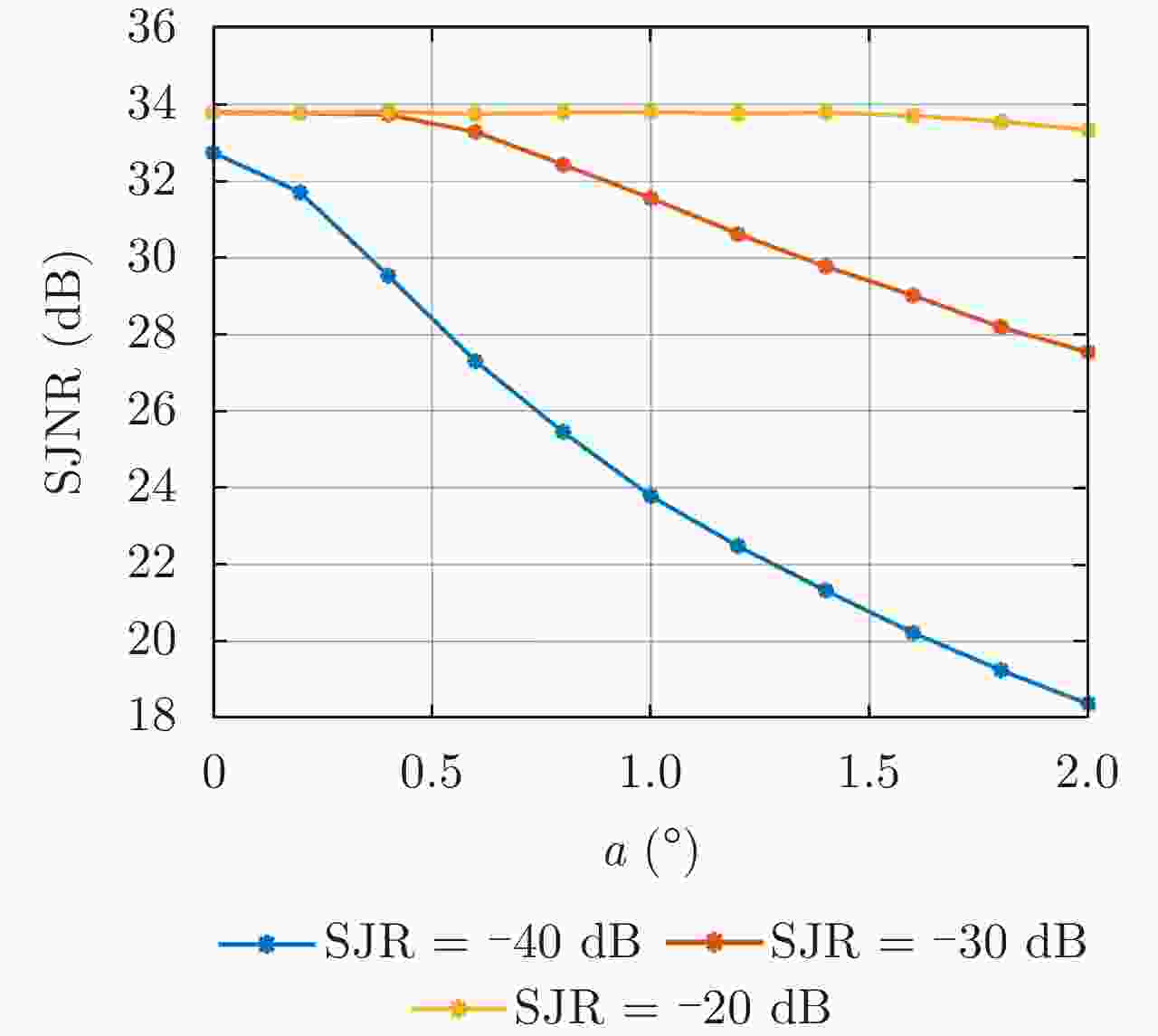
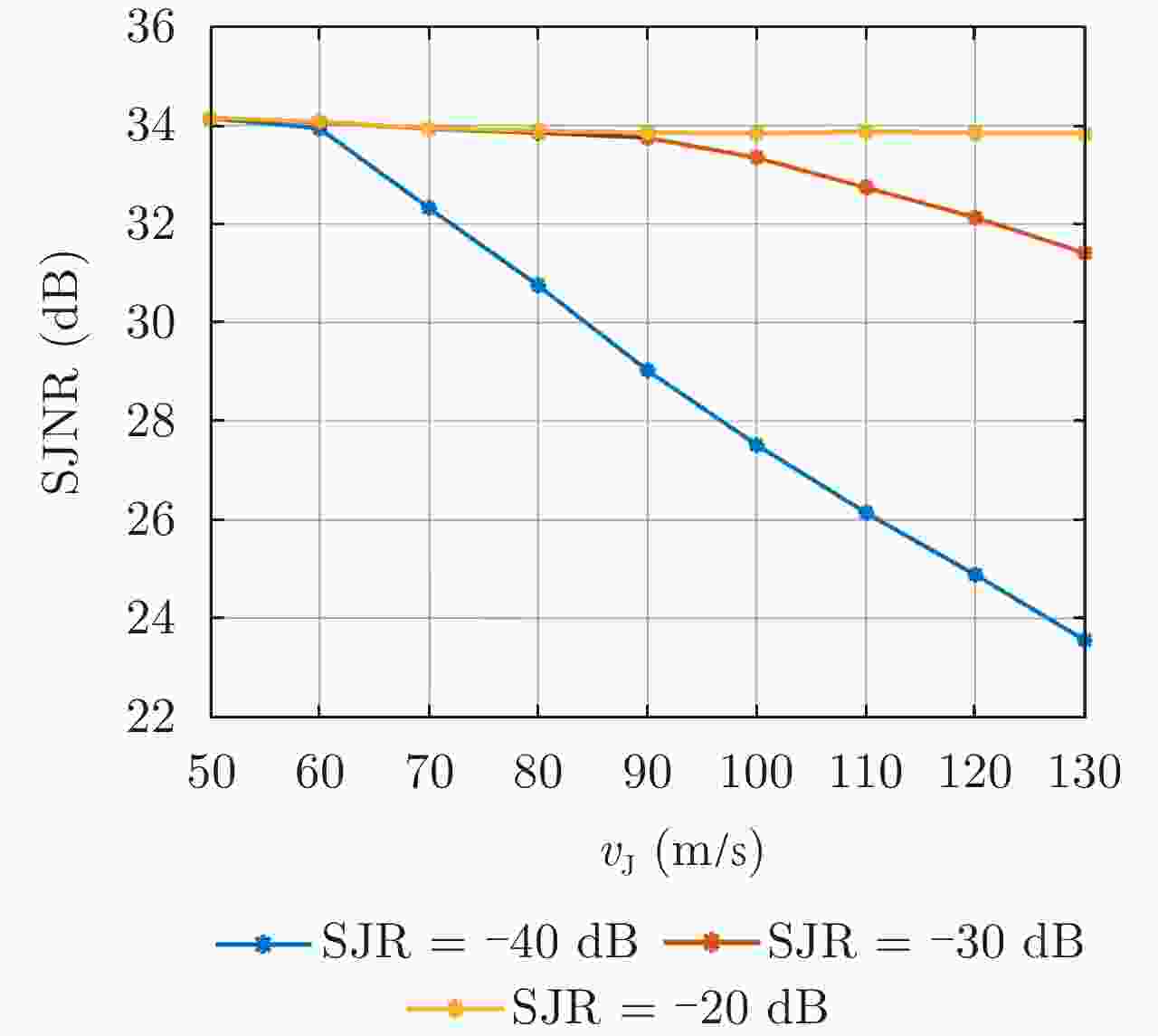
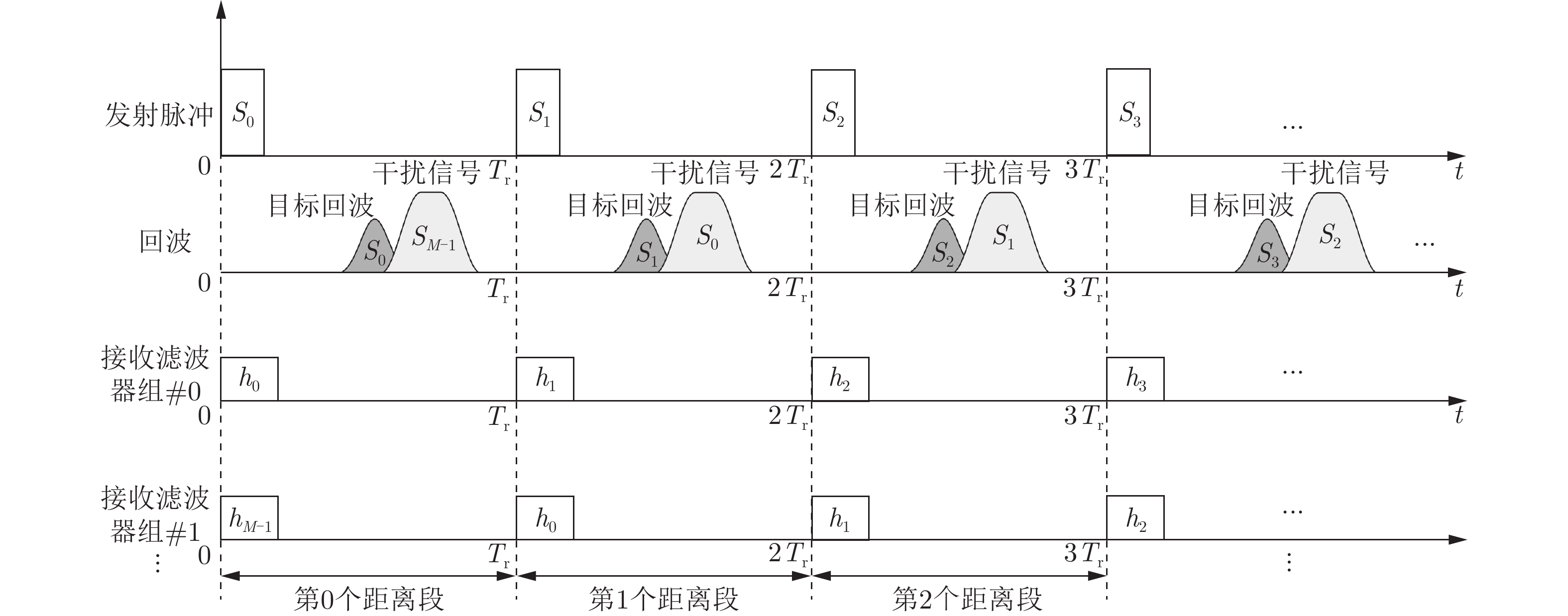
Range-Doppler Two-dimensional Jamming Reconstruction Algorithm Based on Interpulse Code Agile Waveform
-
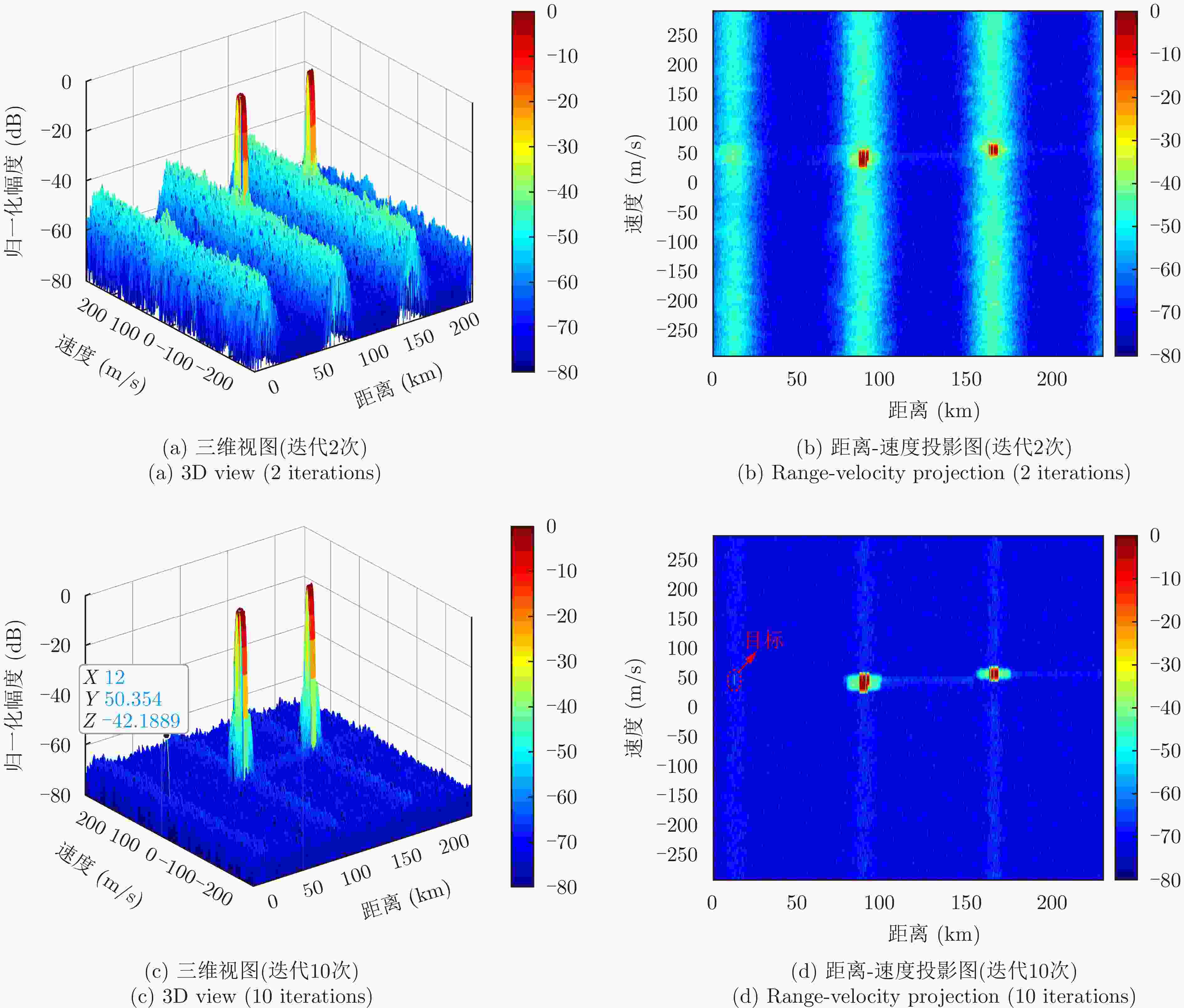
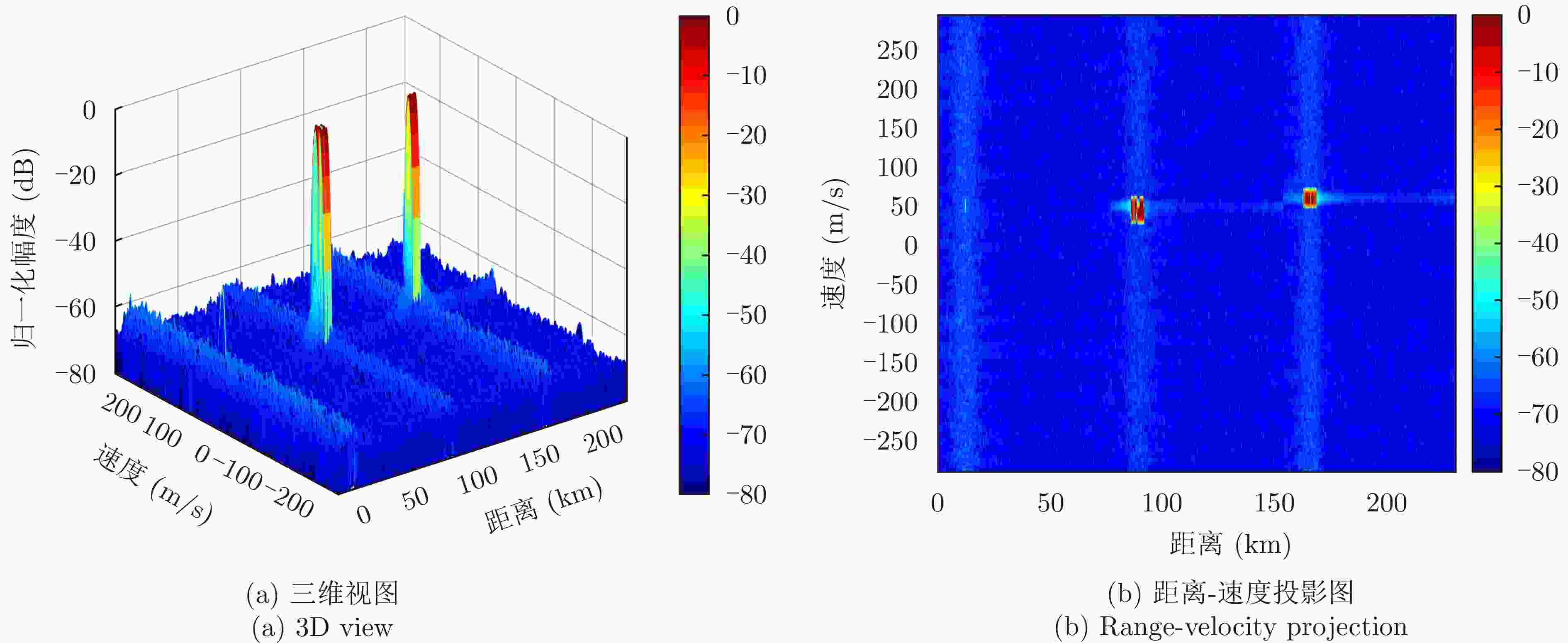
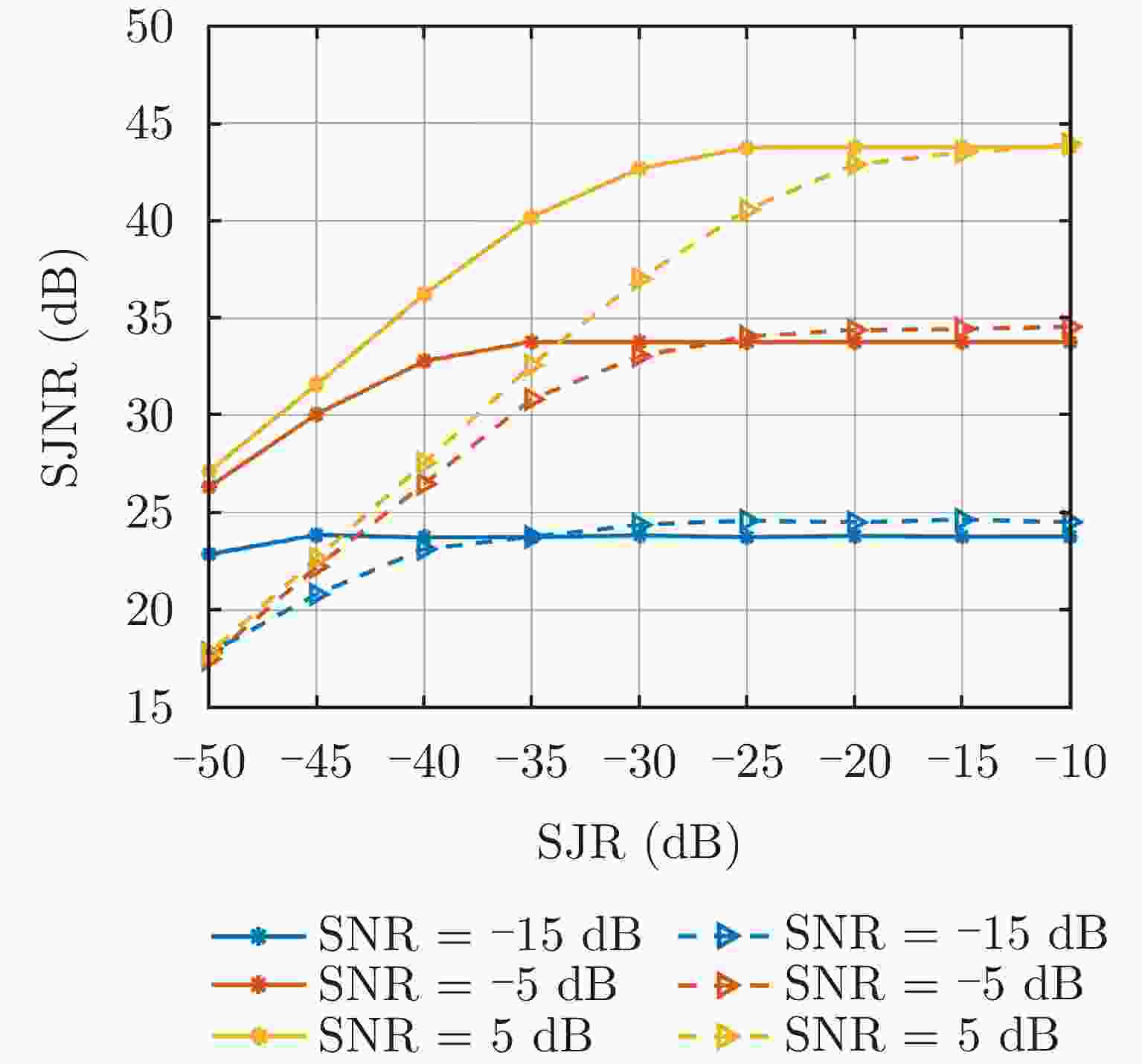
摘要: 密集假目标干扰通过在真实目标周围产生大量假目标,形成欺骗和压制双重干扰效果,严重影响雷达的目标探测能力。为此,该文提出一种基于脉间码型捷变波形的距离-多普勒二维干扰重构算法来抑制密集假目标干扰。该算法基于脉间码型捷变波形的距离选通性,在距离-多普勒域通过交替反演实现干扰和目标重构,并从回波中对消干扰来实现干扰剔除。首先,通过构造不同距离段的接收滤波器组来实现干扰和目标回波的分距离段处理;其次,采用联合失配滤波器组使各脉冲滤波输出的距离旁瓣结构近似相同,减小脉间码型捷变波形经脉冲多普勒处理后沿多普勒维的散布能量;然后,利用干扰和目标回波在不同距离-多普勒平面上的能量分布特性构造滤波矩阵;最后,通过交替反演实现干扰和目标的精准重构,进而实现密集假目标干扰的抑制。仿真结果表明,与传统方法相比,该文所提算法在干扰抑制和运行时间方面展现出优越的性能,显著提升了雷达在强干扰环境中的目标检测能力。Abstract: Dense false target jamming generates a large number of false targets around the real target, leading to dual jamming effects of deception and suppression. This severely affects the target detection ability of the radar. Therefore, this study proposes a range-Doppler two-dimensional jamming reconstruction algorithm based on the interpulse code agile waveform to suppress dense false target jamming. Based on the range-gating characteristics of the interpulse code agile waveform, the jamming and target echo reconstruction in the range-Doppler domain is realized by alternate inversion. Reconstruction jamming is eliminated by the iterative cancellation method. First, the jamming and target echo are processed by constructing receiving filter banks with different range intervals. Second, a joint mismatched filter bank is used to make the range sidelobe structure of each pulse filter output approximately the same. This reduces the divergence energy along the Doppler dimension after the pulse Doppler processing of the interpulse code agile waveform. The filter matrix is then constructed using the energy distribution characteristics of the jamming and target echo in different range-Doppler regions. Finally, accurate jamming and target echo reconstruction are achieved by alternate inversion to suppress dense false target jamming. Simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm in terms of jamming suppression and running time compared with traditional algorithms. These procedures significantly improve the target detection capability of the radar in strong jamming scenarios.
-
1 基于脉间码型捷变波形的距离-多普勒二维干扰重构算法
1. Range-Doppler two-dimensional jamming reconstruction algorithm based on interpulse code agile waveform
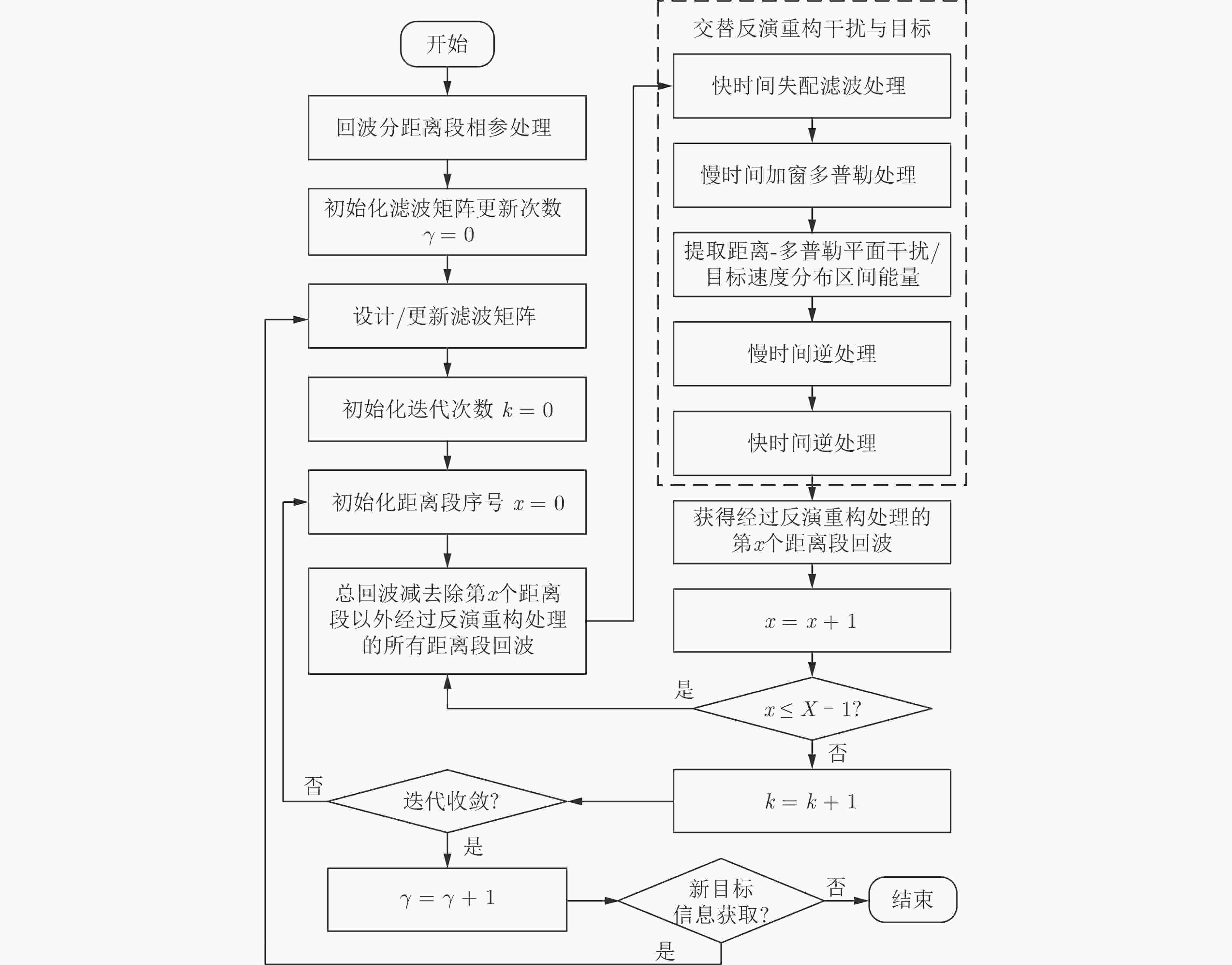
步骤1 根据回波信号的分距离段相参处理结果初步判断干扰信
号所在距离段以及对应多普勒范围,且初始化滤波矩阵更新次数
$\gamma = 0$;步骤2 对于$\forall x \in \left\{ {0,1, \cdots ,X - 1} \right\}$,根据现有干扰、目标信息
设计或更新滤波矩阵${\boldsymbol{J}}_x^{\left\{ \gamma \right\}}$;步骤3 对于$\forall x \in \left\{ {0,1, \cdots ,X - 1} \right\}$,初始化${\boldsymbol{E}}_x^{\left\{ 0 \right\}}$为全0矩阵; 步骤4 初始化迭代序号$k = 0$; 步骤5 根据式(23),对来自不同距离段的回波信号进行迭代重构; 步骤6 令$k = k + 1$,重复步骤5直到满足算法停止条件; 步骤7 根据式(25)获得来自不同距离段回波信号的距离-多普勒
成像结果;步骤8 执行目标检测流程。若检测到新的目标,令$\gamma = \gamma + 1$并
重复步骤2—步骤8;否则,结束算法流程。表 1 交替反演重构干扰/目标的计算复杂度
Table 1. Computational complexity of alternate inversion reconstructed jamming/target
步骤 计算复杂度 快时间失配滤波 $\mathcal{O}\left( {ML} \right)$ 慢时间加窗多普勒处理 $\mathcal{O}\left( {ML + LP\log P} \right)$ 提取距离-多普勒平面干扰/
目标速度分布区间能量$\mathcal{O}\left( {LP} \right)$ 慢时间逆处理 $\mathcal{O}\left( {ML + LP\log P} \right)$ 快时间逆处理 $\mathcal{O}\left( {ML} \right)$ 表 2 波形参数
Table 2. Waveform parameters
参数 数值 码片宽度(μs) 0.4 码片个数 128 信号脉宽(μs) 51.2 信号带宽(MHz) 2.5 脉冲重复周期(μs) 512 载频(GHz) 0.5 脉冲数 128 表 3 运行时间对比(s)
Table 3. Comparison of running time (s)
算法 运行时间 CLEAN 51.58 所提算法 0.52 -
[1] 李永祯, 黄大通, 邢世其, 等. 合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087LI Yongzhen, HUANG Datong, XING Shiqi, et al. A review of synthetic aperture radar jamming technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087 [2] FENG Dejun, XU Letao, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Jamming wideband radar using interrupted-sampling repeater[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1341–1354. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2670958 [3] BUTT F A and JALIL M. An overview of electronic warfare in radar systems[C]. 2013 The International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (TAEECE), Konya, Turkey, 2013: 213–217. [4] HEAGNEY C P. Digital radio frequency memory synthetic instrument enhancing US navy automated test equipment mission[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2018, 21(4): 41–63. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2018.8423745 [5] SOUMEKH M. SAR-ECCM using phase-perturbed LFM chirp signals and DRFM repeat jammer penalization[C]. 2005 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2005: 507–512. [6] AKHTAR J. Orthogonal block coded ECCM schemes against repeat radar jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(3): 1218–1226. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5259195 [7] AKHTAR J. An ECCM scheme for orthogonal independent range-focusing of real and false targets[C]. 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, USA, 2007: 846–849. [8] LI Yongzhe and VOROBYOV S A. Fast algorithms for designing unimodular waveform(s) with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1197–1212. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2787104 [9] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence set design with good correlation properties via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(11): 2866–2879. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2535312 [10] REN Wei, ZHANG Honggang, LIU Quanhua, et al. Greedy code search based memetic algorithm for the design of orthogonal polyphase code sets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 13561–13576. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2893970 [11] 徐乃清. 基于捷变波形的雷达抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2020.XU Naiqing. Research on radar anti-jamming technique based on agile waveform[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020. [12] YANG Ya, CUI Guolong, WU Jian, et al. Optimized phase-coded waveforms design against range repeat jamming[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 395–399. [13] BU Yi, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. A new approach for design of constant modulus discrete phase radar waveform with low WISL[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 187: 108145. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108145 [14] LI Yongzhe and VOROBYOV S A. Efficient single/multiple unimodular waveform design with low weighted correlations[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, USA, 2017: 3226–3230. [15] 徐磊磊. 雷达波形设计及抗主瓣有源干扰若干技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.XU Leilei. Researches on Radar waveform design and several techniques of mainlobe active interference suppression[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [16] XU Leilei, ZHOU Shenghua, LIU Hongwei, et al. Distributed multiple-input-multiple-output radar waveform and mismatched filter design with expanded mainlobe[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(2): 227–238. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0340 [17] BERESTESKY P and ATTIA E H. Sidelobe leakage reduction in random phase diversity radar using coherent CLEAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(5): 2426–2435. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2888652 [18] SUN Yinghao, FAN Huayu, REN Lixiang, et al. Folded clutter suppression for pulse-Doppler radar based on pulse-agile waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 3774–3788. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3190626 [19] BLUNT S D, COOK M R, and STILES J. Embedding information into radar emissions via waveform implementation[C]. 2010 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Niagara Falls, Canada, 2010: 195–199. [20] O’CONNOR A C, KANTOR J M, and JAKABOSKY J. Joint equalization filters that mitigate waveform-diversity modulation of clutter[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6. [21] SUN Yinghao, FAN Huayu, WANG Jingdong, et al. Optimization of diverse PCFM waveforms and joint mismatched filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1840–1854. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3053105 [22] DOERRY A W. Catalog of window taper functions for sidelobe control[R]. SAND2017-4042, 2017. [23] HOU Kaiyue, REN Wei, and LIU Quanhua. Majorization minimization based memetic algorithm for designing polyphase sequences with good correlation properties[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–6. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: