Ultrahigh-resolution ISAR Micro-Doppler Suppression Methodology Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Mode Optimization
-
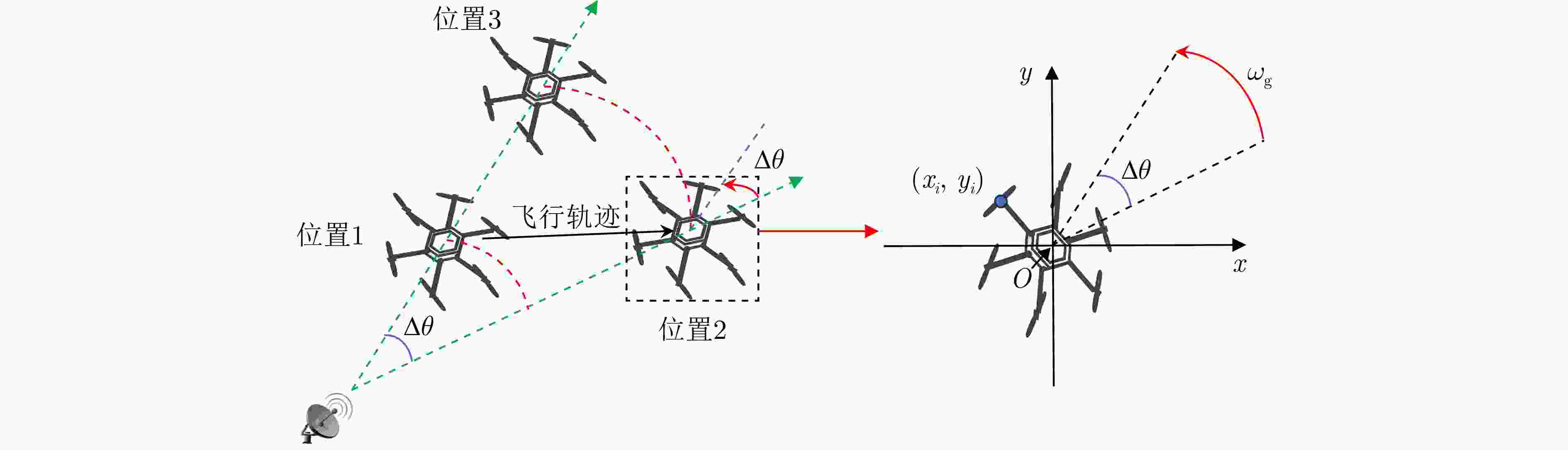
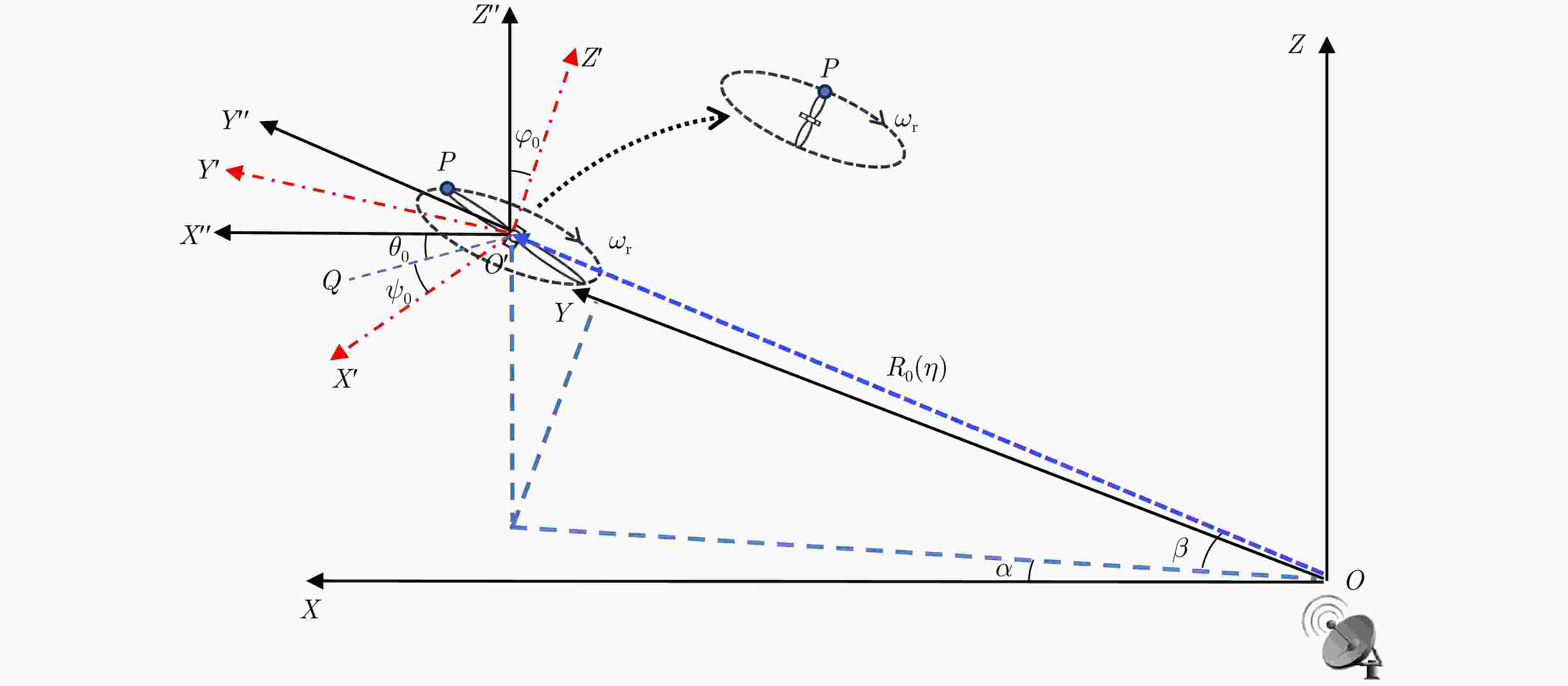
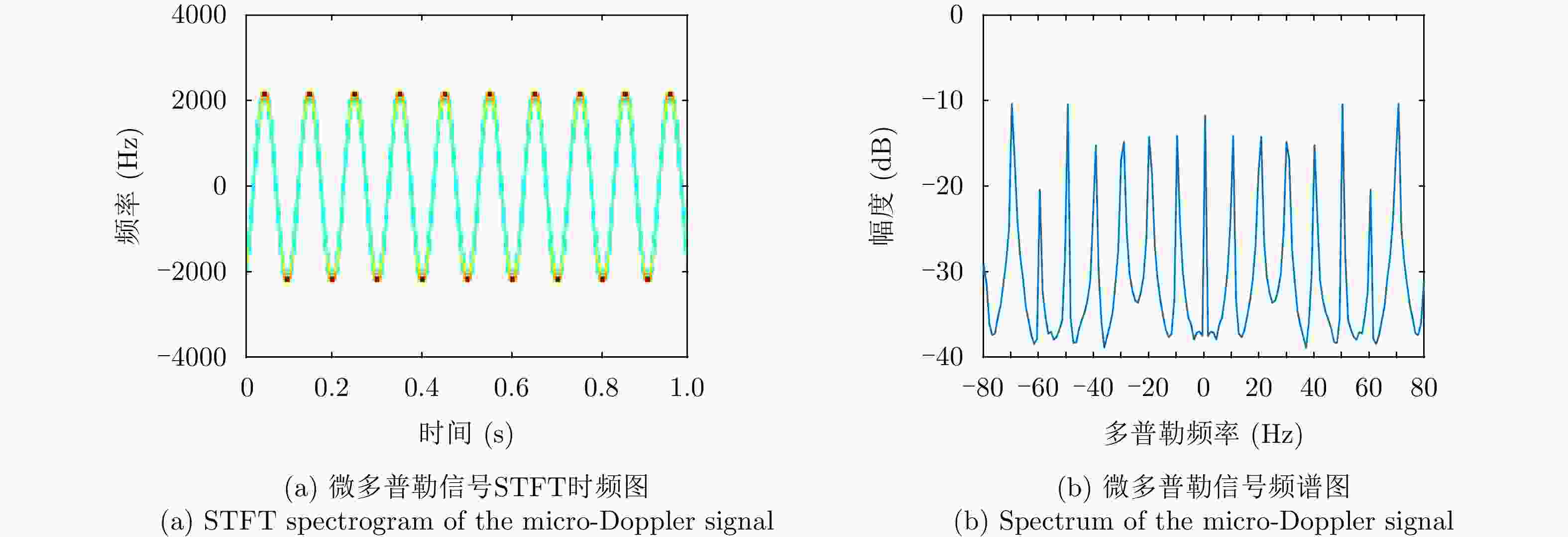
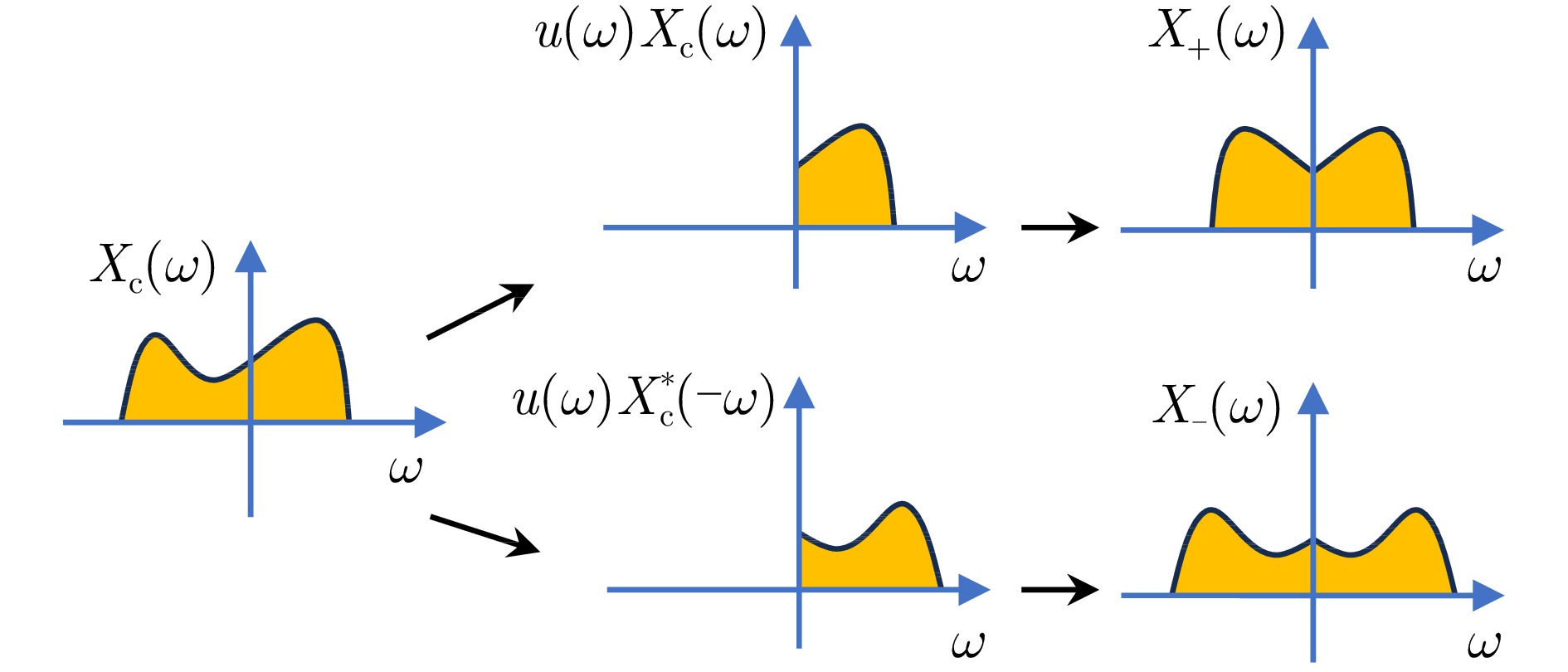
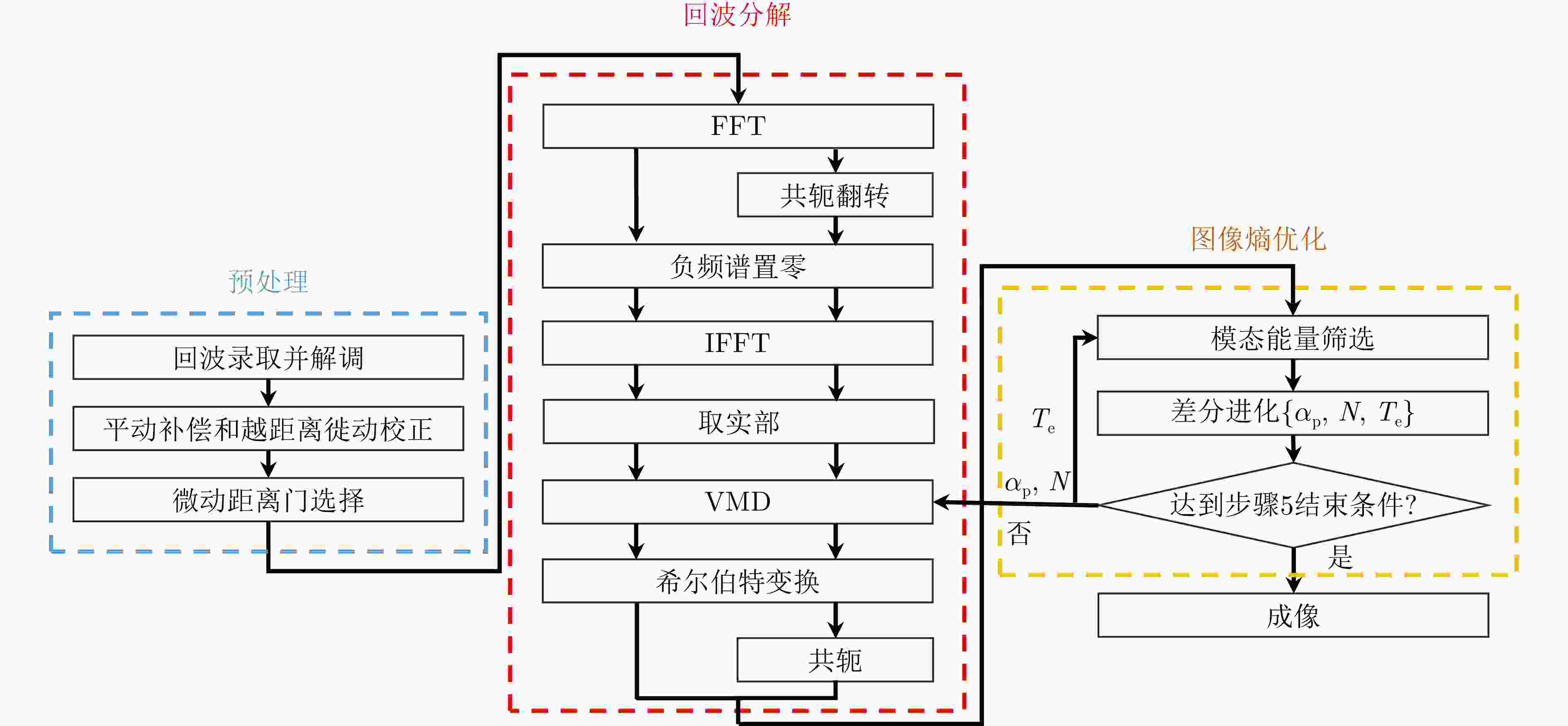
摘要: 逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)在对空中目标成像时,目标自身的转动、振动等局部微动将产生微多普勒效应,回波将附加额外的多普勒调制,造成频谱展宽。在超高分辨条件下,这一微动特性将会影响主体散射点的聚焦,导致目标图像局部散焦模糊,严重影响成像质量。并且,微多普勒相位还具有时变非平稳特性,难以从ISAR目标回波中准确估计或分离出微多普勒。为了解决上述问题,该文利用目标主体回波和微多普勒分量的时频分布差异,提出一种基于变分模态分解(VMD)与优选的非参数化方法抑制了回波中的微多普勒分量,消除了微多普勒对成像的影响,获得超高分辨率的无人机ISAR成像结果。该文首先引入VMD算法并将其扩展到复数域,将ISAR目标回波数据沿方位向分解为若干个中心频率均匀分布于多普勒采样带宽中的模函数,在此基础上利用图像熵指标优化分解参数和筛选成像模态,以保证微多普勒的良好抑制和主体回波的较完整保留。与现有基于经验模态分解(EMD)和局部均值分解(LMD)的方法相比,所提方法在超大带宽条件下对旋翼微动引起的微多普勒干扰有着更为出色的抑制效果,而且对机身部分的保留更为完整。最后,通过仿真对比和超宽带微波光子ISAR无人机实测数据处理,证明了该文所提方法的有效性和优势。Abstract: The imaging of aerial targets using Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) is affected by micro-Doppler effects resulting from localized micromotions, such as rotation and vibration. These effects introduce additional Doppler frequency modulation into the echo, leading to spectral broadening. Under ultrahigh-resolution conditions, these micromotions interfere with the focusing process of subject scatterers, resulting in images with poor focus showing significantly reduced quality. Furthermore, micro-Doppler signals exhibit temporal variability and nonstationary characteristics, posing difficulties in their estimation and differentiation from the echo. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a nonparametric method based on Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) and mode optimization to separate the echo of the subject from micro-Doppler components. This separation is achieved by utilizing differences in their respective time-frequency distributions. This methodology mitigates the effect of micro-Doppler signals on the echo and obtains imaging results of a drone with ultrahigh-resolution. The VMD algorithm is introduced and subsequently extended to the complex domain. The method entails the decomposition of the ISAR echo along the azimuth direction into several mode functions distributed uniformly across the Doppler sampling bandwidth. Subsequently, image entropy indices are employed to optimize the decomposition parameters and select the imaging modes. This ensures the effective suppression of micro-Doppler signals and preservation of the subject echo. Compared to existing methods based on Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and Local Mean Decomposition (LMD), the proposed method exhibits superior performance in suppressing image blurring caused by micro-Doppler effects while ensuring complete retention of fuselage details. Furthermore, the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed method are validated through simulations and processing of ultrawideband microwave photonic data obtained from drone measurements.
-
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1. Simulation parameter table
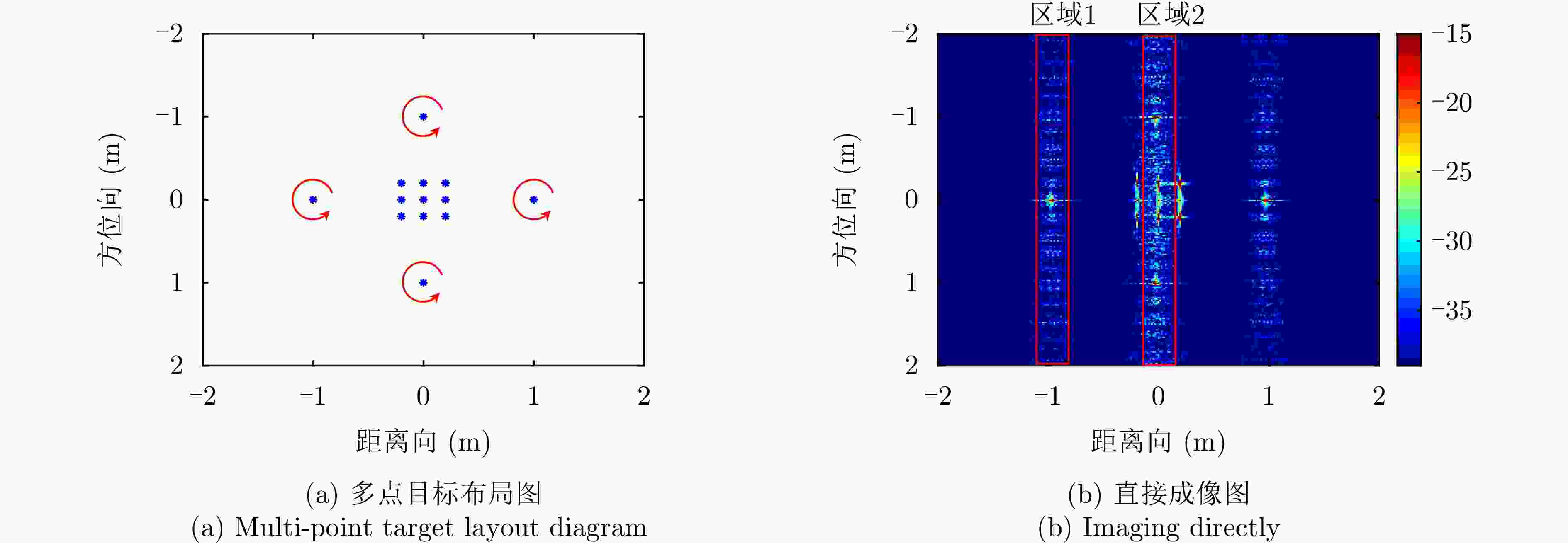
参数 数值 载波频率${f_{\mathrm{c}}}$ 35 GHz 信号带宽${B_{\mathrm{r}}}$ 10 GHz 脉冲重复频率${\text{PRF}}$ 833 Hz 成像积累时间 2.46 s 无人机运动速度 5 m/s 目标俯仰角 15° 旋翼个数 4 单旋翼叶片个数 2 叶片长度l 0.1 m 单叶片微动散射点个数 5 旋翼转速${\omega _{\mathrm{r}}}$ 20$\pi $ rad/s 表 2 各种算法处理后的图像质量比较
Table 2. Comparison of image quality processed by various algorithms
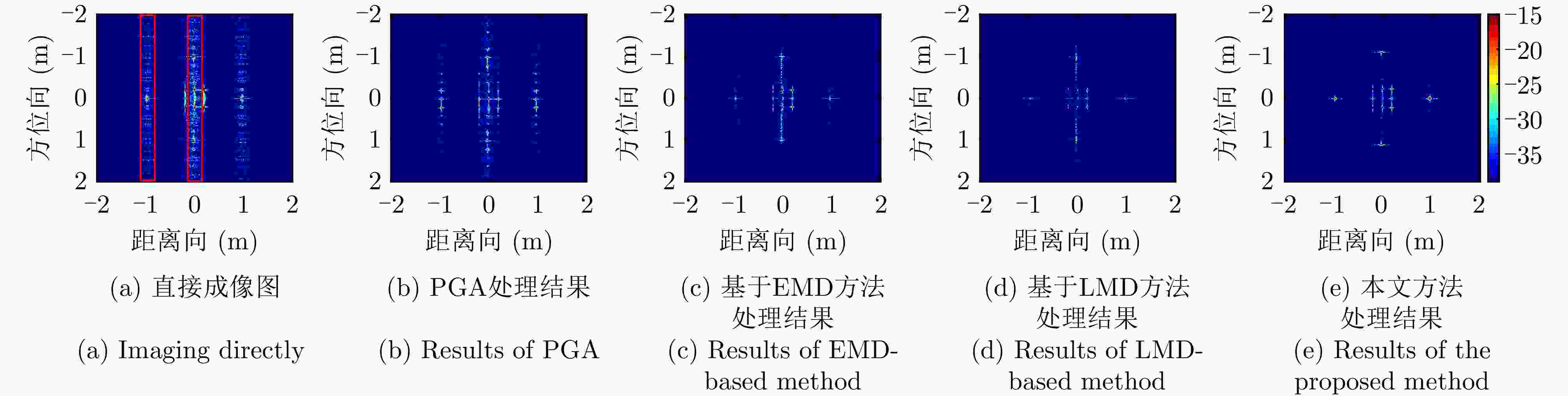
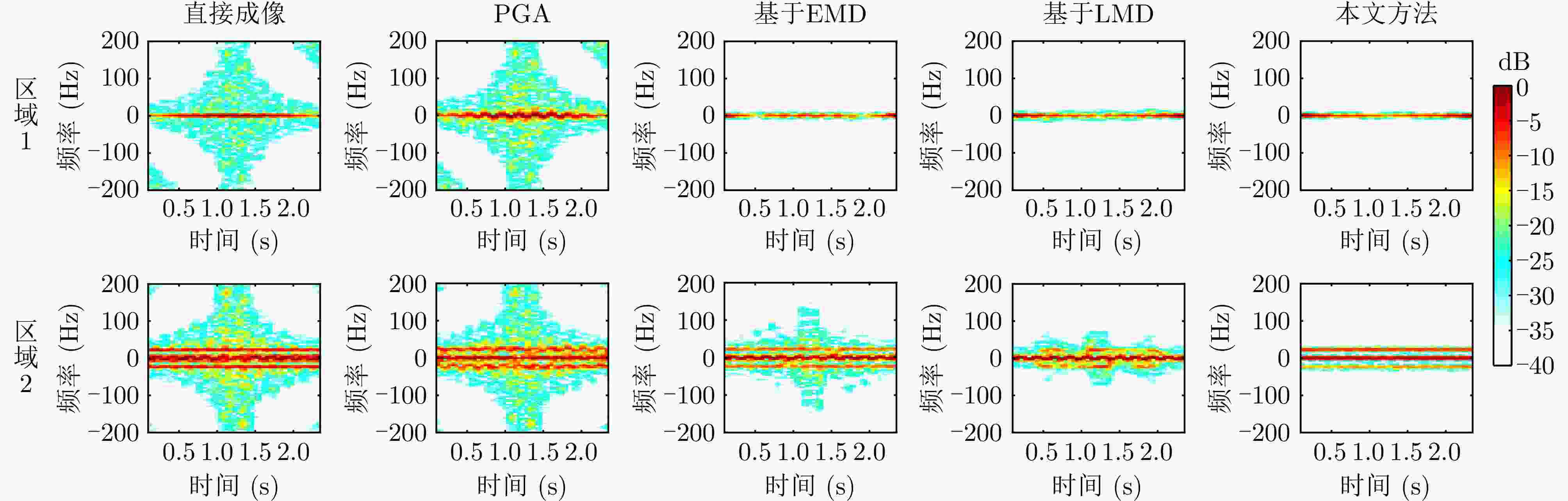
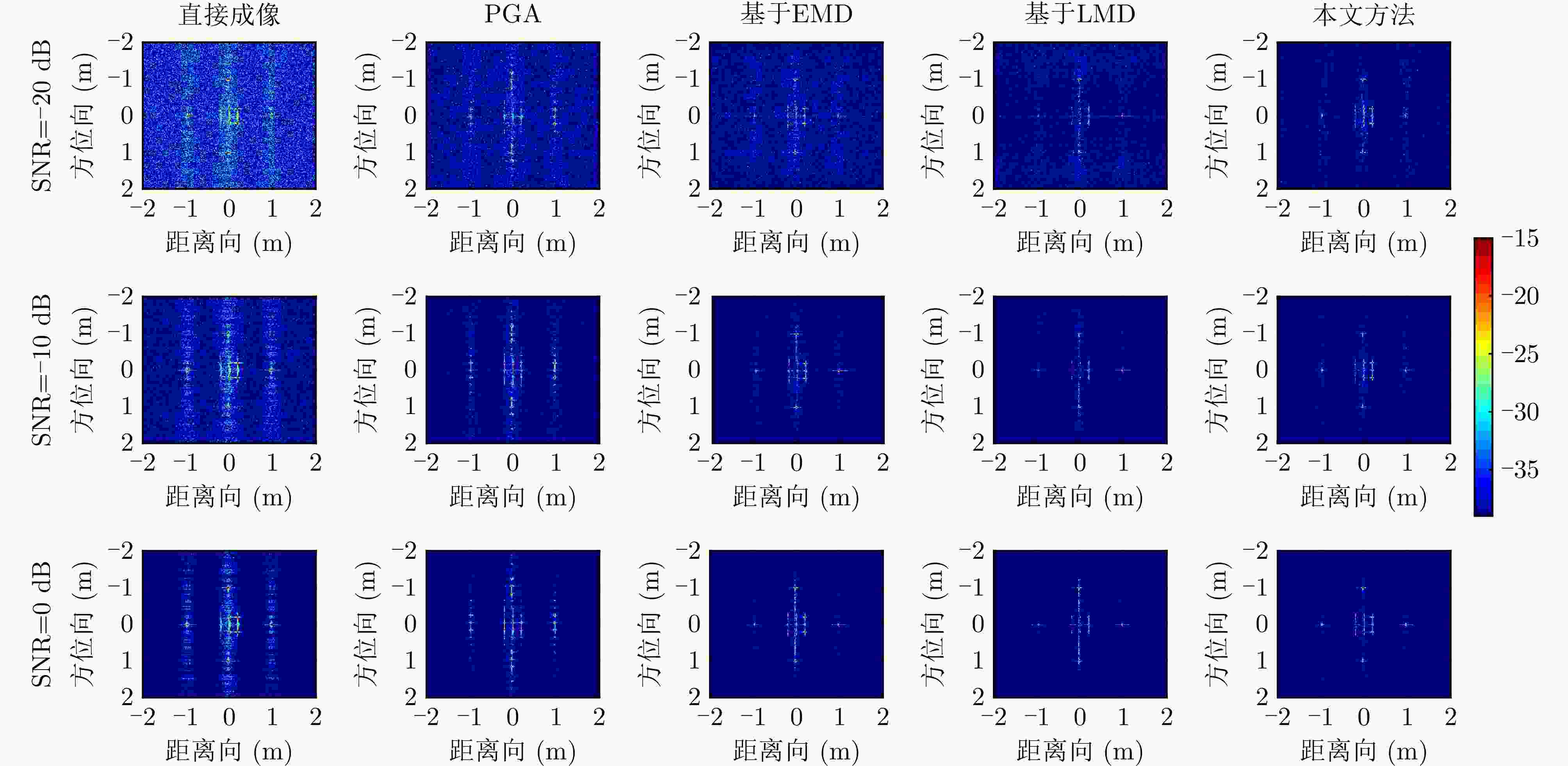
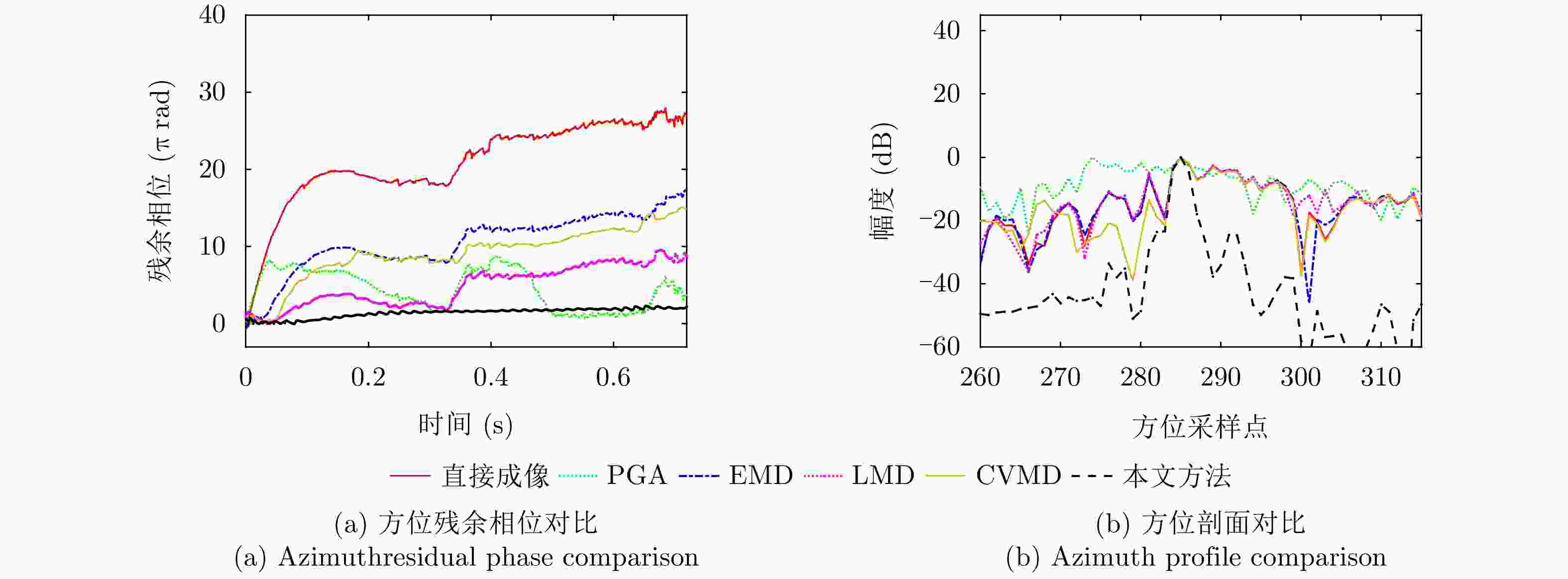
算法 能量相似比(区域1) 能量相似比(区域2) 图像熵 对比度 锐度 直接成像 8.64 3.87 8.84 18.65 1.03E+10 PGA 9.60 4.11 8.75 20.19 9.54E+09 基于EMD 0.22 1.23 8.31 21.44 8.72E+09 基于LMD 0.16 0.84 8.28 20.45 8.58E+09 本文方法 0.15 0.16 8.16 22.71 9.15E+09 表 3 六旋翼无人机实测实验参数表
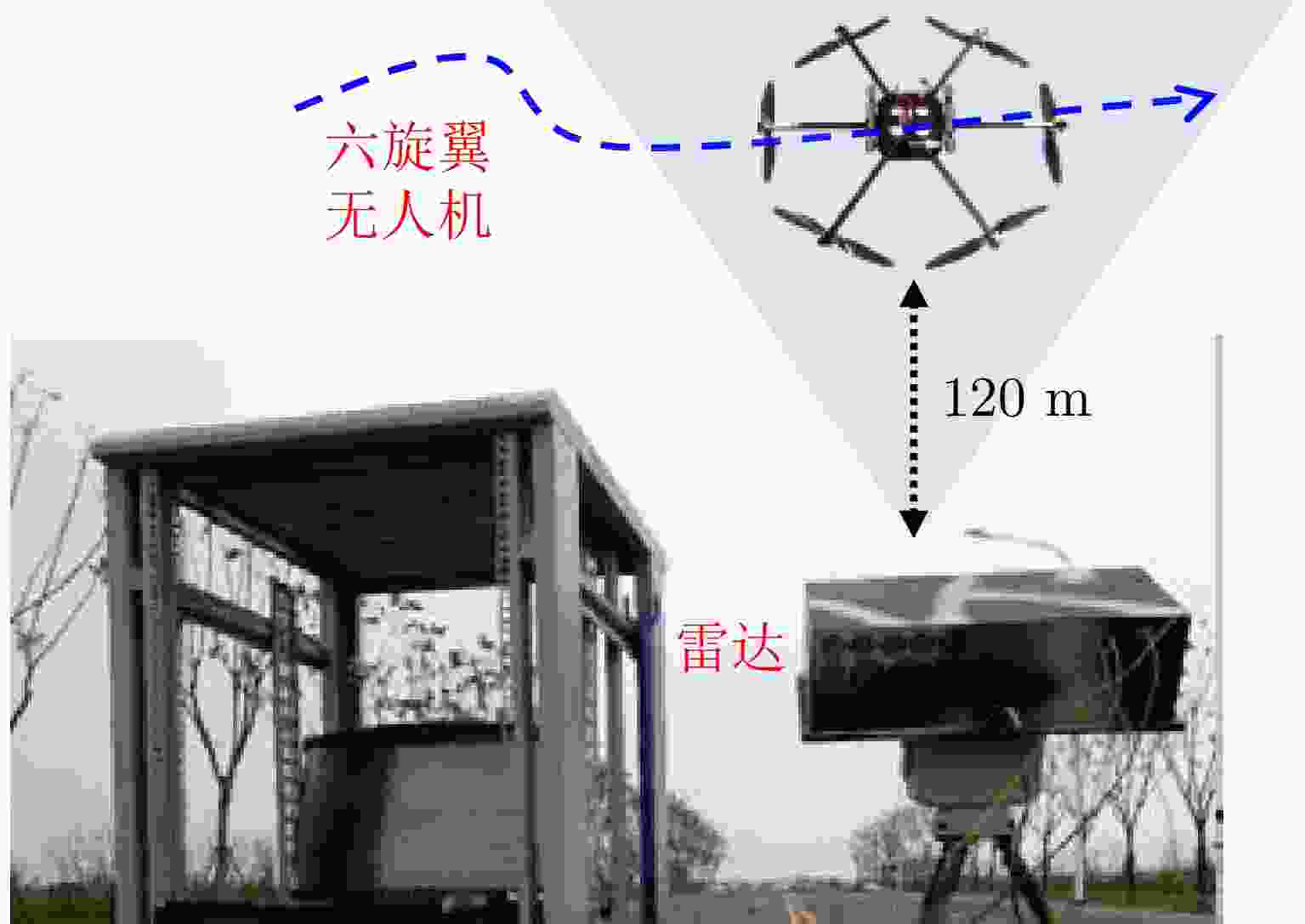
Table 3. Experimental parameter table for the hexacopter UAV
参数 数值 载波频率${f_{\mathrm{c}}}$ 35 GHz 信号带宽${B_{\mathrm{r}}}$ 10 GHz 脉冲重复频率${\text{PRF}}$ 833 Hz 成像积累时间 0.72 s 目标俯仰角 15° 表 4 六旋翼无人机成像质量比较
Table 4. Comparison of imaging quality of the hexacopter
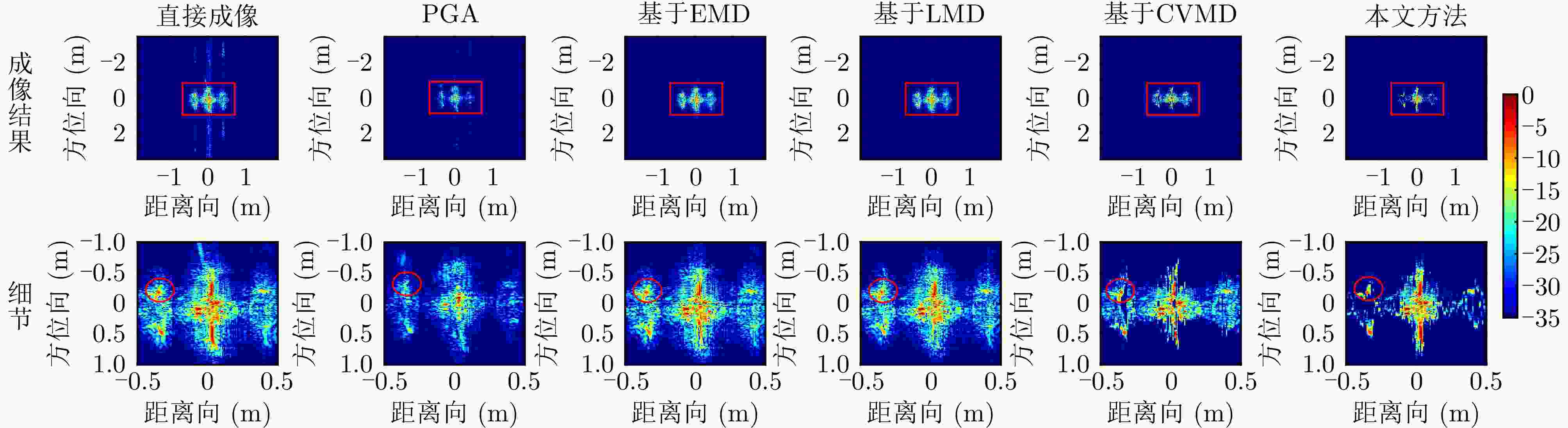
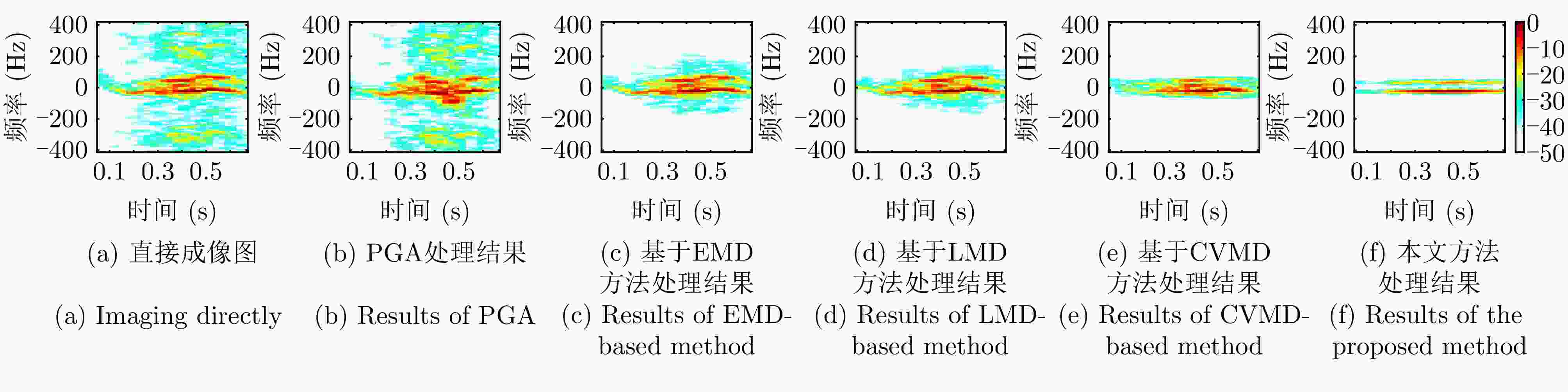
算法 图像熵 对比度 锐度 直接成像 8.19 22.12 5.44E+11 PGA 7.98 23.59 2.90E+11 基于EMD 7.63 23.28 4.17E+11 基于LMD 7.59 23.14 4.11E+11 基于CVMD 7.67 23.66 4.05E+11 本文方法 7.05 25.79 4.33E+11 表 5 不同算法的运算复杂度
Table 5. Computational complexity of different algorithms
-
[1] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 239–241.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 239–241. [2] 李源. 逆合成孔径雷达理论与对抗[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 48–55.LI Yuan. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Theory and Confrontation[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 48–55. [3] 杨建宇. 雷达技术发展规律和宏观趋势分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010.YANG Jianyu. Development laws and macro trends analysis of radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010. [4] 张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049.ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. [5] LIU Zheng and SUN Huixia. Micro-Doppler analysis and application of radar targets[C]. IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Changsha, China, 2008: 1343–1347. doi: 10.1109/ICINFA.2008.4608210. [6] 张群, 罗迎, 何劲. 雷达目标微多普勒效应研究概述[J]. 空军工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 12(2): 22–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2011.02.005.ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, and HE Jin. Overview of research on micro-Doppler effect of radar targets[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 12(2): 22–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2011.02.005. [7] CHEN V C. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler with time-frequency transform[C]. The 10th IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Pocono Manor, USA, 2000: 463–466. doi: 10.1109/SSAP.2000.870167. [8] WANG Anle, ZHENG Daikun, DU Shirui, et al. Microwave photonic radar system with ultra-flexible frequency-domain tunability[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(9): 13887–13898. doi: 10.1364/OE.423952. [9] LUO Xiong, WANG Anle, WO Jianghai, et al. Microwave photonic video imaging radar with widely tunable bandwidth for monitoring diverse airspace targets[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 451: 296–300. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.06.073. [10] CHEN V C, TAHMOUSH D, and MICELI W J. Radar Micro-Doppler Signatures: Processing and Applications[M]. Stevenage: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2014: 187–225. doi: 10.1049/pbra034e. [11] CHEN V C, LI Fayin, HO S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402. [12] TUSZYNSKI M, WOJTKIEWICZ A, and KLEMBOWSKI W. Bimodal clutter MTI filter for staggered PRF radars[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 176–180. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.1990.201158. [13] 万显荣, 谢德强, 易建新, 等. 基于STFT谱图滑窗相消的微动杂波去除方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 794–804. doi: 10.12000/JR22157.WAN Xianrong, XIE Deqiang, YI Jianxin, et al. Micro-Doppler clutter removal method based on the cancelation of sliding STFT spectrogram[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 794–804. doi: 10.12000/JR22157. [14] WANG Yong, ZHOU Xingyu, LU Xiaofei, et al. An approach of motion compensation and ISAR imaging for micro-motion targets[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(1): 68–80. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000008. [15] 何其芳, 张群, 罗迎, 等. 正弦调频Fourier-Bessel变换及其在微动目标特征提取中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 593–601. doi: 10.12000/JR17069.HE Qifang, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. A sinusoidal frequency modulation Fourier-Bessel transform and its application to micro-Doppler feature extraction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 593–601. doi: 10.12000/JR17069. [16] 符吉祥, 邢孟道, 徐丹, 等. 一种基于微波光子超高分辨雷达机翼振动参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001.FU Jixiang, XING Mengdao, XU Dan, et al. Vibration-parameters estimation method for airplane wings based on microwave-photonics ultrahigh-resolution radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001. [17] STANKOVIC L, DJUROVIC I, and THAYAPARAN T. Separation of target rigid body and micro-Doppler effects in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(4): 1496–1506. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.314590. [18] LI Kaiming, LIANG Xianjiao, ZHANG Qun, et al. Micro-Doppler signature extraction and ISAR imaging for target with micromotion dynamics[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 411–415. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2081660. [19] CHOI I, KANG K, KIM K, et al. Use of ICA to separate micro-Doppler signatures in ISAR images of aircraft that has fast-rotating parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 234–246. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098110. [20] BAI Xueru, XING Mengdao, ZHOU Feng, et al. Imaging of micromotion targets with rotating parts based on empirical-mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(11): 3514–3523. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002322. [21] FLANDRIN P, RILLING G, and GONCALVES P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(2): 112–114. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2003.821662. [22] GAO Yunchao, GE Guangtao, SHENG Zhengyan, et al. Analysis and solution to the mode mixing phenomenon in EMD[C]. International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Sanya, China, 2008: 223–227. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2008.193. [23] YUAN Bin, CHEN Zengping, and XU Shiyou. Micro-Doppler analysis and separation based on complex local mean decomposition for aircraft with fast-rotating parts in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1285–1298. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2249588. [24] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675. [25] 杨利超. 超高分辨ISAR成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.000089.YANG Lichao. Study on ISAR ultrahigh-resolution imaging techniques[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.000089. [26] 邵帅. 高分辨ISAR成像与精细化运动补偿技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.003431.SHAO Shuai. Study on high resolution ISAR imaging and fine motion compensation techniques[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.003431. [27] YANG Degui, LI Jin, LIANG Buge, et al. A multi-rotor drone micro-motion parameter estimation method based on CVMD and SVD[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(14): 3326. doi: 10.3390/rs14143326. [28] DAS S and SUGANTHAN P N. Differential evolution: A survey of the state-of-the-art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 15(1): 4–31. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2010.2059031. [29] EICHEL P H and JAKOWATZ C V. Phase-gradient algorithm as an optimal estimator of the phase derivative[J]. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(20): 1101–1103. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.001101. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: