A Through-wall Target Location Algorithm Combing Hough Transform and SVR in Multi-view Detection Mode
-
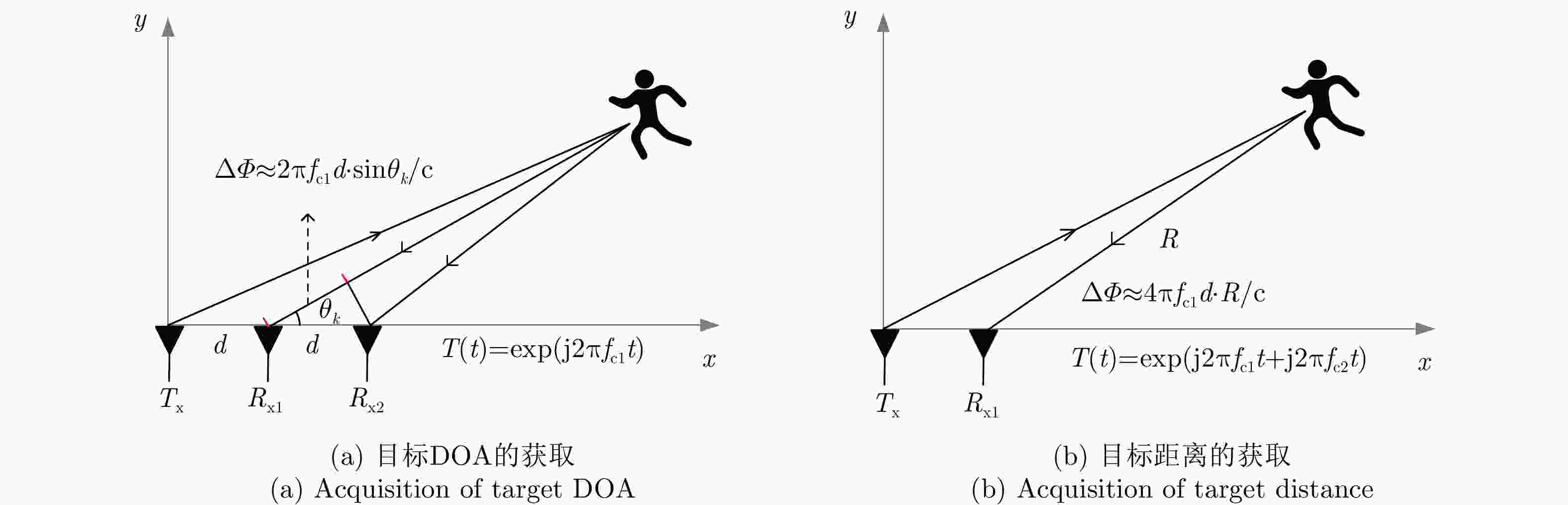
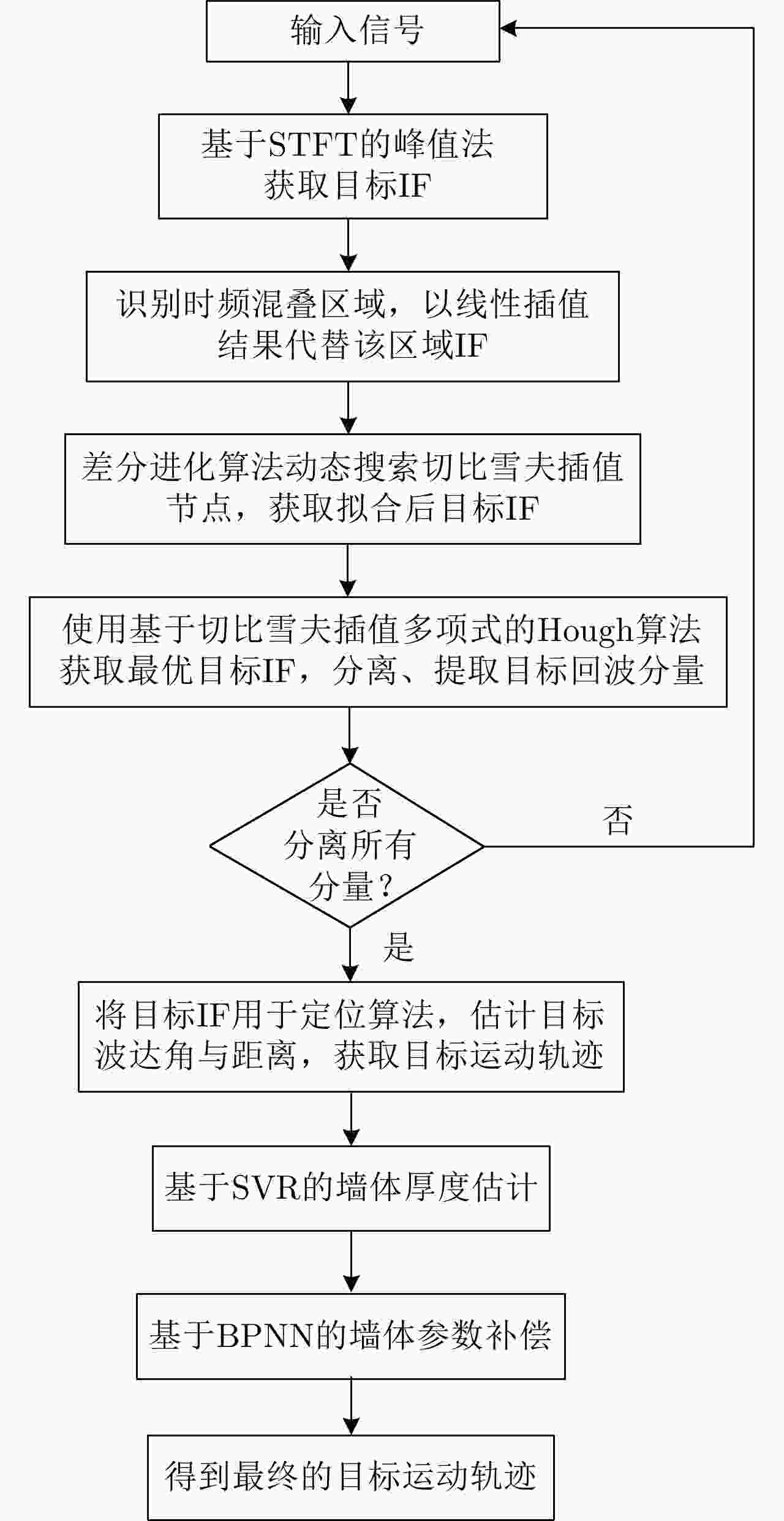
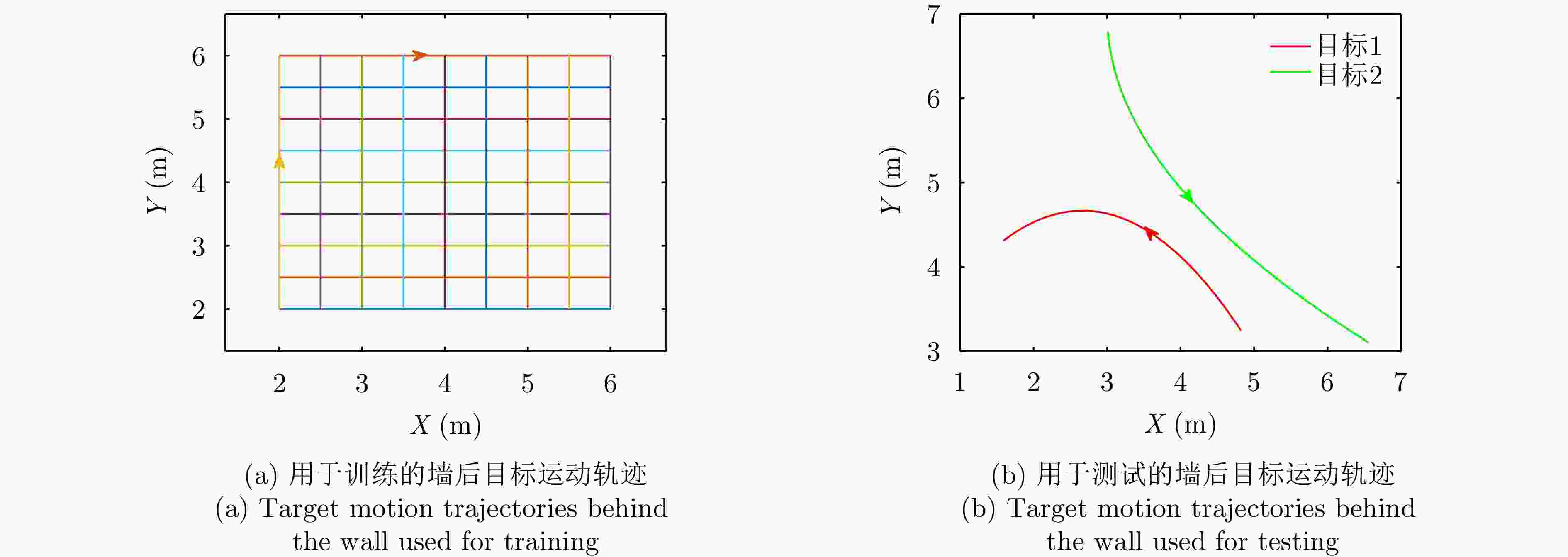
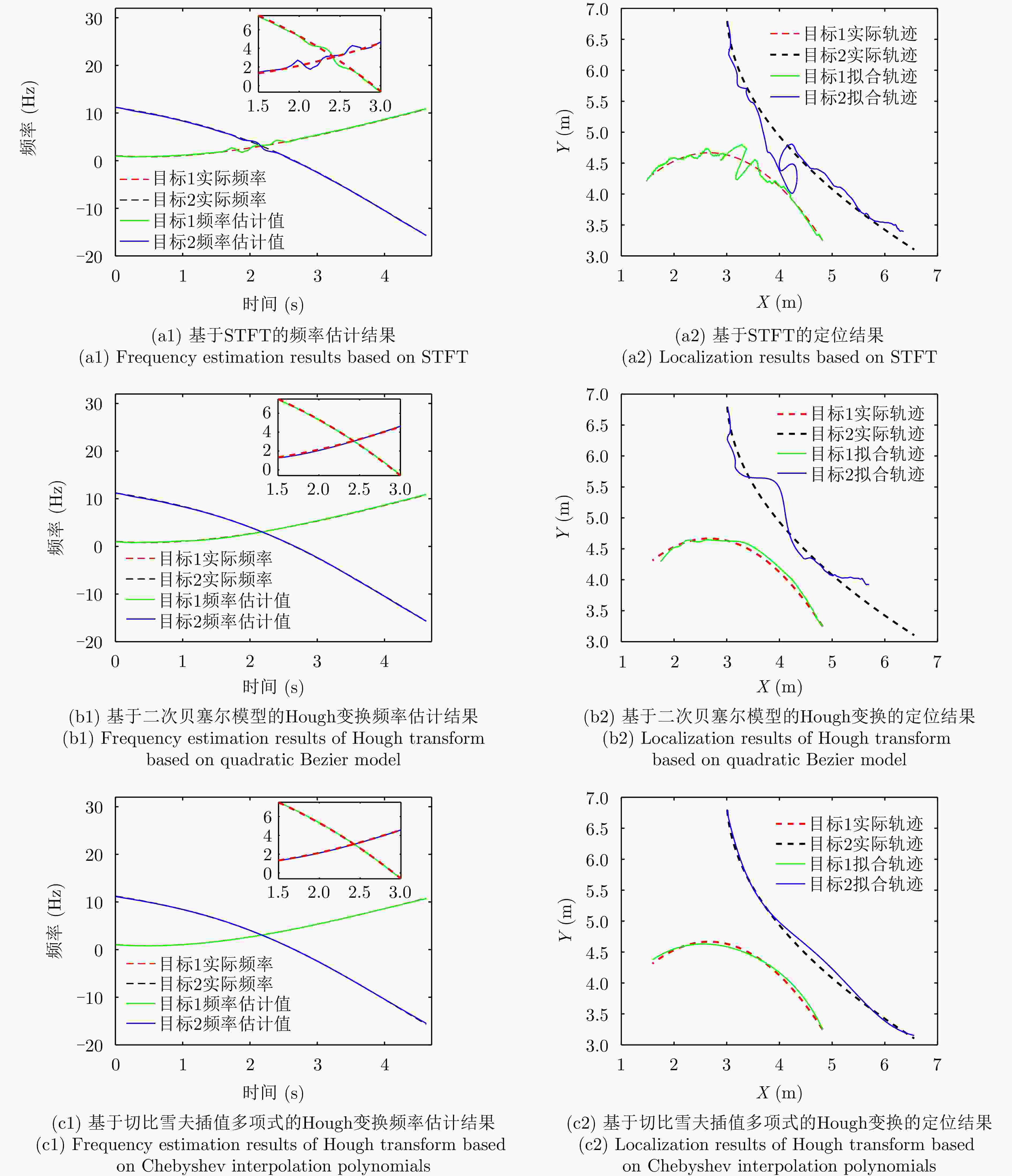
摘要: 多普勒穿墙雷达在定位墙后目标时,存在以下两个难点:(1)准确获取频率混叠区域目标瞬时频率;(2)通过获取精确的墙体参数来减小墙体对定位造成的影响。针对以上问题该文提出了一种结合Hough变换和支持向量回归-BP神经网络的目标定位算法。该文首先设计了一种多视角融合穿墙目标探测模型框架,通过获取不同视角下的目标位置来提供辅助估计墙体参数信息;其次,结合差分进化算法和切比雪夫插值多项式提出了一种目标瞬时频率曲线的高精度提取和估计算法;最后,利用估计的墙体参数信息,提出了一种基于BP神经网络的目标运动轨迹补偿算法,抑制了障碍物对目标定位结果的扭曲影响,实现了对墙后目标的精确定位。实验结果表明,相较于传统的短时傅里叶方法,该文所述方法可以准确提取时频混叠区域的目标瞬时频率曲线并减小墙体造成的影响,从而实现墙后多目标的准确定位,整体定位精度提升了约85%。Abstract: Doppler through-wall radar faces two challenges when locating targets concealed behind walls: (1) precisely determining the instantaneous frequency of the target within the frequency aliasing region and (2) reducing the impact of the wall on positioning by determining accurate wall parameters. To address these issues, this paper introduces a target localization algorithm that combines the Hough transform and support vector regression-BP neural network. First, a multiview fusion model framework is proposed for through-wall target detection, which enables the auxiliary estimation of wall parameter information by acquiring target positions from different perspectives. Second, a high-precision extraction and estimation algorithm for the instantaneous frequency curve of the target is proposed by combining the differential evolutionary algorithm and Chebyshev interpolation polynomials. Finally, a target motion trajectory compensation algorithm based on the Back Propagation (BP) neural network is proposed using the estimated wall parameter information, which suppresses the distorting effect of obstacles on target localization results and achieves the accurate localization of the target behind a wall. Experimental results indicate that compared with the conventional short-time Fourier method, the developed algorithm can accurately extract target instantaneous frequency curves within the time-frequency aliasing region. Moreover, it successfully reduces the impact caused by walls, facilitating the precise localization of multiple targets behind walls, and the overall localization accuracy is improved ~85%.
-
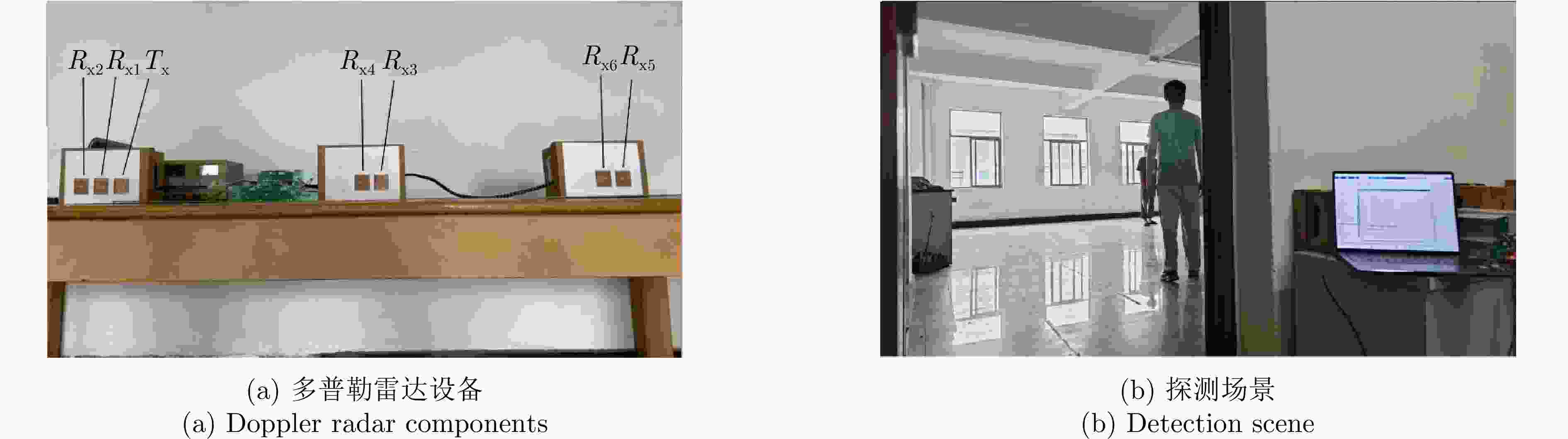
表 1 雷达系统参数设置
Table 1. Radar system parameters settings
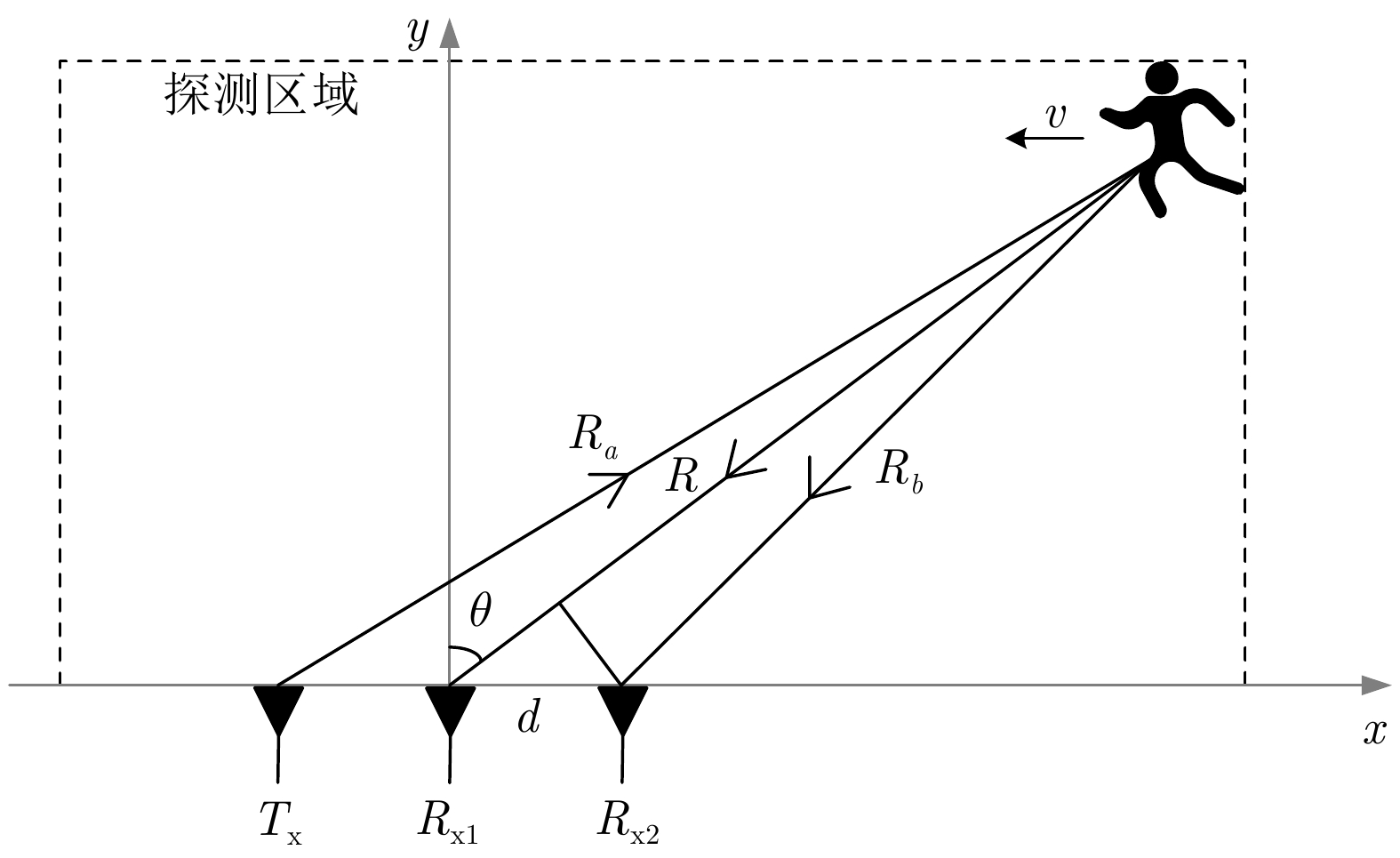
参数 数值 载波频率 fc1, fc2 (GHz) 2.40, 2.39 最大/最小发射功率Pmax, Pmin (dBm) 30, 15 天线增益G (dBi) 3.5 天线带宽B (MHz) 40 天线间隔d (m) 0.06 采样频率(Hz) 200 最大方位角θm (°) 75 表 2 STFT、二次贝塞尔模型、四阶切比雪夫插值多项式模型误差对比(无墙双目标场景)
Table 2. Algorithm errors comparison of STFT, quadratic Bezier model and 4th order Chebyshev interpolating polynomial model (scene of dual target without walls)
算法 目标1频率(Hz) 目标1定位(m) 目标2频率(Hz) 目标2定位(m) STFT 0.17 0.16 0.16 0.31 基于二次贝塞尔模型的Hough变换 0.07 0.13 0.10 0.57 基于四阶切比雪夫插值多项式的Hough变换 0.04 0.07 0.07 0.09 表 3 STFT、二次贝塞尔模型、轨迹相交法、四阶切比雪夫插值多项式模型误差对比(墙后双目标场景)
Table 3. Algorithm errors comparison of STFT, quadratic Bezier model, trajectory intersection method and 4th order Chebyshev interpolating polynomial model (scene of dual target behind a wall)
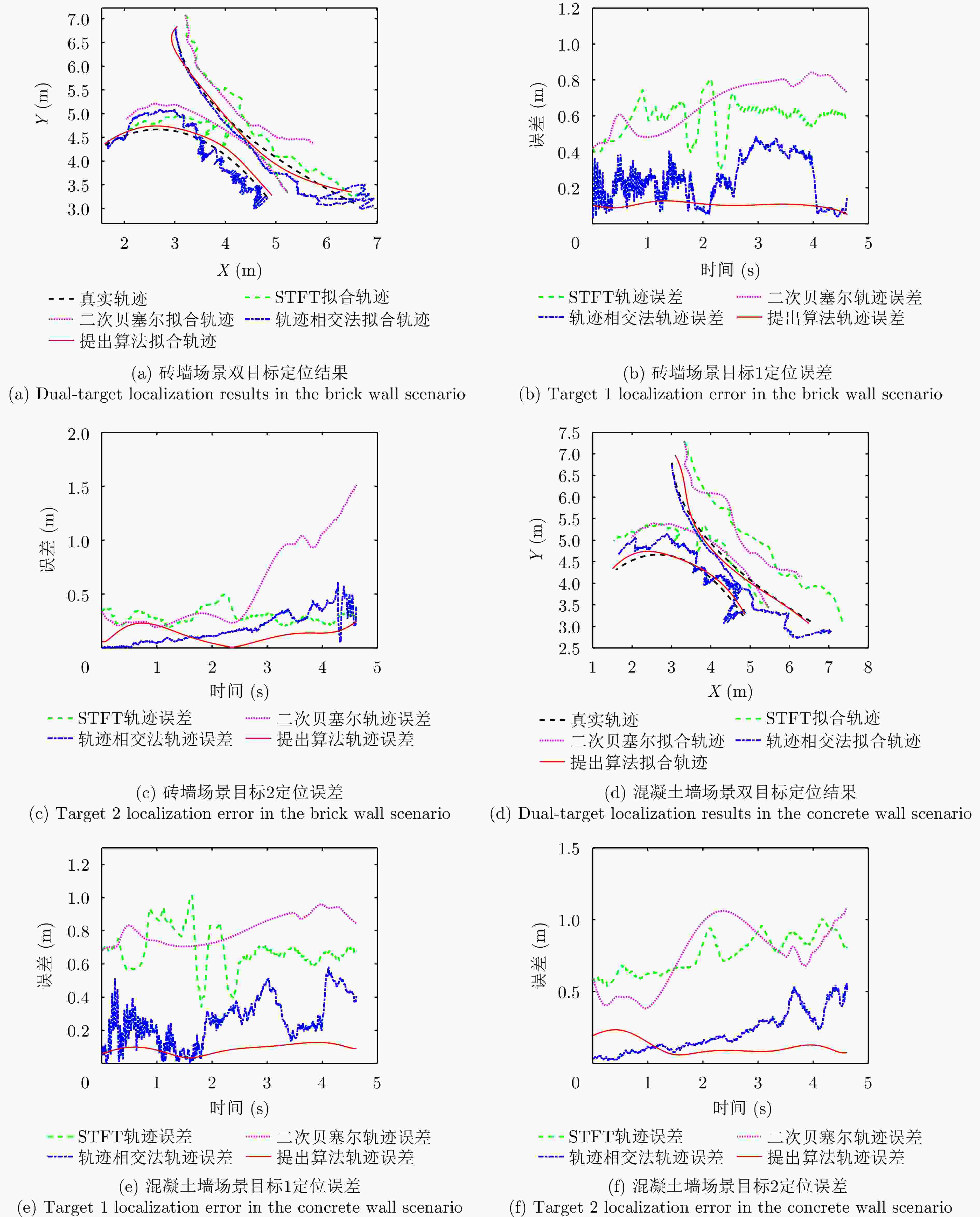
算法 砖墙场景 混凝土墙场景 目标1定位(m) 目标2定位(m) 目标1定位(m) 目标2定位(m) STFT 0.59 0.33 0.70 0.77 基于二次贝塞尔模型的Hough变换 0.68 0.66 0.81 0.79 轨迹相交法 0.27 0.22 0.29 0.25 基于四阶切比雪夫插值多项式的Hough变换 0.10 0.14 0.09 0.13 -
[1] 刘振, 魏玺章, 黎湘. 一种新的随机PRI脉冲多普勒雷达无模糊MTD算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 28–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10063.LIU Zhen, WEI Xizhang, and LI Xiang. Novel method of unambiguous moving target detection in pulse-Doppler radar with random pulse repetition interval[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 28–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10063. [2] 胡程, 廖鑫, 向寅, 等. 一种生命探测雷达微多普勒测量灵敏度分析新方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 455–461. doi: 10.12000/JR16090.HU Cheng, LIAO Xin, XIANG Yin, et al. Novel analytic method for determining micro-Doppler measurement sensitivity in life-detection radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 455–461. doi: 10.12000/JR16090. [3] PENG Yiqun, DING Yipeng, ZHANG Jiawei, et al. Target trajectory estimation algorithm based on time-frequency enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 8500807. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3227997. [4] DING Minhao, DING Yipeng, PENG Yiqun, et al. CNN-based time-frequency image enhancement algorithm for target tracking using Doppler through-wall radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letter, 2023, 20: 3505305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3282700. [5] WANG Genyuan and AMIN M G. Imaging through unknown walls using different standoff distances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(10): 4015–4025. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.879325. [6] 丁一鹏, 厍彦龙. 穿墙雷达人体动作识别技术的研究现状与展望[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1156–1175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211051.DING Yipeng and SHE Yanlong. Research status and prospect of human movement recognition technique using through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1156–1175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211051. [7] ABDOUSH Y, POJANI G, and CORAZZA G E. Adaptive instantaneous frequency estimation of multicomponent signals based on linear time-frequency transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(12): 3100–3112. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2912132. [8] HUANG N E, SHEN Zheng, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903–995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193. [9] LI Po and ZHANG Qinghai. An improved Viterbi algorithm for IF extraction of multicomponent signals[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2018, 12(1): 171–179. doi: 10.1007/s11760-017-1143-2. [10] 金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119.JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. [11] JIN Tian, CHEN Bo, and ZHOU Zhimin. Image-domain estimation of wall parameters for autofocusing of through-the-wall SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(3): 1836–1843. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2206395. [12] PROTIVA P, MRKVICA J, and MACHAC J. Estimation of wall parameters from time-delay-only through-wall radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2011, 59(11): 4268–4278. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2011.2164206. [13] WANG Genyuan, AMIN M G, and ZHANG Yimin. New approach for target locations in the presence of wall ambiguities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 301–315. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603424. [14] ZHANG Huamei, ZHANG Yerong, WANG Fangfang, et al. Application of support vector machines for estimating wall parameters in through-wall radar imaging[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 2015: 456123. doi: 10.1155/2015/456123. [15] DING Yipeng, SUN Yinhua, HUANG Guowei, et al. Human target localization using Doppler through-wall radar based on micro-Doppler frequency estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(15): 8778–8788. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2983104. [16] DING Yipeng, SUN Yinhua, YU Xiali, et al. Bezier-based Hough transforms for Doppler localization of human targets[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(1): 173–177. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2019.2956842. [17] CHEN Gang, CHEN Jin, DONG Guangming, et al. An adaptive non-parametric short-time Fourier transform: Application to echolocation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 87: 131–141. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.06.018. [18] DING Yipeng, YU Xiali, LEI Chengxi, et al. A novel real-time human heart rate estimation method for noncontact vital sign radar detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 88689–88699. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993503. [19] LIN Xiaoyi, DING Yipeng, XU Xuemei, et al. A multi-target detection algorithm using high-order differential equation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(13): 5062–5069. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2901923. [20] ZHOU Can, YU Wentao, HUANG Keke, et al. A New model transfer strategy among spectrometers based on SVR parameter calibrating[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1010413. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3119129. [21] XIE Yaqin, WANG Kailiang, and HUANG Hai. BPNN based indoor fingerprinting localization algorithm against environmental fluctuations[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(12): 12002–12016. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3172860. [22] BOULIC R, THALMANN N M, and THALMANN D. A global human walking model with real-time kinematic personification[J]. The Visual Computer, 1990, 6(6): 344–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01901021. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: