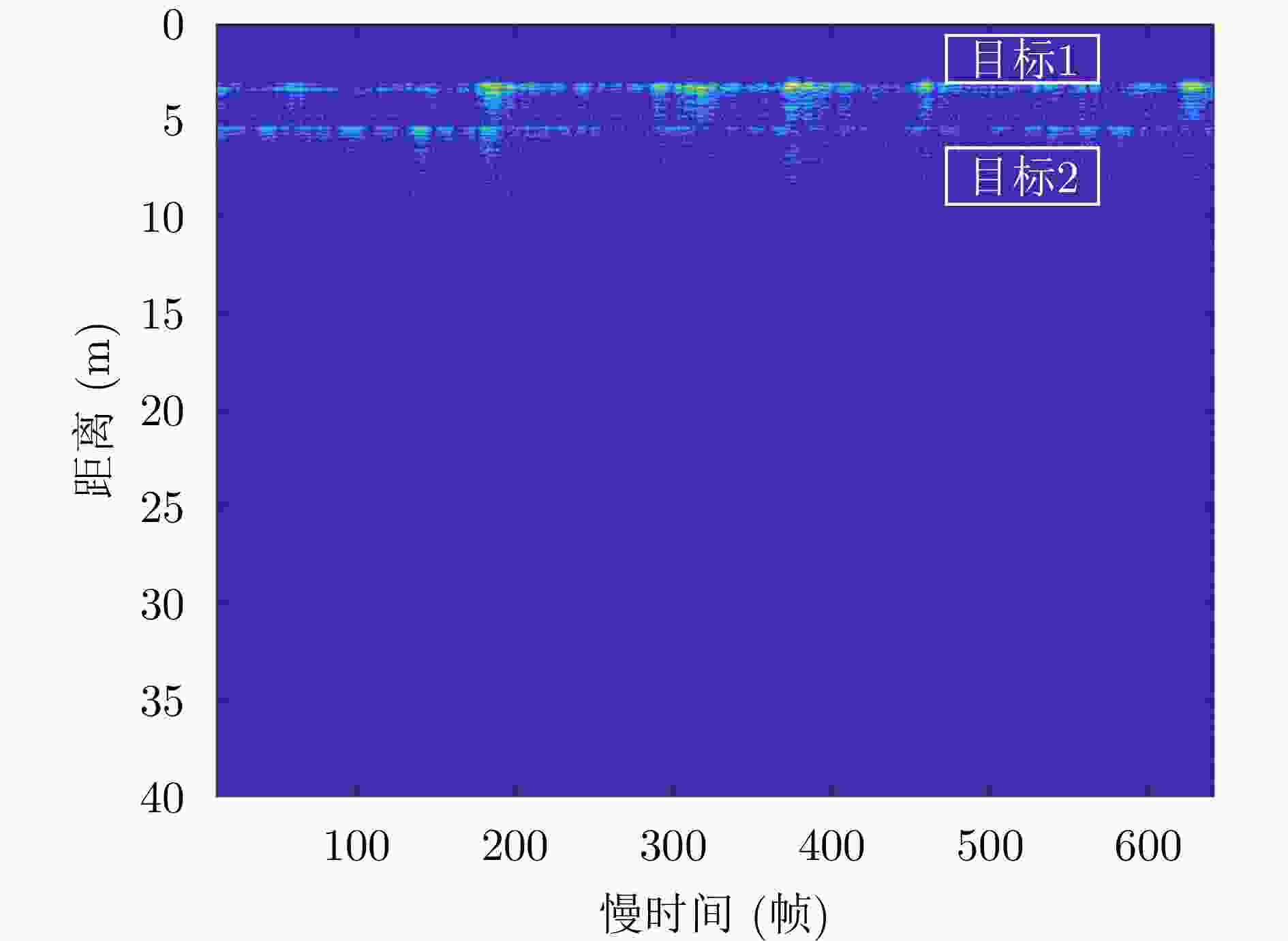
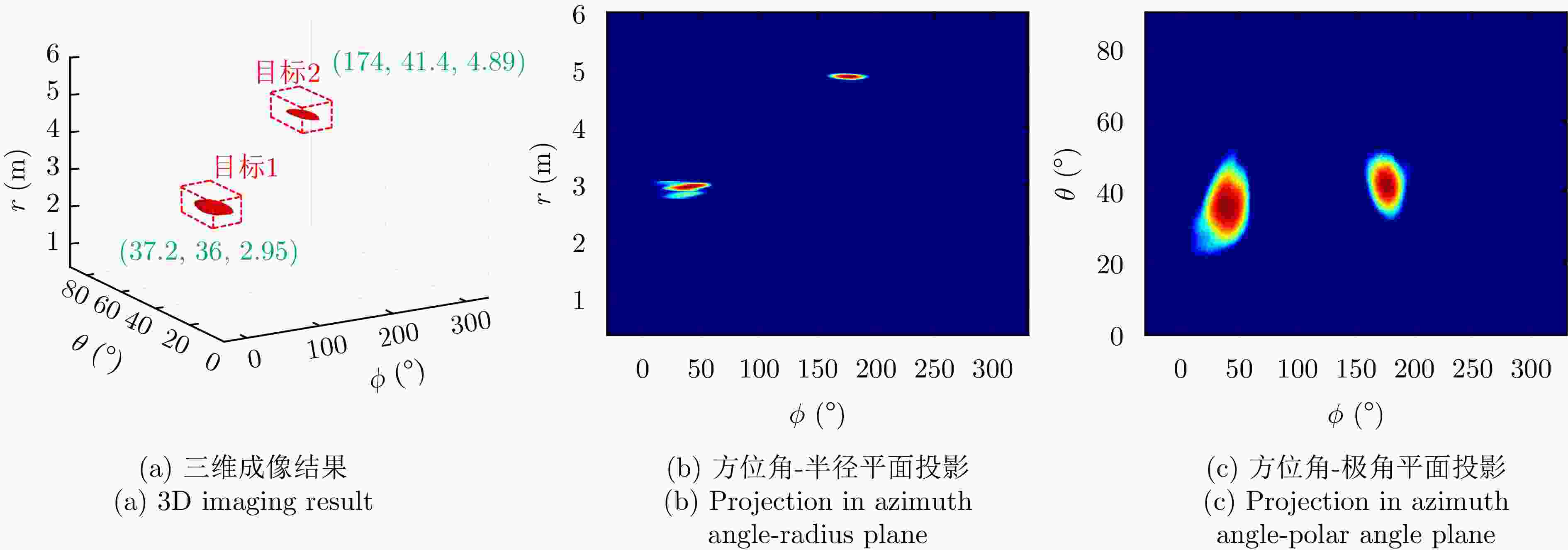
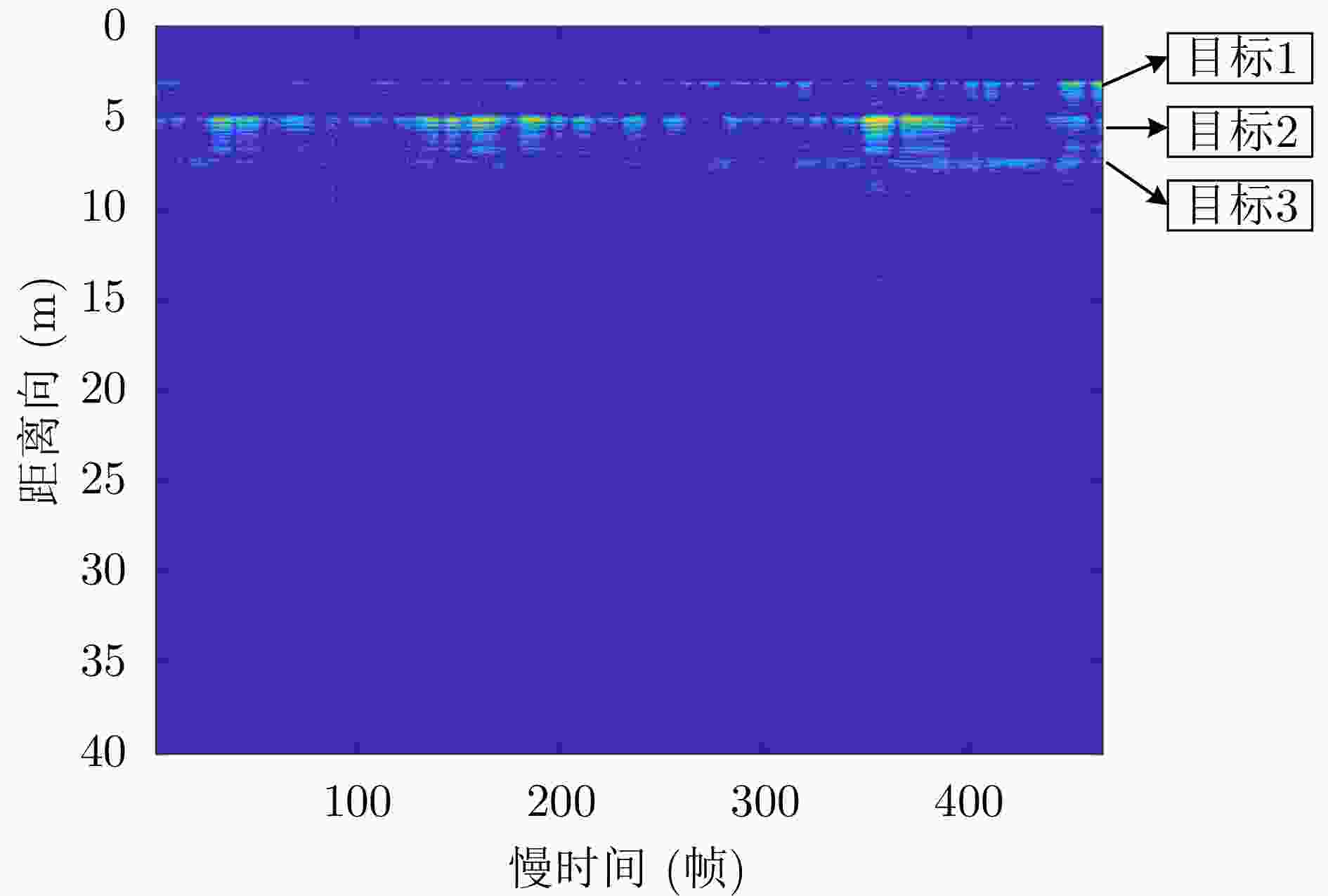
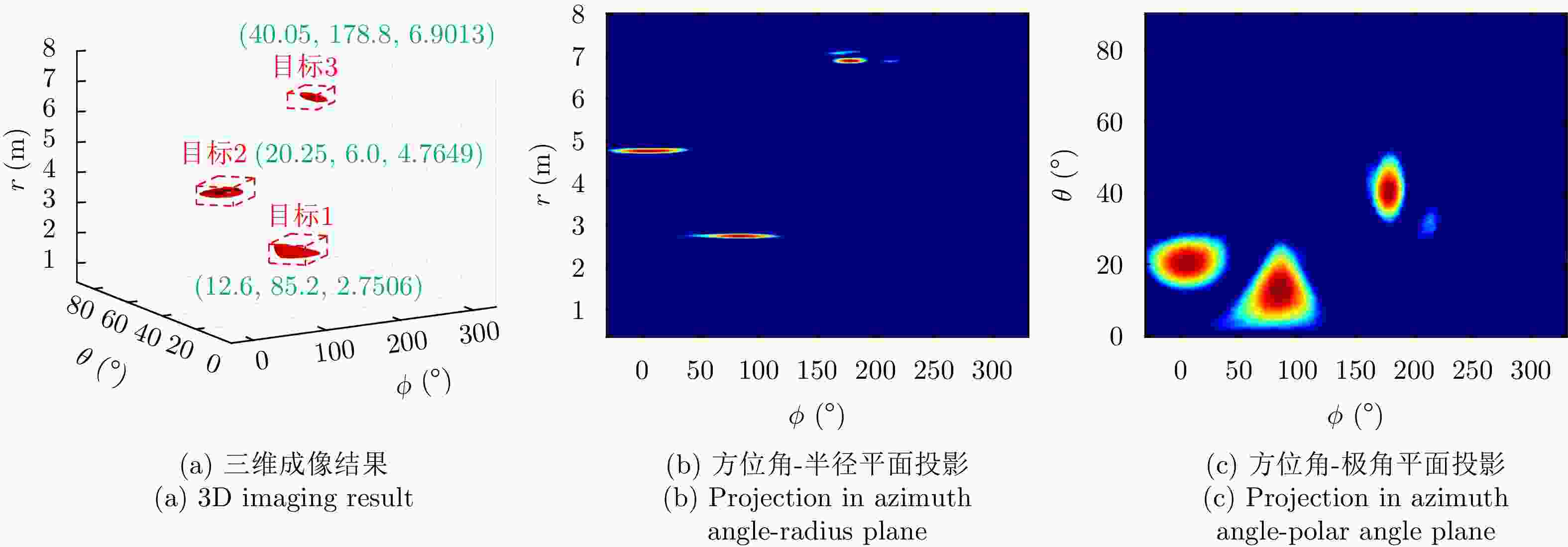
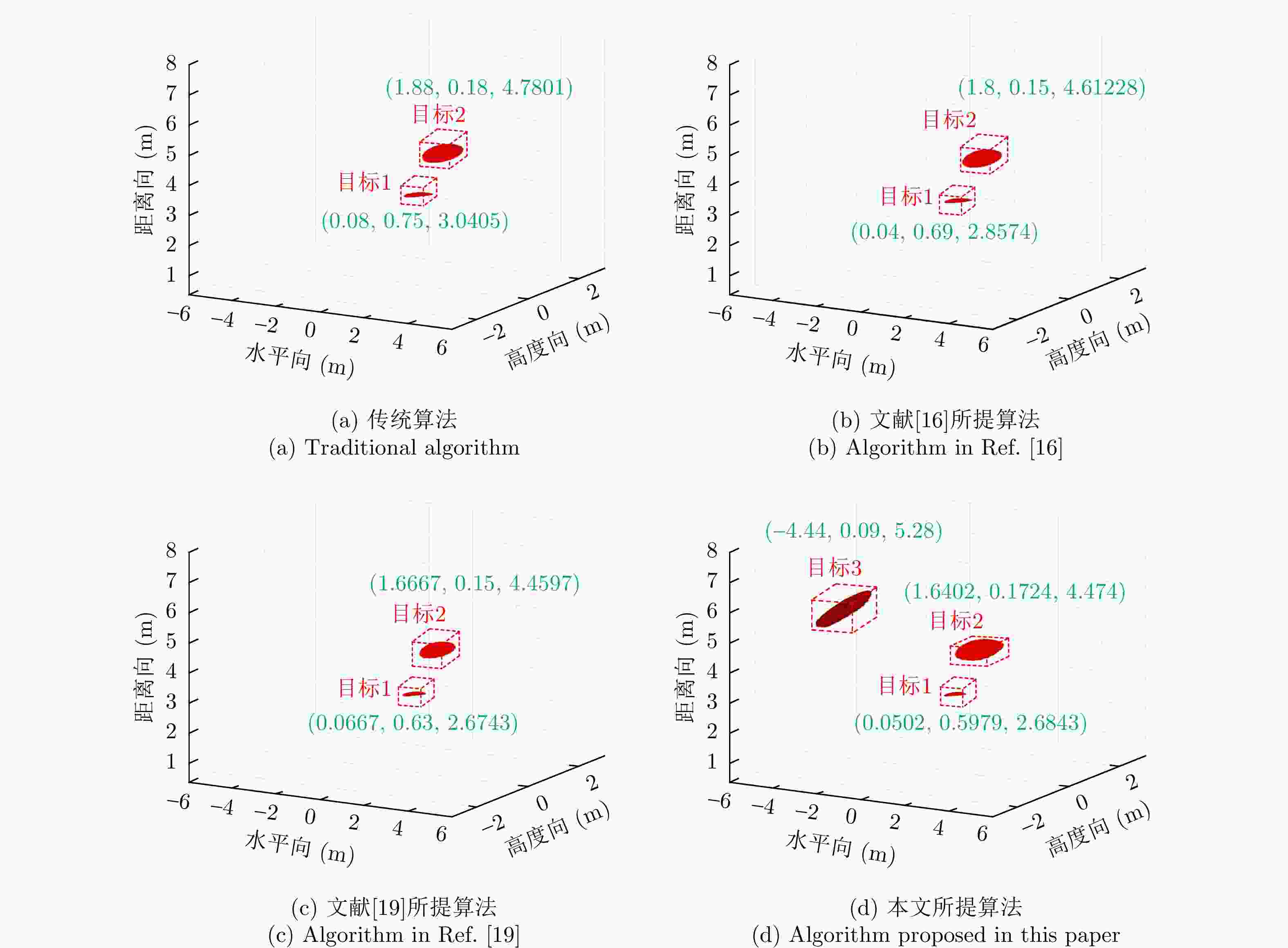
表 4 目标位置(m)
Table 4. Target position (m)
序号 坐标 目标1 (0, 0.6, 2.7) 目标2 (1.6, 0.1, 4.5) 目标3 (–4.4, 0.1, 5.3) 表 5 实验二各方法对目标1定位精度对比(m)
Table 5. Comparison of positioning accuracy of target 1 using various methods in the second experiment (m)
表 6 实验二各方法对目标2定位精度对比(m)
Table 6. Comparison of positioning accuracy of target 2 using various methods in the second experiment (m)
表 7 实验三各方法对目标1定位精度对比(m)
Table 7. Comparison of positioning accuracy of target 1 using various methods in the third experiment (m)
-
[1] MAITI S and BHATTACHARYA A. Microwave detection of respiration rate of a living human hidden behind an inhomogeneous optically opaque medium[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 6133–6144. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3043846. [2] YE Shengbo, ZHOU Bin, and FANG Guangyou. Design of a novel ultrawideband digital receiver for pulse ground-penetrating radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 656–660. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098844. [3] FANG Guangyou. The research activities of Ultrawide-band (UWB) radar in China[C]. IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Singapore, Singapore, 2007: 43–45. doi: 10.1109/ICUWB.2007.4380912. [4] QU Xiaodong, GAO Weicheng, MENG Haoyu, et al. Indoor human behavior recognition method based on wavelet scattering network and conditional random field model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5104815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3276023. [5] 金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119.JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. [6] QIU Lei, JIN Tian, LU Biying, et al. An isophase-based life signal extraction in through-the-wall radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(2): 193–197. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2633622. [7] 金添, 宋勇平. 超宽带雷达建筑物结构稀疏成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031.JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Sparse imaging of building layouts in ultra-wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031. [8] YUAN Yubing, JI Yicai, YE Shengbo, et al. A clutter identification and removal method based on long delay lines and cross-correlation in through-wall detection[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(3): 1299. doi: 10.3390/app14031299. [9] MOHAMMED I, COLLINGS I B, and HANLY S V. Multiple target localization through-the-wall using non-coherent Bi-static radar[C]. 2019 13th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems, Gold Coast, Australia, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCS47537.2019.9008415. [10] 刘新, 阎焜, 杨光耀, 等. UWB-MIMO穿墙雷达三维成像与运动补偿算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356.LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Study on 3D imaging and motion compensation algorithm for UWB-MIMO through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. [11] LIN Bo, LI Chao, JI Yicai, et al. Efficient scaling techniques for 2-D sparse MIMO array far-field imaging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(8): 12604–12615. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3354246. [12] AFTANAS M, ROVNAKOVA J, DRUTAROVSKY M, et al. Efficient method of TOA estimation for through wall imaging by UWB radar[C]. 2008 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Hannover, Germany, 2008: 101–104. doi: 10.1109/ICUWB.2008.4653361. [13] AHMAD F, AMIN M G, and KASSAM S A. Synthetic aperture beamformer for imaging through a dielectric wall[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(1): 271–283. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1413761. [14] WANG Hanning, LU Biying, ZHOU Zhimin, et al. Through-the-wall imaging and correction based on the estimation of wall parameters[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 1327–1330. doi: 10.1109/CIE-Radar.2011.6159802. [15] CUI Guolong, KONG Lingjiang, and YANG Jianyu. A back-projection algorithm to stepped-frequency synthetic aperture through-the-wall radar imaging[C]. 2007 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 2007: 123–126. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2007.4418570. [16] ROVNAKOVA J and KOCUR D. Compensation of wall effect for through wall tracking of moving targets[J]. Radioengineering, 2009, 18(2): 189–195. [17] JIN Tian, CHEN Bo, and ZHOU Zhimin. Image-domain estimation of wall parameters for autofocusing of through-the-wall SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(3): 1836–1843. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2206395. [18] LIU Jiangang, KONG Lingjiang, YANG Xiaobo, et al. Refraction angle approximation algorithm for wall compensation in TWRI[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(7): 943–946. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2555291. [19] ZHAO Yang, LU Biying, and SUN Xin. Three-dimensional imaging for UWB though-the-wall radar[C]. 2013 IEEE Third International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Yangzhou, China, 2013: 1503–1506. doi: 10.1109/ICIST.2013.6747822. [20] AFTANAS I M. Through wall imaging with UWB radar system[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Technical University of Kosice, 2010. [21] GU Xiang and ZHANG Yunhua. Autofocus imaging simulation for through-wall radar by using FDTD with unknown wall characteristics[C]. 2010 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 2010: 1657–1660. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: